Abstract
Global population growth, intensifying climate change, and escalating food security demands are mounting. In response, modern agriculture must transcend the limitations of traditional experience-based cultivation models to address issues such as low resource utilization, poor environmental adaptability, and significant yield fluctuations. As the core technical support of smart agriculture, agricultural sensors have become the key to transformation. This review systematically introduces the classification and working principles of current mainstream agricultural sensors: according to the monitoring parameters, they can be divided into humidity sensors, light sensors, gas sensors, pressure sensors, nutrient sensors, etc. At the same time, breakthroughs in emerging technologies such as microneedle sensing, nanosensing, and wireless sensor networks are being explored, which are breaking the application limitations of traditional sensors in complex agricultural environments. Combined with specific cases, the practical value of sensor technology is improving in agricultural drought monitoring, soil detection, and agricultural product quality assessment. Looking ahead, if agricultural sensors can overcome existing limitations through breakthroughs in material innovation, multi-sensor unit integration, and artificial intelligence algorithm fusion, this will provide stronger technological support for the further advancement of smart agriculture.
1. Introduction
As living standards rise, people are increasingly concerned about agricultural food security. Traditional agricultural production models, with their overreliance on experience-based judgment and inefficient resource utilization [1,2,3], are no longer adequate for current demands [4,5]. These factors collectively drive the accelerated transformation of modern agriculture [6,7]. In this context, agricultural sensors provide core technical support for breaking through the bottleneck of traditional models through real-time perception and accurate analysis of key parameters in agricultural production [8,9,10].
Based on sensing technology, agricultural sensors [11,12,13,14] directly sense crop parameters such as temperature [15], humidity [16], nutrient content [17], and gas concentration [18] through sensitive transducers, convert physical or chemical changes into electrical signals, process them by measurement circuits, and finally realize quantitative monitoring of the agricultural environment and crop status [19]. This real-time monitoring capability can not only respond to adverse environmental factors in agricultural production in a timely manner but also provide data support for key links such as irrigation regulation, pest and disease warning, and fertilization management [20], thereby optimizing resource allocation, improving production efficiency, and reducing environmental load.
In recent years, with the rise of materials science, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence technologies, novel agricultural sensors have been transitioning from laboratory research to field applications, gradually attracting widespread attention. The emergence of novel sensing technologies such as microneedle sensing [21], nanosensing [22], and wireless sensor networks [23] has further broken through the application limitations of traditional sensors in complex agricultural environments, realizing minimally invasive, in situ, and real-time monitoring of plant physiological states [24], soil microenvironment [25], and agricultural product quality [26], which are widely used in agriculture.
This review systematically expounds the classification and working principle of current mainstream agricultural sensors; deeply discusses the research progress of emerging technologies such as microneedle sensing technology, nanosensors, and wireless sensor networks; and expounds the practical value of sensor technology in agricultural drought monitoring, soil detection, and agricultural product quality evaluation, with specific application cases. By reviewing existing technological achievements and challenges, this study aims to provide insights into the future development directions of agricultural sensors, thereby advancing the widespread adoption of smart agriculture.
2. Classification of Agricultural Sensors
Agricultural sensors are used as a detection device for the purpose of building smart agriculture [27], which can respond to the unfavorable factors of the environment in agriculture in a timely manner and facilitate agricultural production. The working principle of agricultural sensors is based on sensor technology. They usually consist of three parts: a sensitive element, a conversion element, and a measurement circuit [28]. The sensitive element, as the core part of the sensor, can directly sense the measured parameters, such as temperature, humidity, nutrient content, gas concentration, etc., and convert them into the corresponding physical or chemical quantity changes [29]. The conversion element converts the changes in physical or chemical quantities output from the sensitive element into electrical signals [30]. The measurement circuit amplifies, filters, and modulates the electrical signal output from the conversion element to facilitate subsequent signal transmission and data processing [31]. According to the types of monitoring parameters and application areas, agricultural sensors are mainly categorized into humidity sensors, light sensors, gas sensors, etc.
2.1. Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors can accurately and reliably measure the moisture content in various environments and materials. These sensors can also constitute an inexpensive alternative to laboratory analytical techniques, so humidity sensors are used in many different areas of human activity, such as food quality monitoring, meteorology, and medical devices [32].
