Nitric Oxide Sensors for Biological Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
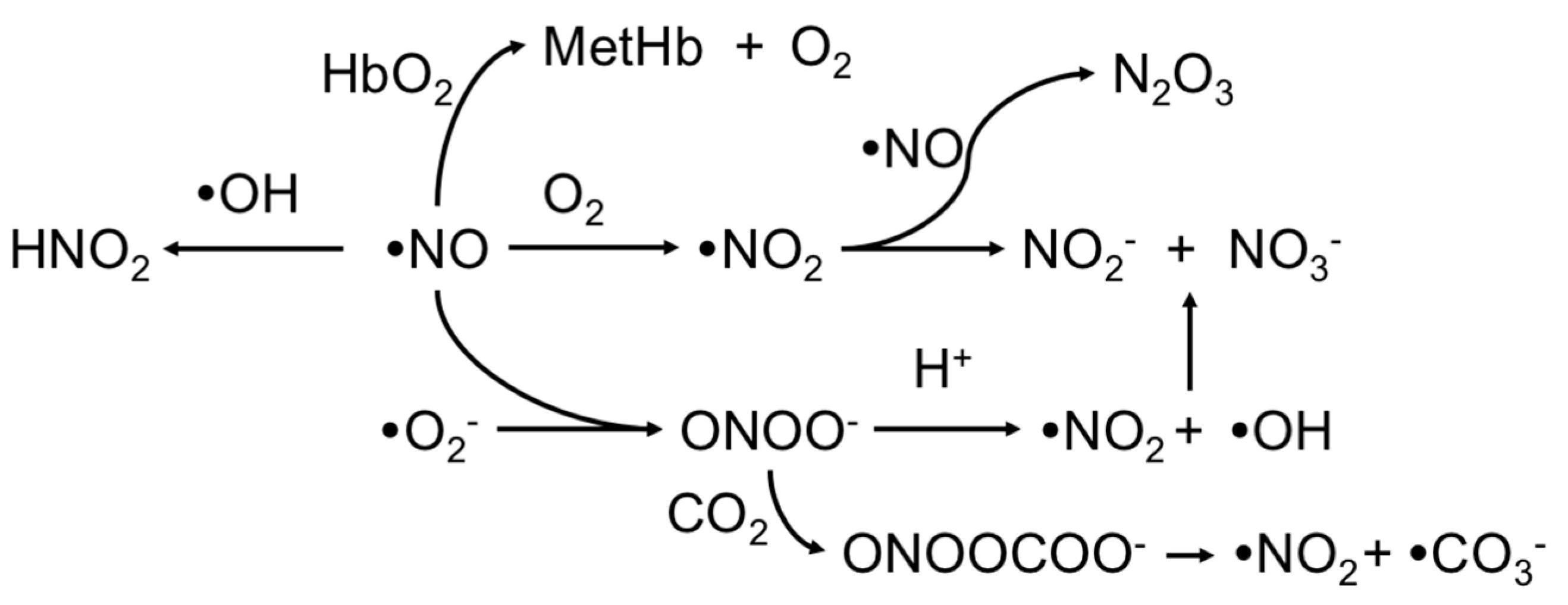
2. Upstream and Downstream Measurements
3. Electrochemical Detection
4. Chemiluminescent Probes
5. Fluorescence Probes
6. Genetic Biosensors
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yetik-Anacak, G.; Catravas, J.D. Nitric oxide and the endothelium: History and impact on cardiovascular disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 45, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C.; Calvani, M.; Rizzarelli, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Giuffrida Stella, A.M. Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: Neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loscalzo, J.; Welch, G. Nitric oxide and its role in the cardiovascular system. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1995, 38, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A. Role of nitric oxide in the gastrointestinal tract. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, P.F.; Power, D.A. Nitric oxide in the kidney: Functions and regulation of synthesis. Acta Physiol. 2006, 187, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Shimoyama, N.; Mizuguchi, T. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor blocks spinal sensitization induced by formalin injection into the rat paw. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 77, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Farr, S.A.; Sell, R.L.; Hileman, S.M.; Banks, W.A. Nitric oxide is a central component in neuropeptide regulation of appetite. Peptides 2011, 32, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, J.M.; Jantos, H. Effects of L-arginine and SIN-1 on sleep and waking in the rat during both phases of the light-dark cycle. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda, A.C.R.; Marubayashi, U.; Coimbra, C.C. Nitric oxide pathway is an important modulator of heat loss in rats during exercise. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 67, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bon, C.L.M.; Garthwaite, J. On the Role of Nitric Oxide in Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinerman, J.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Schell, M.J.; Snowman, A.; Snyder, S.H. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase localized to hippocampal pyramidal cells: Implications for synaptic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4214–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.E. Nitric oxide and homeostatic control: An intercellular signalling molecule contributing to autonomic and neuroendocrine integration? Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2004, 84, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contestabile, A.; Ciani, E. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of neuronal proliferation, survival and differentiation. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccio, A.; Alvania, R.S.; Lonze, B.E.; Ramanan, N.; Kim, T.; Huang, Y.; Dawson, T.M.; Snyder, S.H.; Ginty, D.D. A nitric oxide signaling pathway controls CREB-mediated gene expression in neurons. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Halushka, P.V.; Lincoln, T.M.; Mendelsohn, M.E. Mechanism of platelet inhibition by nitric oxide: In vivo phosphorylation of thromboxane receptor by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4888–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.C.; Hassid, A. Nitric oxide-generating vasodilators and 8-bromo-cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibit mitogenesis and proliferation of cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1774–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Mehta, P.