Colorimetric Sensing of Pb2+ Ion by Using Ag Nanoparticles in the Presence of Dithizone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
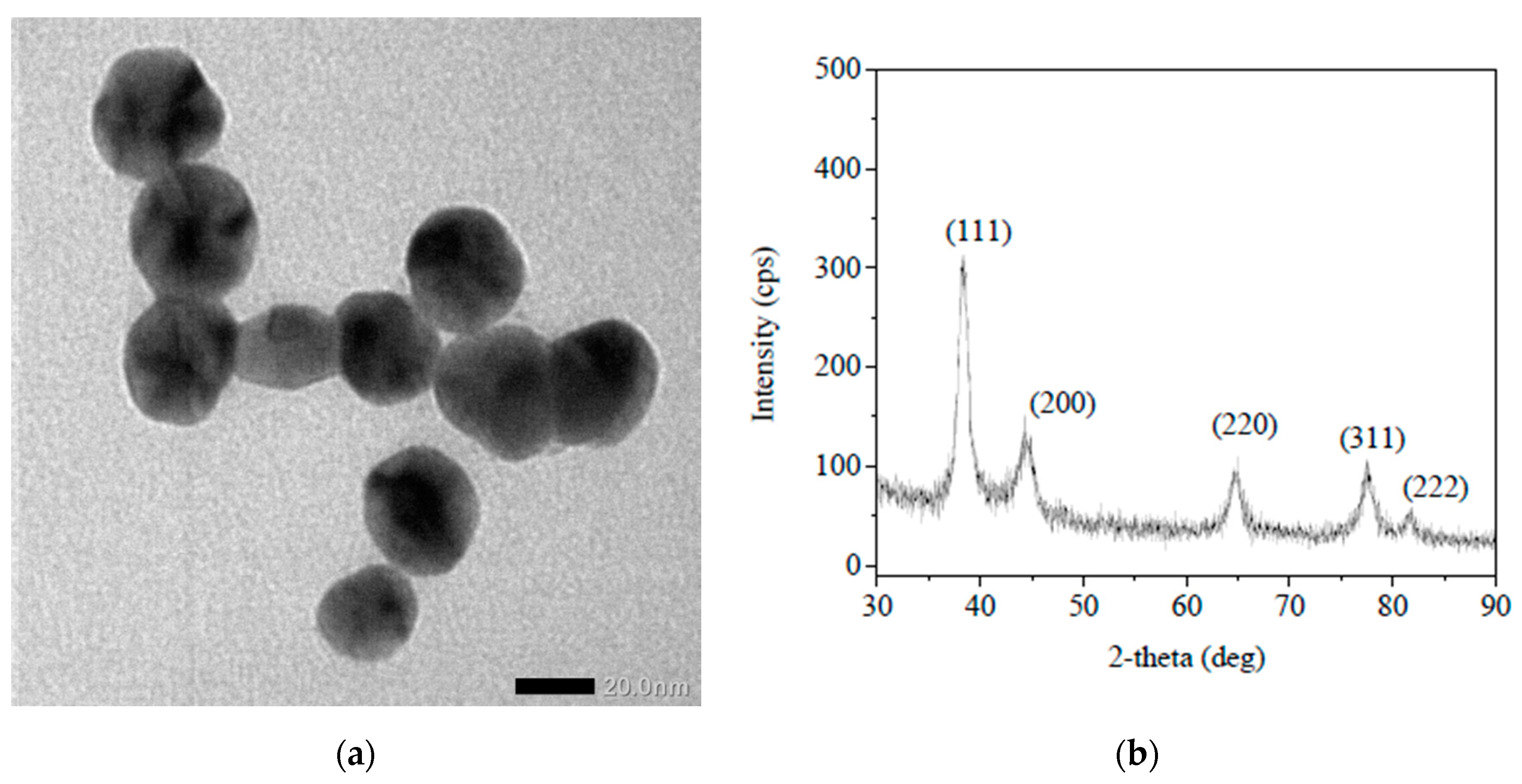
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Ag Nanoparticles
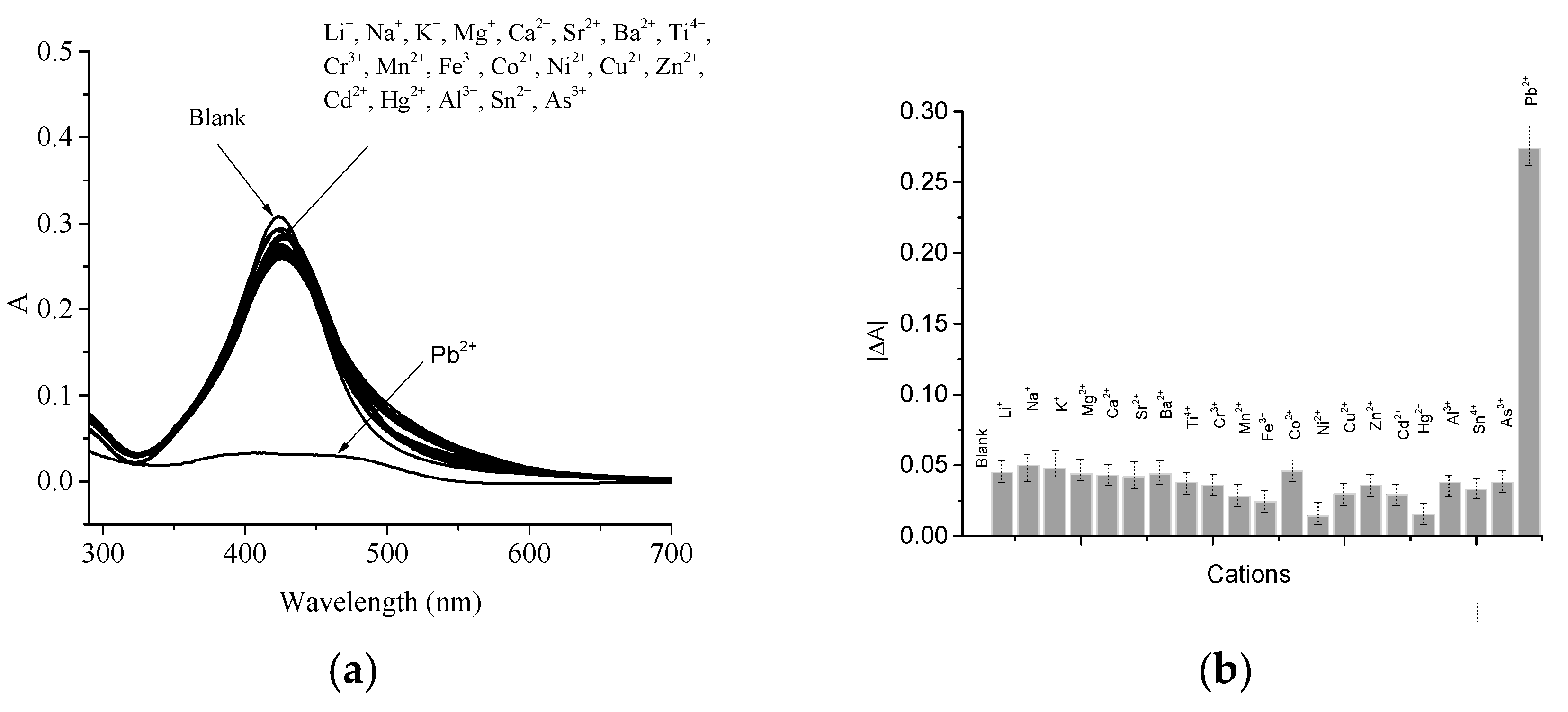
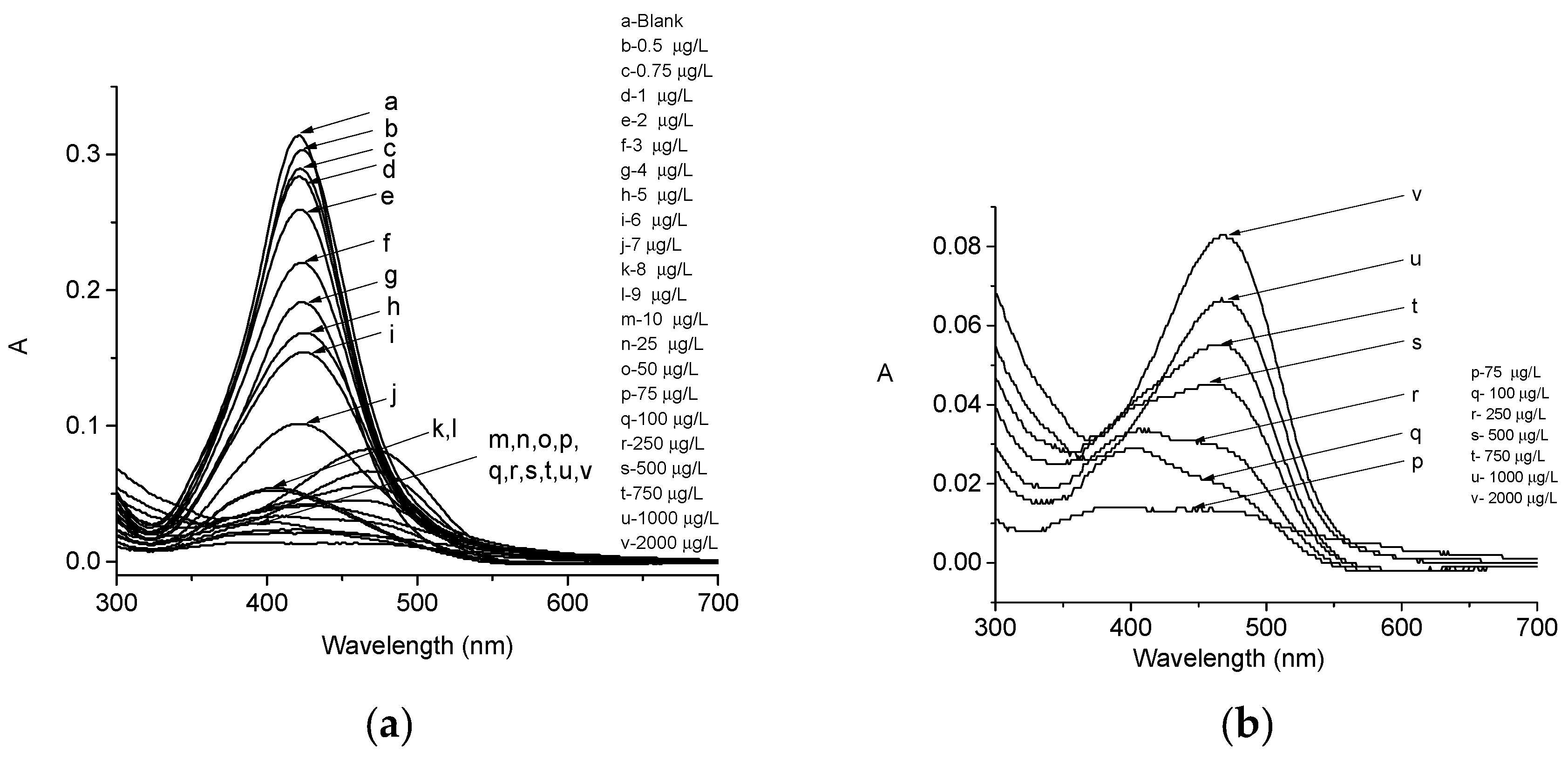
2.2. LSPR Absorbance Measurement of Colloidal AgNPs in the Presence of Pb2+ Ions
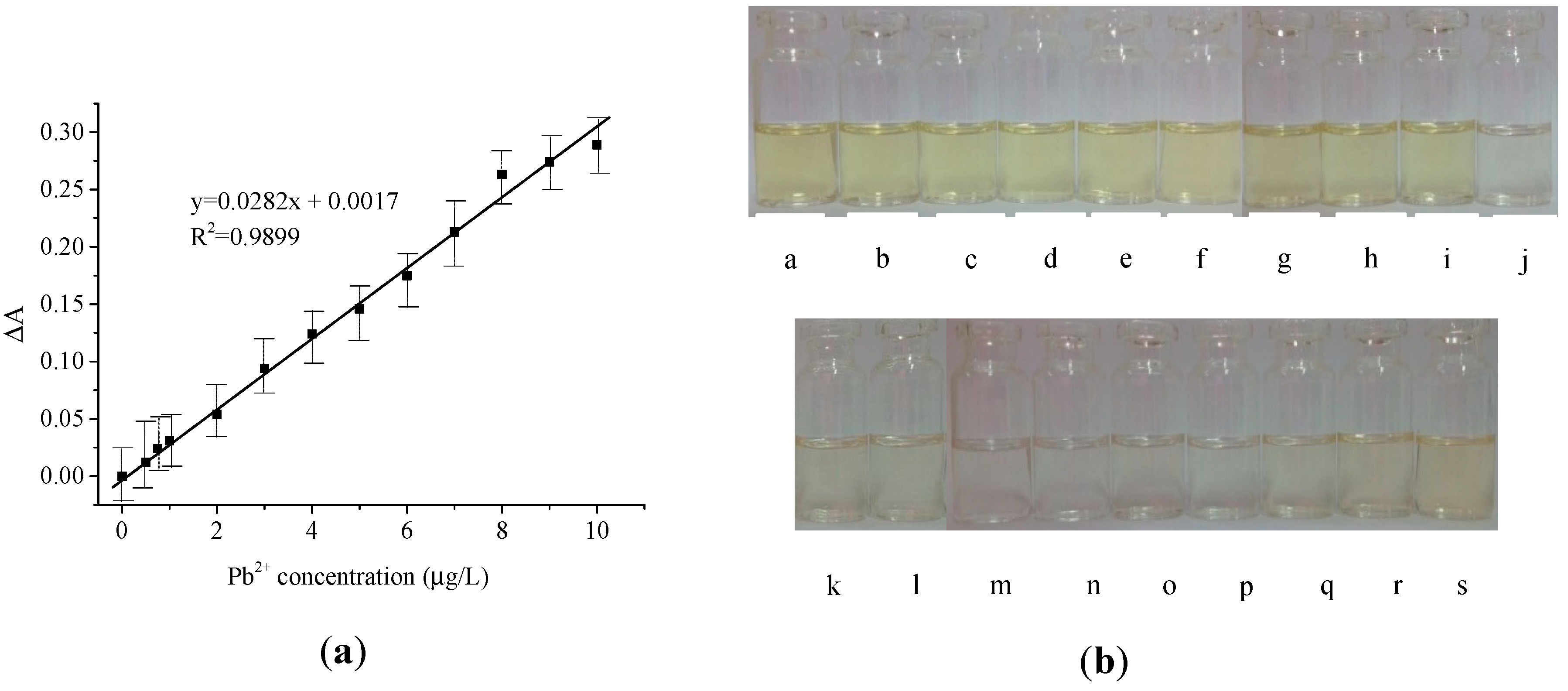
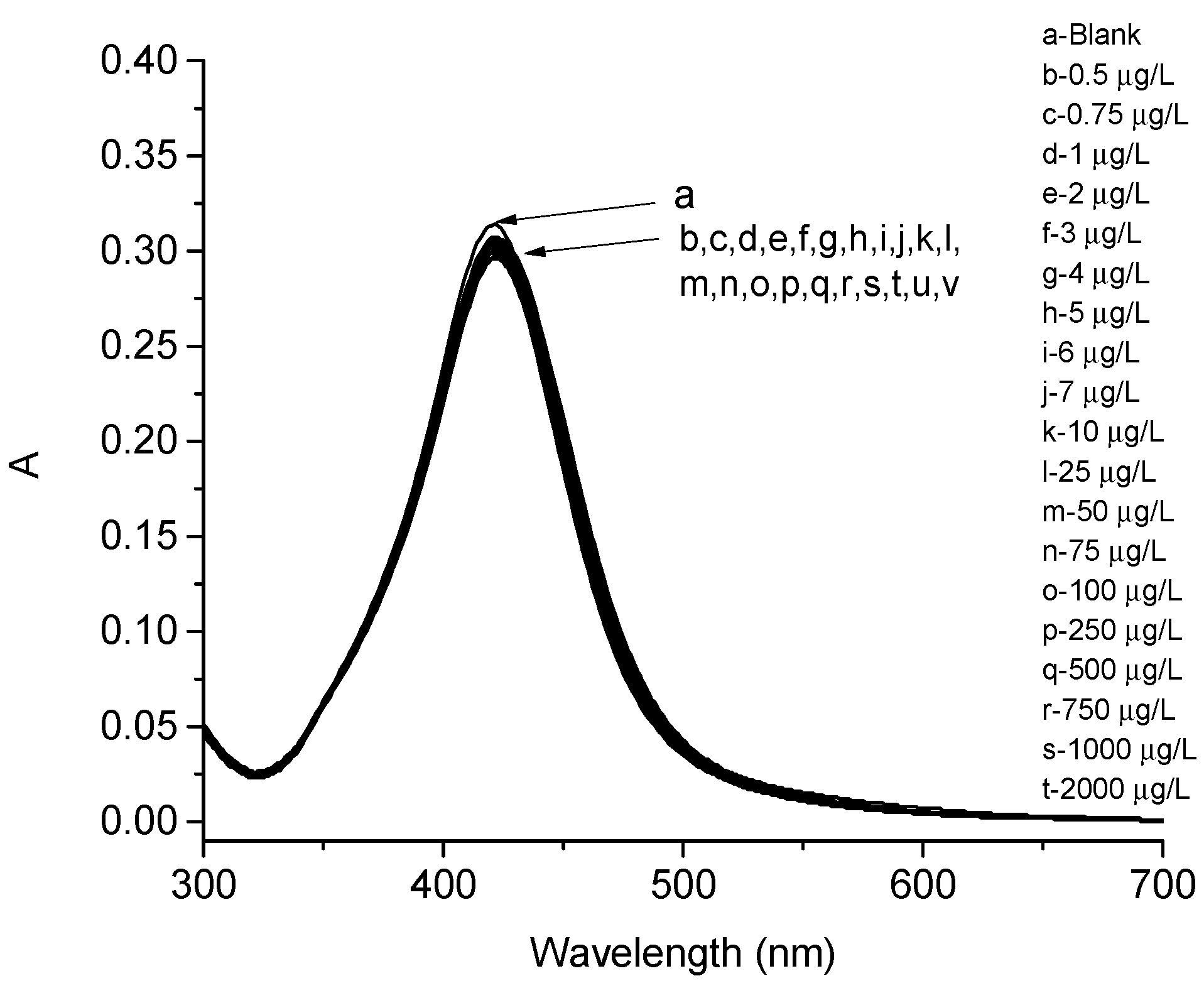
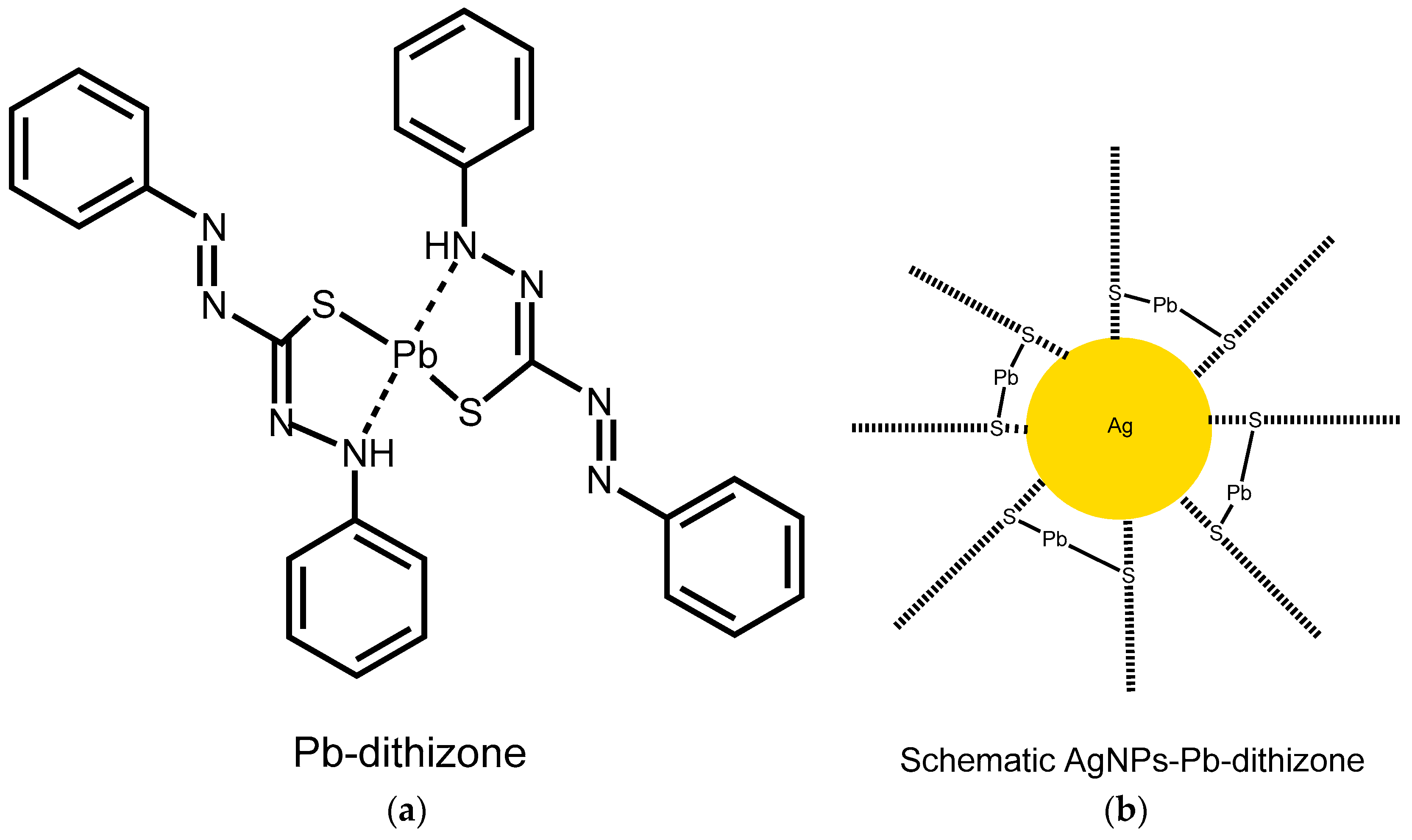
3. Results
4. Discussion
| Method (System) | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Limit of Quantification (LOQ) | Linear Range | Sensitivity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic Absortion Spectrometry (AAS, graphite furnace) | 0.25 mg/L | 0.83 mg/L | 1.0–8.0 mg/L | 0.0408 L/mg | [32] |
| Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) | 0.36 mg/L | 1.2 mg/L | 0.10–2.0 mg/L | 0.303 L/mg | [33] |
| Strip immunosensor (AuNPs) | 0.19 µg/L | 0.60 µg/L | 0.25–2.0 µg/L | N/A | [34] |
| Colorimetry (AuNPs, thiosulfate/4-mercaptobutanol) | 0.04 µg/L | 0.12 µg/L | 0.10–2.07 µg/L | N/A | [35] |
| Colorimetry (AuNPs, thiosulfate, 2-mercaptoethanol) | 0.10 µg/L | 0.31 µg/L | 0.52–2000 µg/L | N/A | [36] |
| Colorimetry (AgNPs, 1-(2-mercaptoethyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione) | 20 µg/L | 60 µg/L | 100–600 µg/L | N/A | [37] |
| Colorimetry (AuNPs, thiosulfate) | 4.1 µg/L | 12.4 µg/L | 5.18–62.2 µg/L | 0.003 L/µg | [38] |
