Abstract
The aim of this electrochemical study was to ascertain which position of hydroxy groups on a benzene ring provides electroactive products after enzymatic oxidation by laccase originating from the Trametes versicolor mushroom, exhibiting intense redox signals that are exploitable for their amperometric determination. The electrochemical properties of phenol together with all isomers of benzenediol and cresol at the bare carbon paste electrode (CPE) and CPE modified with enzyme laccase (CPE/Laccase) were investigated using cyclic voltammetry at various scan rates. Comparison of resulting redox signals and their differences confirmed the suitability of classes of polyphenolic compounds as substrates for Trametes versicolor laccase and their potential use as suitable biological components in the development of amperometric enzyme biosensors for the determination of such species. The feasibility of the proposed approach was verified by electrochemical assays of the enzymatic oxidation of polyphenolic analogues of simple phenols, e.g., gentisic acid, caffeic acid, resveratrol, and others.
1. Introduction
Carbon paste is a typical heterogeneous electrode material [1,2] which can be simply prepared in a laboratory by mixing conductive graphite powder and a lipophilic binder (waxes, vaseline, mineral, and paraffin oils). The homogeneous carbon paste can be pressed mechanically into the Teflon piston-like electrode holder with an electrical conductive screw for the preparation of an unmodified carbon paste electrode (bare CPE). The first generation of amperometric catalytic biosensors were prepared only by mixing bare carbon paste with tissues containing enzymes in a ceramic mortar to produce modified carbon paste electrodes [2]. Generally, electrochemical biosensors are analytical devices containing sensitive components of biological origin as receptors, which may either be part of the physico-chemical transducer or in close contact with it, transmitting a measurable signal [3]. In our study, a carbon paste electrode bulk-modified directly with laccase (CPE/Laccase) was employed. According to above-mentioned definition, the CPE/Laccase can be regarded as a simple, first generation biosensor [4].
As known, laccase (EC 1.10.3.2) is a multi-copper oxidase enzyme capable of catalyzing the oxidation of a wide range of aromatic substances, particularly substituted phenols and aromatic amines, by oxygen, which is then reduced to water [5,6]. Together with tyrosinase and catechol oxidase, laccase belongs to the group of enzymes known as polyphenol oxidases [7]. From a chemical point of view, the laccases of various plant and fungal origins are glycoproteins with molecular weights ranging from about 50 to 130 kDa. The carbohydrate moiety of laccases, which contributes to the stability of the whole enzyme, consists of mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, and galactose, and forms 10% to 45% of the protein mass [8,9]. As evidenced [6,8,10], laccase can catalyze the oxidation of various substrates (but not tyrosine) forming the corresponding radicals, followed by the conversion of phenols to quinones enzymatically or by disproportionation in the second step. Polymerization reactions involving radicals and quinones may also occur [10,11]. The laccase active site contains four copper atoms responsible for specific redox reactions with molecular oxygen and substrates; one type 1 (T1) copper and a trinuclear cluster (T2/T3) consisting of one type 2 (T2) and two type 3 (T3) copper atoms. One-electron oxidation of a phenolic substrate takes place at the T1 copper with subsequent transfer of electrons to the T2/T3 cluster and concomitant four-electron reduction of oxygen, according to Scheme 1 [6,8,9].
Scheme 1.
Enzymatic oxidation of the substrate (hydroquinone) by laccase.
Plant and fungal laccases exhibit rather low substrate specificity due to the outer-sphere mechanism of oxidation depending on the difference in redox potentials between the substrate and T1 site of the enzyme [8,9]. To date, many compounds have been tested as laccase substrates for biotechnological applications [9,11,12] or for the development of biosensors [13,14,15,16]. Although ortho- and/or para-substituted phenols are preferable for fungal laccases [10], numerous publications report on the utilization of meta-substituted phenolic compounds as well [17,18]. The activity of enzymes toward particular aromatic substances is usually determined by potentiometry measuring the uptake of oxygen [5], spectrophotometry [8], high performance liquid chromatography [19], or flow injection analysis with amperometric detection [14].
