Abstract
The conventional CO electrochemical gas sensor uses aqueous H2SO4 solution as electrolyte, with inevitable problems, such as the drying and leakage of electrolyte. Thus, research on new alternative electrolytes is an attractive field in electrochemical gas sensors. In this paper, the application of a new fumed SiO2 gel electrolyte was studied in electrochemical gas sensors. The effects of fumed SiO2 and H2SO4 contents on the performance of the CO gas sensor were investigated. The results showed that the optimized composition of the SiO2 gel electrolyte was 4.8% SiO2, 38% H2SO4, and 0.005% polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Compared with aqueous H2SO4, the gel electrolyte had better water retention ability. The signal current of the sensor was proportional to the CO concentration. The sensitivity to CO was 78.6 nA/ppm, and the response and recovery times were 31 and 38 s, respectively. The detection limit was 2 ppm. The linear range was from 2 to 500 ppm. The gel electrolyte CO sensor possesses equivalent performance to that with aqueous electrolyte.
1. Introduction
Toxic, flammable, explosive and polluting gases in the environment pose a huge threat to human life and property safety. Thus, the online monitoring of gases is necessary. Gas sensors are effective for realizing fast and real-time monitoring of these dangerous gases. At present, the most widely used gas sensors on the market are semiconductor metal oxide, catalytic combustion, optical, and electrochemical sensors [1,2]. Korotcenkov comprehensively compared the advantages and disadvantages of various gas sensors [1]. Mahajan et al. pointed out the disadvantages of different types of gas sensors [2]. The few major disadvantages are as follows. Semiconductor metal oxide sensors operate at high temperature. Catalytic combustion sensors have low selectivity and risk of catalyst poisoning. Optical sensors have difficulty in miniaturization and high cost. Among these sensors, the electrochemical sensor, which has the advantages of room temperature operation, good linearity, and high measurement accuracy, is one of the main sensors used for accurate quantitative monitoring [3].
The electrochemical gas sensor has the above advantages, but usually uses aqueous H2SO4 solution as electrolyte. The conventional electrochemical gas sensor has problems such as water loss or absorption [4], resulting in short lifetime and poor long-term stability. Therefore, searching for alternative electrolytes has become an important aspect in electrochemical gas sensors. The study of alternative electrolytes has been focused on ionic liquids [5], polymers [6] and inorganic solid electrolytes [7]. Considering their low saturated vapor pressure and good stability, ionic liquids have become one of the hotspots of gas sensor studies in recent years and are expected to solve the problems of current aqueous electrolytes. However, the diffusion of reactants in ionic liquids is slow due to high viscosity of ionic liquids, leading to long response time [8]. Nafion is the most widely used polymer electrolyte in gas sensors because of its high proton conductivity, high water diffusivity and good gas permeability [4,9]. Nafion has also been successfully applied to commercialized CO gas sensors, which show good performance to the CO gas [9,10,11]. The ionic conductivity of Nafion results from the mobility of the hydrated H+ that moves through the polymer film by passing from one H2SO4 group to another [3]. The sensor needs a reservoir to store water, resulting in the sensor having a large volume [6].
Inorganic gel electrolytes especially those with SiO2 as gelling agent have many advantages over organic colloids, including physical rigidity and high wear resistance, low expansibility in water and organic solutions, chemical inertia, and high thermal stability [12]. However, gel electrolytes have high viscosity and a short gelling time, leading to long electrolyte injection time, and may also lead to uneven distribution of electrolyte. The high viscosity of the colloidal electrolyte may also reduce the diffusion coefficient of gas and ions in the electrolyte and reduce the sensitivity of the sensor. Gel electrolyte containing SiO2 is prepared using the sol–gel method by using colloidal SiO2 or fumed SiO2 as gelling agent. The gelling agents do not participate in the electrochemical reactions within the gas sensor, and their main function is to form a three-dimensional network structure for the entrapment of the aqueous H2SO4 solution. The gel electrolyte containing SiO2 is widely used in lead–acid batteries [13,14,15], which possess long lifetime, high reliability under depth of discharge cycles, minimal or even no leakage of acid electrolyte, and minimal corrosion [15].
There is an interaction strong force between water and SiO2 in the gel electrolyte [14], and the gel electrolyte has a high viscosity, so it is expected to have a good water retention ability. The “semi-solid” gel electrolyte containing SiO2 brings hope for solving the problems of dryness and the leakage of conventional aqueous electrolyte. At present, few studies have reported the application of SiO2 gel electrolyte in electrochemical gas sensors for the quantitative analysis of monomethyl hydrazine [16], carbon monoxide [17], hydrogen peroxide [18] and gas chromatographic detectors [7]. The gel electrolytes in these sensors are prepared through the hydrolysis of ethyl orthosilicate to form colloid SiO2. The method has problems such as long gelling time and poor stability and reliability. Gel electrolytes prepared with fumed SiO2 can overcome the above shortcomings [14,19]. Nevertheless, fumed SiO2 is often used as gelling agent in the SiO2 gel electrolyte lead–acid battery, and literature regarding fumed SiO2 gel electrolyte used in gas sensors is not available.
