Abstract
The development of reliable and highly sensitive methods for heavy metal detection is a critical task for protecting the environment and human health. In this study, a qualitative colorimetric sensor that used mercaptosuccinic-acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles (MSA-AuNPs) to detect trace amounts of Fe(III) ions was developed. MSA-AuNPs were prepared using a one-step reaction, where mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA) was used for both stabilization, which was provided by the presence of two carboxyl groups, and functionalization of the gold nanoparticle (AuNP) surface. The chelating properties of MSA in the presence of Fe(III) ions and the concentration-dependent aggregation of AuNPs showed the effectiveness of MSA-AuNPs as a sensing probe with the use of an absorbance ratio of A530/A650 as an analytical signal in the developed qualitative assay. Furthermore, the obvious Fe(III)-dependent change in the color of the MSA-AuNP solution from red to gray-blue made it possible to visually assess the metal content in a concentration above the detection limit with an assay time of less than 1 min. The detection limit that was achieved (23 ng/mL) using the proposed colorimetric sensor is more than 10 times lower than the maximum allowable concentration for drinking water defined by the World Health Organization (WHO). The MSA-AuNPs were successfully applied for Fe(III) determination in tap, spring, and drinking water, with a recovery range from 89.6 to 126%. Thus, the practicality of the MSA-AuNP-based sensor and its potential for detecting Fe(III) in real water samples were confirmed by the rapidity of testing and its high sensitivity and selectivity in the presence of competing metal ions.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, control of the quality and composition of consumed drinking water is in extremely demand. The almost ubiquitous increase in the concentration of heavy metals, in particular iron ions, in water is a major concern for centralized water supply. The significant amounts of Fe(III) can come with wastewater from metallurgical, metalworking, textile, paint, and varnish industries, as well as agricultural wastewater [1]. The main form of iron that is present in surface waters is a complex compound of Fe(III) with dissolved organic and inorganic compounds [2]; these ions are the object of study. In surface water, the process of transformation of Fe(III) to Fe(II) may take place [3], but the inorganic Fe(II) oxidizes back to Fe(III) in a few minutes [4]. This process depends on the redox potential of natural water. Since a high consumption of Fe(III) can cause toxic effects [5], the determination of Fe(III) content in drinking water resources is of great importance for human life.
Various effective analytical methods, such as atomic absorption spectrometry [6], inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [7], liquid chromatography [8], and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry [9] are successfully applied for Fe(III) determination. Despite the high sensitivity of these methods, they are complex and time-consuming, and usually require expensive equipment that is operated by skilled personnel. In this regard, the development of rapid and cost-effective methods for Fe(III) determination is still an urgent task. To date, a variety of chemosensors for on-site heavy metal ion determination with high sensitivity and ease of use were reported [10,11,12]. Fluorescent techniques are proposed, which are based on the interaction of Fe(III) ions with carbon nanodots [13,14], metal–organic frameworks [15], copper nanoclusters capped with BSA [16], or fluorescent dyes [17,18]. The described variants differ in their detection methods (quenching or activation of fluorescence), as well as in the mechanism (direct detection or with energy transfer). Furthermore, electrochemical systems are described based on the determination of Fe(III) individually [13] or in a mixture with other heavy metals, such as Pb(II) and Cd(II) [19].
Colorimetric sensors offer a promising approach for heavy metal detection, largely owing to their simplicity and rapidity, as well as the opportunity to visually estimate results [20]. To date, several colorimetric sensors have been proposed that are based on the iron-induced aggregation of nanomaterials accompanied by a color change and a shift in the plasmon resonance peak that is visually observed and spectrophotometrically measured, respectively [20,21,22,23]. The implementation of nanomaterials into the development of colorimetric systems makes it possible to improve the sensitivity of the determination of toxins, as well as the accuracy of the analysis. The most common substrate that is used in colorimetric analysis is metal nanoparticles, especially silver [24,25] and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) [26,27,28], due to their controllable morphology, chemical properties, and strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR). The ability of AuNPs to change color in response to changes in particle size and interparticle space, which is recorded spectrophotometrically as a shift in the absorption peak, makes them an ideal colorimetric sensing probe [28,29]. Previously described work [30] demonstrated the use of native citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles for the simultaneous detection of several ions. It should be noted that the simultaneous detection of several analytes reduces the applicability of these sensors since it does not allow for accurately determining the content of the desired ions in the sample. To ensure the specificity of metal detection, the functionalization of nanomaterial surface by various ligands was proposed [31,32]. Among these, pyrophosphate [33], chitosan [34], oxamic and p-aminobenzoic acids [35], casein [36], and native gold nanoparticles [37] were employed for colorimetric detection of Fe(III) ions in various environmental and biological samples.
