3D-Printed Graphene Electrodes Applied in an Impedimetric Electronic Tongue for Soil Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
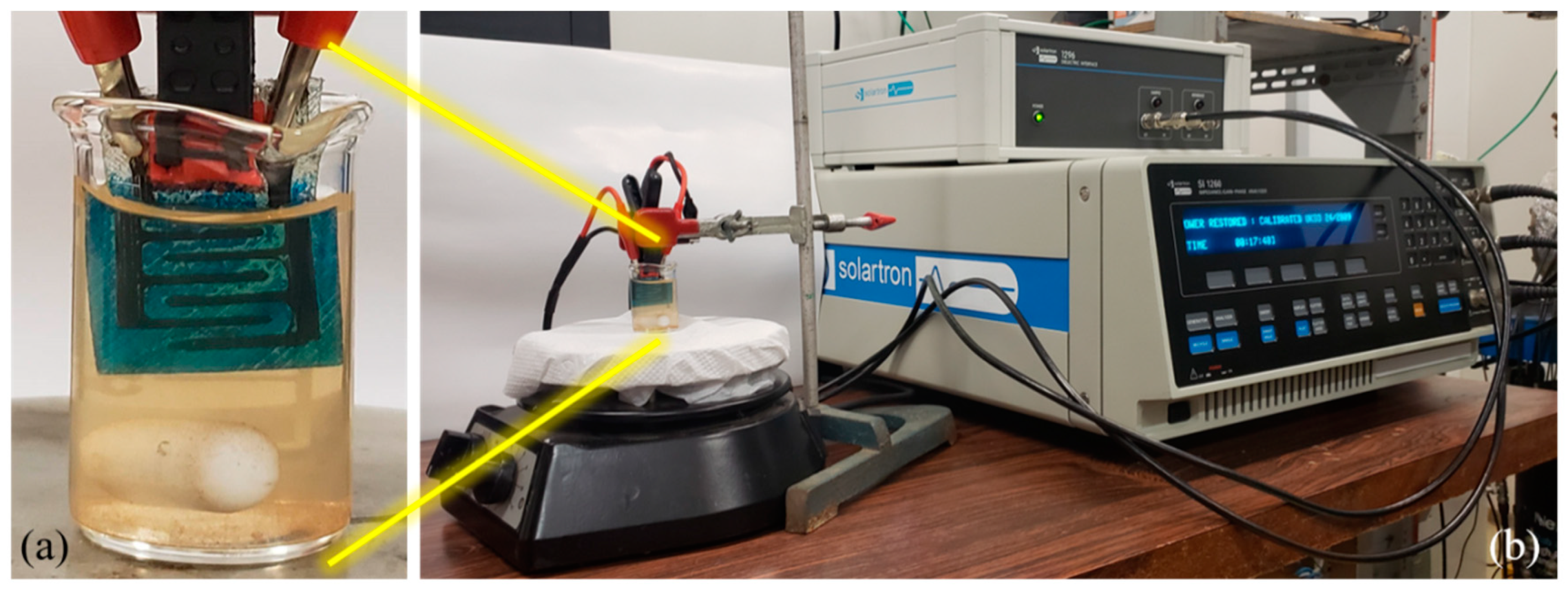
2.1. Electrodes Fabrication
2.2. Layer-by-Layer Films
2.3. Soil Samples
2.4. E-tongue Analysis
2.5. Limit of Detection
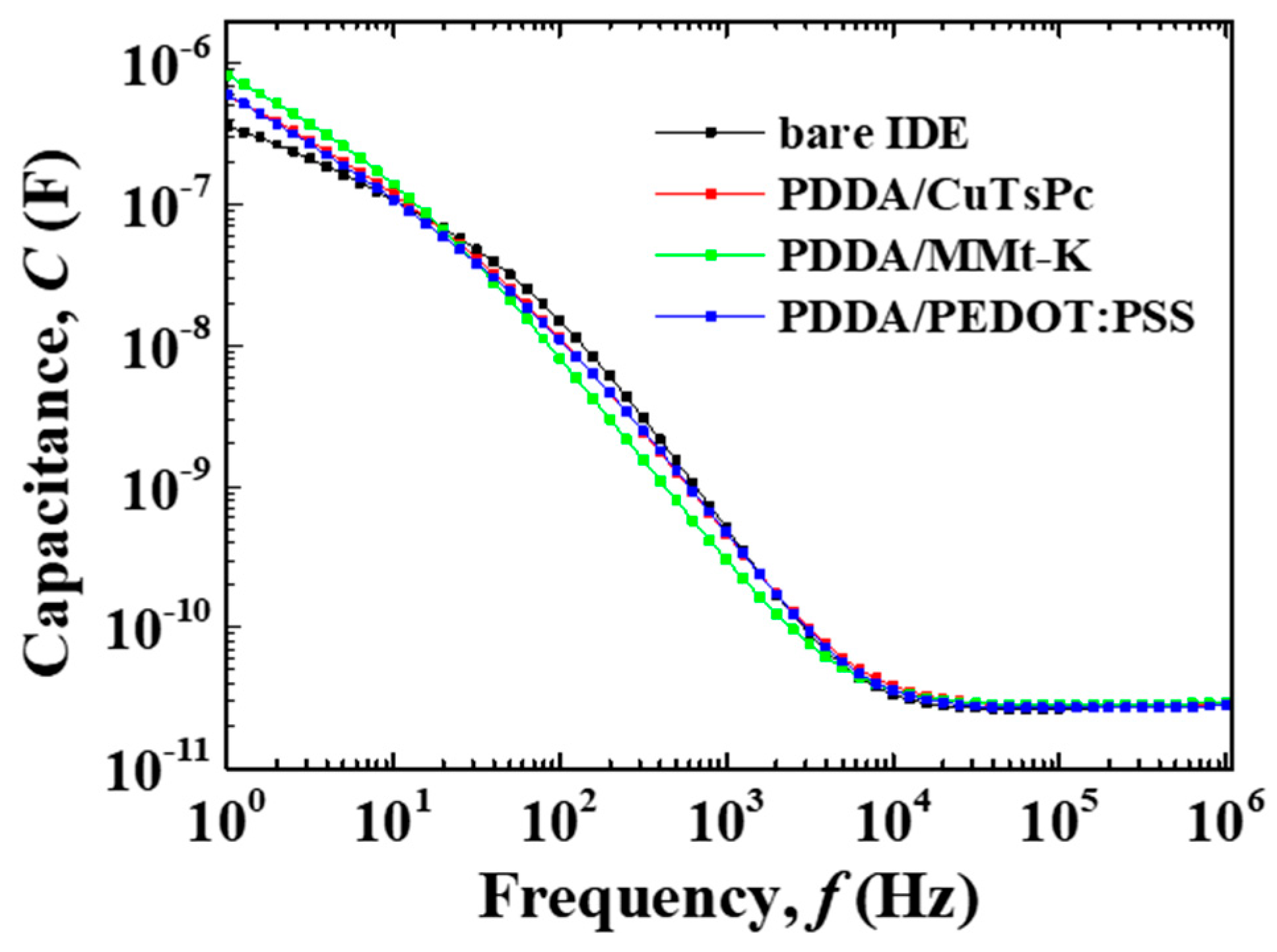
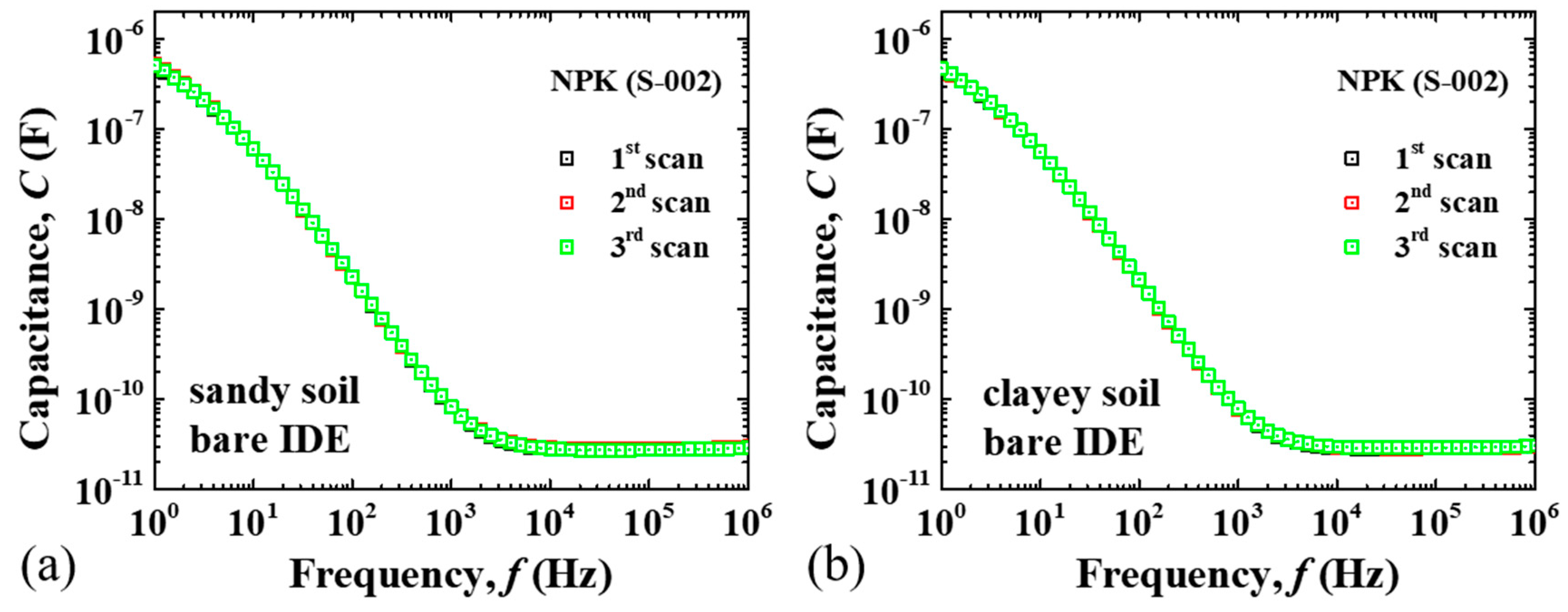
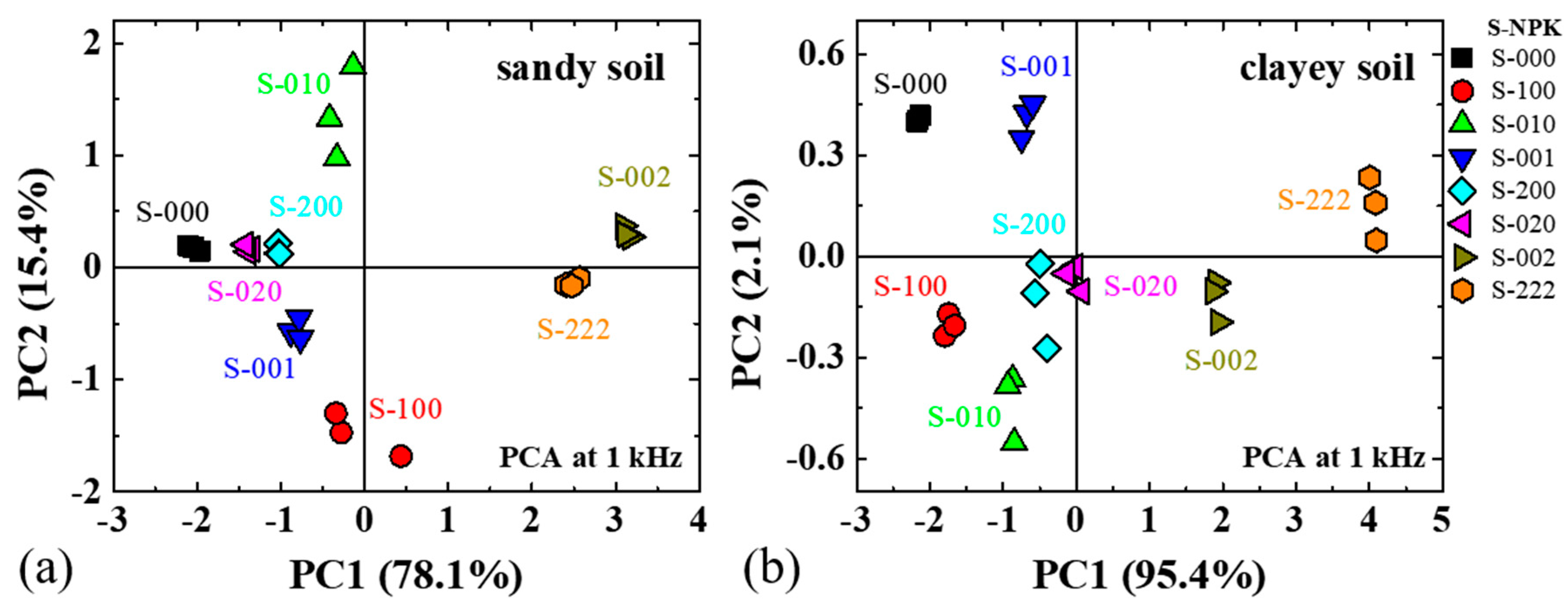
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crist, E.; Mora, C.; Engelman, R. The interaction of human population, food production, and biodiversity protection. Science 2017, 356, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Mapara, S.; Vyas, P. Testing/monitoring of soil chemical level using wireless sensor network technology. Int. J. Appl. Innov. Eng. Manag. 2015, 4, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rogovska, N.; Laird, D.A.; Chiou, C.-P.; Bond, L.J. Development of field mobile soil nitrate sensor technology to facilitate precision fertilizer management. Precis. Agric. 2019, 20, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Camargo, O.A.; Moniz, A.C.; Jorge, J.A.; Valadares, J.M.A.S. Methods of Chemical, Mineralogical and Physical Analysis of Soils of the Agronomic Institute of Campinas, 2nd ed.; Instituto Agronomico de Campinas: Campinas, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin, M.R.; Santi, A.L.; Eitelwein, M.T.; Menegol, D.R.; Da Ros, C.O.; de Castro Pias, O.H.; Berghetti, J. Efficiency of sampling grids used in the characterization of phosphorus and potassium. Ciência. Rural 2014, 44, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, M.R.; Povh, F.P.; Demattê, J.A.M.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Chicati, M.L.; Cezar, E. Optimum size in grid soil sampling for variable rate application in site-specific management. Sci. Agric. 2011, 68, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; McBratney, A.B.; Minasny, B. (Eds.) Proximal Soil Sensing; Springer Netherlands: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 9789048188581. [Google Scholar]