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas produced during incomplete combustion. CO poisoning is a major public health problem; CO may be responsible for more than one half of all fatal poisonings that are reported worldwide each year [20]. The current Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) permissible exposure limit (PEL) for carbon monoxide is 50 parts per million (ppm) parts of air (55 milligrams per cubic meter (mg·m−3)) as an 8 h time-weighted average (TWA) concentration. CO is impossible to detect by a person because it is colorless, odorless. Therefore, it is very necessary to develop carbon monoxide gas sensor to detect CO concentration in the environment.
In this paper, gel electrolytes were prepared through the sol–gel method by using fumed SiO2 as the gelling agent and aqueous H2SO4 solution as the liquid phase. Pt black was used as an electrocatalyst in the working (WE), counter (CE), and reference (RE) electrodes. A three-electrode amperometric electrochemical gas sensor with constant potential was fabricated. The effect of the composition of the gel electrolyte in the performance of the CO sensor was investigated, and the sensing performance of the sensor was extensively evaluated. The purpose of this work is to demonstrate the good water retention ability of fumed SiO2 gel electrolyte and to provide an example of the application of fumed SiO2 gel electrolyte in electrochemical gas sensor.
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Pt Black
99.95% H2PtCl6·xH2O (trace metals basis) solution and 98% NaBH4 (analytically pure)were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China. The Pt black was prepared using the NaBH4 reduction method, and the specific preparation process can be seen in our previous report [21]. 20 mL 10% H2PtCl6 solution was added into a 200 mL beaker, then 150 mL deionized water was added. The solution was frozen to 0 °C in a refrigerator. 5 g NaBH4 was added into a 500 mL beaker, then the above frozen H2PtCl6 solution was slowly added into the 500 mL beaker. The reaction produced black precipitate and a lot of bubbles. The precipitation was washed five times with deionized water, filtered, and dried at 50 °C to obtain platinum black catalyst. The morphology of the Pt black catalyst and the screen-printed electrodes were observed using transmission (FEI TalosF200S, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and scanning (Auriga-bu, Oberkochen, Germany) electron microscope. The electrode materials of the sensor were characterized using an X-ray diffractometer (D8 Advance, Bruker, Hamburg, Germany).
2.2. Preparation of the Gel Electrolyte
The fumed SiO2 (model Hydrophilic-200) with a specific surface area of 200 m2·g−1 and a particle size of 7–40 nm was purchased from Shanghai Tengzhun Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China. H2SO4 (98%, analytically pure) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA chemically pure) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China.
Dilute H2SO4 with a mass concentration of 60% was prepared and placed in the refrigerator to cool down for later use. The 4.8% SiO2-38%-H2SO4-0.005% PVA sol electrolyte preparation process was as follows: 35.67 mL deionized water and 5.0420 g SiO2 were added to a 250 mL glass beaker. The mixture was stirred at 2000 r/min for 3 min. Then, 42.39 mL 60% H2SO4 solution and 1.00 mL 0.05% PVA solution were added and stirred at 600 r/min for 1 h to obtain the sol electrolyte. The PVA solution (0.05%) was prepared in water baths maintained at 99 °C and cooled before use. SiO2 gel solutions with mass content of 9%–25% were prepared on site and used immediately. A certain amount of the as-prepared H2SO4, SiO2 gel, and PVA solutions were mixed under stirring to prepare gel electrolytes with different content of SiO2 and H2SO4.
2.3. Fabrication and Measurement of the Sensor
The CO electrochemical sensor was a three-electrode structure in the experiment. Pt black was printed on polytetrafluoroethylene film by screen-printing technology to obtain the WE, CE, and RE [21]. The electrodes were prepared with the help of Zhengzhou Winsen Electronic Technology Co. Ltd., Zhengzhou, China. The preparation process of electrodes included screen printing, drying, ethanol washing, deionized water washing, drying and so on. According to the assembly process, the CE, glass mat, RE, glass mat, and WE were loaded into the sensor holder in sequence, which was purchased from Zhengzhou Winsen Electronic Technology Co. Ltd., Zhengzhou, China. The top cover was sealed by ultrasonic bonding. The gel electrolyte was injected into the shell through the injection hole. The injection hole was sealed by ultrasonic bonding. The sensor was stored at room temperature for 24 h until the electrolyte formed a stable gel. Finally, the performance of the sensor was measured after 24 h of electrical aging, as shown in Figure 1.
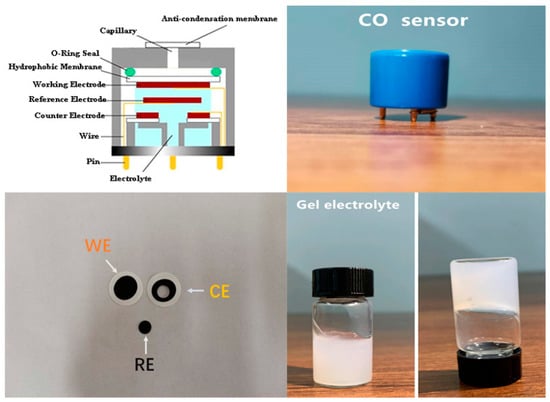
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram of the sensor structure with the photos of electrodes, sensor and gel.