When the air is fully saturated with moisture, the pressure exerted by the water vapor contained therein is defined as the saturated water vapor pressure (Ps), which is temperature-dependent. Therefore, the ratio of the water vapor pressure in the current environment to the saturated water vapor pressure at a specific temperature is defined as the relative humidity (RH) [33], which is one of the most commonly used methods to quantify the amount of water vapor contained in the air. In agricultural production, air humidity is one of the key environmental factors influencing the growth, development, and yield of crops. Agricultural air humidity sensors provide data support for irrigation decisions, early pest and disease warning, and crop growth regulation by sensing water vapor and converting it into electrical signals. According to the working principle, air humidity sensors are mainly divided into capacitive sensors [34] and resistive sensors [35].
2.1.1. Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors represent a classic type of humidity sensor, with their core functionality residing in an intermediate sensing layer that exhibits humidity-sensing properties. This intermediate layer serves as a dielectric layer sandwiched between two electrodes, forming a parallel-plate capacitor. When a water vapor molecule in the air enters the sensing layer, its dielectric constant changes [36]. Since the capacitance value is directly proportional to the dielectric constant of the dielectric, the change in the dielectric constant directly leads to a change in the capacitance of the capacitor. The circuitry inside the sensor converts small changes in capacitance into an easy-to-measure electrical signal, which ultimately produces the corresponding relative humidity value [37,38].
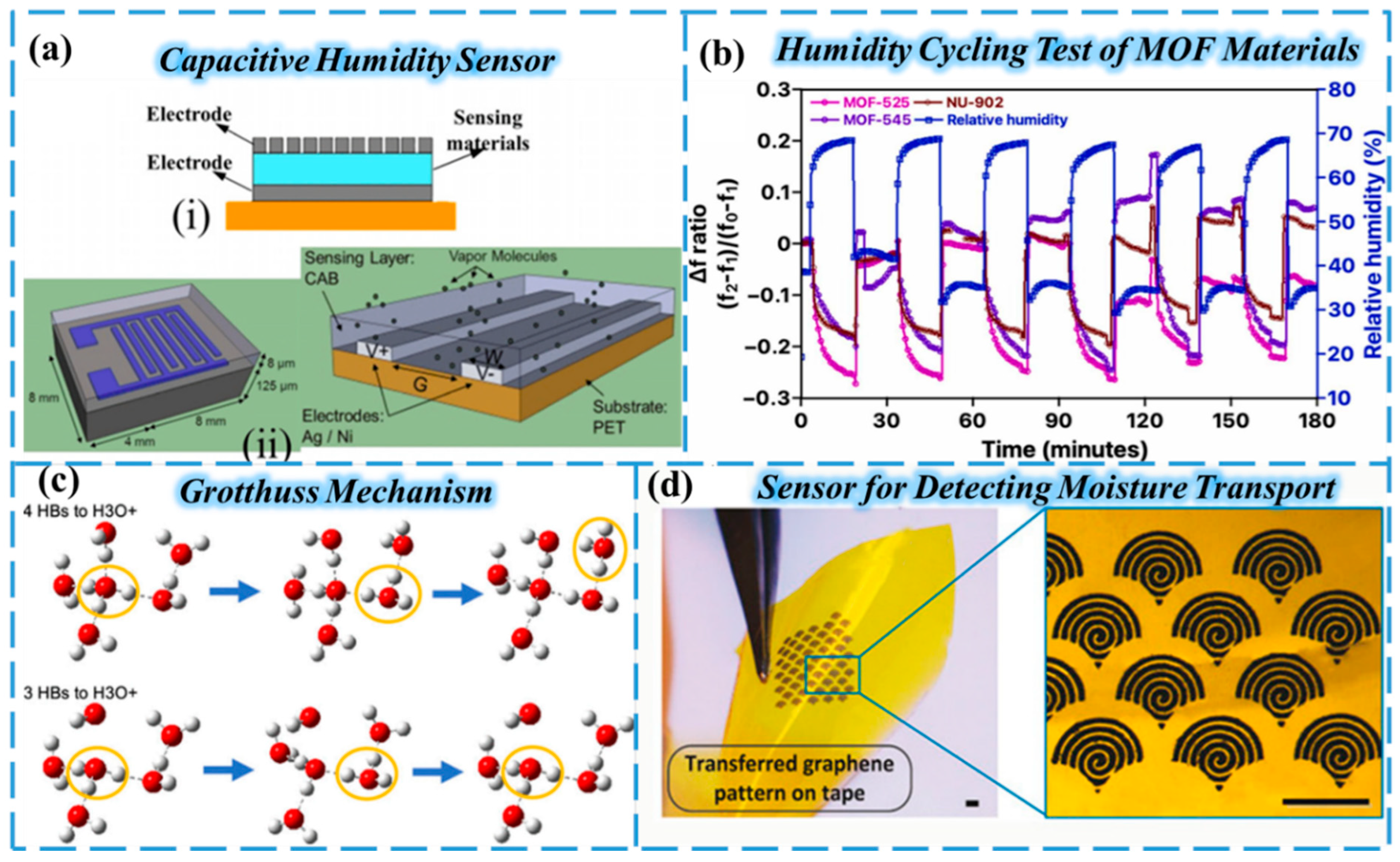
From the perspective of electrode configuration structure, capacitive humidity sensors are mainly divided into two types: parallel-plate electrodes [37] and interdigital electrodes [34,39] (Figure 1a), both of which have their own characteristics. Capacitive sensors with parallel-plate electrode structures typically exhibit outstanding sensitivity. Due to the uniform electric field between electrodes, they can keenly detect minute changes in the dielectric constant of the humidity-sensing film. With its unique plane design, the interdigital electrode structure is more convenient in the manufacturing process and easier to mass produce. However, its performance is directly affected by a number of structural parameters, such as the width, length, and spacing of the interdigitated electrodes, as well as the thickness of the sensitive film coating, which can have a significant impact on the accuracy and stability of the sensor [40,41,42].