- Podrazka, M.; Baczynska, E.; Kundys, M.; Jelen, P.S.; Nery, E.W. Electronic tongue—A tool for all tastes? Biosensors 2018, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K. Taste sensor with global selectivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1996, 4, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legin, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Vlasov, Y.; Di Natale, C.; Davide, F.; D’Amico, A. Tasting of beverages using an electronic tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Davide, F.; D’Amico, A.; Legin, A.; Vlasov, Y.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Selezenev, B. Multicomponent analysis on polluted waters by means of an electronic tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikuzono, C.M.; Shimizu, F.M.; Manzoli, A.; Riul, A.; Piazzetta, M.H.O.; Gobbi, A.L.; Correa, D.S.; Paulovich, F.V.; Oliveira, O.N. Information visualization and feature selection methods applied to detect gliadin in gluten-containing foodstuff with a microfluidic electronic tongue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19646–19652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbó, N.; López Carrero, J.; Garcia-Castillo, F.; Tormos, I.; Olivas, E.; Folch, E.; Alcañiz Fillol, M.; Soto, J.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Martínez-Bisbal, M. Quantitative determination of spring water quality parameters via electronic tongue. Sensors 2018, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo-Comino, C.; García-Hernández, C.; García-Cabezón, C.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L. Discrimination of milks with a multisensor system based on layer-by-layer films. Sensors 2018, 18, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikuzono, C.M.; Delaney, C.; Morrin, A.; Diamond, D.; Florea, L.; Oliveira, O.N. Paper based electronic tongue-a low-cost solution for the distinction of sugar type and apple juice brand. Analyst 2019, 144, 2827–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, T.C.B.; Rodrigues, D.R.; de Carvalho Polari Souto, U.T.; Lemos, S.G. A simple voltammetric electronic tongue for the analysis of coffee adulterations. Food Chem. 2019, 273, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, L.; Guanais Gonçalves, C.; Petropoulos, K.; Micheli, L.; Volpe, G.