Abstract
CO-sensing properties of diode-type sensors employing an anodized TiO2 film and noble-metal (M) electrodes (M/TiO2 sensor, M: Pd, Pt, and Pd-nPt, n: the amount of Pt (wt %) in the Pd-nPt electrode) were investigated at 50–250 °C in dry or wet H2. All the M/TiO2 sensors showed nonlinear I–V characteristics as a diode device in air and N2, but the I–V characteristics of the sensors were actually linear in H2 because of the negligible small height of Schottky barrier at their M/TiO2 interface. The Pd/TiO2 sensor showed no CO response in H2, but the Pt/TiO2 and Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensors responded to CO in H2. Among them, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor showed the largest CO response at 100 °C in H2. The reason why the mixing of Pd with Pt was effective in improving the CO response is probably because of a decrease in the amount of dissolved hydrogen species, an increase in the amount of dissociatively adsorbed hydrogen species, and an increase in the amount of adsorbed CO species in CO balanced with H2 by the mixing of Pt into Pd. The interference from moisture in the target gas on the CO response should be largely improved from a practical application perspective.
1. Introduction
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) have great potential as main power-supplying devices for transportation systems such as fuel cell electric vehicles (PEFCs) as well as distributed stationary and portable applications, in the near future, because of zero emission, compact size, low temperature operation, and other advantages. The fuel of the PEMFCs, hydrogen (H2), is mainly produced by steam reforming of common natural gas containing methane in our modern society, and thus the given amount of carbon monoxide (CO) is mixed in the produced H2-based gas. However, even a small number of CO molecules strongly reduce the electrocatalytic activity of platinum (Pt)-based nanoparticles loaded on the carbon substrate of gas-diffusion electrodes for PEMFCs, which is well known as the “CO-poisoning effect” [1]. Therefore, highly sensitive CO sensors operable under H2-based atmosphere are very convenient for monitoring the concentration of CO in the steam-reforming and various other processes such as a water gas shift reaction.
Various types of gas sensors, such as chemiresistor-type sensors using oxides [2,3,4,5,6], polymers [7], or metal salts [8,9,10], electrochemical sensors [11,12,13], and solid-electrolyte sensors [14,15], have been developed to detect CO sensitively and selectively, under reducing atmosphere. However, none of the sensors have CO-sensing properties sufficient to quantify the concentration of residue CO left in the reformed gas. On the other hand, we have already demonstrated that the diode-type gas sensors employing a titania (TiO2) [16,17,18,19,20,21] or niobia (Nb2O5) [22,23] film, which was prepared by the anodization of a constituent metal plate, and noble-metal electrodes (mainly, palladium (Pd) and/or Pt) showed quite excellent H2-sensing properties, especially under inert atmosphere (N2), because H2 was dissociatively adsorbed and dissolved into the noble-metal electrode and thus the drastic reduction of the work function as well as the height of the Schottky barrier of noble-metal/oxide interface. The excellent H2-sensing properties of the diode-type gas sensors under inert atmosphere motivated us to investigate their sensing properties to other gases under a more specific environment. In this study, therefore, CO-sensing properties of the diode-type sensors employing an anodized TiO2 film and Pd and/or Pt electrodes have been investigated in comparison with their H2-sensing properties in air as well as in N2.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Diode-Type Gas Sensors
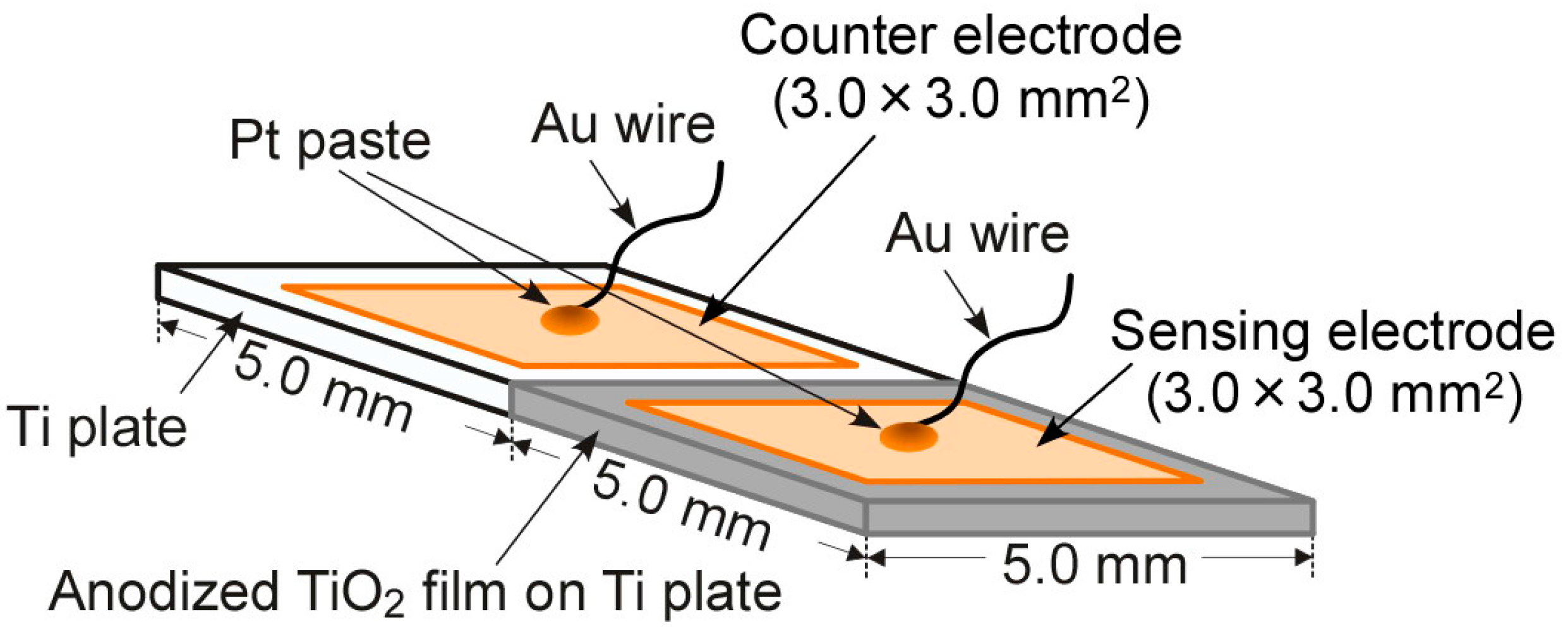
Figure 1 shows schematic drawing of a diode-type gas sensor employing an anodized TiO2 film on a Ti plate and Pd and/or Pt electrodes, which was fabricated as follows. A half part of a Ti plate (5.0 × 10.0 × 0.5 mm3) was anodized in 0.5 M H2SO4 aqueous solution at 20 °C for 30 min at a current density of 50 mA·cm−2, after the Ti plate was polished by using a buffing machine (Marumoto Struers K. K., Osaka, Japan, S5629) employing 3 kinds of diamond aqueous suspensions (diameter of diamond powders suspended: 9 μm, 3 μm, and 0.5 μm) sequentially. A pair of noble-metal (Pd or Pt) electrodes was fabricated on the surface of both the TiO2 thin film and the Ti plate by radio-frequency (rf) magnetron sputtering (Shimadzu, HSR-552S). The mixing of Pd with Pt was also conducted by simultaneous deposition utilizing both Pd and Pt targets, and the obtained electrodes were denoted as Pd-nPt, where n is the amount of Pt (wt %) in the Pd-nPt electrodes. The fabrication conditions of all the electrodes were shown in Table 1, together with their composition and thickness, and the deposition time for all the films was 7 min. The composition of the Pd-nPt electrodes was measured by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS; JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, JED-2300) equipped with scanning electron microscopy (SEM; JEOL Ltd., JSM-7500F). The obtained sensors with noble-metal (M) electrodes were denoted as M/TiO2 (M: Pd, Pt, or Pd-nPt). Each electrode was connected with an Au lead wire by using a Pt paste, and the electrical contact was ensured by firing at 600 °C for 1 h in air.
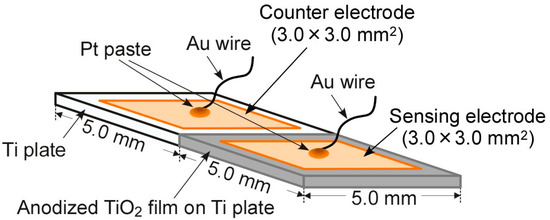
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of a diode-type gas sensor.

Table 1.
Composition and fabrication conditions of Pd, Pt, and Pd-nPt electrodes fabricated on a TiO2 film by rf magnetron sputtering.
2.2. Measurements of Gas-Sensing Properties
In order to confirm fundamental properties as their diode-type sensing devices, the current (I)–voltage (V) characteristics of the representative 3 sensors (Pd/TiO2, Pt/TiO2, and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors) were investigated in a base gas (dry air or N2) and in 8000 ppm H2 balanced with a base gas, and their sensing properties to 8000 ppm H2 balanced with dry air or N2 were measured at 250 °C when a dc voltage of +100 mV was applied to the sensors under forward bias condition (M(+)–TiO2–Ti(−)). In addition, a dc voltage of +1.0 mV was applied to all the sensors under the forward bias condition and the sensing properties to 1–80 ppm CO balanced with H2 under dry or wet (absolute humidity (AH): ca. 12.8 g·m−3) atmospheres were measured at 50–250 °C (mainly, at 100 °C) after annealing under H2 atmosphere at 400 °C for 1 h. The I–V characteristics of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor as a representative were also evaluated in an applied voltage range of −1.0 to +1.0 V in dry N2, dry H2 or 80 ppm CO balanced with dry H2. All the sensors were externally heated in a test chamber by utilizing an electric furnace, and all the test gases were continuously supplied into the test chamber at a flow rate of 100 cm3·min−1.
