An Ascorbic Acid-Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine)/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA for Electrochemical Sensing Ascorbic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Synthesis of AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA
2.4. Preparation of nMIP/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA and NIP/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA
2.5. Preparation of Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of COFTFPB-NBPDA and AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA
3.2. Electrochemical Behaviors of COFTFPB-NBPDA/GCE and AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA/GCE
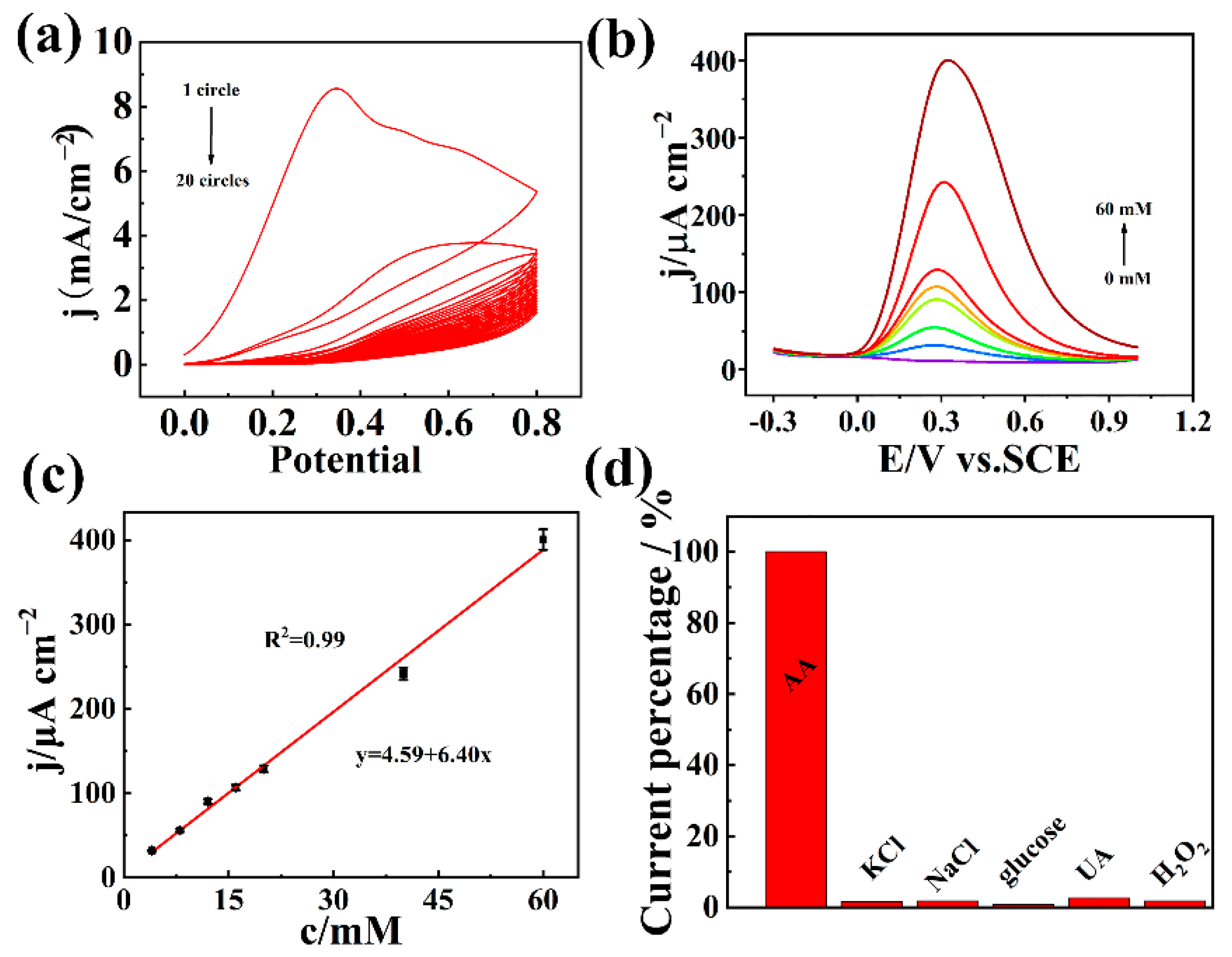
3.3. Electrochemical Detection of AA by AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA/GCE and nMIPs/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA/GCE
3.4. Detection of AA in Effervescent Tablets
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, J.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. COFBTLP-1/three-dimensional macroporous carbon electrode for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 321, 128498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. An Immunosensor Using Electroactive COF as Signal Probe for Electrochemical Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5352–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wu, N.; Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. A novel N,S-rich COF and its derived hollow N,S-doped carbon@Pd nanorods for electrochemical detection of Hg2+ and paracetamol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Du, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. Double signal ratiometric electrochemical riboflavin sensor based on macroporous carbon/electroactive thionine-contained covalent organic framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-San-Miguel, D.; Yazdi, A.; Guillerm, V.; Perez-Carvajal, J.; Puntes, V.; Maspoch, D.; Zamora, F. Confining Functional Nanoparticles into Colloidal Imine-Based COF Spheres by a Sequential Encapsulation-Crystallization Method. Chem.–A Eur. Journal. 2017, 23, 8623–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, X.; Hua, R.; Zhang, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, T.; Zheng, J.; Lu, G. Remarkably catalytic activity in reduction of 4-nitrophenol and methylene blue by Fe3O4@COF supported noble metal nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 260, 118142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-Q.; Zhang, W.-W.; Zhang, H.-W.; Yuan, R.; He, H. Elaborately manufacturing an electrochemical aptasensor based on gold nanoparticle/COF composites for amplified detection performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 16984–16991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntern, Y.T.; Vavra, J.; Karve, V.V.; Varandili, S.B.; Lecina, O.S.; Gadiyar, C.; Buonsanti, R. Synthetic Tunability of Colloidal Covalent Organic Framework/Nanocrystal Hybrids. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, S.; Song, G. Amino Acids as the Nitrogen Source to Synthesize Boron Nitride Quantum Dots for Fluorescence Turn-off-on Detection of Ascorbic Acid. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 3828–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; He, L.; Zhou, C.; Qian, Z.-J.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Li, C. Fluorescent detection of ascorbic acid using glutathione stabilized Au nanoclusters. Chem. Phys. 2019, 522, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.T. Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorescence Turn-Off-On Probe for Detecting Fe3+ and Ascorbic Acid. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pu, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Bai, R.; Kan, J.; Jin, C. Reaction Mechanisms and Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Caffeic Acid Grafted Chitosan Synthesized in Ascorbic Acid and Hydroxyl Peroxide Redox System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Qi, X.; Yang, J. Preparation and antioxidant properties of low molecular holothurian glycosaminoglycans by H2O2/ascorbic acid degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njus, D.; Kelley, P.M.; Tu, Y.-J.; Schlegel, H.B. Ascorbic acid: The chemistry underlying its antioxidant properties. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 159, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.L.; Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Li, G.D.; Wang, C.; Snyders, R.; Bittencourt, C.; Li, W.J. Bi2S3/rGO Composite Based Electrochemical Sensor for Ascorbic Acid Detection. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuru, R.Y.; Roy, A.; Bera, S. Antagonistic Roles of Gallates and Ascorbic Acid in Pyomelanin Biosynthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3843–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinska-Pirog, J.; Skowron, K.; Bogiel, T.; Bialucha, A.; Przekwas, J.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Vitamin C in the Presence of Sub-Inhibitory Concentration of Aminoglycosides and Fluoroquinolones Alters Proteus mirabilis Biofilm Inhibitory Rate. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, P.; Parmar, K.; Patel, D.; Kumar, S.; Trivedi, M.; Das, M. Inhibition of amyloid fibril formation of lysozyme by ascorbic acid and a probable mechanism of action. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortolini, C.; Tasca, F.; Venneri, M.A.; Marchese, C.; Antiochia, R. Gold Nanoparticles/Carbon Nanotubes and Gold Nanoporous as Novel Electrochemical Platforms for L-Ascorbic Acid Detection: Comparative Performance and Application. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Non-oxidation reduction strategy for highly selective detection of ascorbic acid with dual-ratio fluorescence and colorimetric signals. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 281, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, R.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Q.; Cui, T. Flexible micro-sensors with self-assembled graphene on a polyolefin substrate for dopamine detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, I.R. Higher doses of ascorbic acid may have the potential to promote nutrient delivery via intestinal paracellular absorption. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 6750–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turak, F.; Güzel, R.; Dinç, E. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid and caffeine in commercial soft drinks using reversed-phase ultraperformance liquid chromatography. J. Food Drug. Anal. 2017, 25, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Tang, J.; Tu, X.; Chen, W. Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Total Ascorbic Acid, and Dehydroascorbic Acid in Bee Pollen Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Ultraviolet Detection. Molecules. 2020, 25, 5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Lv, W.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Li, F. One-Step Synthesis of Methylene Blue-Encapsulated Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework for Dual-Signal Fluorescent and Homogeneous Electrochemical Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lv, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, F. Label-free homogeneous electrochemical detection of MicroRNA based on target-induced anti-shielding against the catalytic activity of two-dimension nanozyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniazzi, C.; Lima, C.; Marangoni, R.; Castro, E.; Santana, E.; Spinelli, A. Molybdenum trioxide incorporated in a carbon paste as a sensitive device for bisphenol A monitoring. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Li, F. Two-Dimensional MnO2 Nanozyme-Mediated Homogeneous Electrochemical Detection of Organophosphate Pesticides without the Interference of H2O2 and Color. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4084–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, K.; Debiprosad, R.M. Review on nanomaterials-enabled electrochemical sensors for ascorbic acid detection. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 586, 113415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savk, A.; Ozdil, B.; Demirkan, B.; Nas, M.S.; Calimli, M.H.; Alma, M.H.; Inamuddin; Asiri, A.M.; Sen, F. Multiwalled carbon nanotube-based nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of uric acid, dopamine, and ascorbic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 99, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, B.; Ning, W.; Wang, X. Highly Sensitive Ascorbic Acid Sensor Based on Ionic Liquid Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, G.; Han, K.; Gu, H. Facile Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor for In Vivo/Online Repetitive Measurements of Cerebral Ascorbic Acid in Brain Microdiaysate. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Electroactive Covalent Organic Frameworks/Carbon Nanotubes Composites for Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. An electrochemical sensor based on the modification of platinum nanoparticles and ZIF-8 membrane for the detection of ascorbic acid. Talanta 2021, 226, 122105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hassine, A.; Raouafi, N.; Moreira, F.T.C. Novel Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Biosensor for Tau Protein Detection. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Fan, D.; Xue, X.; Guo, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, D. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Functionalized Bi2S3/Ti3C2TX MXene Nanocomposites for Photoelectrochemical/Electrochemical Dual-Mode Sensing of Chlorogenic Acid. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, H.