| Colorimetry (AuNPs, gallic acid) | 5.2 µg/L | 15.5 µg/L | 10.4–200 µg/L | N/A | [39] |
| Colorimetry (AuNPs, maleic acid) | 0.50 µg/L | 1.5 µg/L | 1.0–10.0 µg/L | 0.059 L/µg | [40] |
| Colorimetry (AgNPs, dithizone) | 0.64 µg/L | 2.1 µg/L | 0.5–10 µg/L | 0.0282 L/µg | This work |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willets, K.A.; van Duyne, R.P. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy and Sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U.J. Localized surface plasmon resonance: Nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Han, G. Characteristics of major elements and heavy metals in atmospheric dust in Beijing, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Lee, T.G. A simultaneous stabilization and solidification of the top five most toxic heavy metals (Hg, Pb, As, Cr, and Cd). Chemosphere 2017, 178, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Horckmans, L.; Spooren, J.; Vrancken, K.C.; Quaghebeur, M.; Broos, K. Selective leaching of Pb, Cu, Ni and Zn from secondary lead smelting residues. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huo, X.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Z.; Cong, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, X. Elevated lead levels from e-waste exposure are linked to decreased olfactory memory in children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.R.; Jarrett, J.M.; Tevis, D.S.; Franklin, M.; Mullinix, N.J.; Wallon, K.L.; Quarles, D., Jr.; Caldwella, K.L.; Jonesa, R.L. Analysis of whole human blood for Pb, Cd, Hg, Se, and Mn by ICP-DRC-MS for