For the selection of the intermediate sensing layer material of the capacitive humidity sensor, it usually has strong hygroscopicity, enabling it to quickly adsorb or release water molecules in the air, and its dielectric constant will change significantly with the change of the number of adsorbed water molecules, which is the key to achieving accurate humidity measurements. At the same time, in order to adapt to the complex agricultural environment, the sensing layer material also needs to have good stability and aging resistance, and it must not easily fail due to factors such as temperature and humidity alternations and dust pollution during long-term use. Among these, polymers are one of the most widely used humidity-sensitive materials. Due to their high water molecule responsiveness, room-temperature operation, low cost, and ease of coating, they are commonly employed as humidity-sensitive layers in surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices. For example, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and sulfonated tetrafluoroethylene copolymer (Nafion) are used as moisture-sensing films in SAW devices [43]. In addition, ceramic materials [44] such as alumina and zirconia are made into porous structures through special processes; these materials have a large specific surface area, strong moisture absorption capacity, and high stability, and they perform well in harsh agricultural environmental conditions such as high temperature and high humidity [45]. In recent years, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and their derivatives have attracted much attention in the field of moisture-sensitive materials due to their outstanding characteristics—such as large specific surface area, high porosity, strong skeleton modification, and excellent stability—and have become a class of promising candidates [46,47,48]. Nicholaus Prasetya et al. cycled sensors using three MOF materials between approximately 35–45% and 70% RH to investigate the repeatability of the sensor response, and the results are shown in Figure 1b [49]. All MOF sensors respond to water vapor molecules at different relative humidity levels, with excellent sensitivity, especially in the range of relative humidity between 40% and 100%. This makes them extremely suitable for the regulation of relative humidity in indoor environments [50]. With the continuous progress of materials science, the original shortcomings of MOFs, such as poor film formation, insufficient conductivity, and weak hydrophilicity, have been gradually solved, which has laid a solid foundation for their application as high-performance intermediate sensing layer materials in capacitive humidity sensors, making their large-scale application possible [51,52,53,54]. However, MOFs still face challenges in practical applications, such as poor mechanical stability in field environments (e.g., collapse under repeated moisture cycles) and high synthesis costs limiting large-scale production. Recent advancements in materials science have addressed shortcomings like poor film formation and weak hydrophilicity, laying a foundation for their application.
2.1.2. Resistive Sensors
Resistive air humidity sensors are mainly made of materials with moisture-sensing properties. The resistance values of these materials change significantly with changes in the humidity of the surrounding air. When the humidity in the air increases, the moisture-sensitive material will adsorb a large number of water molecules, resulting in closer contact between the conductive particles inside the material, so that the resistance value of the moisture-sensing element will be reduced [55]. Conversely, when the air humidity drops, the moisture-sensitive material releases water molecules, the distance between the conductive particles increases, and the resistance value increases [56,57]. The circuitry inside the sensor detects this change in resistance and converts it into a corresponding electrical signal, which is processed and calibrated to obtain the corresponding air humidity value.
From a principled point of view, the basic mechanism of the conductivity of humidity sensors can be explained by the Grotthuss reaction (Figure 1c) [58], which is usually reduced to a proton-hopping process. The signal strength of the humidity sensor intuitively reflects the number of water molecules adsorbed on the surface of the moisture-sensitive material, so the hydrophilicity of the moisture-sensitive material plays a decisive role in the sensitivity performance of the sensor.
