Unlocking the Future: Carbon Nanotubes as Pioneers in Sensing Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Material Type | Electrical Conductivity | Surface Area | Mechanical Strength | Sensitivity to Analytes | Functionalization Possibility | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | High (102–105 S/m) | Very High (>1000 m2/g) | Exceptional (Young’s modulus~1 TPa) | Very high (down to ppb/ppt levels) | Excellent (Covalent and Non-Covalent) | [17] |
| Graphene | High (~104 S/m) | High (~2630 m2/g) | High (Young’s modulus~1 TPa) | High | Excellent | [21,27] |
| Metal Oxides (e.g., SnO2, ZnO) | Moderate to Low (~10−2–100 S/m) | Moderate (~10–50 m2/g) | Brittle | Moderate | Limited (Surface Modification) | [28] |
| Conducting Polymers (e.g., Polyanilin, Polypyrrole) | Low to Moderate (~10−3–102 S/m) | Moderate (~50–100 m2/g) | Low to moderate | High (selective in certain environments) | Moderate | [29] |
| Noble Metals (e.g., Au, Pt, Ag) | High (~107 S/m) | Low (<10 m2/g) | High (ductile) | High (surface plasmon effect) | Limited (Surface Adsorption) | [30] |
Objectives of the Review
- To provide a fundamental understanding of CNT structures, properties, and their relevance to sensing mechanisms.
- To systematically discuss the integration of CNTs in various sensor types, including gas sensors, chemical sensors, biosensors, and pressure sensors.
- To highlight recent advancements in CNT-based sensor design, fabrication techniques, and performance optimization.
- To explore current challenges and limitations hindering the commercialization and large-scale deployment of CNT-based sensors.
- To present future perspectives and emerging trends in the development of CNT-enabled sensing platforms for real-time and smart sensing applications.
2. Properties of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
2.1. Structural Characteristics of CNTs
2.2. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of CNTs
2.2.1. Electrical Properties of CNTs
2.2.2. Mechanical Properties of CNTs
2.2.3. Synergistic Role of Electrical and Mechanical Properties in Sensing
2.2.4. Influence of Defects and Functionalization on Properties
2.3. Surface Area and Chemical Reactivity of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
2.4. Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) for Sensing Applications
| Functionalization Method | Mechanism | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covalent Functionalization | Formation of chemical bonds (e.g., carboxyl, amine groups) on CNT surface | Strong and stable attachment, improved dispersion, enhanced sensitivity | Disruption of CNT π-conjugation, reduced conductivity | Gas sensors, biosensors, chemical sensors | [104,105,106] |
| Non-Covalent Functionalization | Physical adsorption via π–π stacking, van der Waals, hydrophobic interactions | Preserves electrical properties, maintains structural integrity, easy processing | Relatively weaker attachment, potential desorption under harsh conditions | Biosensors, flexible and wearable sensors | [107] |
| Polymer Functionalization | Wrapping or grafting of conductive or selective polymers on CNTs | Enhanced selectivity, improved analyte interaction, tunable properties | Possible decrease in conductivity, complex synthesis | Chemical sensors, environmental sensors, gas sensors | [108,109] |
| Metal Nanoparticle Decoration | Decoration of CNT surface with metal nanoparticles (Au, Pt, Pd, Ag) | Improved catalytic activity, increased sensitivity, enhanced electron transfer | Aggregation of nanoparticles, cost of noble metals | Electrochemical biosensors, gas sensors, glucose sensors | [110] |
| Supramolecular Functionalization | Host–guest chemistry using cyclodextrins, calixarenes, crown ethers | High selectivity, reversible interactions, minimal damage to CNT structure | Selectivity limited to specific analytes, complex synthesis | Chemical sensors, ion detection, small molecule sensing | [111] |
3. Types of Carbon Nanotubes and Their Applications
3.1. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs)
3.2. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
Applications of MWCNTs in Sensing Technologies
3.3. Comparison of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs) and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) in Sensing Applications
3.4. Hybrid CNT-Based Sensing Materials
| Type of CNTs | Structure Features | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Walled CNTs (SWCNTs) | Single graphene sheet rolled into a cylinder (diameter ~0.4–3 nm) | Sensors, drug delivery, nanoelectronics, energy storage devices | [185,186] |
| Multi-Walled CNTs (MWCNTs) | Multiple concentric graphene cylinders (diameter ~2–100 nm) | Biosensors, structural composites, supercapacitors, emi shielding | [187,188] |
| Double-Walled CNTs (DWCNTs) | Two concentric graphene cylinders | Biomedical imaging, gas sensing, flexible electronics | [189] |
| Functionalized CNTs | Chemically or physically modified CNTs with functional groups | Biosensors, environmental monitoring, targeted drug delivery | [190,191,192] |
| Doped CNTs | CNTs doped with heteroatoms (N, B, P, S) to enhance properties | Gas sensing, catalysis, energy storage | [193] |
| CNT Composites | CNTs embedded in polymers, metals, or ceramics | Smart textiles, flexible electronics, antibacterial coatings | [194] |
4. CNT-Based Sensors
4.1. Gas Sensors
4.2. Environmental and Industrial Monitoring
4.3. Chemical Sensors
4.3.1. Sensing of Chemical Pollutants
4.3.2. Chemical Reaction Monitoring
4.4. Biosensors
- Detection of glucose for diabetes management.
- Monitoring of DNA hybridization events for genetic screening.
- Detection of specific proteins and enzymes as disease biomarkers.
- Identification of pathogens (bacteria and viruses) for infection control.
- Detection of hormones and neurotransmitters for physiological monitoring [241].
4.4.1. Role of CNTs in Medical Diagnostics
4.4.2. CNT-Based Electrochemical Biosensors in Medical Diagnostics
4.4.3. CNT-Based Optical Biosensors for Medical Diagnostics
4.4.4. CNT-Based Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Biosensors in Medical Diagnostics
4.5. Pressure and Strain Sensors
4.5.1. Structural Monitoring in Aerospace and Engineering
4.5.2. Flexible Electronics
| Type of CNT-Based Sensor | Sensing Mechanism | Target Analyte/Parameter | Key Advantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical CNT Sensor | Electron transfer, redox reaction enhancement | Glucose, heavy metals, biomolecules | High sensitivity, fast response, low detection limit | [1,2] |
| Gas CNT Sensor | Adsorption-induced conductivity change | NH3, H2, CO2, NO2, VOCs | High surface area, room temperature operation | [3,4] |
| Optical CNT Sensor | Fluorescence quenching/enhancement, Raman scattering | DNA, proteins, metal ions | Label-free detection, real-time monitoring | [5] |
| Field-Effect Transistor (FET) CNT Sensor | Modulation of electrical conductivity via field effect | Biomolecules, gases, pathogens | High selectivity, low power consumption | [6,7] |
| Piezoelectric CNT Sensor | Strain-induced charge generation | Pressure, vibration, motion | Flexibility, mechanical robustness | [8] |
| Biosensor with Functionalized CNTs | Specific bioreceptor–analyte interaction | Glucose, DNA, antigens, enzymes | High specificity, enhanced biocompatibility | [9,10] |
5. Mechanisms of Sensing with CNTs
5.1. Electrical Conductivity Changes
5.2. Surface Interaction and Adsorption
5.3. Optical Properties in Sensing
5.4. Molecular Recognition and Specificity
| Sensing Mechanism | Working Principle | Key Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemiresistive Mechanism | Change in electrical resistance due to analyte adsorption on CNT surface | Simple design, fast response, low cost | Poor selectivity, environmental sensitivity | [271] |
| Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Mechanism | Modulation of current flow in CNT channel under applied electric field after analyte interaction | High sensitivity, low power consumption | Complex fabrication, limited stability | [272] |
| Electrochemical Mechanism | Electron transfer between analyte and CNT-modified electrode surface | High sensitivity, real-time monitoring | Need for electrolyte, possible fouling | [273] |
| Optical Sensing Mechanism | Change in optical properties (fluorescence, absorbance, Raman scattering) upon analyte binding | Non-invasive, label-free detection | Optical signal instability, expensive equipment | [274] |
| Piezoelectric/Strain Sensing Mechanism | Mechanical deformation induces electrical signals in CNT composites | High flexibility, suitable for wearable sensors | Limited to mechanical stimuli sensing | [275] |
6. Advancements in CNT-Based Sensing
6.1. Nanostructured CNT Sensors for Enhanced Sensitivity
6.1.1. Strategies for Nanostructured CNT Sensors
6.1.2. Enhanced Electrical and Electrochemical Properties
6.1.3. Nanocomposites and Hybrid Materials
6.1.4. Applications in Ultra-Sensitive Detection
6.2. Integration of CNTs with Other Nanomaterials
6.2.1. Metal Nanoparticles and CNT Hybrids
6.2.2. Metal Oxide–CNT Nanocomposites
6.2.3. Polymer–CNT Hybrid Sensors
6.2.4. CNT–Graphene and 2D Nanomaterial Hybrids
6.3. Smart Sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
6.4. Wearable and Portable CNT-Based Sensors
| Type of Sensor Device | Sensing Target | Device Configuration | Key Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT-Based Sweat Sensor | Electrolytes (Na+, K+), glucose, lactate | Flexible CNT electrode on patch or textile | Non-invasive monitoring, real-time analysis | [53] |
| CNT-Based Strain/Pressure Sensor | Body motion, pulse, respiration | CNT/polymer composite films or fibers | High flexibility, stretchability, skin-conformability | [294,295] |
| CNT-Based Gas Sensor Wearable | Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), NH3, CO | CNT-coated flexible substrates or masks | Lightweight, low power, room temperature sensing | [204] |
| CNT-Based Temperature Sensor | Body temperature monitoring | CNT-integrated fabric or tattoo sensors | Continuous monitoring, fast response | [296] |
| CNT-Based Biosensor Patch | Biomolecules (glucose, DNA, uric acid) | Functionalized CNT arrays on skin patches | High sensitivity, biocompatible, portable | [297] |
| CNT-Integrated Smart Textiles | Multiple parameters (pressure, strain, moisture) | CNT yarns, CNT-coated fibers in fabric | Washable, durable, multiplexed sensing | [298] |
6.5. Integration of CNT-Based Sensors with AI, Machine Learning, and IoT Technologies
7. Challenges in CNT-Based Sensing Technologies
7.1. Functionalization and Stability Issues
- Covalent Functionalization: This approach entails forming chemical bonds between functional groups and the CNT structure. While it can significantly enhance solubility and provide specific binding sites, it may introduce defects into the CNTs, potentially altering their intrinsic properties such as electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. For instance, oxidation processes can introduce carboxyl groups, but excessive oxidation can compromise the CNT structure.
- Non-Covalent Functionalization: This method relies on physical interactions, such as π–π stacking or van der Waals forces, to attach functional molecules to the CNT surface without altering its inherent structure. While this preserves the CNTs’ original properties, the stability of the attached molecules can be a concern, as desorption may occur over time.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to varying temperatures, humidity levels, and chemical environments can affect the integrity of functionalized CNTs. For example, high humidity can lead to the desorption of non-covalently attached molecules, reducing sensor reliability [198].
- Chemical Stability: Functional groups introduced during covalent functionalization may degrade over time or under specific conditions, leading to a loss of functionality. Ensuring that these groups remain stable throughout the sensor’s operational life is a significant challenge.
- Mechanical Stability: The process of functionalization, especially covalent methods, can introduce defects that compromise the mechanical integrity of CNTs. This can affect the durability and lifespan of the sensor [8].
- Optimized Functionalization Techniques: Carefully controlling reaction conditions during covalent functionalization can minimize defects. For instance, using milder oxidizing agents or shorter reaction times can reduce damage to the CNT structure [303].
- Protective Coatings: Applying protective polymer coatings can shield functionalized CNTs from environmental factors, enhancing their stability without significantly impacting their sensing capabilities [50].
- Hybrid Functionalization: Combining covalent and non-covalent methods can leverage the advantages of both approaches, achieving stable functionalization while preserving the CNTs’ intrinsic properties [304].
7.2. Sensitivity and Selectivity Limitations
- Baseline Drift: Over time, CNT sensors may exhibit changes in baseline resistance or current, affecting the accuracy of measurements. This drift can result from environmental factors or the gradual desorption of functional groups [305].
- Response Time: While CNT sensors often exhibit rapid response times, certain functionalizations or environmental conditions can slow the interaction between the analyte and the sensor surface, delaying detection [195].
- Non-Specific Binding: CNTs can interact with a wide range of molecules, leading to non-specific binding and false positives. For instance, gases like NH3 and NO2 can both donate or accept electrons, making it challenging to differentiate between them using pristine CNTs [90].
- Environmental Interference: Factors such as humidity and temperature can affect sensor responses. High humidity levels, for example, can lead to water molecule adsorption, altering the sensor’s baseline and response to target analytes.
