ZnO Quasi-1D Nanostructures: Synthesis, Modeling, and Properties for Applications in Conductometric Chemical Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
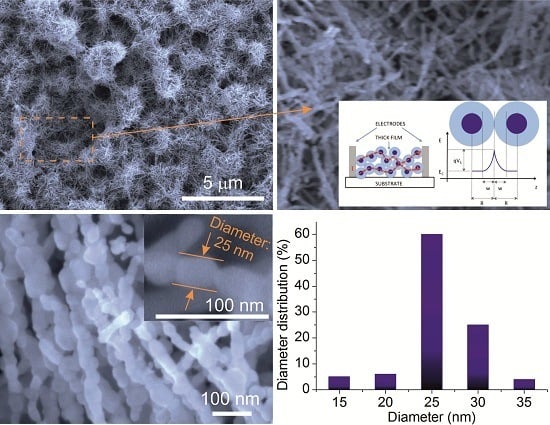
2. Synthesis of Quasi-1D ZnO Nanostructures
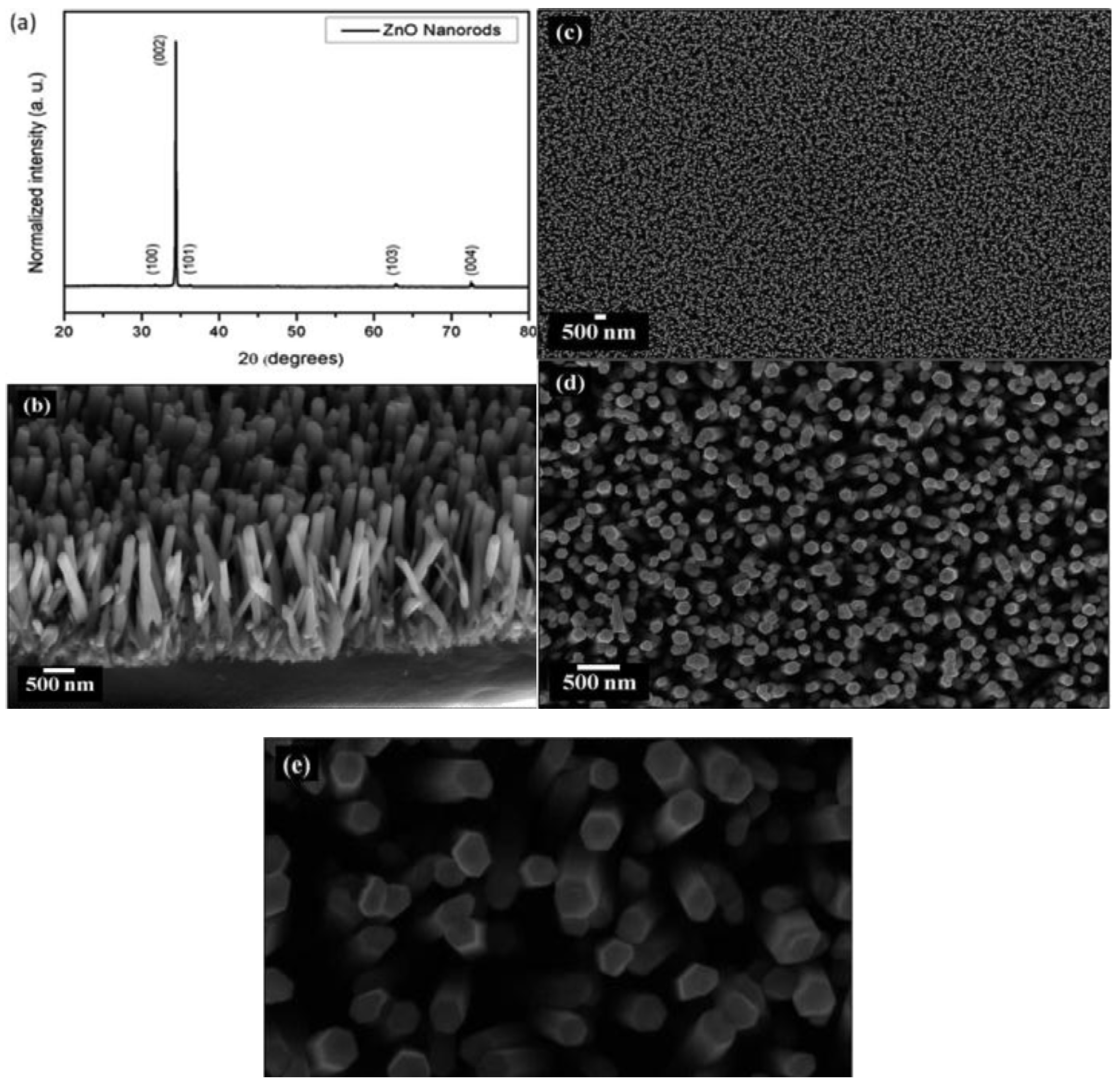
2.1. Hydrothermal Synthesis
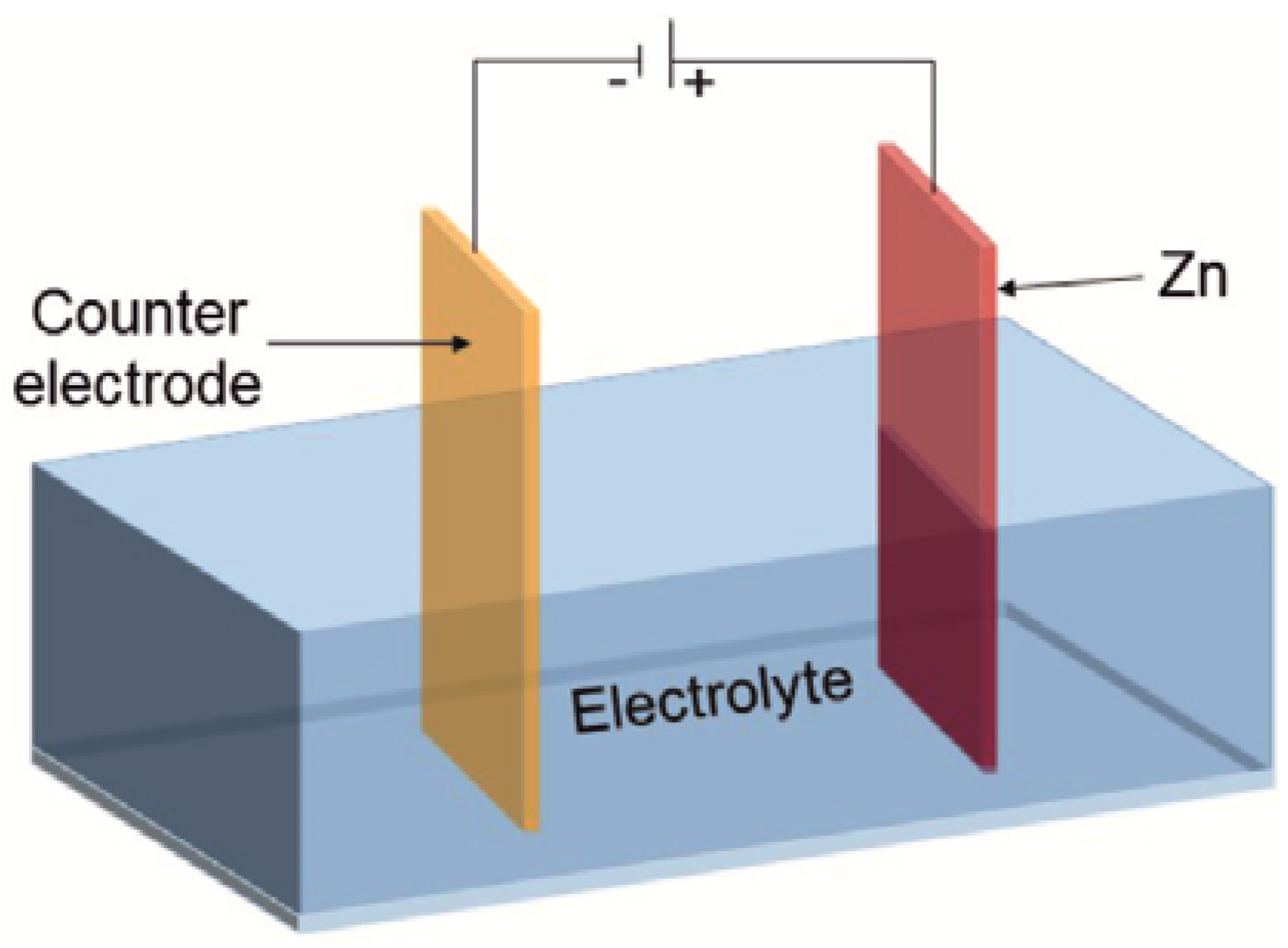
2.2. Electrochemical Anodization
2.3. Chemical Vapor Deposition
2.4. Atomic Layer Deposition
2.5. Physical Vapor Deposition
2.6. Synthesis of Doped and FUNCTIONALIZED ZnO Nanostructures
3. Modeling
3.1. Basic Transduction Mechanism
3.2. Single Nanowire Device
3.3. Layers with Polycrystalline Microstructure
3.4. Surface Functionalization
4. Functional Properties
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Vomiero, A.; Sberveglieri, G. Quasi-one dimensional metal oxide semiconductors: Preparation, characterization and application as chemical sensors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Li, L.; Wang, T. Ab initio study of ZnO-based gas-sensing mechanisms: Surface reconstruction and charge transfer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6107–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, F.J. Semiconductors; Renhold Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Morkoç, H.; Özgür, Ü. General Properties of ZnO, in Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, M.J.S. Gas sensing applications of 1d-nanostructured zinc oxide: Insights from density functional theory calculations. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 437–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Z.L. Nanogenerator as self-powered vibration sensor. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.T.; Odom, T.W.; Lieber, C.M. Chemistry and physics in one dimension: Synthesis and properties of nanowires and nanotubes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, W. Hmt assisted hydrothermal synthesis of various ZnO nanostructures: Structure, growth and gas sensor properties. Phys. E-Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2011, 44, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, H.; Ma, X. A comparative study of porous ZnO nanostructures synthesized from different zinc salts as gas sensor materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 578, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Han, D.; Gu, F.; Guo, G. High-sensitivity NO2 gas sensors based on flower-like and tube-like ZnO nanomaterials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, S. ZnO nanorod gas sensor for ethanol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 162, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catto, A.C.; da Silva, L.F.; Ribeiro, C.; Bernardini, S.; Aguir, K.; Longo, E.; Mastelaro, V.R. An easy method of preparing ozone gas sensors based on ZnO nanorods. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 19528–19533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Raj, S.; Ko, K.-J.; Park, K.-K.; Yu, Y.