Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters for Potential Chemosensor Applications
Abstract
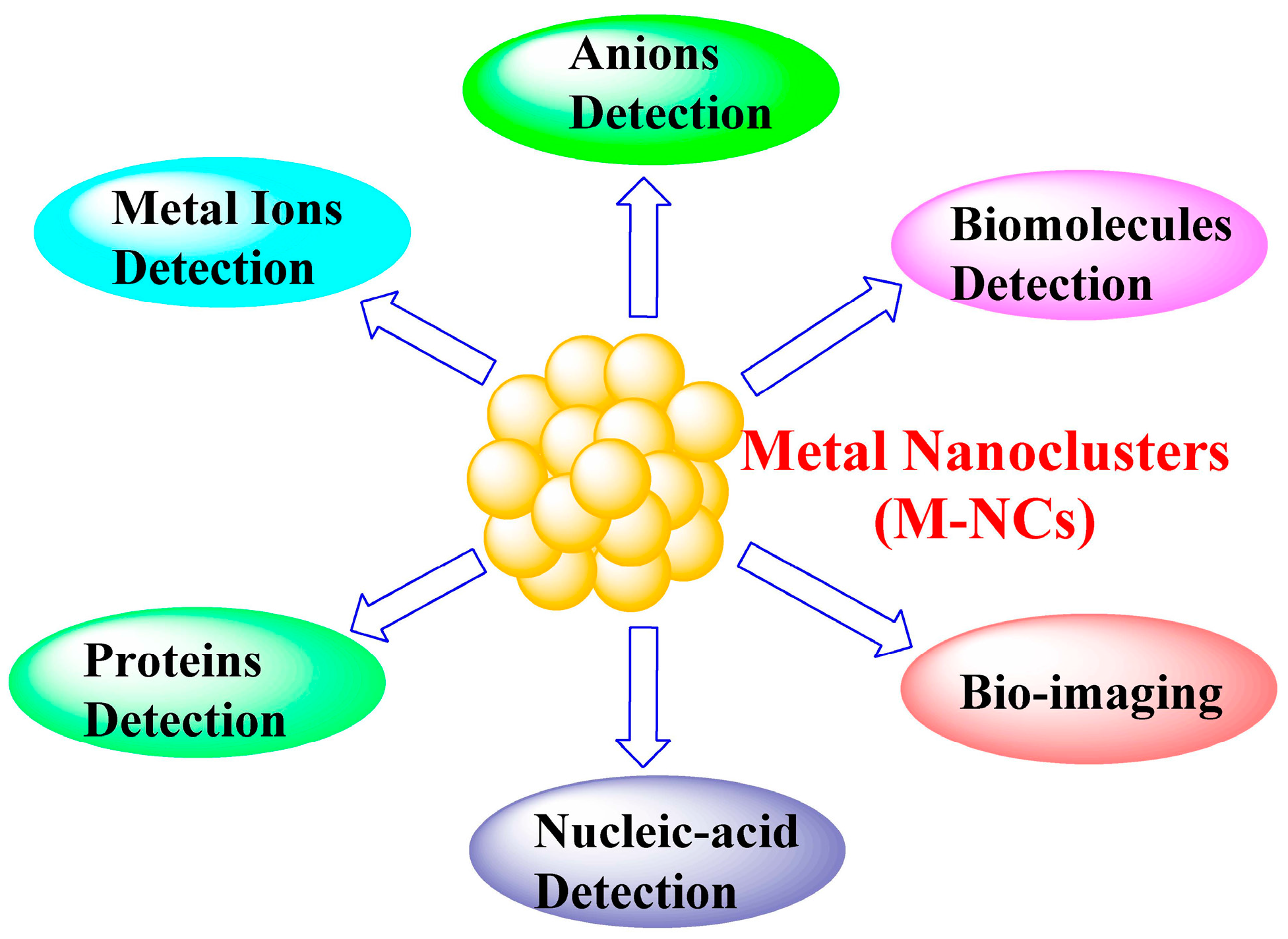
1. Introduction
2. Optimization Requirements
- Ligands: Suitable ligands must be selected to achieve enhanced fluorescence and tunable emissive colors, such as blue, green, red, orange, and yellow. Thiols, dendrimers, polymers, DNA-oligonucleotides, peptides, and proteins have been commonly used as ligands. Among them, ligands consisting of thiol groups have displayed outstanding results [34]. For example, Huang and Goswami’s reports [35,36] on Au NCs described the use of thiolated ligands for capping. In both studies, diverse emissive colors were observed by optimizing the ligand or its concentrations. Several NC specimens are presented in this paper with various ligands, which have been already explored in many sensor studies. Thus, selection of suitable ligands and optimization of their concentration play vital roles in the luminescent property of NCs.
- Quantum Yield (Φ): The quantum yield (Φ) of the probe should be effectively tuned by optimizing the reaction conditions, functionalizing the appropriate ligands at affordable concentration, and selecting solvents for assay methods to maximize the application of luminescent M-NCs in analyte detection. For example, Aldeek and Deng et al. presented Au NCs with polyethylene glycol with zwitterion and L-arginine functionalization and revealed diverse quantum yields of 14% and 65% [37,38]. Prof. Mattoussi and Chowdhury’s research [39,40] on Ag NCs with diverse stabilizers demonstrated the enhancement of quantum yields. Lysozyme- and glutathione-stabilized Cu NCs have also been reported to have diverse quantum yields of 18% and 43%, respectively, for LED applications [41,42]. Fernández et al. presented lipoic-acid-capped Pt NCs with 47% quantum yields, which was due to the presence of a suitable stabilizer [43], thus confirming that an appropriate stabilizer affects the quantum yield or brightness of NCs.
- Stability of NCs: Stability is an important property that must be optimized prior to performing assay studies. Researchers verify the stability of their probes by using suitable stabilizers, solvents, temperatures, and pH levels [44]. Taylor et al. theoretically proposed thermodynamic stability [45] for design of M-NC-based probes for sensory and bio-imaging studies.
- Toxicity: The biological applications of M-NCs are attributed to toxicity optimization [46]. The probes must initially undergo MTT assay to authenticate their biocompatibility and intracellular permeability. Therefore, researchers have focused on developing less toxic M-NCs for drug delivery and imaging applications.
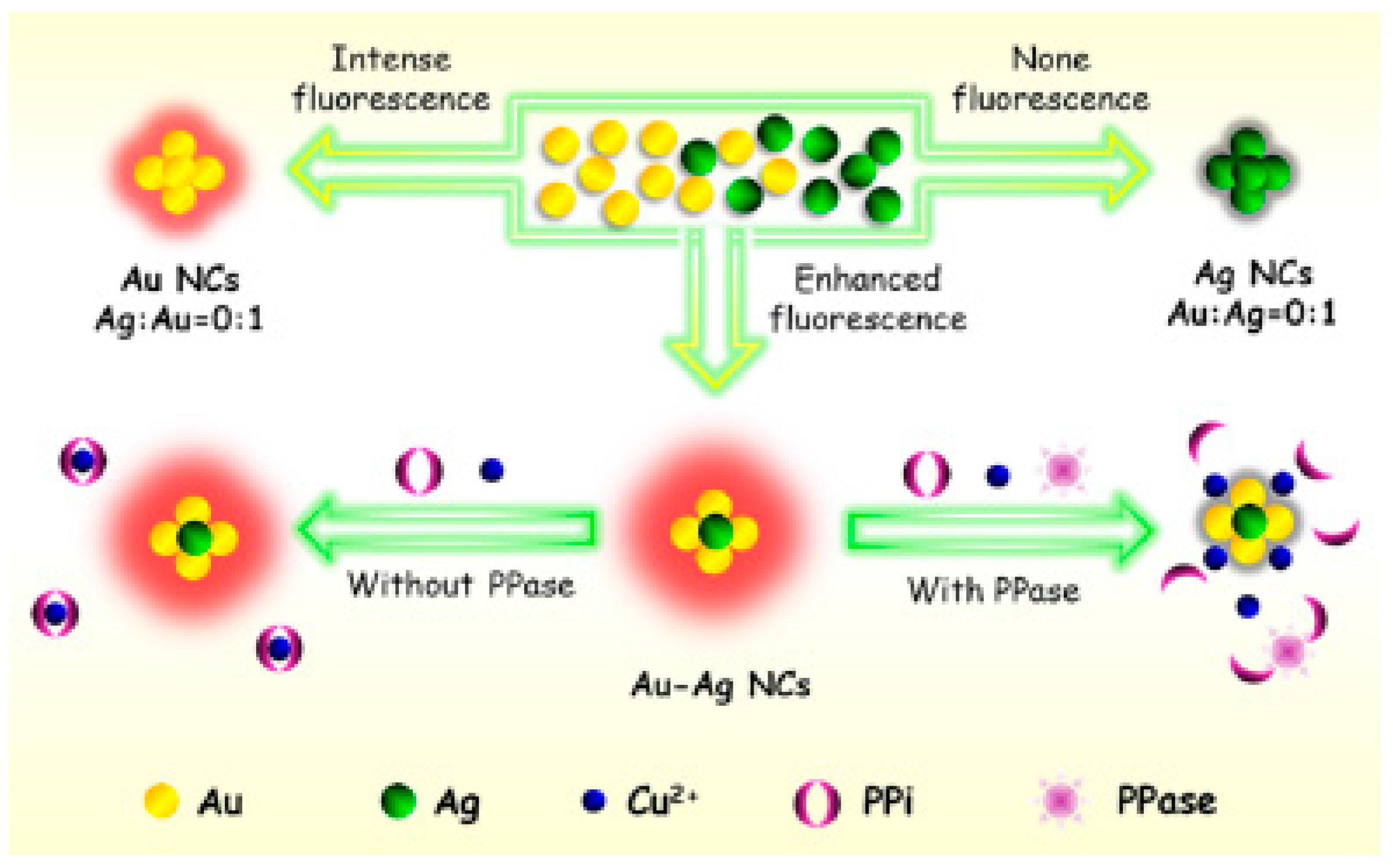
3. AuNCs in Sensor Studies
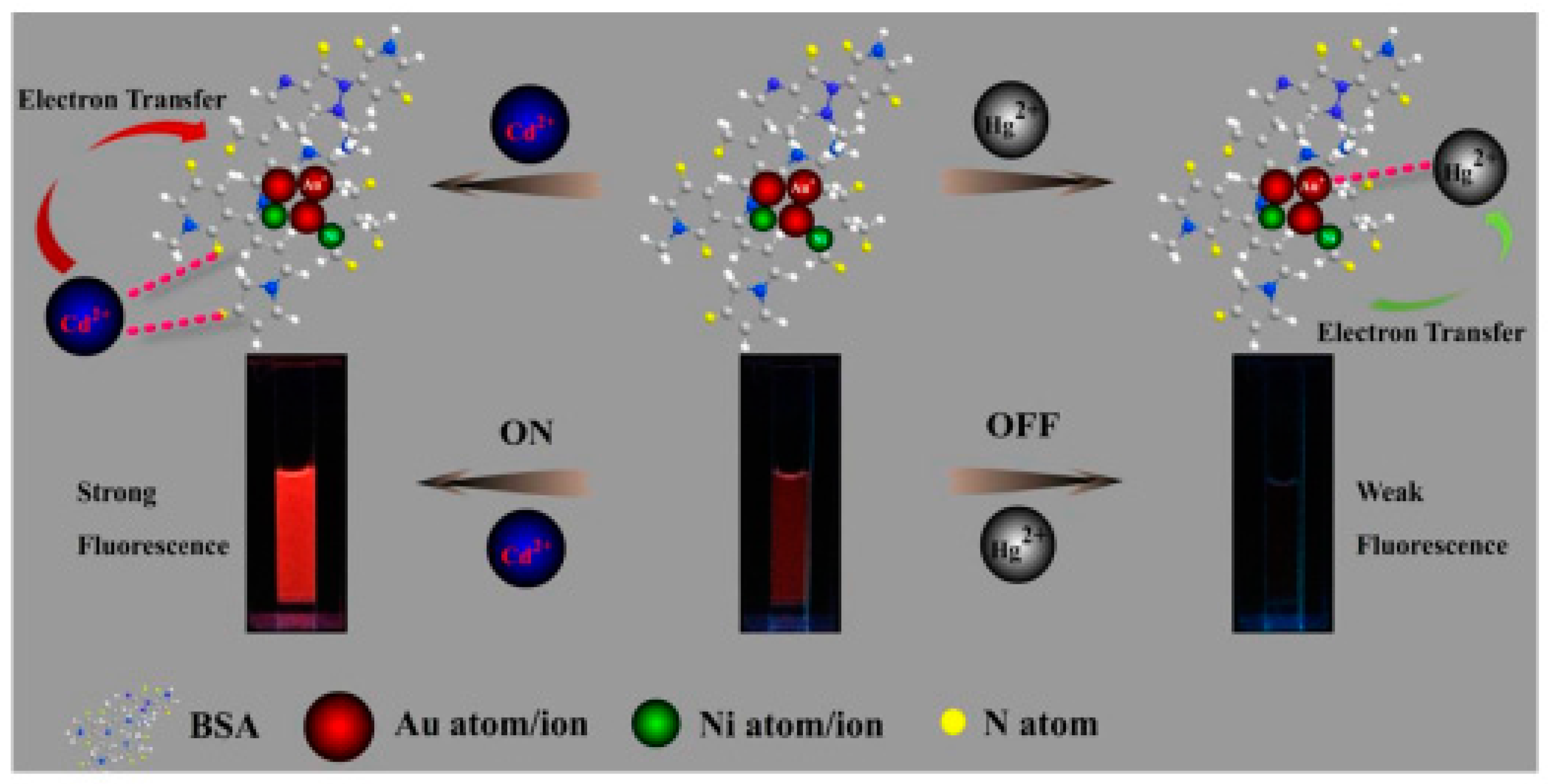
4. Ag NCs as Sensory Probes
