Geographical Origin Identification of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Broad Learning System and SHapley Additive exPlanations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
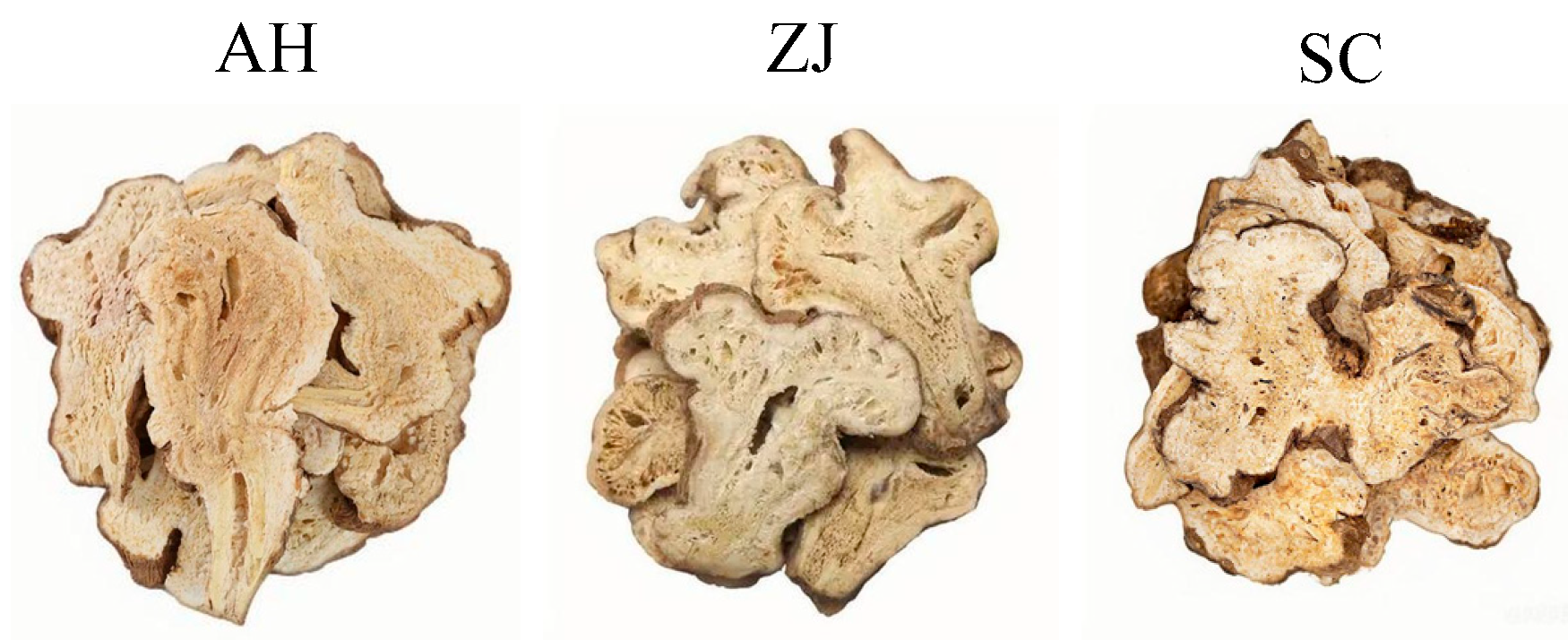
2.1. Sample Preparation
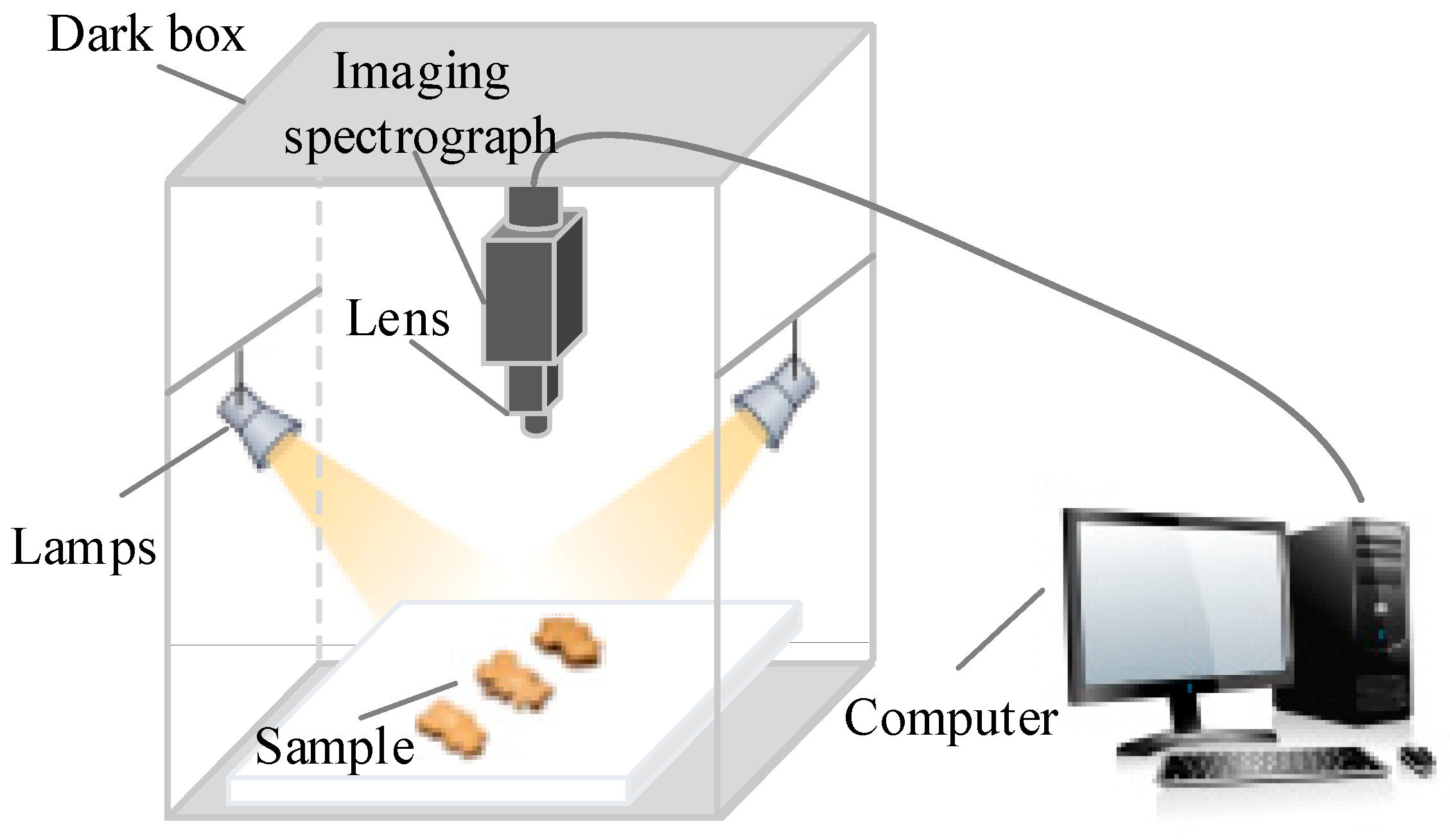
2.2. Hyperspectral Imaging System
2.3. Spectral Data Extraction
2.4. Spectral Preprocessing Method
2.5. Classification Model
2.5.1. Broad Learning System (BLS)
2.5.2. Traditional Machine Learning Methods
2.6. Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP)
2.7. Traditional Wavelength Selection Methods
2.8. Software
3. Results
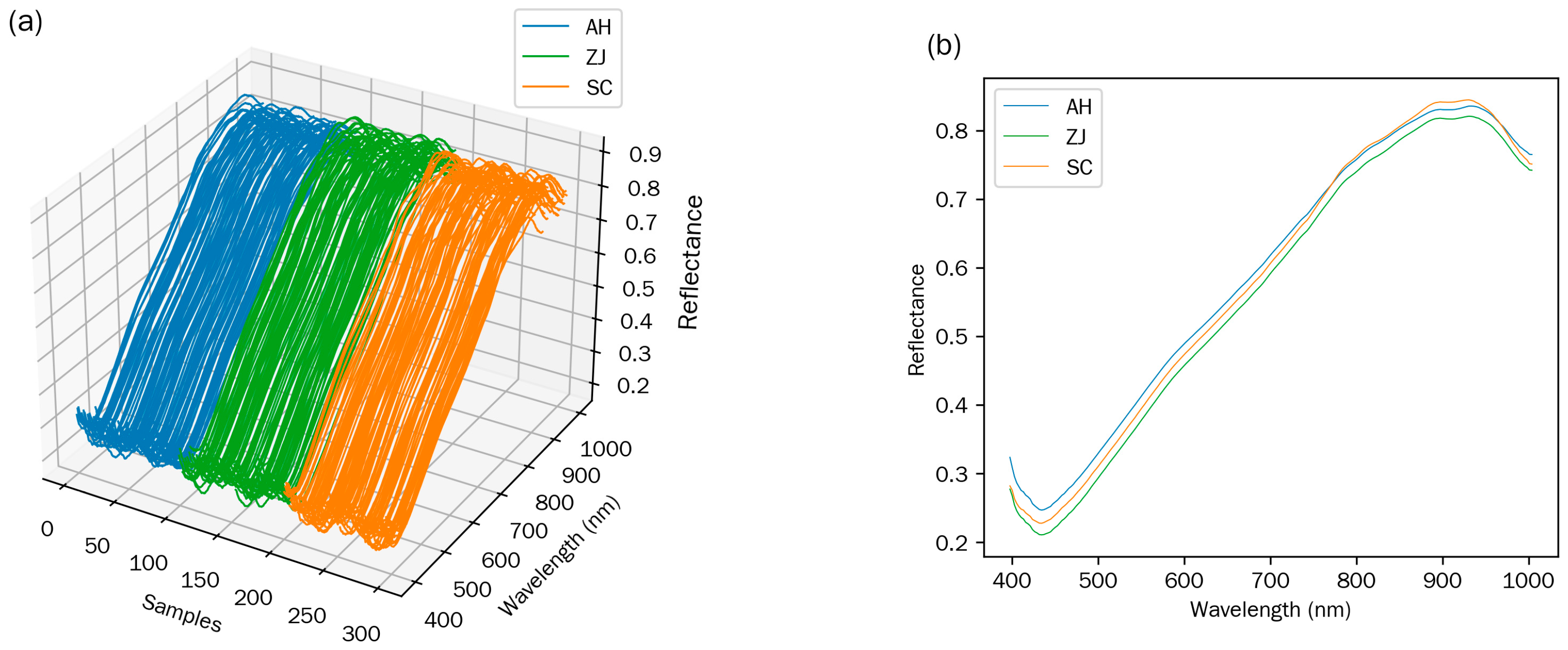
3.1. Raw Spectral Analysis
3.2. Principal Component Analysis for Raw Spectra
3.3. Modeling Using Full Wavelengths
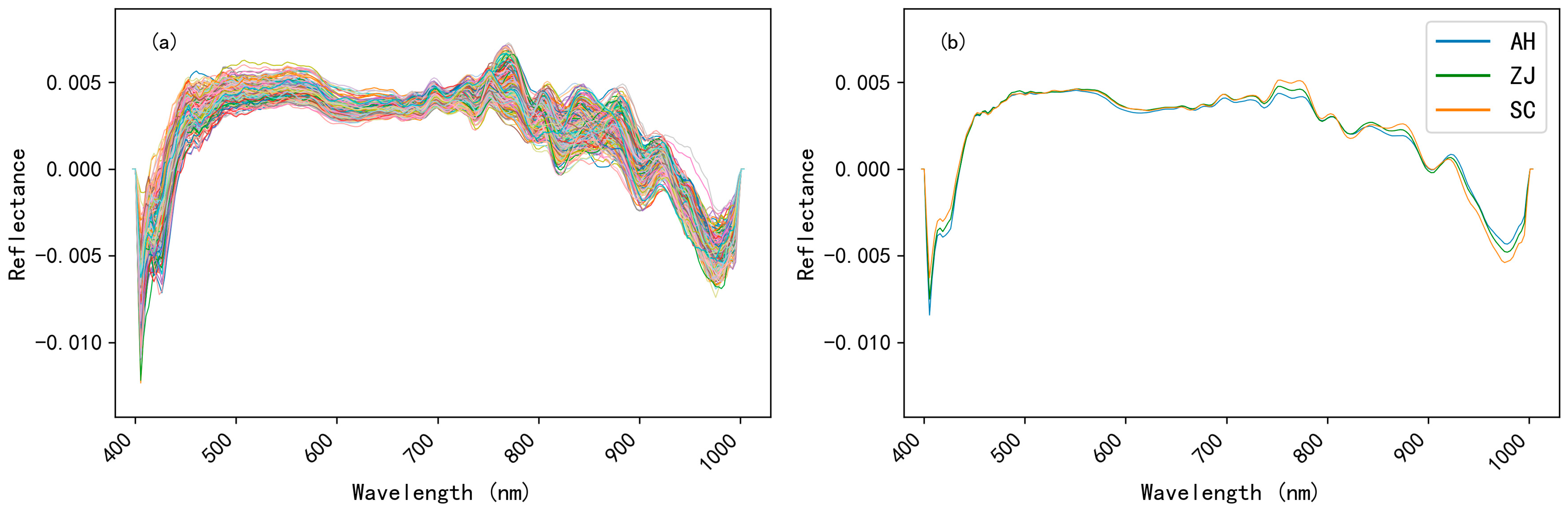
3.3.1. Spectral Preprocessing Analysis
3.3.2. Model Comparison Analysis
3.3.3. Confusion Matrix Analysis
3.4. Model Explanation and Important Wavelengths Selection via SHAP
3.5. Important Wavelengths Selection Using CARS and SPA
3.6. Modeling Using Important Wavelengths
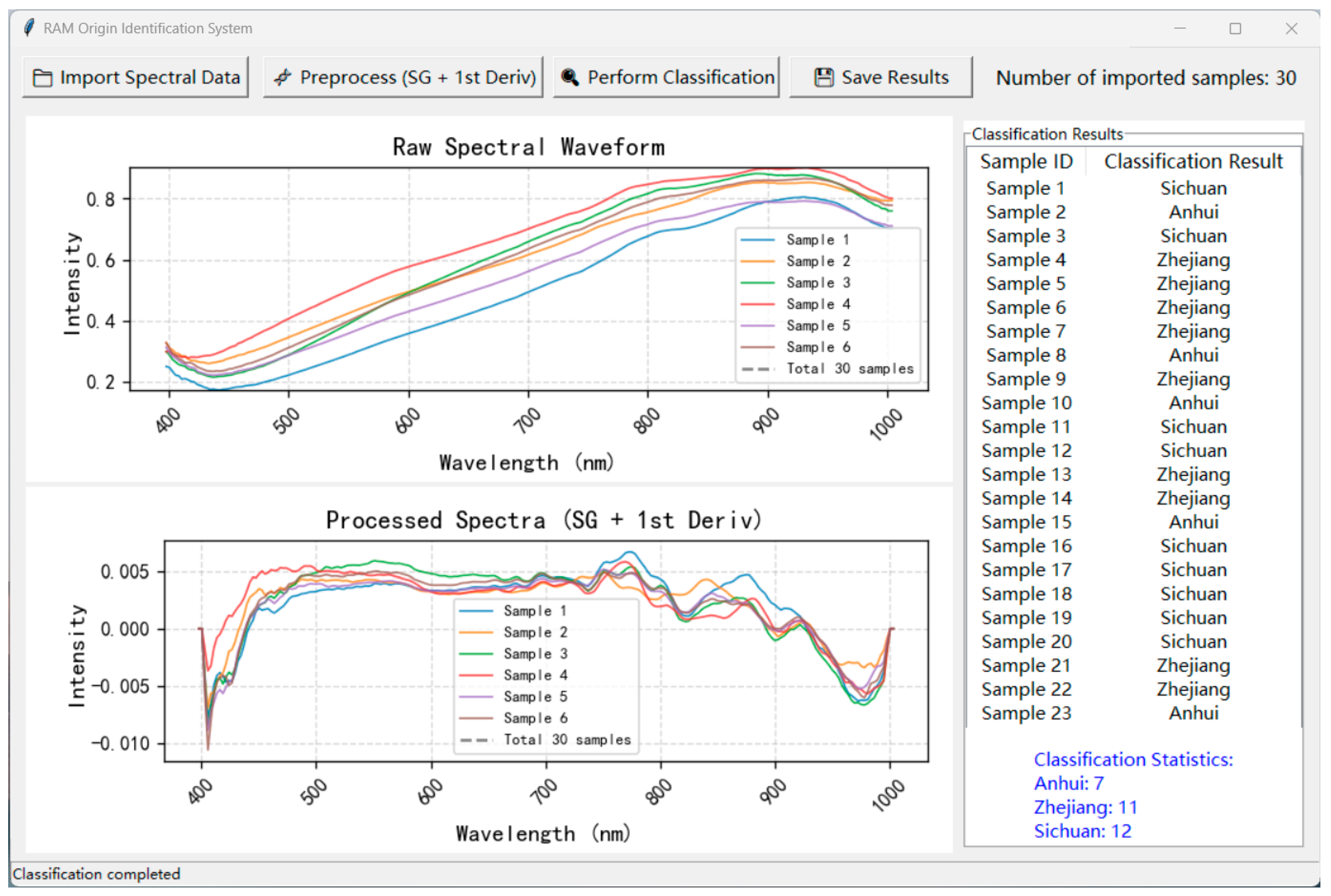
3.7. Model Deployment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Zhu, X.; Zou, H.; Yan, Y. Geographical Origin Traceability of Atractylodis macrocephalae Rhizoma Based on Chemical Composition, Chromaticity, and Electronic Nose. Molecules 2024, 29, 4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Wu, H.L.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Fu, H.Y.; Yang, X.L.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, G.; Yu, R.Q. Geographical Origin Traceability of Traditional Chinese Medicine Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. by Using Multi-Way Fluorescence Fingerprint and Chemometric Methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 269, 120737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, G.Y.; Wu, H.L.; Wang, T.