The described methods for the determination of Fe(III) ions in water are based on the aggregation of AuNPs. However, most of these aggregation techniques require a rather long incubation stage (up to 30 min) of functionalized nanoparticles with an analyte solution [33,38]. Therefore, the present research has demonstrated that selectivity and the ability to achieve a low minimum detectable concentration of Fe(III) ions in the shortest possible time (less than 1 min) depended on the choice of the ligand for the functionalization of the nanoparticle surface. Thus, this study was used to suggest the modification of AuNPs with mercaprosuccinic acid (MSA), which benefits from its succinic acid functional group for selective recognition and is believed to have great potential for the highly sensitive detection of Fe(III) ions.
The studies mentioned above demonstrate that the selectivity and ability to achieve the minimum detectable concentrations largely depends on the choice of the ligand for the functionalization of the nanoparticle surface. Thus, the present study suggests the modification of AuNPs with mercaptosuccinic acid, which is believed to have great potential for the highly sensitive detection of Fe(III) ions. For the development of homogeneous aggregation analysis, it is preferable to use nanoparticles with a size of 20–40 nm, as previously described [39,40]. Particles larger than this have a smaller surface area, and particles smaller than this aggregate worse and have a higher degree of polydispersity [32,41].
Herein, a colorimetric sensor based on AuNPs functionalized with mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA) for simple, rapid, selective, and cost-effective detection of trace Fe(III) in water was developed. The choice of the functionalizing agent stemmed from the ability of MSA to form coordination compounds with iron due to two carboxyl groups [42,43,44]. The preparation of MSA-AuNPs was greatly simplified and included a one-step process with the simultaneous functionalization of the nanoparticles with a chelating ligand. The MSA-AuNPs colorimetric probe showed excellent sensitivity and selectivity to Fe(III) in the presence of other interfering metal ions. The reliability and practicability of the proposed colorimetric sensor were confirmed via analysis of drinking, tap, and spring water. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported MSA-functionalized AuNPs-based sensing probe for the colorimetric determination of trace levels of Fe(III) in aqueous media.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
An aqueous solution of Fe(III) (1 g/L) was obtained from the Center of Standardization of Samples and High-Purity Substances (St. Petersburg, Russia). Salts of Hg2+, Cd2+, As3+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Sn2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ag+, Ba2+, Mo4+, Ni2+, Mg2+, WO42−, Fe2+, Cr2O72−, NO3−, Cl−, and SO42− were also purchased from the Center of Standardization of Samples and High-Purity Substances. 2-MSA and tetrachloroauric(III) acid (HAuCl4) were sourced from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Milli-Q-purified water was obtained using a Milli-Q Simplicity water purification system from Millipore (Bedford, MA, USA) and used to prepare all aqueous solutions.
2.2. Synthesis of MSA-Functionalized AuNPs
The AuNPs were synthesized through the reduction of HAuCl4 using MSA [45] with slight modifications. First, 100 mL of 0.01% HAuCl4 solution was heated to its boiling point and stirred using a magnetic stirrer. Then, 12.5 mL of 1 mM aqueous solution of MSA was added to the reaction mixture. The MSA solution was preliminarily neutralized with sodium hydroxide in a stoichiometric ratio of 1:2 (mole per mole). Next, the reaction mixture was incubated with continuous stirring for 15 min and cooled to room temperature. The synthesized MSA-AuNPs were concentrated 10× using centrifugation before being resuspended in Milli-Q water with an adjustment to pH 3–4 and stored at 4–6 °C until analysis. The newly synthesized gold nanoparticles were able to be stored and remain functional for a year.
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
The prepared MSA-AuNPs were applied to 300-mesh grids (Pelco International, Redding, CA, USA) that were coated with a support film of polyvinyl formal that was deposited from chloroform. A JEM-100 CX electron microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) operating at 80 kV was used for obtaining the images. The digital images were analyzed using ImageTool software (University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX, USA).
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering of the AuNPs and Their Complex with Fe(III)
Dynamic light scattering investigations were provided with the use of a Malvern Zetasizer Nano (Malvern, UK). The data processing was carried out using Malvern Software 7.11 (Malvern, UK). All measurements were taken according to the recommendations in the manual [46]. The solutions were kept in thermostatic cell glass cuvettes for 5 min to measure the size characteristics of the nanoparticles and determine the zeta potential. For the last measurements, ZDTS 1070 zeta cell cuvettes were used. The accumulation of the autocorrelation function was performed for 1 min. The hydrodynamic radii were measured in triplicate for each sample. The size determination of particles was performed in the range from 0.3 nm to 10 μm. The zeta potential of the nanoparticles before and after the addition of Fe(III) was estimated in the range from −200 to +200 mV.