Cyclic voltammetry can provide valuable information about the redox properties of laccase [13] and studied substances and the resulting enzymatic action can be monitored by detecting the presence of electroactive products. The comparison of cyclic voltammograms of studied substrates at the bare CPE and CPE/Laccase could help to estimate which position of substituents on the aromatic ring is suitable for the laccase active site. Moreover, such a study can help to understand the possibilities of analytical applications of laccase-based enzyme biosensors for the subsequent amperometric determination of e.g., polyphenolic compounds in real samples. Chemical structures similar to cresol isomers can be found in antioxidants such as phenolic acids, which are classified as derivatives of benzoic or coumaric acid. Benzenediol isomers are usually present in complex polyphenolic compounds such as stilbenes and flavonoids. The above-mentioned polyphenols have significant antioxidant properties beneficial for human health [20] and they are also electrochemically active. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, cyclic voltammetry analysis of substituted phenols was performed at bare and laccase-modified CPEs and the resulting redox characteristics were correlated to the positions of hydroxy groups on an aromatic ring, thus monitoring the laccase activity towards a particular substrate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Phenol, catechol (benzene-1,2-diol), resorcinol (benzene-1,3-diol), hydroquinone (benzene-1,4-diol), o‑cresol (2‑methylphenol), m‑cresol (3‑methylphenol), p‑cresol (4‑methylphenol), caffeic acid (3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid), gentisic acid (2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid), salicylic acid (2-hydroxybenzoic acid), resveratrol ((E)-5-(4-hydroxystyryl)benzene-1,3-diol), dopamine (4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol), paracetamol (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanamide), (+)‑catechin (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol), and fungal laccase (EC 1.10.3.2, 12.9 U·mg−1 solid) from Trametes (Polyporpus, Coriolus [10]) versicolor were purchased from Sigma‑Aldrich (Germany). Carbon powder type CR‑2 (average particle diameter 2 μm) was obtained from Maziva Týn nad Vltavou (Czech Republic). Paraffin oil was from Merck (Germany). Glacial acetic acid and sodium acetate from Lachema (Neratovice, Czech Republic) were used for the preparation of 0.01 mol·L−1 acetate buffer solution (pH 5.0). Highly purified water (resistivity 18 MΩ·cm) was prepared by a Milli-Q purification system (Millipore S.A.S., Molsheim, France).
2.2. Instrumentation
For all electrochemical experiments, a conventional three-electrode arrangement was used which consisted of the laccase biosensor as a working electrode, an Ag/AgCl/3.0 mol·L−1 KCl reference electrode, and platinum wire auxiliary electrode. A miniaturized potentiostat EmStat (PalmSens, The Netherlands) operated with the corresponding software (PSTrace, version 4.2) was used for all electrochemical measurements. All potentials discussed in this work refer to the above-mentioned reference electrode.
2.3. Preparation of Carbon Paste Electrode Modified by Laccase
Bare CPE was prepared by the following procedure: carbon powder (0.5 g) and paraffin oil (0.125 g) were homogenized together by mixing in a porcelain mortar for 30 min. The prepared carbon paste was pressed into a Teflon, piston-like electrode holder with a conductive screw for electrical contact to the potentiostat. To prepare the laccase-modified electrode, the resulting bare carbon paste was easily modified by mixing the enzyme to a content of 10% (w/w) for 10 min. The modified carbon paste was pressed in the electrode holder with the same diameter of 3 mm. When not in use, the CPE/Laccase biosensor was stored dry in a refrigerator at 5 °C.
Before each experiment, the surface of the carbon paste electrodes was renewed by extruding less than 1.0 mm of carbon paste. Usual polishing of the carbon paste surface by wet filter paper can cause a loss of enzyme due to its solubility in water, in the case of CPE/Laccase. Therefore, acceptable reproducibility of repetitive measurements could not be achieved. For this reason, the surface of the biosensor had to be polished using dry filter paper before each electrochemical measurement. The surface of the bare CPE was renewed in the same manner to maintain identical method of electrode surface regeneration.