Compared to capacitive humidity sensors, resistive air humidity sensors feature relatively simpler manufacturing processes and structures, resulting in lower production costs. However, due to the relatively slow adsorption and desorption of water molecules by the humidity-sensitive material and its susceptibility to temperature variations, resistive humidity sensors exhibit lower accuracy. They are suitable for applications requiring large-scale deployment without high monitoring precision, such as vegetable greenhouses and orchards. For example, Oren et al. successfully constructed a humidity sensor that could detect moisture transport in maize roots and leaves (Figure 1d) [59].
In recent years, infrared humidity sensors have emerged as non-contact devices specifically designed for complex agricultural environments, overcoming the limitations of capacitive/resistive sensors—such as soil particle contamination and salinity interference. Infrared sensors operate based on the principle that water vapor molecules strongly absorb infrared light in the 2.5–7.5-micrometer wavelength band [60,61]. This enables non-contact measurement, avoiding direct contact with soil- or dust-laden air, and reducing sensor contamination. They also exhibit strong resistance to interference and are less susceptible to temperature fluctuations or soil salinity compared to resistive sensors. Primarily used for large-scale soil moisture monitoring via drones, infrared sensors demonstrate significantly improved long-term stability over capacitive sensors [62,63].
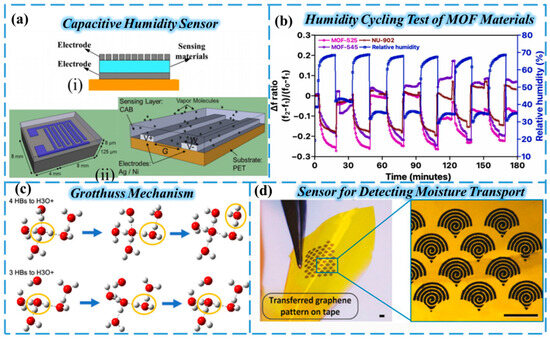
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of capacitive humidity sensor structure: (i) parallel-plate capacitors; (ii) interdigitated electrodes. Reproduced from Ref. [36]. (b) The periodic cycling experiment of MOF−525, MOF−545, and NU−902 QCM sensors between relative humidity of 40 % and 70 %. Reproduced from Ref. [49]. Copyright (2024), with permission from Elsevier. (c) Grotthuss Mechanism Schematic: In the hydrogen bond network formed by water molecules (each water molecule can form hydrogen bonds with 4 surrounding water molecules), the transport of protons is not achieved by “shuttling” through the solvent like ordinary ions (such as Na+, Cl−), but through a two-step cycle of proton transfer and hydrogen bond recombination. Reproduced from Ref. [58]. Copyright (2019), with permission from the American Chemical Society. (d) Schematic diagram of a graphene-based nanomaterial moisture sensor for plant protection detection. Reproduced from Ref. [59].
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of capacitive humidity sensor structure: (i) parallel-plate capacitors; (ii) interdigitated electrodes. Reproduced from Ref. [36]. (b) The periodic cycling experiment of MOF−525, MOF−545, and NU−902 QCM sensors between relative humidity of 40 % and 70 %. Reproduced from Ref. [49]. Copyright (2024), with permission from Elsevier. (c) Grotthuss Mechanism Schematic: In the hydrogen bond network formed by water molecules (each water molecule can form hydrogen bonds with 4 surrounding water molecules), the transport of protons is not achieved by “shuttling” through the solvent like ordinary ions (such as Na+, Cl−), but through a two-step cycle of proton transfer and hydrogen bond recombination. Reproduced from Ref. [58]. Copyright (2019), with permission from the American Chemical Society. (d) Schematic diagram of a graphene-based nanomaterial moisture sensor for plant protection detection. Reproduced from Ref. [59].
2.2. Light Sensors
Light sensors are core devices used in smart agriculture to accurately monitor light parameters in the agricultural environment. By capturing light signals closely related to crop growth in real time, they provide data support for regulating crop photosynthesis, optimizing cultivation management, and efficiently utilizing resources. The core principle of a light sensor is photoelectric conversion [64] (Figure 2a), which is then processed by circuits to output target values such as light intensity and photosynthetically active radiation. The response characteristics of light are classified by photoreceptive transducers, and the main light sensors currently used are photoresistors [65] and photodiodes [66].
Photoresistors are mainly made from semiconductor materials [67] like cadmium, which exhibit a significant change in resistivity under light exposure. In the absence of light, the valence band electrons in the semiconductor are trapped in covalent bonds, resulting in a very low carrier concentration and a high resistance; when exposed to light, the valence band electrons absorb photon energy to jump to the conduction band, simultaneously generating an equivalent number of holes, leading to a dramatic increase in carrier concentration and a significant decrease in material resistivity [68]. In general, the stronger the light intensity, the more carriers are generated per unit time in the photosensitive layer composed of the semiconductor, resulting in lower resistance.