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Fu, H.Y.; Yang, X.L.; Li, X.F.; Yu, R.Q. Analysis of Active Compounds and Geographical Origin Discrimination of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. by Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detection Fingerprints Combined with Chemometrics. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1674, 463121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Guo, L. Geographic Authentication of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (Baizhu) Using Stable Isotope and Multielement Analyses. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Lyu, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; et al. Authenticating the Geographic Origins of Atractylodes lancea Rhizome Chemotypes in China through Metabolite Marker Identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1237800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, C.; Li, Z.; Tang, R. A Hyperspectral Imaging Approach for Classifying Geographical Origins of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae Using the Fusion of Spectrum-Image in VNIR and SWIR Ranges (VNIR-SWIR-FuSI). Sensors 2019, 19, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.L.; Wang, T.; Ding, Y.J.; Yu, R.Q. Geographical Origin Traceability of Medicine Food Homology Species Based on an Extract-and-Shoot Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Method and Chemometrics. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 107937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Xu, Z.; Bian, Q.; Forsberg, E.; Tan, Q.; Peng, X.; He, S. Machine Learning Classification of Origins and Varieties of Tetrastigma Hemsleyanum Using a Dual-Mode Microscopic Hyperspectral Imager. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 261, 120054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Hui, X.; Qu, P.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Machine Learning in TCM with Natural Products and Molecules: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Bai, X.; Guo, J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W. Hyperspectral Discrimination of Ginseng Variety and Age from Changbai Mountain Area. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 307, 123613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lu, L.; Song, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, M.; Yuan, X.; et al. Non-Destructive Identification of Pseudostellaria heterophylla from Different Geographical Origins by Vis/NIR and SWIR Hyperspectral Imaging Techniques. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1342970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, S.; Yazdanpanah, H.; Feizy, J. Geographical Origin Differentiation and Quality Determination of Saffron Using a Portable Hyperspectral Imaging System. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y. A Lightweight Neural Network Approach for Identifying Geographical Origins and Predicting Nutrient Contents of Dried Wolfberries Based on Hyperspectral Data. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 7519–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.P.; Liu, Z. Broad Learning System: An Effective and Efficient Incremental Learning System Without the Need for Deep Architecture. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Huo, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, J.; Zhou, S. Multi-Modal Biological Feature Selection for Parkinson’s Disease Staging Based on Binary PSO with Broad Learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 94, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.; Zhao, C. An Adaptive Imbalance Modified Online Broad Learning System-Based Fault Diagnosis for Imbalanced Chemical Process Data Stream. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.L.P.; Zhang, Y. Hyperspectral Image Classification via Active Learning and Broad Learning System. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 15683–15694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, S.X. Broad Learning System with Takagi–Sugeno Fuzzy Subsystem for Tobacco Origin Identification Based on near Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 134, 109970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, F.; Ge, H.