The magnitude of response was defined as the absolute value of “Is − Ib”, where Is and Ib represented sensor-current values in a sample gas (at 10 min after switching to the sample gas) and in a base gas, respectively. 90% response time (TRS) was defined as a period necessary to reach 90% sensor-current value of “Is − Ib” from the time switching to the sample gas, while 90% recovery time (TRC) was defined as that necessary to reach 90% sensor-current value of “Ib – Is” from the time switching to the base gas. The 90% response and recovery times numerically contain a delay period from the gas-switching time to the response- and recovery-starting times, ca. 64 s, in this study, since the dead volume of the gas-flow pathway and the chamber in the measurement apparatus is ca. 106 cm3.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure
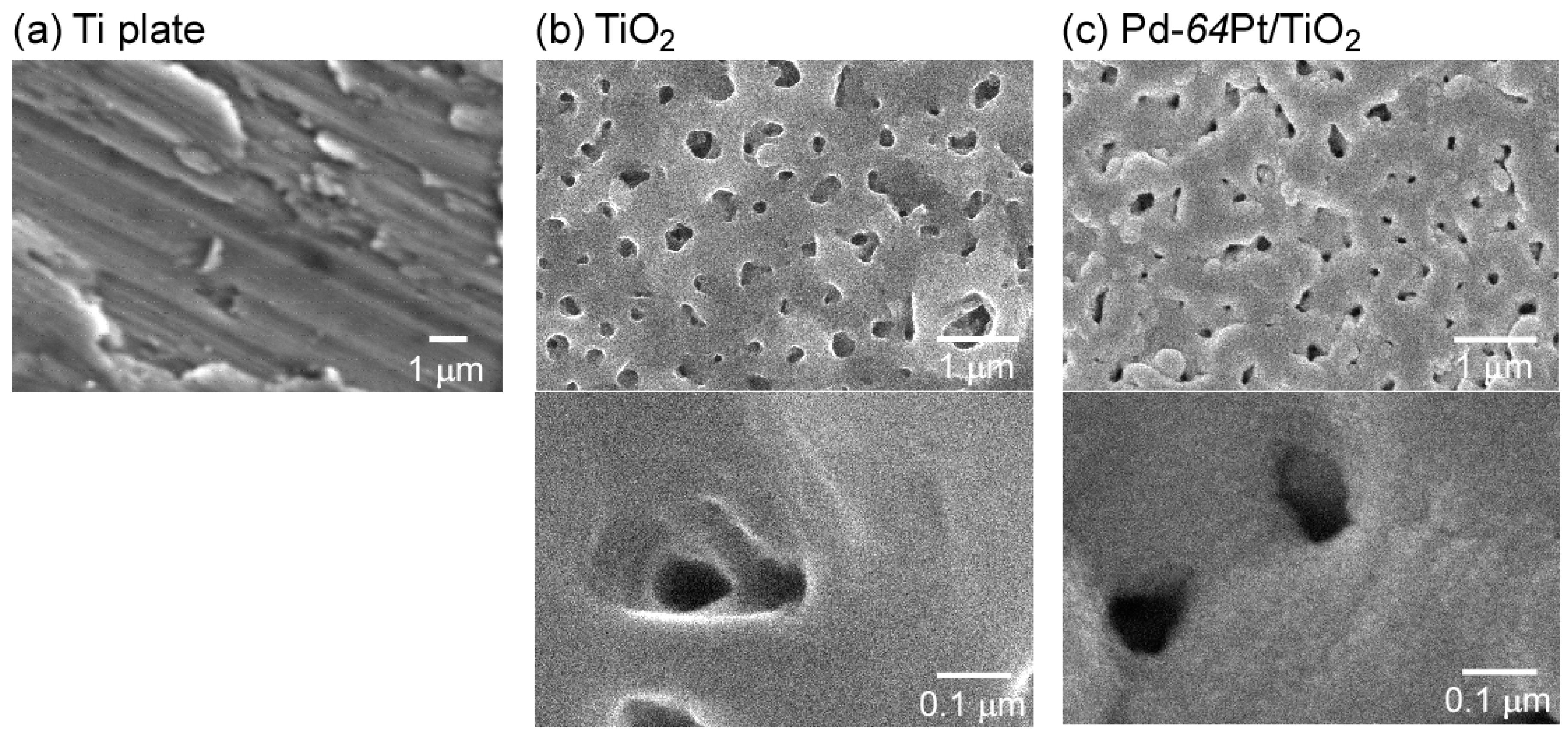
Figure 2 shows SEM photographs of surfaces of a Ti plate, a bare TiO2 film fabricated on a Ti plate by anodization, and a TiO2 film coated with a Pd-64Pt, as a representative of M/TiO2, by rf magnetron sputtering. The surface of a Ti plate polished with diamond suspensions became smoother than that of an untreated Ti plate, but many scratch lines with submicron intervals were observed in the same direction on the surface, since it was finally polished by using a buffing machine employing an aqueous suspension containing diamond powders with a diameter of ca. 0.5 μm. The anodization of the Ti plate in 0.5 M H2SO4 aqueous solution produced a relatively planar TiO2 film with submicron pores, on the surface, without harmful effects of the submicron scratches. The prepared TiO2 film (thickness: around 1 μm) consisted of dense columnar TiO2 polycrystallites (main crystal phase: anatase and rutile for the TiO2 film before and after heat treatment at 600 °C, respectively) and the microstructure remained unchanged even after the heat treatment, as shown in our previous studies [16]. The Pd-64Pt film was uniformly deposited on the surface of the anodized TiO2 film, and then the submicron pores of the anodized TiO2 film were partly filled with the Pd-64Pt agglomerates (estimated size: several tens of nm in diameter) and the size of the pores considerably reduced after the Pd-64Pt deposition. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis of the Pd-64Pt electrode, which was fabricated with the same procedure, has demonstrated the effect of heat treatment on the composition, as below [19]. The bulk composition of the Pd-64Pt electrode right after the sputtering deposition (Pd: 36–33 wt %, Pt: 64–67 wt %) was very comparable to that which was estimated from the sputtering rate of Pd and Pt (Pd: 36 wt %, Pt: 64 wt %), while the weight percentage of Pt on the electrode surface right after the sputtering deposition (ca. 55 wt %) was smaller than that which was estimated from the sputtering rate of Pd and Pt (namely n: 64 wt %). After firing at 600 °C for 1 h in air, Pd and Pt on the surface of the Pd-64Pt electrode was oxidized to PdO and PtO, respectively and the amount of the Pd component on the electrode surface increased by ca. 90 wt %, because the given amount of Pd diffused toward the electrode surface due to the higher affinity of Pd for oxygen than Pt. The annealing at elevated temperatures under H2 atmosphere reduced the PdO and PtO on the electrode to Pd and Pt, respectively.
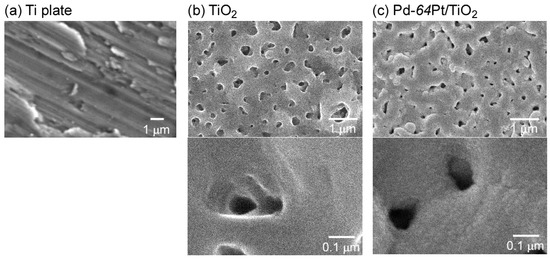
Figure 2.
SEM photographs of surfaces of (a) a Ti plate; (b) a bare TiO2 film; and (c) a Pd-64Pt-coated TiO2 film. The TiO2 film was fabricated on a Ti plate by anodization.