Photoresistors are very suitable for light detection in greenhouse environments, due to their low cost and simple structure. In agriculture, CdS photoresistors are typically embedded in greenhouse environment monitoring systems to monitor light intensity in real time (Figure 2b). When light levels fall below crop requirements, the electrical signal is transmitted to the controller to activate LED supplementary lights in a timely manner; when the light is too strong, it triggers the shading net to unfold, preventing crop burns. In recent years, Jing Liu et al. successfully prepared ZnO/CdS heterojunctions on silica nanocolumn substrates for photoconductors for the first time, and they tested their photoconductive properties [69,70]. The results show that the ZnO/CdS structure can enhance photoconductive properties, while the SiO2 nanocolumns can improve the photoconductive response, further enhancing the performance of the photoconductor.
The function of the photodiode is based on the separation and transport of photogenerated carriers from semiconductors. When a photon with energy greater than the bandgap width of the semiconductor is incident on the device, the valence electrons absorb the photon energy and transition to the conduction band, forming electron–hole pairs (photogenerated carriers) [71]. Driven by the device’s built-in electric field (e.g., the self-created electric field of the PN junction, the depletion region of the intrinsic layer (layer I) of the PIN structure) or the external reverse bias [72], the photogenerated electrons are separated from the holes and transported in opposite directions, and finally a photocurrent is formed in the external circuitry to achieve the linear conversion of the “optical-electrical” signal.
Since they were first put into practical use in the mid-20th century, the performance boundaries of photodiodes have been pushed through, and their application scenarios have expanded from simple light intensity detection in the early days to cutting-edge fields such as optical communications, quantum information, biosensing, and environmental monitoring. Bernhard Gol et al. recently designed a novel type of point PIN photodiode [73] (Figure 2c). Compared to conventional PIN finger photodiodes, spot PIN photodiodes significantly reduce capacitance. While ensuring low power consumption and noise performance, they also have better temperature stability and can adapt to harsh wide temperature environment detection in agricultural production [74].
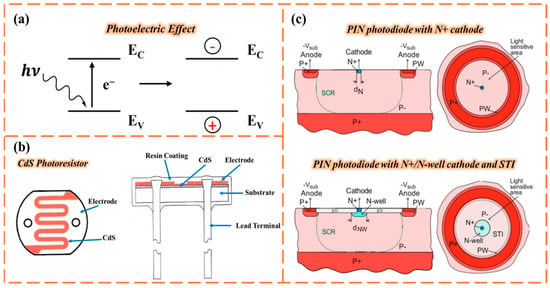
Figure 2.
(a) The principle of the photoelectric effect: a schematic diagram of the generation of light-induced charge carriers. Reproduced from Ref. [64]. (b) Schematic diagram of the structure of a CdS photoresistor. The top view is on the left, and the side view is on the right. (c) Cross-sections (left) and top views (right) of spot PIN photodiode with N+ cathode and spot PIN photodiode with N+/N−well cathode and STI. Reproduced from Ref. [73]. Copyright (2023), with permission from the IEEE.
Figure 2.
(a) The principle of the photoelectric effect: a schematic diagram of the generation of light-induced charge carriers. Reproduced from Ref. [64]. (b) Schematic diagram of the structure of a CdS photoresistor. The top view is on the left, and the side view is on the right. (c) Cross-sections (left) and top views (right) of spot PIN photodiode with N+ cathode and spot PIN photodiode with N+/N−well cathode and STI. Reproduced from Ref. [73]. Copyright (2023), with permission from the IEEE.
2.3. Gas Sensors
A gas sensor is a device that converts information such as gas composition and concentration into measurable electrical signals. In agricultural production, changes in the gas environment directly affect crop growth, agricultural product storage, and livestock and poultry health, so appropriate types of sensors should be used to monitor different gases [75,76,77].