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M. Classification of Unsound Wheat Grains in Terahertz Images Based on Broad Learning System. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 4973–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhou, M.; Yan, P.; Li, D.; Lai, W.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y. Selection of Characteristic Wavelengths Using SPA for Laser Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Mine Water Inrush. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; Xu, Q.S.; Liang, Y.Z. LibPLS: An Integrated Library for Partial Least Squares Regression and Linear Discriminant Analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 176, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.H.; Bin, J.; Liu, D.L.; Xu, L.; Yan, T.L.; Cao, D.S.; Xu, Q.S. A Hybrid Variable Selection Strategy Based on Continuous Shrinkage of Variable Space in Multivariate Calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Enhancing Corn Quality Prediction: Variable Selection and Explainable AI in Spectroscopic Analysis. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Wijewardane, N.K.; Lu, Y.; Jones, D.S.; Kudenov, M.; Williams, C.; Villordon, A.; Kamruzzaman, M. Advancing Sweetpotato Quality Assessment with Hyperspectral Imaging and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilio, W.E.; Eler, D.M. From Explanations to Feature Selection: Assessing SHAP Values as Feature Selection Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2020 33rd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), Porto de Galinhas, Brazil, 7–10 November 2020; pp. 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, S.; Zeng, Z. Synergizing Wood Science and Interpretable Artificial Intelligence: Detection and Classification of Wood Species Through Hyperspectral Imaging. Forests 2025, 16, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lv, A.; Zhong, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, A. Rapid