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Viaggiu, E.; Congestri, R.; Guzzella, L.; et al. Electronic tongue for microcystin screening in waters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.S.; Cruz, M.G.N.; Gomes, M.T.S.R.; Rudnitskaya, A. Potentiometric chemical sensors for the detection of paralytic shellfish toxins. Talanta 2018, 181, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, F.M.; Braunger, M.L.; Riul, A., Jr. Heavy metal/toxins detection using electronic tongues. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facure, M.H.M.; Mercante, L.A.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Detection of trace levels of organophosphate pesticides using an electronic tongue based on graphene hybrid nanocomposites. Talanta 2017, 167, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Qian, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H. A colorimetric sensor array based on sulfuric acid assisted KMnO4 fading for the detection and identification of pesticides. Talanta 2018, 181, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Jing, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Continuously evolving ‘chemical tongue’ biosensor for detecting proteins. Talanta 2017, 165, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, T.; Moufid, M.; Zaim, O.; El Bari, N.; Bouchikhi, B. Voltammetric electronic tongue combined with chemometric techniques for direct identification of creatinine level in human urine. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2018, 115, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieva, S.; Karnaukh, M.; Panchuk, V.; Andreev, E.; Kartsova, L.; Bessonova, E.; Legin, A.; Wang, P.; Wan, H.; Jahatspanian, I.; et al. Potentiometric multisensor system as a possible simple tool for non-invasive prostate cancer diagnostics through urine analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 289, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimendia, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Alcañiz, J.M.; del Valle, M. Discrimination of soils and assessment of soil fertility using information from an ion selective electrodes array and artificial neural networks. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunger, M.L.; Shimizu, F.M.; Jimenez, M.J.M.; Amaral, L.R.; de Oliveira Piazzetta, M.H.; Gobbi, Â.L.; Magalhães, P.S.G.; Rodrigues, V.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Riul, A., Jr. Microfluidic electronic tongue applied to soil analysis. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, G.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Inkjet printing of conductive materials: A review. Circuit World 2012, 38, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, K.T.; Gaál, G.; Almeida, G.F.B.; Andrade, M.B.; Facure, M.H.M.; Correa, D.S.; Riul, A.; Rodrigues, V.; Mendonça, C.R. Femtosecond laser micromachining of polylactic acid/graphene composites for designing interdigitated microelectrodes for sensor applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 101, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Kong, B.; Zhang, M.; Qian, X.; Mi, S.; Sun, W. The Boom in 3D-Printed Sensor Technology. Sensors 2017, 17, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaál, G.; Silva, T.A.; Gaál, V.; Hensel, R.C.; Amaral, L.R.; Rodrigues, V.; Riul, A., Jr. 3D Printed e-tongue. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science 1997, 277, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, M.A.N.; Alari, F.d.O.; Ferreira, M.M.C.; Amaral, L.R.d. Influence of soil sample preparation on the quantification of NPK content via spectroscopy. Geoderma 2019, 338, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, C.; Kuroda, K.; Takahara, H. Preparation and electrical properties of quaternary ammonium montmorillonite-polystyrene complexes. Clays Clay Miner. 1981, 29, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Lovinger, A.J.; Dodabalapur, A. Organic field-effect transistors with high mobility based on copper phthalocyanine. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 3066–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardes, A.M.; Kemerink, M.; Janssen, R.A.J.; Bastiaansen, J.A.M.; Kiggen, N.M.M.; Langeveld, B.M.W.; van Breemen, A.J.J.M.; de Kok, M.M. Microscopic understanding of the anisotropic conductivity of PEDOT: PSS thin films. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A., Jr.; dos Santos, D.S., Jr.; Wohnrath, K.; Di Tommazo, R.; Carvalho, A.C.P.L.F.; Fonseca, F.J.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Taylor, D.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Artificial taste sensor: Efficient combination of sensors made from Langmuir-Blodgett films of conducting polymers and a ruthenium complex and self-assembled films of an azobenzene-containing polymer. Langmuir 2002, 18, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, A.; Constantino, C.J.L.; da Cruz, N.C.; Bortoleto, J.R.R.; Ferreira, M. High performance of electrochemical sensors based on LbL films of gold nanoparticles, polyaniline and sodium montmorillonite clay mineral for simultaneous detection of metal ions. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Pei, X.; Rusinek, C.A.; Bange, A.; Haynes, E.N.; Heineman, W.R.; Papautsky, I. Determination of lead with a copper-based electrochemical sensor. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucena, N.C.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Shimizu, F.M.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Ferreira, M. Layer-by-layer composite film of nickel phthalocyanine and montmorillonite clay for synergistic effect on electrochemical detection of dopamine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.H.S.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Rubira, R.J.G.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Ferreira, M. Layer-by-layer films of graphene nanoplatelets and gold nanoparticles for methyl parathion sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo, D.E.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Shimizu, F.M.; Ferreira, M. Improving direct immunoassay response by layer-by-layer films of gold nanoparticles—Antibody conjugate towards label-free detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Code (S-NPK) | Sandy Soil | Clayey Soil |