- Specific Functionalization: Introducing functional groups or biomolecules that have a high affinity for the target analyte can enhance selectivity. For example, attaching antibodies specific to a biomarker can enable the detection of that biomarker amidst a complex mixture [306].
- Hybrid Nanomaterials: Combining CNTs with other nanomaterials, such as metal nanoparticles or polymers, can create synergistic effects that enhance both sensitivity and selectivity. These hybrids can provide additional binding sites or catalytic properties that improve sensor performance [307].
- Sensor Arrays: Employing arrays of CNT sensors, each functionalized differently, can allow for pattern recognition techniques to distinguish between multiple analytes, improving overall selectivity [308].
| Type of CNT Sensor | Sensitivity Limitations | Selectivity Limitations | Influencing Factors | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemiresistive CNT Sensors | Low response to low-concentration analytes | Poor selectivity towards similar molecules | Surface defects, ambient conditions | [309] |
| Electrochemical CNT Sensors | Signal interference from non-target species | Cross-reactivity in complex samples | Electrode fouling, electrolyte effects | [310] |
| Optical CNT Sensors | Weak optical signals at low analyte levels | Overlapping fluorescence or Raman signals | Background noise, optical quenching | [311] |
| FET-Based CNT Sensors | Drift in signal over time | Non-specific adsorption of analytes | Device instability, surface contamination | [312] |
| Gas CNT Sensors | Poor detection at ultra-low gas concentrations | Cross-sensitivity to humidity or other gases | Adsorption-desorption kinetics | [313] |
| Biosensors with Functionalized CNTs | Sensitivity affected by bio-receptor degradation | Limited specificity in complex biological media | Stability of functionalization layer | [314] |
8. Future Perspectives and Trends
8.1. Emerging Trends in CNT-Based Sensing
8.2. Potential Applications in Healthcare and Environmental Monitoring
| Application Sector | Commercialization Status | Key Challenges for Industrial Adoption | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare and Biomedical Sensors | Early-stage commercial products (wearables, glucose sensors) | Biocompatibility, regulatory approval, long-term stability | [317] |
| Environmental Monitoring Sensors | Pilot-scale and niche commercial products | Sensitivity in real-world conditions, sensor calibration | [318] |
| Gas Sensing for Industrial Safety | Limited commercial prototypes | Cross-sensitivity, long-term performance, harsh environment tolerance | [4] |
| Smart Textiles and Wearables | Emerging commercial interest (sports and fitness devices) | Durability, washability, mass production cost | [319] |
| Automotive and Aerospace Sensors | Research and prototype stage | Reliability, integration with existing systems | [321] |
| Food Safety and Agricultural Sensors | Limited commercial deployment | Selectivity in complex samples, cost-effectiveness | [322] |
| Military and Defense Applications | Advanced prototypes in specific projects | Harsh operational conditions, sensor security | [324] |
9. Conclusions
9.1. Summary of Key Findings
9.2. Prospects for CNTs in Sensing Technologies
9.3. Final Thoughts and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, K.J.; Iyer, K.A.; Bird, R.E.; Ivanov, J.; Banerjee, S.; Georges, G.; Zhou, Q.A. Review of Carbon Nanotube Research and Development: Materials and Emerging Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 18695–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LV Radushkevich, V.L. About the Structure of Carbon Formed by Thermal Decomposition of Carbon Monoxide on Iron Substrate. J. Phys. Chem. 1952, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Peng, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Peng, Z.; Fu, X. Advances in Carbon Nanotube-Based Gas Sensors: Exploring the Path to the Future. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 518, 216049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavel, S.; Priyadharshini, K.; Panda, D. A Review on Carbon Nanotube: An Overview of Synthesis, Properties, Functionalization, Characterization, and the Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 268, 115095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorio-Rodriguez, S.A.; Williams, A.; Poulsen, S.S.; Knudsen, K.B.; Jensen, K.A.; Clausen, P.A.; Danielsen, P.H.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U.; Halappanavar, S. Single-Walled vs. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Influence of Physico-Chemical Properties on Toxicogenomics Responses in Mouse Lungs. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Zhou, K.; Sun, W.; Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Kong, X.; Jia, D.; Wu, M.; Fu, Y. Enhancement Mechanisms of Mechanical, Electrical and Thermal Properties of Carbon Nanotube-Copper Composites: A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1395–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Alshehri, A.H.; Arockiarajan, A. Carbon Nanotube Characteristics and Enhancement Effects on the Mechanical Features of Polymer-Based Materials and Structures—A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 6495–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, S.-E.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Fang, X.; Fan, F.; Han, J. Carbon Nanotube-Based Heterostructures for High-Performance Photodetectors: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19655–19663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T. Recent Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Energy Storage and Conversion Devices. Carbon Trends 2025, 19, 100470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Hou, L.; Jiang, J.; Xu, T. Applications of Nanomaterial Technology in Biosensing. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 9, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.A.; Abd-Elaziem, W.; Elsheikh, A.; Zayed, A.A. Advancements in Nanomaterials for Nanosensors: A Comprehensive Review. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 4015–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Alamry, K.A. Surface Modified Carbon Nanotubes: An Introduction. In Surface Modified Carbon Nanotubes Volume 1: Fundamentals, Synthesis and Recent Trends; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Benko, A.; Duch, J.; Gajewska, M.; Marzec, M.; Bernasik, A.; Nocuń, M.; Piskorz, W.; Kotarba, A. Covalently Bonded Surface Functional Groups on Carbon Nanotubes: From Molecular Modeling to Practical Applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 10152–10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Gao, L. Sensors Based on the Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistors for Chemical and Biological Analyses. Biosensors 2022, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjith, K.S.; Mohammadi, A.; Ezhil Vilian, A.T.; Han, S.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Synergistic Effects of CNT-Bridged Dual-Phase MoS2 on MXene as a Ternary Hybrid Electrode for Rapid Sensing of Chloramphenicol in Aqueous Media. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimata, K.C.; Abraham, J.; Thomas, M.G.; Vahabi, H.; Maria, H.J.; Thomas, S. Carbon Nanotube Filled Rubber Nanocomposites. Front. Carbon 2024, 3, 1339418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, R.; Yin, P.; Zhang, C.; Yang, N.; Liang, K.; Kong, B. Carbon-Based SERS Biosensor: From Substrate Design to Sensing and Bioapplication. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syduzzaman, M.; Islam Saad, M.S.; Piam, M.F.; Talukdar, T.A.; Shobdo, T.T.; Pritha, N.M. Carbon Nanotubes: Structure, Properties and Applications in the Aerospace Industry. Results Mater. 2025, 25, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Shu, H.; Cui, X.; Luo, Z.; Chang, C.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q. Facile Covalent Preparation of Carbon Nanotubes / Amine-Functionalized Fe3O4 Nanocomposites for Selective Extraction of Estradiol in Pharmaceutical Industry Wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R. Advanced Functional Carbon Nanotube Fibers from Preparation to Application. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obitayo, W.; Liu, T. A Review: Carbon Nanotube-Based Piezoresistive Strain Sensors. J. Sens. 2012, 2012, 652438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, B.; Laslau, C.; Yip, R.; Sun, Y. Development of Carbon Nanotube-Based Sensors—A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M. Analytical Applications of Carbon Nanotubes: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Thostenson, E.T.; Chou, T.-W. Sensors and Actuators Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Their Composites: A Review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrones, M. Science and Technology of the Twenty-First Century: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2003, 33, 419–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, N.; Kumar, V.; Joo, S.W.; Park, S.-S.; Mandal, T.K. Recent Advances in the Characterized Identification of Mono-to-Multi-Layer Graphene and Its Biomedical Applications: A Review. Electronics 2022, 11, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H. Highly Sensitive, Selective, Flexible and Scalable Room-Temperature NO2 Gas Sensor Based on Hollow SnO2/ZnO Nanofibers. Molecules 2021, 26, 6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Hussein, A.M.; Ahmad, I.; Latef, R.; Abbas, J.K.; Ali, A.T.A.; Saeed, S.M.; Abdulwahid, A.S.; Ramadan, M.F.; Rasool, H.A.; et al. Conducting Polymers in Industry: A Comprehensive Review on the Characterization, Synthesis and Application. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 88, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Orouji, A.; Ghamsari, M.; Sahoo, S.K.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Plasmonic Noble Metal (Ag and Au) Nanoparticles: From Basics to Colorimetric Sensing Applications. In Gold and Silver Nanoparticles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Madikere Raghunatha Reddy, A.K.; Darwiche, A.; Reddy, M.V.; Zaghib, K. Review on Advancements in Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Purification, and Multifaceted Applications. Batteries 2025, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, F.; Wei, X.; Zhou, W.; Kataura, H.; Xie, S.; Liu, H. Chirality-Dependent Electrical Transport Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Obtained by Experimental Measurement. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Xu, B.; Liang, J. Direct Application of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Grown by Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for Integrated Circuits (ICs) Interconnection: Challenges and Developments. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, R.; Shanmugavel, B.P. A Critical Review of the Role of Carbon Nanotubes in the Progress of Next-Generation Electronic Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 2786–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, H.; Nag, A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Deng, S. A Review of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes-Based Electrochemical Sensors to Detect Heavy Metals for Food Packaging Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1017, 179106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaran, V.; Balasubramanian, V.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Viswabaskaran, V.; Gourav Rao, A.; Selvamani, S. Carbon Nanotubes, Nanorings, and Nanospheres: Synthesis and Fabrication via Chemical Vapor Deposition—A Review. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2022, 12, 184798042210794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, D.C.; Honeychurch, K.C. Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Biosensors. Biosensors 2021, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griger, S.; Sands, I.; Chen, Y. Comparison between Janus-Base Nanotubes and Carbon Nanotubes: A Review on Synthesis, Physicochemical Properties, and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Ding, L.; Yang, W.; Xiao, H.; Ong, W.-J. Function-Driven Engineering of 1D Carbon Nanotubes and 0D Carbon Dots: Mechanism, Properties and Applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1475–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, F.; Chen, H.; Noh, K.; Sue, H.-J. Critical Challenges and Advances in the Carbon Nanotube–Metal Interface for next-Generation Electronics. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 942–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zou, Y.; Lu, J.; Wei, J.; Zhu, H. The Structural Stability, Electronic Properties Regulation and Feasibility of Controllable Preparation of a C0.5/(BN)0.5 Heterojunction Single-Walled Nanotube. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajale, S.N.; Yadav, S.; Cai, Y.; Joy, B.; Sarkar, D. 2D Material Based Field Effect Transistors and Nanoelectromechanical Systems for Sensing Applications. iScience 2021, 24, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Rosenblatt, S.; Yaish, Y.; Sazonova, V.; Üstünel, H.; Braig, S.; Arias, T.A.; Brouwer, P.W.; McEuen, P.L. Electron−Phonon Scattering in Metallic Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, K.; Karttunen, A.J. Bridging the Junction: Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube Networks. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 17266–17274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem Anwer, A.; Saadaoui, M.; Mohamed, A.T.; Ahmad, N.; Benamor, A. State-of-the-Art Advances and Challenges in Wearable Gas Sensors for Emerging Applications: Innovations and Future Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 157899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cheng, H.M.; Bai, S.; Su, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Tensile Strength of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Directly Measured from Their Macroscopic Ropes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 3161–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Rawat, H.; Kumar, A.; Gandhi, Y.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, S.K.; Narasimhaji, C.V. Graphene and Its Hybrid Nanocomposite: A Metamorphoses Elevation in the Field of Tissue Engineering. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchi, S.; Cristoforo, G.; Piatti, E.; Torsello, D.; Ghigo, G.; Tagliaferro, A.; Rosso, C.; Bartoli, M. A Concise Review of Recent Advancements in Carbon Nanotubes for Aerospace Applications. Micromachines 2024, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.; Ali, Z.; Ali, S.; D’Amore, A. Polystyrene–Carbon Nanotube Composites: Interaction Mechanisms, Preparation Methods, Structure, and Rheological Properties—A Review. Physchem 2025, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandrarao, M.; Khan, S.H.; Abdullah, K. Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers—Reinforcement to Carbon Fiber Composites—Synthesis, Characterizations and Applications: A Review. Compos. Part C Open Access 2025, 16, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Baxendale, M.; Peijs, T. Universal Resistivity–Strain Dependence of Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composites. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 195433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barišić, N.; Gaál, R.; Kézsmárki, I.; Mihály, G.; Forró, L. Pressure Dependence of the Thermoelectric Power of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 241403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Li, Z.; Yang, E.-H. Trends on Carbon Nanotube-Based Flexible and Wearable Sensors via Electrochemical and Mechanical Stimuli: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 20102–20125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haick, H. Nature-Inspired Sensors, 1st ed.; Haick, H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; ISBN 9780443156847. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Detection of Nonpolar Molecules by Means of Carrier Scattering in Random Networks of Carbon Nanotubes: Toward Diagnosis of Diseases via Breath Samples. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachan, A.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.-F. Volatolomics for Anticipated Diagnosis of Cancers with Chemoresistive Vapour Sensors: A Review. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, H.; Hur, O.-N.; Park, S.-H. Comparative Study of Carbon Nanotube Composites as Capacitive and Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors under Varying Conditions. Materials 2022, 15, 7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.K.; Gautham, S.; Sasmal, S. A Comprehensive Review on Carbon Nanotubes Based Smart Nanocomposites Sensors for Various Novel Sensing Applications. Polym. Rev. 2024, 64, 575–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, E.W.; Mebratie, B.A. Advancements in Carbon Nanotube-Polymer Composites: Enhancing Properties and Applications through Advanced Manufacturing Techniques. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Ning, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhou, R.; Jin, S.; Zheng, J.; Yao, R.; Peng, J. Flexible Piezoresistive Sensor Based on CNT/PVA Composite with Wide Linear Detection Range for Human Motion Monitoring. Polymers 2025, 17, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, Z.; Terzyk, A.P.; Boncel, S. Covalent Functionalization of 1D and 2D Sp 2 -Carbon Nanoallotropes—Twelve Years of Progress (2011–2023). Nanoscale 2024, 16, 9197–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ramasamy, R. Non-Covalent Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes for Electrochemical Biosensor Development. Sensors 2019, 19, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Singh, J.; Goyat, R.; Saharan, Y.; Chaudhry, V.; Umar, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Akbar, S.; Ameen, S.; Baskoutas, S. Nanomaterials-Based Biosensor and Their Applications: A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-Y.; Hou, P.-X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.-M. Gas Sensors Based on Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. Molecules 2022, 27, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakash, N.; Elumalai, K.; Manickam, S.; Bakthavatchalam, G.; Tamilselvan, P. Carbon Nanomaterials: Revolutionizing Biomedical Applications with Promising Potential. Nano Mater. Sci. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Pint, C.L.; Islam, A.E.; Weatherup, R.S.; Hofmann, S.; Meshot, E.R.; Wu, F.; Zhou, C.; Dee, N.; Amama, P.B.; et al. Carbon Nanotubes and Related Nanomaterials: Critical Advances and Challenges for Synthesis toward Mainstream Commercial Applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11756–11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janas, D.; Koziol, K.K. The Effect of the Gaseous Environment on the Electrical Conductivity of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Films over a Wide Temperature Range. Materials 2020, 13, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguin, N.S.G.; Maulik, G.; Cao, X.; Luo, X.; Nag, A.; Gao, J.; Deng, S.; Wong, J.W.C. CNTs-Based Biosensors for Enzyme Detection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 377, 115753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Terrones, M.; Wang, Y. Surface Modification Methods and Mechanisms in Carbon Nanotubes Dispersion. Carbon 2023, 212, 118133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Burghard, M. Chemically Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. Small 2005, 1, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Dutta, D.; Sarkar, A.; Chattopadhyay, P. Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in Water Purification, Drug Delivery, and Material and Biomedical Sciences. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 5722–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh Raman, A.P.; Meena, H.; Goswami, A.G.; Bhawna; Kumar, V.; Jain, P.; Kumar, G.; Sagar, M.; Rana, D.K.; et al. An Update on Graphene Oxide: Applications and Toxicity. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35387–35445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani McCord, M.R.; Seppälä, A.; Pourakbari-Kasmaei, M.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Rojas, O.J. From Low Conductivity to High Energy Efficiency: The Role of Conductive Polymers in Phase Change Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. An Overview of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene for Biosensing Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2017, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, S.; Manojkumar, K.; Muthuramalingam, M.; Hajra, S.; Panda, S.; Sahu, R.; Joon Kim, H.; Sundaramoorthy, A.; Nithyavathy, N.; Vivekananthan, V. Progress and Recent Advances in Self-Powered Gas Sensing Based on Triboelectric and Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, N.; Kumar, A.; Chakroborty, S.; Soren, S.; Barik, A.; Pal, K.; de Souza, F.G. Carbon Nanostructure Embedded Novel Sensor Implementation for Detection of Aromatic Volatile Organic Compounds: An Organized Review. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4436–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H. Bioreceptors as the Key Components for Electrochemical Biosensing in Medicine. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, P.C.O.; Aakyiir, M.; Su, X.; Alam, J.; Tran, L.C.; Dai, J.; Meng, Q.; Kuan, H.-C.; Ma, J. Challenges and Advancements in Elastomer/CNT Nanocomposites with Mechanochemical Treatment, Reinforcement Mechanisms and Applications. Smart Mater. Manuf. 2024, 2, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Quick and Surfactant-Free Dispersion of Various Carbon Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution as Casting Technique for Devices. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 12, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Niu, K. Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes in Polystyrene and Properties of Their Composites: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Mahapatra, C. Smart Nano-Hybrid Metal-Organic Frameworks: Revolutionizing Advancements, Applications, and Challenges in Biomedical Therapeutics and Diagnostics. Hybrid Adv. 2025, 9, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Barcelos, K.; Garg, J.; Ferreira Soares, D.C.; de Barros, A.L.B.; Zhao, Y.; Alisaraie, L. Recent Advances in the Applications of CNT-Based Nanomaterials in Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology and Biomedical Engineering. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 104834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiyani, M.; Pathak, M.; Bohra, B.S.; Sahoo, N.G. Noncovalent Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes. In Handbook of Carbon Nanotubes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Logeswari, J.; Kamatchi, T.; Kumaresan, P. Simultaneous Purification and Oxidation of the As-Synthesized MWCNTs with KMnO4 Using Phase Transfer Catalyst at Three Different PH Medium by the Hydrothermal Method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 323, 129673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaz, S.V.; Nobar, H.M.; Sarıgül, H.; Soylukan, C.; Akyüz, L.; Yüce, M. Nanomaterial Surface Modification Toolkit: Principles, Components, Recipes, and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 322, 103035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nurazzi, N.