biomonitoring and acute exposures. Talanta 2017, 162, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavicini, P.; Taglietti, A.; Dacarro, G.; Diaz-Fernandez, Y.A.; Galli, M.; Grisoli, P.; Patrini, M.; De Magistris, G.S.; Zanon, R. Self-assembled monolayers of silver nanoparticles firmly grafted on glass surfaces: Low Ag+ release for an efficient antibacterial activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 350, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Fu, X.; Chen, L. Novel Optical Nanoprobes for Chemical and Biological Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vasileva, P.; Donkova, B.; Karadjova, I.; Dushkin, C. Synthesis of starch-stabilized silver nanoparticles and their application as a surface plasmon resonance-based sensor of hydrogen peroxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 382, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qu, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. Highly Sensitive, Colorimetric Detection of Mercury (II) in Aqueous Media by Quaternary Ammonium Group-Capped Gold Nanoparticles at Room Temperature. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9606–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beqa, L.; Singh, A.K.; Khan, S.A.; Senapati, D.; Arumugam, S.R.; Ray, P.C. Gold nanoparticle-based simple colorimetric and ultrasensitive dynamic light scattering assay for the selective detection of Pb(II) from paints, plastics, and water samples. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; He, S.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Colorimetric Detection of Iron Ions (III) Based on the Highly Sensitive Plasmonic Response of the N-acetyl-L-cysteine-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhan, J. Synthesis of starch-stabilized Ag nanoparticles and Hg2+ recognition in aqueous media. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Wen, L.; Miao, F.; Tian, D.; Zhu, X.; Li, H. Synthesis of a pyridyl-appended calix[4]arene and its application to the modification of silver nanoparticles as an Fe3+ colorimetric sensor. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, D.; González, M.C.; Escarpa, A. Analytica Chimica Acta Sensing colorimetric approaches based on gold and silver nanoparticles aggregation: Chemical creativity behind the assay. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 751, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarlaida, F.; Adlim, M. Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury (II) ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 184, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Gong, A.; Shen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, A. Colorimetric Response of Dithizone Product and He×adecyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide Modi fi ed Gold Nanoparticle Dispersion to 10 Types of Heavy Metal Ions: Understanding the Involved Molecules from Experiment to Simulation. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7591–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargoosh, K.; Babadi, F.F. Highly selective and sensitive optical sensor for determination of Pb2+ and Hg2+ ions based on the covalent immobilization of dithizone on agarose membrane. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 137, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, V.M.; Lyle, S.J. Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron and Cobalt with Ferrozine and Dithizone. Talanta 1990, 37, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.K.; Oh, S.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, Y. Colorimetric detection of Co2+ ion using silver nanoparticles with spherical, plate, and rod shapes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8978–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chan, L.; Fu, X.; Lu, W. Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric sensing of Hg2+ based on the morphology transition of silver nanoprisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, T.J.B.; Redfern, S.A.T. Unit cell refinement from powder diffraction data: The use of regression diagnostics. Miner. Mag. 1997, 61, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.W.; Ong, K.; Rea, T.; Chan, I.Y. On the estimation of average crystallite size of zeolites from the Scherrer equation: A critical evaluation of its application to zeolites with one-dimensional pore systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarujamrus, P.; Amatatongchai, M.; Thima, A.; Khongrangdee, T.; Mongkontong, C. Selective colorimetric sensors based on the monitoring of an unmodified silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) reduction for a simple and rapid determination of mercury. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 142, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Ahmed, M.J.; Bhanger, M.I. A simple spectrophotometric method for the determination of trace level lead in biological samples in the presence of aqueous micellar solutions. Spectroscopy 2006, 20, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. A fast colourimetric assay for lead detection using label-free gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Micromachines 2015, 6, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrovčík, J. Strategy for determination of LOD and LOQ values—Some basic aspects. Talanta 2014, 119, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Miao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C. A Colorimetric Sensor for the Highly Selective Detection of Sulfide and 1,4-Dithiothreitol Based on the In Situ Formation of Silver Nanoparticles Using Dopamine. Sensors 2017, 17, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Atiya, M.; Mandler, D. Studying thiol adsorption on Au, Ag and Hg surfaces by potentiometric measurements. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 550–551, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Danwittayakul, S.; Suzuki, T.M. Dithizone nanofiber-coated membrane for filtration-enrichment and colorimetric detection of trace Hg(ii) ion. Analyst 2009, 134, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakırdere, S.; Yaroğlu, T.; Tırık, N.; Demiröz, M.; Fidan, A.K.; Maruldalı, O.; Karaca, A. Determination of As, Cd, and Pb in tap water and bottled water samples by using optimized GFAAS system with Pd-Mg and Ni as matrix modifiers. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, B.; Mikula, B.; Pytlakowska, K.; Puzio, B.; Buhl, F. Determination of heavy metals by ICP-OES and F-AAS after preconcentration with 2,2′-bipyridyl and erythrosine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Xing, C.; Hao, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Rapid and highly sensitive detection of lead ions in drinking water based on a strip immunosensor. Sensors 2013, 13, 4214–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.L.; Hsiung, T.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Huang, C.C. A label-free colorimetric detection of lead ions by controlling the ligand shells of gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2010, 82, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi-You, C.; Huan-Tsung, C.; Yen-Chun, S.; Yu-Lun, H.; Cheng-Kang, C.; Chih-Ching, H. Colorimetric Assay for Lead Ions Based on the Leaching of Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9433–9439. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, K.C.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.B. A colorimetric probe to determine Pb2+ using functionalized silver nanoparticles. Analyst 2015, 140, 8209–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, Y.Q.; Li, J.J.; Zhao, J.W. Colorimetric detection of lead(ii) ions based on accelerating surface etching of gold nanorods to nanospheres: The effect of sodium thiosulfate. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25611–25619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, L.; He, Y.; Xiang, K.; Wang, G. Colorimetric assay for determination of lead (II) based on its incorporation into gold nanoparticles during their synthesis. Sensors 2010, 10, 11144–11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnarathorn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Dungchai, W. Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of lead using maleic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 132, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roto, R.; Mellisani, B.; Kuncaka, A.; Mudasir, M.; Suratman, A. Colorimetric Sensing of Pb2+ Ion by Using Ag Nanoparticles in the Presence of Dithizone. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030028
Roto R, Mellisani B, Kuncaka A, Mudasir M, Suratman A. Colorimetric Sensing of Pb2+ Ion by Using Ag Nanoparticles in the Presence of Dithizone. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoto, Roto, Bella Mellisani, Agus Kuncaka, Mudasir Mudasir, and Adhitasari Suratman. 2019. "Colorimetric Sensing of Pb2+ Ion by Using Ag Nanoparticles in the Presence of Dithizone" Chemosensors 7, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030028
APA StyleRoto, R., Mellisani, B., Kuncaka, A., Mudasir, M., & Suratman, A. (2019). Colorimetric Sensing of Pb2+ Ion by Using Ag Nanoparticles in the Presence of Dithizone. Chemosensors, 7(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030028