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Surface Imprinted Polymers Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Infectious Diseases. Sensors 2020, 20, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singhal, A.; Parihar, A.; Kumar, N.; Khan, R. High throughput molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical nanosensors for point-of-care diagnostics of COVID-19. Mater. Lett. 2022, 306, 130898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hong, J.; Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, L. An Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensor for Rapid beta-Lactoglobulin Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.H.; Razaq, A.; Akbar, N.; Danielsson, B.; Sultana, I. Facile synthesis of multisegment Au/Ni/Au nanowire for high performance electrochemical glucose sensor. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 095028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, C.; Qileng, A.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. Capsulation of AuNCs with AIE Effect into Metal-Organic Framework for the Marriage of a Fluorescence and Colorimetric Biosensor to Detect Organophosphorus Pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7275–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Meng, T.; Yang, X. Au and Au-Based nanomaterials: Synthesis and recent progress in electrochemical sensor applications. Talanta 2020, 206, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Peng, C.; Song, Y. A ascorbic acid-imprinted poly(o-phenylenediamine)/zeolite imidazole frameworks-67/carbon cloth for electrochemical sensing ascorbic acid. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 9425–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Xu, F.; Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Fan, G.; Song, G.; Chai, B. Mixed valence state cerium metal organic framework with prominent oxidase-mimicking activity for ascorbic acid detection: Mechanism and performance. Colloids Surf. A–Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 641, 128610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, L.; Han, X.; Ha, M.N.; Li, K.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H. A portable ascorbic acid in sweat analysis system based on highly crystalline conductive nickel-based metal-organic framework (Ni-MOF). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 616, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Meng, J.; Song, Q.; Wen, D. Superhydrophilic edge-rich graphene for the simultaneous and disposable sensing of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Wu, D.; Ji, W.; Zhang, S.; Tang, W.; Su, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, R. Manipulating the Selectivity of OECT-Based Biosensors via the Surface Engineering of Carbon Cloth Gate Electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1905361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.d.S.; Fernandes, D.S.; Do Carmo, D.R. A modified hybrid silsesquioxane/histidine composite for copper and zinc adsorption and it behavior in the electro-oxidation of ascorbic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wei, C.; Dong, J.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J. Dimeric phthalocyanine-involved double-decker complex-based electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of acetaminophen and ascorbic acid. J. Mater. Sci.–Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzara, F.; Patella, B.; Aiello, G.; O’Riordan, A.; Torino, C.; Vilasi, A.; Inguanta, R. Electrochemical detection of uric acid and ascorbic acid using r-GO/NPs based sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 388, 138652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, J.H.H.; Oliveira, M.E.; Lopes, B.V.; Gallo, B.B.; La Rosa, A.B.; Piva, E.; Barba, D.; Rosei, F.; Carreño, N.L.V.; Escote, M.T. A Flexible Electrochemical Biosensor Based on NdNiO3 Nanotubes for Ascorbic Acid Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 3394–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarlucea, B.; Roig, A.P.; Belyaev, D.; Baraban, L.; Cuniberti, G. Electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid in artificial sweat using a flexible alginate/CuO-modified electrode. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; Song, Y.; Ma, G. An Ascorbic Acid-Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine)/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA for Electrochemical Sensing Ascorbic Acid. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100407
Chen Y, Peng X, Song Y, Ma G. An Ascorbic Acid-Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine)/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA for Electrochemical Sensing Ascorbic Acid. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(10):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100407
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yaqin, Xia Peng, Yonghai Song, and Guangran Ma. 2022. "An Ascorbic Acid-Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine)/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA for Electrochemical Sensing Ascorbic Acid" Chemosensors 10, no. 10: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100407
APA StyleChen, Y., Peng, X., Song, Y., & Ma, G. (2022). An Ascorbic Acid-Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine)/AuNPs@COFTFPB-NBPDA for Electrochemical Sensing Ascorbic Acid. Chemosensors, 10(10), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100407