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Khalina, A.; Abdullah, N.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Kamarudin, S.H.; Ahmad, S.; Mahat, A.M.; Lee, C.L.; Aisyah, H.A.; et al. Fabrication, Functionalization, and Application of Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polymer Composite: An Overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Crescenzo, A.; Ettorre, V.; Fontana, A. Non-Covalent and Reversible Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Roy, S.; Dinda, S.C.; Bose, A.; Mahapatra, C.; Basu, B.; Prajapati, B. Carbon Nanotubes in Brain Targeted Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. Results Chem. 2025, 15, 102206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, Y.; Singh, K.; Mudila, H.; Lokhande, P.E.; Singh, L.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Dehghani, M.H. Insights into Properties, Synthesis and Emerging Applications of Polypyrrole-Based Composites, and Future Prospective: A Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Cheng, G.; Nakamura, T.; Hiraoka, K.; Tabata, H.; Kubo, O.; Komatsu, N.; Katayama, M. NH 3 Gas Sensors Based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Interlocked with Metal-Tethered Tetragonal Nanobrackets. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 13417–13425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharisov, B.I.; Kharissova, O.V.; Ortiz Méndez, U.; De La Fuente, I.G. Decoration of Carbon Nanotubes With Metal Nanoparticles: Recent Trends. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Nano-Met. Chem. 2016, 46, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Latif, H.; Anjum, D.H.; Ammar Shabbir, S.; Sattar, A.; Usman, A. Au/NG/SWCNTs/FTO-Glass Modified Electrode Based Electrochemical Biosensor for DNA Detection. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin Mei, C.; Ainliah Alang Ahmad, S. A Review on the Determination Heavy Metals Ions Using Calixarene-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Shuang, S. Cyclodextrin Hybrid Inorganic Nanocomposites for Molecular Recognition, Selective Adsorption, and Drug Delivery. In Handbook of Macrocyclic Supramolecular Assembly; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, T.; Srinives, S. Electrochemically Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Ultrasensitive Detection of BTEX Vapors. Microelectron. Eng. 2021, 247, 111584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Talib, M.; Arsenin, A.V.; Volkov, V.S.; Mishra, P. Polyethyleneimine-Starch Functionalization of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Carbon Dioxide Sensing at Room Temperature. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; DeVoe, E.; Andreescu, S. Carbon-Based Electrochemical Biosensors as Diagnostic Platforms for Connected Decentralized Healthcare. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 529–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Mendez, D.; Fernández, L.; Uribe, R.; Cunalata-Castro, A.; González, G.; Rojas, I.; Chico-Proano, A.; Debut, A.; Celi, L.A.; Espinoza-Montero, P. Evaluation of a Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor Based on Co(OH)2-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes for Glucose Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, S.; Vasini, I.; Giannetto, M.; Mattarozzi, M.; Porchetta, A.; Bertucci, A.; Careri, M. Controlling Dynamic DNA Reactions at the Surface of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Electrodes to Design Hybridization Platforms with a Specific Amperometric Readout. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5075–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Lin, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, W.; Shi, J.; Hong, Y. Ionic Imprinted CNTs-Chitosan Hybrid Sponge with 3D Network Structure for Selective and Effective Adsorption of Gd(III). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 269, 118792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Hu, Z. Thiol Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis by Sulfur Chemistry and Their Multi-Purpose Applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, L.S.; Ouslimani, N.; Bousba, D.; Huynen, I.; Danlée, Y.; Aksas, H. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) from Synthesis to Functionalized (CNTs) Using Conventional and New Chemical Approaches. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 4972770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsola, S.S.; Oladipo, M.E.; Oladoye, P.O.; Kadhom, M. Carbon Nanotubes for Sustainable Environmental Remediation: A Critical and Comprehensive Review. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 37, 101099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Kumar, K.; Venkatesu, P. Covalent Functionalization of Carbon Nanotube. In Handbook of Carbon Nanotubes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 393–420. [Google Scholar]
- Dyke, C.A.; Tour, J.M. Covalent Functionalization of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Materials Applications. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 11151–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, G. Carbon Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Functionalization and Sensing Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-H.; Luo, J.; Mao, Y.-L.; Lai, S.; Gong, Y.-N.; Zhong, D.-C.; Lu, T.-B. π-π Stacking Interactions: Non-Negligible Forces for Stabilizing Porous Supramolecular Frameworks. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Verma, A.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S.; Ogata, S. Recent Progressive Developments in Conductive-Fillers Based Polymer Nanocomposites (CFPNC’s) and Conducting Polymeric Nanocomposites (CPNC’s) for Multifaceted Sensing Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 5921–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, I.J.; Vázquez Sulleiro, M.; Mantione, D.; Alegret, N. Carbon Nanomaterials Embedded in Conductive Polymers: A State of the Art. Polymers 2021, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channabasavana Hundi Puttaningaiah, K.P. Innovative Carbonaceous Materials and Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Electrochemical Biosensor Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Biomedical Applications of Supramolecular Systems Based on Host–Guest Interactions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7794–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, S.; Sun, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Chemically Robust Covalent Organic Frameworks: Progress and Perspective. Matter 2020, 3, 1507–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, A.; Hegde, M.; Krishna, S.; Ayippadath Gopi, J.; Kotresh, T.M.; Prabhu, T.N. Non-Covalent Surface Functionalization of Nanofillers towards the Enhancement of Thermal Conductivity of Polymer Nanocomposites: A Mini Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 198, 112379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Khojin, A.; Khalili-Araghi, F.; Kuroda, M.A.; Lin, K.Y.; Leburton, J.-P.; Masel, R.I. On the Sensing Mechanism in Carbon Nanotube Chemiresistors. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, S.; Lim, J.; Srirangarajan, A.; Mulchandani, A.; Deshusses, M.A.; Myung, N.V. Gas Sensing Mechanism of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, H.; Shi, H.; Yu, W. Supramolecular Host–Guest System That Realizes Adaptive Selection of the Guest through Ligand Regulation. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 64, 4345–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Voggu, R.; Govindaraj, A. Selective Generation of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Metallic, Semiconducting and Other Unique Electronic Properties. Nanoscale 2009, 1, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Ding, F. Understanding Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Growth for Chirality Controllable Synthesis. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lim, E.G.; Hoettges, K.; Song, P. A Review of Carbon Nanotubes, Graphene and Nanodiamond Based Strain Sensor in Harsh Environments. J. Carbon Res. 2023, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monavari, S.M.; Marsusi, F.; Memarian, N.; Qasemnazhand, M. Carbon Nanotubes and Nanobelts as Potential Materials for Biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Yin, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, M.; Ma, D.; Shao, F.; Hu, N.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y. Gas Sensing Performance and Charge-Transfer Mechanism of Semiconducting Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 609, 155357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Ren, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Ballistic Transport in Bent-Shaped Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 2019, 149, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, I.; Hassan, M.A.; Maidin, N.N.M.; Mohamed, M.A. SWCNT Network-FET Device for Human Serum Albumin Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.; Schnitzler, M.C.; da Silva, W.M.; Santos, A.P. Purification of Carbon Nanotubes Produced by the Electric Arc-Discharge Method. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Alahi, M.E.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Liu, Z. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes-Based Sensors for Strain Sensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Farha, F.I.; GE, Y.; Xu, F. Incandescent Annealing Purification of Carbon Nanotube Films with High Efficiency and Non-Destructiveness. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, L.R.M.; Andrade, L.N.; Bahú, J.O.; Cárdenas Concha, V.O.; Machado, A.T.; Pires, D.S.; Santos, R.; Cardoso, T.F.M.; Cardoso, J.C.; Albuquerque-Junior, R.L.C.; et al. Biomedical Applications of Carbon Nanotubes: A Systematic Review of Data and Clinical Trials. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 99, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, D. Non-Covalent Interactions between Carbon Nanotubes and Conjugated Polymers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidawanyika, W.; Nyokong, T. Characterization of Amine-Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Low Symmetry Phthalocyanine Conjugates. Carbon 2010, 48, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Ding, W.; Zang, H.; Li, L. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Sensors: Preparation and Bio-Application Advances. Pharm. Sci. Adv. 2025, 3, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, L.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S. Innovations in WO3 Gas Sensors: Nanostructure Engineering, Functionalization, and Future Perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Hou, Y.; Suematsu, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Shimanoe, K.; Hu, J. Noble Metal Nanoparticles Functionalized Conductive Co3(Hexaiminotriphenylene)2 Chemiresistor for Hydrogen Sulfide Detection at Room-Temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, H.M.; Lamb, A.; Budhathoki-Uprety, J. Recent Advances on Applications of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as Cutting-Edge Optical Nanosensors for Biosensing Technologies. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 16344–16375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, J.; Metternich, J.T.; Herbertz, S.; Kruss, S. Biosensing with Fluorescent Carbon Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalvand, A.R.; Karami, M.M. Roles of Nanotechnology in Electrochemical Sensors for Medical Diagnostic Purposes: A Review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2025, 47, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Romano, J.