-T. Synthesis of flower-like ZnO microstructures for gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, S. Diameter regulated ZnO nanorod synthesis and its application in gas sensor optimization. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.K.; Lee, K.; Hahn, R.; Schmuki, P. Anodic growth of hierarchically structured nanotubular ZnO architectures on zinc surfaces using a sulfide based electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 34, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, K.; Choi, J. Formation of ZnO nanowires during short durations of potentiostatic and galvanostatic anodization. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Ponzoni, A.; Bontempi, E.; Brisotto, M.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. Synthesis of self-assembled chain-like ZnO nanostructures on stiff and flexible substrates. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Peng, L.-M. Large-scale and rapid synthesis of ultralong ZnO nanowire films via anodization. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. Nanostructured zno chemical gas sensors. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 14239–14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. TiO2 nanotubes: Recent advances in synthesis and gas sensing properties. Sensors 2013, 13, 14813–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.C.; Hitchman, M.L. Overview of chemical vapour deposition. Chem. Vap. Depos. Precursors Process. Appl. 2008, Chapter 1. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Salman, H.S.; Abdullah, M.J. Rf sputtering enhanced the morphology and photoluminescence of multi-oriented ZnO nanostructure produced by chemical vapor deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 547, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.S.-S.; Wang, C.-R.; Chan, Y.-L.; Lin, H.-L.; Chen, M.-H.; Wu, R.-J. Fast-response ozone sensor with ZnO nanorods grown by chemical vapor deposition. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.O.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.S. Substrate dependent growth modes of ZnO nanorods grown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 355, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A. Old chemistries’ for new applications: Perspectives for development of precursors for MOCVD and ALD applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 3332–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, D.J.H.; Chadha, P.; Price, J.S. Metal ald and pulsed CVD: Fundamental reactions and links with solution chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 3282–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Ren, W.; Ye, Z.-G. Well-ordered ZnO nanotube arrays and networks grown by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 340, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.T.; Son, J.Y.; Rhee, J.S. Vertical ZnO nanorod array as an effective hydrogen gas sensor. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E. One- and two-dimensional metal oxide nanostructures for chemical sensing. In Semiconductor Gas Sensors; Jaaniso, R., Tan, O.K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 299–315. [Google Scholar]
- Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Concina, I.; Faglia, G.; Falasconi, M.; Ferroni, M.; Galstyan, V.; Gobbi, E.; Ponzoni, A.; Vomiero, A.; et al. Metal oxide nanoscience and nanotechnology for chemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 179, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Cadena, G.; Comini, E.; Ferroni, M.; Vomiero, A.; Sberveglieri, G. Synthesis of different ZnO nanostructures by modified PVD process and potential use for 1dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-K.; Hsu, M.-H. Ce-doped ZnO nanorods based low operation temperature NO2 gas sensors. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10867–10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Arshi, N.; Anwar, M.S.; Danish, R.; Koo, B.H. Mn-doped ZnO nanorod gas sensor for oxygen detection. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, S64–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mei, J.; Gui, P.; Tao, P.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Fang, G.-J. The investigation of Al-doped ZnO as an electron transporting layer for visible-blind ultraviolet photodetector based on n-ZnO nanorods/p-si heterojunction. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 2015, 38, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Gao, Y.-D.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hsueh, T.-J. Vertical Ti doped ZnO nanorods based on ethanol gas sensor prepared on glass by furnace system with hotwire assistance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, F.; Lide, D.R. CRC handbook of chemistry and physics: From paper to web. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 225, U552. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, K.; Park, S.-I.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-I. Characteristics of Ga and Ag-doped ZnO-based nanowires for an ethanol gas sensor prepared by hot-walled pulsed laser deposition. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 40, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, P. Unexpected ferromagnetism in n-type polycrystalline K-doped ZnO films prepared by RF-magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 8451–8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.K.; Hong, S.H.; Hwang, S.-H.; Choi, W.M.; Kim, S.; Park, H.; Jeong, M.G. Synthesis of Al-doped ZnO nanorods via microemulsion method and their application as a CO gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Z.S.; Mortezaali, A.; Zad, A.I.; Fardindoost, S. Sensitive and selective room temperature H2S gas sensor based on Au sensitized vertical ZnO nanorods with flower-like structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 628, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, V.N.; Jain, K.; Senguttuvan, T.D. Pulse-like highly selective gas sensors based on ZnO nanostructures synthesized by a chemical route; effect of In doping and Pd loading. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Q.; Barreca, D.; Gasparotto, A.; Maccato, C.; Tondello, E.; Sada, C.; Comini, E.; Devi, A.; Fischer, R.A. Ag/ZnO nanomaterials as high performance sensors for flammable and toxic gases. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 025502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, M.; Ju, D.; Xu, H.; Cao, B. High-performance gas sensor based on ZnO nanowires functionalized by au nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W. A Au-functionalized ZnO nanowire gas sensor for detection of benzene and toluene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 17179–17186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, Y.; Park, S.; An, S.; Lee, C.; Kim, H.W. NO2 gas sensing properties of Au-functionalized porous ZnO nanosheets enhanced by UV irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 8615–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Jeon, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Yu, Y.-T. Functionalization of ZnO nanorods by CuO nanospikes for gas sensor applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 23604–23609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, V.E.; Cox, P.A. The Surface Science of Metal Oxides; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Conduction model of metal oxide gas sensors. J. Electroceram. 2001, 7, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.S.; Park, J.Y.; Oh, H.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, S.S. Electrical transport properties of size-tuned ZnO nanorods. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, U.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Dogan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantto, V.; Rompplainen, P.; Leppävuori, S. A study of the temperature dependence of the barrier energy in porous tin dioxide. Sensors Actuators 1988, 14, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, J.; Bonanati, P.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Grain shape influence on semiconducting metal oxide based gas sensor performance: Modeling versus experiment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3977–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-C.; Shen, G.; Zhou, C. Chemical sensors and electronic noses based on 1-D metal oxide nanostructures. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2008, 7, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwamb, T.; Burg, B.R.; Schirmer, N.C.; Poulikakos, D. On the effect of the electrical contact resistance in nanodevices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 243106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysoev, V.V.; Goschnick, J.; Schneider, T.; Strelcov, E.; Kolmakov, A. A gradient microarray electronic nose based on percolating SnO2 nanowire sensing elements. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3182–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzoni, A.; Comini, E.; Concina, I.; Ferroni, M.; Falasconi, M.; Gobbi, E.; Sberveglieri, V.; Sberveglieri, G. Nanostructured metal oxide gas sensors, a survey of applications carried out at sensor lab, Brescia (Italy) in the security and food quality fields. Sensors 2012, 12, 17023–17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazoe, N.; Sakai, G.; Shimanoe, K. Oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Catal. Surv. Asia 2003, 7, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Ponzoni, A.; Zappa, D.; Sberveglieri, G. Metal oxide nanowire chemical and biochemical sensors. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 2911–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.C.; Shaikh, J.S.; Suryavanshi, S.S.; Patil, P.S. Growth of ZnO nanodisk, nanospindles and nanoflowers for gas sensor: PH dependency. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Guo, J.; Yang, W.; Shi, C.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Huang, T.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of three-dimensional flower-like hierarchical ZnO nanostructure and its enhanced acetone gas sensing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 654, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, A.L.; Hu, L.Z.; Qiu, Y.; Cao, G.Y.; Yu, J.J.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, H.Q.; Yin, B.; Xu, L.L. High performance of 1-D ZnO microwire with curve-side hexagon as ethanol gas sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4908–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.D.; Patil, G.E.; Kajale, D.D.; Gaikwad, V.B.; Jain, G.H. Synthesis of ZnO nanorods by spray pyrolysis for H2S gas sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 528, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Kumar, R.; Al-Dossary, O.; Kumar, G.; Umar, A. Zinc oxide nanostructures for NO2 gas-sensor applications: A review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Y.; Ozturk, S.; Kilinc, N.; Kosemen, A.; Erkovan, M.; Ozturk, Z.Z. Electrical conduction and NO2 gas sensing properties of ZnO nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 303, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. UV light activation of tin oxide thin films for NO2 sensing at low temperatures. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2001, 78, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, G.; Yu, R.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Piezotronic effect enhanced detection of flammable/toxic gases by ZnO micro/nanowire sensors. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusior, A.; Radecka, M.; Rekas, M.; Lubecka, M.; Zakrzewska, K.; Reszka, A.; Kowalski, B.J. Sensitization of gas sensing properties in TiO2/SnO2 nanocomposites. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; An, X.; Wang, Y.; Shu, Z.; An, X.; Hua, F. ZnO@ZnS hollow dumbbells-graphene composites as high-performance photocatalysts and alcohol sensors. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Shen, X.; Yuan, A. Co3O4/ZnO nanocomposites for gas-sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, S. CuO nanoparticle decorated ZnO nanorod sensor for low-temperature H2S detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2012, 32, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, J. Cr2O3-sensitized ZnO electrospun nanofibers based ethanol detectors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 143, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Hydrogen gas sensors based on semiconductor oxide nanostructures. Sensors 2012, 12, 5517–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Bing, Y.-F.; Liu, C.; Zheng, W.-T.; Zou, G.-T. Self-assembly of hierarchical ZnSnO3-SnO2 nanoflakes and their gas sensing properties. Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc. China 2012, 22, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.W.; Woo, H.-S.; Kim, I.-D.; Lee, J.-H. Selective detection of NO2 and C2H5OH using a Co3O4-decorated ZnO nanowire network sensor. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5148–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.-S.; Na, C.; Kim, I.-D.; Lee, J.-H. Highly sensitive and selective trimethylamine sensor using one-dimensional ZnO-Cr2O3 hetero-nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 245501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Fan, H.; Tian, H. PVP assisted in situ synthesis of functionalized graphene/ZnO (FGZnO) nanohybrids with enhanced gas-sensing property. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, S.M.J.; Abdi, Y.; Darbari, S.; Ostovari, F. Investigating the effect of gas absorption on the electromechanical and electrochemical behavior of graphene/ZnO structure, suitable for highly selective and sensitive gas sensors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, G.; Xie, T.; Yuan, H.; Tai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z. A sensitive film structure improvement of reduced graphene oxide based resistive gas sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 033502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, P.; Abdi, Y.; Arzi, E. Directional reduction of graphene oxide sheets using photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanowires for the fabrication of a high sensitive oxygen sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, K.; Furue, R.; Hayami, S. Recent progress in applications of graphene oxide for gas sensing: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 878, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, T.; Tai, H.; Xie, G. A novel sensing mechanism for resistive gas sensors based on layered reduced graphene oxide thin films at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wei, H.; Wei, L.; Zhang, Y. Ultrafast and sensitive room temperature NH3 gas sensors based on chemically reduced graphene oxide. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 025502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Lee, J.M.; Il Park, W. Vertically aligned ZnO nanorods and graphene hybrid architectures for high-sensitive flexible gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Singh, O.; Singh, M.P.; Kaur, J.; Singh, R.C. Hydrogen sensor based on graphene/ZnO nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesakumar, N.