3.2. Basic Diode Characteristics and H2-Sensing Properties in Dry Air and N2
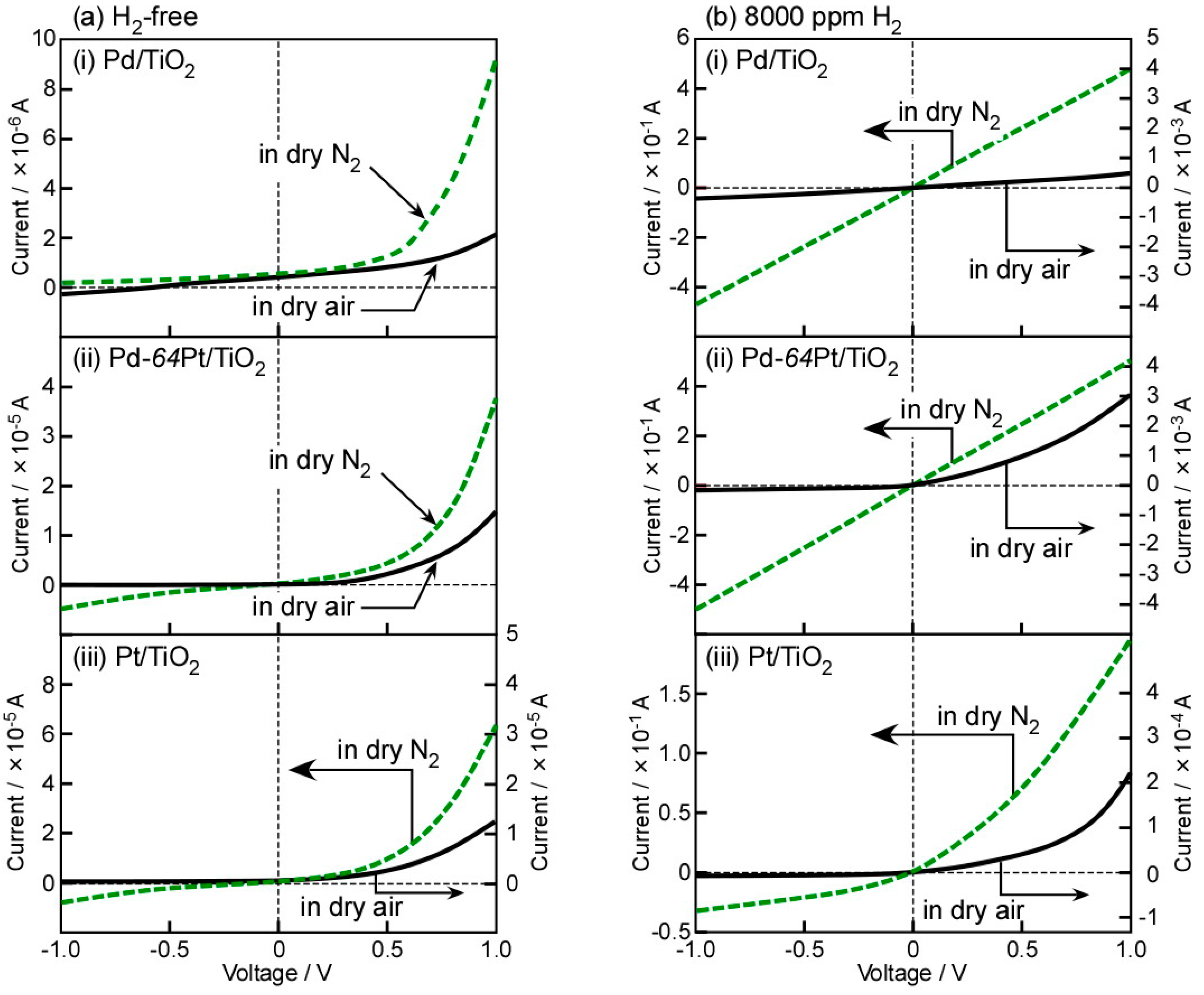
In order to confirm the diode-type behavior of the M/TiO2 sensors fabricated in this study, I–V characteristics of typical three sensors, Pd/TiO2, Pt/TiO2, and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors, were investigated at 250 °C in base gases (dry air and N2) and in 8000 ppm H2 balanced with the base gases, as shown in Figure 3. These sensors obviously showed nonlinear I–V characteristics under dry H2-free atmospheres, indicating that the Schottky contact was formed at all the M/TiO2 interfaces. In addition, the magnitude of current of all the M/TiO2 sensors in dry N2 under the forward bias was larger than that in dry air, and the magnitude of current of these sensors tended to increase with an increase in the amount of Pt in the M electrodes, especially in dry N2. Generally, the work function of Pt (5.26–5.69 eV) is larger than that of Pd (4.87–5.25 eV) [24], and thus the Schottky barrier of the Pt/TiO2 interface (1.7–1.8 eV) tends to be larger than that of the Pd/TiO2 interface (1.2–1.3 eV) [25]. On the other hand, the surface of the Pd electrode is easily oxidized to PdO under heat treatment at 600 °C in air, and the PdO is partially reduced in N2 at elevated temperatures [19,21]. In contrast, the surface of the Pt electrode is not easily oxidized even under heat treatment at 600 °C in air [21]. These results which were obtained by utilizing the XPS analysis have already been demonstrated in our previous papers [19,21]. The electron affinity of PdO (ca. 5.5 eV) is larger than the work function of Pd [26], and various defect and impurity levels are easily produced at the M/TiO2 interface [27,28]. On the other hand, Pd and Pt in the bulk of the Pd-64Pt electrode was alloyed and the alloy Pd-Pt phase in the bulk is likely to be chemically and thermally stable as a metal at elevated temperatures, even in air [19,21]. After the heat treatment at 600 °C in air, however, most of Pd in the vicinity of the surface of the Pd-64Pt film were oxidized to PdO, while Pt just on the surface was only oxidized to PtO [19]. The degree of oxidation on the electrode surface probably had an impact on the electric properties of the M/TiO2 interface and thus these I–V characteristics dependent on the gaseous atmosphere.
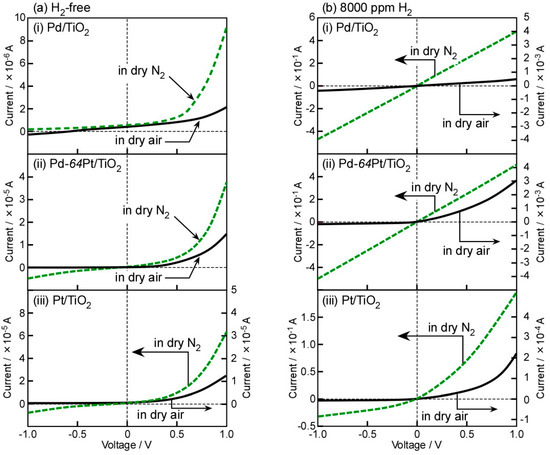
Figure 3.
I–V characteristics of (i) Pd/TiO2, (ii) Pd-64Pt/TiO2, and (iii) Pt/TiO2 sensors at 250 °C (a) in base gases (dry air and N2) and (b) in 8000 ppm H2 balanced with base gases.
The addition of H2 into both the base gases enhanced the magnitude of currents of these sensors. The behavior is due to dissociative adsorption of H2 molecules on the surface of M electrodes, subsequent dissolution of the hydrogen species into the M electrodes, and in turn reduction in these work functions, leading to a decrease in the height of the Schottky barrier at the M/TiO2 interface. In addition, the magnitude of currents in 8000 ppm H2 balanced with dry N2 was more than two orders of magnitude larger than those in 8000 ppm H2 balanced with dry air, under the same applied forward bias. Namely, the mixing of oxygen into the H2-containing gaseous atmosphere largely reduced the magnitude of current of all the sensors. This indicates that the certain percentage of H2 was oxidized with oxygen species (e.g., oxygen adsorbates) on the surface of M electrodes and thus the effective H2 concentration on the surface reduced in dry air, whereas the H2 concentration on the M electrodes hardly decrease in dry N2 [21]. Furthermore, the Pd/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors showed ohmic-like I–V characteristics in H2 balanced with dry N2, due to the quite small Schottky barrier at the M/TiO2 interface. On the other hand, the Pt/TiO2 sensor managed to maintain the nonlinear I–V characteristics even in dry N2, which showed the smaller magnitude of currents in both dry N2 and air than the Pd/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors.
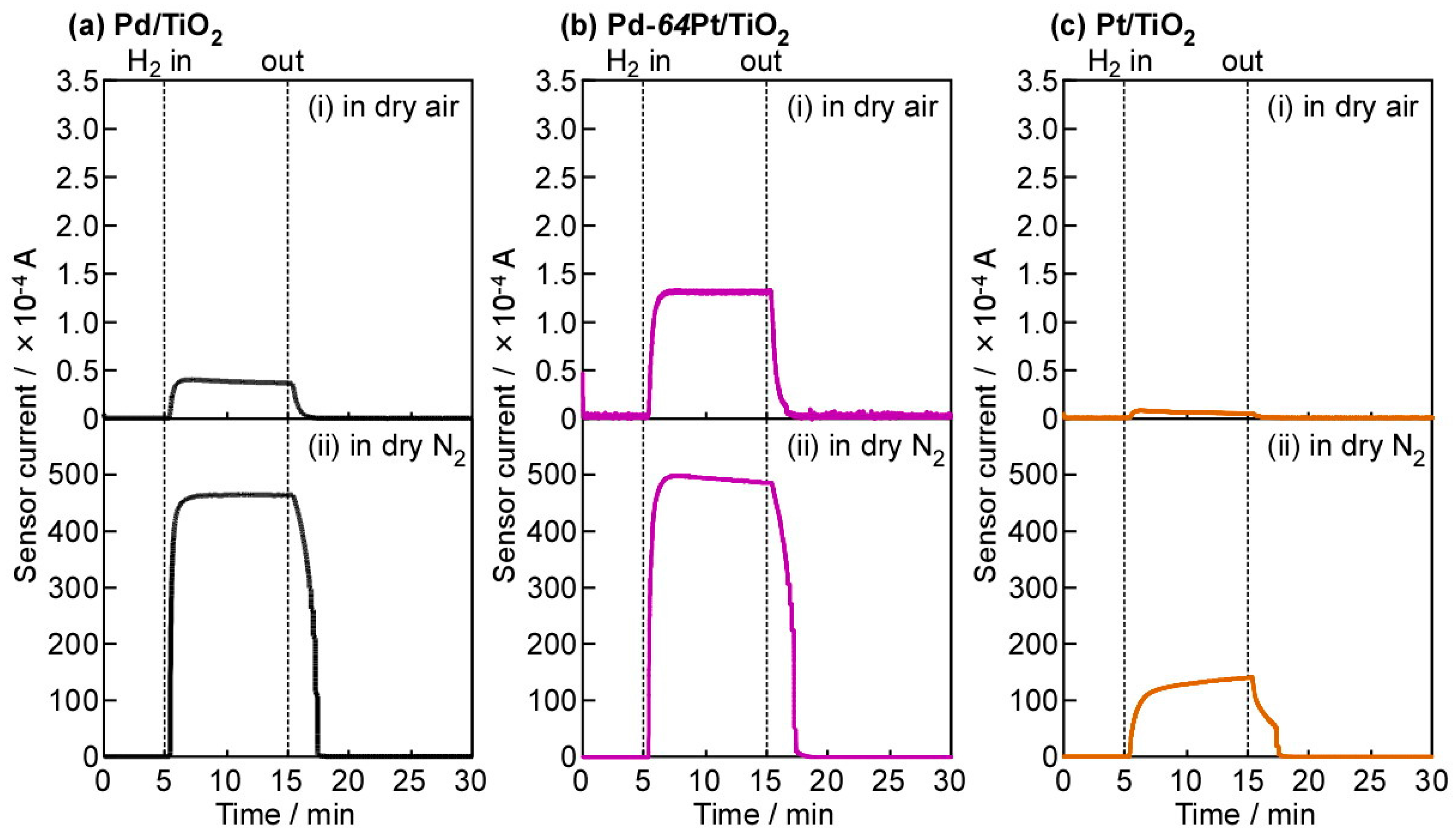
Figure 4 shows response transients of Pd/TiO2, Pt/TiO2, and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors to 8000 ppm H2 at 250 °C at a forward bias of +100 mV, in dry air and N2. As expected from these I–V characteristics (Figure 3), the magnitude of currents of all the sensors was quite low in both the base gases, and the addition of H2 into the base gases drastically enhanced the magnitude of currents especially in dry N2. Thus, these sensors showed very large H2 responses, but these H2-sensing properties are quite dependent on oxygen concentration. Among these sensors, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors showed relatively large H2 responses in both dry air and N2.