Standard CO gas samples were purchased from Henan Yuanzheng Science and Technology Development Co. Ltd., China. The sensing performance was measured using a gas sensor test system (EC–CALS00, EC-Sense GmbH, Ebenhausen, Germany). The sensor test system consisted of a gas mixing control unit, a signal acquisition unit, computer control and a storage unit, as shown in Figure 2. The gas mixture control unit included standard CO gas, clean air and a digital flow meter. The required concentration of the CO gas was obtained by controlling the standard CO gas and clean air flow through a digital flow meter. The signal acquisition unit comprised a signal collector and a sensor adapter connected thereto, and the sensor was inserted into the adapter. When testing the sensor, the required CO concentration and humidity are set by the software on the computer, and the information is received by the digital flow meter and used to automatically adjust CO and air flow. The mixed gas enters the sensor adapter, and the data acquisition system automatically collects and stores sensor signals.
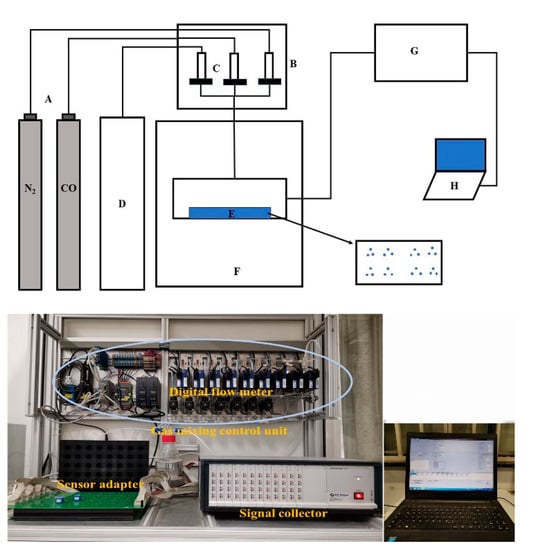
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram of the sensor test system with the photos of gas mixing control unit, signal acquisition unit, computer control and storage unit. A: Gas cylinder, B: Gas mixing control unit, C: Digital flow meter, D: Clean air, E: Sensor adapter, F: Climate Chamber, G: Signal acquisition unit, H: Computer control and storage unit.
Through software control, the system can complete the sensor performance tests, i.e., gas concentration, temperature and humidity control; sensor signal acquisition; data storage and analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Electrode Materials
The TEM image of the Pt black is shown in Figure 3a. The prepared Pt black particles were spherical and uniform. The particles had a size distribution of 5–11 nm, as shown in Figure 3c. The average diameter was 8 nm calculated from TEM image. The crystal lattice was calculated to be 0.225 nm, which is assigned to a (111) plane according to the standard reference from the Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (PDF01-087-0640). Figure 3b shows the SEM image of the screen-printed WE. The nanosized Pt black particles were dispersed on the surface of the rod-shaped hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene. The hydrophilic Pt black and the hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene formed a gas diffusion electrode favorable for the gas liquid solid three-phase contact.
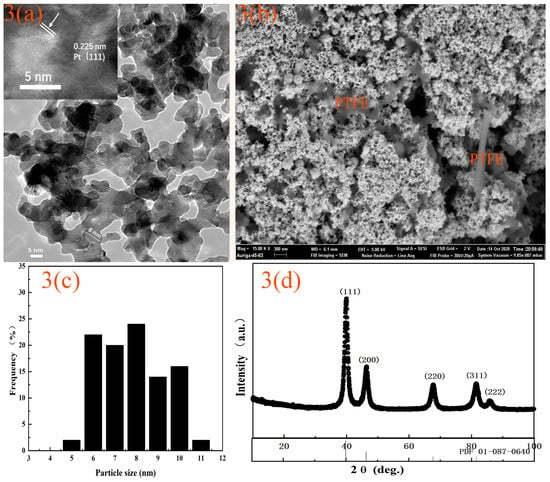
Figure 3.
Characterization of Platinum black and electrode. (a) TEM and HRTEM image of Pt black, (b) SEM of electrode, (c) Size distribution of Pt black particles, (d) XRD spectra of the Pt black.
Figure 3d shows the XRD patterns of the as-prepared Pt black. The XRD patterns revealed that Pt black particles agreed well with the JCPDS reference (PDF01-087-0640), in which the diffraction peaks at 2θ = 39.89°, 41.71°, 67.71°, 39.14°, 81.57°, and 86.04° were assigned to the (111), (200), (220), (311), and (222) diffraction planes. These results indicated that the Pt black prepared had a cubic structure. The particle size of the Pt black calculated using the Scherer formula from the strongest diffraction peak was 7.7 nm, which was consistent with the results obtained using TEM.