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Electrospun Bundled Carbon Nanofibers for Skin-Inspired Tactile Sensing, Proprioception and Gesture Tracking Applications. npj Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, M.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Z. Toward the Commercialization of Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, H.; Pervaiz, M.; Shahzadi, R.; Saeed, Z.; Khan, R.R.M.; Younas, U. Graphene and CNT-Based Hybrid Nanocomposite and Its Application in Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage Devices. Synth. Met. 2025, 311, 117847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Z.; Williams, R.M. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as Optical Transducers for Nanobiosensors In Vivo. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 35164–35181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagautdinov, B.; Ohara, K.; Babaev, A.A. High-Energy X-Ray Diffraction Study of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Fabricated by Arc Discharge Plasma Process. Carbon 2022, 191, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudyak, V.; Pryazhnikov, M.; Minakov, A.; Shupik, A. Electrical Conductivity of Nanofluids with Single- and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Experimental Study. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2024, 38, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauti, R.; Musto, M.; Bosi, S.; Prato, M.; Ballerini, L. Properties and Behavior of Carbon Nanomaterials When Interfacing Neuronal Cells: How Far Have We Come? Carbon 2019, 143, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldoni, A.; Petaccia, L.; Lizzit, S.; Larciprete, R. Sensing Gases with Carbon Nanotubes: A Review of the Actual Situation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondavalli, P.; Legagneux, P.; Pribat, D. Carbon Nanotubes Based Transistors as Gas Sensors: State of the Art and Critical Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.-F. Review on Sensor Array-Based Analytical Technologies for Quality Control of Food and Beverages. Sensors 2023, 23, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Fabrication and Implementation of Carbon Nanotubes for Piezoresistive-Sensing Applications: A Review. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A Review of Synthesis Methods, Properties, Recent Progress, and Challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H. Carbon Nanotubes in Perovskite-Based Optoelectronic Devices. Matter 2022, 5, 448–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Lei, X.; Chen, B.; Hao, H.; Luo, J.; Sun, T.; Jian, M.; Gao, E.; Wu, X.; et al. Fabricating Ultrastrong Carbon Nanotube Fibers via a Microwave Welding Interface. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 14377–14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norizan, M.N.; Moklis, M.H.; Ngah Demon, S.Z.; Halim, N.A.; Samsuri, A.; Mohamad, I.S.; Knight, V.F.; Abdullah, N. Carbon Nanotubes: Functionalisation and Their Application in Chemical Sensors. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43704–43732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Jaime, A.F.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Electrochemical Functionalization of Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes with Phosphorus and Nitrogen Species. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 340, 135935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji Ahmed, Y.; Faiad naief, M.; Naser Mohammed, S.; Mishaal Mohammed, A. MWCNT-Based Material as a Gas Sensor for H2S and NO2, Synthesise and Characterisation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 152, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sidhu, H.K.; Paul, A.K.; Bhardwaj, N.; Thakur, N.S.; Deep, A. Bioengineered Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube (MWCNT) Based Biosensors and Applications Thereof. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 1390–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Patil, T.V.; Dutta, S.D.; Lee, J.; Ganguly, K.; Kim, H.; Randhawa, A.; Lim, K. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Optical Nano/Biosensors for Biomedical Applications: Role in Bioimaging, Disease Diagnosis, and Biomarkers Detection. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Afroj, S.; Li, D.; Islam, M.R.; Wu, J.; Cai, G.; Karim, N.; Zhao, Z. Highly Sensitive and Extremely Durable Wearable E-Textiles of Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid for Cardiorespiratory Monitoring. iScience 2023, 26, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasley, A.T.; Li, E.; Galeana, J.M.; Bulumulla, C.; Beyene, A.G.; Demirer, G.S. Carbon Nanomaterial Fluorescent Probes and Their Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 3085–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B.; Luo, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, T. CNT Enabled Co-Braided Smart Fabrics: A New Route for Non-Invasive, Highly Sensitive & Large-Area Monitoring of Composites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Schulz, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shanov, V.; Shi, D. A Carbon Nanotube Strain Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Thostenson, E.T.; Zhang, Z.; Chou, T.-W. Coupled Carbon Nanotube Network and Acoustic Emission Monitoring for Sensing of Damage Development in Composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemartinel, A.; Castro, M.; Fouché, O.; De-Luca, J.-C.; Feller, J.-F. A Review of Nanocarbon-Based Solutions for the Structural Health Monitoring of Composite Parts Used in Renewable Energies. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Narjinary, M.; Sen, A.; Pal, M. Beneficial Effect of Pd and MWCNT Co-Loading in SnO 2 Nanoparticles towards the Low Temperature Detection of n -Butane Gas: Synergistic Effect on Sensing Performance. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Prajapati, P.K.; Bapanapalle, C.O.; Sadhu, K.K.; Ghosh, R.; Mandal, N. Effect of MWCNTs on Micromechanical and High-Temperature Tribological Behavior of ZTA-MgO Ceramic Composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamova, M.V.; Kramberger, C. Applications of Filled Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Romate, X.F.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Ureña, A. Electrical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes. In Handbook of Carbon Nanotubes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 213–247. [Google Scholar]
- Abousalman-Rezvani, Z.; Eskandari, P.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes by Combination of Controlled Radical Polymerization and “Grafting to” Method. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 278, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovais, M.; You, M.; Ahmad, J.; Djellabi, R.; Ali, A.; Akhtar, M.H.; Abbas, M.; Chen, C. Engineering Carbon Nanotubes for Sensitive Viral Detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 153, 116659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, P.K.; Chandu, B.; Puvvada, N. Recent Advances in Nanostructured Materials for Application as Gas Sensors. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 3092–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. MXene/MWCNTs-Based Capacitive Pressure Sensors Combine High Sensitivity and Wide Detection Range for Human Health and Motion Monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 379, 115858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, B.; Anand, N.; Lubloy, E.; Andrushia, A.D. Influence of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube (MWCNT) on Flexural Behavior and Microstructure Characteristics of Geopolymer Concrete Beams. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, P.; Ujjain, S.K.; Urita, K.; Furuse, A.; Moriguchi, I.; Kaneko, K. Chemically and Mechanically Robust SWCNT Based Strain Sensor with Monotonous Piezoresistive Response for Infrastructure Monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, J.A. Aqueous Two-Polymer Phase Extraction of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Using Surfactants. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 3307–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H. Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes by Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition and Their Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Gwon, Y.; Kim, Y.-O.; Kim, J. Engineering Plants with Carbon Nanotubes: A Sustainable Agriculture Approach. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leau, S.-A.; Lete, C.; Lupu, S. Nanocomposite Materials Based on Metal Nanoparticles for the Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotransmitters. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Ionescu, R.; Chambon, B.; Bedis, G.; Sotter, E.; Bittencourt, C.; Felten, A.; Pireaux, J.; Correig, X.; Llobet, E. Hybrid Metal Oxide and Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Films for Low Temperature Gas Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulos, D.D.; Saini, H.; Tantis, I.; Zbořil, R.; Jayaramulu, K.; Otyepka, M. Carbon Nanotube Based Metal–Organic Framework Hybrids From Fundamentals Toward Applications. Small 2022, 18, 2104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundwal, A.; Kumar, H.; Binoj, B.J.; Sharma, R.; Kumari, R.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, G.; Dhayal, A.; Yadav, A.; Singh, D.; et al. Conducting Polymers and Carbon Nanotubes in the Field of Environmental Remediation: Sustainable Developments. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 500, 215533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Zhao, J.; Yun, X. Hybrid Graphene and Carbon Nanotube–Reinforced Composites: Polymer, Metal, and Ceramic Matrices. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbari, S.; Bolourinezhad, M.; Kesharwani, P.; Rezayi, M.; Sahebkar, A. Applications of Carbon Nanotube Biosensors: Sensing the Future. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Tu, M. Device Fabrication and Sensing Mechanism in Metal-Organic Framework-Based Chemical Sensors. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Slaughter, G. PtNPs Decorated Chemically Derived Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes for Sensitive and Selective Glucose Biosensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 861, 113990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Kan, H.; Niu, H.; Wang, W.; Guo, Y. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for the Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds: A Review. Carbon 2021, 180, 274–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Polymer Nanocomposites for Detecting Breast Cancer: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 309, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; Yan, X.; Lv, Y. Recent Advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks: Synthesis, Application and Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 165944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzar, N.; Hasan, R.; Tyagi, M.; Yadav, N.; Narang, J. Carbon Nanotube—A Review on Synthesis, Properties and Plethora of Applications in the Field of Biomedical Science. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Solati, N.; Amiri, M.; Mirshekari, H.; Mohamed, E.; Taheri, M.; Hashemkhani, M.; Saeidi, A.; Estiar, M.A.; Kiani, P.; et al. Carbon Nanotubes Part I: Preparation of a Novel and Versatile Drug-Delivery Vehicle. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1071–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, Y.-J.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Chung, D.-C.; Kim, B.-J. Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composites for Functional Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.; Jacques, D.; Qian, D.; Rantell, T. Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis and Application. ChemInform 2003, 34, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.; Yuda, A.; Abu-Reesh, I.M.; Kumar, A. Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Sorting, and Applications. In Handbook of Carbon Nanotubes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 449–484. [Google Scholar]