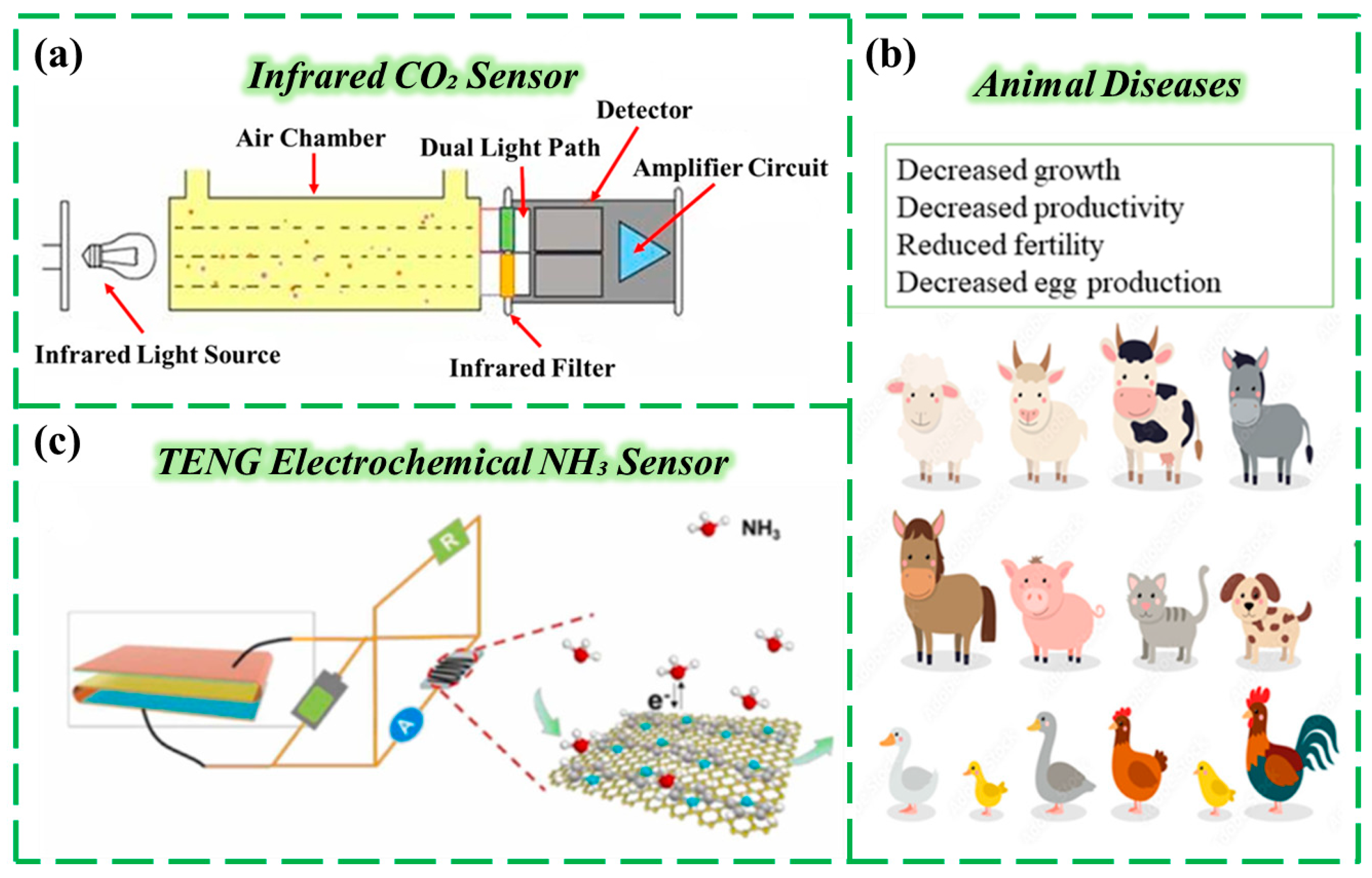
CO2 directly affects the photosynthesis efficiency of plants, and the appropriate CO2 content can effectively increase the yield of crops and reduce the scale of greenhouse gases in agricultural activities [78,79]. Due to the strong and specific absorption of infrared rays at a wavelength of 4.26 μm, CO2 is often monitored with infrared spectral sensors [80]. This wavelength was selected because it corresponds to the strongest absorption peak of carbon dioxide, thereby minimizing interference from other gases such as water vapor at the 1.9-micrometer wavelength. The working process is as follows: First, the infrared light emitted by the infrared light source passes through the gas chamber containing CO2, part of which is absorbed by CO2, and the transmitted infrared light is received through detectors such as photodiodes to convert the light signal into an electrical signal, so that the CO2 concentration can be calculated [81] (Figure 3a). Although the use of infrared carbon dioxide sensors in agriculture is very widespread, the fluctuation of temperature and humidity in agricultural environments is significant. Furthermore, particulate matter such as dust, water vapor, and pesticide aerosols can easily adhere to the gas chamber window or the surface of the detector, obstructing the infrared light and significantly affecting the measurement accuracy of the infrared sensors [82]. Current practical solutions include equipping gas chambers with hydrophobic filters to prevent water vapor condensation and implementing regular automated cleaning. In order to improve the accuracy of CO2 detection, it is necessary to choose a light source with a wavelength consistent with the CO2 absorption characteristics, thereby reducing sensitivity to other gases. Sun et al. proposed a single-channel wide-range CO2 detection method based on differential range non-dispersive infrared spectroscopy (NNDIR), which has good gas monitoring repeatability and stability [83]. Compared to traditional NDIR, NNDIR uses a single light source and differential range detection, reducing component complexity and improving stability across 0–5000 ppm CO2. This method has good monitoring repeatability and stability.