2.5. Fe(III) Ion Detection
A stock solution of Fe(III) (0.1 mg/mL in deionized water) was used to prepare standard solutions via serial dilution. To achieve the appropriate sensitivity and selectivity of the MSA-AuNPs sensing probe toward Fe(III), the pHs and the volume ratios of the components were preliminarily optimized. To detect the Fe(III) ions, 5 μL of concentrated MSA-AuNPs were added to an aqueous solution (pH 5) containing different amounts of Fe(III). After 5 min, the absorption spectra were measured with an EnSpire Multimode Plate Reader (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). When applying this technique for real water samples, a preliminary ten times dilution of the samples was used. To test the selectivity of the developed technique and the interference from other heavy metal ions, the solutions containing 100 ng/mL of Hg2+, Cd2+, As3+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Sn2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ag+, Ba2+, Mo4+, Ni2+, Mg2+, WO42−, Fe2+, Cr2O72−, NO3−, Cl−, and SO42− were examined. The limit of detection was determined as the concentration that generated a signal that was three times higher than the standard deviation of the background signal (signal in the absence of Fe(III)).
2.6. Analysis of Water Samples
Characterized samples of drinking, tap, and spring water were acidified to pH 5 with 1 M HCl and filtered through a syringe filter with a pore size of 0.2 µm (Sartorius, Germany). A preliminary assessment of the Fe(III) content in the real water samples revealed that dilution of the samples was required for analysis using the MSA-AuNPs-based colorimetric sensor. The Fe(III) concentration in the analyzed samples was determined using the additive method. For this purpose, different concentrations of Fe(III) were introduced into diluted water samples, and a colorimetric analysis was carried out on each sample.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensing Mechanism
In this study, MSA was chosen as a reducing, stabilizing, and capping agent due to its ability to convert Au(III) to Au(0) and to form chelate complexes in the presence of metal ions (see Figure 1a). The preferred coordination of MSA and Fe(III) toward forming a stable chelate complex was similarly demonstrated experimentally in an electrochemical system using a gold electrode modified with MSA [47]. The gold nanoparticles that were prepared using MSA had a surface plasmon resonance absorption peak of 530 nm and produced a red-colored solution. When the Fe(III) ions were added, the MSA-AuNPs aggregated, and the solution acquired a blue-gray color (see Figure 1b). The aggregation of MSA-AuNPs in the presence of Fe(III) ions caused the delocalization of conduction electrons of the AuNPs through the neighboring particles, which led to a shift in the surface plasmon resonance toward lower energies. This shift, in turn, caused a shift of the absorption and scattering peaks, resulting in longer wavelengths (see Figure 2c).
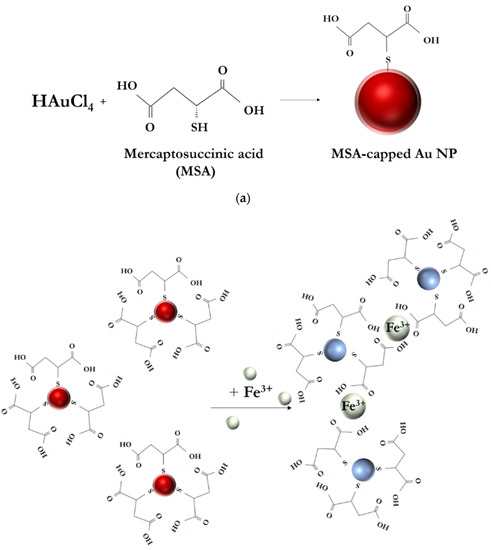
Figure 1.
(a) Scheme of MSA-AuNPs synthesis. (b) Scheme of colorimetric detection of Fe(III) ions using MSA-AuNPs.
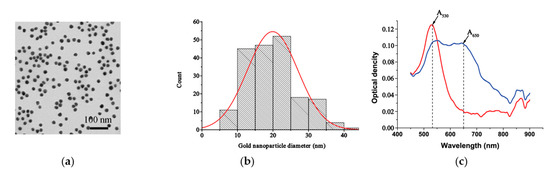
Figure 2.