3.2. Gel Preparation
Gel properties, including stability, strength, and gelling time, are important for forming a gel electrolyte suitable for gas sensors. The electrolyte of a commercial CO electrochemical sensor is composed of aqueous H2SO4 solution. Thus, the effects of SiO2 and H2SO4 contents on the strength and gelling time of gel electrolyte should be investigated. Many studies prove that SiO2 influences the properties of gel electrolytes. Tantichanakul et al. showed that electrolytes containing 3.0%–4.0% SiO2 took more than 5 h to form a gel, whereas those containing 5.0% and 6.0% SiO2 started to form a gel after 3 and 2 h, respectively [13]. Most researchers believe that electrolyte with 4.0%–6.0% SiO2 has improved performance [13,14]. Gençten et al. showed that gel structures with 6.0%–8.0% SiO2 are good [19]. The range of the SiO2 content in this study was 4.0%–8.0%, to ensure the formation of a stable gel. According to reports in the literature, the H2SO4 concentration range in the gel electrolyte is 30%–42% [13,14,15]. In this experiment, the H2SO4 concentration range was between 30% and 40%.
Experimental results showed that the stable gel can be formed at PVA of 0.005%, SiO2 of 4.0%–8.0% and H2SO4 of 30%–40%. The content of fumed SiO2 is a key factor affecting the gel properties. With increasing SiO2 content, the gelling time shortened, and the viscosity increased rapidly. Figure 4 shows the influence of the SiO2 content on gelling time at 38% H2SO4 and 0.005% PVA. As shown in Figure 4, when the SiO2 content increased from 4.0% to 5.6%, the gelling time decreased rapidly from 360 to 80 min. Further increasing the SiO2 content resulted in slowly decreased gelling time and rapidly increased viscosity. When the SiO2 content was 8%, the gelling time decreased to 35 min.
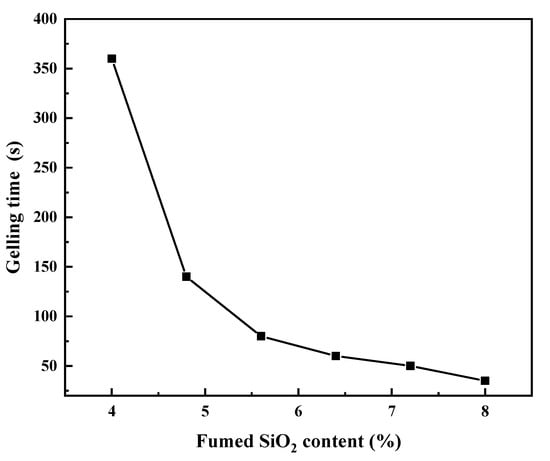
Figure 4.
Effect of fumed SiO2 content on the gelling time.
When the fumed SiO2 is dispersed in aqueous media, the isolated silanols may form hydrogen bonds with both the isolated silanols on other silica particles (weak hydration forces) and water molecules (strong hydration forces). When fumed SiO2 is used in H2SO4 solution, most of its isolated surface silanols link to form weak hydrogen bonds with each other. This gives a three-dimensional network gel structure, entrapping the H2SO4 solution [14]. With the increase of SiO2 content, the number of hydrogen bonds increases, resulting in short gelling time and high viscosity.
EIS of the sensors integrated with the gel and the aqueous H2SO4 solution electrolyte are compared in Figure 5. Obviously, the resistance of electrolyte of the gel-based sensor reaches 38 Ω, much larger than that of the aqueous H2SO4-based sensor (3.5 Ω). The major reason is presumably the lower conductivity of the gel. On the other hand, the resistance of charge transference of the gel-based sensor is also larger, reflecting the sluggish electrochemical kinetics in the gel-based electrolyte.
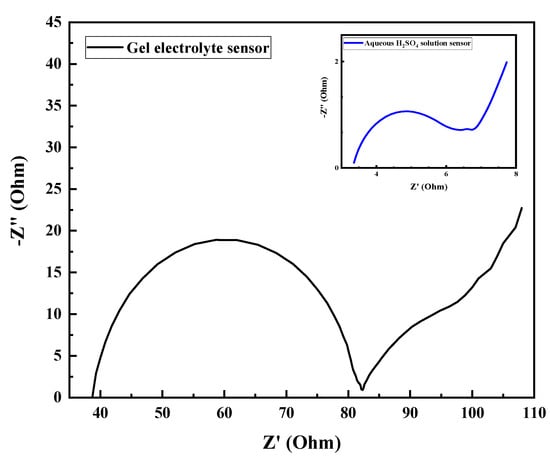
Figure 5.
Electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) of the SiO2 gel electrolyte and the aqueous H2SO4 solution sensors.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed in air with a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1 on Shimadzu DTG-60 instruments, Shimadzu, Japan. Figure 6 shows the typical TGA curves for aqueous H2SO4 solution and SiO2 gel electrolytes. The TGA curves of aqueous and gel electrolytes the showed apparent weight loss from 40 °C to 170 °C. The weight loss was due to the loss of water in the electrolyte. The weight loss of aqueous H2SO4 solution is obviously greater than that of colloidal electrolyte. The water loss of aqueous solution was 1.52 times that of gel at 100 °C. The weight loss of water in the gel electrolyte was reduced by 34% at 100 °C. Better water retention of gel electrolyte is beneficial to prolonging the life of the sensor under dry conditions.