- Merum, S.; Veluru, J.B.; Seeram, R. Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes in Bio-World: Applications, Limitations and Future Directions. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 223, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murjani, B.O.; Kadu, P.S.; Bansod, M.; Vaidya, S.S.; Yadav, M.D. Carbon Nanotubes in Biomedical Applications: Current Status, Promises, and Challenges. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1207–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Wu, R.R.; Lee, D.J. Morphological Aspects of Carbon Nanofillers and Their Hybrids for Actuators and Sensors. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, E373–E382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Q.; Ye, Y.; Yan, W.; Tian, Z.; Liang, C. S,N Dual-Doped Carbon Nanotubes as Substrate to Enhance the Methanol Oxidation Performance of NiO Nanoparticles. Carbon 2019, 152, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Teblum, E.; Kostikov, Y.; Pedrana, A.; Re, V.; Nessim, G.D.; Rosace, G. Sol-Gel Approach to Incorporate Millimeter-Long Carbon Nanotubes into Fabrics for the Development of Electrical-Conductive Textiles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Hassan, A.A.; Kausar, F.; Sher, F.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Carbon Nanotubes Assisted Analytical Detection—Sensing/Delivery Cues for Environmental and Biomedical Monitoring. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, S.; Angeli, M.A.C.; Polo, A.; Costantini, A.; Petrelli, M.; Avancini, E.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M.; Gaiardo, A.; Valt, M.; et al. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Gas Monitoring with Carbon Nanotube Sensors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Shi, Y.; Hou, Z.; Wei, L. Carbon Nanotube-Based Chemiresistive Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Savagatrup, S.; He, M.; Lin, S.; Swager, T.M. Carbon Nanotube Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 599–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.M.; Khalifa, Z.; Elhaddad, G.M.; Abdel Azzem, M. The Role of Electrolytically Deposited Palladium and Platinum Metal Nanoparticles Dispersed onto Poly(1,8-Diaminonaphthalene) for Enhanced Glucose Electrooxidation in Biofuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 355, 136781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.H.; Rao, M.V.; Li, Q. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for Detecting Toxic Gases: NO2, SO2 and H2S. Sensors 2019, 19, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filice, S.; Boscarino, S.; Scuderi, M.; Libertino, S.; Galati, C.; Terrasi, A.; Scalese, S. AZO Nanoparticles-Decorated CNTs for UV Light Sensing: A Structural, Chemical, and Electro-Optical Investigation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podyacheva, O.Y.; Cherepanova, S.V.; Romanenko, A.I.; Kibis, L.S.; Svintsitskiy, D.A.; Boronin, A.I.; Stonkus, O.A.; Suboch, A.N.; Puzynin, A.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Nitrogen Doped Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers: Composition, Structure, Electrical Conductivity and Capacity Properties. Carbon 2017, 122, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalchik, A.L.; Ding, W.; Porter, D.W.; McLoughlin, C.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Sisler, J.D.; Stefaniak, A.B.; Snyder-Talkington, B.N.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Terrones, M.; et al. Effects of Nitrogen-Doped Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Compared to Pristine Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells. Toxicology 2015, 333, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, A. Carbon Nanotube Based Wearable Room Temperature Gas Sensors. In Functional Nanomaterials: Advances in Gas Sensing Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 329–348. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Debnath, A.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Mahajan, A. Room Temperature Ppb Level Detection of Chlorine Using Peripherally Alkoxy Substituted Phthalocyanine/SWCNTs Based Chemiresistive Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 350, 130870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyabadza, A.; McCarthy, É.; Makhesana, M.; Heidarinassab, S.; Plouze, A.; Vazquez, M.; Brabazon, D. A Review of Physical, Chemical and Biological Synthesis Methods of Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Applications in Sensing, Water Treatment, Biomedicine, Catalysis and Hydrogen Storage. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 321, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drera, G.; Freddi, S.; Emelianov, A.V.; Bobrinetskiy, I.I.; Chiesa, M.; Zanotti, M.; Pagliara, S.; Fedorov, F.S.; Nasibulin, A.G.; Montuschi, P.; et al. Exploring the Performance of a Functionalized CNT-Based Sensor Array for Breathomics through Clustering and Classification Algorithms: From Gas Sensing of Selective Biomarkers to Discrimination of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 30270–30282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, X. Advancements in Carbon Nanotube-Based Sensors for Human Motion Detection. Matéria 2025, 30, e20240811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Abdelghani, A.; Bahoumina, P.; Tantot, O.; Baillargeat, D.; Frigui, K.; Bila, S.; Hallil, H.; Dejous, C. CNT-Based Inkjet-Printed RF Gas Sensor: Modification of Substrate Properties during the Fabrication Process. Sensors 2019, 19, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Z. Advancement in Carbon Nanotubes Optoelectronic Devices for Terahertz and Infrared Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 2400124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurazzi, N.M.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Harussani, M.M.; Kamarudin, S.H.; Rayung, M.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Aisyah, H.A.; Norrrahim, M.N.F.; Ilyas, R.A.; Abdullah, N.; et al. Mechanical Performance and Applications of CNTs Reinforced Polymer Composites—A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, I.; Chaturvedi, P.; Chouksey, A.; Tandon, R.P.; Chaudhury, P.K. Study of Simultaneous Reversible and Irreversible Adsorption on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Gas Sensor. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakre, O.K.; Medupin, R.O.; Akintunde, I.B.; Jimoh, O.T.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Muriana, R.A.; James, J.A.; Ukoba, K.O.; Jen, T.-C.; Yoro, K.O. Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polymer Nanocomposites for Sustainable Biomedical Applications: A Review. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2023, 8, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydas, B.; Atılgan, A.; Ajjaq, A.; Acar, S.; Öktem, M.F.; Yildiz, A. Flexible NH3 Gas Sensors Based on ZnO Nanostructures Deposited on Kevlar Substrates via Hydrothermal Method. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 32477–32489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, I.; Shahzad, M.I.; Tutsak, E.; Mahfouz, M.M.K.; Al Adba, M.S.; Abbasi, S.A.; Rathore, H.A.; Asif, Z.; Chen, Z. Carbon Based Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring Networks; Middle East Perspective. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1391409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhail, M.H.; Abdullah, O.G.; Kadhim, G.A. Hydrogen Sulfide Sensors Based on PANI/f-SWCNT Polymer Nanocomposite Thin Films Prepared by Electrochemical Polymerization. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, S.; Kassanos, P.; Keshavarz, M.; Duru, P.; Kayalan, C.I.; Kale, İ.; Bayazit, M.K. Wearable Nano-Based Gas Sensors for Environmental Monitoring and Encountered Challenges in Optimization. Sensors 2023, 23, 8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civera, M.; Naseem, A.; Chiaia, B. Recent Advances in Embedded Technologies and Self-sensing Concrete for Structural Health Monitoring. Struct. Concr. 2024; Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilli, L.; Passacantando, M. Advances on Sensors Based on Carbon Nanotubes. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.H.; Chandraprabha, M.N.; Samrat, K.; Krishna Murthy, T.P.; Manjunatha, C.; Kumar, S.G. Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene-Based Materials for Adsorptive Removal of Metal Ions—A Review on Surface Functionalization and Related Adsorption Mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2023, 16, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Toward Highly Sensitive, Selective, and Stable Palladium-based MEMS Gas Sensors for Hydrogen Energy Security. SmartMat 2024, 5, e1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, P.; Abousalman-Rezvani, Z.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Polymer-Functionalization of Carbon Nanotube by in Situ Conventional and Controlled Radical Polymerizations. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haoduo, Y.; Nian, L.; Zhi, L. Novel Application of Carbon Nanotube Electrodes for Electrochemical Detection of Amino Acids in Athlete’s Biological Samples. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 108, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutunaru, O.; Mihailescu, C.M.; Savin, M.; Tincu, B.C.; Stoian, M.C.; Muscalu, G.S.; Firtat, B.; Dinulescu, S.; Craciun, G.; Moldovan, C.A.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase Entrapment onto Carboxyl-Modified Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Poly (3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Nanocomposite, Film Electrosynthesis Characterization, and Sensor Application for Dichlorvos Detection in Apple Juice. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshmanesh, F.; Thurgood, P.; Pirogova, E.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S. Wearable Sensors: At the Frontier of Personalised Health Monitoring, Smart Prosthetics and Assistive Technologies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godja, N.-C.; Munteanu, F.-D. Hybrid Nanomaterials: A Brief Overview of Versatile Solutions for Sensor Technology in Healthcare and Environmental Applications. Biosensors 2024, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Murthy, C.N.; Prabha, C.R. Recent Advances in Carbon Nanotube Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, N.H.; Karri, R.R.; Mubarak, N.M.; Mazari, S.A.; Sharma, B.P. Holistic Insights into Carbon Nanotubes and MXenes as a Promising Route to Bio-Sensing Applications. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 21216–21263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.M.; Bourgognon, M.; Wang, J.T.-W.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Functionalised Carbon Nanotubes: From Intracellular Uptake and Cell-Related Toxicity to Systemic Brain Delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.; Azzouzi, S.; Zucchi, G.; Lebental, B. Electrical and Electrochemical Sensors Based on Carbon Nanotubes for the Monitoring of Chemicals in Water—A Review. Sensors 2021, 22, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, V.; Bisker, G. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as Fluorescent Probes for Monitoring the Self-Assembly and Morphology of Peptide/Polymer Hybrid Hydrogels. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 9205–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Amiri, H.; Zare, H.; Masroor, M.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Beyzavi, A.; Aref, A.R.