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidized LDL decreases L-arginine uptake and nitric oxide synthase protein expression in human platelets: Relevance of the effect of oxidized LDL on platelet function. Circulation 1996, 93, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.F.; Keates, A.C.; Hanson, P.J.; Whittle, B.J. Nitric oxide generators and cGMP stimulate mucus secretion by rat gastric mucosal cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, G418–G422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; Tigley, A.W. Review article: New insights into prostaglandins and mucosal defence. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 9, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubes, P.; Suzuki, M.; Granger, D.N. Nitric oxide: An endogenous modulator of leukocyte adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4651–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.; Redeen, S.; Grenegard, M.; Ericson, A.C.; Sjostrand, S.E. Nitric oxide inhibits gastric acid secretion by increasing intraparietal cell levels of cGMP in isolated human gastric glands. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Han, M.K.; Choi, K.S.; Park, I.H.; Park, S.Y.; Sohn, M.H.; Kim, U.H.; McGregor, J.R.; Samlowski, W.E.; Yim, C.Y. Cytokines secreted by lymphokine-activated killer cells induce endogenous nitric oxide synthesis and apoptosis in DLD-1 colon cancer cells. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 203, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C. The Function of Nitric Oxide in the Immune System in Nitric Oxide; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Liu, L.; Smith, G.C.M.; Charles, l.G. Nitric oxide upregulates expression of DNA-PKcs to protect cells from DNA-damaging anti-tumour agents. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Ganopolsky, J.G.; Labbe, A.; Wahl, C.; Prakash, S. Antimicrobial properties of nitric oxide and its application in antimicrobial formulations and medical devices. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, D.S.A.; Navar, L.G. Nitric oxide in the control of renal hemodynamics and excretory function. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 74S–82S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.D.; Ridnour, L.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Flores-Santana, W.; Switzer, C.H.; Donzelli, S.; Hussain, P.; Vecoli, C.; Paolocci, N.; Ambs, S.; et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: Implications in cellular signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Kummer, M.P.; Stutz, A.; Delekate, A.; Schwartz, S.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Griep, A.; Axt, D.; Remus, A.; Tzeng, T.C.; et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 2013, 493, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J. Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Beckman, J.S.; Koppenol, W.H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1996, 271, C1424–C1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.; Lirk, P.; Rieder, J. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in tumor biology: The two sides of the same coin. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Sterk, P.J.; Gaston, B.; Folkerts, G. Nitric Oxide in Health and Disease of the Respiratory System. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 731–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C. The Multiplex Function of Nitric Oxide in (Auto)immunity. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Huang, S.; Dong, Z.; Juang, S.H.; Gutman, M.; Xie, Q.W.; Nathan, C.; Fidler, I.J. Transfection with the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene suppresses tumorigenicity and abrogates metastasis by K-1735 murine melanoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massi, D.; Franchi, A.; Sardi, I.; Magnelli, L.; Paglierani, M.; Borgognoni, L.; Maria Reali, U.; Santucci, M. Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in benign and malignant cutaneous melanocytic lesions. J. Pathol. 2001, 194, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Stamler, J.S. NO: An inhibitor of cell death. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, B.; von Knethen, A.; Sandau, K.B. Nitric oxide (NO): An effector of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frostell, C.; Fratacci, M.D.; Wain, J.C.; Jones, R.; Zapol, W.M. Inhaled nitric oxide. A selective pulmonary vasodilator reversing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Circulation 1991, 83, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nablo, B.J.; Rothrock, A.R.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Nitric oxide-releasing sol-gels as antibacterial coatings for orthopedic implants. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Colletta, A.; Koley, D.; Wu, J.; Xi, C.; Major, T.C.; Bartlett, R.H.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Thromboresistant/anti-biofilm catheters via electrochemically modulated nitric oxide release. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 104, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.R.; Flitney, F.W.; Williams, D.L.H. NO, nitrosonium ions, nitroxide ions, nitrosothiols and iron-nitrosyls in biology: A chemist’s perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, B. Nitric oxide and thiol groups. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1999, 1411, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, R.; Kelm, M.; Motz, W.; Strauer, B. The biology of nitric oxide. Enzymol. Biochem. Immunol. 1994, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Miller, M.J.; Joshi, M.S.; Thomas, D.D.; Lancaster, J.R. Accelerated reaction of nitric oxide with O2 within the hydrophobic interior of biological membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2175–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: From basic research to clinical application. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, S31–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, C. Endothelium in control. Br. Heart J. 1991, 66, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelm, M.; Feelisch, M.; Grube, R.; Motz, W.; Strauer, B.E. The Biology of Nitric Oxide, Physiological and Clinical Aspects; Portland Press: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.S.; Jaraki, O.; Osborne, J.; Simon, D.I.; Keaney, J.; Vita, J.; Singel, D.; Valeri, C.R.; Loscalzo, J. Nitric oxide circulates in mammalian plasma primarily as an S-nitroso adduct of serum albumin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7674–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinski, T.; Taha, Z.; Grunfeld, S.; Patton, S.; Kapturczak, M.; Tomboulian, P. Diffusion of nitric oxide in the aorta wall monitored in situ by porphyrinic microsensors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 193, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelm, M.; Yoshida, K. Metabolic Fate of Nitric Oxide and Related N-Oxides; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kelm, M. Nitric oxide metabolism and breakdown. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1411, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miller, M.J.; Joshi, M.S.; Sadowska-Krowicka, H.; Clark, D.A.; Lancaster, J.R., Jr. Diffusion-limited reaction of free nitric oxide with erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18709–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardman, P. The importance of radiation chemistry to radiation and free radical biology (The 2008 Silvanus Thompson Memorial Lecture). Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griess, P. Bemerkungen zu der Abhandlung der HH. Weselsky und Benedikt Ueber einige Azoverbindungen. Ber. Deutsch. Chem. Ges. 1879, 12, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promega. Griess Reagent System, Instructions for Use of Product G2930; Promega: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, A.J.; Sullivan, F.J.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. The yin and yang of nitric oxide in cancer progression. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, R.G.; Palacios, M.; Palmer, R.M.; Moncada, S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: A transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5159–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, J.S.; Martasek, P.; McMillan, K.; Salerno, J.; Liu, Q.; Gross, S.S.; Masters, B.S. Modular structure of neuronal nitric oxide synthase: Localization of the arginine binding site and modulation by pterin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 210, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.J.; Mellouk, S.; Hoffman, S.L.; Meltzer, M.S.; Nacy, C.A. Cellular mechanisms of nonspecific immunity to intracellular infection: Cytokine-induced synthesis of toxic nitrogen oxides from L-arginine by macrophages and hepatocytes. Immunol. Lett. 1990, 25, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomski, M.W.; Palmer, R.M.; Moncada, S. The anti-aggregating properties of vascular endothelium: Interactions between prostacyclin and nitric oxide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1987, 92, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.M.; Ashton, D.S.; Moncada, S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature 1988, 333, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, M.; Sessa, W.C.; Harris, H.J.; Anggard, E.E.; Vane, J.R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: Cultured endothelial cells recycle L-citrulline to L-arginine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8612–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredt, D.S.; Snyder, S.H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfstein, J.S.; Keaney, J.F.; Slivka, A.; Welch, G.N.; Vita, J.A.; Stamler, J.S.; Loscalzo, J. In vivo transfer of nitric oxide between a plasma protein-bound reservoir and low molecular weight thiols. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassaf, T.; Kleinbongard, P.; Preik, M.; Dejam, A.; Gharini, P.; Lauer, T.; Erckenbrecht, J.; Duschin, A.; Schulz, R.; Heusch, G.; et al. Plasma nitrosothiols contribute to the systemic vasodilator effects of intravenously applied NO: Experimental and clinical Study on the fate of NO in human blood. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, W.; Meyerhoff, M.E. S-Nitrosothiol Detection via Amperometric Nitric Oxide Sensor with Surface Modified Hydrogel Layer Containing Immobilized Organoselenium Catalyst. Langmuir 2006, 22, 10830–10836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinski, T.; Taha, Z. Nitric oxide release from a single cell measured in situ by a porphyrinic-based microsensor. Nature 1992, 358, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallance, P.; Bhagat, K.; MacAllister, R.; Patton, S.; Malinski, T.; Radomski, M.; Moncada, S. Direct measurement of nitric oxide in human beings. Lancet 1995, 346, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovative Instruments, Inc. All-Plastic Leak-Free Reference Electrode: Handles over 5 M Hydroxide and Hydrofluoric Acid. Available online: http://www.2in.com/index.html (accessed on 27 November 2017).
- Dunham, A.J.; Barkley, R.M.; Sievers, R.E. Aqueous nitrite ion determination by selective reduction and gas phase nitric oxide chemiluminescence. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelakis, E.D.; Archer, S.L. The measurement of NO in biological systems using chemiluminescence. Meth. Mol. Biol. 1998, 100, 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Woldman, Y.Y.; Eubank, T.D.; Mock, A.J.; Stevens, N.C.; Varadharaj, S.; Turco, J.; Gavrilin, M.A.; Branchini, B.R.; Khramtsov, V.V. Detection of nitric oxide production in cell cultures by luciferin–luciferase chemiluminescence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldman, Y.Y.; Sun, J.; Zweier, J.L.; Khramtsov, V.V. Direct chemiluminescence detection of nitric oxide in aqueous solutions using the natural nitric oxide target soluble guanylyl cyclase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulissi, Z.W.; Sen, F.; Gong, X.; Sen, S.; Iverson, N.; Boghossian, A.A.; Godoy, L.C.; Wogan, G.N.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Strano, M.S. Spatiotemporal Intracellular Nitric Oxide Signaling Captured Using Internalized, Near-Infrared Fluorescent Carbon Nanotube Nanosensors. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4887–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasim, N.; Branton, R.L.; Clarke, D.J. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunohistochemistry and 4,5-diaminofluorescein diacetate: Tools for nitric oxide research. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 112, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathel, T.R.; Leikert, J.J.; Vollmar, A.M.; Dirsch, V.M. Application of 4,5-diaminofluorescein to reliably measure nitric oxide released from endothelial cells in vitro. Biol. Proced. Online 2003, 5, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leikert, J.F.; Rathel, T.R.; Muller, C.; Vollmar, A.M.; Dirsch, V.M. Reliable in vitro measurement of nitric oxide released from endothelial cells using low concentrations of the fluorescent probe 4,5-diaminofluorescein. FEBS Lett. 2001, 506, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijdom, H.; Muller, C.; Lochner, A. Direct intracellular nitric oxide detection in isolated adult cardiomyocytes: Flow cytometric analysis using the fluorescent probe, diaminofluorescein. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 37, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, H.; Hirotani, M.; Nakatsubo, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Urano, Y.; Higuchi, T.; Hirata, Y.; Nagano, T. Bioimaging of nitric oxide with fluorescent indicators based on the rhodamine chromophore. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kim, W.S.; Hatcher, N.; Potgieter, K.; Moroz, L.L.; Gillette, R.; Sweedler, J.V. Interfering with nitric oxide measurements. 4,5-diaminofluorescein reacts with dehydroascorbic acid and ascorbic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48472–48478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Sweedler, J.V. Simultaneous Nitric Oxide and Dehydroascorbic Acid Imaging by Combining Diaminofluoresceins and Diaminorhodamines. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 168, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Johannes, L.; Goud, B.; Antony, C.; Lingwood, C.A.; Daneman, R.; Grinstein, S. Noninvasive measurement of the pH of the endoplasmic reticulum at rest and during calcium release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2997–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llopis, J.; McCaffery, J.M.; Miyawaki, A.; Farquhar, M.G.; Tsien, R.Y. Measurement of cytosolic, mitochondrial, and Golgi pH in single living cells with green fluorescent proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6803–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Seidlits, S.K.; Adams, M.M.; Lynch, V.M.; Schmidt, C.E.; Anslyn, E.V.; Shear, J.B. A Highly Selective Low-Background Fluorescent Imaging Agent for Nitric Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13114–13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilderbrand, S.A.; Lim, M.H.; Lippard, S.J. Dirhodium tetracarboxylate scaffolds as reversible fluorescence-based nitric oxide sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4972–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.C.; Tennyson, A.G.; Lim, M.H.; Lippard, S.J. Conjugated Polymer-Based Fluorescence Turn-On Sensor for Nitric Oxide. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3573–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tian, X.; Shin, I.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and luminescent probes for detection of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4783–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terai, T.; Urano, Y.; Izumi, S.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T. A practical strategy to create near-infrared luminescent probes: Conversion from fluorescein-based sensors. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2840–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z. An N-nitrosation reactivity-based two-photon fluorescent probe for the specific in situ detection of nitric oxide. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4533–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, C.R.A.; Oliveira, A.D.P.R.; Firmino, T.V.C.; Tenório, D.P.L.A.; Pereira, G.; Carvalho, L.B.; Santos, B.S.; Correia, M.T.S.; Fontes, A. Biomedical applications of glyconanoparticles based on quantum dots. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Han, M.