(a) TEM image of MSA-AuNPs. (b) Histogram of MSA-AuNP particles’ diameter distribution. (c) Absorption spectrum of the MSA-AuNPs before (red) and after (blue) the addition of 35 ng/mL of Fe(III) ions. The concentration of MSA-AuNPs was 1.36 × 10−10 M.
3.2. Characterization of MSA-AuNPs
The procedure for the synthesis of MSA-AuNPs involved mixing the HAuCl4 and MSA solution at an optimal molar ratio of 2:1. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) image of MSA-AuNPs (see Figure 2a) and the nanoparticle size distribution (see Figure 2b) revealed that the resulting nanoparticles had a spherical morphology with an average diameter of 19.9 ± 7.1 nm (based on the examination of 195 particles). Furthermore, the shell around the AuNPs that was visualized in the TEM image confirmed the successful functionalization and preparation of the MSA-AuNPs sensing probe.
The aqueous colloidal dispersion of MSA-AuNPs was red with a surface plasmon resonance peak at 530 nm in the absorption spectrum (see Figure 2c). Upon the addition of 20 ng/mL Fe(III), the color of the MSA-AuNP solution rapidly changed from red to gray-blue, accompanied by a decrease in the intensity of the visible absorption band at 530 nm and the formation of a new peak at 650 nm (see Figure 2c). In this regard, the absorbance ratio A530/A650 was used to further assess the analytical performance of the colorimetric sensor.
The study of nanoparticles using the method of dynamic light scattering (DLS) showed that the synthesized nanoparticles had an average value of the hydrodynamic radius of 27.4 nm. The data obtained were consistent with the data of transmission electron microscopy. However, in the case of DLS, we had an additional contribution from the shell due to the hydration of the nanoparticle surface in an aqueous medium. In this case, the surface charge of the nanoparticles was negative (zeta potential was −27.9 mV). However, when the Fe(III) ions were added to a suspension of nanoparticles, their enlargement and a decrease in charge occurred due to the electrostatic interaction of positively charged iron ions and negative charges on the surface (Table 1), which confirmed the mechanism. With an increase in the Fe(III) concentration to a concentration of 100 ng/mL, the Fe(III) ions stuck to the nanoparticles with a critical approach and an increase in the size of the aggregate up to 600–700 nm. Thus, the surface charge changed to positive (zeta potential was +14.9) due to the screening of the surface with cations.

Table 1.
Characteristics of MSA-capped AuNPs obtained with the use of Malvern Zetasizer Nano (Malvern, UK).
3.3. Optimization of Conditions for Fe3+ Detection
To investigate the optimal conditions under which a colorimetric sensor based on MSA-AuNPs can effectively detect Fe(III) ions, the effects of pH and volumetric ratios of the reaction components were tested. The pH of the medium is a crucial factor for the selective detection of Fe(III) in the aggregation-based method because it can affect the surface charge of the sensing probes, binding sites of molecules, and complexation. Therefore, to determine the optimal pH, the spectrophotometric determination of Fe(III) ions was carried out in the pH range of 3.5–8.5. As shown in Figure 3a, when the Fe(III) ions were added to MSA-AuNPs, an obvious absorption change was observed under acidic conditions at a pH of 4–5. At a higher pH, the aggregation of MSA-AuNPs decreased and was zero at a pH greater than 6. Therefore, a pH of 4–5 was selected as optimal for further experiments.
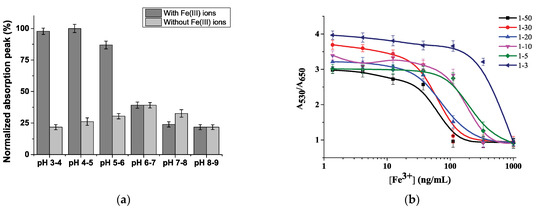
Figure 3.
Effect of the pH (a) and volume ratio of MSA-AuNPs and Fe(III) solutions on the absorbance change (b).
It is known that Fe(III) compounds are hydrolyzed and capable of forming insoluble iron hydroxide compounds (Fe(OH)3). One of the studies noted the effect of the combined presence of ions on the solubility and distribution of Fe(III) compounds in natural water [48]. For this study, seawater was taken, as well as various combinations of salts. It was shown that the dominant ion at pH 4–5 is (Fe(OH))2+ [48].