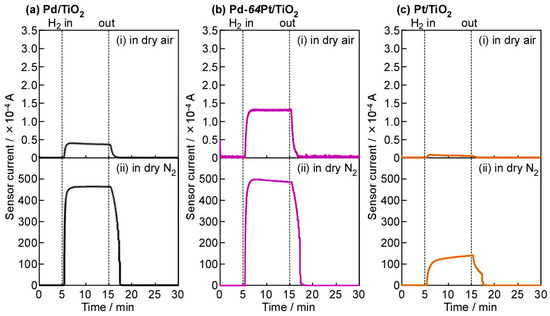
Figure 4.
Response transients of (a) Pd/TiO2, (b) Pt/TiO2, and (c) Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors to 8000 ppm H2 at 250 °C in (i) dry air and (ii) dry N2 (applied forward bias: +100 mV).
3.3. Typical I–V Characteristics and CO-Sensing Properties in H2
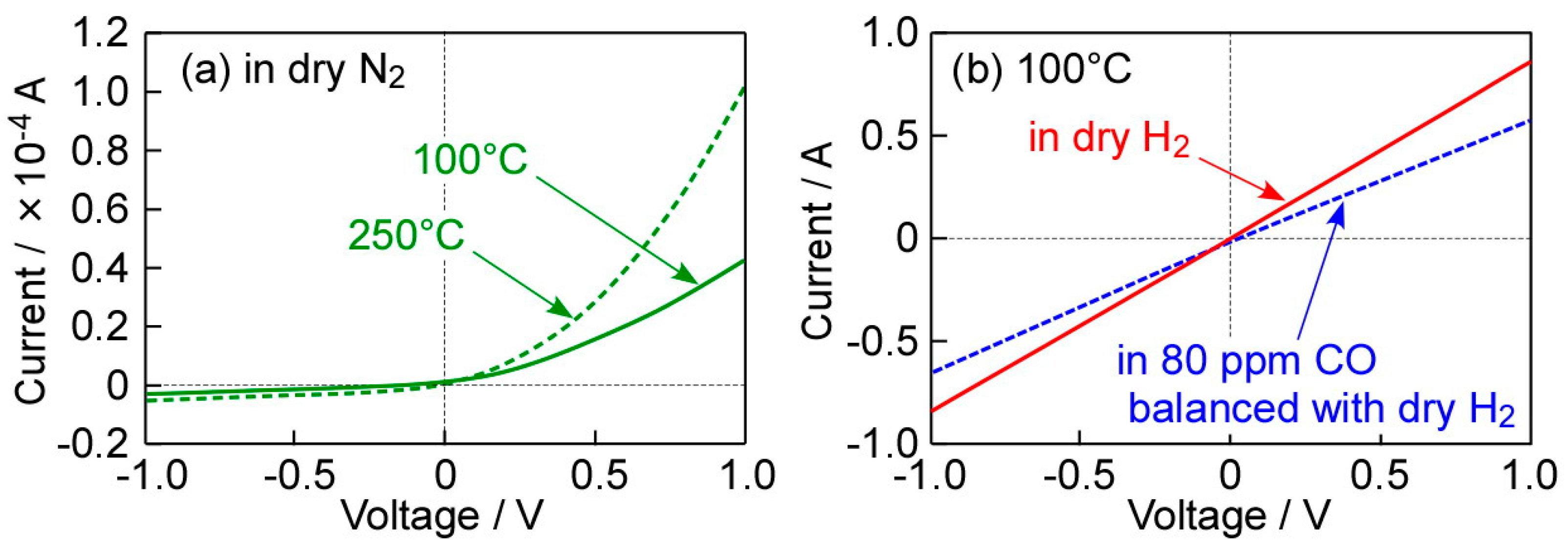
Figure 5 shows I–V characteristics of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor as a representative, in dry N2 at 100 °C and 250 °C, and in dry H2 and 80 ppm CO balanced with dry H2 at 100 °C. This sensor was annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h, before the measurement, because of the enhancement in the thermal and chemical stability. The annealing at 400 °C in H2 increased the magnitude of current of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor in dry N2, and the current of the annealed Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor was a little larger than that of the non-annealed Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor at 250 °C (see Figure 3a(ii)), in dry N2. In addition, a decrease in the operating temperature reduced the magnitude of current, the nonlinearity of these I–V characteristics of the annealed Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor was comparable to that of the non-annealed Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor at 250 °C in dry N2. On the other hand, the I–V relationship in dry H2 was considerably linear, due to the negligibly small Schottky barrier, and the I–V relationship of the Pd/TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 sensors at 100 °C in dry H2 was also quite similar to that of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor (not shown here). The addition of 80 ppm CO into dry H2 reduced the magnitude of current of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor at 100 °C, which means that the sensor is capable of detecting CO in dry H2 at least.
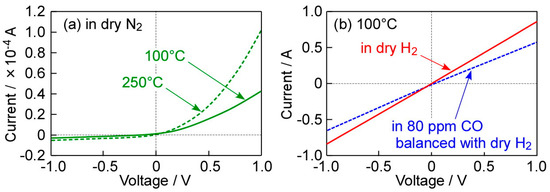
Figure 5.
I–V characteristics of a Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor, which was annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h, as a representative, (a) in dry N2 at 100 °C and 250 °C, and (b) in dry H2 and 80 ppm CO balanced with dry H2 at 100 °C.
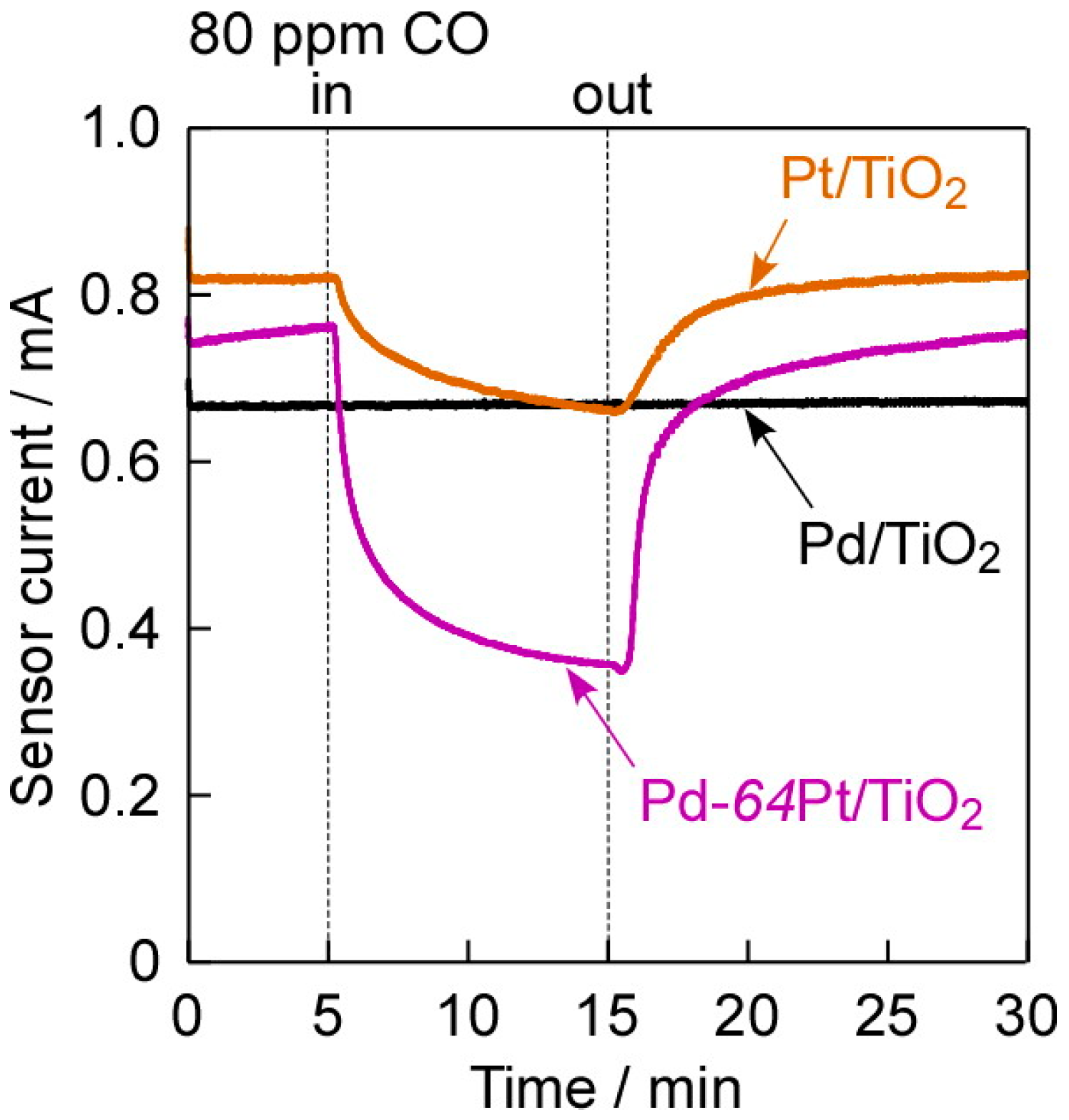
Figure 6 shows response transients of three kinds of the annealed M/TiO2 sensors (M: Pd, Pt, and Pd-64Pt) to 80 ppm CO at 100 °C in dry H2. The surface of the M electrodes is totally reduced with H2 in both pre-treatment and operating conditions, and thus metallic Pd and/or Pt on the electrode surface were directly exposed to target gas [19]. In addition, H2 molecules as a base-gas component are dissociatively adsorbed on the surface and the part of the adsorbed hydrogen species is dissolved into the metals, which largely decrease the work function of the metals and thus change the M/TiO2 interface entirely from the Schottky contact to quasi-ohmic contact. As they resulted in a large reduction in the sensor resistances, the quite small forward voltage, +1.0 mV, was applied to the sensors for the CO sensing at 100 °C in dry H2. The dependence of the I–V characteristics of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor under the reducing atmospheres (Figure 5) promised that the addition of CO into dry H2 increases the sensor resistance. Actually, the Pt/TiO2 sensor expectedly showed a clear CO response in the negative direction, while the Pd/TiO2 sensor showed no CO response. The solubility of hydrogen into Pt is extremely smaller than that into Pd [29], but H2 molecules easily and largely adsorb on the Pt surface [30]. In addition, CO molecules are well known to strongly adsorb on the Pt surface [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15], especially at around 100 °C (temperatures at which PEMFCs generally operate) under H2-based reducing atmospheres. Therefore, the strongly adsorbed CO species probably interrupted the dissociatively adsorption of H2 molecules, to increase the work function of Pt and the height of Schottky barrier at the M/TiO2 interface, and thus to decrease the magnitude of current. In contrast, the solubility of hydrogen into Pd is quite large [29], and thus the amount of CO adsorbed on the Pd surface is generally much smaller than the total amount of hydrogen adsorbed on the Pd surface and dissolved into the Pd bulk. Therefore, the adsorption of CO molecules probably had negligible influence on the adsorption and absorption behavior of H2 molecules. Furthermore, the mixing of Pt with a Pd electrode was quite effective in improving the magnitude of CO response. This is probably because a decrease in the amount of Pd (namely, an increase in the amount of Pt) in the M electrode decreased the amount of dissolved hydrogen species in H2 [29] and increased the amount of dissociatively adsorbed hydrogen species [30], and then the adsorbed CO on the electrode surface interrupted the dissociatively adsorption of hydrogen, in 80 ppm CO balanced with H2. Further discussion will be done based on the additional data in the following section. On the other hand, the response and recovery speeds of the Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors were much slower than those for the H2 response in both dry air and N2, and thus their drastic improvement is indispensable from a practical application perspective.