|---|---|---|
| S-000 | 406, 6, 0.9 | 945, 1, 0.5 |
| S-100 | 378, 6, 1 | 994, 12, 0.6 |
| S-010 | 406, 21, 0.9 | 917, 220, 0.7 |
| S-001 | 462, 4, 4.7 | 924, 1, 4 |
| S-200 | 379, 6, 0.9 | 994, 15, 0.4 |
| S-020 | 364, 314, 0.9 | 973, 419, 1 |
| S-002 | 378, 4, 16 | 910, 1, 8.4 |
| S-222 | 371, 126, 11.7 | 1057, 464, 7.3 |
| Sensing Unit | Soil Group | Sample Code (S-NPK) | Sensitivity (pF·mL·mg−1) | LOD (mg·mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare IDE | sandy | S-000 | 12 ± 2 | 0.30 ± 0.04 |
| S-002 | 92 ± 6 | 0.101 ± 0.006 | ||
| clayey | S-000 | 30 ± 5 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | |
| S-002 | 63 ± 2 | 0.065 ± 0.003 | ||
| PDDA/PEDOT:PSS | sandy | S-000 | 20 ± 5 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| S-002 | 115 ± 7 | 0.091 ± 0.006 | ||
| clayey | S-000 | 25 ± 1 | 0.087 ± 0.004 | |
| S-002 | 70 ± 6 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Americo da Silva, T.; Braunger, M.L.; Neris Coutinho, M.A.; Rios do Amaral, L.; Rodrigues, V.; Riul, A., Jr. 3D-Printed Graphene Electrodes Applied in an Impedimetric Electronic Tongue for Soil Analysis. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040050
Americo da Silva T, Braunger ML, Neris Coutinho MA, Rios do Amaral L, Rodrigues V, Riul A Jr. 3D-Printed Graphene Electrodes Applied in an Impedimetric Electronic Tongue for Soil Analysis. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmerico da Silva, Tatiana, Maria Luisa Braunger, Marcos Antonio Neris Coutinho, Lucas Rios do Amaral, Varlei Rodrigues, and Antonio Riul, Jr. 2019. "3D-Printed Graphene Electrodes Applied in an Impedimetric Electronic Tongue for Soil Analysis" Chemosensors 7, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040050
APA StyleAmerico da Silva, T., Braunger, M. L., Neris Coutinho, M. A., Rios do Amaral, L., Rodrigues, V., & Riul, A., Jr. (2019). 3D-Printed Graphene Electrodes Applied in an Impedimetric Electronic Tongue for Soil Analysis. Chemosensors, 7(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040050