To optimize the detection sensitivity of the proposed colorimetric sensor, different volume ratios of MSA-AuNPs and Fe(III)-containing solutions were investigated. As follows from Figure 3b, the dilution of MSA-AuNPs in a larger volume of Fe(III)-containing solution increased the aggregation efficiency because of the optimal ratio of the binding sites of the analyte with the chelating ligand on the surface of the nanoparticles. The investigated ratios of the reaction components showed different working ranges for the Fe(III) ion determination. As shown in Figure 3b, the lowest detection limit and the highest signal-to-noise ratio occurred with the volume ratio of 1:30, which was chosen as optimal for further research.
3.4. Colorimetric Determination of Fe(III) Ions and the Analytical Performance
To assess the sensitivity of the proposed colorimetric sensor, the absorption spectra of MSA-AuNPs were studied after adding solutions containing Fe(III) in concentrations of 10 to 50 ng/mL. With an increase in the Fe(III) concentration, the absorption peak at 530 nm gradually decreased, whereas the peak at 650 nm, corresponding to the aggregation process, increased. Accordingly, the absorption ratio of A530/A650 decreased linearly over the range of Fe(III) concentrations from 20 to 30 ng/mL, with a correlation coefficient R2 = 0.98 (Figure 4). The RSD in this range did not exceed 13.5%. Since this is an aggregation method of analysis, we present it as a qualitative method since when a certain concentration was reached, a critical approach of nanoparticles and their aggregation occurred. For some time, an equilibrium was formed by the approaching particles, which made it possible to trace the linear portion of the curve. After that irreversible aggregation happened, the limit of detection was calculated as 23 ng/mL (0.4 nmol/mL); this value was more than 10 times lower than the maximum permissible concentration for drinking water, which is 300 ng/mL according to WHO regulations [49]. Upon aggregation, the color of the solution gradually changed from red to gray-blue, which allowed for the detection of Fe(III) with the naked eye. Visual assessment of the color change of MSA-AuNPs in the presence of metal ions revealed an Fe(III) detection limit of 30 ng/mL.
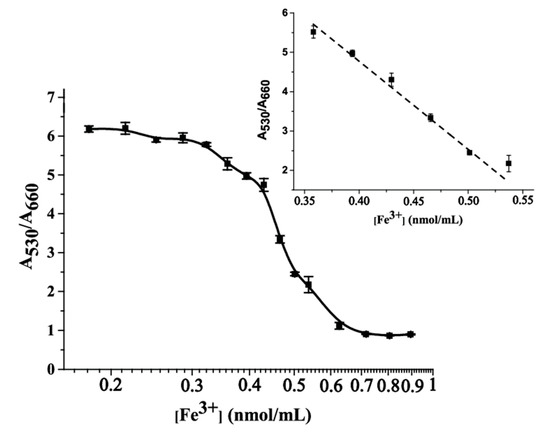
Figure 4.
Calibration curve for Fe(III) ion detection using MSA-AuNPs. Insert: Linear range of the calibration curve.
3.5. Selectivity of Fe(III) Ion Detection
Under optimal conditions, the selectivity of MSA-AuNPs toward Fe(III) ions in the presence of satellite metal ions (Hg2+, Cd2+, As3+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Sn2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ag+, Ba2+, Mo4+, Ni2+, Mg2+, WO42−, Fe2+) and anions (Cr2O72−, NO3−, Cl−, and SO42−) was studied. As shown in Figure 5, the color of the MSA-AuNP solution and the recorded absorption spectra changed only in the presence of Fe(III) ions, which indicated a specific coordination between the MSA and Fe(III) ions. In the presence of other metal ions, the color of the MSA-AuNP solution remained red without significant changes, even with a fivefold increase in the concentration of the competing metals. With the introduction of foreign ions, the value of the analytical signal did not exceed 20% of that for Fe(III) ions taken in equal concentrations (100 ng/mL). Therefore, among the investigated metal ions, only Fe(III) caused an increase in the absorption ratio of A530/A650, which confirmed the selectivity of the proposed sensing probe.
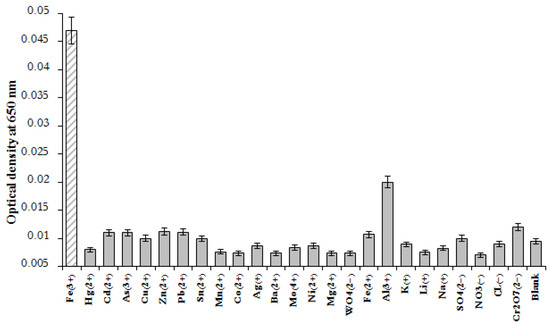
Figure 5.
Optical density of MSA-functionalized Au NPs at 650 nm after the addition of 100 ng/mL metal ions. The concentration of MSA-AuNPs was 5.4 × 10−11 M.