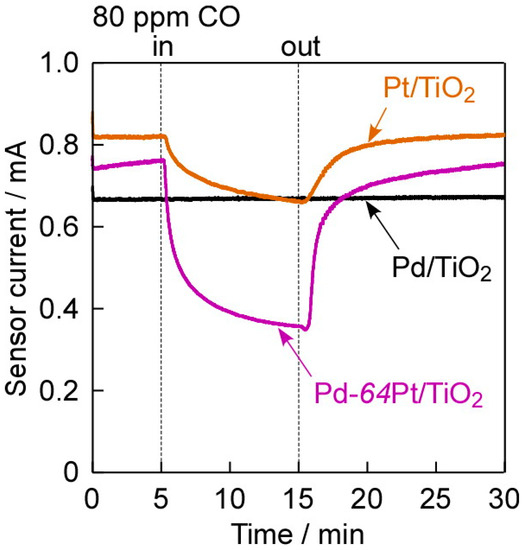
Figure 6.
Response transients of Pd/TiO2, Pt/TiO2, and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors, which were annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h, to 80 ppm CO at 100 °C in dry H2 (applied forward bias: +1.0 mV).
3.4. Impacts of Various Factors on CO-Sensing Properties in H2
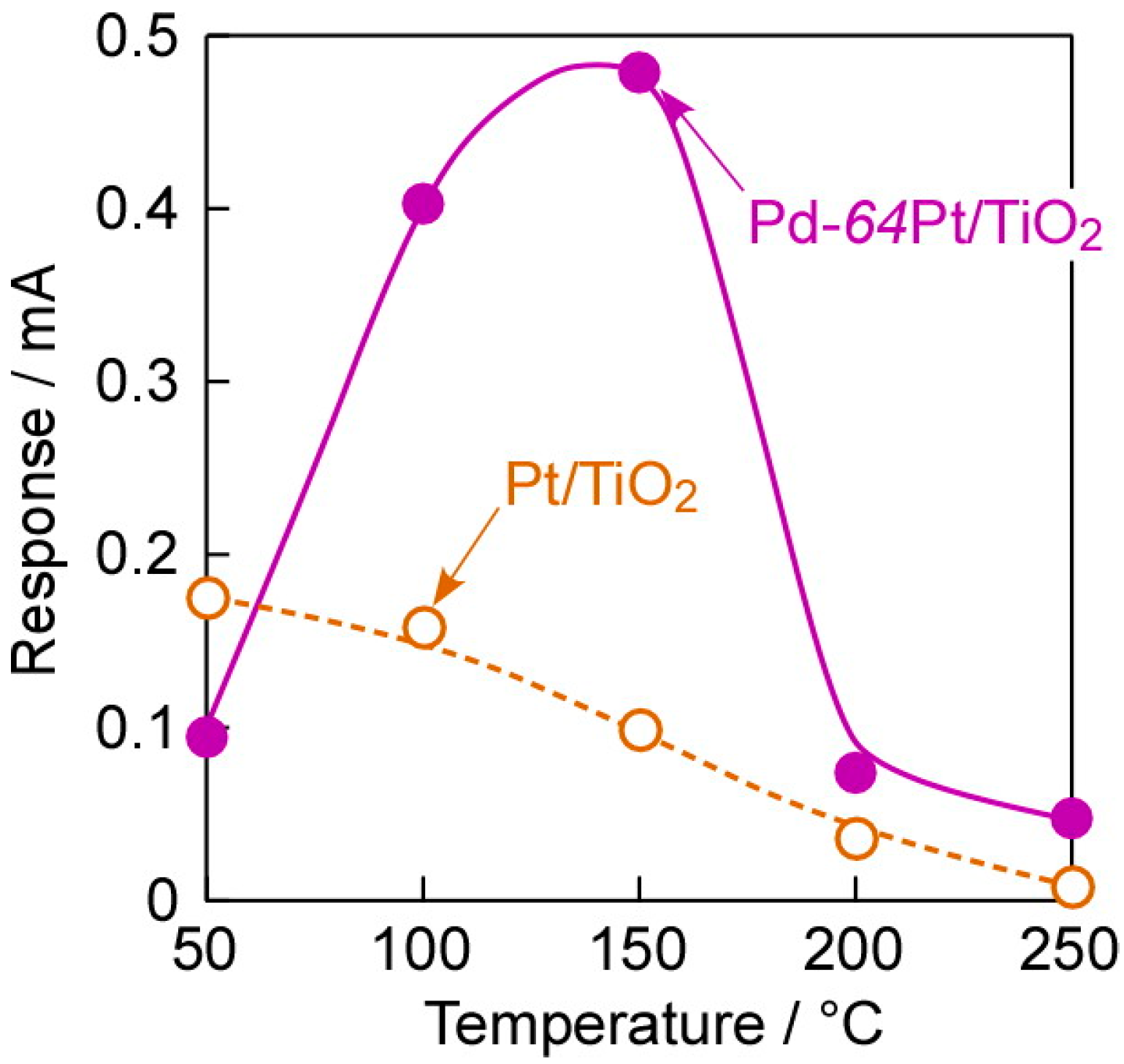
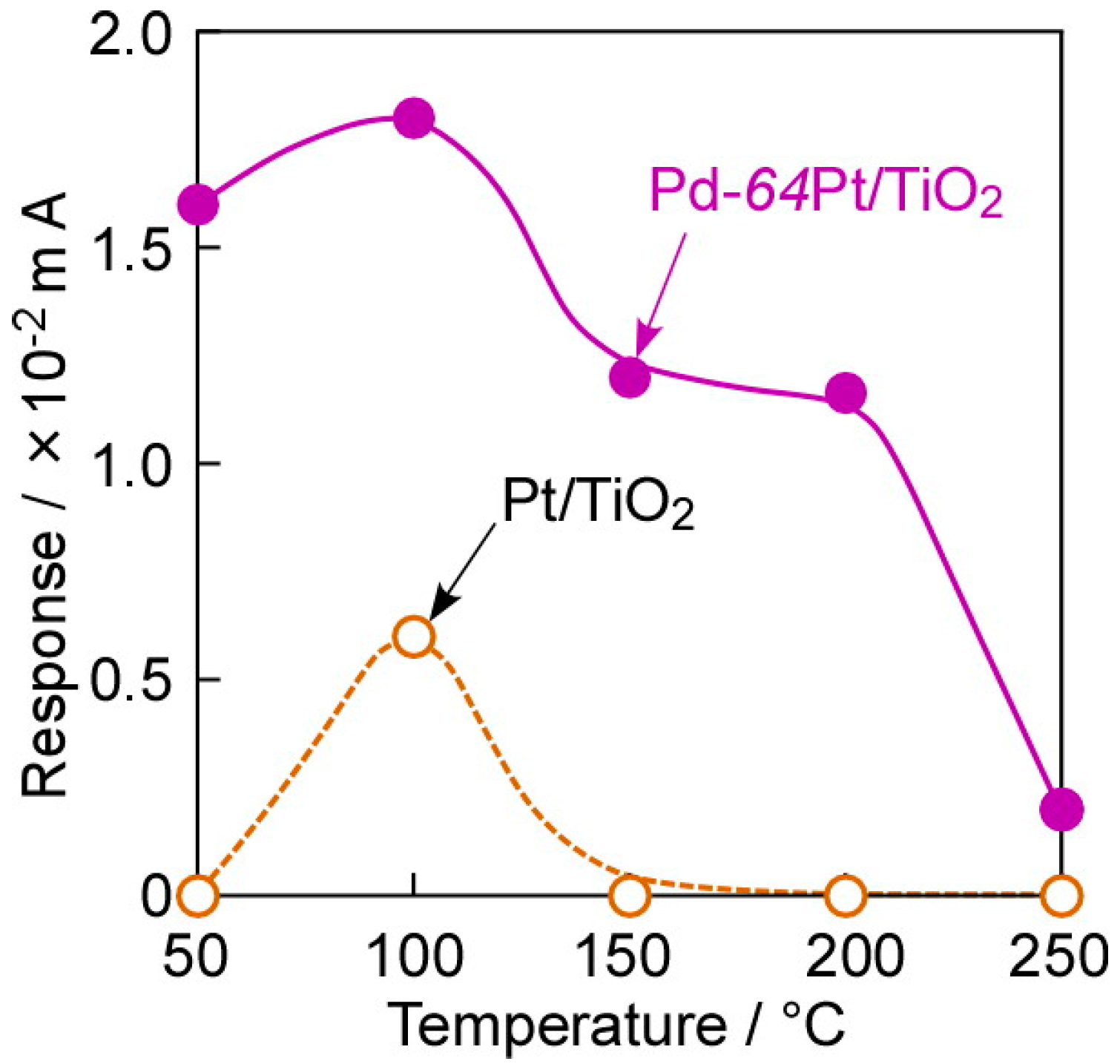
Figure 7 shows operating temperature dependences of responses of the annealed Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors to 80 ppm CO in dry H2. The magnitude of CO response of the Pt/TiO2 sensor monotonically decreased with an increase in operating temperature. The solubility of hydrogen into Pt was generally much smaller than that into Pd, and gradually increased with an increase in temperature [29]. In addition, the CO coverage on Pt also decreased monotonically with an increase in temperature [31]. These factors probably determined the relatively large CO response of the Pt/TiO2 sensor at lower operating temperatures. On the other hand, the CO response of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor was smaller than that of the Pt/TiO2 sensor at 50 °C, probably due to the large amounts of dissociatively adsorbed and dissolved hydrogen species and relatively small amount of adsorbed CO on Pd-64Pt in comparison with those of Pt. However, the magnitude of the CO response increased with an increase in operating temperature, and the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor showed quite large CO responses at 100–150 °C. The amount of hydrogen dissolved into Pd abruptly decreases with an increase in the temperature, especially in the temperature range of 100–150 °C [29], whereas the CO coverage on Pt also decreased monotonically with an increase in the temperature [31]. These two factors may increase the ratio of the amount of adsorbed CO species to the amounts of dissociatively adsorbed and dissolved hydrogen species at around 100–150 °C. In addition, the magnitude of CO responses at 200–250 °C were smaller than those at 50 °C, probably because the amount of CO adsorbed on the electrode surface decreased with an increase in the operating temperature. However, even the CO response of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor at 200–250 °C was still a little larger than that of the Pt/TiO2 sensor. Meanwhile, this gaseous atmosphere, namely dry H2 containing CO, have a high possibility of progressing