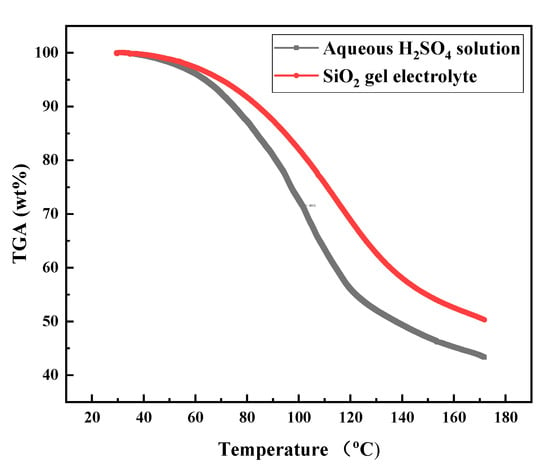
Figure 6.
TGA curves of the SiO2 gel and aqueous H2SO4 solution electrolytes.
3.3. Effect of Fumed SiO2 Content on the Response of CO Sensor
The three-electrode electrochemical gas sensor adopted the structure of WE, CE, and RE, in which no current passing between RE and WE were observed, and RE was used as a standard to stabilize the voltage of WE. At WE potential of 0 V (vs. Pt RE), the CO sensor has the best performance [9]. The commercial electrochemical gas sensor usually uses 0 V bias voltage [22]. In this paper, the amperometric measurements were performed at 0 V vs. Pt RE. It is known from [9,10,11] that electrode reactions are as follows:
The content of SiO2 greatly influenced the performance of the gel electrolyte, thereby influencing the performance of the electrochemical gas sensor. Therefore, CO gas sensors with 4.0%, 4.8%, 5.6%, 6.4% and 7.2% fumed SiO2 were prepared, and the PVA and H2SO4 in the gel electrolyte were fixed at 0.005% and 38%, respectively. The influence of the SiO2 content on the response current I of the CO sensor was investigated Figure 7. With increasing SiO2 content, the response of the sensor to 200 ppm CO first increased and then decreased. When the SiO2 content increased from 4.0% to 5.6%, I increased from 8.4 μA to 19.8 μA. When the SiO2 content was further increased to 6.4%, I decreased to 11.9 μA. At SiO2 content of 7.2%, I decreased slightly. For clarity, the response curve of the sensor with 7.2% SiO2 content was not given in Figure 7. When the SiO2 content reached 8.0%, the gelling time decreased to 35 min, and the viscosity was too high to complete glue injection. The decreased response may be due to the increased SiO2 content, which sharply increased the electrolyte viscosity and significantly shortened the gelling time. This phenomenon resulted in difficult liquid injection and the even distribution of electrolyte in the sensor.
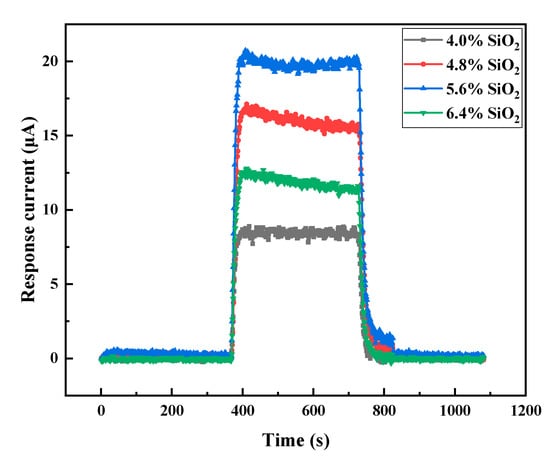
Figure 7.
Effect of SiO2 content on the response of the gel electrolyte electrochemical CO gas sensor. Test conditions: 25 °C, 50% RH, 200 ppm CO, and 1000 sccm CO.
The sensor containing the gel electrolyte with 5.6% SiO2 had the highest sensitivity but had a gelling time of only 80 min. At the same time, electrolyte with high SiO2 content resulted in high viscosity of the electrolyte and long injection time, which brought difficulties to the mass production of the sensors. The sensor with 4.8% SiO2 had high sensitivity to CO, and used as electrolyte the subsequent tests.
3.4. Effect of H2SO4 Concentration on the Response of the CO Sensor
The H2SO4 concentration is another important factor affecting the properties of the gel electrolyte and the gas-sensing performance of sensor. Thus, the effect of H2SO4 concentration on the CO sensing properties was investigated. The PVA and the fumed SiO2 in the gel electrolyte were fixed at 0.005% and 4.8%, respectively. Gel electrolyte electrochemical gas sensors with H2SO4 concentration of 32%, 35% and 38% were prepared. The test results are shown in Figure 8.
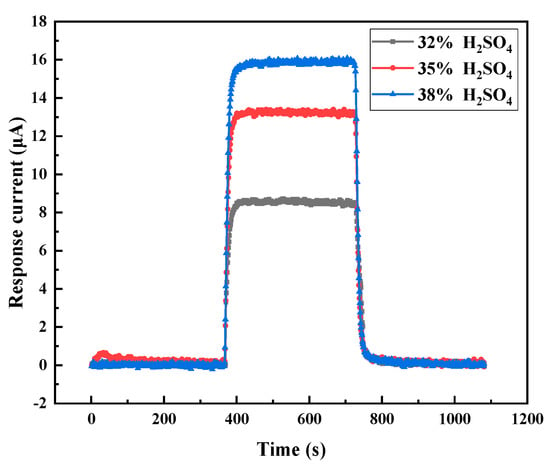
Figure 8.