2.4. Electrochemical Experiments
Cyclic voltammetry was used for all electrochemical experiments. Usually, 1.0 mL of solution of each tested phenolic compound with a concentration equal to 0.01 mol·L−1 was pipetted into 19 mL of 0.01 mol·L−1 non-deaerated acetate buffer (pH 5.0) as the supporting electrolyte. The potential range for cyclic voltammetry was set from –0.4 to +1.0 V, scan rate 10 mV·s−1, potential step 5 mV, with five scans.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Amount of Laccase in Carbon Paste on Sensitivity
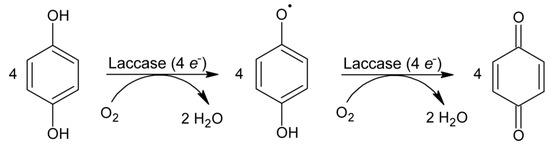
It is very important to prepare sensitive biological devices for monitoring an enzymatic reaction to properly assess the suitability of selected phenolic compounds as a laccase substrate. Generally, the polyphenolic substrate is oxidized by laccase to the corresponding phenoxyl radical with the concomitant four-electron reduction of oxygen as a co-substrate to water. In the next step, quinones are formed via the following enzymatic or non-enzymatic reactions (Scheme 1). Figure 1 depicts the comparison of cyclic voltammograms for hydroquinone recorded at the bare carbon paste and laccase-modified electrode. It is evident that the enzyme quickly converts the substrate (hydroquinone) at the electrode surface, showing no oxidation response. On the contrary, the peak corresponding to electrochemical reduction of quinone is greatly enhanced in the reverse scan. The height of the measured voltammetric response is influenced by the amount of enzyme on the surface of the CPE. The dependence of the peak current on different amounts of enzyme in the carbon paste is shown in the inset of Figure 1a. The peak currents increased with the amount of laccase in the carbon paste up to 10% (w/w); no significant change was observed with higher contents of the enzyme in the paste. Thus, the amount of 10% (w/w) laccase was chosen as an optimum value for further investigations.
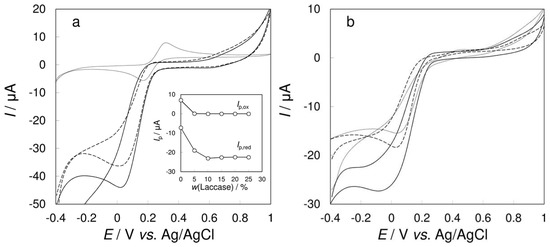
Figure 1.
Cyclic voltammetry of 5 × 10−4 mol·L−1 hydroquinone at bare CPE and CPE/Laccase in 0.01 mol·L−1 acetate buffer (pH 5.0), scan rate 10 mV·s−1: (a) 0% (dotted line), 5% (dashed line), and 10% (solid line) amount of enzyme, inset: peak currents of oxidation and reduction signals obtained at CPE/Laccase with different enzyme contents; (b) air saturated acetate buffer (solid line), acetate buffer deaerated with nitrogen for 30 min (dashed line) and 60 min (dotted line).
Furthermore, the oxygen-dependent enzymatic function of laccase was verified by deaeration of the acetate buffer with nitrogen for different periods. As shown in Figure 1b, the reduction signal of hydroquinone decreases after a longer period of bubbling with nitrogen using simple tubing, which corresponds to lower activity of the enzyme due to the lower concentration of oxygen (co-substrate) in the solution. Simultaneously, a small oxidation signal of hydroquinone, which is not converted by the enzyme and can be detected electrochemically, started to appear. The voltammetric response of hydroquinone at the CPE/Laccase did not change completely to a non-enzymatic response (reversible redox pair) even in the deaerated solution due to traces of oxygen, present at micromolar concentrations.
3.2. Effect of Scan Rate on the Electrochemical Detection of Biocatalysis
To further study the biocatalytic activity of the enzyme towards a particular substrate with the aid of the electrochemical sensor, it was necessary to find an optimal value of the scan rate (ν) of the voltammetric experiment, when the tested phenolic substrates are converted predominantly by the enzyme instead of oxidized electrochemically. Hydroquinone is a typical substrate for laccases [10], so it was selected as a model compound for this study. After performing cyclic voltammetry measurements at the bare CPE, a reversible redox couple was observed with the ratio of anodic and cathodic peak currents Ip,ox/Ip,red constantly equal to 1.0 for each selected scan rate. No oxidation peak of hydroquinone was observed at the CPE/Laccase using a scan rate of 10 mV·s−1. Lower scan rates were not tested but similar electrochemical behaviour of hydroquinone can be expected. The value of the Ip,ox/Ip,red ratio was still equal to 1.0 for hydroquinone analysed at the CPE/Laccase using scan rates higher than 60 mV·s−1. However, for scan rates less than this critical value, the Ip,ox/Ip,red ratios at the CPE/Laccase were significantly lower (see Figure 2), which indicates a quick conversion of the substrate by the enzyme and decreasing influence of the electrochemical oxidation itself.