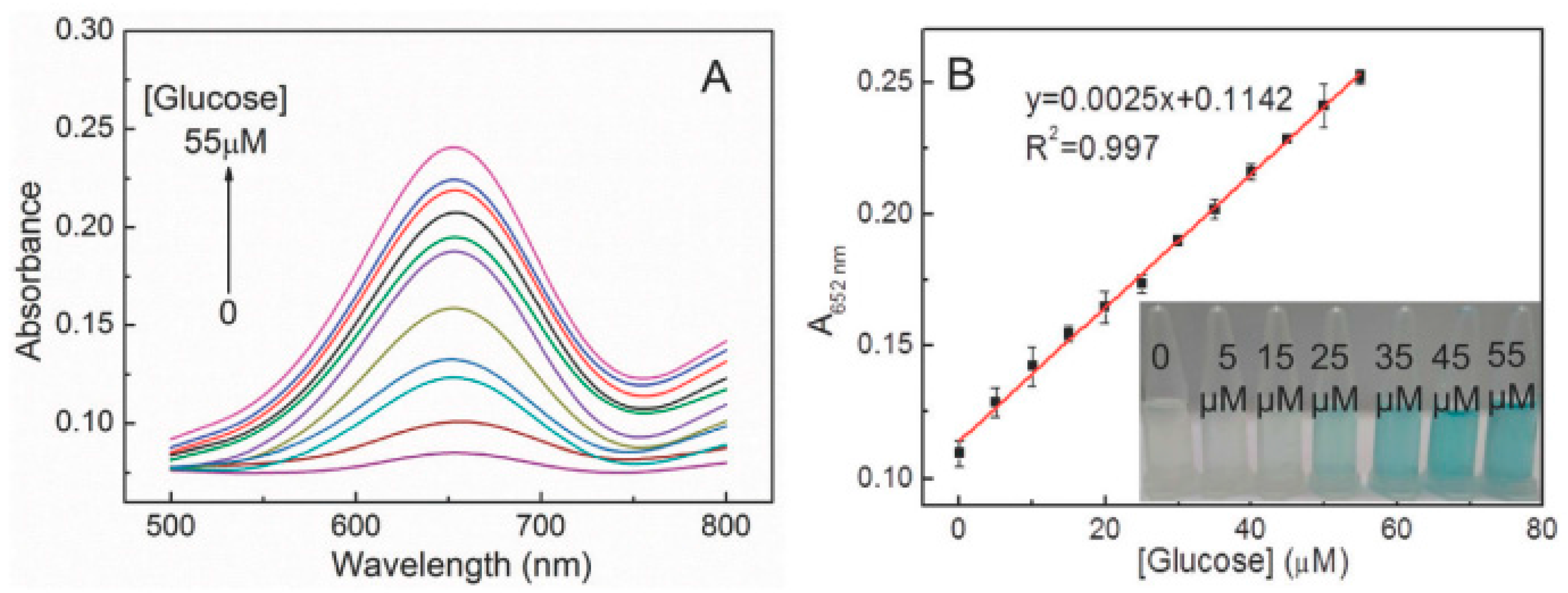
5. Sensor Applications of Cu NCs
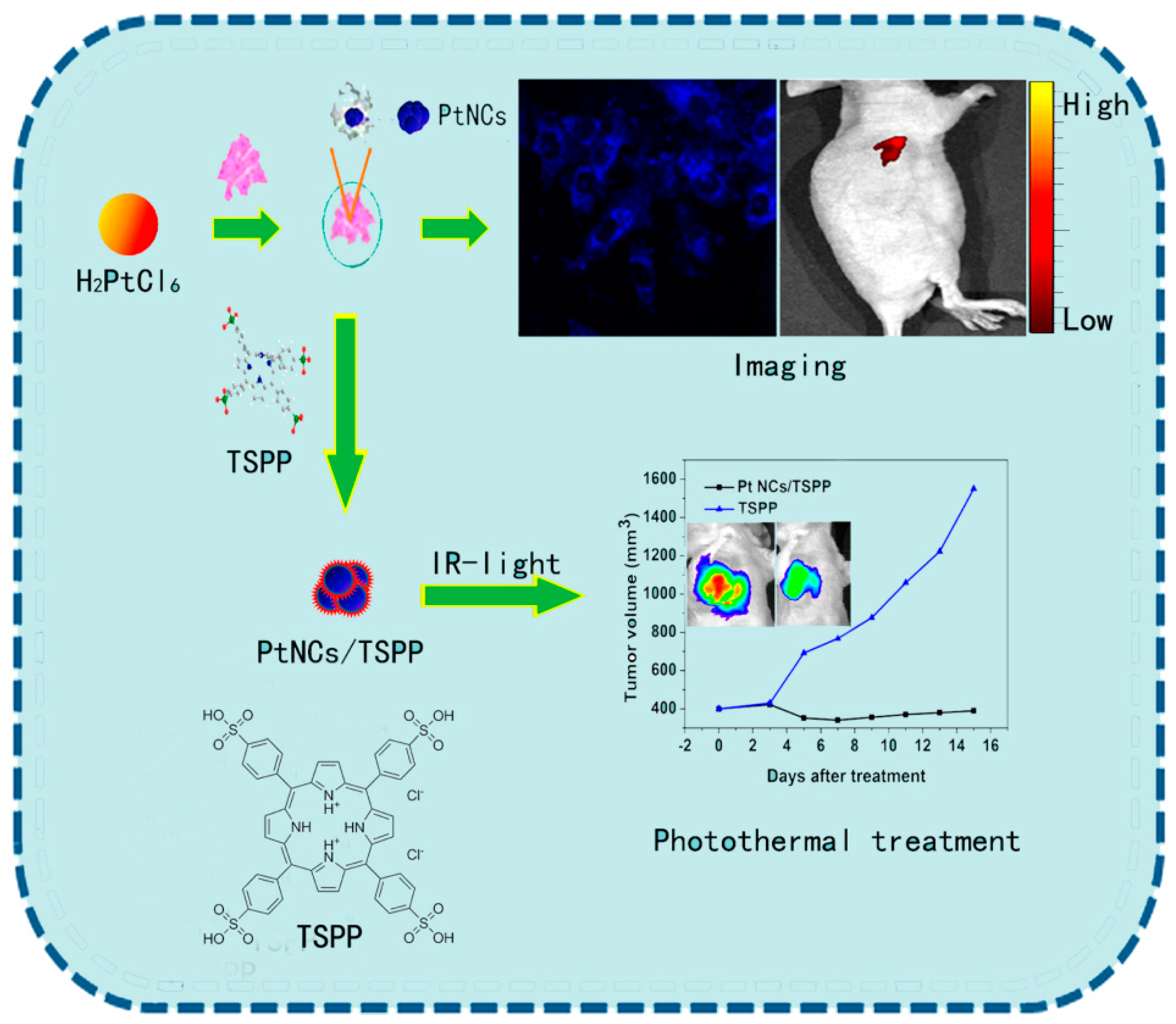
6. Pt NCs in Sensory and Bio-Imaging Studies
7. Other Metal Nanoclusters as Sensors
8. Bi-Metallic Nanoclusters in Sensors and Bio-Imaging
9. Advantages and Limitations
- In contrast to plasmonic nanoparticles, M-NCs have an ultra-small size with ultimate fluorescence. Hence, they can be used as fluorescent “Off” or “On” probes in a variety of analytical studies.
- Contrary to fluorescent quantum dots, the optical properties of M-NCs can be enhanced by controlling the surface functionalization, which also leads to NCs with diverse emissive colors.
- M-NCs can be synthesized via a one-pot synthesis compared with the complicated synthesis of organic sensory probes.
- Luminescent M-NCs exhibit less toxicity and good biocompatibility compared with fluorescent quantum dots and organic fluorophores. Hence, they can be used in biological applications, such as imaging and drug delivery studies.
- The emissive characteristics of M-NCs are limited to the ligands functionalized on the surface and to stability with respect to temperature, time, and pH values.
- The optical properties are also limited to overall uniform cluster particle sizes. Similar functional groups on the NC surface with diverse particle sizes may also possibly emit different colors. Therefore, maintenance of the experimental procedure is highly essential to obtain reproducible results.
10. Conclusions and Perspectives
- The relation between structure and emission properties of many reported M-NCs remains insufficient. Hence, fundamental investigations on the structural properties of M-NCs need to be focused along with fluorescence studies.
- Optimization of precursor/template concentration for stabilizing the M-NCs has been uncertain in many cases and must be clarified. Notably, in many reports, similar probes with various template or metal ion concentrations have been reported for diverse analyte detection. However, clear fundamental evidence to support their diverse optical properties has not been provided. This is an essential point to be addressed in future reports.
- Mechanistic evidence for a few M-NC-based sensory reports remain inadequate. Hence, essential theoretical interrogations should be supplemented in the future.
- NC-based based sensory applications by using optical devices have led them towards promising nanodevice-based commercial utilities.
- Pt NCs based sensory research remains insufficient, with emitted fluorescence between 700 nm to 950 nm by utilization of diverse templates. Hence, much effort is needed to develop such probes for enhanced biological utilities.
- The development of multifunctional M-NCs is helpful in biomedical diagnosis and treatment. Hence, considerable efforts are required to develop promising candidates.