As a result of the experimental work, cross interactions with other ions in the studied concentrations were not revealed. As for the possibility of interaction of the residues of MCA with other ions, such as aluminum, several works showed the determination of aluminum in the joint presence with copper ions [50,51]. At the same time, in the developed electrochemical systems with potentiometric detection, the same interaction of copper and aluminum ions was observed. It was shown in our system that the presence of third-party ions (copper, aluminum, Fe(II), magnesium, cobalt, and others) did not interfere with the determination of Fe(III) ions. However, we could conclude that the presence of aluminum ions at a concentration above 300 ng/mL led to a change in the absorption spectrum of the studied nanoparticles.
3.6. Practical Application of Colorimetric Sensing Probe
To validate the practicability of the proposed colorimetric sensor, an analysis of tap, spring, and drinking water was performed. A preliminary assessment of the Fe(III) content showed its increased level in the real samples (Table 2). Because the achieved limit of detection was 23 ng/mL (0.4 nmol/mL), it was possible to dilute natural water samples by 10 times with the suitable buffer solution to provide the analysis without loss of sensitivity. Experimental assessment on the applicability of the developed technique was provided through the use of several samples, including spiked distilled water and diluted real water samples with added Fe(III). Water samples were spiked with standard Fe(III) solutions (15–30 ng/mL) and then analyzed. The results summarized in Table 3 demonstrated the recovery range of 89.6 to 126% and clearly confirmed the applicability of the developed colorimetric sensor for the accurate determination of Fe(III) ions in water.

Table 2.
Characteristics of spring water chemical composition (determined in an analytical laboratory using the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method with the use of a Nexion 300D quadrupole mass spectrometer (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA)).

Table 3.
Detection of Fe3+ in real water samples.
Comparison with existing methods of homogeneous analysis did not reveal many works (Table 4). Mainly for this purpose, gold nanoparticles and silver particles with various modifications were used. Table 4 shows that not every modification of nanoparticles made it possible to detect Fe ions with the required sensitivity. These values often exceeded the maximum allowable levels. The advantages of this work are the short analysis time (less than 1 min) and high analysis sensitivity, which made it possible to work, including with diluted samples. For the determination of iron ions, nanoparticles that were synthesized in one stage with the introduction of mercaptosuccinic acid as a reducing and stabilizing agent were used.

Table 4.
Examples of homogenous colorimetric assays for Fe(III) determination.
4. Conclusions
A highly sensitive approach involving an MSA-AuNP-based sensing probe for selective Fe(III) detection was developed. The results of the analysis can be easily determined visually or quantified by recording the absorption spectra and plotting the concentration dependence of the absorption ratios. Combining the advantages of one-step preparation of MSA-AuNPs with both rapidity and simplicity of analysis, the proposed colorimetric sensing probe allowed for visual detection of Fe(III) ions with a detection limit of 23 ng/mL (0.4 nmol/mL) under optimal conditions. The effectiveness of the developed system for the analysis of real samples was confirmed via the determination of Fe(III) ions in water samples. The main advantages of the developed technique are (i) the possibility of the rapid (within 1 min) assessment of Fe(III) ions in water samples, (ii) the possibility of determination with the naked eye and an observable color change occurring under the limit of detection, (iii) the high selectivity of the technique over the satellite divalent ions, and (iv) its cost-effectiveness. The method has application prospects, including with the use of other types of samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.K., K.V.S. and A.N.B.; methodology, A.N.B.; software, N.S.K.; validation, N.S.K. and K.V.S.; formal analysis, N.S.K.; investigation, N.S.K., K.V.S. and S.M.P.; resources, N.S.K., K.V.S., S.M.P. and A.N.B.; data curation, A.N.B. and A.V.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.K.; writing—review and editing, K.V.S., A.N.B. and A.V.Z.; visualization, N.S.K.; supervision, B.B.D.; project administration, A.V.Z. and B.B.D.; funding acquisition, A.N.B. and B.B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project # 19-44-02020, assay development) and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, Russian Federation (study of assay selectivity).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. The study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article. Data of experiments, calculations, and verifications are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, T.-T.; Yang, J.-X.; Song, J.-M.; Chen, J.-S.; Niu, H.-L.; Mao, C.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Shen, Y.-H. Synthesis of high fluorescence graphene quantum dots and their selective detection for Fe3+ in aqueous solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Iron in Drinking-water. Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/08. In Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Santana-Casiano, J.M.; González-Dávila, M.