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Chemometric methods for the evaluation of electron transfer properties of zinc oxide nanorods modified gold electrode for lactate detection in food products. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, M.; Escuder-Gilabert, L. A 21st century technique for food control: Electronic noses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 638, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concina, I.; Falasconi, M.; Sberveglieri, V. Electronic noses as flexible tools to assess food quality and safety: Should we trust them? IEEE Sensors J. 2012, 12, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, O.; Ursaki, V.V.; Chai, G.; Chow, L.; Emelchenko, G.A.; Tiginyanu, I.M.; Gruzintsev, A.N.; Redkin, A.N. Selective hydrogen gas nanosensor using individual ZnO nanowire with fast response at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoza-Contreras, M.N.; Romo-Herrera, J.M.; Rios, L.A.; Garcia-Gutierrez, R.; Zepeda, T.A.; Contreras, O.E. Single ZnO nanowire-based gas sensors to detect low concentrations of hydrogen. Sensors 2015, 15, 30539–30544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Chang, Y.; Long, Y. High performance of nanostructured ZnO film gas sensor at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, H.-I.; Hsu, C.-S.; Huang, C.-C.; Wu, J.-S.; Chou, P.-C.; Liu, W.-C. Characteristics of ZnO nanorods-based ammonia gas sensors with a cross-linked configuration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Preferential growth of long ZnO nanowires and its application in gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Deng, X.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H.L.; Gengzang, D.J. Morphology controlled syntheses of Cr doped ZnO single-crystal nanorods for acetone gas sensor. Mater. Lett. 2016, 165, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.S.M.I.; Yaqoob, U.; Phan, D.-T.; Chung, G.-S. A novel flexible acetylene gas sensor based on PI/PTFE-supported Ag-loaded vertical ZnO nanorods array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y. High performance indium-doped ZnO gas sensor. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 954747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Ding, F.; Cao, Y.; Hu, P.; Fan, J.; Lu, C.; Yuan, F.; Shi, C.; Chen, Y. Sn doped ZnO layered porous nanocrystals with hierarchical structures and modified surfaces for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
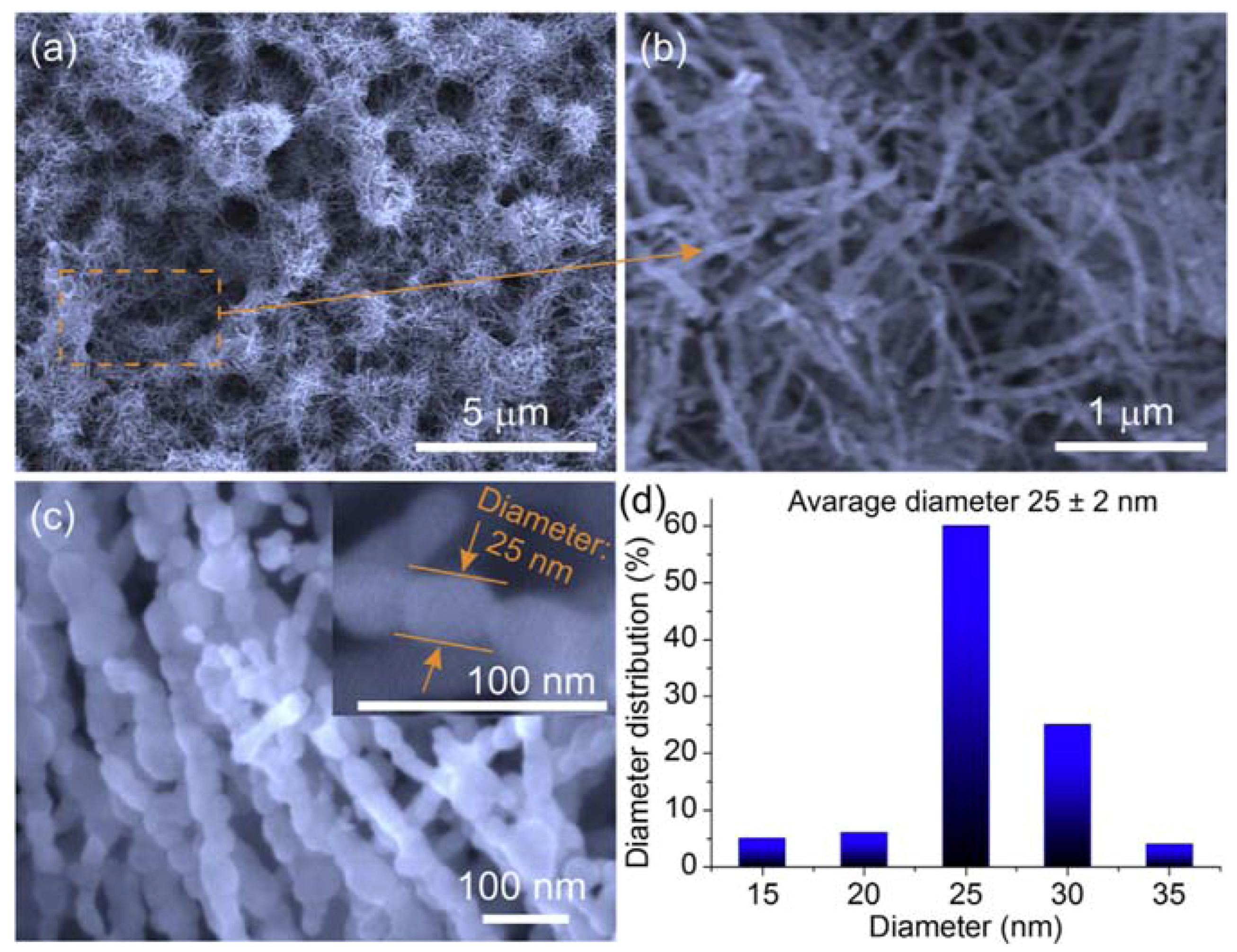
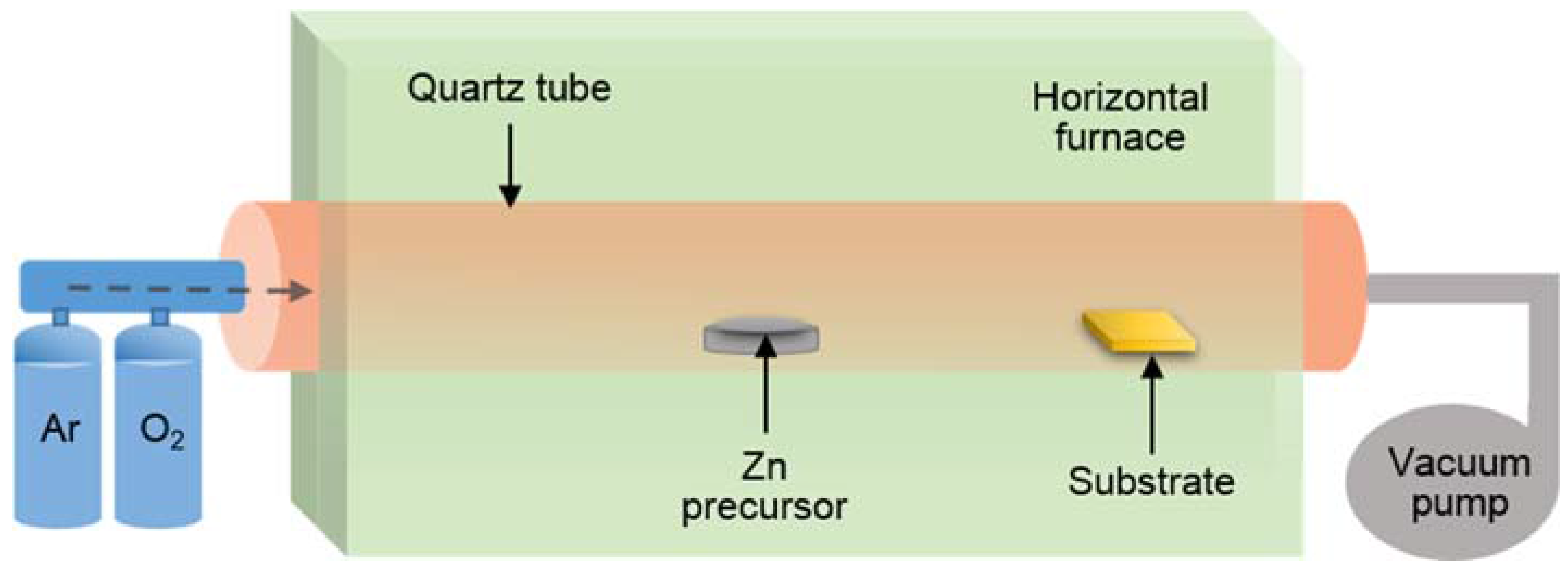
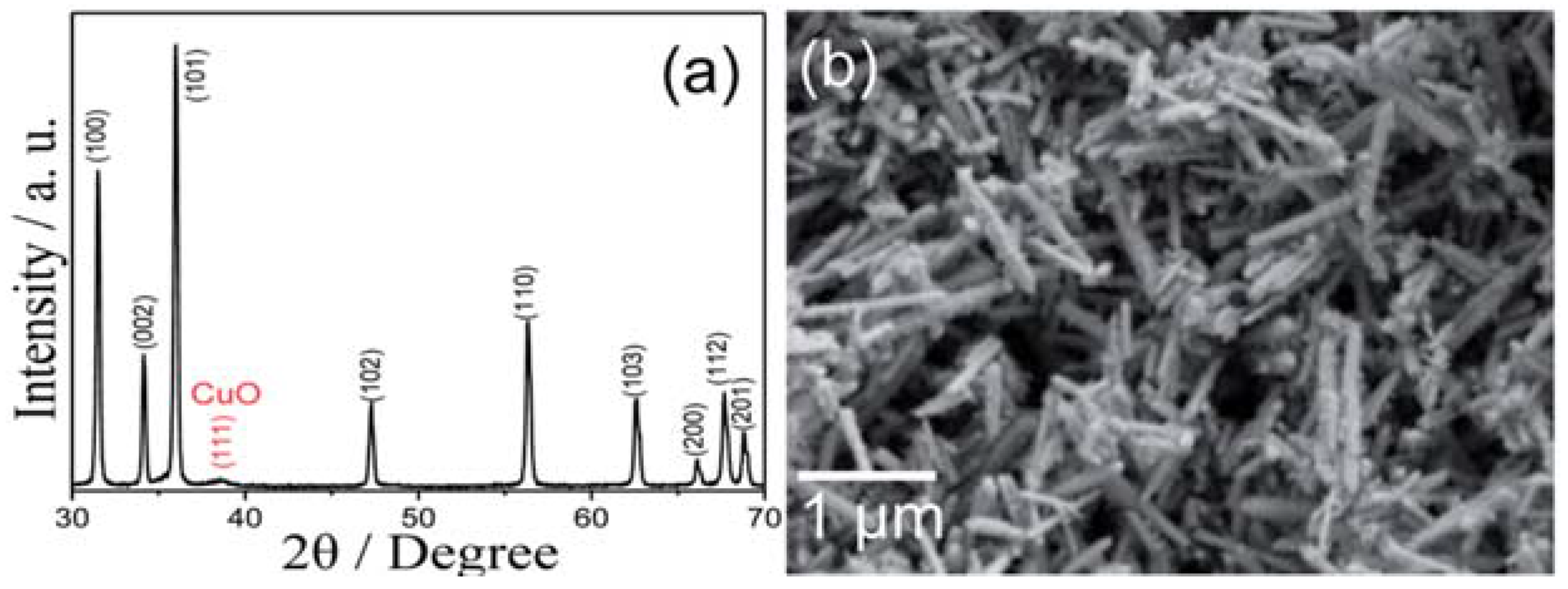
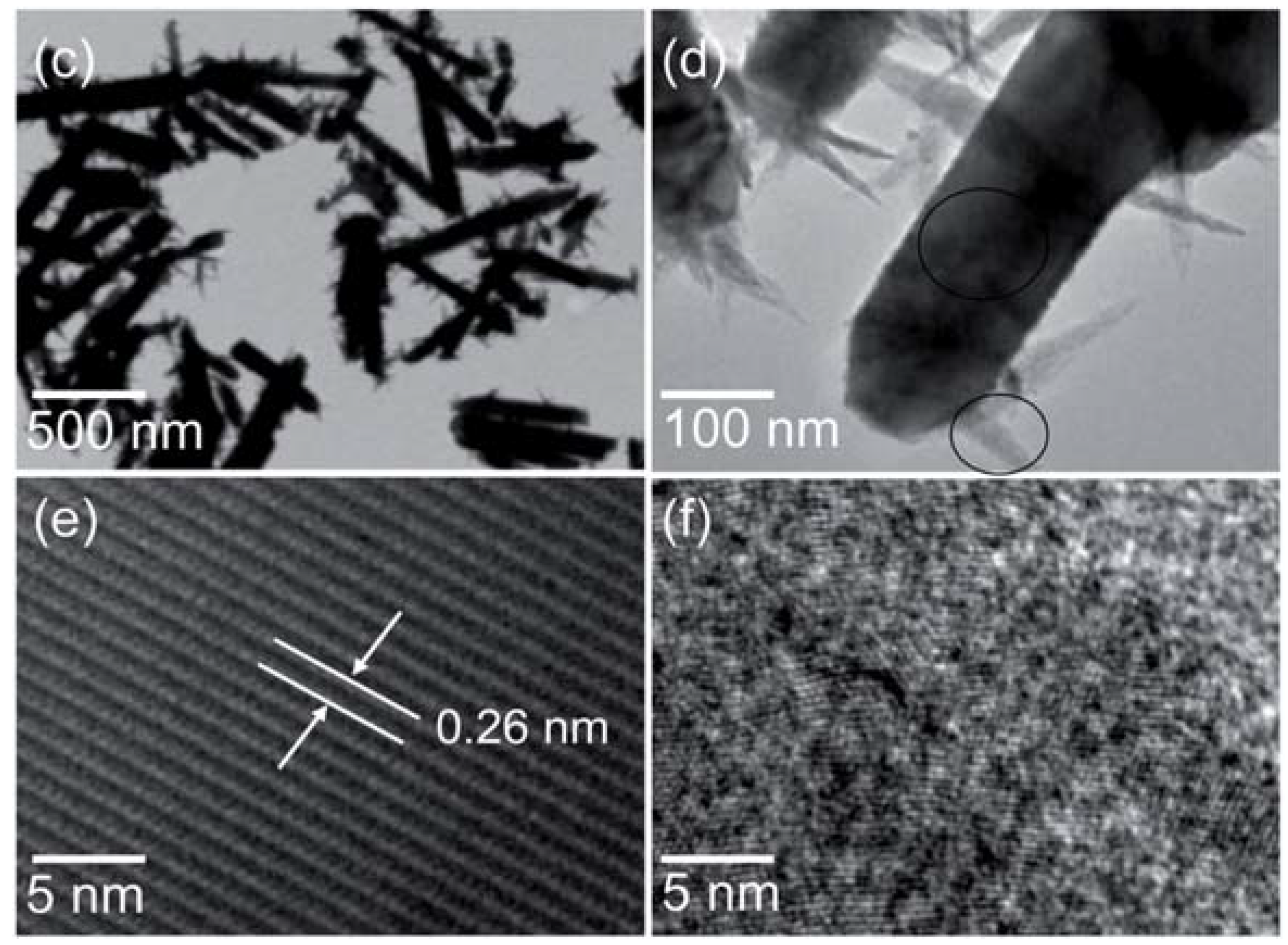
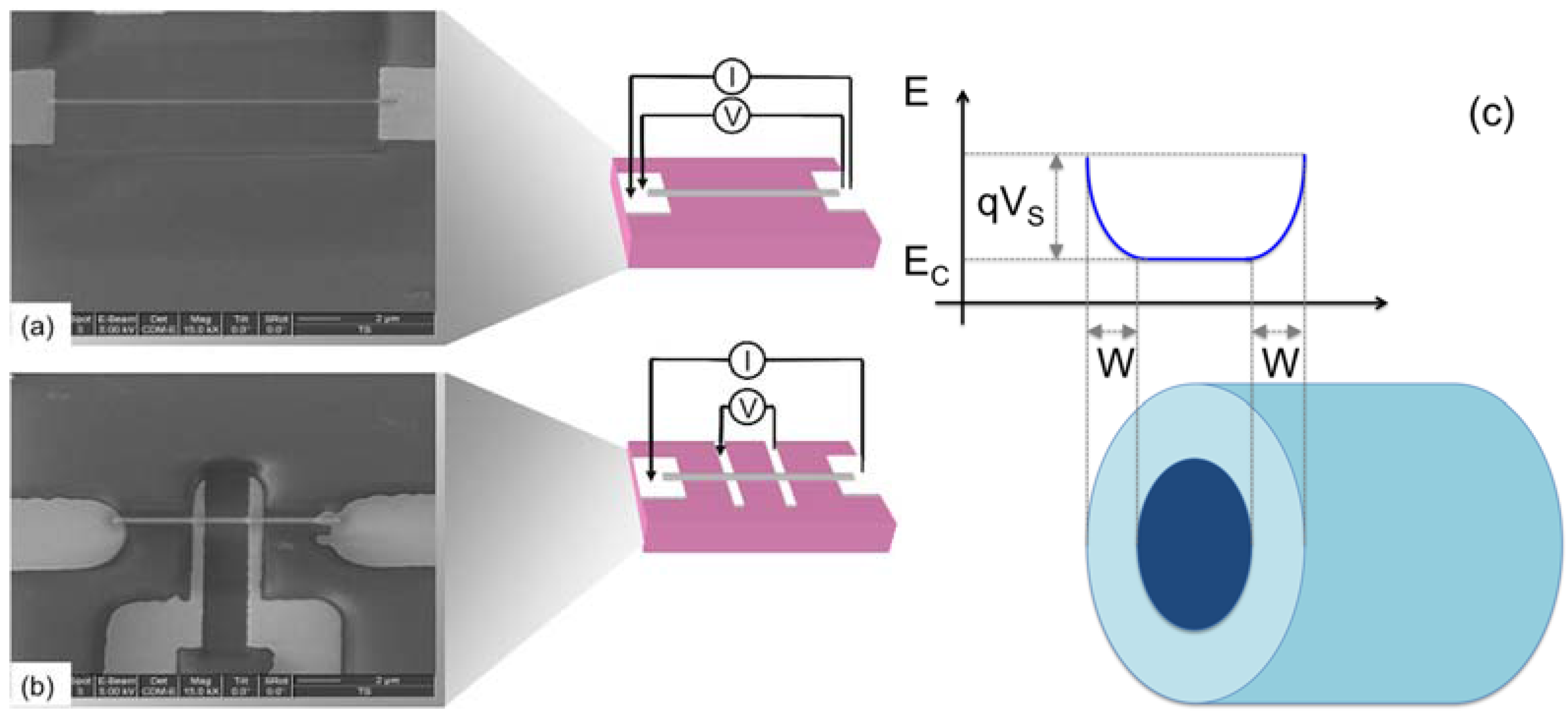
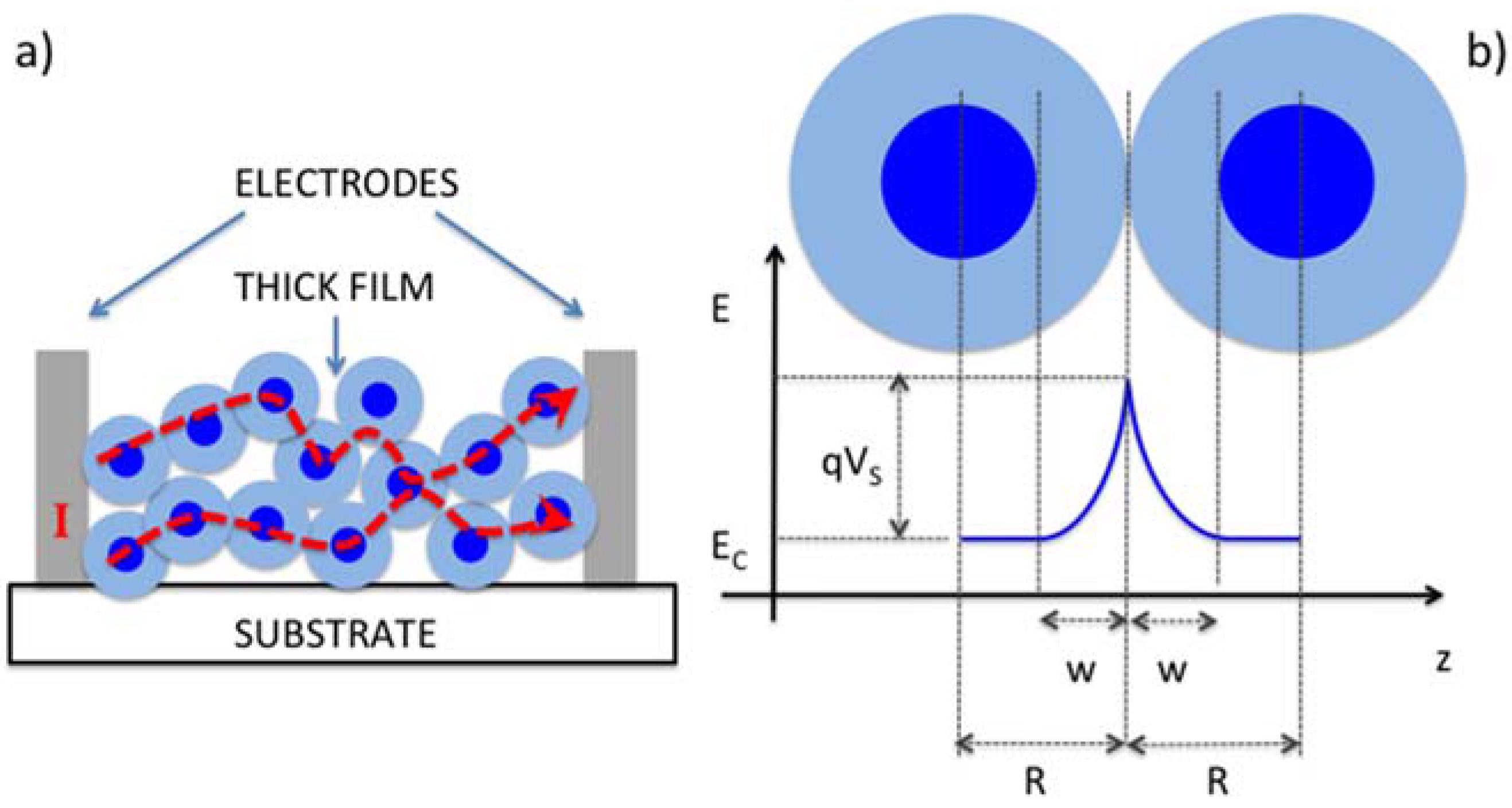
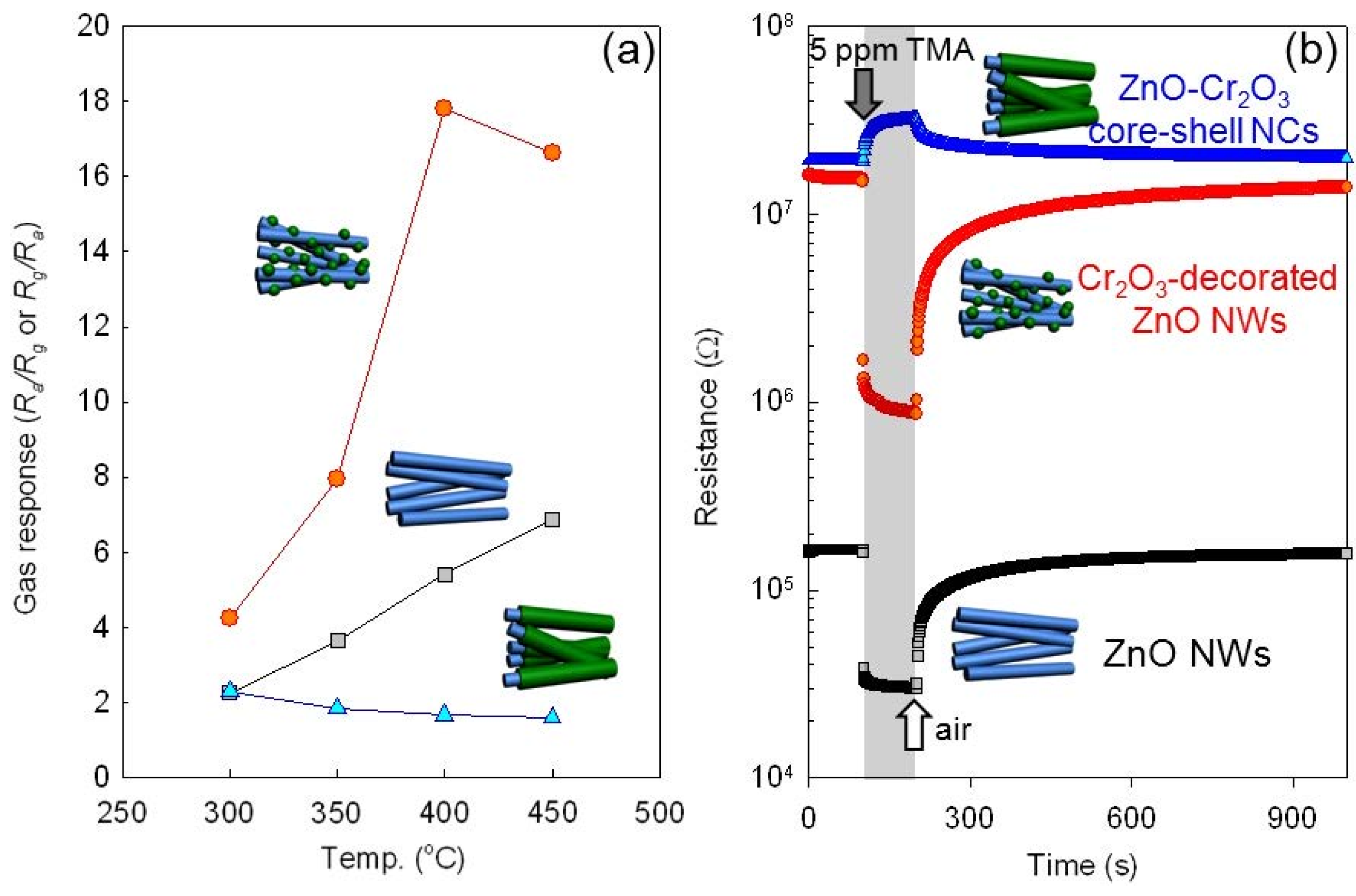
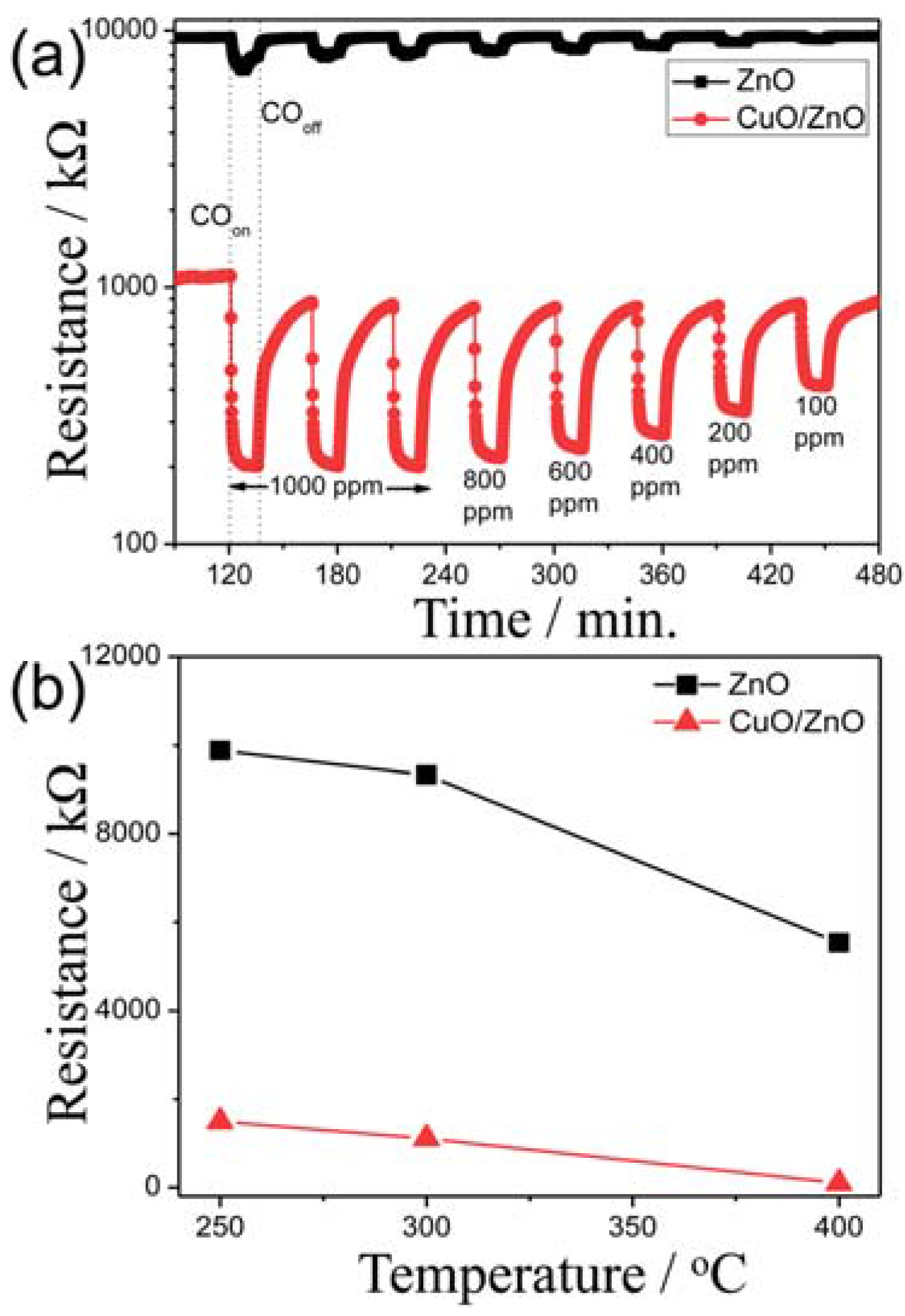
| Reference | Structure | Fabrication Method | Shape | Working Temperature | Tested Gas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | ZnO | ALD | Nanorods | From RT to 350 °C | H2 |
| [88] | ZnO | CVD | Nanowire | RT | H2 |