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakraborty, I.; Pradeep, T. Atomically Precise Clusters of Noble Metals: Emerging Link between Atoms and Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8208–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.-R.; Goswami, N.; Yang, H.-H.; Xie, J. Functionalization of metal nanoclusters for biomedical applications. Analyst 2016, 141, 3126–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-T.; Yoshio, S. Luminescent metal nanoclusters: Controlled synthesis and functional applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 014205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zhou, T.; Yao, Q.; Hao, C.; Chen, X. Metal Nanoclusters: Applications in Environmental Monitoring and Cancer Therapy. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 2015, 33, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Gonzalez, B.; Monguzzi, A.; Caputo, M.; Villa, C.; Prato, M.; Santambrogio, C.; Torrente, Y.; Meinardi, F.; Brovelli, S. Metal Nanoclusters with Synergistically Engineered Optical and Buffering Activity of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species by Compositional and Supramolecular Design. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Li, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Metal nanoclusters: Novel probes for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8636–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcoxon, J.P.; Abrams, B.L. Synthesis, structure and properties of metal nanoclusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1162–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Wen, X.; Toh, Y.-R.; Ma, X.; Tang, J. Fluorescent Metallic Nanoclusters: Electron Dynamics, Structure, and Applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, E. Metal nanoclusters: New fluorescent probes for sensors and bioimaging. Nano Today 2014, 9, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, W. Sub-nanometre sized metal clusters: From synthetic challenges to the unique property discoveries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3594–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Yan, N. Recent advances in the synthesis and catalytic applications of ligand-protected, atomically precise metal nanoclusters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 322, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, J.-J.; Xu, K. Fluorescent metal nanoclusters: From synthesis to applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 58, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, B.; Zhao, G. Highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters stabilized by food proteins: From preparation to application in detection of food contaminants and bioactive nutrients. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gou, H.; Al-Ogaidi, I.; Wu, N. Nanostructured Sensors for Detection of Heavy Metals: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Luo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Xie, J. Luminescent Noble Metal Nanoclusters as an Emerging Optical Probe for Sensor Development. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-W.; Yuan, Z.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters: Recent Advances in Sensing and Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Jin, Y. Fluorescent Au nanoclusters: Recent progress and sensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8000–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, I.; Ras, R.H.A. Fluorescent silver nanoclusters. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Suslick, K.S. Water-Soluble Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, W. Copper nanoclusters: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Rogach, A.L. Synthesis, optical properties and applications of light-emitting copper nanoclusters. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017, 2, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Bhuin, R.G.; Bhat, S.; Pradeep, T. Blue emitting undecaplatinum clusters. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8561–8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.-I.; Aoki, K.; Muratsugu, A.; Ishitobi, H.; Jin, T.; Inouye, Y. Synthesis of green-emitting Pt8 nanoclusters for biomedical imaging by pre-equilibrated Pt/PAMAM (G4-OH) and mild reduction. Opt. Mater. Express 2013, 3, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Q. Tunable near-infrared fluorescent gold nanoclusters: Temperature sensor and targeted bioimaging. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 5412–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, C.; Yan, X.-P. Fabrication of folate bioconjugated near-infrared fluorescent silver nanoclusters for targeted in vitro and in vivo bioimaging. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14341–14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, H.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, C. Rapid Sonochemical Synthesis of Luminescent and Paramagnetic Copper Nanoclusters for Bimodal Bioimaging. ChemNanoMat 2015, 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.-I.; Miyazaki, J.; Tiwari, D.K.; Jin, T.; Inouye, Y. Fluorescent Platinum Nanoclusters: Synthesis, Purification, Characterization, and Application to Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.-J. Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters: Promising Fluorescent Probes for Sensors and Bioimaging. J. Anal. Test. 2017, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Dörlich, R.M.; Trouillet, V.; Bruns, M.; Ulrich Nienhaus, G. Ultrasmall fluorescent silver nanoclusters: Protein adsorption and its effects on cellular responses. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, J.; Wang, E. Cu Nanoclusters with Aggregation Induced Emission Enhancement. Small 2013, 9, 3873–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ishitobi, H.; Inouye, Y. Formation of fluorescent platinum nanoclusters using hyper-branched polyethylenimine and their conjugation to antibodies for bio-imaging. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 9709–9716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Dong, S.; Nienhaus, G.U. Ultra-small fluorescent metal nanoclusters: Synthesis and biological applications. Nano Today 2011, 6, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Dou, X.; Zheng, K.; Xie, J. Recent Advances in the Synthesis and Applications of Ultrasmall Bimetallic Nanoclusters. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercis, M.-B.; Francisco, H.; Cecilia, N. On the stability of noble-metal nanoclusters protected with thiolate ligands. Europhys. Lett. 2017, 119, 56002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-C.; Yang, Z.; Lee, K.-H.; Chang, H.-T. Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Gold Nanoparticles for Sensing Mercury(II). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6824–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Lin, F.; Liu, Y.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Highly Luminescent Thiolated Gold Nanoclusters Impregnated in Nanogel. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldeek, F.; Muhammed, M.A.H.; Palui, G.; Zhan, N.; Mattoussi, H. Growth of Highly Fluorescent Polyethylene Glycol- and Zwitterion-Functionalized Gold Nanoclusters. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.-H.; Shi, X.-Q.; Wang, F.-F.; Peng, H.-P.; Liu, A.-L.; Xia, X.-H.; Chen, W. Fabrication of Water-Soluble, Green-Emitting Gold Nanoclusters with a 65% Photoluminescence Quantum Yield via Host–Guest Recognition. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M.A.H.; Aldeek, F.; Palui, G.; Trapiella-Alfonso, L.; Mattoussi, H. Growth of In Situ Functionalized Luminescent Silver Nanoclusters by Direct Reduction and Size Focusing. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8950–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaz, S.; Poddar, S.; Bayen, S.P.; Mondal, M.K.; Roy, D.; Mondal, S.K.; Chowdhury, P.; Saha, S.K. Tenfold enhancement of fluorescence quantum yield of water soluble silver nanoclusters for nano-molar level glucose sensing and precise determination of blood glucose level. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Sahoo, A.K.; Ghosh, S.S.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Blue-Emitting Copper Nanoclusters Synthesized in the Presence of Lysozyme as Candidates for Cell Labeling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3822–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Susha, A.S.; Wang, W.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Chen, R.; Zhong, H.; Rogach, A.L. All-Copper Nanocluster Based Down-Conversion White Light-Emitting Devices. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1600182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenifer García, F.; Laura, T.-A.; José, M.C.-F.; Rosario, P.; Alfredo, S.-M. Aqueous synthesis of near-infrared highly fluorescent platinum nanoclusters. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 215601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R. Atomically precise metal nanoclusters: Stable sizes and optical properties. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.G.; Mpourmpakis, G. Thermodynamic stability of ligand-protected metal nanoclusters. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Luo, Z.; Yuan, X.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Engineering gold-based radiosensitizers for cancer radiotherapy. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
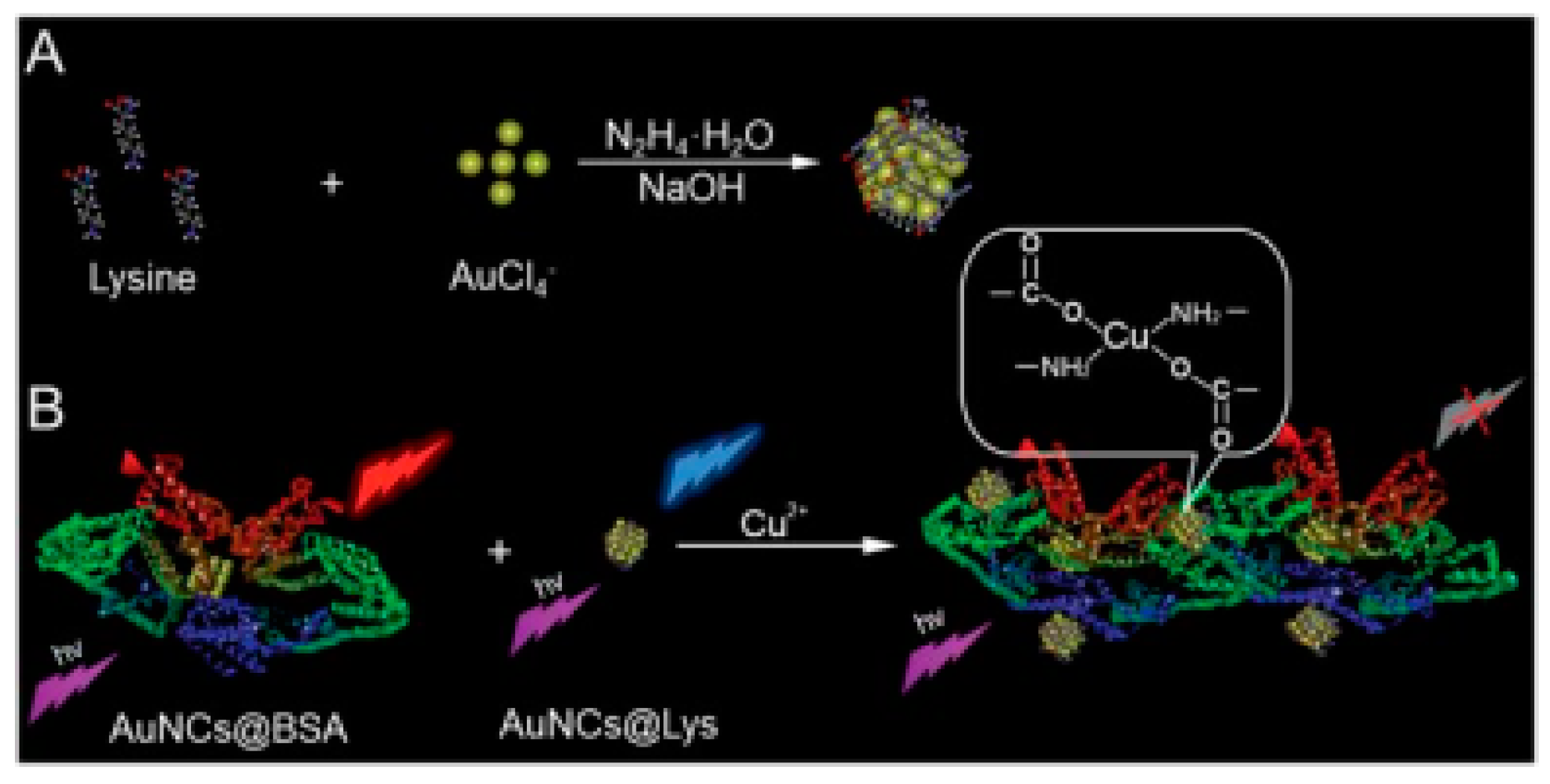
- Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Dou, Y.; Zhu, S. Synthesis of highly fluorescent lysine-stabilized Au nanoclusters for sensitive and selective detection of Cu2+ ion. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 6748–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.-H.; Zhang, L.-N.; He, S.-B.; Liu, A.-L.; Li, G.-W.; Lin, X.-H.; Xia, X.-H.; Chen, W. Methionine-directed fabrication of gold nanoclusters with yellow fluorescent emission for Cu2+ sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. On−off−on gold nanocluster-based near infrared fluorescent probe for recognition of Cu(II) and vitamin C. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shang, L.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hiltunen, J.K.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J. Synthesis of fluorescent α-chymotrypsin A-functionalized gold nanoclusters and their application to blot-based technology for Hg2+ detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 31536–31543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamizhan, A.; Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Real-time selective visual monitoring of Hg2+ detection at ppt level: An approach to lighting electrospun nanofibers using gold nanoclusters. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-J.; Ling, J.; Han, C.-L.; Chen, L.-Q.; Cao, Q.-E.; Ding, Z.-T. Chicken Egg White-stabilized Au Nanoclusters for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Hg(II). Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Wen, A.; Zeng, X.; Feng, R.; Nie, H.; Jiang, X.; Long, Y. A dual-functional spectroscopic probe for simultaneous monitoring Cu2+ and Hg2+ ions by two different sensing nature based on novel fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 253, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, T.; Huang, L.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, T.; Wei, S. Red-emitting Au7 nanoclusters with fluorescence sensitivity to Fe2+ ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4448–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y. 11-Mercaptoundecanoic acid directed one-pot synthesis of water-soluble fluorescent gold nanoclusters and their use as probes for sensitive and selective detection of Cr3+ and Cr6+. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, A.; Basu, K.; Roy, S.; Banerjee, A. Blue Emitting Gold Cluster formation from Gold Nanorods: Selective and Sensitive Detection of Iron(III) ions in Aqueous Medium. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
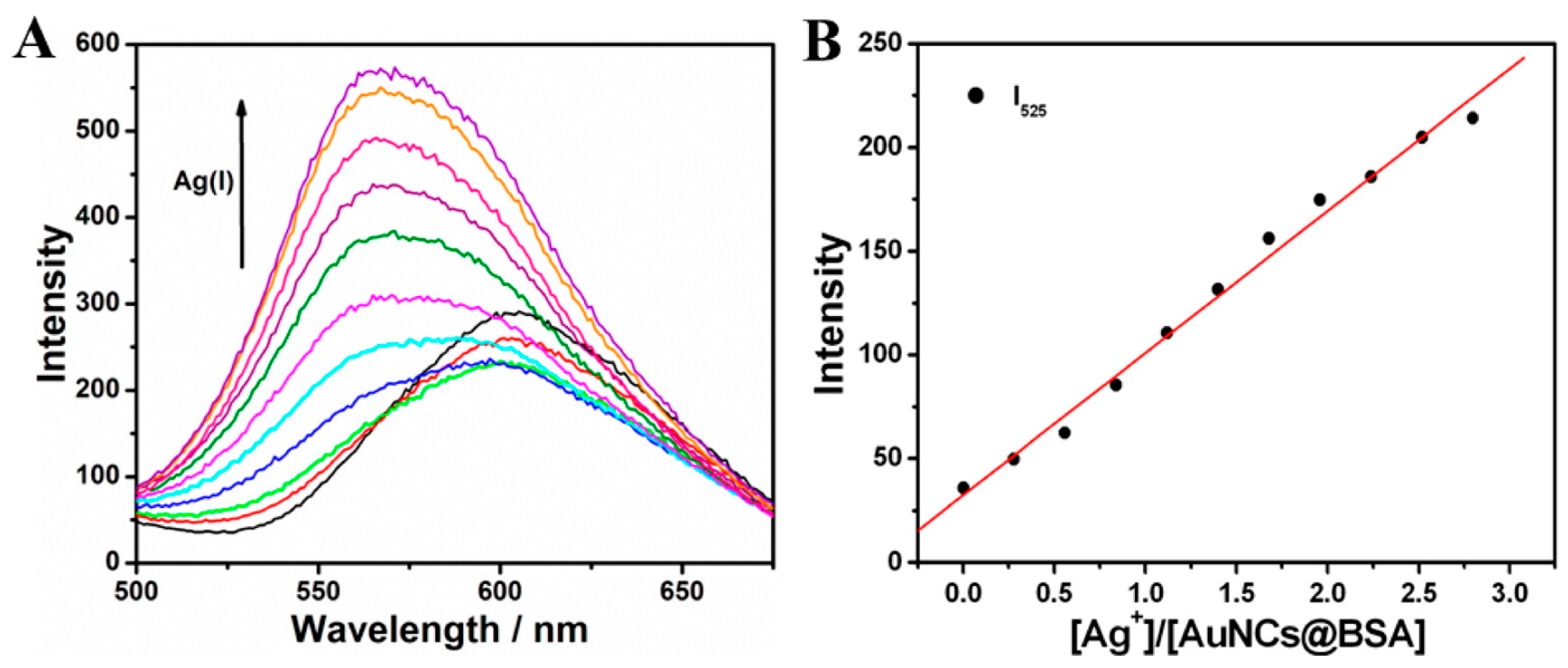
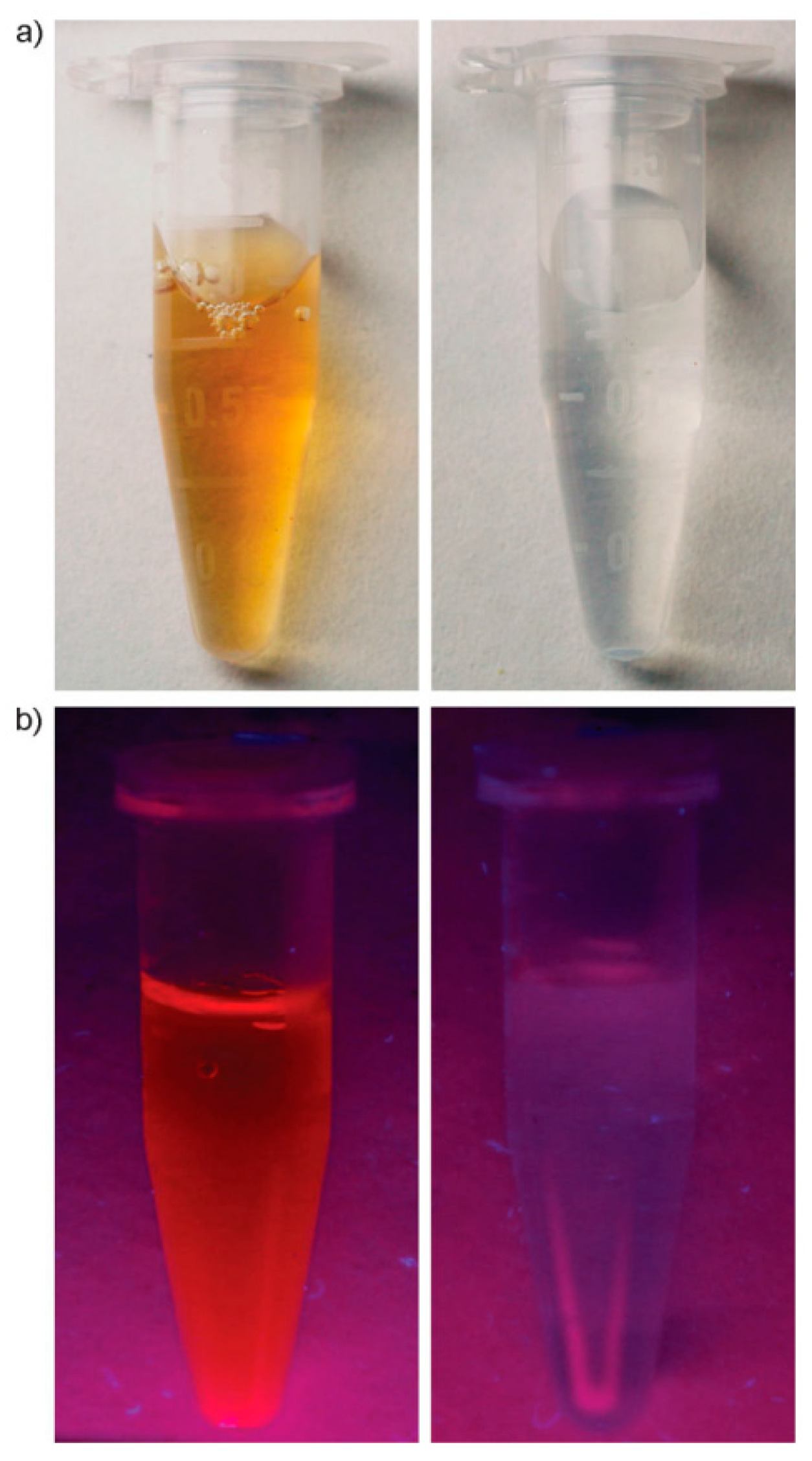
- Li, H.-W.; Yue, Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Li, D.; Wu, Y. Fluorescence-Enhanced Sensing Mechanism of BSA-Protected Small Gold-Nanoclusters to Silver(I) Ions in Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 16159–16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Cheng, X.; Huo, L.; Lu, L. Gold-Nanocluster-Based Fluorescent Sensors for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Cyanide in Water. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Highly selective and sensitive nanoprobes for cyanide based on gold nanoclusters with red fluorescence emission. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12666–12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaeifard, Z.; Hemmateenejad, B.; Shamsipur, M. Efficient On–Off Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe for Cyanide Ion Based on Perturbation of the Interaction between Gold Nanoclusters and a Copper(II)-Phthalocyanine Complex. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15177–15186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopu, C.L.; Shanti Krishna, A.; Sreenivasan, K. Fluorimetric detection of hypochlorite using albumin stabilized gold nanoclusters. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 209, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.-L.; Liu, J.-M.; Wang, X.-X.; Lin, L.-P.; Jiao, L.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Zhang, L.-H.; Jiang, S.-L. A promising gold nanocluster fluorescent sensor for the highly sensitive and selective detection of S2−. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 188, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
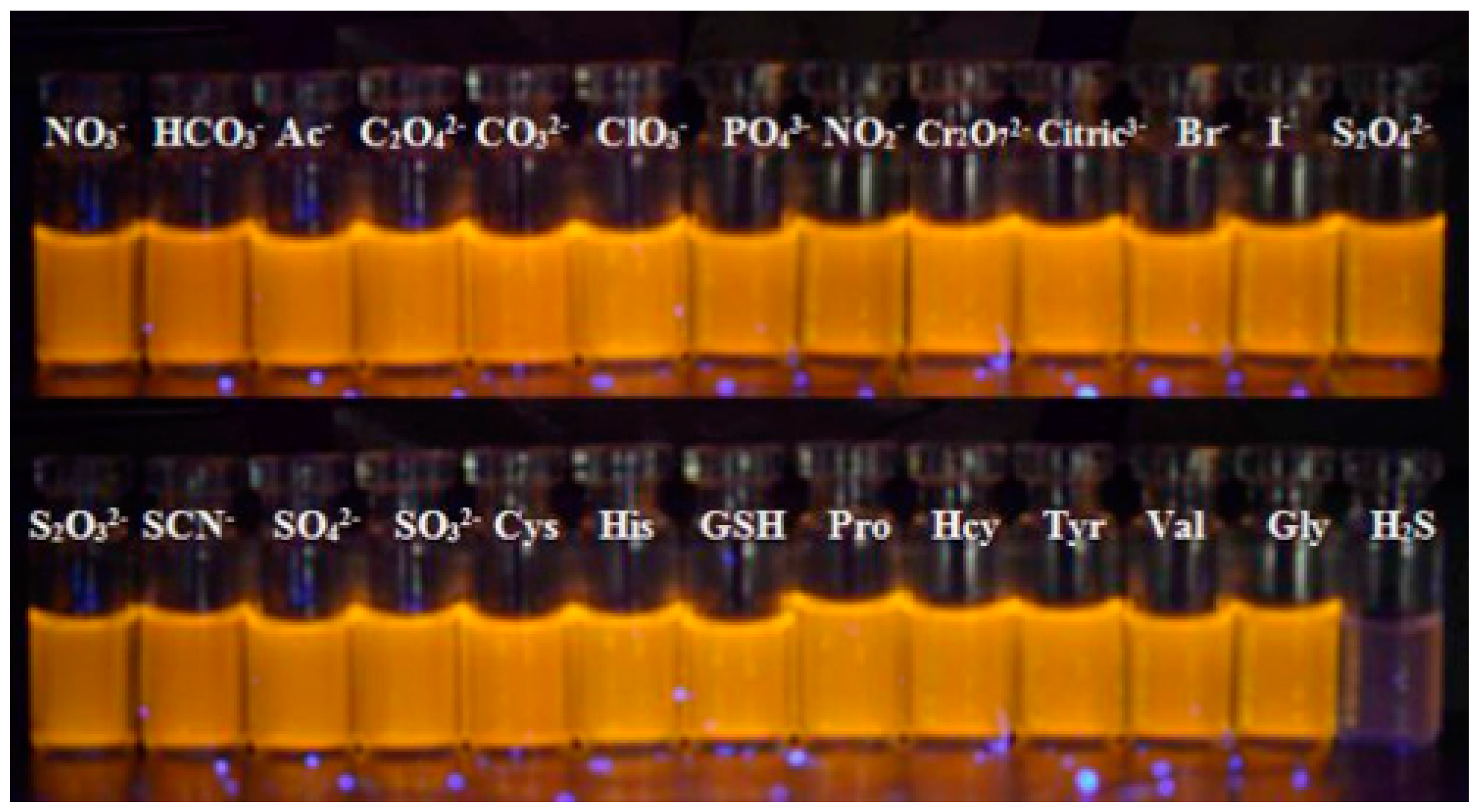
- Liu, H.; Yang, G.; Abdel-Halim, E.S.; Zhu, J.-J. Highly selective and ultrasensitive detection of nitrite based on fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Talanta 2013, 104, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-M.; Cui, M.-L.; Jiang, S.-L.; Wang, X.-X.; Lin, L.-P.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, L.-H.; Zheng, Z.-Y. BSA-protected gold nanoclusters as fluorescent sensor for selective and sensitive detection of pyrophosphate. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3942–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Synthesis of functionalized fluorescent gold nanoclusters for acid phosphatase sensing. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16372–16380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Niu, Q.; Gao, P.; Zhang, G.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Gold nanoclusters as fluorescent sensors for selective and sensitive hydrogen sulfide detection. Talanta 2017, 171, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Baker, G.A. Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes. Analyst 2013, 138, 7299–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, S.; Ankireddy, S.R.; Viswanath, B.; Kim, J.; Yun, K. Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters for Selective Detection of Dopamine in Cerebrospinal fluid. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Dong, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Horseradish Peroxidase Functionalized Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters for Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, S.; Song, G. Ni2+-modified gold nanoclusters for fluorescence turn-on detection of histidine in biological fluids. Analyst 2012, 137, 4005–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Ni, P.; Li, Z. Label-free turn-on fluorescent detection of melamine based on the anti-quenching ability of Hg2+ to gold nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Liang, R.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, J.-D. Green synthesis of peptide-templated gold nanoclusters as novel fluorescence probes for detecting protein kinase activity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10006–10009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Qian, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters based sensor for the detection of quercetin. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, P.; Wu, F. Highly selective and sensitive detection of heparin based on competition-modulated assembly and disassembly of fluorescent gold nanoclusters. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