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Millero, F.J. The effect of organic compounds in the oxidation kinetics of Fe(II). Mar. Chem. 2000, 70, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Sotolongo, S.; Izaguirre, M. The oxidation kinetics of Fe (II) in seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. Iron toxicity and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 2002, 180, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Afkhami, A.; Saber-Tehrani, M.; Khoshsafar, H. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of Schiff base/silica/magnetite as a preconcentration phase for the trace determination of heavy metal ions in water, food and biological samples using atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 97, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Boyle, E.A. Determination of iron in seawater by high-resolution isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after Mg(OH)2 coprecipitation. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 367, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, T.; Ito, K.; Imura, Y.; Yoshimura, E. High-performance liquid chromatography method for ferric iron chelators using a post-column reaction with Calcein Blue. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 2015, 985, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didukh-Shadrina, S.L.; Losev, V.N.; Samoilo, A.; Trofimchuk, A.K.; Nesterenko, P.N. Determination of Metals in Natural Waters by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy after Preconcentration on Silica Sequentially Coated with Layers of Polyhexamethylene Guanidinium and Sulphonated Nitrosonaphthols. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1467631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fayed, T.A.; El-Nahass, M.N.; El-Daly, H.A.; Shokry, A.A. Development of nanomaterial chemosensors for toxic metal ions sensing. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Acha, N.; Elosúa, C.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J. Fluorescent Sensors for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media. Sensors 2019, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Bin, D.; Wei, Q. Highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for detection of Fe3+ based on Fe3O4@ZnO. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arvapalli, D.M.; Sheardy, A.T.; Alapati, K.C.; Wei, J. High Quantum Yield Fluorescent Carbon Nanodots for detection of Fe (III) Ions and Electrochemical Study of Quenching Mechanism. Talanta 2020, 209, 120538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shi, L.; Jia, J.; Chang, D.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Fe3+ detection, bioimaging, and patterning based on bright blue-fluorescent N-doped carbon dots. Analyst 2020, 145, 5450–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yang, Q.; Guo, C.; Sun, Y.; Xie, L.-H.; Li, J.-R. Stable Zr(IV)-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks with Predesigned Functionalized Ligands for Highly Selective Detection of Fe(III) Ions in Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10286–10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasree, M.; Aparna, R.S.; Anjana, R.R.; Anjali Devi, J.S.; John, N.; Abha, K.; Manikandan, A.; George, S. Fluorescence turn on detection of bilirubin using Fe (III) modulated BSA stabilized copper nanocluster; A mechanistic perception. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1031, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgung, H.; Kim, J.; Gwon, Y.; Lee, T.S. Synthesis of poly (p-phenylene) containing a rhodamine 6G derivative for the detection of Fe (III) in organic and aqueous media. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39852–39858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harathi, J.; Thenmozhi, K. AIE-active Schiff base compounds as fluorescent probes for the highly sensitive and selective detection of Fe3+ ions. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göde, C.; Yola, M.L.; Yılmaz, A.; Atar, N.; Wang, S. A novel electrochemical sensor based on calixarene functionalized reduced graphene oxide: Application to simultaneous determination of Fe(III), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Jin, S.; Wang, L. Metal nanoparticles-based nanoplatforms for colorimetric sensing: A review. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chae, J.B.; Kim, C.; Harrison, R.G. A visible chemosensor based on carbohydrazide for Fe(ii), Co(ii) and Cu(ii) in aqueous solution. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.-Q.; Wang, C.-X.; Yang, J.-X.; Gao, H.-W.; Tian, Y.-P.; Tao, X.-T.; Jiang, M.-H. A highly selective colorimetric chemosensor for detecting the respective amounts of iron(ii) and iron(iii) ions in water. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piriya, V.S.A.; Joseph, P.; Daniel, S.C.G.K.; Lakshmanan, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Muthusamy, S. Colorimetric sensors for rapid detection of various analytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; He, S.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Colorimetric detection of iron ions (III) based on the highly sensitive plasmonic response of the N-acetyl-l-cysteine-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunoğlu, D.; Ergüt, M.; Kodaman, C.G.; Özer, A. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Detection of Fe3+ Ions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lu, M.; Huang, X.; Li, T.; Xu, D. Application of Gold-Nanoparticle Colorimetric Sensing to Rapid Food Safety Screening. Sensors 2018, 18, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berlina, A.N.; Sharma, A.K.; Zherdev, A.V.; Gaur, M.S.; Dzantiev, B.B. Colorimetric determination of lead using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Komova, N.S.; Zherdev, A.V.; Gaur, M.S.; Dzantiev, B.B. Colorimetric Technique for Antimony Detection Based on the Use of Gold Nanoparticles Conjugated with Poly-A Oligonucleotide. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Pridvorova, S.M.; Gaur, M.S.; Dzantiev, B.B. Rapid Visual Detection of Lead and Mercury via Enhanced Crosslinking Aggregation of Aptamer-Labeled Gold Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 5489–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.S.; Dempsey, M.J.; Whitehead, D.E. The response of citrate functionalised gold and silver nanoparticles to the addition of heavy metal ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 518, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, S.; Tiwari, A. Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties and Applications-A Review. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 1869–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Progress in rapid optical assays for heavy metal ions based on the use of nanoparticles and receptor molecules. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-P.; Chen, Y.-P.; Sung, Y.-M. Colorimetric detection of Fe3+ ions using pyrophosphate functionalized gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 1887–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-J.; Wang, X.-F.; Huo, D.-Q.; Hou, C.-J.; Fa, H.-B.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L. Colorimetric measurement of Fe3+ using a functional paper-based sensor based on catalytic oxidation of gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buduru, P.; BC, S.R.R. Oxamic acid and p-aminobenzoic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles as a probe for colorimetric detection of Fe3+ ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Shinde, S.; Saratale, R.; Syed, A.; Ameen, F.; Ghodake, G. Spectrophotometric determination of Fe(III) by using casein-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4695–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatai, S.; Khurana, P.; Prasad, S.; Kumar, D. A new way in nanosensors: Gold nanorods for sensing of Fe(III) ions in aqueous media. Microchem. J. 2014, 113, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.K.; Woo, J.Y.; Han, C.-S. Colorimetric detection of Fe(III) ions using label-free gold nanoparticles and acidic thiourea mixture. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.C.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Awazu, K. Colorimetric detection of controlled assembly and disassembly of aptamers on unmodified gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 51, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarossi, M.; Schiattarella, C.; Rea, I.; De Stefano, L.; Fittipaldi, R.; Vecchione, A.; Velotta, R.; Ventura, B.D. Colorimetric Immunosensor by Aggregation of Photochemically Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3805–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.; Nazari, Z. A Review on Gold Nanoparticles Aggregation and Its Applications. J. Chem. Rev. 2020, 2, 228–242. [Google Scholar]
- Cheney, G.E.; Fernando, Q.; Freiser, H. Some Metal Chelates of Mercaptosuccinic Acid. J. Phys. Chem. A 1959, 63, 2055–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkworthy, L.F.; Sattari, D. Some complexes of thiomalate with bivalent transition metal ions and gold (I). J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1980, 42, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelec, M.; Stochel, G.; van Eldik, R. Mechanistic information on the copper-catalysed autoxidation of mercaptosuccinic acid in aqueous solution. Dalton Trans. 2004, 2004, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilev, K.; Zhu, T.; Glasser, G.; Knoll, W.; Kreiter, M. Preparation of gold nanoparticles in an aqueous medium using 2-mercaptosuccinic acid as both reduction and capping agent. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta Potential Measurement. In Characterization of Nanoparticles Intended for Drug Delivery; McNeil, S.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Shervedani, R.K.; Hatefi-Mehrjardi, A.; Asadi-Farsani, A. Sensitive determination of iron(III) by gold electrode modified with 2-mercaptosuccinic acid self-assembled monolayer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 601, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F. Speciation of metals in natural waters. Geochem. Trans. 2001, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mashhadizadeh, M.H.; Talemi, R.P. Used gold nano-particles as an on/off switch for response of a potentiometric sensor to Al(III) or Cu(II) metal ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 692, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, W.P.; Heng, L.Y.; Nathan, S. Highly Sensitive Aluminium(III) Ion Sensor Based on a Self-assembled Monolayer on a Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-printed Carbon Electrode. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koç, Ö.K.; Üzer, A.; Apak, R. A colorimetric probe based on 4-mercaptophenol and thioglycolic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles for determination of phytic acid and Fe(III) ions. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M. Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles as a Probe for the Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Water. J. Clust. Sci. 2014, 25, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.T.-T.; Dang, C.-H.; Huynh, T.K.-C.; Hoang, T.K.-D.; Nguyen, T.-D. In situ synthesis of gold nanoparticles on novel nanocomposite lactose/alginate: Recyclable catalysis and colorimetric detection of Fe(III). Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 116998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreani, A.S.; Kunarti, E.S.; Hashimoto, T.; Hayashita, T.; Santosa, S.J. Fast and selective colorimetric detection of Fe3+ based on gold nanoparticles capped with ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).