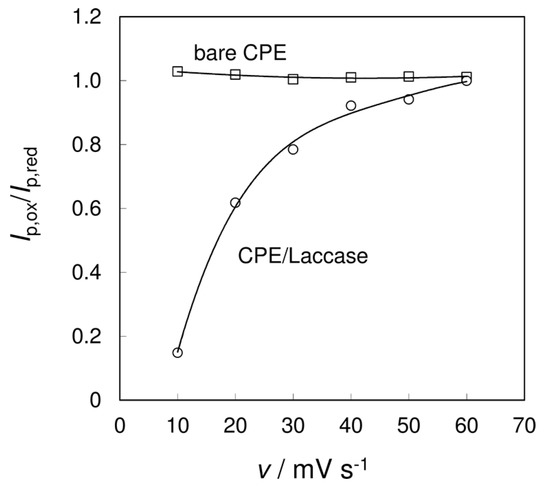
Figure 2.
Dependency of the Ip,ox/Ip,red ratio on applied scan rates.
The type of mass transport of the analyte to the electrode surface can be recognized from the relationships between Ip and ν½ or log Ip versus log ν. Both dependencies obtained for the bare CPE were linear with slope values of 0.46 for Ip,ox and –0.52 for Ip,red, which were close to the theoretical value of 0.5 for the dependence of log Ip versus log ν, which testifies to the diffusion control. Both dependencies were nonlinear when the CPE/Laccase biosensor was used for the measurements. It is obvious that the mass transport of the analyte to the surface of the bare CPE was diffusion‑controlled while the adsorption of hydroquinone is required for the enzyme-modified CPE.
3.3. Cyclic Voltammetry of Phenol at CPE/Laccase vs. Bare CPE
To further study the influence of the number and position of hydroxy substituents in the benzene ring on the suitability of the enzyme substrate, cyclic voltammetry of the phenol alone was first performed. The phenolic unit is regularly present in the structure of various polyphenolic compounds [20], which are often used as laccase substrates. Cyclic voltammetry of 5 × 10−4 mol·L−1 phenol at the bare CPE and CPE/Laccase biosensor revealed a difference in the voltammetric response (see Figure 3a). At the bare CPE, phenol gave only one wide oxidation peak at a potential of +0.775 V in 0.01 mol·L−1 non‑deaerated acetate buffer (pH 5.0). Using identical working conditions, an oxidation of phenol at the same peak potential was observed at the CPE/Laccase biosensor. However, contrary to the bare CPE, a wide reduction peak was also recorded at a potential of –0.055 V that confirms the utilization of phenol by the enzyme laccase. Both electrodes were also subjected to measurements in pure acetate buffer to elucidate if there is some current contribution from the electrode material itself. As shown in Figure 3b, the usual response with low background currents was obtained at the bare CPE. A small irreversible oxidation signal at a potential around 0.9 V, which can be attributed to oxidation of the enzyme itself, and slowly increasing background currents starting from 0.2 V to more negative potentials, are visible for the CPE/Laccase. The addition of phenol then induces significant change in the voltammetric response for both electrodes, resulting in the oxidation and reduction signals intensifying several times, which can be clearly distinguished from the background.
Figure 3.
Cyclic voltammetry with bare CPE (dashed line) and CPE/Laccase (solid line) at a scan rate of 10 mV·s−1: (a) 5 × 10−4 mol·L−1 phenol in 0.01 mol·L−1 non‑deaerated acetate buffer (pH 5.0); (b) pure acetate buffer.