the hydrogenation of CO on the electrode surface, to produce some kinds of hydrocarbons and alcohols (Fischer-Tropsch process; e.g., nCO + (2n + 1)H2 → CnH2n+2 + nH2O) [32] and thus decrease the effective concentration of CO. The effect of these catalytic reactions on the electrode surface on the CO-sensing mechanism should be clarified in the future, in order to enhance the CO-sensing properties in dry H2.
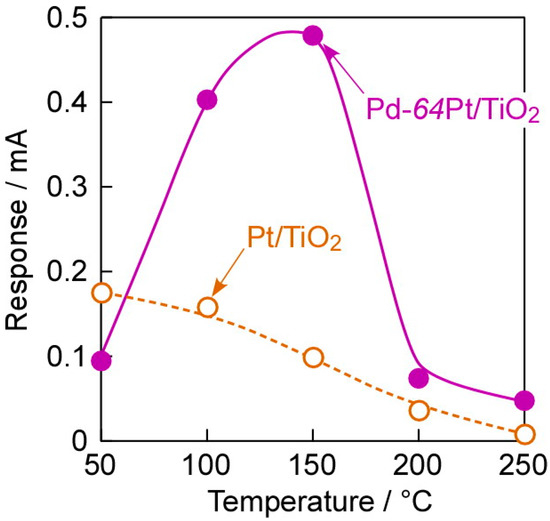
Figure 7.
Operating temperature dependences of responses of Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors, which were annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h in advance, to 80 ppm CO in dry H2 (applied forward bias: +1.0 mV).
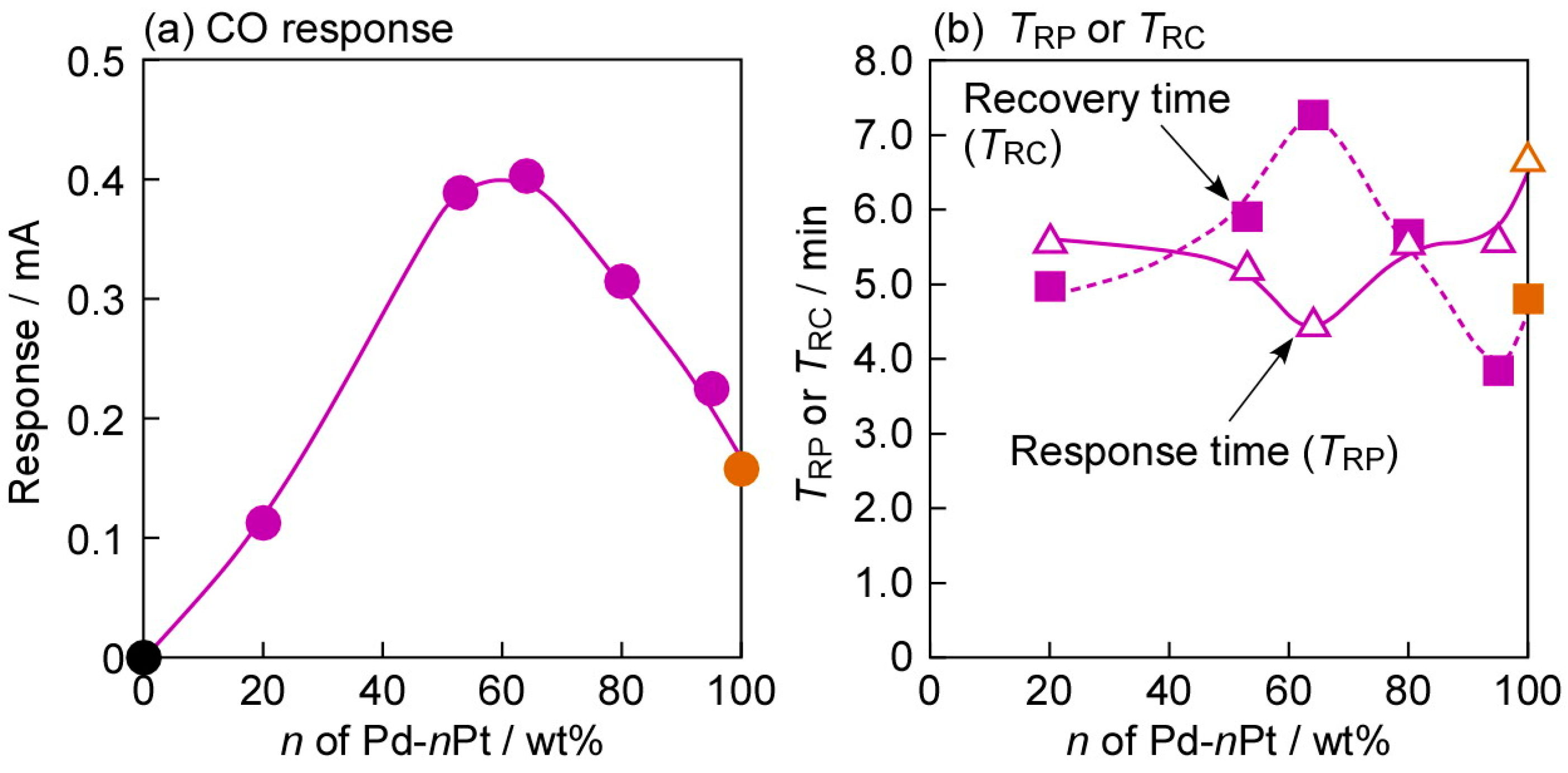
Figure 8 shows variations in responses to 80 ppm CO and response and recovery times of all annealed Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensors at 100 °C in dry H2, as a function of the amount of Pt in the Pd-nPt electrodes. The mixing of Pt into Pd enhanced the magnitude of CO response, and vice versa. This fact indicates that the balance between the adsorption property of CO and the adsorption and dissolution properties of H2 on the electrode surface is the most important in enhancing the CO-sensing properties of the Pd-nPt sensors in H2. Consequently, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor showed the largest CO response among all the Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensors. On the other hand, the composition of the electrode had a minimal effect on the response and recovery speeds of the Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensors, too. Namely, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor showed the fastest response speed and the slowest recovery speed among them, probably because the response and recovery speeds were simply dependent on only the magnitude of CO responses.
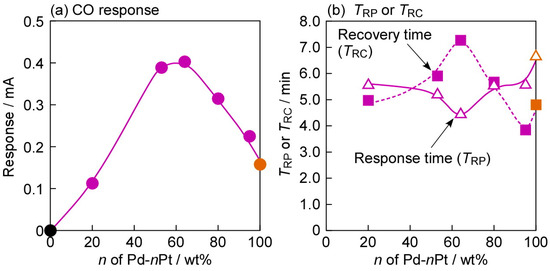
Figure 8.
Variations in (a) responses to 80 ppm CO and (b) response and recovery times (TRP and TRC, respectively) of Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensors (including Pd/TiO2 (n = 0) and Pt/TiO2 (n = 100)), which were annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h in advance, at 100 °C in dry H2 (applied forward bias: +1.0 mV), as a function of the amount of Pt (wt %) in the Pd-nPt electrodes (n). TRP and TRC of the Pd/TiO2 (Pd-0Pt/TiO2) sensor are not shown in this figure, because the sensor showed no response to CO.