-Y.; Huang, D. Nitric Oxide Switches on the Photoluminescence of Molecularly Engineered Quantum Dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11692–11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Heller, D.A.; Kalbacova, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Zhang, J.; Boghossian, A.A.; Maheshri, N.; Strano, M.S. Detection of single-molecule H2O2 signalling from epidermal growth factor receptor using fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, D.A.; Jin, H.; Martinez, B.M.; Patel, D.; Miller, B.M.; Yeung, T.K.; Jena, P.V.; Hobartner, C.; Ha, T.; Silverman, S.K.; et al. Multimodal optical sensing and analyte specificity using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Heller, D.A.; Kim, J.H.; Strano, M.S. Stochastic Analysis of Stepwise Fluorescence Quenching Reactions on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Single Molecule Sensors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4299–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, M.J.; Bachilo, S.M.; Huffman, C.B.; Moore, V.C.; Strano, M.S.; Haroz, E.H.; Rialon, K.L.; Boul, P.J.; Noon, W.H.; Kittrell, C.; et al. Band Gap Fluorescence from Individual Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Science 2002, 297, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Eklund, P.C. Science of Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachilo, S.M.; Strano, M.S.; Kittrell, C.; Hauge, R.H.; Smalley, R.E.; Weisman, R.B. Structure-Assigned Optical Spectra of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Science 2002, 298, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, J.P.; Landry, M.P.; Faltermeier, S.M.; McNicholas, T.P.; Iverson, N.M.; Boghossian, A.A.; Reuel, N.F.; Hilmer, A.J.; Sen, F.; Brew, J.A.; et al. Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Heller, D.A.; Jin, H.; Barone, P.W.; Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Trudel, L.J.; Wogan, G.N.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Strano, M.S. The rational design of nitric oxide selectivity in single-walled carbon nanotube near-infrared fluorescence sensors for biological detection. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Boghossian, A.A.; Barone, P.W.; Rwei, A.; Kim, J.H.; Lin, D.H.; Heller, D.A.; Hilmer, A.J.; Nair, N.; Reuel, N.F.; et al. Single Molecule Detection of Nitric Oxide Enabled by d(AT)(15) DNA Adsorbed to Near Infrared Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, N.M.; Barone, P.W.; Shandell, M.; Trudel, L.J.; Sen, S.; Sen, F.; Ivanov, V.; Atolia, E.; Farias, E.; McNicholas, T.P.; et al. In vivo biosensing via tissue-localizable near-infrared-fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, D.A.; Baik, S.; Eurell, T.E.; Strano, M.S. Single-walled carbon nanotube spectroscopy in live cells: Towards long-term labels and optical sensors. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuri, P.; Bachilo, S.M.; Litovsky, S.H.; Weisman, R.B. Near-infrared fluorescence microscopy of single-walled carbon nanotubes in phagocytic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15638–15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, M.L.; Nakayama-Ratchford, N.; Davis, C.R.; Kam, N.W.; Chu, P.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Dai, H.; Gambhir, S.S. A pilot toxicology study of single-walled carbon nanotubes in a small sample of mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, R.A.; Swanson, J.P.; Barone, P.W.; Baik, S.; Heller, D.A.; Strano, S.M. Achieving individual-nanotube dispersion at high loading in single-walled carbon nanotube composites. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, E.; Gottschalk, B.; Charoensin, S.; Blass, S.; Bischof, H.; Rost, R.; Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.T.; Pelzmann, B.; Bernhart, E.; Sattler, W. Development of novel FP-based probes for live-cell imaging of nitric oxide dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, M.; Ghosh, T.; Tucker, N.; Zhang, X.; Dixon, R. Transcriptional Regulation by the Dedicated Nitric Oxide Sensor, NorR: A Route towards NO Detoxification; Portland Press Limited: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- D’autréaux, B.; Tucker, N.P.; Dixon, R.; Spiro, S. A non-haem iron centre in the transcription factor NorR senses nitric oxide. Nature 2005, 437, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Detection Method | Sensitivity | Molecule Detected | Rate of Detection | Scale | In Vivo, In Vitro, Both | Strengths | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
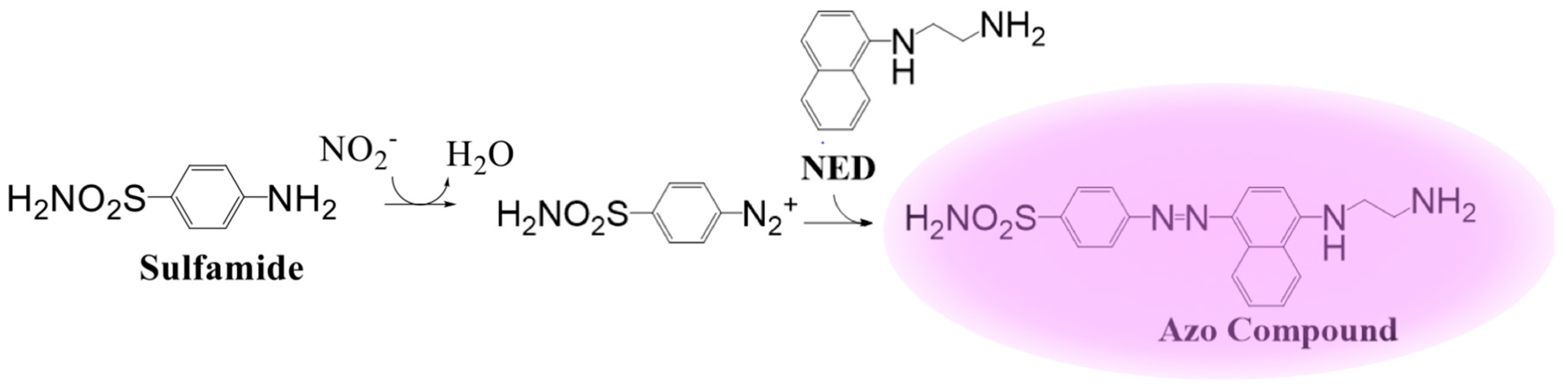
| Griess Assay [58,59,60] | 1.0 µM | NO2 | End-Point | System | In Vitro | Availability, NO2 is stable and provides an estimate of NO in the system | Does not detect NO directly, inconsistent results from system to system |
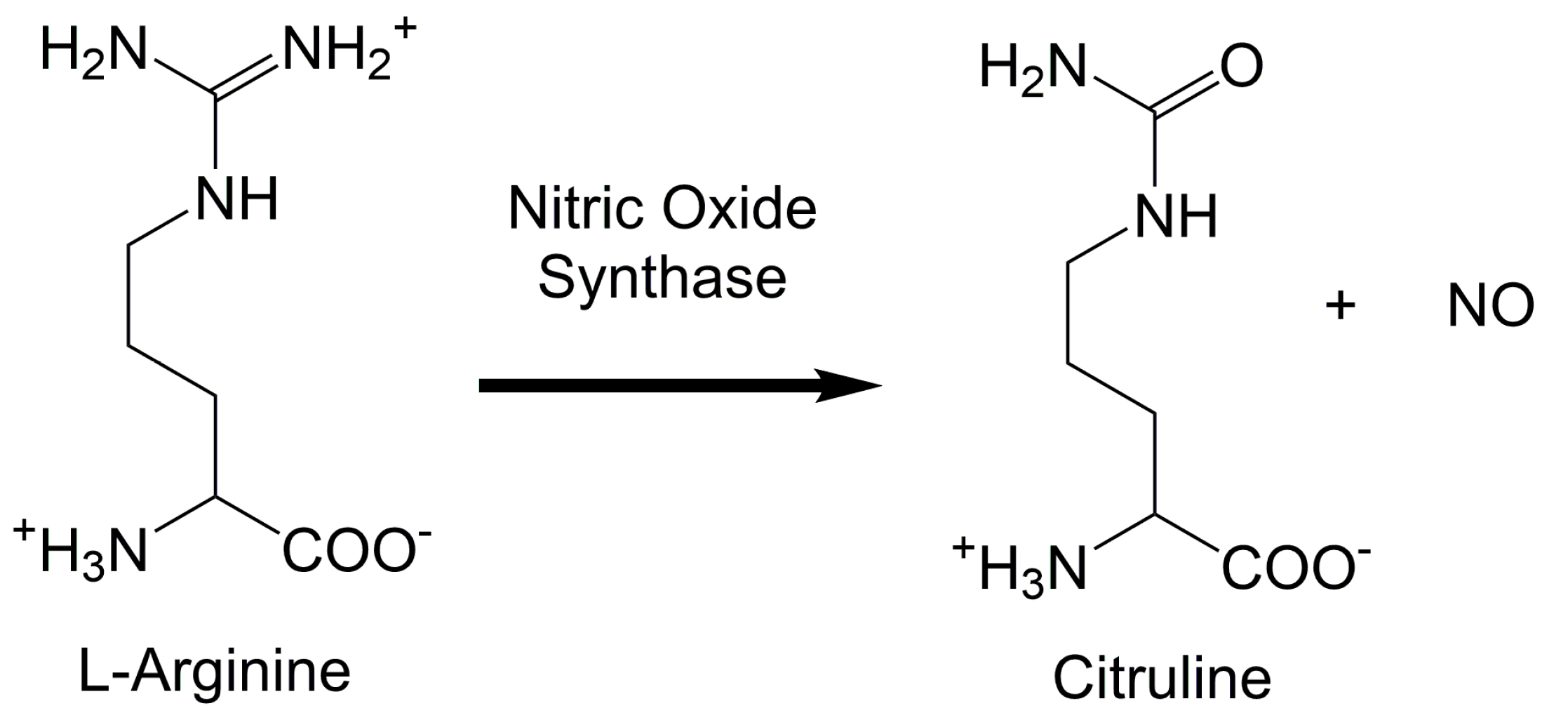
| NOS Activity Assay [61,67] | 5.0 µU | L-Citrulline | End-Point | System | In Vitro | Availability, L-citrulline is stable and estimates NO generated by NOS | Does not detect NO directly, natural L-arginine sources will interfere with readings |
| Electrochemical Probe [71,72,73] | 1.0 nM | NO | Real-Time | System | Both | Availability, Real-time detection, High sensitivity | Detects on a system level, cannot detect over long time intervals |
| Chemiluminescent Probes [76,77] | 50 pM | NO | End-Point | System | In Vitro | High sensitivity to NO | Detects on a system level, Cannot detect in vivo |
| o-diamino Aromatic Compounds [83,86,88] | 5.0 µM | NO | Real-Time | Single Cell | In Vitro | Real-time detection of NO at a cellular level | Limited aqueous solubility, false positives with DHA and AA |
| Luminescent Lanthanide Complexes [92] | ~0.5 µM | NO, N-Nitrosation | Real-Time | Single Cell | Both | Real-time detection at a cellular level | Does not detect NO directly |
| Transition-Metal Complexes [90,91] | 4.0 µM | NO | Real-Time | System | In Vitro | Sensitivity, real-time detection of NO | Limited aqueous solubility |
| Quantum Dots [95] | 3.3 µM | NO | Real-Time | Single Cell | Both | Real-time detection of NO at a cellular level | Irreversibly altered by NO |
| Carbon Nanotubes [103,104,105] | 1.0 µM | NO | Real-Time | Single Cell | Both | Real-time detection of NO at a cellular level | Turn off sensing of NO |
| Genetic Biosensors [110] | 50–94 nM | NO | Real-Time | Single Cell | In Vitro | Real-time detection of NO at a cellular level | Fluorescence emission is not detectable through tissue |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iverson, N.M.; Hofferber, E.M.; Stapleton, J.A. Nitric Oxide Sensors for Biological Applications. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010008
Iverson NM, Hofferber EM, Stapleton JA. Nitric Oxide Sensors for Biological Applications. Chemosensors. 2018; 6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleIverson, Nicole M., Eric M. Hofferber, and Joseph A. Stapleton. 2018. "Nitric Oxide Sensors for Biological Applications" Chemosensors 6, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010008
APA StyleIverson, N. M., Hofferber, E. M., & Stapleton, J. A. (2018). Nitric Oxide Sensors for Biological Applications. Chemosensors, 6(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010008