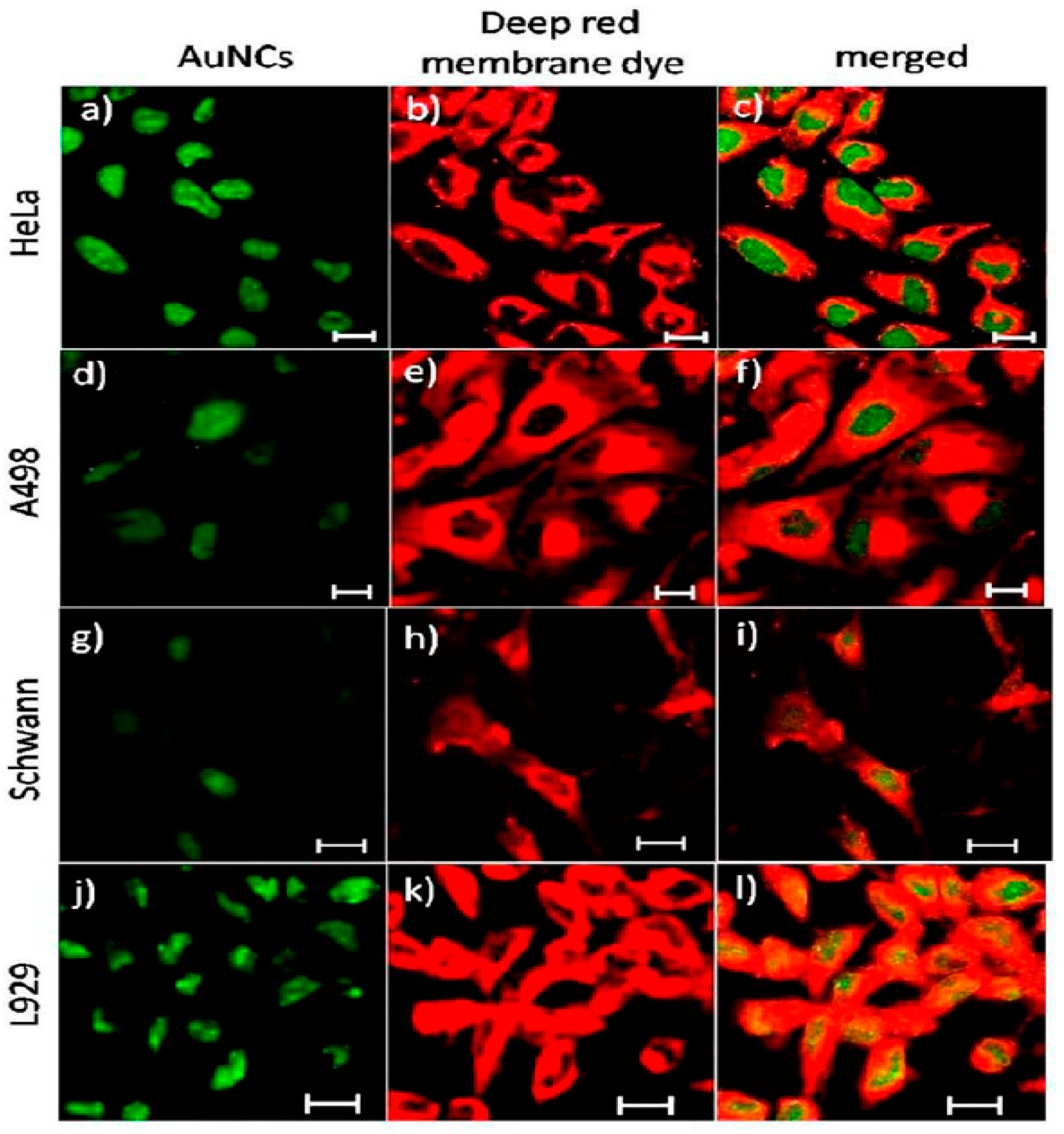
- Shang, L.; Nienhaus, G.U. Gold nanoclusters as novel optical probes for in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging. Biophys. Rev. 2012, 4, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, V.; Shukla, A.; Sivakumar, S.; Verma, S. Purine-Stabilized Green Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters for Cell Nuclei Imaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.-T.; Yan, X.-P. Fabrication of Transferrin Functionalized Gold Nanoclusters/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Turn-On Near-Infrared Fluorescent Bioimaging of Cancer Cells and Small Animals. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, A.K.; Chaturbedi, A.; Subramaniam, K.; Verma, S. Imaging C. elegans with thiolated tryptophan-based NIR fluorescent gold nanoclusters. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cao, Y.; Sui, D.; Guan, W.; Lu, C.; Xie, J. Ultrastable BSA-capped gold nanoclusters with a polymer-like shielding layer against reactive oxygen species in living cells. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 9614–9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Banerjee, S.; Gart, E.V.; Nagaraja, A.T.; McShane, M.J. Gold Nanocluster Containing Polymeric Microcapsules for Intracellular Ratiometric Fluorescence Biosensing. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhou, J.; Tian, Y. Single Probe for Imaging and Biosensing of pH, Cu2+ Ions, and pH/Cu2+ in Live Cells with Ratiometric Fluorescence Signals. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5333–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.-H.; Wu, G.-W.; Zou, Z.-Q.; Peng, H.-P.; Liu, A.-L.; Lin, X.-H.; Xia, X.-H.; Chen, W. pH-Sensitive gold nanoclusters: Preparation and analytical applications for urea, urease, and urease inhibitor detection. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7847–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Shanmugam, C.; Tseng, W.-B.; Hiseh, M.-M.; Tseng, W.-L. A gold nanocluster-based fluorescent probe for simultaneous pH and temperature sensing and its application to cellular imaging and logic gates. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11210–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Saleh, S.M.; Aly, S.M. Fluorescent gold nanoclusters as pH sensors for the pH 5 to 9 range and for imaging of blood cell pH values. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3309–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Anand, U.; Mukherjee, S. Luminescent Silver Nanoclusters Acting as a Label-Free Photoswitch in Metal Ion Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3188–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Dong, S. Silver nanocluster-based fluorescent sensors for sensitive detection of Cu(ii). J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4636–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Cai, N.; Du, Y.; He, Y.; Yeung, E.S. Sensitive and Selective Detection of Copper Ions with Highly Stable Polyethyleneimine-Protected Silver Nanoclusters. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Liang, S.; Peng, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Long, Y.; Zeng, R. Copper ion detection using novel silver nanoclusters stabilized with amido black 10B. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3239–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Qi, W.; Wang, H. Silver Nanoclusters with Specific Ion Recognition Modulated by Ligand Passivation toward Fluorimetric and Colorimetric Copper Analysis and Biological Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, B.; Banerjee, A. Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters and HgII Sensing. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4364–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, J.L.; Morishita, K.; Liu, J. DNA stabilized silver nanoclusters for ratiometric and visual detection of Hg2+ and its immobilization in hydrogels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; He, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, F. Highly sensitive label-free fluorescent detection of Hg2+ ions by DNA molecular machine-based Ag nanoclusters. Analyst 2013, 138, 2350–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Hee Lee, H.; Park, H.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, W.J. Fluorescence switch for silver ion detection utilizing dimerization of DNA-Ag nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhu, Q.; Kong, X.-Y.; Meng, L. A sensitive detection of Cr(vi) in wide pH range using polyethyleneimine protected silver nanoclusters. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5684–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, D.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Glutathione capped silver nanoclusters-based fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of Fe3+. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 202, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Jiang, K.; Humphrey, M.G.; Zhang, C. Stable Ag nanoclusters-based nano-sensors: Rapid sonochemical synthesis and detecting Pb2+ in living cells. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 238, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Shangguan, D. Ratiometric fluorescent silver nanoclusters for the determination of mercury and copper ions. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8019–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Rong, M.; Cai, Z.; Yang, C.J.; Chen, X. Sonochemical synthesis of highly fluorescent glutathione-stabilized Ag nanoclusters and S2- sensing. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4103–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; Zhao, M.; Shao, N. Lysozyme-stabilized Ag nanoclusters: Synthesis of different compositions and fluorescent responses to sulfide ions with distinct modes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 66233–66241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shahzad, S.A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, H.; Kam-Wing Lo, K.; Yu, C. Silver nanoclusters capped silica nanoparticles as a ratiometric photoluminescence nanosensor for the selective detection of I− and S2−. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 988, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yuan, Z.; Chang, H.-T.; Lu, F.; Li, Z.; Lu, C. Silver nanoclusters as fluorescent nanosensors for selective and sensitive nitrite detection. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2628–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
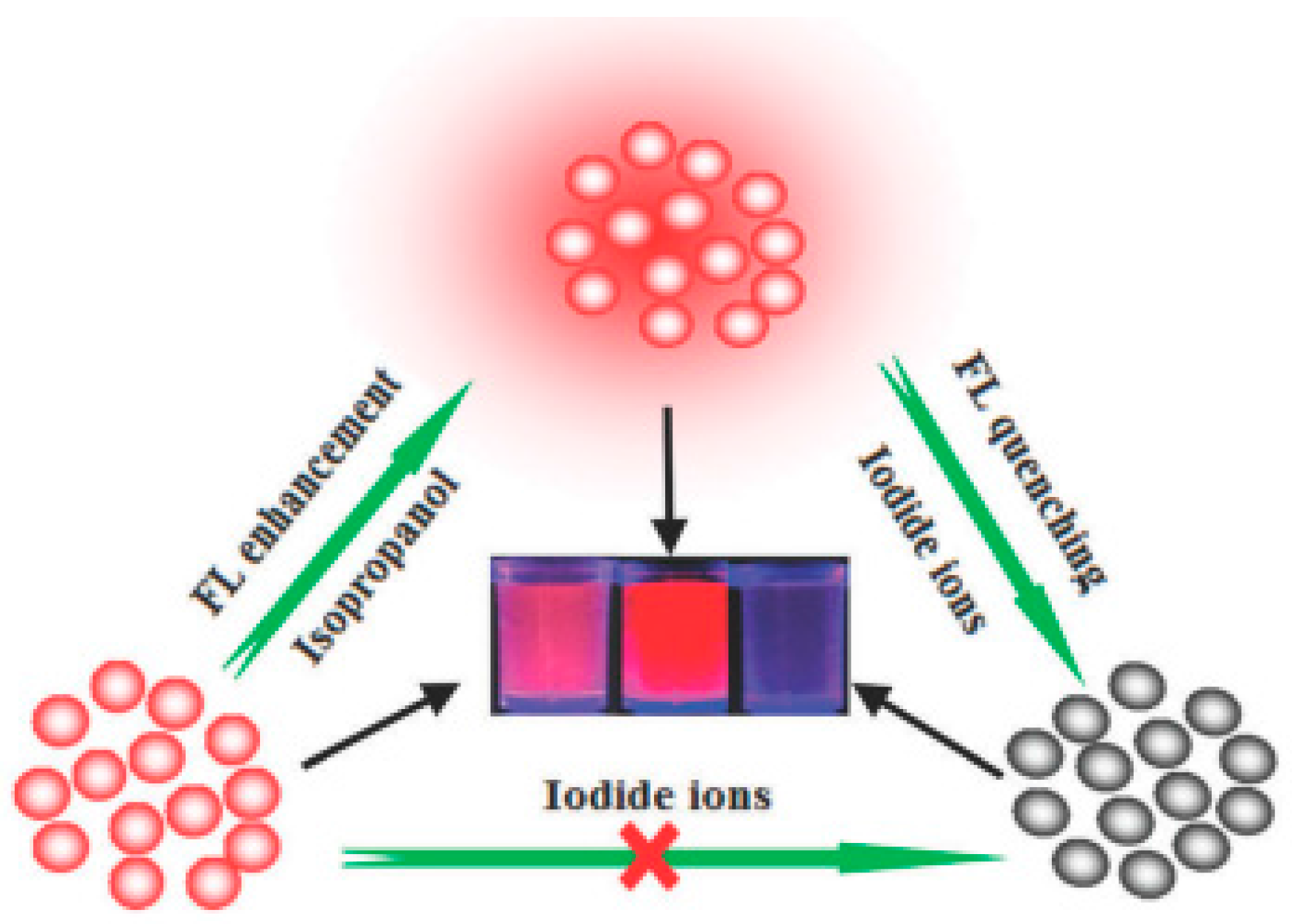
- Feng, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, H. Silver nanoclusters with enhanced fluorescence and specific ion recognition capability triggered by alcohol solvents: A highly selective fluorimetric strategy for detecting iodide ions in urine. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 9466–9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Long, Y.; Zeng, R. Simultaneous determination of iodide and bromide using a novel LSPR fluorescent Ag nanocluster probe. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 240, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bing, T.; Shangguan, D.; Zhao, M.; Shao, N. Ratiometric Fluorescent Biosensing of Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydroxyl Radical in Living Cells with Lysozyme–Silver Nanoclusters: Lysozyme as Stabilizing Ligand and Fluorescence Signal Unit. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10631–10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Su, Y.; Song, H.; Lv, Y. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of ultrasmall fluorescent water-soluble silver nanoclusters and its application in chiral recognition of amino acids. Analyst 2013, 138, 6558–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Pu, F.; Lin, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Modulating DNA-templated silver nanoclusters for fluorescence turn-on detection of thiol compounds. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3487–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Qu, F.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Sensitive and selective detection of biothiols based on target-induced agglomeration of silvernanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
