Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Anthraquinone Hair Dyes in Wastewaters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
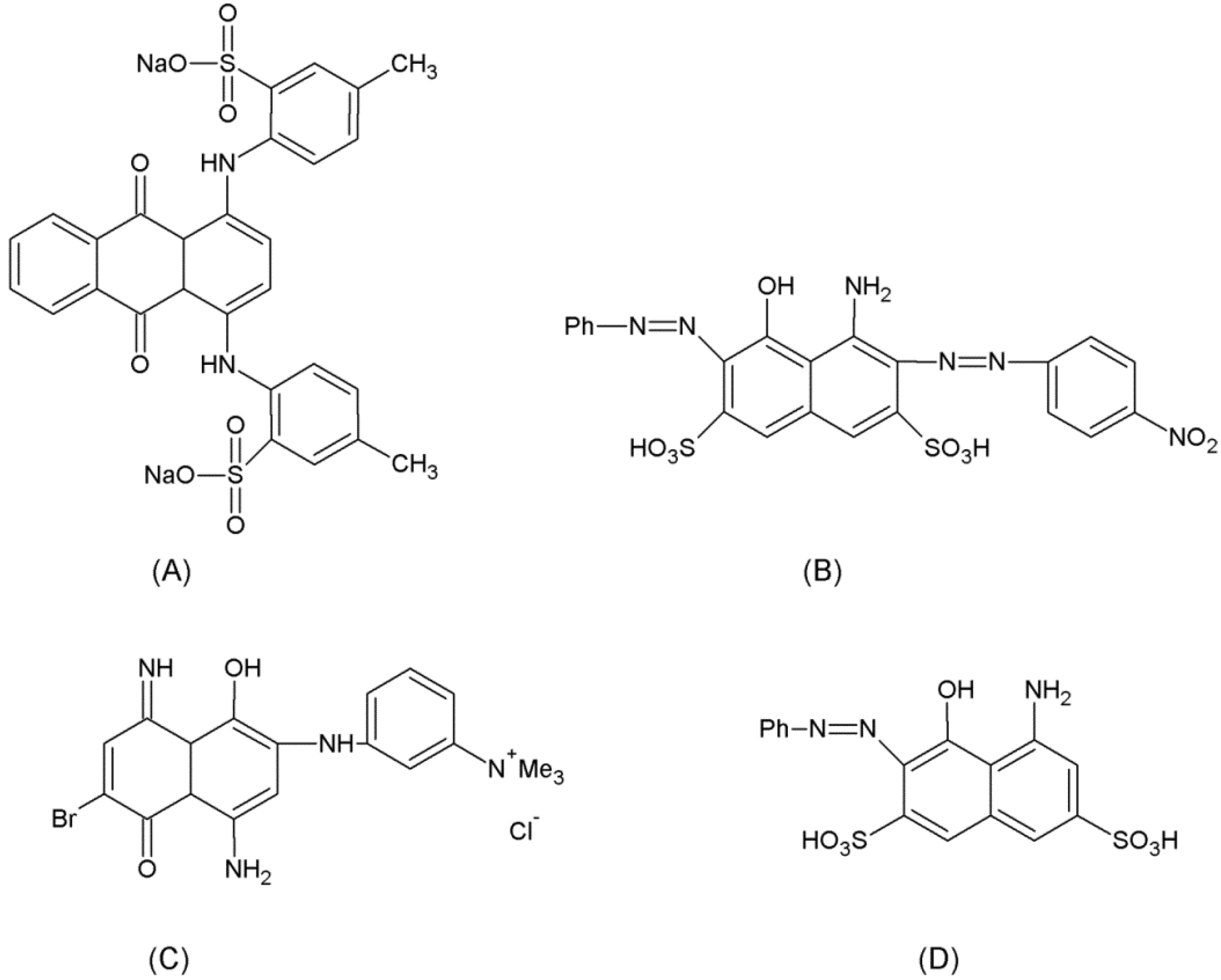
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Preparation of the Electrode
2.4. Analysis of Dyes in Tap Water and Wastewater
3. Results and Discussion
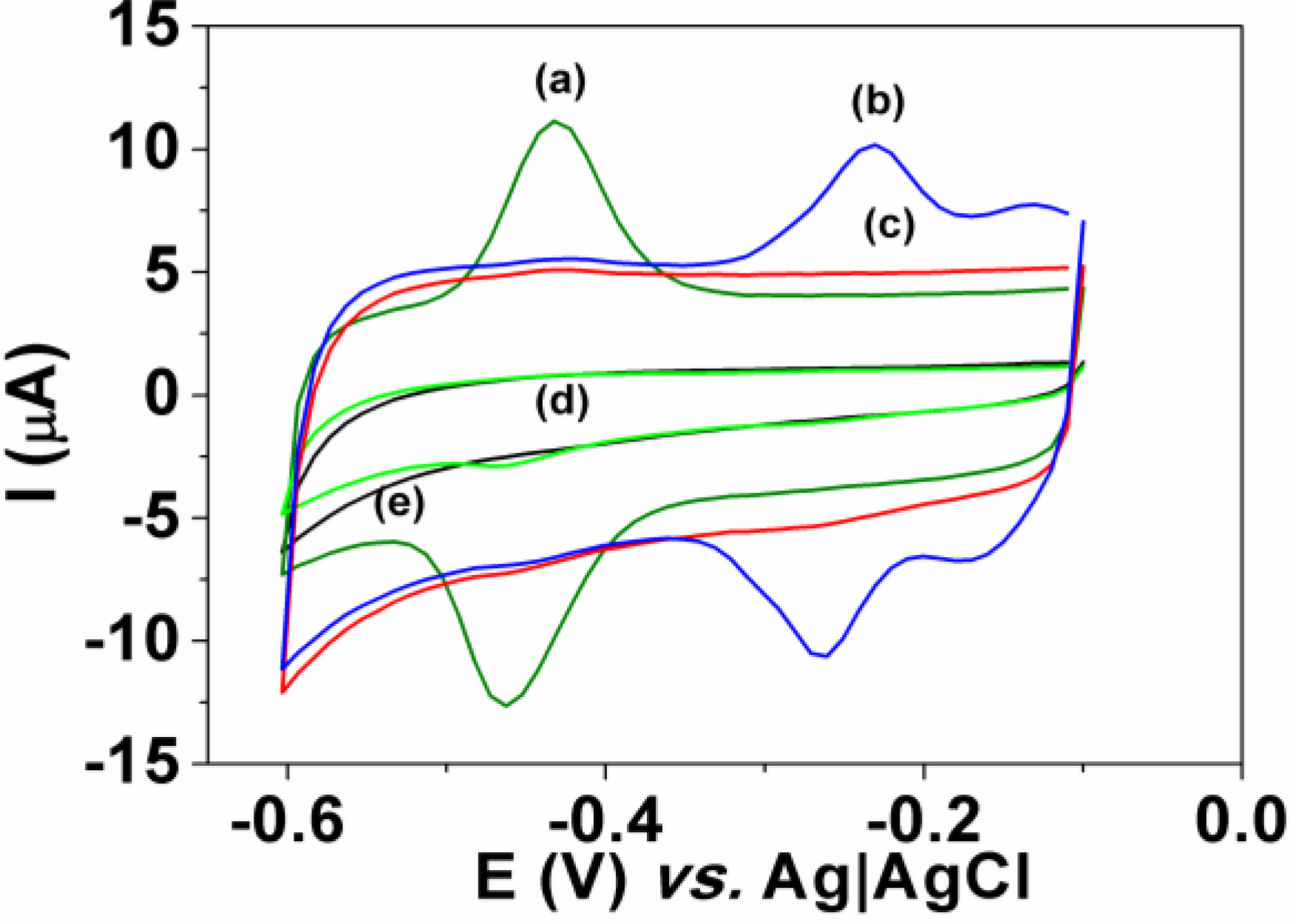
3.1. Voltammetric Behavior
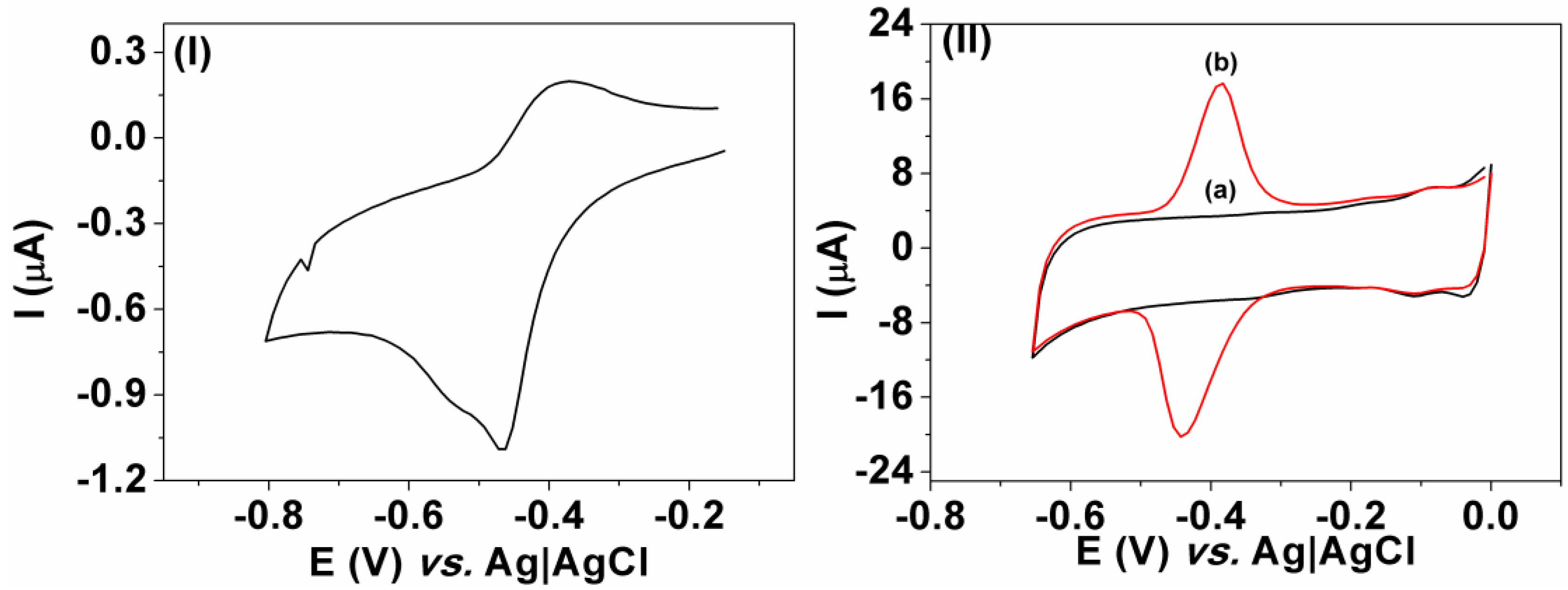
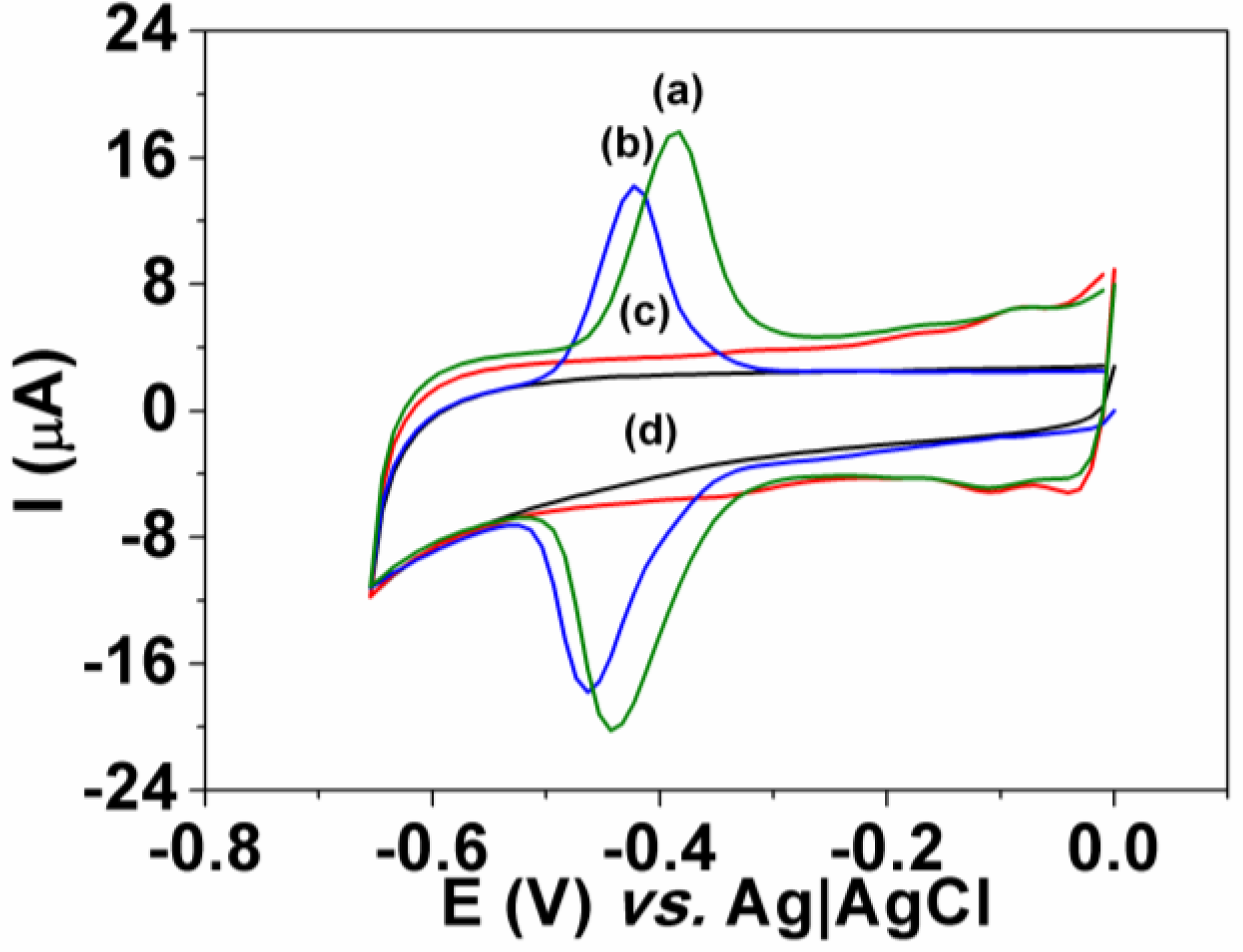
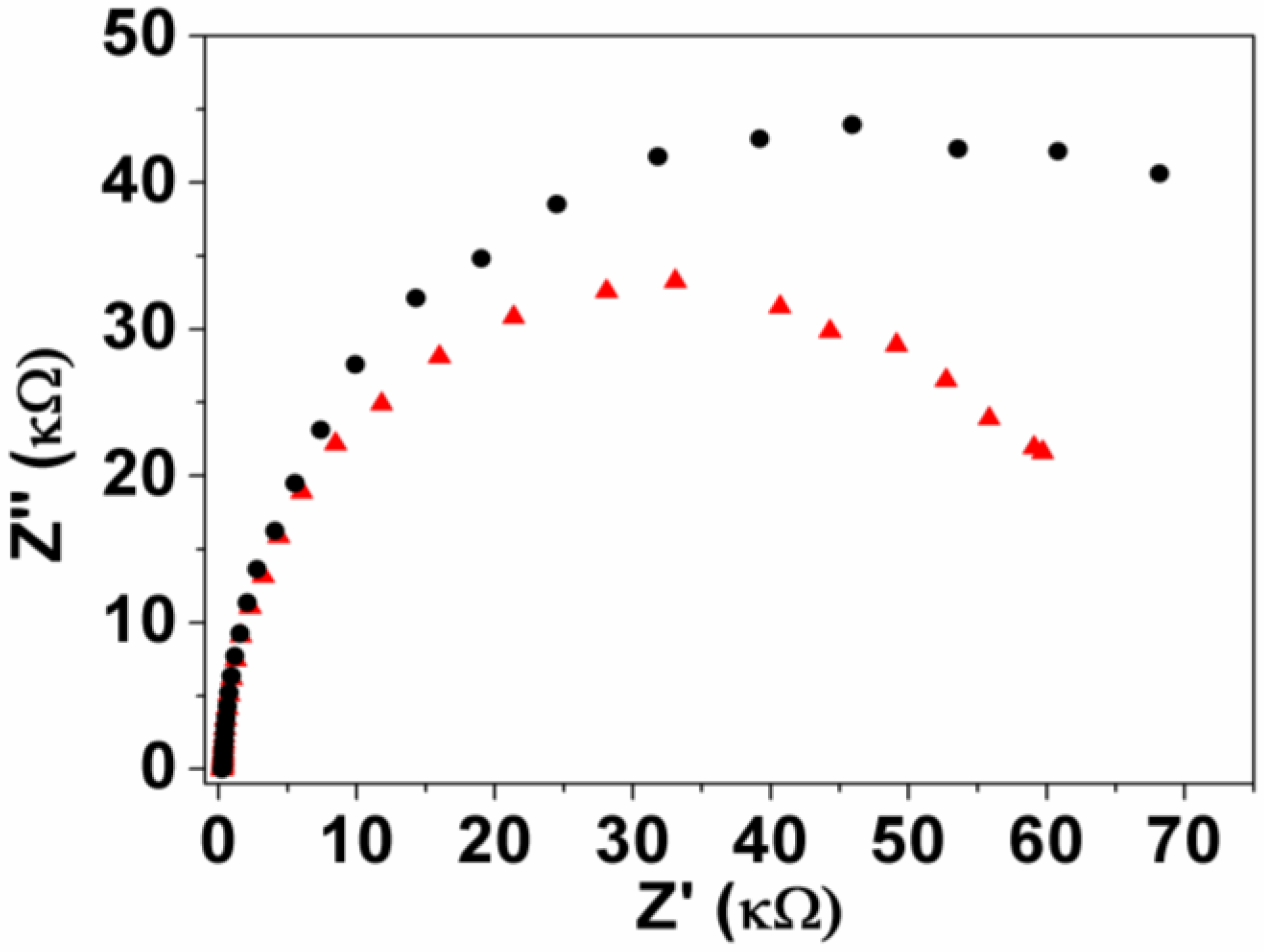

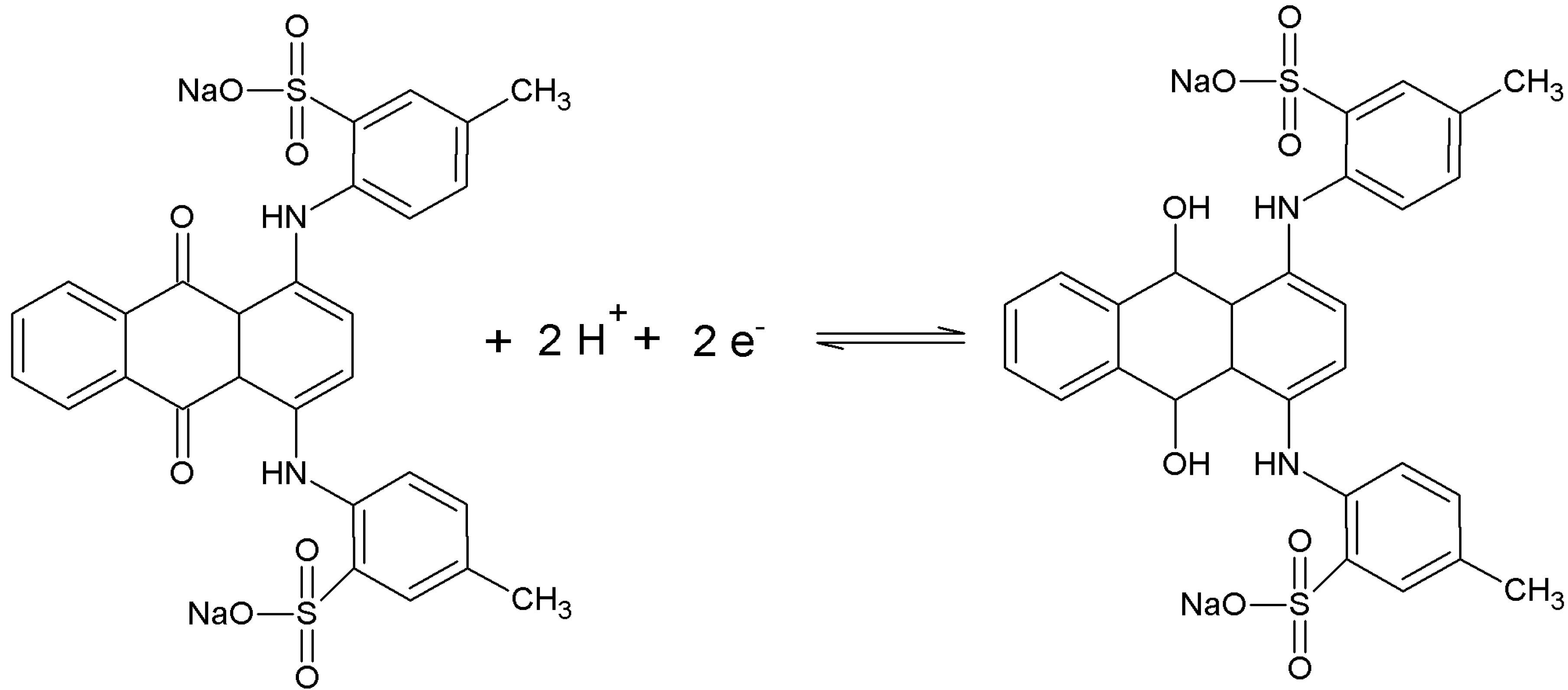
3.2. Interference
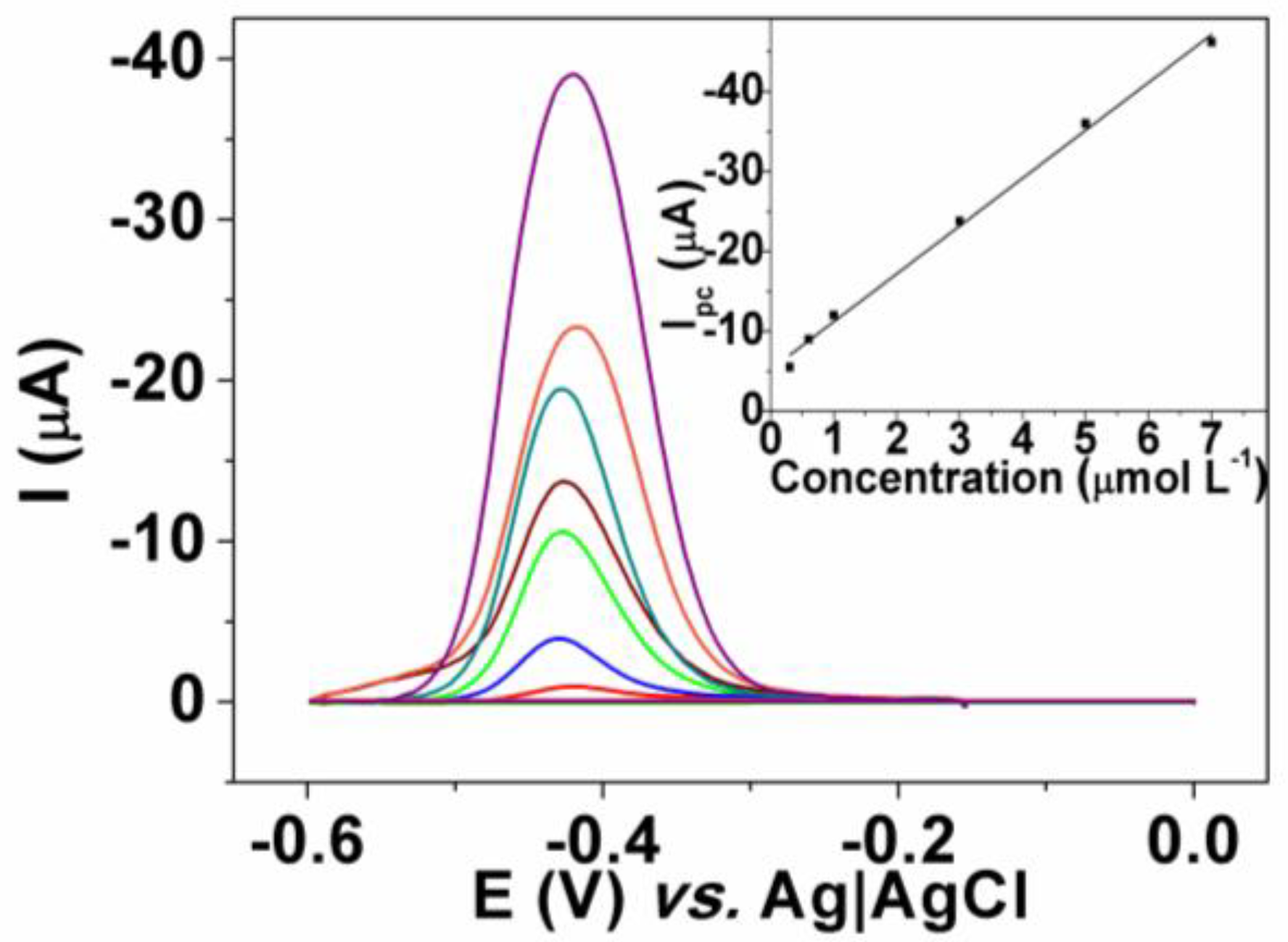
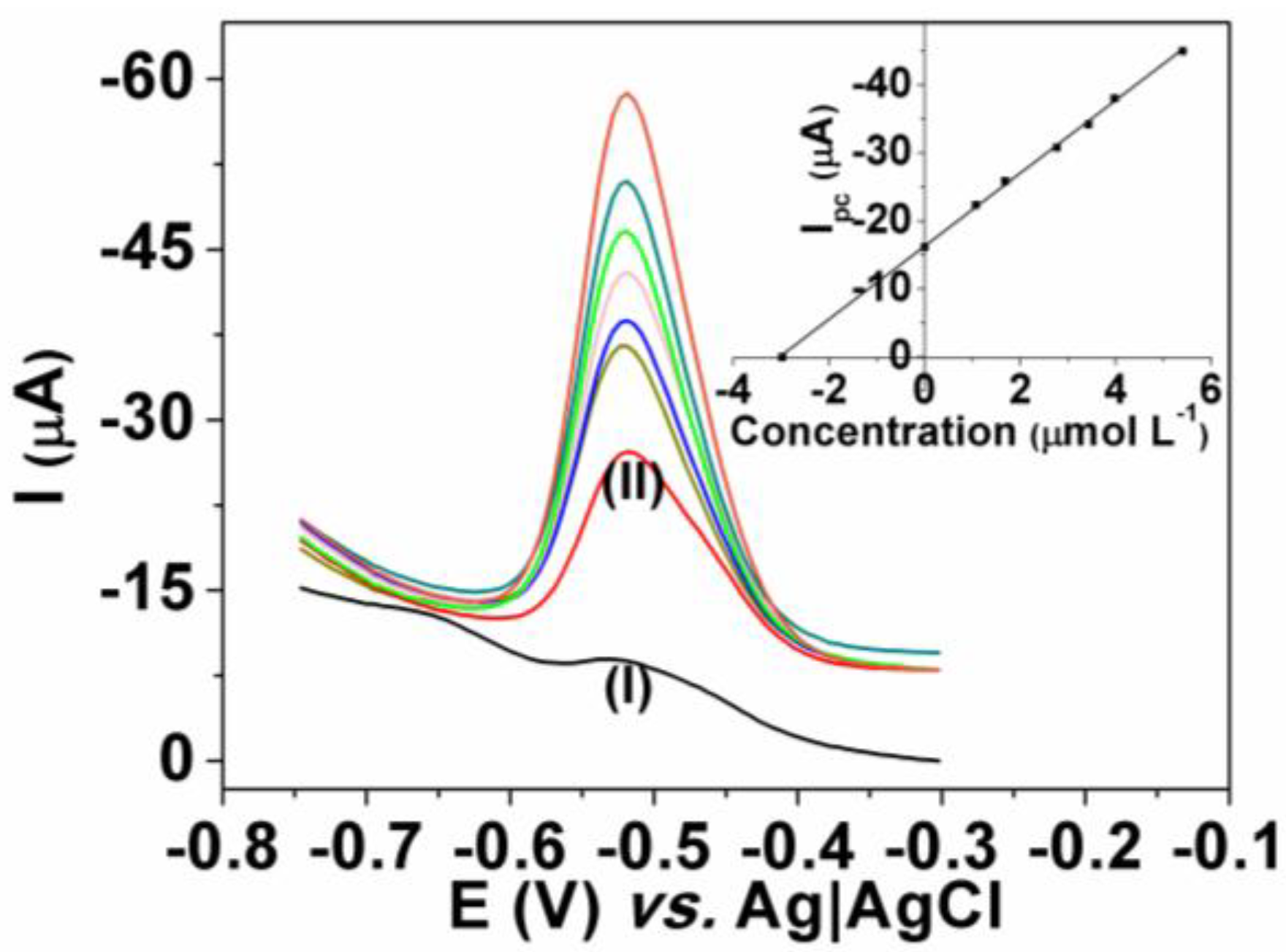
3.3. Dye Determination
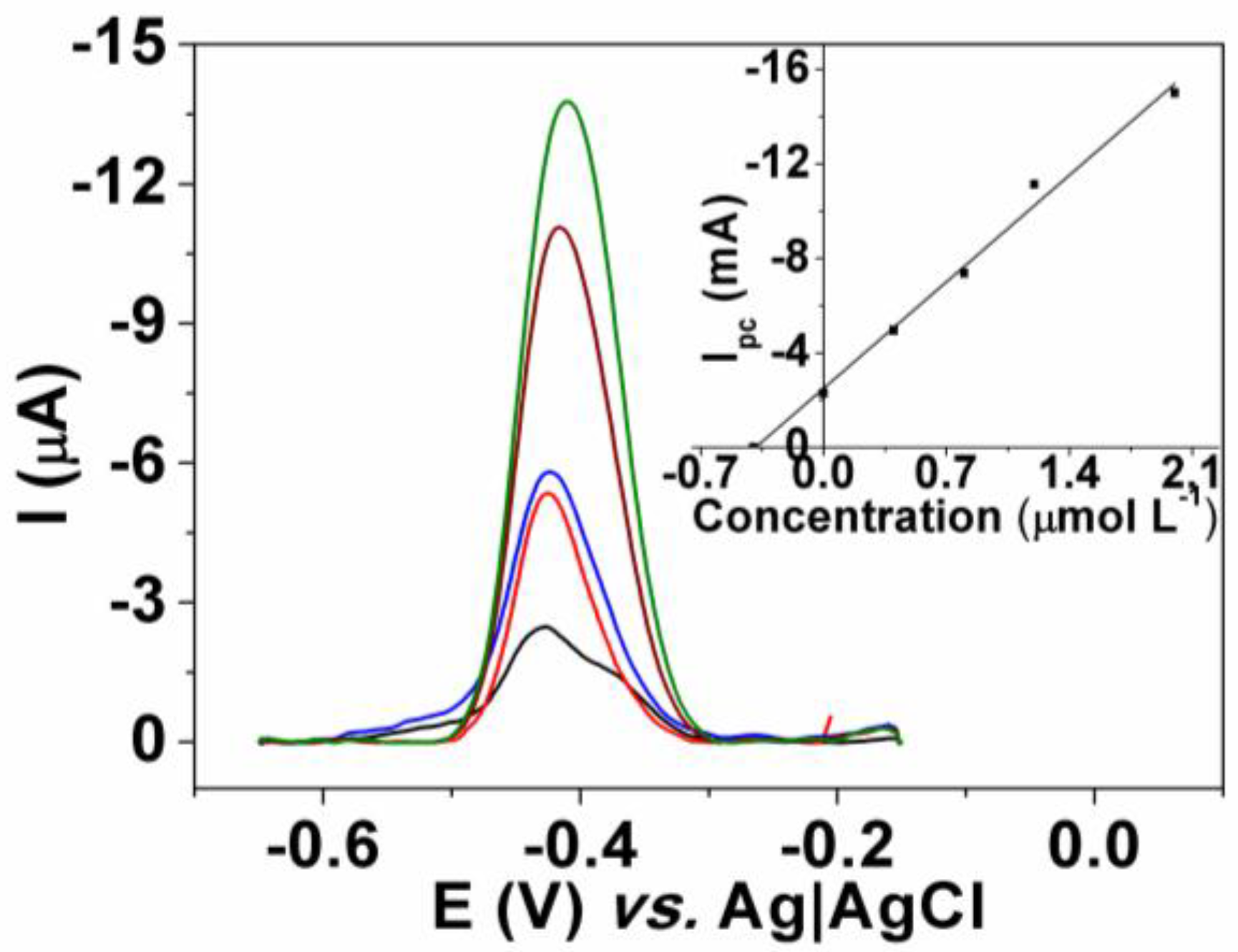
3.4. Analytical Application
| Method | CNTME | HPLC-DAD | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Found values (10−4 mol∙L−1) | 2.98 ± 0.038 | 2.96 ± 0.321 | 3 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hueber-Beckera, F.; Nohyneka, G.J.; Meulingb, W.J.A.; Benech-Kiefferc, F.; Toutain, H. Human systemic exposure to a [14C]-para-phenylenediamine-containing oxidative hair dye and correlation with in vitro percutaneous absorption in human or pig skin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, C.; Wilkinson, J. The Science of Hair Care, 2nd ed.; Francis & Taylor: London, UK, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, C.R. Chemical and Physical Behavior of Human Hair, 4th ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chisvert, A.; Cháfer, A.; Salvador, A. 4.3—Hair Dyes in Cosmetics. Regulatory Aspects and Analytical Methods, in Analysis of Cosmetic Products; Chisvert, A., Cháfer, A., Salvador, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 190–209. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, J.F. Chemistry of hair colorant processesScience as an aid to formulation and development. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1984, 35, 297–310. [Google Scholar]
- Lademanna, J.; Richtera, H.; Jacobia, U.; Patzelta, A.; Hueber-Beckerb, F.; Ribaudc, C.; Benech-Kiefferc, F.; Dufourb, E.K.; Sterrya, W.; Schaefera, H. Human percutaneous absorption of a direct hair dye comparing in vitro and in vivo results: Implications for safety assessment and animal testing. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, J.F. Principles of Efficients (r2) Greater Than 0.990 Was Obtained in the Cosmetics for the Dermatologist; Frost, S.N.H.F., Ed.; C.V. Mosby: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, G. Gas-liquid chromatographic determination of toxic diamines in permanent hair dyes. J. Chromatogr. A 1980, 193, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, H.; Kimura, Y.; Takano, S. Determination of dye intermediates in oxidative hair dyes by fused-silica capillary gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1986, 367, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B. Determination of 4-aminophenol in water by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1984, 299, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowle, C.J.; Malyan, A.P.; Matheson, A.M. Separation of the ortho, meta and para isomers of aminophenol by high-performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 1990, 115, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaro, M.C.; Bertolo, P.L.; Marengo, E. Determination of aromatic amines at trace levels by ion interaction reagent reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: Analysis of hair dyes and other water-soluble dyes. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 518, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrisano, V.; Gotti, R.; DiPietra, A.M.; Cavrini, V. Analysis of basic hair dyes by HPLC with on-line post-column photochemical derivatisation. Chromatographia 1994, 39, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrisano, V.; Gotti, R.; Roveri, P.; Cavrini, V. Analysis of semipermanent hair dyes by HPLC with on-line post-column photochemical derivatisation. Chromatographia 1997, 44, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prchal, V.; Krejčová, J.; Vyskočil, V.; Pecková, K.; Fischer, J.; Zima, J.; Barek, J. Determination of 4-Aminobiphenyl and 4-Nitrobiphenyl by HPLC with Electrochemical, UV Spectrophotometric, and Fluorescent Detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar]