3.4. Cyclic Voltammetry of Cresols at CPE/Laccase vs. Bare CPE
Each cresol isomer provides only one wide oxidation peak at the bare CPE in the acetate buffer solution at pH 5.0. The highest peak height was observed for m-cresol. The peak potentials of the oxidation of cresols were experimentally determined as +0.755 V for o‑cresol, +0.735 V for m‑cresol, and +0.695 V for p‑cresol. On the contrary, distinct reduction signals were recorded only at the CPE/Laccase electrode for o‑cresol and m‑cresol at potentials of –0.080 V and −0.090 V, respectively; only a weak electrochemical response was obtained for p‑cresol (see Figure 4). It is evident that phenolic compounds based on mono‑substituted hydroxybenzene with hydroxy groups in the ortho and meta positions can be utilized by testing laccase and they can be most probably electrochemically determined by using a biosensor containing laccase Trametes versicolor.
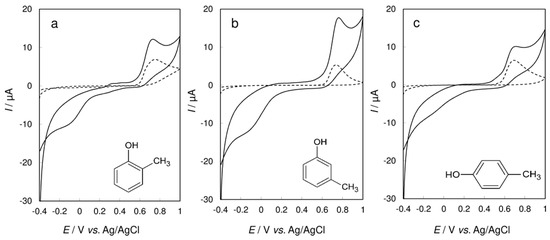
Figure 4.
Cyclic voltammetry of 5 × 10−4 mol·L−1 (a) o‑cresol; (b) m‑cresol and (c) p‑cresol at bare CPE (dashed lines) and CPE/Laccase (solid lines) in 0.01 mol·L−1 non‑deaerated acetate buffer (pH 5.0) at scan rate 10 mV·s−1.
3.5. Cyclic Voltammetry of Benzenediols at CPE/Laccase vs. Bare CPE
From cyclic voltammograms of each benzenediol (see Figure 5) it is clear that resorcinol could not be electrochemically detected after conversion by Trametes versicolor laccase: the characteristic reduction peak of the enzyme-oxidized substrate at ca. +0.1 V is missing. It is interesting that the methyl group in the meta- position does not have any influence on the enzymatic oxidation of the free hydroxy group in m‑cresol and enables the formation of the electroactive product, while it is not the case with the hydroxy group in resorcinol. Both the methyl and hydroxy groups are electron donors to the benzene ring (the hydroxy group is even more active due to the combination of larger positive mesomeric effects and smaller negative inductive effects) and both direct subsequent substitution to the ortho- or para- position. The possible explanation for different voltammetric characteristics of resorcinol and m-cresol at CPE/Laccase probably lies in the formation of subsequent products by the cross-coupling of phenoxyl radicals. These products can be electrochemically reduced in the case of m-cresol, contrary to the polymeric products of laccase-transformed resorcinol. According to the cyclic voltammogram recorded with the used carbon paste biosensor (Figure 5b), amperometric detection of this specific phenolic unit, which is a part of stilbene and flavonoid molecules, will not be possible.
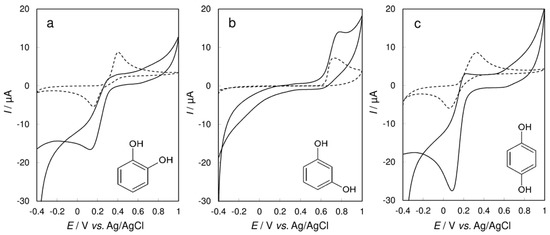
Figure 5.
Cyclic voltammetry of 5 × 10−4 mol·L−1 (a) catechol; (b) resorcinol; and (c) hydroquinone at bare CPE (dashed lines) and CPE/Laccase (solid lines) in 0.01 mol·L−1 non‑deaerated acetate buffer (pH 5.0) at a scan rate of 10 mV·s−1.
The electrochemical behaviour of tested benzenediols at the bare CPE is already known. Contrary to the redox behaviour of catechol and hydroquinone shown in Figure 5a,c, respectively, resorcinol exhibits only one wide oxidation peak at a potential of +0.735 V, similarly to cresols. Therefore, it can be assumed that only one hydroxy group on the benzene ring is electrochemically oxidized. Both catechol and hydroquinone provide typical redox couples, exchanging two protons and two electrons during their oxidation; therefore, they are frequently used as model analytes for the characterisation of electrode materials [21].