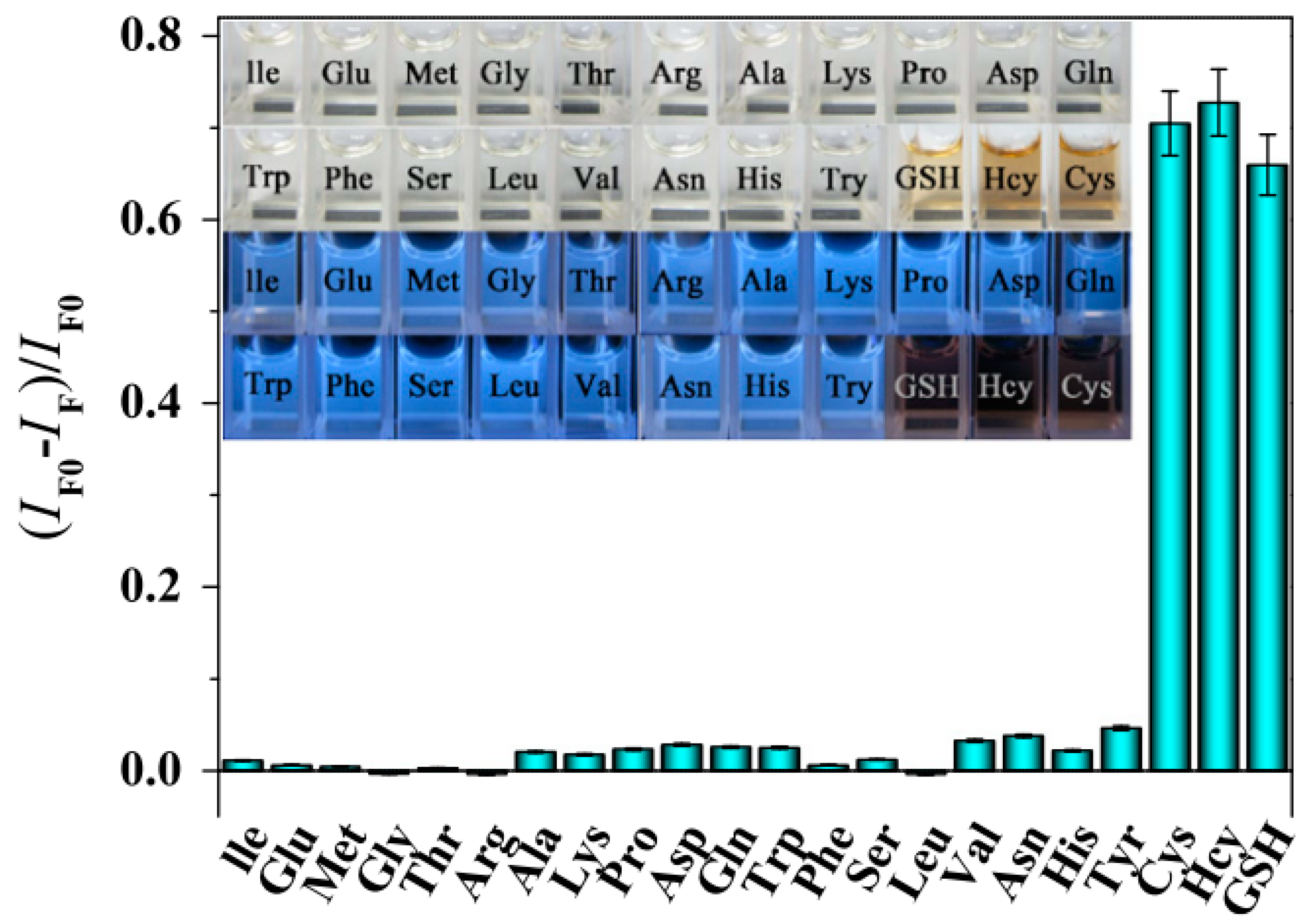
- Yuan, X.; Tay, Y.; Dou, X.; Luo, Z.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Glutathione-Protected Silver Nanoclusters as Cysteine-Selective Fluorometric and Colorimetric Probe. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Song, X.; Gao, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ding, S.; Zou, S.; He, Y. A highly selective sensor of cysteine with tunable sensitivity and detection window based on dual-emission Ag nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.X.; Gao, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.L.; Zhang, W.; Lei, J.L.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. The pH-switchable agglomeration and dispersion behavior of fluorescent Ag nanoclusters and its applications in urea and glucose biosensing. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Jin, L. Silver nanoclusters functionalized by chromotropic acid and layered double hydroxides for the turn-on detection of melamine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 6104–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Song, R.; Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Yu, C.; Lin, Q. Fluorometric “Turn-On” glucose sensing through the in situ generation of silver nanoclusters. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Qu, F.; Zhu, S.; You, J. Fluorescence turn-on strategy based on silver nanoclusters-Cu2+ system for trace detection of quinolones. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 234, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Yeh, H.-C.; Yoo, H.; Werner, J.H.; Martinez, J.S. Silver nanocluster aptamers: In situ generation of intrinsically fluorescent recognition ligands for protein detection. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2294–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.W.; Li, C.M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.Z. Effective detection and cell imaging of prion protein with new prepared targetable yellow-emission silver nanoclusters. Analyst 2013, 138, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yu, Y.; Du, Y.Q.; Wang, W.; Huang, C.Z. DNA-templated silver nanoclusters as label-free fluorescent probes for detection of bleomycin. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 6200–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiruddin, S.K.; Chakraborty, A. One step synthesis of maltose functionalized red fluorescent Ag cluster for specific glycoprotein detection and cellular imaging probe. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43098–43104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Vosch, T. Rapid Detection of MicroRNA by a Silver Nanocluster DNA Probe. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6935–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Zhang, M.; Yin, B.-C.; Ye, B.-C. Attomolar Ultrasensitive MicroRNA Detection by DNA-Scaffolded Silver-Nanocluster Probe Based on Isothermal Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5165–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Target-induced quenching for highly sensitive detection of nucleic acids based on label-free luminescent supersandwich DNA/silver nanoclusters. Analyst 2014, 139, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Tan, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. DNA-Templated Silver Nanoclusters for Multiplexed Fluorescent DNA Detection. Small 2015, 11, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Teng, Y.; Lou, B.; Jia, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, E. G-quadruplex enhanced fluorescence of DNA-silver nanoclusters and their application in bioimaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13224–13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guével, X.; Spies, C.; Daum, N.; Jung, G.; Schneider, M. Highly fluorescent silver nanoclusters stabilized by glutathione: A promising fluorescent label for bioimaging. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Highly Sensitive Fluorescent and Colorimetric pH Sensor Based on Polyethylenimine-Capped Silver Nanoclusters. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, M.; Deng, C.; He, Y.; Ge, Y.; Song, G. Fluorescence Detection of p-Nitrophenol in Water Using Bovine Serum Albumin Capped ag Nanoclusters. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkin, N.; Sharon, E.; Golub, E.; Willner, I. Ag Nanocluster/DNA Hybrids: Functional Modules for the Detection of Nitroaromatic and RDX Explosives. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4918–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y. Copper nanoclusters as a highly sensitive and selective fluorescence sensor for ferric ions in serum and living cells by imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.K.; Ghosh, S.; Priya, A.; Datta, S.; Mukherjee, S. Luminescent Copper Nanoclusters as a Specific Cell-Imaging Probe and a Selective Metal Ion Sensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24657–24664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-C.; Qi, J.-W.; Hu, C.; Zhang, L.; Song, W.; Liang, R.-P.; Qiu, J.-D. Cu nanoclusters-based ratiometric fluorescence probe for ratiometric and visualization detection of copper ions. Anal. Chimica Acta 2015, 895, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y. Copper nanocluster-based fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ in water and food stuff. Talanta 2016, 154, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, C. Facile sonochemical synthesis of pH-responsive copper nanoclusters for selective and sensitive detection of Pb2+ in living cells. Analyst 2015, 140, 5634–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.-Y.; Hou, X.-F.; Xiang, R.-C.; Yu, M.-B.; Li, Y.; Peng, T.-T.; He, G.-H. Detection of Lead Ion Based on Aggregation-induced Emission of Copper Nanoclusters. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, N.; Giri, A.; Bootharaju, M.S.; Xavier, P.L.; Pradeep, T.; Pal, S.K. Copper Quantum Clusters in Protein Matrix: Potential Sensor of Pb2+ Ion. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9676–9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Mao, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. One-step synthesis of orange fluorescent copper nanoclusters for sensitive and selective sensing of Al3+ ions in food samples. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 247, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, S. Photoluminescence light-up detection of zinc ion and imaging in living cells based on the aggregation induced emission enhancement of glutathione-capped copper nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Lu, C. A highly selective fluorescent probe for sulfide ions based on aggregation of Cu nanocluster induced emission enhancement. Analyst 2015, 140, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khonkayan, K.; Sansuk, S.; Srijaranai, S.; Tuntulani, T.; Saiyasombat, C.; Busayaporn, W.; Ngeontae, W. New approach for detection of chromate ion by preconcentration with mixed metal hydroxide coupled with fluorescence sensing of copper nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Ge, Y.; Song, G. A novel fluorescence and naked eye sensor for iodide in urine based on the iodide induced oxidative etching and aggregation of Cu nanoclusters. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 209, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-J.; Liang, R.-P.; Li, Z.-J.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, J.