Prediction of Adulteration Content in Atractylodis Rhizoma Based on Data and Image Features Fusions from Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging Techniques. Foods 2023, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Nan, T.; Yang, J.; Huang, L. Rapid and Nondestructive Identification of Origin and Index Component Contents of Tiegun Yam Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and Chemometric Method. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 6104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Sahin, E.K. An Investigation of Feature Selection Methods for Soil Liquefaction Prediction Based on Tree-Based Ensemble Algorithms Using AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, and XGBoost. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 3173–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liao, M.; Liu, J. Geographical Origin Identification of Panax Notoginseng Using a Modified K-Nearest Neighbors Model with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 13832–13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yan, B.; Xiong, F.; Bai, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Yang, J. Tanshinone Content Prediction and Geographical Origin Classification of Salvia Miltiorrhiza by Combining Hyperspectral Imaging with Chemometrics. Foods 2024, 13, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tang, S.; Li, P.; Lin, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, N. Feasibility Study of Combining Hyperspectral Imaging with Deep Learning for Chestnut-Quality Detection. Foods 2023, 12, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Ou, X.; Guo, J. Hyperspectral imaging combined with chemometrics for rapid detection of talcum powder adulterated in wheat flour. Food Control 2023, 144, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cao, Y.; Wu, E.; Yang, R.; Xu, H.; Qiao, Y. A Discriminative Model for Early Detection of Anthracnose in Strawberry Plants Based on Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wan, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Tao, Q.; Wu, Z. Development of a Data Fusion Strategy Combining FT-NIR and Vis/NIR-HSI for Non-Destructive Prediction of Critical Quality Attributes in Traditional Chinese Medicine Particles. Vib. Spectrosc. 