Effect of H2SO4 concentration on the response of the gel electrolyte electrochemical CO gas sensor. Test conditions: 25 °C, 50%RH, 200 ppm CO, and 1000 sccm CO.
Figure 8 shows that increasing the H2SO4 concentration resulted in significantly increased response to 200 ppm CO. When the H2SO4 concentration increased from 32% to 35% and from 35% to 38%, the response increased by 4.6 and 2.8 µA, respectively. At H2SO4 concentrations greater than 38%, the viscosity of the solution increased rapidly, and the gelling time shortened, which was not conducive to the liquid injection operation. Thus, the H2SO4 concentration was not further increased in this experiment and set to 38%.
3.5. Performance of the CO Sensor Based on the SiO2 Gel Electrolyte
Based on the above discussion, gel electrolytes with 4.8% SiO2, 38% H2SO4, and 0.005% PVA were chosen, and the aqueous electrolyte was 38% H2SO4 solution. The test parameters were set as follows: 25 °C temperature, 50% relative humidity (RH), and 1000 sccm CO gas flow rate.
The responses of the two sensors to 200 ppm CO were tested to compare the performances of the aqueous H2SO4 solution and the gel electrolyte sensors. The transient response curve is shown in Figure 9. The response curves of the two sensors had a similar trend, and the response/recovery curves of the two sensors overlapped almost completely. After stabilization, the aqueous H2SO4 and the gel electrolyte sensor had I values of 17.57 μA and 15.71 μA, respectively, and sensitivity values of 87.9 and 78.6 nA/ppm, respectively. The sensitivity of the aqueous H2SO4 electrolyte sensor was slightly higher than that of the gel electrolyte sensor. The transient response of the gel electrolyte sensor was similar to that of the conventional aqueous H2SO4 solution electrolyte sensor.
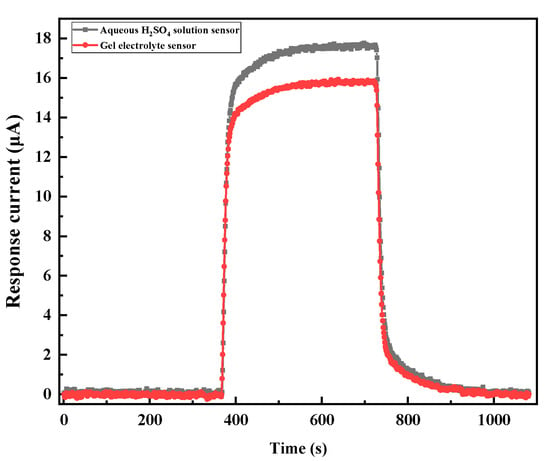
Figure 9.
Transient response curves of the sensors to 200 ppm CO.
The transient response curves of gel electrolyte sensors towards different concentrations of CO are shown in Figure 10. The baseline of the sensor was stable in air. When 200 ppm CO gas was injected, the electrochemical reaction occurred, and I increased rapidly, reached the maximum value, and entered a stable platform area. After the adoption of air replacement CO, the concentration of CO decreased rapidly, and the I signal dropped rapidly. The sensitivity was 78.6 nA/ppm, and the response and the recovery times (T90) were 31 and 38 s, respectively. Therefore, the gel electrolyte electrochemical CO gas sensor had excellent response/recovery characteristics.
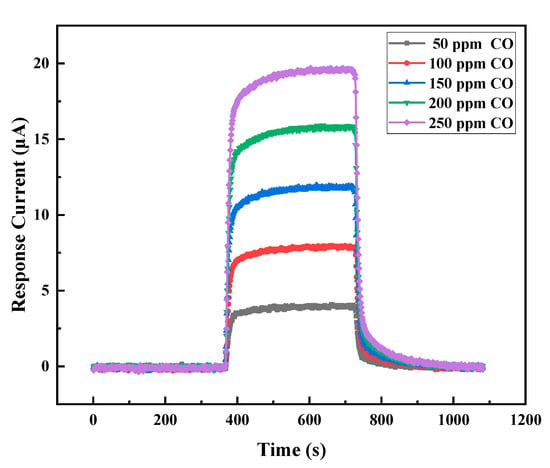
Figure 10.
Transient response curves of the sensor to different concentrations of CO.
Figure 11 shows the relationship between the I of the sensor and the concentration of CO. The signal current of the sensor was proportional to the CO concentration, which was an important advantage of the electrochemical gas sensor and ensured the quantitative detection of CO. The electrode reaction rate was fast because of the high catalytic activity of the nanosized Pt black. The diffusion is the rate-determining step [22,23]. In a steady-state diffusion, the CO diffusion flux can be described by Fick’s first Law:
where is the diffusion flux of the CO gas (mol·[cm−2·s−1]); is the diffusion coefficient of the CO gas in the gel electrolyte (cm2·s−1), and is the concentration gradient of CO (mol·cm−4). The negative sign indicates that the direction of diffusion is opposite to that of the concentration increase.