-D. One-step, stabilizer-free and green synthesis of Cu nanoclusters as fluorescent probes for sensitive and selective detection of nitrite ions. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 230, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-L.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. Sensitive and selective detection of nitrite ions with highly fluorescent glutathione-stabilized copper nanoclusters. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5668–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, J.; Wang, C.-W.; Chen, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Control of pH for separated quantitation of nitrite and cyanide ions using photoluminescent copper nanoclusters. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhan, L.; Du, Y.Q.; Leng, F.; Huang, C.Z. A new spectrofluorometric method for pyrophosphate assay based on the fluorescence enhancement of trypsin-stabilized copper clusters. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, T.; Chu, X.; Yu, R. Double-strand DNA-templated synthesis of copper nanoclusters as novel fluorescence probe for label-free detection of biothiols. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Majeed, S.; Xu, G. Copper nanoclusters as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 762, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.J.; Huang, C.Z. Water-soluble luminescent copper nanoclusters reduced and protected by histidine for sensing of guanosine 5’-triphosphate. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3673–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Liu, J.-W.; Duan, L.-Y.; Liu, S.-J.; Jiang, J.-H. Aptamer-based fluorometric determination of ATP by using target-cycling strand displacement amplification and copper nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4183–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shu, S.; Yao, Y.; Song, Q. A fluorescent biosensor of lysozyme-stabilized copper nanoclusters for the selective detection of glucose. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101599–101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghei, Y.-S.; Hosseini, M.; Khoobi, M.; Ganjali, M.R. Novel Fluorometric Assay for Detection of Cysteine as a Reducing Agent and Template in Formation of Copper Nanoclusters. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-G.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Huo, J.-Z.; Zhao, X.-J. Facile synthesis of red emitting 3-aminophenylboronic acid functionalized copper nanoclusters for rapid, selective and highly sensitive detection of glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Qian, Z.; Zhong, M.; Chen, Z.; Ao, H.; Feng, H. Fabrication of Stable and Luminescent Copper Nanocluster-Based AIE Particles and Their Application in β-Galactosidase Activity Assay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32887–32895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-P.; Yin, B.-C.; Ye, B.-C. A novel fluorescence probe of dsDNA-templated copper nanoclusters for quantitative detection of microRNAs. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8633–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghei, Y.-S.; Hosseini, M.; Ganjali, M.R. Fluorescence based turn-on strategy for determination of microRNA-155 using DNA-templated copper nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2671–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, A.-J.; Zhong, S.-X.; Fang, K.-M.; Feng, J.-J. Green synthesis of peptide-templated fluorescent copper nanoclusters for temperature sensing and cellular imaging. Analyst 2014, 139, 6536–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, K.; Gayen, K.; Mitra, T.; Baral, A.; Roy, S.S.; Banerjee, A. Different Color Emissive Copper Nanoclusters for Cancer Cell Imaging. ChemNanoMat 2017, 3, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Leng, F.; Zhan, L.; Chang, Y.; Yang, X.X.; Lan, J.; Huang, C.Z. One-step prepared fluorescent copper nanoclusters for reversible pH-sensing. Analyst 2014, 139, 2990–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, T.; Du, H.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Ma, H. A reversible fluorescent pH-sensing system based on the one-pot synthesis of natural silk fibroin-capped copper nanoclusters. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 3540–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, D. Förster resonance-energy-transfer detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol using copper nanoclusters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4607–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, R.; Xiong, Y.; Cepe, K.; Schneider, J.; Zboril, R.; Lee, C.-S.; Rogach, A.L. Incorporating Copper Nanoclusters into Metal-Organic Frameworks: Confinement-Assisted Emission Enhancement and Application for Trinitrotoluene Detection. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2017, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, H.; Ye, Y.; Tang, C.; Ao, H.; Zhao, M.; Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Qian, Z. Luminescent Nanoswitch Based on Organic-Phase Copper Nanoclusters for Sensitive Detection of Trace Amount of Water in Organic Solvents. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7429–7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Liu, J. pH-Guided Self-Assembly of Copper Nanoclusters with Aggregation-Induced Emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3902–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchesne, P.N.; Zhang, P. Local structure of fluorescent platinum nanoclusters. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4199–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.; Gopalakrishnan, H.; Mandal, S. Surfactant free platinum nanocluster as fluorescent probe for the selective detection of Fe (III) ions in aqueous medium. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 243, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Novel fabrication of highly fluorescent Pt nanoclusters and their applications in hypochlorite assay. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25365–25368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Shang, L.; Shen, Y. Ultrasmall Pt Nanoclusters as Robust Peroxidase Mimics for Colorimetric Detection of Glucose in Human Serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10027–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Li, H.-W.; Wu, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of polyethylenimine-protected high luminescent Pt-nanoclusters and their application to the detection of nitroimidazoles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 958, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Gao, S.; Ge, W.; Li, Q.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. One-step rapid synthesis of fluorescent platinum nanoclusters for cellular imaging and photothermal treatment. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40141–40145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, C.; Ye, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Su, M.; Jiang, H.; Amatore, C.; Selke, M.; Wang, X. In Situ Biosynthesis of Fluorescent Platinum Nanoclusters: Toward Self-Bioimaging-Guided Cancer Theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18163–18169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, N.S.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Cerjan, B.; Everitt, H.O.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Fano Resonant Aluminum Nanoclusters for Plasmonic Colorimetric Sensing. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10628–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, N.F.; El-Kady, M.F.; Galal, A. Palladium nanoclusters-coated polyfuran as a novel sensor for catecholamine neurotransmitters and paracetamol. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 141, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarparast, M.; Noori, A.; Ilkhani, H.; Bathaie, S.Z.; El-Kady, M.F.; Wang, L.J.; Pham, H.; Marsh, K.L.; Kaner, R.B.; Mousavi, M.F. Cadmium nanoclusters in a protein matrix: Synthesis, characterization, and application in targeted drug delivery and cellular imaging. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 3229–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankayala, R.; Gollavelli, G.; Mandal, B.K. Highly fluorescent and biocompatible iridium nanoclusters for cellular imaging. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 24, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-T.; Lan, G.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chang, H.-T. Detection of Copper Ions Through Recovery of the Fluorescence of DNA-Templated Copper/Silver Nanoclusters in the Presence of Mercaptopropionic Acid. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8566–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.-Y.; Lin, L.-P.; Rong, M.-C.; Jiang, Y.-Q.; Chen, X. Silver–Gold Alloy Nanoclusters as a Fluorescence-Enhanced Probe for Aluminum Ion Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9839–9844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Si, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, H. Rapid, Selective, and Ultrasensitive Fluorimetric Analysis of Mercury and Copper Levels in Blood Using Bimetallic Gold-Silver Nanoclusters with “Silver Effect”—Enhanced Red Fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11714–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zheng, J.; Yu, T.; Sang, A.; Du, J.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, D.; Choi, M.M.F. Fast microwave-assisted synthesis of AuAg bimetallic nanoclusters with strong yellow emission and their response to mercury(II) ions. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 221, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, H.; Feng, J.-J.; Wang, A.-J. One-step green synthesis of fluorescent bimetallic Au/Ag nanoclusters for temperature sensing and in vitro detection of Fe3+. Sens. Actuators, B 2016, 223, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liao, S.; Wu, Z.; Yu, R. Bimetallic gold-silver nanocluster fluorescent probes for Cr(iii) and Cr(vi). Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7237–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Xu, S.; Dong, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, H. DNA stabilized Ag-Au alloy nanoclusters and their application as sensing probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 51609–51618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-N.; Guo, Y.-X. One-pot synthesis of dual-emitting BSA-Pt-Au bimetallic nanoclusters for fluorescence ratiometric detection of mercury ions and cysteine. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5787–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Guo, Y.-X.; Ding, S.-N. Fluorometric determination of cadmium(II) and mercury(II) using nanoclusters consisting of a gold-nickel alloy. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Lan, G.-Y.; Chang, H.-T. Use of Fluorescent DNA-Templated Gold/Silver Nanoclusters for the Detection of Sulfide Ions. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9450–9455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yin, Y. Bimetallic nanoclusters with strong red fluorescence for sensitive detection of hypochlorite in tap water. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3781–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lin, Y.; Xu, M.; Gao, Z.; Yang, H.; Tang, D. Facile Synthesis of Enhanced Fluorescent Gold-Silver Bimetallic Nanocluster and Its Application for Highly Sensitive Detection of Inorganic Pyrophosphatase Activity. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8886–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Xing, G.; Wang, T.; Liu, S. A novel fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for iodide determination using DNA-templated gold/silver nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Ling, J.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Yan, J.; Zha, L.; Cai, J. A rapid evaluation of acute hydrogen sulfide poisoning in blood based on DNA-Cu/Ag nanocluster fluorescence probe. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Ding, S.-N.; Jomma Narjh, E.Y. Determination of Thiols by Fluorescence using Au@Ag Nanoclusters as Probes. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, F.; Zhao, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, X. Integrated Logic Gate for Fluorescence Turn-on Detection of Histidine and Cysteine Based on Ag/Au Bimetallic Nanoclusters–Cu2+ Ensemble. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6860–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Huang, P.; Wu, F.-Y. Gold-platinum bimetallic nanoclusters with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and their integrated agarose hydrogel-based sensing platform for the colorimetric analysis of glucose levels in serum. Analyst 2017, 142, 4106–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Baek, S.; Park, H.G. A new s-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-linked method for adenosine detection based on DNA-templated fluorescent Cu/Ag nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Shen, Q.; Nie, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yao, S. A fluorometric assay for acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor detection based on DNA-templated copper/silver nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.-H.; Sheng, Z.-H.; Zhang, P.-F.; Yang, D.-Z.; Liu, S.-H.; Gong, P.; Gao, D.-Y.; Fang, S.-T.; Ma, Y.-F.; Cai, L.-T. Hybrid gold-gadolinium nanoclusters for tumor-targeted NIRF/CT/MRI triple-modal imaging in vivo. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Cationic BSA Templated Au–Ag Bimetallic Nanoclusters As a Theranostic Gene Delivery Vector for HeLa Cancer Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. Cytidine Mediated AuAg Nanoclusters as Bright Fluorescent Probe for Tumor Imaging in vivo. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-C.; Ma, J.-Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Lin, G.-L.; Shih, C.-C.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chang, H.-T. Photoluminescent AuCu bimetallic nanoclusters as pH sensors and catalysts. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3503–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Hou, X.; Xiang, R.; He, G. Synthesis of highly luminescent Cu/Ag bimetal nanoclusters and their application in a temperature sensor. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4028–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, N.; Yao, Q.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters with Aggregation-Induced Emission. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Xiong, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, H.; Jin, S.; Song, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, L.; Pan, C.; Pei, Y.; et al. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Trimetallic Nanoclusters: Structure Elucidation and Properties Investigation. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 17145–17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

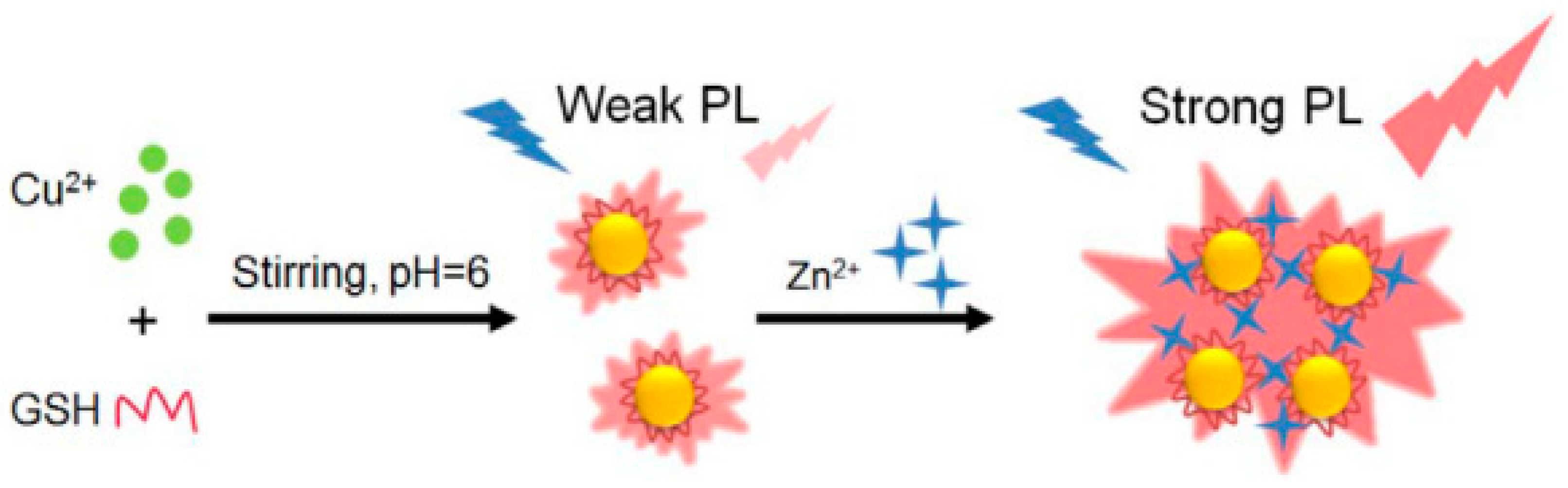
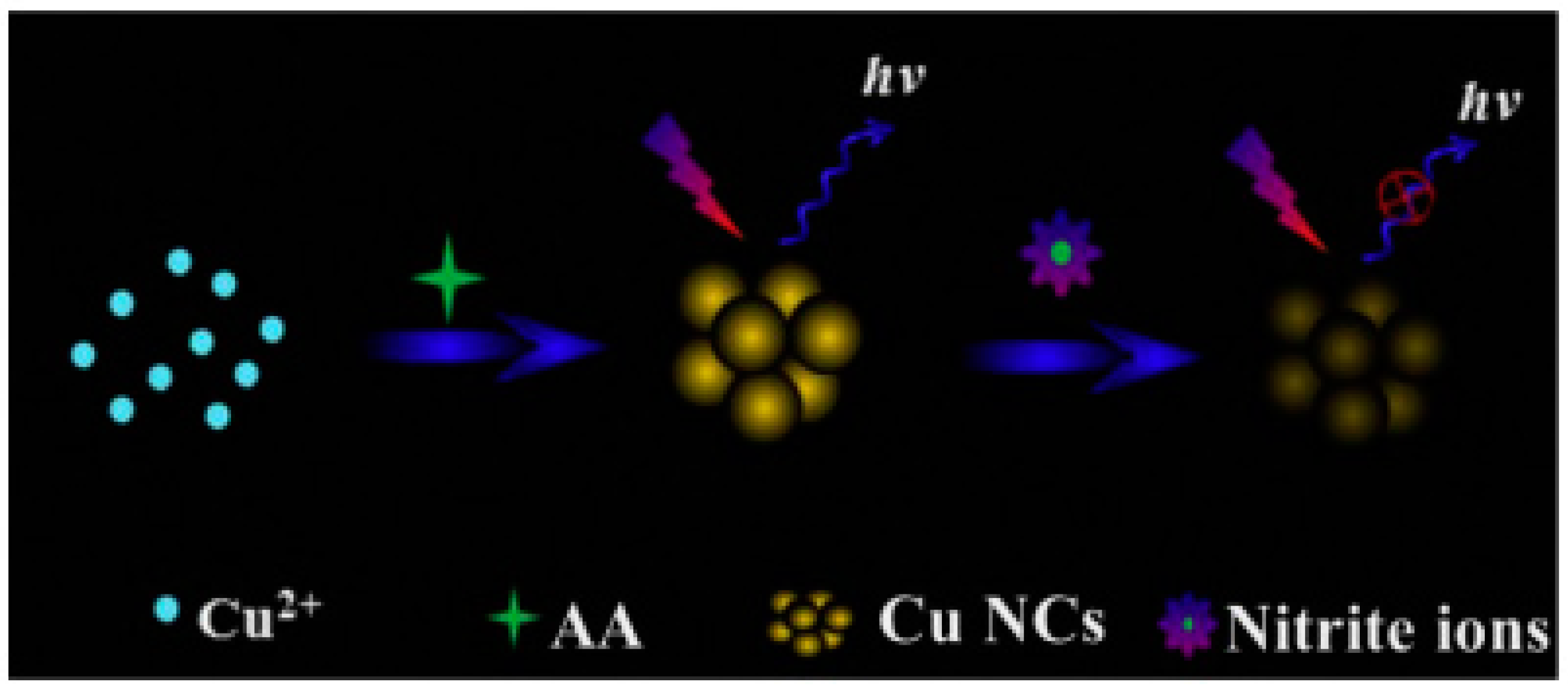
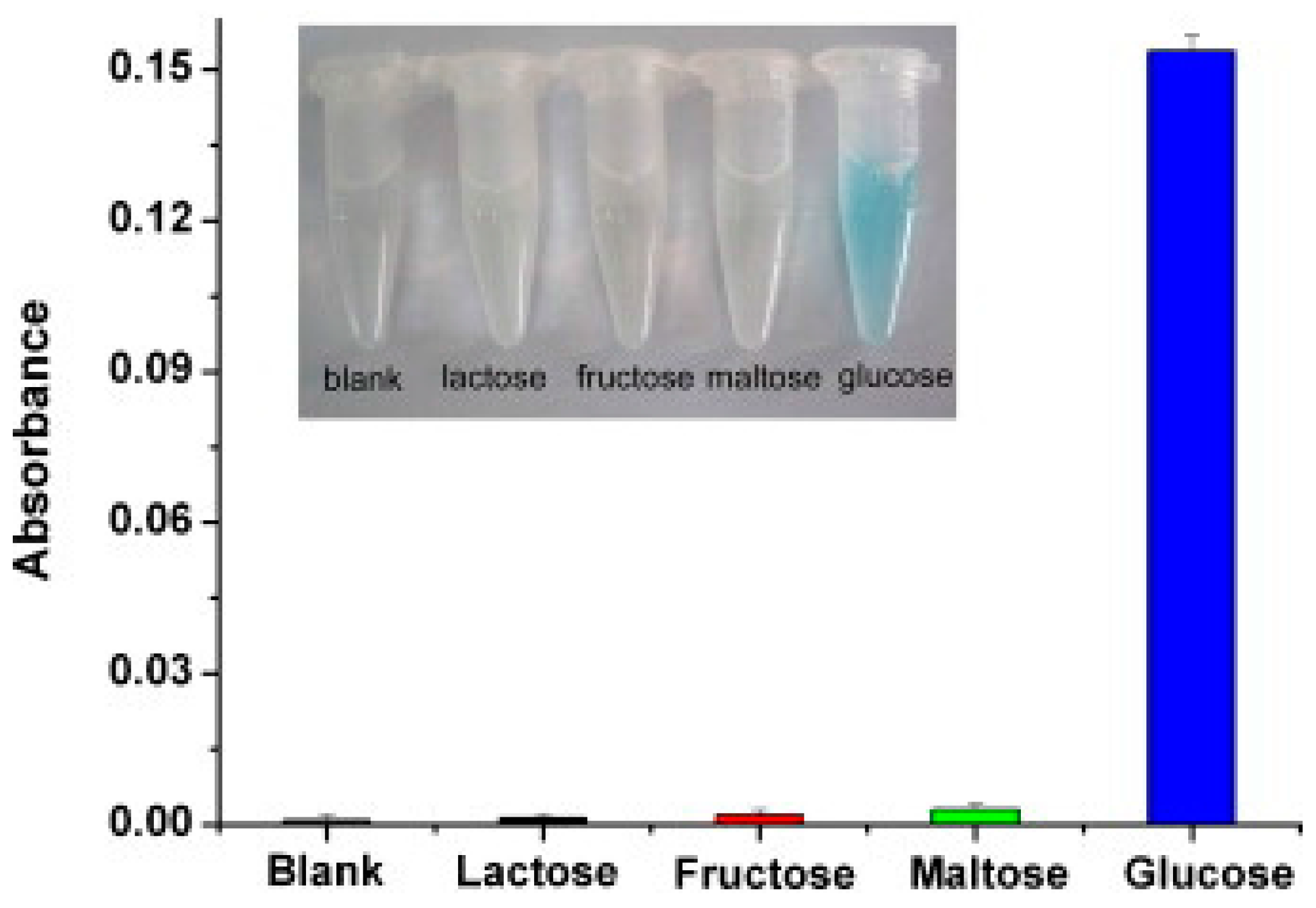
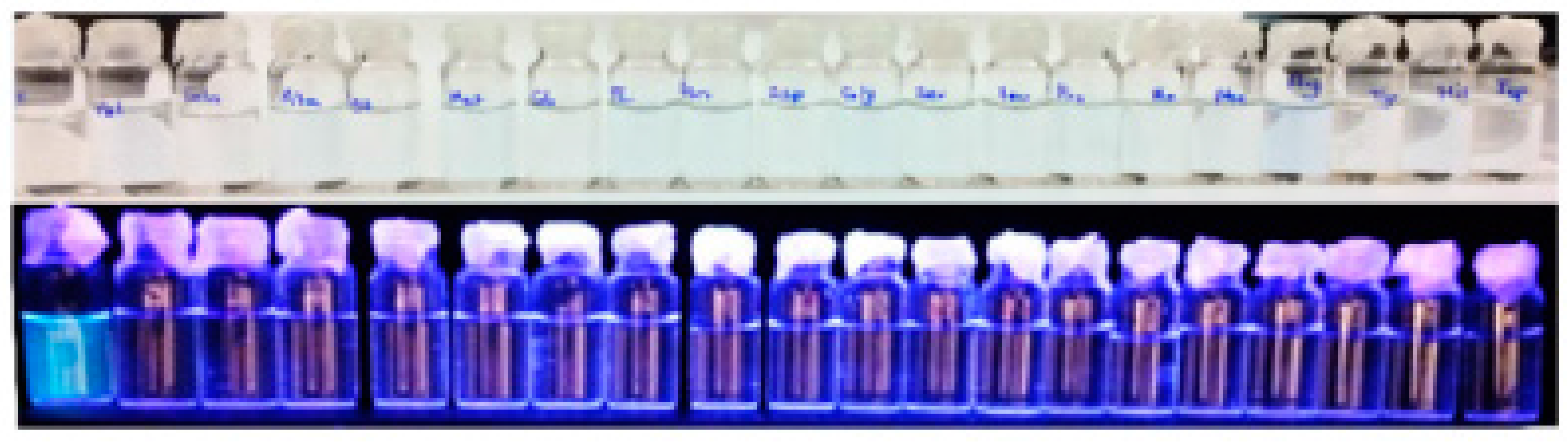
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shellaiah, M.; Sun, K.W. Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters for Potential Chemosensor Applications. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040036
Shellaiah M, Sun KW. Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters for Potential Chemosensor Applications. Chemosensors. 2017; 5(4):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleShellaiah, Muthaiah, and Kien Wen Sun. 2017. "Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters for Potential Chemosensor Applications" Chemosensors 5, no. 4: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040036
APA StyleShellaiah, M., & Sun, K. W. (2017). Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters for Potential Chemosensor Applications. Chemosensors, 5(4), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040036