2025, 137, 103780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Tao, Q.; Wu, Z. An Accurate Prediction of the Physicochemical Properties of Traditional Chinese Medicine Granules Using a Multi-Source Data Model Fusion Strategy Based on Deep Ensemble Learning Algorithms. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Bei, Y. Medical Health Big Data Classification Based on KNN Classification Algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28808–28819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wen, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Xiang, X.; Liang, X. Improving the Model Robustness of Flood Hazard Mapping Based on Hyperparameter Optimization of Random Forest. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 241, 122682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, H.; Lv, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Non-Destructive Detection and Classification of Textile Fibres Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and 1D-CNN. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1224, 340238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Hua, H.; Yi, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, C. Quality Evaluation of Decoction Pieces of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae by near Infrared Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 221, 117169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirere, A.; Sun, J.; Yuhao, Z. A Rapid Non-Destructive Detection Method for Wolfberry Moisture Grade Using Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2023, 42, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bai, R.; Long, W.; Wan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, H.; Yang, J. Rapid Qualitative and Quantitative Detection for Adulteration of Atractylodis Rhizoma Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Chemometric Methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 327, 125426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ma, S.; Qi, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C. Nondestructive Detection of Rice Milling Quality Using Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine and Deep Learning Regression. Foods 2025, 14, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Rao, Z.; Li, M.; Yu, X.; Zou, L. Identification of Coal Geographical Origin Using Near Infrared Sensor Based on Broad Learning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.; Paramesha, M.; Choudhary, S.; Rane, J. Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Big Data Analytics: A Review of Methods and Applications. Partn. Univers. Int. Innov. J. PUIIJ 2024, 2, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



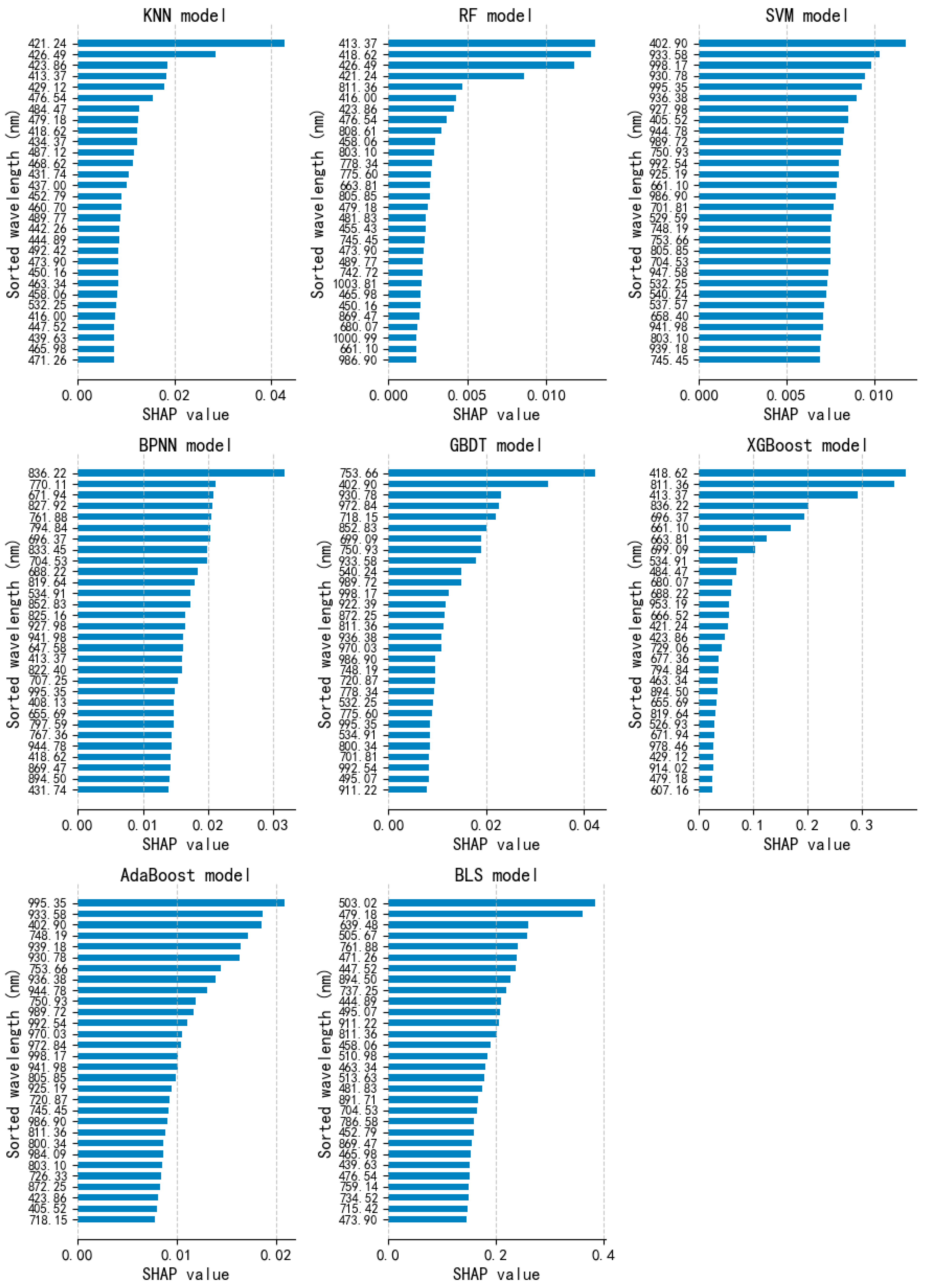
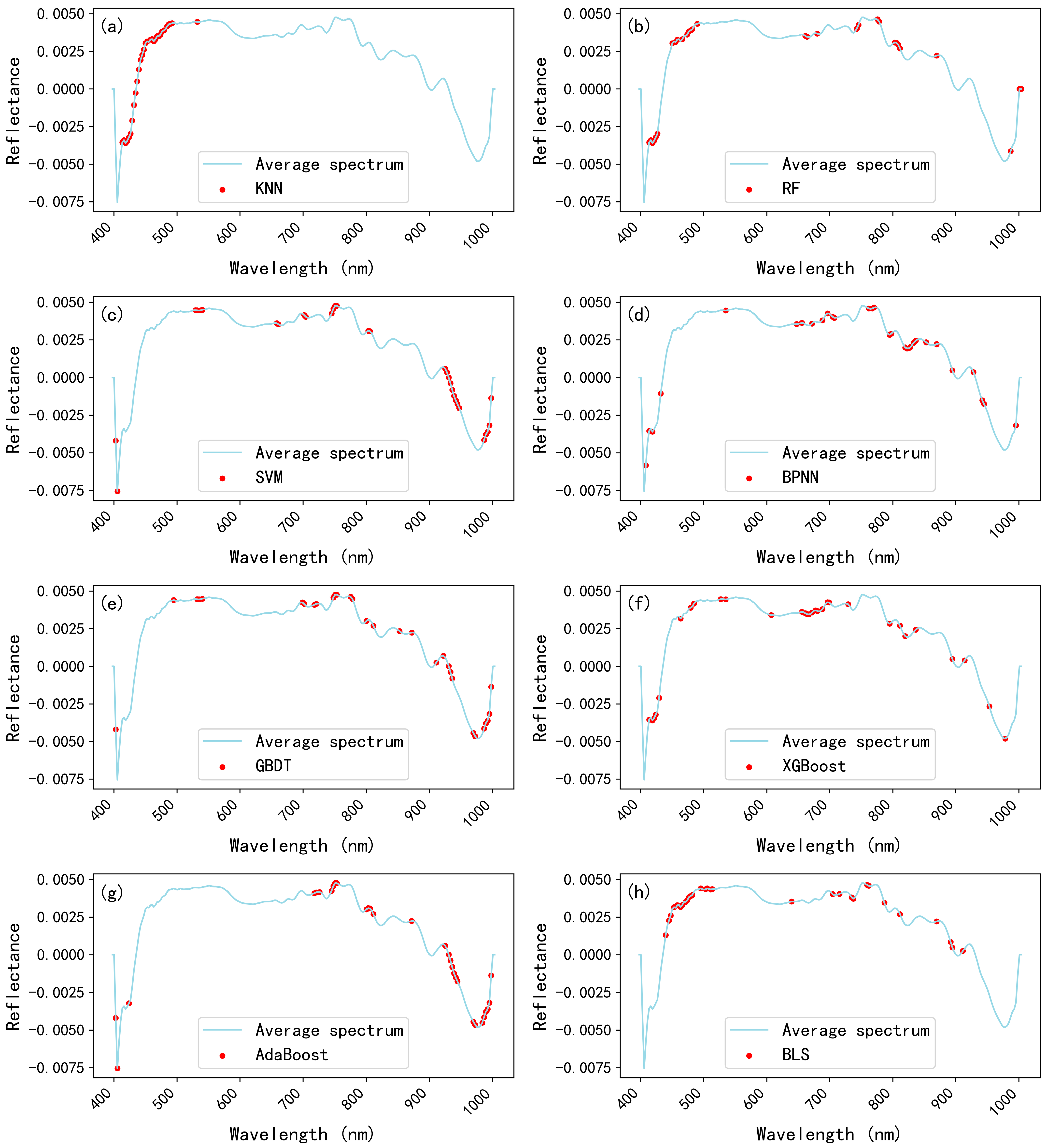


| Model | Dataset | Classification Accuracy (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | SG | SNV | MSC | SG-D1 | BS | DT | ||
| KNN | Training set | 74.29 | 73.81 | 68.10 | 68.10 | 80.95 | 76.67 | 75.24 |
| Test set | 67.78 | 68.89 | 63.33 | 63.33 | 77.78 | 56.67 | 73.33 | |
| RF | Training set | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Test set | 77.78 | 75.56 | 72.22 | 46.67 | 85.56 | 65.56 | 76.67 | |
| SVM | Training set | 86.19 | 84.29 | 89.52 | 90.00 | 100 | 90.95 | 91.90 |
| Test set | 74.44 | 74.44 | 78.89 | 60.00 | 94.44 | 70.00 | 83.33 | |
| BPNN | Training set | 89.52 | 89.05 | 98.10 | 98.57 | 100 | 93.33 | 100 |
| Test set | 81.11 | 78.89 | 86.67 | 62.22 | 91.11 | 81.11 | 85.56 | |
| GBDT | Training set | 100 | 96.67 | 100 | 96.67 | 100 | 96.19 | 98.10 |
| Test set | 72.22 | 72.22 | 76.67 | 55.56 | 88.89 | 67.78 | 81.11 | |
| XGBoost | Training set | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Test set | 73.33 | 71.11 | 75.56 | 51.11 | 92.22 | 76.67 | 80.00 | |
