Discovery of Lithospermate B as a Potential Ligand for the Malarial E2 Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme via Multiplexed Native Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Malarial Proteins
2.3. TCM Materials
2.4. Extraction of the TCMs
2.5. Compound Isolation from Danshen
2.6. Protein Preparation
2.7. Mass Spectrometry Instrument Control and Acquisition
2.8. Lithospermate B
2.9. Kd Determination
3. Results
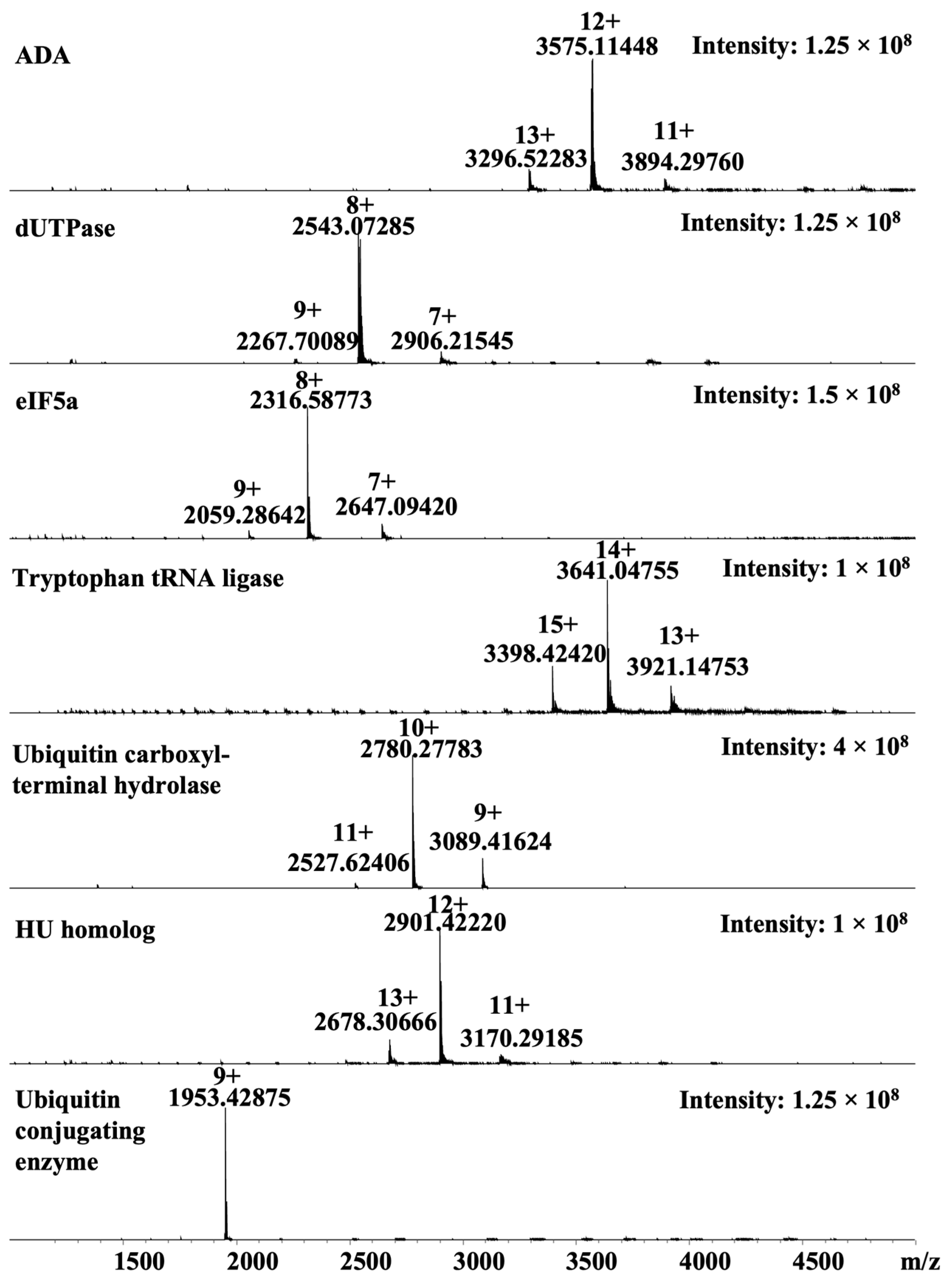
3.1. Malarial Proteins
3.2. Native Mass Spectrometry Platform
3.3. Native MS Screening
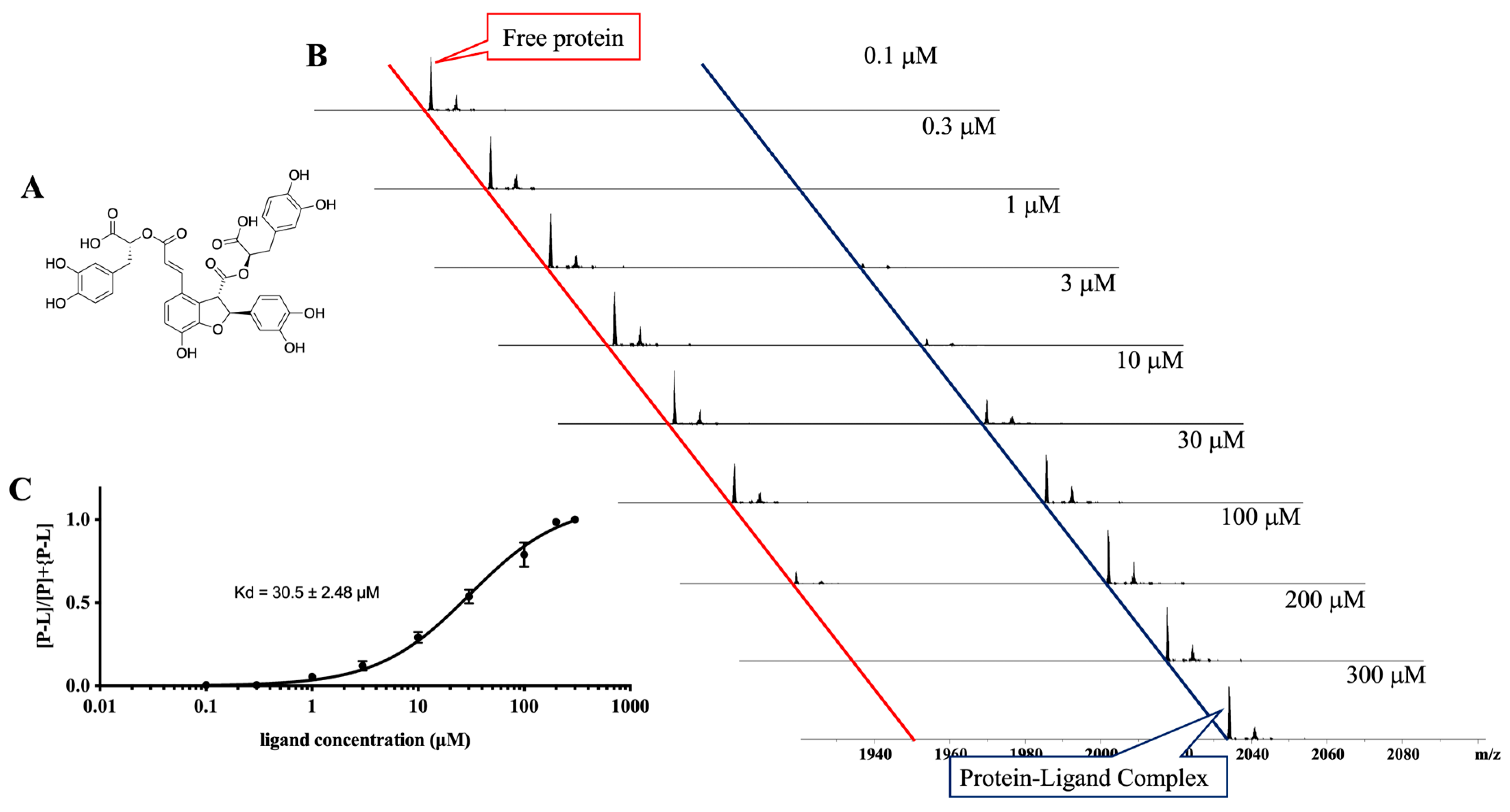
3.4. Ligand Purification, Identification, and Evaluation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Malaria Report 2024; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–50.