In the context of agricultural production, the generation of NH3 mainly comes from the decomposition of livestock manure, the evaporation of chemical fertilizers, and the storage of moldy materials [84,85]. Excessive NH3 levels may affect the growth conditions of animals and even increase their likelihood of developing diseases [86] (Figure 3b). This makes the monitoring of NH3 levels closely related to factors such as animal health, crop safety, and environmental control. NH3 is an alkaline, reducing gas, and sensors can measure its concentration by detecting its chemical or physical properties. Research on NH3 sensors now centers on TENG-powered devices. Traditional TENG sensors require energy storage in batteries to maintain real-time operation, whereas novel sensors integrating TENG with electrochemical sensing units can harvest energy from environmental vibrations—such as wind or equipment operation—for self-powering, eliminating battery dependency [87] (Figure 3c). Therefore, the most commonly used type of sensor among these is the electrochemical sensor [88]. The specific principle is to generate an electrical signal through the redox reaction of NH3 gas on the surface of the electrode. The sensor contains a working electrode, a counter electrode, and a reference electrode, with an electrolyte (such as an acidic solution) serving as the conductive medium. When NH3 gas enters the gas chamber, it reacts with the electrolyte and is oxidized at the working electrode, producing a current that is proportional to the concentration of NH3 gas [89,90]. The intensity of the current can be used to monitor the NH3 gas content. This type of sensor can detect low concentrations of NH3 (0–100 ppm), making it very suitable for monitoring and regulating livestock breeding environments. When the concentration exceeds the standard (e.g., more than 30 ppm in pigsties), it automatically triggers the ventilation fan and cooling pad system to reduce ammonia levels; at the same time, it assesses the manure cleaning cycle based on concentration changes [86]. Additionally, the application range of electrochemical sensors covers various scenarios, such as animal houses and greenhouses, with high accuracy, making them a mainstream choice for small agricultural equipment.
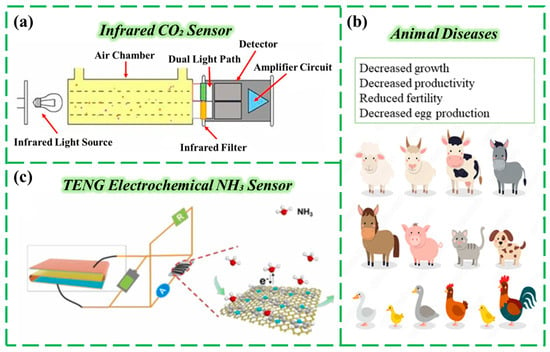
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic diagram of an infrared sensor monitoring CO2 concentration. (b) Negative effects of excessively high NH3 concentrations on animals. Reproduced from Ref. [86]. (c) Schematic diagram of an electrochemical sensor for NH3 monitoring, manufactured using TENG technology. Reproduced from Ref. [87]. Copyright (2024), with permission from Elsevier.
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic diagram of an infrared sensor monitoring CO2 concentration. (b) Negative effects of excessively high NH3 concentrations on animals. Reproduced from Ref. [86]. (c) Schematic diagram of an electrochemical sensor for NH3 monitoring, manufactured using TENG technology. Reproduced from Ref. [87]. Copyright (2024), with permission from Elsevier.
2.4. Others
In addition to the aforementioned three classic agricultural sensors, other types of sensors can also be observed in agricultural production. For example, pressure sensors [15] can be used in agricultural scenarios to monitor changes in fluid (water, gas) pressure, mechanical pressure, and soil pressure [91,92]. They can be used to monitor the water pressure in the pipeline in the irrigation system to ensure the uniformity of irrigation. They can also detect the compaction of the soil to ensure its looseness for seed germination [93]. Nutrient sensors [94] are used to monitor the elemental contents of nutrient solutions in soilless cultivation environments, or the contents of nutrients (N, P, K) in ordinary soil, and guide farmers to carry out precise fertilization and improve fertilizer utilization [95,96,97]. Overall, there are many types of agricultural sensors, each playing an irreplaceable role in agricultural production.