Catechol and hydroquinone are definitely proper substrates of laccase Trametes versicolor because no oxidation signals were detected at the CPE/Laccase biosensor, indicating effective enzymatic oxidation. Distinct reduction peaks were found at potentials of +0.160 V for catechol and +0.065 V for hydroquinone, respectively. For example, the reduction current for hydroquinone was five times higher at the CPE/Laccase comparing to the bare CPE. A peak current nearly two times as intense was recorded for hydroquinone (–27.51 µA) than for catechol (–16.59 µA). Such findings confirmed that the para- position of the hydroxy group leads to enzymatic oxidation products more electroactive than in the case of ortho- substitution.
3.6. Final Discussion and Confirmation of Obtained Results
According to the comparison of the cyclic voltammograms of the chosen phenolic compounds obtained at the bare CPE and CPE/Laccase, the suitability of particular phenolic substances to be enzymatically converted into electroactive products by the selected laccase enzyme can be explicitly determined. This knowledge can be then utilized for the development of enzyme biosensors to determine such classes of compounds in various kinds of samples. For example, all analogues of catechol (caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, dopamine, piceatannol, quercetin, catechin, etc.), hydroquinone (gentisic acid, homogentisic, etc.), o‑cresol (salicylic acid, o‑coumaric acid, guaiacol, etc.), and m‑cresol (m‑coumaric acid, etc.) are significant antioxidants that are commonly occurring in food, which can be possibly determined by the laccase biosensor. On the contrary, used laccase would not produce electroactive products from the analogues of p-cresol (p-hydroxycinnamic acid, pterostilbene, resveratrol, etc.) and resorcinol.
To verify and confirm the abovementioned findings and conclusions, we assayed several phenolic and polyphenolic compounds, sharing a similar position of substitution of the free hydroxy group (Figure 6). As documented for gentisic acid, dopamine, and caffeic acid in Figure 6a–c, respectively, both ortho- and para- dihydroxy benzene rings undergo quick enzymatic conversion and intense signal reduction of quinone at ca. +0.1 V. The presence of other substituents then influences the intensity of this signal depending on the structure of the resulting oxidation products, which is demonstrated in the comparison of voltammograms in Figure 6b,c.
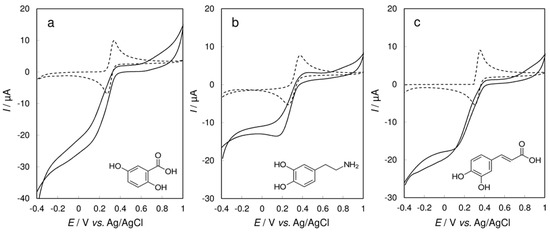
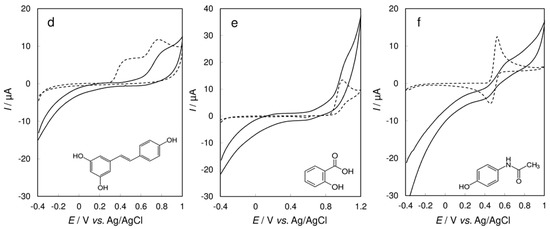
Figure 6.
Cyclic voltammetry of 5 × 10−4 mol·L−1 (a) gentisic acid; (b) dopamine; (c) caffeic acid; (d) resveratrol; (e) salicylic acid; and (f) paracetamol at bare CPE (dashed lines) and CPE/Laccase (solid lines) in 0.01 mol·L−1 non‑deaerated acetate buffer (pH 5.0) at a scan rate of 10 mV·s−1.
The opposite situation is shown for resveratrol as an example of a meta-dihydroxy substituted polyphenol (Figure 6d). The redox response change completely when using the CPE/Laccase and the quinone reduction peak is not present in the voltammograms. The second benzene ring contains a hydroxy group in the para- position and similar to p-cresol, such a structure is not favorable for the formation of electroactive species after laccase action. Various substituents on the benzene ring may have diverse effects, which is depicted in Figure 6e for salicylic acid. Even though it is structurally similar to o-cresol, which gives a distinct quinone reduction signal (Figure 4a), the electronic effects of the carboxylic group, different from those of the methyl group in o-cresol, lead to electroinactive species. Finally, paracetamol can be easily and reversibly oxidized electrochemically at the bare CPE, but in presence of laccase the reduction signal does not manifest (Figure 6f), which can again be attributed to structure similarity with p-cresol (Figure 4c).