| AdaBoost | Training set | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Test set | 76.67 | 75.56 | 81.11 | 55.56 | 90.00 | 76.67 | 85.56 | |
| BLS | Training set | 99.05 | 100 | 99.52 | 100 | 100 | 98.57 | 100 |
| Test set | 93.33 | 92.22 | 88.89 | 68.89 | 95.56 | 90.00 | 91.11 | |
| Model | No. 1 | Classification Accuracy (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | RF | SVM | BPNN | GBDT | XGBoost | AdaBoost | BLS | ||
| SHAP | Top 20 | 68.89 | 71.11 | 77.78 | 87.78 | 75.56 | 73.33 | 77.78 | 91.11 |
| Top 25 | 68.89 | 71.11 | 84.44 | 88.89 | 71.11 | 74.44 | 78.89 | 94.44 | |
| Top 30 | 68.89 | 77.78 | 85.56 | 88.89 | 72.22 | 70.00 | 73.33 | 93.33 | |
| CARS | 36 | 73.33 | 85.56 | 93.33 | 90.00 | 87.78 | 90.00 | 92.22 | 95.56 |
| SPA | 28 | 73.33 | 82.22 | 90.00 | 93.33 | 84.44 | 81.11 | 84.44 | 94.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Han, L.; Li, C. Geographical Origin Identification of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Broad Learning System and SHapley Additive exPlanations. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110400
Li P, Liu H, Liu D, Han L, Li C. Geographical Origin Identification of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Broad Learning System and SHapley Additive exPlanations. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(11):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110400
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peng, Huaming Liu, Defang Liu, Liguo Han, and Chuanzong Li. 2025. "Geographical Origin Identification of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Broad Learning System and SHapley Additive exPlanations" Chemosensors 13, no. 11: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110400
APA StyleLi, P., Liu, H., Liu, D., Han, L., & Li, C. (2025). Geographical Origin Identification of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Broad Learning System and SHapley Additive exPlanations. Chemosensors, 13(11), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110400