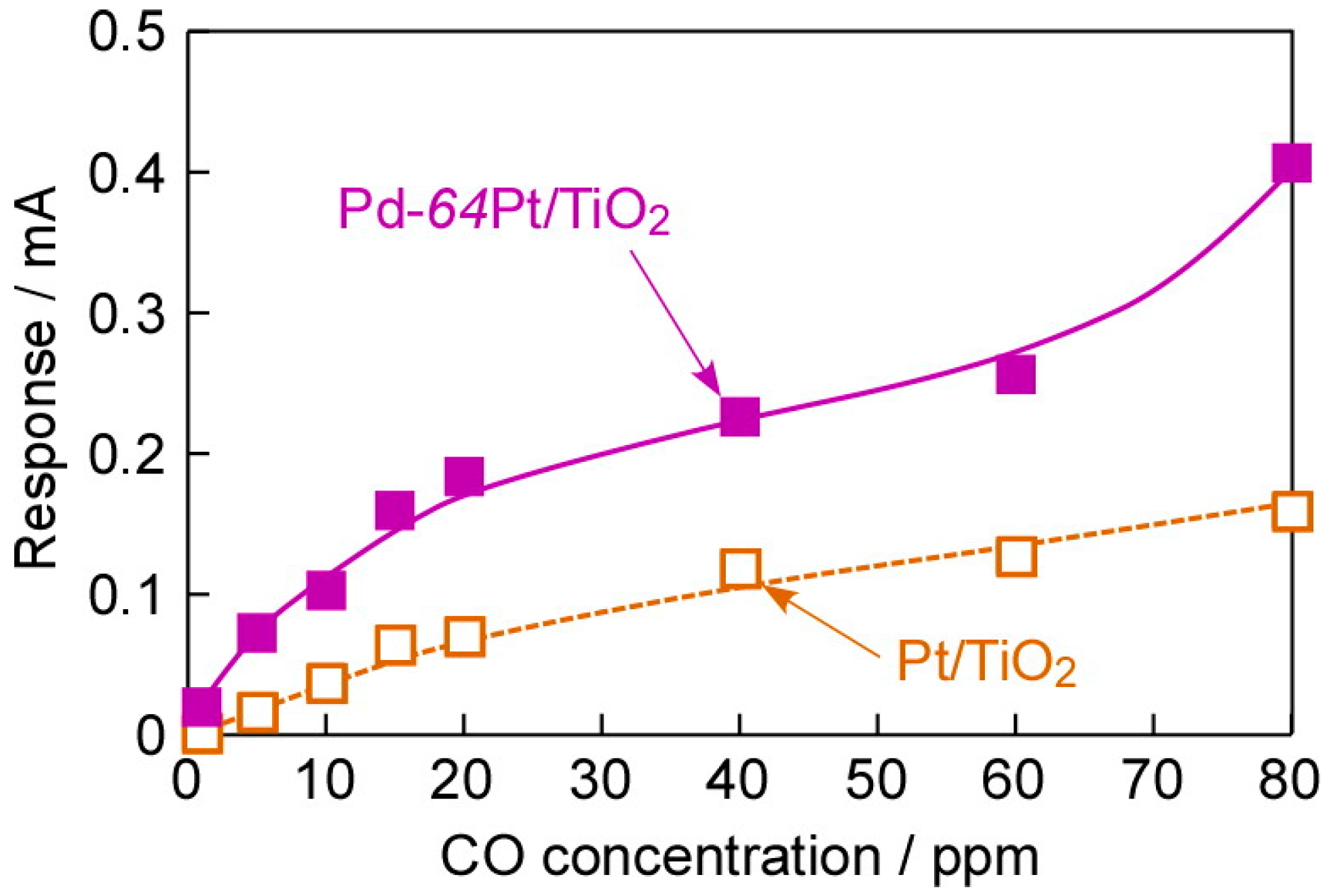
Figure 9 shows concentration dependences of CO responses of the annealed Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors to 80 ppm CO at 100 °C in dry H2. The Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor showed a large response to a high concentration of CO (ca. 403 μA for 80 ppm CO) with the excellent signal/noise (S/N) ratio (ca. 143 for 80 ppm CO), but the response of the Pt/TiO2 sensor to 80 ppm CO and the S/N ratio was relatively small (ca. 20 μA and ca. 10, respectively). In addition, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor easily detected even 1 ppm CO (the magnitude of response: ca. 20 μA, S/N ratio: ca. 10), while the Pt/TiO2 sensor showed no response to 1 ppm CO. As mentioned above, the CO response of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor was larger than that of the Pt/TiO2 sensor in all the concentration range. Unfortunately, both the sensors did not show a linear relationship between the CO response and the concentration.
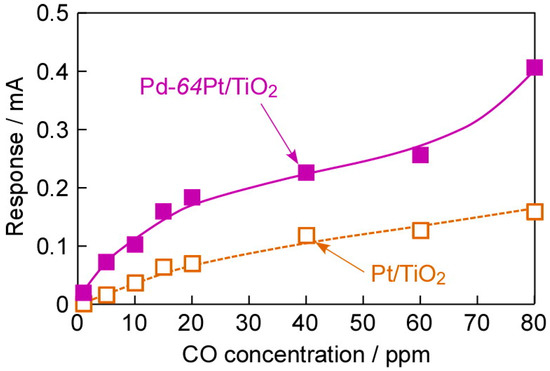
Figure 9.
Concentration dependences of CO responses of Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors, which were annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h in advance, at 100 °C in dry H2 (applied forward bias: +1.0 mV).
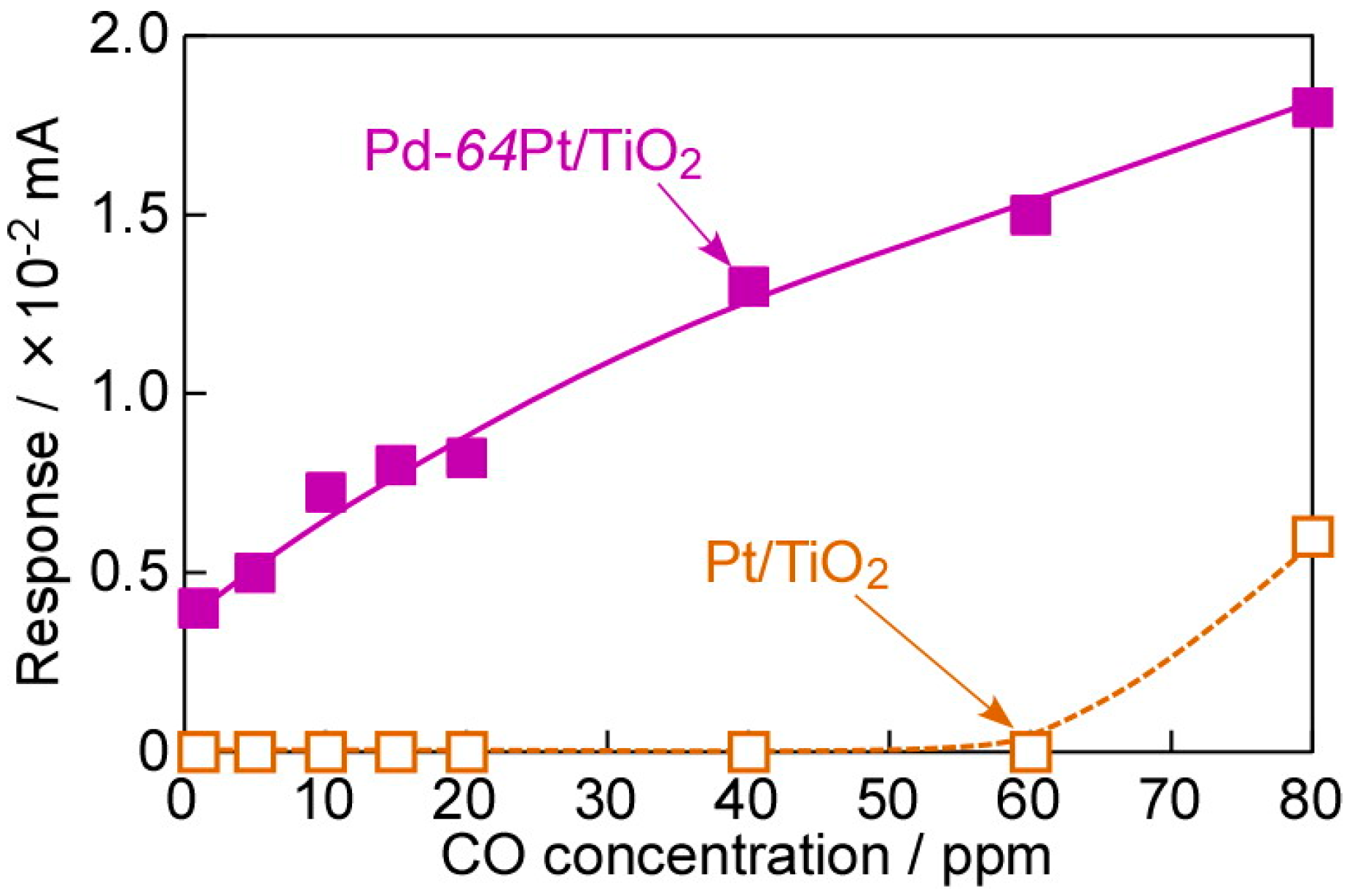
Figure 10 shows operating temperature dependences of responses of the annealed Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors to 80 ppm CO at 100 °C in wet H2 (AH: ca. 12.8 g·m−3), and Figure 11 shows concentration dependences of CO responses of the annealed sensors at 100 °C in wet H2. Both the sensors showed the largest responses to 80 ppm CO at 100 °C in wet H2 (ca. 18 μA (S/N ratio: ca. 2.5) for the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor and ca. 6.0 μA (S/N ratio: ca. 2.0) for the Pt/TiO2 sensor). In addition, the CO response of the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor was much larger than that of the Pt/TiO2 sensor, and the magnitude of both the CO responses in wet H2 was much smaller than that in dry H2 in every operating temperature range. Nevertheless, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor managed to show a clear response even to 1 ppm CO (ca. 4 μA, S/N ratio: ca. 1.5) in wet H2. The addition of moisture into the H2 base gas probably induced the adsorption of water molecules on the electrode surface. Thus, the inhibition of the adsorption of CO by the large amount of the adsorbed water molecules is one of important reasons to decrease the CO responses of both the sensors. However, the magnitude of current of these sensors in wet CO-free H2 (base gas) was quite comparable to that in dry H2, probably because the adsorbed water molecules had little effect on the dissociatively adsorption and dissolution of hydrogen species. This behavior may indicate that the amounts of dissociatively adsorbed and dissolved hydrogen species were sufficiently saturated in the H2 base gas.