- Duffey, M.; Shafer, R.W.; Timm, J.; Burrows, J.N.; Fotouhi, N.; Cockett, M.; Leroy, D. Combating Antimicrobial Resistance in Malaria, HIV and Tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turschner, S.; Efferth, T. Drug Resistance in Plasmodium: Natural Products in the Fight Against Malaria. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamara, S.; den Boer, M.A.; Heck, A.J.R. High-Resolution Native Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 7269–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, N. Protein Ligand Interactions Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2365, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Damian, L. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry for Studying Protein-Ligand Interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1008, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Groftehauge, M.K.; Hajizadeh, N.R.; Swann, M.J.; Pohl, E. Protein-ligand interactions investigated by thermal shift assays (TSA) and dual polarization interferometry (DPI). Acta Crystallogr. D 2015, 71, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leney, A.C.; Heck, A.J. Native Mass Spectrometry: What is in the Name? J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.L.; Nguyen, G.T.H.; Donald, W.A. Protein-Small Molecule Interactions in Native Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 7327–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Schmidt, C. Native Mass Spectrometry-A Valuable Tool in Structural Biology. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, F.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A. Native Mass Spectrometry-directed Drug Discovery: Recent Advances in Investigating Protein Function and Modulation. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilidou, A.F.M.; Sokratous, K.; Yen, H.Y.; De Colibus, L. High-Throughput Native Mass Spectrometry Screening in Drug Discovery. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 837901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.S.; Liu, M.M.; Staker, B.L.; Buchko, G.W.; Quinn, R.J. Drug-Repurposing Screening Identifies a Gallic Acid Binding Site on SARS-CoV-2 Non-structural Protein 7. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. 2023, 6, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, R.J.; Mak, T.; Littler, D.R.; Rossjohn, J.; Liu, M.M. Discovery of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nsp9 Binders from Natural Products by a Native Mass Spectrometry Approach. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.; Pedro, L.; Mak, T.; McCormick, B.; Rowley, J.; Liu, M.M.; Di Capua, A.; Williams-Noonan, B.; Pham, N.B.; Pouwer, R.; et al. Fragment-based Screening of a Natural Product Library against 62 Potential Malaria Drug Targets Employing Native Mass Spectrometry. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, H.; Roullier, C.; Campitelli, M.; Trenholme, K.R.; Gardiner, D.L.; Andrews, K.T.; Skinner-Adams, T.; Crowther, G.J.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Quinn, R.J. Gametocyte Inhibition Identified from a Natural-Product-Based Fragment Library. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaas, A.R.; Grice, D.; Han, J.Y.; Feng, Y.J.; Capua, A.D.; Mak, T.; Laureanti, J.A.; Buchko, G.W.; Myler, P.J.; Cook, G.; et al. Discovery of a Natural Product That Binds to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Protein Rv1466 Using Native Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajsa, J.; McCluskey, A.; Gordon, C.P.; Stewart, S.G.; Hill, T.A.; Sahu, R.; Duke, S.O.; Tekwani, B.L. The Antiplasmodial Activity of Norcantharidin Analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6688–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suberu, J.O.; Gorka, A.P.; Jacobs, L.; Roepe, P.D.; Sullivan, N.; Barker, G.C.; Lapkin, A.A. Anti-Plasmodial Polyvalent Interactions in Artemisia annua L. Aqueous Extract-Possible Synergistic and Resistance Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Du, Y. Native Mass Spectrometry for Characterization of Proteins Binding with Small Molecules and Application in Drug Discovery. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2024, 174, 117701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruwat, A.; Riangrungroj, P.; Ubonprasert, S.; Sae-ueng, U.; Kuaprasert, B.; Yuthavong, Y.; Leartsakulpanich, U.; Chitnumsub, P. Crystal Structure of Adenosine Deaminase Reveals a Novel Binding Pocket for Inosine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 667, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, P.C.; Taylor, E.A.; Fröhlich, R.F.G.; Schramm, V.L. Synthesis of 5′-methylthio Coformycins: Specific Inhibitors for Malarial Adenosine Deaminase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6872–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittingham, J.L.; Leal, I.; Nguyen, C.; Kasinathan, G.; Bell, E.; Jones, A.F.; Berry, C.; Benito, A.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Dodson, E.J.; et al. dUTPase as a Platform for Antimalarial Drug Design: Structural Basis for the Selectivity of a Class of Nucleoside Inhibitors. Structure 2005, 13, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Moreno, G.; Sánchez-Carrasco, P.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M.; Johansson, N.G.; Müller, S.; Baragana, B.; Hampton, S.E.; Gilbert, I.H.; Kaiser, M.; Sarkar, S.; et al. Validation of dUTPase as the Target of 5′-tritylated Deoxyuridine Analogues with Anti-malarial Activity. Malaria J. 2019, 18, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragaña, B.; McCarthy, O.; Sánchez, P.; Bosch-Navarrete, C.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Whittingham, J.L.; Roberts, S.M.; Zhou, X.X.; Wilson, K.S.; et al. β-Branched Acyclic Nucleoside Analogues as Inhibitors of dUTPase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2378–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molitor, I.M.; Knöbel, S.; Dang, C.; Spielmann, T.; Alléra, A.; König, G.M. Translation Initiation Factor eIF-5A from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2004, 137, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Heiss, K.; Mueller, A.K.; Fimmers, R.; Matthes, J.; Njuguna, J.T. Inhibition of EIF-5A Prevents Apoptosis in Human Cardiomyocytes after Malaria Infection. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhibber-Goel, J.; Yogavel, M.; Sharma, A. Structural Analyses of the Malaria Parasite Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases Provide New Avenues for Antimalarial Drug Discovery. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaje, C.F.A.; Cheung, V.; Kennedy, K.; Lim, E.E.; Baell, J.B.; Griffin, M.D.W.; Ralph, S.A. Selective Inhibition of Apicoplast Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase Causes Delayed Death in Plasmodium falciparum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.F.; Lima-Pinheiro, A.; Ferreira, P.E. Ubiquitin-proteasome System in Plasmodium: A Potential Antimalarial Target to Overcome Resistance-A Systematic Review. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1441352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Jain, S.K.; Walker, L.A.; Tekwani, B.L. Inhibitors of Ubiquitin E3 Ligase as Potential New Antimalarial Drug Leads. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, R.D.; Rosenthal, M.R.; Ashraf, K.; Bhanot, P.; Ng, C.L.; Flaherty, D.P. Identification of Covalent Fragment Inhibitors for Plasmodium falciparum UCHL3 with Anti-malarial Efficacy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 94, 129458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Hirai, M.; Maeda, K.; Yui, R.; Itoh, K.; Namiki, S.; Morita, T.; Hata, M.; Murakami-Murofushi, K.; Matsuoka, H.; et al. The Plasmodium HU Homolog, Which Binds the Plastid DNA Sequence-independent Manner, Is Essential for the Parasite’s Survival. Febs Lett. 2009, 583, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.T.H.; Bennett, J.L.; Liu, S.; Hancock, S.E.; Winter, D.L.; Glover, D.J.; Donald, W.A. Multiplexed Screening of Thousands of Natural Products for Protein-Ligand Binding in Native Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 21379–21387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Quinn, R.J. Development of a Target Identification Approach Using Native Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Lee, H.C.; Ahn, C.W.; Park, W.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.; Cho, D.; Lee, G.T.; Li, H.R. Effective Isolation ofMmagnesium Lithospermate B and Its Inhibition of Aldose Reductase and Fibronectin on Mesangial Cell Line. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, L.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Song, W.B.; Chen, C.G.; Li, D.X.; Zhou, X.Y.; Gu, Y.L.; Hu, L.; Zhao, J.; Xu, W.W.; et al. High-Purity Magnesium Lithospermat B and Preparation Method Therefor. European Patent No. EP3127905, 9 February 2015. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=EP192181374&_fid=WO2015149589 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Guo, Y.X.; Shi, C.Z.; Zhang, L.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Extraction and Isolation of Lithospermic Acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Using Aqueous Two-phase Extraction Followed by High-performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3624–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.H.; Chung, T.Y.; Li, F.Y.; Chen, H.A.; Tzen, J.T.C. Enhancing the Potency of Lithospermate B for Inhibiting Na/K-ATPase Activity by Forming Transition Metal Ion Complexes. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.L.; Lu, X. Magnesium Lithospermate B Improves Pulmonary Artery Banding Induced Right Ventricular Dysfunction by Alleviating Inflammation via p38MAPK Pathway. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 63, 101935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, W.; Mackeen, M.M.; Kramer, H.B. Natural Product Inhibitors of Ubiquitin Conjugation and Deconjugation. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2016, 49, 207–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Faulkner, D.J. Leucettamines A and B, Two Antimicrobial Lipids from the Calcareous Sponge Leucetta microraphis. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M.; Ohta, T.; Yokosawa, H. Leucettamol A: A new inhibitor of Ubc13-Uev1A interaction isolated from a marine sponge, Leucetta aff. microrhaphis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6319–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushiyama, S.; Umaoka, H.; Kato, H.; Suwa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Manadosterols A and B, Sulfonated Sterol Dimers Inhibiting the Ubc13-Uev1A Interaction, Isolated from the Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, E.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Variabines A and B: New β-carboline Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Quinn, R.J.; Liu, M. Discovery of Lithospermate B as a Potential Ligand for the Malarial E2 Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme via Multiplexed Native Mass Spectrometry. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050166
Han J, Van Voorhis WC, Quinn RJ, Liu M. Discovery of Lithospermate B as a Potential Ligand for the Malarial E2 Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme via Multiplexed Native Mass Spectrometry. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(5):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050166
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jianying, Wesley C. Van Voorhis, Ronald J. Quinn, and Miaomiao Liu. 2025. "Discovery of Lithospermate B as a Potential Ligand for the Malarial E2 Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme via Multiplexed Native Mass Spectrometry" Chemosensors 13, no. 5: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050166
APA StyleHan, J., Van Voorhis, W. C., Quinn, R. J., & Liu, M. (2025). Discovery of Lithospermate B as a Potential Ligand for the Malarial E2 Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme via Multiplexed Native Mass Spectrometry. Chemosensors, 13(5), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050166