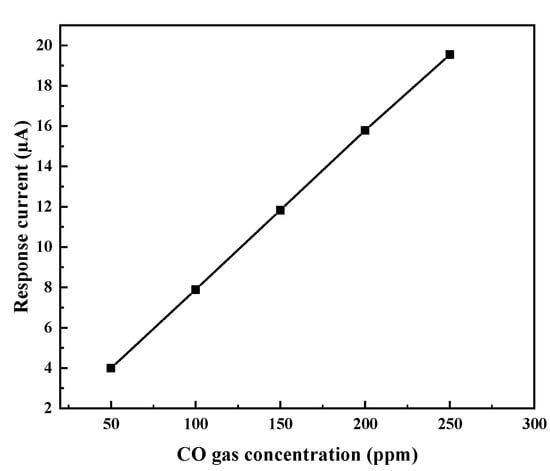
Figure 11.
Relationship between the response of sensor and the CO gas concentration.
The thickness of the liquid layer on the catalyst surface was constant due to the semi-wetting state of the catalyst surface. The reactant was a flowing gas in the gas phase, The CO concentration in the gas phase could be considered constant. The mass transfer process of the electrochemical gas diffusion electrode was a typical steady-state diffusion. According to Faraday’s law, the current density is proportional to the diffusion flux of the CO gas:
where i represents current density (A·cm−2), n is the number of electrons exchanged during the electrode process, F is the Faraday constant (C·mol−1); and are the bulk concentration of CO in the liquid and the surface concentration of the electrode, respectively (mol·cm−3), and l is the thickness of the diffusion layer (the thickness of the liquid layer on the surface of the catalyst, cm).
The concentration of CO in the gas phase () is proportional to the concentration of the bulk CO in the liquid phase ().
where k is the proportional coefficient, and A is the electrode area. Combining Equations (2) and (3), I is:
In the rate-determining diffusion process, the electron transfer step can be considered to be a quasi-reversible process, and the surface reaction can be considered to be in an equilibrium state, which conforms to the Nernst equation. is a constant value at 0 V. Therefore, a linear relationship between the I and CO concentration was observed. As shown in Figure 11, I was directly proportional to the CO gas concentration (), which agreed with the finding that the reactant diffusion was the rate-determining step. Moreover, the linear extension line in Figure 11 intersected with the coordinate (0, 0). From the Formula (4), the CO concentration () on the electrode surface tended to be zero, indicating the high catalytic activity of the Pt black.
The ambient temperature influenced the performance of the CO gas sensor, whereas the ambient humidity had almost no effect on the sensitivity of the sensor. Therefore, the influences of ambient temperature (−15 °C to 50 °C) on the sensors of conventional aqueous H2SO4 and SiO2 gel electrolytes were compared. The gas-sensing measurement for 200 ppm CO was carried out in 50% RH ambient humidity. The relative sensitivity (Sr) is defined as:
where represents the sensitivity at 25 °C, and S is the sensitivity at a certain temperature. is based on the sensitivity at 25 °C, and the Sr at other temperatures is obtained. The Sr is 100% at 25 °C.
As shown in Figure 12, the two curves had the same trend, and the sensitivity increased with increasing temperature. These findings were due to the electrode reaction process being controlled by CO diffusion, and the diffusion rate () became faster when the temperature increased. The result showed that the Sr increased with increasing ambient temperature. At the same time, Figure 12 shows no significant difference in the effect of ambient temperature in the performance of the two sensors. Therefore, the gel electrolyte sensor had the same resistance to environmental impact as the conventional aqueous H2SO4 electrolyte sensor.
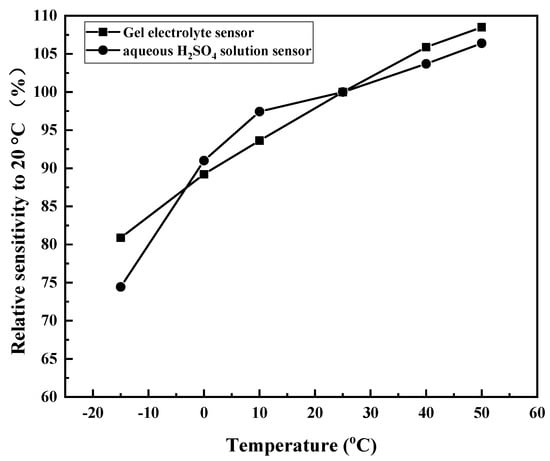
Figure 12.
Influence of ambient temperature on the relative sensitivity of the two sensors.
4. Conclusions
The feasibility of applying fumed SiO2 gel electrolytes in electrochemical gas sensors was studied. A three-electrode amperometric CO gas sensor was fabricated using Pt black as catalyst and fumed SiO2 gel as electrolyte. First, the reasonable composition range of the electrolyte was determined in accordance with the physical properties of the gel and the requirements of the CO electrochemical sensor. Then, according to the performance of the sensor, the composition of the gel electrolyte influenced the I of the sensor. The sensors with electrolyte containing 4.8% SiO2 had the maximum sensitivity. With increasing H2SO4 concentration, the I of the sensor increased. However, further increasing the H2SO4 concentration resulted in rapidly increased solution viscosity, thereby causing difficulties for electrolyte injection. Finally, the optimum composition of the gel electrolyte was 4.8% SiO2, 38% H2SO4 and 0.005% PVA.