| [61] | ZnO | CVD | Nanowire | RT (UV activated) | Ethanol |
| [9] | ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Porous | 400 °C | Acetone, chlorophenol, methanol, formaldehyde |
| [14] | ZnO | Solvothermal method | Nanorods | 200–400 °C | Ethanol |
| [12] | ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | RT (UV activated) | O3 |
| [10] | ZnO | Solvothermal method | Flower-like, tubes | 100–300 °C | NO2 |
| [11] | ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | 260–320 °C | Ethanol |
| [89] | ZnO | CVD | Nanowire | From RT to 100 °C | H2 |
| [90] | ZnO | CVD | Nanorods | RT | Ethanol |
| [13] | ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Flower-like | 200–400 °C | NO2, CO, ethanol, acetaldehyde |
| [91] | ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | 200 °C | NH3 |
| [92] | ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanowires | 260–320 °C | Ethanol, 2-propanol, acetone, methanol, n-butanol |
| [19] | ZnO | Anodization, post-growth annealing | Nanowires | 300–500 °C | NO2, H2, CH4 |
| [23] | ZnO | CVD | Nanorods | 440–600 °C | O3 |
| [33] | Mn-ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | RT | O2 |
| [35] | Ti-ZnO | CVD | Nanorods | 250 °C | Ethanol |
| [40] | Au-ZnO | PVD | Nanorods | RT | H2S |
| [44] | Au-ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanowires | 340 °C | Toluene, benzene |
| [43] | Au-ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanowires | 380 °C | Ethanol |
| [93] | Cr-ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | 300 °C | Acetone |
| [94] | Ag-ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | 200 °C | C2H2 |
| [95] | In-ZnO | PVD | Nanobelt | 175–300 °C | Ethanol, Acetone |
| [83] | Graphene-ZnO | Hydrothermal synthesis | Nanorods | 300 °C | Ethanol |
| [96] | Sn-ZnO | Solvothermal | Porous | 300–500 °C | Benzene, acetone, toluene |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Ponzoni, A.; Sberveglieri, V.; Sberveglieri, G. ZnO Quasi-1D Nanostructures: Synthesis, Modeling, and Properties for Applications in Conductometric Chemical Sensors. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4020006
Galstyan V, Comini E, Ponzoni A, Sberveglieri V, Sberveglieri G. ZnO Quasi-1D Nanostructures: Synthesis, Modeling, and Properties for Applications in Conductometric Chemical Sensors. Chemosensors. 2016; 4(2):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4020006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalstyan, Vardan, Elisabetta Comini, Andrea Ponzoni, Veronica Sberveglieri, and Giorgio Sberveglieri. 2016. "ZnO Quasi-1D Nanostructures: Synthesis, Modeling, and Properties for Applications in Conductometric Chemical Sensors" Chemosensors 4, no. 2: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4020006
APA StyleGalstyan, V., Comini, E., Ponzoni, A., Sberveglieri, V., & Sberveglieri, G. (2016). ZnO Quasi-1D Nanostructures: Synthesis, Modeling, and Properties for Applications in Conductometric Chemical Sensors. Chemosensors, 4(2), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4020006