The assumption that (+)‑catechin (analogue of catechol) is a substrate for laccase Trametes versicolor was confirmed by the change of colour of the supporting electrolyte to yellow during cyclic voltammetry at the CPE/Laccase biosensor (not shown), which was caused by formation of (+)‑catechin quinone [22,23]. This phenomenon was not observed at the bare CPE with the same working conditions. This experiment is also confirmed by previous studies published in the literature [24].
The laccase from Trametes versicolor is not capable of oxidizing phenolic compounds having structure similar to p‑cresol, because it lacks the cresolase activity like tyrosinase isolated from Agaricus bisporus [25], which catalyses an addition of a hydroxy group to the free ortho position [26]. It is important to note that most of the naturally occurring antioxidants (non‑synthetic) represent only ortho- and para- substituted polyphenolic compounds [27]. Unfortunately, none of the mentioned enzymes can be utilized for enzymatic conversion of resorcinol analogues with subsequent electrochemical monitoring of the oxidation products [28].
It should be mentioned that the mechanism of benzenediol oxidation with the participation of laccase cannot be described universally using the reaction scheme presented by Yaropolov et al. [29]. It is evident that laccase from Trametes versicolor cannot oxidize resorcinol to m‑quinone. This was also confirmed by Sun et al. [30] who measured the UV‑Vis and FT‑IR spectrometry of each benzenediol with the same additions of laccase and observed subsequent time-dependent polymerization. In the case of resorcinol, the oxidation was significantly slower than that of other diphenols, as also reported by Witayakrana and Ragauskas [9], where the mechanism of hydroquinone oxidation catalysed by laccase was presented. Thus, it seems that the resorcinol radical is also formed and participates in the polymerization.
4. Conclusions
In this contribution, cyclic voltammetry of phenol, cresols, and benzenediols was performed at the bare CPE and CPE/Laccase biosensor to evaluate if a particular polyphenol could be efficiently utilized by the laccase enzyme to provide an electroactive product, which exhibits an intense redox signal(s). Such a response can be taken into account and potentially utilized in the development of a corresponding laccase biosensor. It is evident from the comparison of the measured cyclic voltammograms that the biosensor based on laccase isolated from the mushroom Trametes versicolor cannot be used universally for the determination of any phenolic species. Fortunately, the laccase is very sensitive to the presence of many significant phenolic compounds, whose determination is important in many fields such as food analysis, clinical analysis, and medicine. It can be assumed that various substitutions by alkyl chains or functional groups in the molecules of the substrate will have a significant effect on the rate of the corresponding enzymatic reaction and the structure of the resulting oxidation products, determining their electrochemical properties. Moreover, it was found that it is possible to monitor the kinetics of enzymatic reactions electrochemically using a scan rate study of chosen phenolic substrates, but only in cases when the oxidation process leads to a similar product electrochemically and enzymatically. The Ip,ox/Ip,red ratio will approach unity for slow enzymatic reactions at low applied scan rates, because the direct electrochemical process prevails. Fast enzymatic reactions will only approach this critical value at high values of scan rates. In favorable conditions, the whole study can be performed with only the laccase biosensor; (i) the enzymatic activity can be followed at low scan rates, whereas (ii) the electrochemical properties of the assayed polyphenol can be monitored at fast scan rates. Finally, the proposed simple approach can be easily extended to test other polyphenolic compounds with functional groups of interest in conjunction with different laccases immobilized in the electrode.
Acknowledgments
The support received from the Faculty of Chemical Technology, University of Pardubice is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are also grateful to the CEEPUS CIII-CZ-0212-08-1415 network for mobility funding.