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Carbon Nanotubes in Microfluidic Lab-on-a-Chip Technology: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2017, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, J.N.; Vij, V.; Kemp, K.C.; Kim, K.S. Engineered Carbon-Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Biomolecules. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 46–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqaderi, A.I.J.; Ramakrishnan, N. Carbon-Based Flexible Strain Sensors: Recent Advances and Performance Insights in Human Motion Detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 513, 162609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Ahmad, I. Highpoints of Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Sensors—A Review. e-Prime Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2024, 7, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, Y.A.; Chang, M. Carbon Nanomaterials as Versatile Platforms for Biosensing Applications. Micromachines 2020, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, J.; An, J.M.; Surwase, S.S.; Chakraborty, K.; Sutradhar, S.C.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.-K. Carbon Nanotube and Its Derived Nanomaterials Based High Performance Biosensing Platform. Biosensors 2022, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, T. Promising Graphene-Based Nanomaterials and Their Biomedical Applications and Potential Risks: A Comprehensive Review. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 5363–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadian, N.S.; Faridnouri, H.; Zare, E.N. Glucose Biosensing Based on Glucose Oxidase Immobilization on Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Polyaniline/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 148, 111423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Cai, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.-J. Probe-Screened Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor to Enhance Breast Cancer-Related Gene Assay. Green Anal. Chem. 2025, 13, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredj, Z.; Singh, B.; Bahri, M.; Qin, P.; Sawan, M. Enzymatic Electrochemical Biosensors for Neurotransmitters Detection: Recent Achievements and Trends. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S. Electrochemical Biosensors: Perspective on Functional Nanomaterials for on-Site Analysis. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Rebelo, R.; Reis, R.L.; Bhattacharya, M.; Correlo, V.M. Current Nanotechnology Advances in Diagnostic Biosensors. Med. Devices Sens. 2021, 4, e10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J. Carbon Nanostructures for Tagging in Electrochemical Biosensing: A Review. J. Carbon Res. 2017, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, J.B.; Raut, P.; Kumar, S. Organic Electronics in Biosensing: A Promising Frontier for Medical and Environmental Applications. Biosensors 2023, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, S.K.; Srivastava, R. Drug Delivery With Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Versatile Nanocarriers: Progress and Prospects. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 644564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-H.; Gupta, S.; Chang, C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Tai, N.-H. Carbon Nanotubes/Polyethylenimine/Glucose Oxidase as a Non-Invasive Electrochemical Biosensor Performs High Sensitivity for Detecting Glucose in Saliva. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskher, H.; Mustansar, H.C.; Thakur, A.K.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Lynch, I.; Singh, P.; Han, T.K.; Saidur, R. Recent Trends in Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Biosensors for the Fast and Sensitive Detection of Human Viruses: A Critical Review. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 992–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, W.; Sun, W.; Fan, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, T.; Huang, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Analysis Platform for Tumor Cells and Biomarkers Detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2024, 960, 118194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.; Koh, D.; Shin, S.; Tian, C.; Song, Y.; Kang, J.; Cho, S.-Y. A NIR Fluorescent Single Walled Carbon Nanotube Sensor for Broad-Spectrum Diagnostics. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimekala, T.; Sivasubramanian, R.; Dharmalingam, G. Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors Using Field-Effect Transistors: A Review. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 1950–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, M.A.; Rabbani, G.; Ahmad, A.; Basalah, A.A.; Al-Sabban, W.H.; Nate Ahn, S.; Choudhry, H. Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor (CNT-FET)-Based Biosensor for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Surface Spike Protein S1. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 143, 107982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Peng, H. Implantable Fiber Biosensors Based on Carbon Nanotubes. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N. Wearable MOF Biosensors: A New Frontier in Real-Time Health Monitoring. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 184, 118156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Natsuki, J.; Dinh Trung, V.; Li, H.; Tan, J.; Yang, W.; Natsuki, T. AgNPs/CNTs Modified Nonwoven Fabric for PET-Based Flexible Interdigitated Electrodes in Pressure Sensor Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmi, R.; Banerjee, P.; Singh, M.; Singh, R.; Chhillar, S.; Sharma, N.; Chandra, A.; Singh, N.; Qamar, I. Revolutionizing Biomedicine: Aptamer-Based Nanomaterials and Nanodevices for Therapeutic Applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 42, e00843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Hendler-Neumark, A.; Bisker, G. Dynamic Tracking of Biological Processes Using Near-Infrared Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 54960–54975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Rao, P.T.; Ghorui, S.; Bahadur, J.; Jain, V.; Dasgupta, K. Tailoring Surface Properties with O/N Doping in CNT Aerogel Film to Obtain Sensitive and Selective Sensor for Volatile Organic Compounds Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, C.; Alvarez, L.; Bantignies, J.-L.; Bendiab, N.; Cambré, S.; Campidelli, S.; Fagan, J.A.; Flahaut, E.; Flavel, B.; Fossard, F.; et al. Advanced 1D Heterostructures Based on Nanotube Templates and Molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 8457–8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M, M.; Sagadevan, S.; E, B.; Fatimah, I.; Lett, J.A.; Moharana, S.; Garg, S.; Al-Anber, M.A. Enhancing Biocompatibility and Functionality: Carbon Nanotube-Polymer Nanocomposites for Improved Biomedical Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 99, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.C.F.G.; Rocha, B.G.M.; Maçôas, E.M.S.; Marques, E.F.; Martinho, J.M.G. Combining Metal Nanoclusters and Carbon Nanomaterials: Opportunities and Challenges in Advanced Nanohybrids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 304, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, A.; Alexander, R.; Prakash, J.; Dasgupta, K. Engineering Challenges and Innovations in Controlled Synthesis of CNT Fiber and Fabrics in Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition (FC-CVD) Process. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 148, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosime, E.M. A Review on Surface Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes: Methods and Applications. Discov. Nano 2023, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeniyurt, Y.; Kilic, S.; Güner-Yılmaz, Ö.Z.; Bozoglu, S.; Meran, M.; Baysak, E.; Kurkcuoglu, O.; Hizal, G.; Karatepe, N.; Batirel, S.; et al. Fmoc-PEG Coated Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube Carriers by Non-Covalent Functionalization: An Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 648366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veetil, J.V.; Ye, K. Development of Immunosensors Using Carbon Nanotubes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 23, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Davenport, A.; Li, B. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 249, 116018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbgoo, F.; Soltani, F.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M. Nanoparticles Application in High Sensitive Aptasensor Design. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, G. Carbon Nanotube-Based Fluorescence Sensors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2014, 19, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M.; Tung, T.T.; Losic, D. Carbon Nanomaterial Based Biosensors for Non-Invasive Detection of Cancer and Disease Biomarkers for Clinical Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, S.F.; Abdallah, I.A.; Bedair, A.; Abdelhameed, R.M.; Locatelli, M.; Mansour, F.R. Metal Organic Framework-Derived Carbon Nanomaterials and MOF Hybrids for Chemical Sensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 170, 117425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, M.; Fahrenthold, E.P. Internal Doping of Metallic Carbon Nanotubes for Chemiresistive Sensing of Explosive Molecules. Chem. Phys. 2023, 566, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Hu, Y.; Cui, Y. Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor-Based Chemical and Biological Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Yang, D. High-Sensitivity Flexible Electrochemical Sensor for Real-Time Multi-Analyte Sweat Analysis. Talanta 2025, 287, 127644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, A.; Xian, X. Optical Sensors for Transdermal Biomarker Detection: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Piezoelectric Materials for Flexible and Wearable Electronics: A Review. Mater. Des. 2021, 211, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls, A.; Maurer Ditty, M.; Dehghandehnavi, F.; Zheng, S.-Y. Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanotubes as a Unique Material for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6287–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, S.S.; Yadav, S.; Pratap Singh, A.; SanthiBhushan, B.; Srivastava, A. Investigation of Pristine and B/N/Pt/Au/Pd Doped Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube as Phosgene Gas Sensor: A First-Principles Analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 588, 152989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanek, B.; Milowska, K.Z.; Przypis, Ł.; Stando, G.; Matuszek, K.; MacFarlane, D.; Payne, M.C.; Janas, D. Doping Engineering of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Nitrogen Compounds Using Basicity and Alignment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25861–25877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Hao, B.; Ma, P.-C. Flexible Sensor Based on Polymer Nanocomposites Reinforced by Carbon Nanotube Foam Derivated from Cotton. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 192, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargoletti, E.; Cappelletti, G. Breakthroughs in the Design of Novel Carbon-Based Metal Oxides Nanocomposites for VOCs Gas Sensing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Hamimed, S.; Slimi, H.; Othmani, A.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M.; Bechelany, M. Modern Designs of Electrochemical Sensor Platforms for Environmental Analyses: Principles, Nanofabrication Opportunities, and Challenges. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 38, e00199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toksha, B.; Gupta, P.; Rahaman, M. Hydrogen Sensing with Palladium-Based Materials: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities. Chem. Asian J. 2024, 19, e202400127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashkoor, F.; Shoeb, M.; Khan, M.N.; Choo, G.; Baek, S.-S.; Jeong, C. CNT Functionalized GdCoBi Ternary Metal Oxide Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Energy Storage Applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Song, M.; Lee, D.-J.; Han, S.-S.; Park, S.-S. Properties of Silicone Rubber-Based Composites Reinforced with Few-Layer Graphene and Iron Oxide or Titanium Dioxide. Polymers 2021, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, N.; Kumar, V.; Manikkavel, A.; Park, S.-S.; Kumar Mandal, T.; Woo Joo, S. Great New Generation Carbon Microsphere-Based Composites: Facile Synthesis, Properties and Their Application in Piezo-Electric Energy Harvesting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 156078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.S.; Ha, N.H.; Thinh, D.D.; Nam, N.H.; Huong, N.T.; Thi Hue, N.; Hoang, T.V. Enhanced Sensitivity of Self-Powered NO2 Gas Sensor to Sub-Ppb Level Using Triboelectric Effect Based on Surface-Modified PDMS and 3D-Graphene/CNT Network. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mahajan, P.; Alsubaie, A.S.; Khanna, V.; Chahal, S.; Thakur, A.; Yadav, A.; Arya, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, G. Next-Generation Nanomaterials-Based Biosensors: Real-Time Biosensing Devices for Detecting Emerging Environmental Pollutants. Mater. Today Sustain. 2025, 29, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, D.; Gill, N.S. Smart Sensors: Analysis of Different Types of IoT Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Manjakkal, L.; Mitra, S.; Petillot, Y.R.; Shutler, J.; Scott, E.M.; Willander, M.; Dahiya, R. Connected Sensors, Innovative Sensor Deployment, and Intelligent Data Analysis for Online Water Quality Monitoring. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13805–13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh Fakhr, M.; Lopez Carrasco, I.; Belyaev, D.; Kang, J.; Shin, Y.; Yeo, J.-S.; Koh, W.-G.; Ham, J.; Michaelis, A.; Opitz, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Wearable Electrochemical Biosensors towards Technological and Material Aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2024, 19, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-F. Fundamental Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes: Current Understanding and the Related Experimental Studies. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2004, 126, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, S.; Lee, C.W.; Sakthivelpathi, V.; Chung, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Continuous Biopotential Monitoring via Carbon Nanotubes Paper Composites (CPC) for Sustainable Health Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhu, M.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. A Microfluidic-Integrated Lateral Flow Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (MI-IF-RPA) Assay for Rapid COVID-19 Detection. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Shi, J.; Hao, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. PEDOT:PSS/CNT Composites Based Ultra-Stretchable Thermoelectrics and Their Application as Strain Sensors. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parvin, N.; Joo, S.W.; Mandal, T.K.; Park, S.S. Great Carbon Nano Materials Based Composites for Electronic Skin: Intelligent Sensing, and Self-Powered Nano Generators. Nano Energy 2025, 137, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, K. Wearable Thermoelectric-Powered Textile-Based Temperature and Pressure Dual-Mode Sensor Arrays. Org. Electron. 2022, 106, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücer, S.; Sarac, B.; Ciftci, F. Tissue Engineering and Biosensing Applications of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2025, 9, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yao, D.; Hu, S.; Du, D.; Shao, W.; Tang, B.; Fan, J.-M.; Tang, X.-G.; Gao, J. Highly Conductive, Washable and Super-Hydrophobic Wearable Carbon Nanotubes e-Textile for Vacuum Pressure Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Zhang, X.; Yong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, R.; Li, Q. Carbon-Nanotube Fibers for Wearable Devices and Smart Textiles. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10529–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.-Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.S. Real-Time Position Detecting of Large-Area CNT-Based Tactile Sensors Based on Artificial Intelligence. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2022, 60, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, D.-M. Machine Learning as a “Catalyst” for Advancements in Carbon Nanotube Research. Nanomater 2024, 14, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of Deep Learning: Concepts, CNN Architectures, Challenges, Applications, Future Directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ni, P.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Carbon Nanotubes Regulated by Oxidizing Functional Groups as Peroxidase Mimics for Total Antioxidant Capacity Determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 11, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, M. Advanced Functionalization Strategies for Carbon Nanotube Polymer Composites: Achieving Superior Dispersion and Compatibility. Polym. Technol. Mater. 2025, 64, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, N.M.; Vasudevan, A.; Jurov, A.; Korent, A.; Slobodian, P.; Zavašnik, J.; Cvelbar, U. Improving Sensing Properties of Entangled Carbon Nanotube-Based Gas Sensors by Atmospheric Plasma Surface Treatment. Microelectron. Eng. 2020, 232, 111403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalia, A.; Zhang, L.; Sundah, N.R.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H. Analytical Device Miniaturization for the Detection of Circulating Biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwen, T.; Shu, D.; Zou, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Carbon Nanotubes: A Powerful Bridge for Conductivity and Flexibility in Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamansky, K.K.; Fedorov, F.S.; Shandakov, S.D.; Chetyrkina, M.; Nasibulin, A.G. A Gas Sensor Based on Free-Standing SWCNT Film for Selective Recognition of Toxic and Flammable Gases under Thermal Cycling Protocols. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 417, 136116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulemo, P.M.; Kim, D.-H.; Shin, H.; Cho, H.-J.; Koo, W.-T.; Choi, S.-J.; Park, C.; Ahn, J.; Güntner, A.T.; Penner, R.M.; et al. Selectivity in Chemiresistive Gas Sensors: Strategies and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2025, 125, 4111–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Guan, J.-F.; Zhao, G.-Q.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-P.; Yu, J.-G.; Li, W.-J. Construction of a Highly Sensitive Signal Electrochemical Sensor Based on Self-Assembled Cobalt Oxide-Hydroxylated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Composite for Detection of Dopamine in Bovine Serum Samples. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrera, C.; Torres Andón, F.; Feliu, N. Carbon Nanotubes as Optical Sensors in Biomedicine. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10637–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseingholipourasl, A.; Syed Ariffin, S.H.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Petru, M.; Hamzah, A. Analytical Prediction of Highly Sensitive CNT-FET-Based Sensor Performance for Detection of Gas Molecules. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 12655–12661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Nag, A.; Chandra Mukhopadhyay, S.; Xu, Y. Carbon Nanotubes and Its Gas-Sensing Applications: A Review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 291, 107–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtera, K.; Walczak, M.; Pietrzak, L.; Fraczyk, J.; Szymanski, L.; Sobczyk-Guzenda, A. Synthesis of Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes for Fluorescent Biosensors. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, A.; Amadi, E.V.; Chen, Y.; Papadopoulos, C. Carbon Nanotube Assembly and Integration for Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, S.; Iftikhar, F.J.; Shah, A.; Rehman, H.A.; Iwuoha, E. Novel Interfaces for Internet of Wearable Electrochemical Sensors. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 36713–36732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Kwon, M.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.S. Biomedical Applications of CNT-Based Fibers. Biosensors 2024, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, L.R.; Ettore, N.; Jacobs, Z.L.; Zarr, A.; Weir, M.H.; Scheuerman, P.R.; Kanel, S.R.; Dubey, B. Novel Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Based Ultrasensitive Sensors for Trace Mercury(II) Detection in Water: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Gandhi, B. CNT Based Textiles for Smart ECG Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Recent Developments in Control, Automation & Power Engineering (RDCAPE), Noida, India, 10–11 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, C.R.; Avani, A.V.; Xavier, T.S.; Tomy, M.; Shaji, S.; Anila, E.I. Symmetric Supercapacitor Based on Co3O4 Nanoparticles with an Improved Specific Capacitance and Energy Density. J. Energy Storage 2024, 80, 110382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Saeed, A.; Ul-Hamid, A. A Review Featuring the Fundamentals and Advancements of Polymer/CNT Nanocomposite Application in Aerospace Industry. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, Y.; Chen, M.; Xie, L. Recent Advances in CNTs-Based Sensors for Detecting the Quality and Safety of Food and Agro-Product. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 3061–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Babele, P.; Kumar Verma, M.; Kant Bhatia, R. Carbon Nanotubes: A Review on Risks Assessment, Mechanism of Toxicity and Future Directives to Prevent Health Implication. Biocell 2021, 45, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harussani, M.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Nadeem, G.; Rafin, T.; Kirubaanand, W. Recent Applications of Carbon-Based Composites in Defence Industry: A Review. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 1281–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
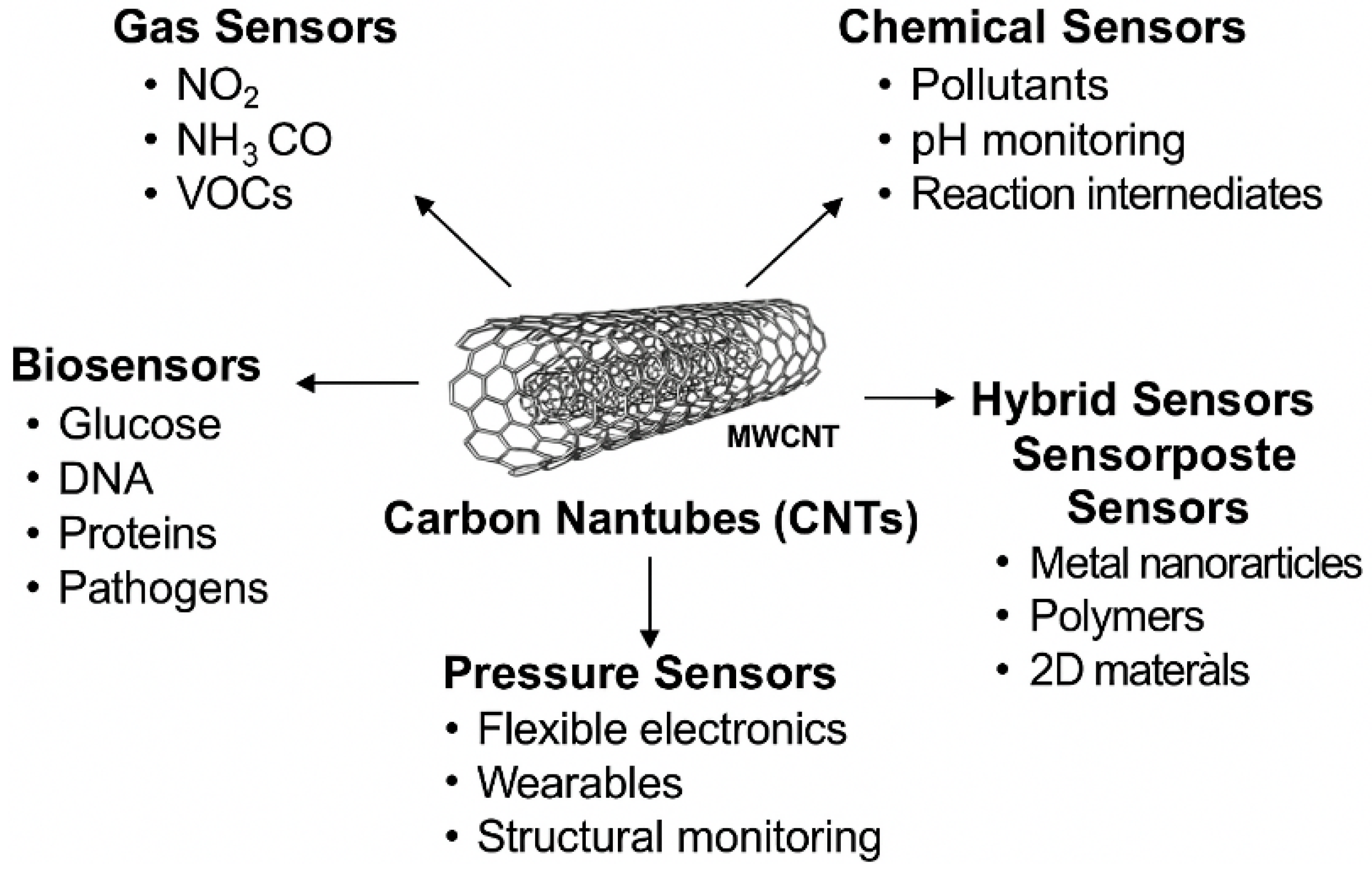
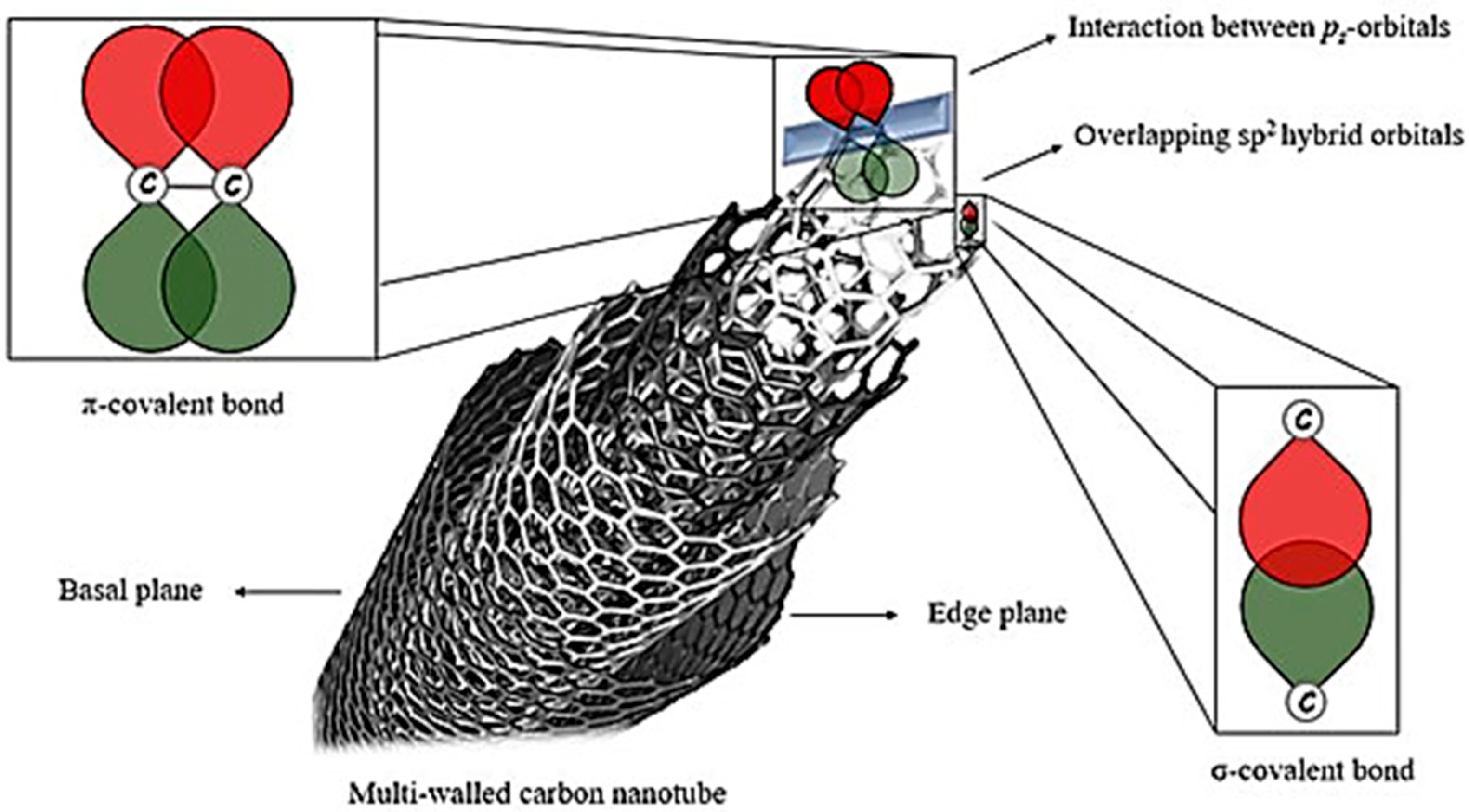
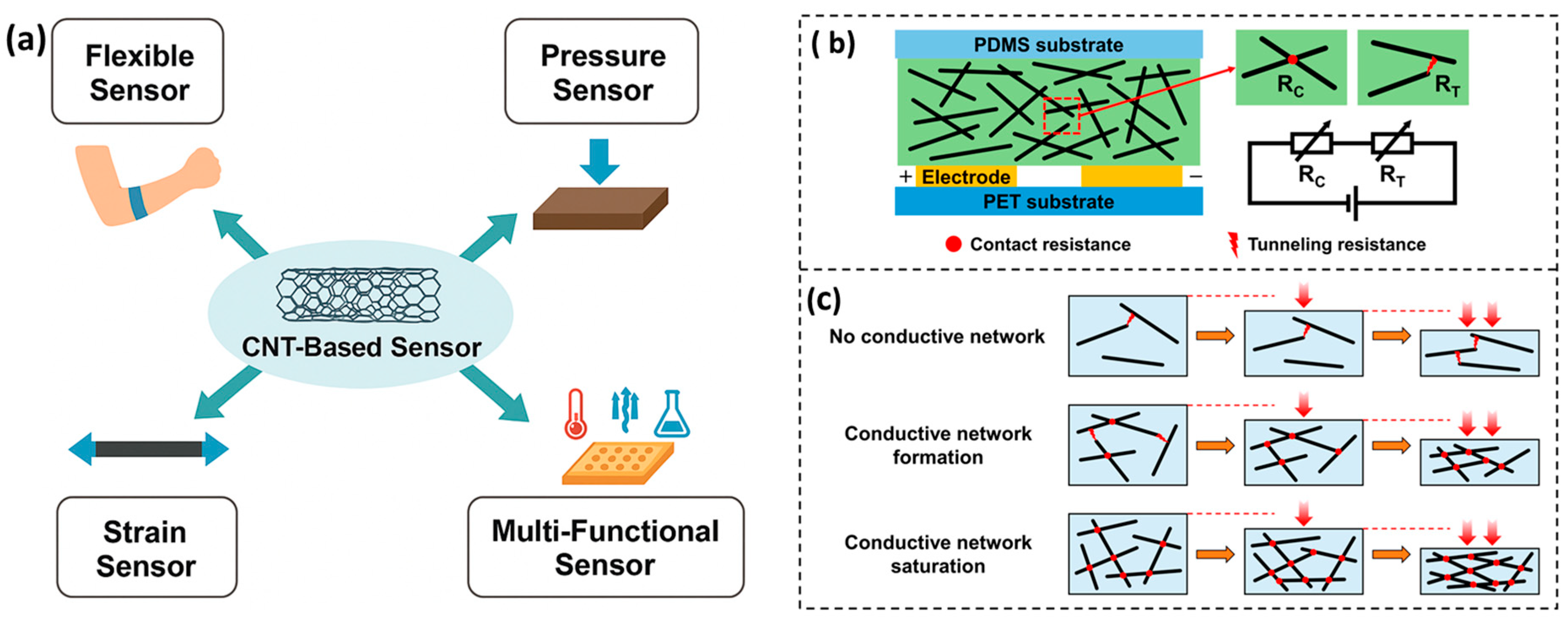
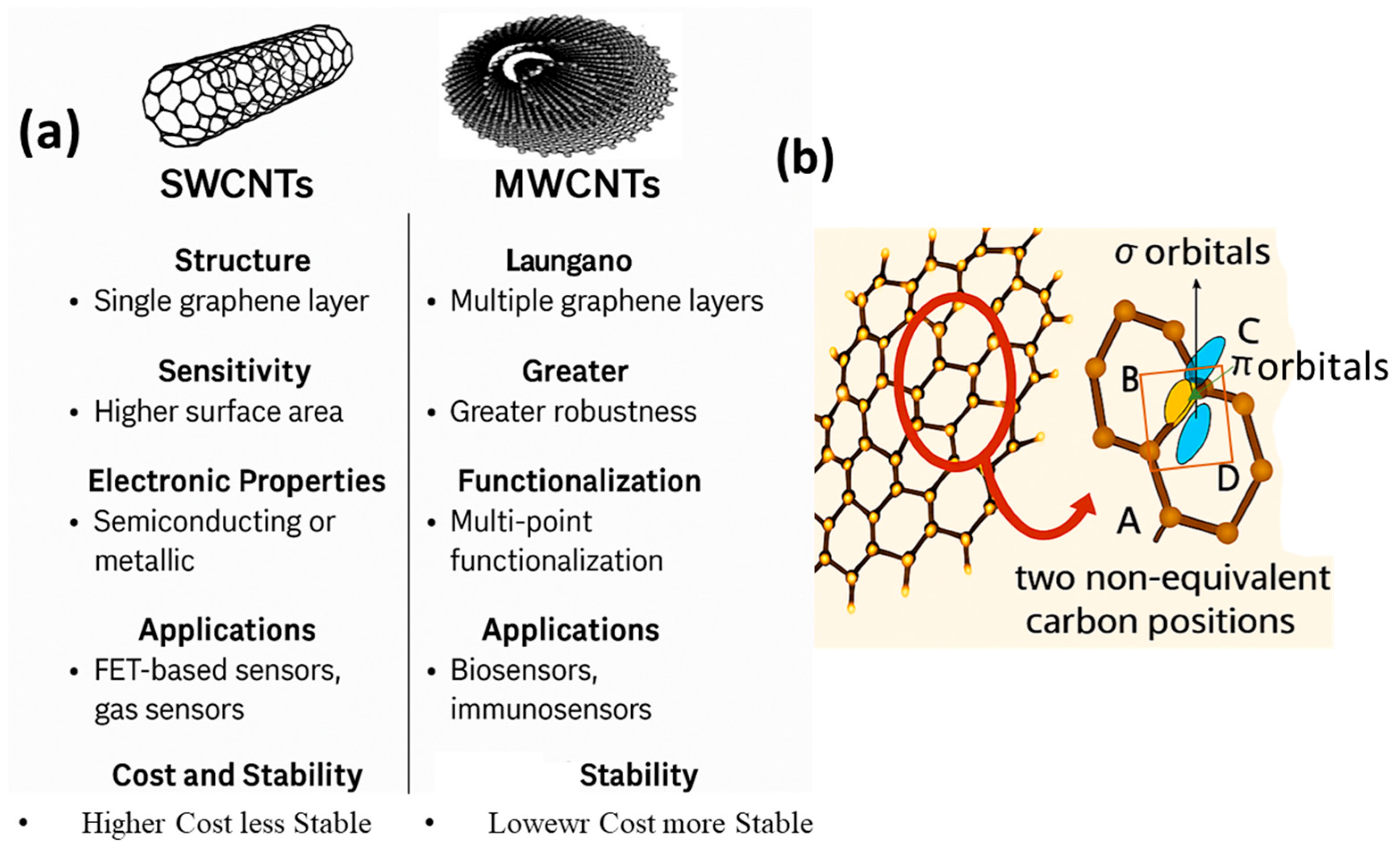
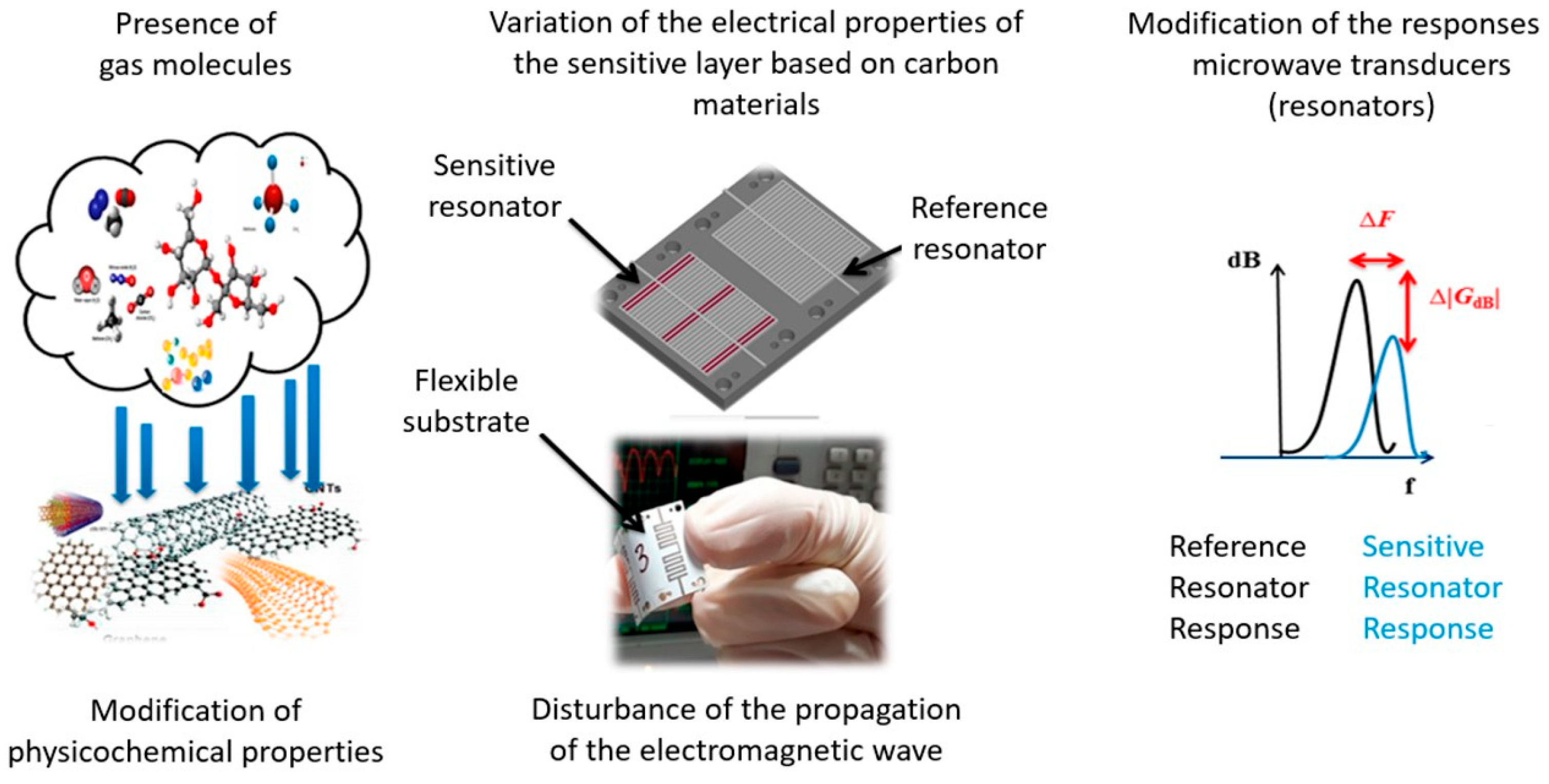
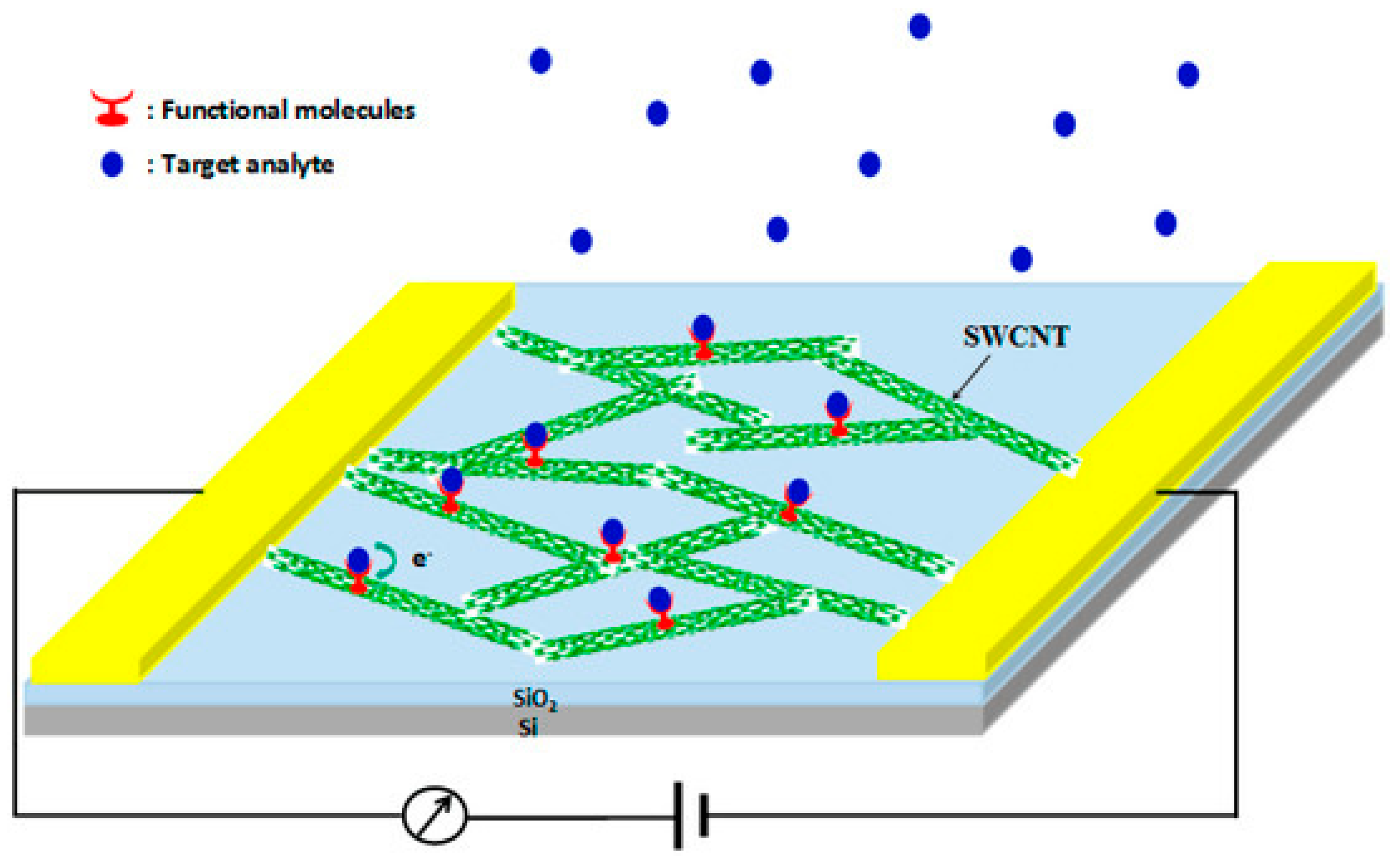
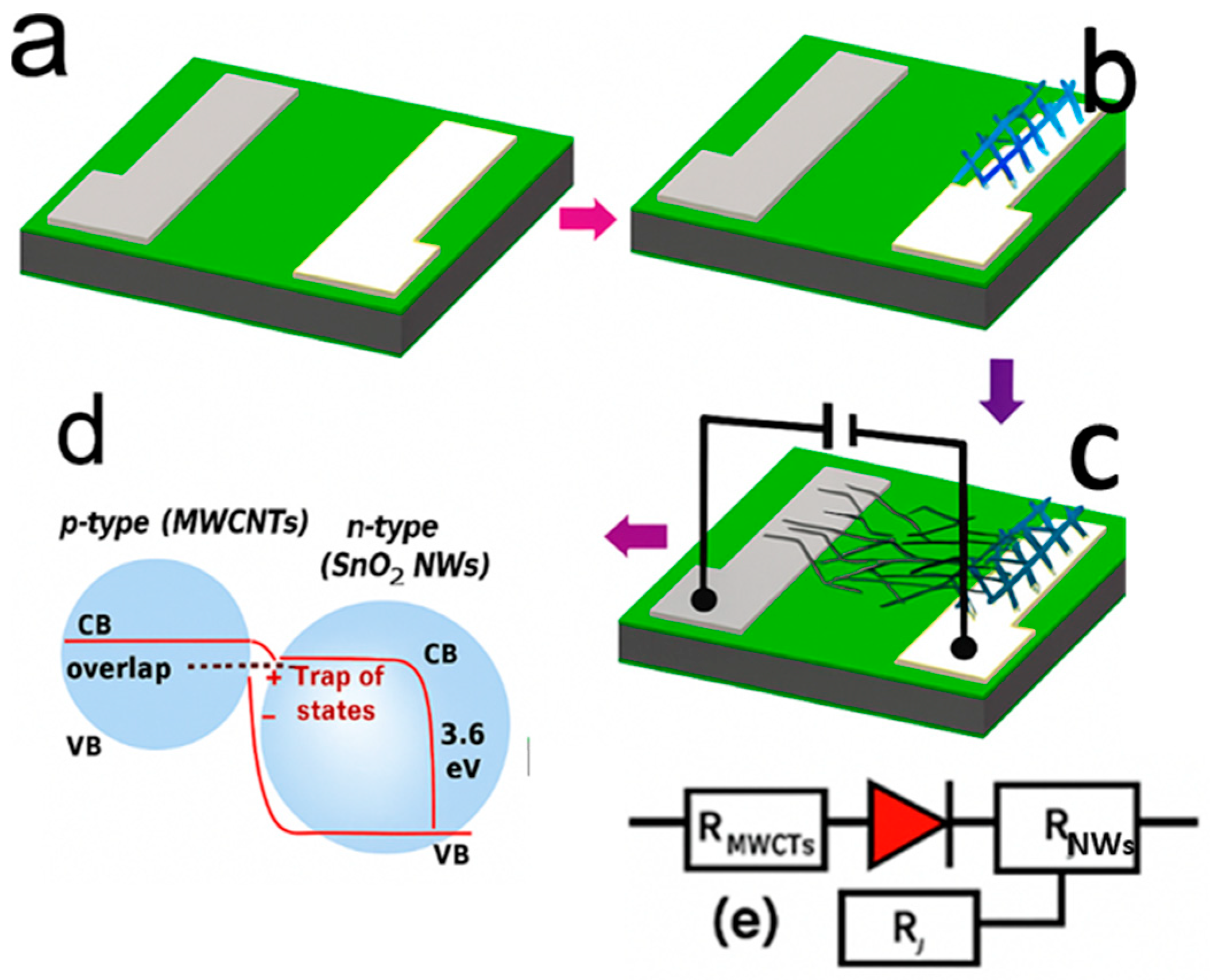
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parvin, N.; Joo, S.W.; Jung, J.H.; Mandal, T.K. Unlocking the Future: Carbon Nanotubes as Pioneers in Sensing Technologies. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13070225
Parvin N, Joo SW, Jung JH, Mandal TK. Unlocking the Future: Carbon Nanotubes as Pioneers in Sensing Technologies. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(7):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13070225
Chicago/Turabian StyleParvin, Nargish, Sang Woo Joo, Jae Hak Jung, and Tapas K. Mandal. 2025. "Unlocking the Future: Carbon Nanotubes as Pioneers in Sensing Technologies" Chemosensors 13, no. 7: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13070225
APA StyleParvin, N., Joo, S. W., Jung, J. H., & Mandal, T. K. (2025). Unlocking the Future: Carbon Nanotubes as Pioneers in Sensing Technologies. Chemosensors, 13(7), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13070225