Thermogravimetric analysis showed that the weight loss of water in the gel electrolyte was 34% lower than that of sulfuric acid solution at 100 °C. Good water retention of the gel electrolyte is beneficial to prolonging the life of the sensor under dry conditions. However, gel electrolyte sensors have higher resistance of charge transference than that of aqueous H2SO4 solution electrolyte sensors.
The new electrolyte may bring new advantages to the electrochemical sensor. Thus, further studying the other properties of the gel electrolyte electrochemical sensor, especially the sensor performance under harsh environment and long-term stability, should be conducted.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft; D.C.; Z.W.; and F.L. software, formal analysis, validation; F.F.; Z.Z. writing—review and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22008223), Research program on planar electrochemical gas sensor (20180712, Zhengzhou Winsen Electronic Technology Co. Ltd., Zhengzhou, Henan 450001, China).
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Zhengzhou Winsen Electronics Co. Ltd., Zhengzhou, Henan 450001, China.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflict to declare.
References
- Korotcenkov, G. Metal oxides for solid–state gas sensors: What determines our choice? Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Jagtap, S. Metal-oxide semiconductors for carbon monoxide (CO) gas sensing: A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, J.R.; Li, J. Amperometric Gas Sensors—A Review. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyodo, T.; Goto, T.; Takamori, M.; Ueda, T.; Shimizu, Y. Effects of Pt loading onto SnO2 electrodes on CO-sensing properties and mechanism of potentiometric gas sensors utilizing an anion-conducting polymer electrolyte. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 300, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Review—Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids for Electrochemical Application with Special Focus on Gas Sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Dai, M.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Suo, H.; Sun, P.; Lu, G. Effect of the dispersants on the performance of fuel cell type CO sensor with Pt–C/Nafion electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinecker, W.H.; Miecznikowski, K.; Kulesza, P.J.; Sandlin, Z.D.; Cox, J.A. Amperometric detector for gas chromatography based on a silica sol-gel solid electrolyte. Talanta 2017, 174, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.W.; Lu, J.M.; Qi, D.Z. Applications of ionic liquids in amperometric electrochemical gas sensors. Chem. Ind. Eng. Pro. 2013, 32, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wal, P.; De Rooij, N.; Koudelka-Hep, M. Extremely stable Nafion based carbon monoxide sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 35, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, A.; Shimidzu, T. Electrochemical carbon monoxide sensor with a Nafion® film. React. Funct. Polym. 1999, 41, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Liang, X.; Suo, H.; Sun, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J.; et al. Highly sensitive amperometric Nafion-based CO sensor using Pt/C electrodes with different kinds of carbon materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, O.; Tsionsky, M.; Rabinovich, L.; Glezer, V.; Sampath, S.; Pankratov, I.; Gun, J. Organically modified sol-gel sensors. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 22A–30A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantichanakul, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Tantavichet, N. Influence of fumed silica and additives on the gel formation and performance of gel valve-regulated lead–acid batteries. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Shu, D.; Li, A.; Finlow, D. Effects of preparation condition and particle size distribution on fumed silica gel valve-regulated lead–acid batteries performance. J. Power Sources 2008, 181, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantichanakul, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Tantavichet, N. Gelled electrolytes for use in absorptive glass mat valve-regulated lead–acid (AGM VRLA) batteries working under 100% depth of discharge conditions. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8764–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrom, S.D.; Sandlin, Z.D.; Steinecker, W.H. Mediated Oxidation and Determination of Gaseous Monomethyl Hydrazine in a Solid–State Voltammetric Cell Employing a Sol–Gel Electrolyte. Electroanalysis 2015, 12, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tess, M.E.; Cox, J.A. Humidity-independent solid–state amperometric sensor for carbon monoxide based on an electrolyte prepared by sol–gel chemistry. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrom, S.D.; Cox, J.A. Solid–state voltammetric determination of gaseous hydrogen peroxide using nanostructured silica as the electrolyte. Electroanalysis 2015, 10, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencten, M.; Dönmez, K.B.; Sahin, Y.; Pekmez, K.; Suvaci, E.; Suvacı, E. Voltammetric and electro–chemical impedimetric behavior of silica-based gel electrolyte for valve-regulated lead-acid battery. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raub, J.A.; Mathieu-Nolf, M.; Hampson, N.B.; Thom, S.R. Carbon monoxide poisoning—A public health perspective. Toxicology 2000, 145, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L. CO Electrochemical Gas Sensor Based on Water-Based Electrode. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China, 2012. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD2012&filename=1012353871.nh (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Carter, M.T.; Stetter, J.R.; Findlay, M.W.; Patel, V. Printed Amperometric Gas Sensors. ECS Trans. 2013, 50, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, P.R.; Pagano, M.P.; Hoover, R.; Logman, M.; Crytzer, K.; Warburton, Y.J. Amperometric Gas Sensor Response Times. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).