Author Contributions
M.S. conceived and designed the experiments; M.S. and A.F. performed the experiments; K.V., T.A., and R.M. analyzed the data and contributed to the discussion of results; R.M. and M. S. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CPE | Carbon paste electrode |
| CPE/Laccase | Carbon paste electrode modified with enzyme laccase |
References
- Kalcher, K. Chemically modified carbon paste electrodes in voltammetric analysis. Electroanalysis 1990, 2, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švancara, I.; Vytřas, K.; Kalcher, K.; Walcarius, A. Electroanalysis with Carbon Paste Electrodes; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pohanka, M.; Skladal, P. Electrochemical biosensors—Principles and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2008, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gorton, L. Carbon-paste electrodes modified with enzymes, tissues, and cells. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F. Oxidation of phenols, anilines, and benzenethiols by fungal laccases: Correlation between activity and redox potentials as well as halide inhibition. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 7608–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardina, P.; Faraco, V.; Pezzella, C.; Piscitelli, A.; Vanhulle, S.; Sannia, G. Laccases: A never-ending story. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, R.M.; Cairney, J.W.G. Laccases and other polyphenol oxidases in ecto- and ericoid mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 2002, 12, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, E.I.; Sundaram, U.M.; Machonkin, T.E. Multicopper oxidases and oxygenases. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2563–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witayakran, S.; Ragauskas, A.J. Synthetic applications of laccase in green chemistry. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, C.F. The Structure and Function of Fungal Laccases. Microbiology 1994, 140, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, S. Laccases: Blue enzymes for green chemistry. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.; Staples, R.C. Laccase: New functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, B.; Rahmati-Panah, A.; Shleev, S.; Gorton, L. Carbon ceramic electrodes modified with laccase from Trametes hirsuta: Fabrication, characterization and their use for phenolic compounds detection. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A.; Ruzgas, T.; Gorton, L. Amperometric detection of mono- and diphenols at Cerrena unicolor laccase-modified graphite electrode: Correlation between sensitivity and substrate structure. Talanta 2005, 66, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, B.; Gorton, L.; Ruzgas, T.; Jonsson, L.J. Characterization of graphite electrodes modified with laccase from Trametes versicolor and their use for bioelectrochemical monitoring of phenolic compounds in flow injection analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 487, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, B.; Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A.; Ruzgas, T.; Gorton, L.; Leonowicz, A. Characterization of graphite electrodes modified with laccases from Trametes hirsuta and Cerrena unicolor and their use for flow injection amperometric determination of some phenolic compounds. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2005, 85, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P. Fungal laccases—Occurrence and properties. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavi, V.; Lele, S.S. Laccase: Properties and Applications. Bioresources 2009, 4, 1694–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Lante, A.; Crapisi, A.; Krastanov, A.; Spettoli, P. Biodegradation of phenols by laccase immobilised in a membrane reactor. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quideau, S.; Deffieux, D.; Douat-Casassus, C.; Pouységu, L. Plant polyphenols: Chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, M.; Jiao, K. Electrochemical behaviors of hydroquinone on a carbon paste electrode with ionic liquid as binder. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, 29, 915–920. [Google Scholar]
- Janeiro, P.; Brett, A.M.O. Catechin electrochemical oxidation mechanisms. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bark, K.M.; Yeom, J.E.; Yang, J.I.; Yang, I.J.; Park, C.H.; Park, H.R. Spectroscopic Studies on the Oxidation of Catechin in Aqueous Solution. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E. Enzyme Initiated Radical Polymerizations. Polymers 2012, 4, 759–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolff, M.; Schottenheim, J.; Decker, H.; Tuczek, F. Copper-O2 reactivity of tyrosinase models towards external monophenolic substrates: Molecular mechanism and comparison with the enzyme. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4077–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eicken, C.; Krebs, B.; Sacchettini, J.C. Catechol oxidase—Structure and activity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999, 9, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratford, M.R.L.; Ramsden, C.A.; Riley, P.A. Mechanistic studies of the inactivation of tyrosinase by resorcinol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaropolov, A.I.; Shleev, S.V.; Morozova, O.V.; Zaitseva, E.A.; Marko-Varga, G.; Emneus, J.; Gorton, L. An amperometric biosensor based on laccase immobilized in polymer matrices for determining phenolic compounds. J. Anal. Chem. 2005, 60, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fan, X.; Yuan, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, P. Laccase-catalyzed oxidative polymerization of phenolic compounds. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).