- Phirke, S.S.; Saha, M. Determination of Lawsone by HPTLC in Lawsonia Inermis L. Callus and Plantlets Regenerated in vitro. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 764–766. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, N.; Lasserre, P.; Boré, P.; Kalopissis, G. Percutaneous absorption of p-phenylene diamine during an actual hair dyeing procedure. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1988, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyüz, M.; Ata, Ş. Determination of aromatic amines in hair dye and henna samples by ion-pair extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainthorant, C.; Morin, Ph.; Dreux, M.; Baudry, A.; Goetz, N. Separation of phenylenediamine, phenol and aminophenol derivatives by micellar electrokinetic chromatography Comparison of the role of anionic and cationic surfactants. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 717, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, S. Host-guest complexation in capillary isotachophoresis: II. Determination of aminophenol and diaminobenzene isomers in permanent hair colorants by using capillary isotachophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 1989, 470, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-E.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, T.-Z. Separation of benzenediamines, benzenediols and aminophenols in oxidative hair dyes by micellar electrokinetic chromatography using cationic surfactants. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 837, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, E.; Neuhoff, C.; Villa, C. Application of high-performance liquid chromatography in the analysis of direct dyes in semipermanent hair colouring cosmetics. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1997, 19, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, E.; Bargagna, A.; Longobardi, M.; Dorato, S. Application of TLC and HPTLC in the analysis of semipermanent hair dyes. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1994, 16, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpi, C.; Ninci, F.; Centini, M.; Anselmi, C. High-performance liquid chromatography determination of direct and temporary dyes in natural hair colourings. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 796, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, R.A.G.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Highly Ordered TiO2 Nanotubes for Electrochemical Sensing of Hair Dye Basic Brown 17. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudari, F.F.; Almeida, L.C.; Silva, B.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of p-phenylenediamine and resorcinol in permanent hair dyeing and tap water by composite carbon nanotubes/chitosan modified electrode. Microchem. J. 2014, 116, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, B. Ultrasound-assisted matrix solid-phase dispersive liquid extraction for the determination of intermediates in hair dyes with ion chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 752, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hu, S. Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensors: Principles and Applications in Biomedical Systems. J. Sens. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Hallaj, R. Catalytic oxidation of thiols at preheated glassy carbon electrode modified with abrasive immobilization of multiwall carbon nanotubes: Applications to amperometric detection of thiocytosine, L-cysteine and glutathione. Talanta 2005, 66, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, A.; Mahdioun, M.; Noorbakhsh, A.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Ghavami, R. A novel non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on single walled carbon nanotubes–manganese complex modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 3387–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhian, S.; Asadian, E. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and isoniazid using thionine immobilized multi-walled carbon nanotube modified carbon paste electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Pundir, C.S. An amperometric biosensor based on acetylcholinesterase immobilized onto iron oxide nanoparticles/multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified gold electrode for measurement of organophosphorus insecticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 701, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Amiri-Aref, M.; Baghayeri, M. Electrodeposition of quercetin at a multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode as a novel and efficient voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of levodopa, uric acid and tyramine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keihan, A.H.; Sajjadi, S. Improvement of the electrochemical and electrocatalytic behavior of Prussian blue/carbon nanotubes composite via ionic liquid treatment. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, C.C.; Jannuzzi, S.A.V.; Santhiago, M.; Timm, R.A.; Formiga, A.L.B.; Kubota, L.T. Modified electrode using multi-walled carbon nanotubes and a metallopolymer for amperometric detection of L-cysteine. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Sharma, S. Glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes sensor for the quantification of antihistamine drug pheniramine in solubilized systems. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Chu, X.; Ling, Y.; Huang, J.; Lin, Y.; Chang, J. Simultaneous determination of dyes in wines by HPLC coupled to quadrupole orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, P.A.; Boralle, N.; Stradiotto, N.R.; Furlan, M.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Decolourization of anthraquinone reactive dye by electrochemical reduction on reticulated glassy carbon electrode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2004, 15, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Ye, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Yu, C. A voltammetric sensor based on graphene-modified electrode for simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 650, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Sekar, C.; Wilson, J.; Kim, S.J. A promising electrochemical sensing platform based on ternary composite of polyaniline-Fe2O3-reduced graphene oxide for sensitive hydroquinone determination. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.S.; Swetha, P. Simple adsorption of anthraquinone on carbon nanotube modified electrode and its efficient electrochemical behaviors. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, N.B.T.A.; Rinaldi, J.-P.T.A.; Reiche, S.; Kutty, M.G. Chemically Modified Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) with Anchored Acidic Groups. Sains Malays. 2012, 41, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Oliveira, R.; Hudari, F.; Franco, J.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Anthraquinone Hair Dyes in Wastewaters. Chemosensors 2015, 3, 22-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3010022
De Oliveira R, Hudari F, Franco J, Zanoni MVB. Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Anthraquinone Hair Dyes in Wastewaters. Chemosensors. 2015; 3(1):22-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Oliveira, Ricardo, Felipe Hudari, Jefferson Franco, and Maria Valnice Boldrin Zanoni. 2015. "Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Anthraquinone Hair Dyes in Wastewaters" Chemosensors 3, no. 1: 22-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3010022
APA StyleDe Oliveira, R., Hudari, F., Franco, J., & Zanoni, M. V. B. (2015). Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Anthraquinone Hair Dyes in Wastewaters. Chemosensors, 3(1), 22-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3010022