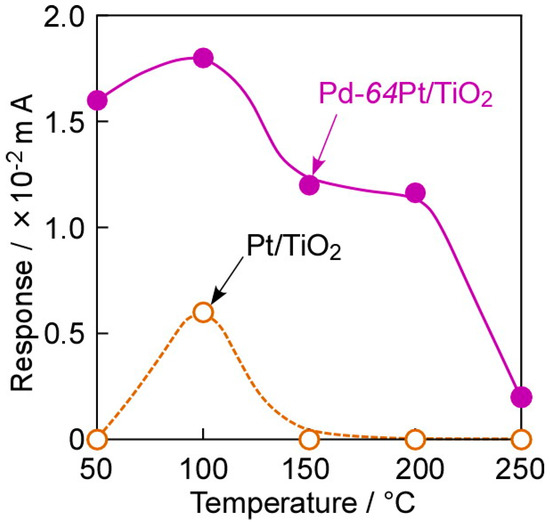
Figure 10.
Operating temperature dependences of responses of Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors, which were annealed at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h in advance, to 80 ppm CO at 100 °C in wet H2 (applied forward bias: +1.0 mV).
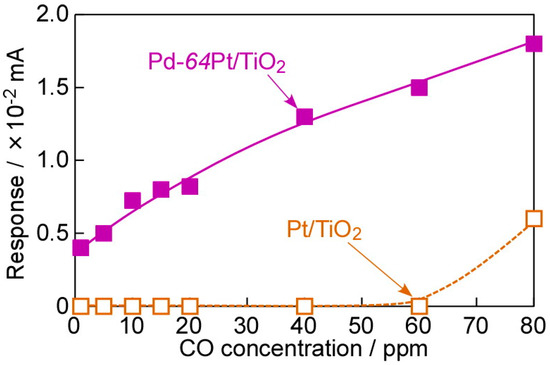
Figure 11.
Concentration dependences of CO responses of Pt/TiO2 and Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensors, which were heat-treated at 400 °C in H2 for 1 h in advance, at 100 °C in wet H2 (applied forward bias: +1.0 mV).
Another possible reason is that the water gas shift reaction (CO + H2O CO2 + H2) [33], which proceeds on the electrode surface, decreases the effective concentration of CO on the electrode surface. The clarification of these adsorption and/or reaction mechanism of CO on the electrode surface is indispensable in enhancing these CO-sensing properties in future.
4. Conclusions
CO-sensing properties of M/TiO2 sensors (M: Pd, Pt, and Pd-nPt) in H2 were investigated in this study. The I–V characteristics of all the M/TiO2 sensors were nonlinear in air and N2, as a typical diode device, and they all showed large H2 responses under the same atmospheres. On the other hand, only the Pd/TiO2 sensor showed no CO response in H2, but the Pt/TiO2 and Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensors responded also to CO in H2, after they were annealed under H2 atmosphere at 400 °C. Among them, the Pd-64Pt/TiO2 sensor showed the largest CO response at 100 °C in H2. The Schottky barrier of all the sensors was negligibly small in H2, but the mixing of Pt into Pd decreased the amount of dissolved hydrogen species, and increased the amount of dissociatively adsorbed hydrogen on the electrode surface. In addition, the mixing of Pt into Pd also increased the amount of CO adsorbed on the electrode surface and the adsorbed CO species interrupted the adsorption of hydrogen species. The optimal balance between them, which was attained by the compositional control of the Pd-nPt electrode, probably enhanced the CO-sensing properties of the Pd-nPt/TiO2 sensor.
Author Contributions
N.M. performed the experiments; T.H. and Y.S. analyzed the data; all the authors contributed to writing the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pérez, L.C.; Koski, P.; Ihonen, J.; Sousa, J.M.; Mendes, A. Effect of fuel utilization on the carbon monoxide poisoning dynamics of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 258, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Hirao, S.; Yahiro, H. CuO/SnO2–In2O3 sensor for monitoring CO concentration in a reducing atmosphere. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 153, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.M.; Gurlo, A.; Riedel, R.; Hübner, M.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Microporous ceramic coated SnO2 sensors for hydrogen and carbon monoxide sensing in harsh reducing conditions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 149, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, H.; Nakaoka, M.; Hirao, S.; Fujiwara, A.; Yahiro, H. CO sensing property of transition metal oxide-loaded SnO2 in a reducing atmosphere. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2010, 25, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, H.; Nakaoka, M.; Yahiro, H. Effect of supported transition metal on CO sensing performance using SnO2 in reducing atmosphere. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 47–50, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurzinger, O.; Reinhardt, G. CO-sensing properties of doped SnO2 sensors in H2-rich gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 103, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Noda, Z.; Sasaki, K.; Hayashi, K. Development of a polyaniline nanofiber-based carbon monoxide sensor for hydrogen fuel cell application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 13529–13535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal Reddy, C.V.; Dutta, P.K.; Akbar, S.A. Detection of CO in a reducing, hydrous environment using CuBr as electrolyte. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 92, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.T.; Azad, A.-M.; Swartz, S.L.; Rao, R.R.; Dutta, P.K. Carbon monoxide sensor for PEM fuel cell systems. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 87, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.K.; Rao, R.R.; Swartz, S.L.; Holt, C.T. Sensing of carbon monoxide gas in reducing environments. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 84, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijolat, C.; Tournier, G.; Viricelle, P. CO detection in H2 reducing atmosphere with mini fuel cell. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, R.; Brosha, E.L.; Garzon, F.H. A low temperature sensor for the detection of carbon monoxide in hydrogen. Solid State Ion. 2004, 175, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, K.W.; Chu, A.C.; Fuller, K.C. Detection of low level carbon monoxide in hydrogen-rich gas streams. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 95, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijolat, C.; Tournier, G.; Viricelle, P. Detection of CO in H2-rich gases with a samarium doped ceria (SDC) sensor for fuel cell applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, A.; Hibino, T.; Sano, M. Solid oxide fuel cells that enable the detection of CO in reformed gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 86, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Kuwano, N.; Hyodo, T.; Egashira, M. High H2 sensing performance of anodically oxidized TiO2 film contacted with Pd. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 83, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T.; Hyodo, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Egashira, M. H2 sensing properties and mechanism of anodically oxidized TiO2 film contacted with Pd Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 93, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, H.; Hyodo, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Egashira, M. Hydrogen-sensing properties of anodically oxidized TiO2 film sensors: Effects of preparation and pretreatment conditions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 93, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, T.; Nakaoka, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Egashira, M. Diode-type H2 sensors using anodized TiO2 films-structural and compositional controls of noble metal sensing electrodes. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, G.; Yamashita, T.; Matsuo, K.; Hyodo, T.; Shimizu, Y. Effects of polytetrafluoroethylene or polyimide coating on H2 sensing properties of anodized TiO2 films equipped with Pd–Pt electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, T.; Yamashita, T.; Shimizu, Y. Effects of surface modification of noble-metal sensing electrodes with Au on the hydrogen-sensing properties of diode-type gas sensors employing an anodized titania film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, T.; Ohoka, J.; Shimizu, Y. Design of anodically oxidized Nb2O5 films as a diode-type H2 sensing material. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 117, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, T.; Shibata, H.; Shimizu, Y. H2 sensing properties of diode-type gas sensors fabricated with Ti- and/or Nb-based materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 142, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh-Miller, N.E.; Marzari, N. Surface energies, work functions, and surface relaxations of low index metallic surfaces from first-principles. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 235407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, P.; Umezawa, N.; Abe, H.; Ye, J.; Shiraishi, K.; Ohta, A.; Miyazaki, S. Bonding and electron energy-level alignment at metal/TiO2 interfaces: A density functional theory study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 5549–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, S.; Maekawa, T.; Tamaki, J.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. Dispersion and electric interaction of palladium particles supported on tin oxide. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1991, 1991, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirner, U.K.; Schierbaum, K.D.; Göpel, W. Interface-reactions of Pt/TiO2: Comparative electrical, XPS-, and AES-depth profile investigations. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1991, 341, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, T.; Zinchuk, V.; Shryshevskyy, V.; Urban, I.; Hilt, O. Electrical transport in passivated Pt/TiO2/Ti Schottky diodes. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.A.; Kandasamy, K.; Tong, X.Q. Platinum and palladium-hydrogen. In Hydrogen in Metal Systems II; Lewis, F.A., Aladjem, A., Eds.; Scitec Publications Ltd.: Uetikon, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 207–501. ISBN 3-908450-55-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, J.; Nie, A.; Forrey, R.C.; Tachibana, A.; Cheng, H. On the sequential hydrogen dissociative chemisorption on small platinum clusters: A density functional theory study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12773–12778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, R.M.; Hoefelmeyer, J.D.; Grass, M.; Song, H.; Niesz, K.; Yang, P.; Somorjai, G.A. Adsorption and co-adsorption of ethylene and carbon monoxide on silica-supported monodisperse Pt nanoparticles: Volumetric adsorption and infrared spectroscopy studies. Langmuir 2008, 24, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, H. Hydrogenation of carbon monoxide with solid catalysts. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1978, 27, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinon, O.; Rachedi, K.; Diehl, F.; Avenier, P.; Schuurman, Y. Kinetics and mechanism of the water-gas shift reaction over platinum supported catalysts. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).