The trade-off between sensor accuracy and cost remains an issue that needs to be addressed. The following “Comparison Table of Mainstream Agricultural Sensors’ Costs and Sensitivities” (Table 1) consolidates key parameters such as sensor types, detection targets, sensitivity, cost, and applicable scenarios mentioned above, offering a more intuitive understanding of this balancing act. In summary, while diverse sensors play a pivotal role in agriculture, there is still a long way to go.

Table 1.
Performance, Cost, and Application Evaluation of Different Types of Sensors.
3. Novel Agricultural Sensing Technology
With the rapid development of smart agriculture, efficient and accurate environmental monitoring technology is not only the basic guarantee for environmental protection but also an important means to achieve sustainable development. Novel agricultural sensing technologies have achieved breakthroughs in precision, adaptability, and versatility, especially in complex agricultural environments.
3.1. Microneedle-Based Sensing Technology
Microneedle (MN) technology [98] was first proposed in 1976 and first entered practical application as a medical drug delivery system in 1990 [99,100]. With its significant technological advantages in the field of medicine, MN technology is rapidly expanding into other areas of research, including sensors and agricultural sciences. In medical applications, the minimally invasive nature of MNs provides novel ideas for tissue-free drug/biomolecule delivery [101], and this core advantage has greatly inspired agricultural researchers. MN-based agricultural sensing technology is an emerging field that has developed rapidly in recent years, and the micron-level needle-like structure can achieve minimally invasive or non-invasive detection of plant physiological states and environmental parameters. Its core strengths include high sensitivity [102], in situ real-time monitoring [103], and multi-parameter integration [104], especially in in-plant or complex agricultural environments that are difficult to reach with traditional methods.
MN sensing technology combines materials science, microfabrication, and electrochemical/optical inspection. The working principle is to break through physical barriers such as plant skin and soil surface through micron-scale needle-like structures [105,106] (diameter 5–500 μm, length 10–1000 μm), and to combine electrochemical, optical, electrical, and other detection methods to convert target substances (such as ions, molecules, or biological signals) into quantifiable electrical or optical signals [107] (Figure 4a). Among them, microneedles for optical signal measurement feature a core design that integrates microneedle scaffolds with optical transmission elements and sensitive layers, enabling non-destructive in situ detection of target analytes based on specific optical interactions. The core of such microneedles comprises three components: (1) Optical Waveguide Core: Utilizing high-transmittance, biocompatible materials running through the needle body to achieve dual functions of “transmitting excitation light + collecting response light signals” [108]; (2) Tip Sensitization Layer: Modified onto the microneedle tip to enhance light–target interaction, enabling the capture of trace pesticides/plant hormones [109,110]; (3) Protective Coating: A thin layer of SiO2 or hydrogel applied to the waveguide surface prevents interference from soil particles/plant sap while ensuring biocompatibility. For optical detection mechanisms, such technologies enable qualitative and quantitative analysis of crop parameters through FRET, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), and absorption spectroscopy, making them suitable for the rapid detection of plant physiological indicators [111].
With MN technology, researchers can achieve real-time monitoring of plant health without damaging plant tissue, effectively overcoming the inherent shortcomings of traditional testing tools—which are invasive, less efficient, and do not enable continuous monitoring of plant health. In recent years, MN technology has shown a wide range of application prospects in agricultural production, including plant disease control, health status monitoring, and accurate detection of agrochemicals/pathogens in plants.
At present, the most used method is ion-selective microneedling, which mainly uses electrochemical response to specifically bind to the target ion through the sensitive membrane on the surface of the microneedle, producing a measurable potential difference that reflects the ion concentration. This feature is highly consistent with the core needs of precision agriculture for monitoring plant sap’s chemical parameters. Figure 4b shows the preparation process of a wearable MN sensor used to monitor the sap pH of the leaves of a variety of plants [112], such as Eight Immortals and colorful grass. The preparation process is as follows: First, a solid MN array with a single-needle diameter of 300 μm is prepared using low-cost stereolithography 3D printing technology. Subsequently, it is given pH-responsiveness by polyaniline (PANI) functionalization modification, and a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) membrane is used to ensure its potential stability.
Traditional methods, such as gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), have long been widely used to detect pesticides, but they require complex instruments and have high costs [113,114]. These are technically demanding and time-consuming methods that are difficult to use in the field. These shortcomings give MN-based sensing technology the potential to monitor pesticides in fruits and vegetables in real time [115,116,117,118,119]. Yi et al. constructed a novel Ag-PVA-HA-based microneedle [120] (PVA-HA-MN), prepared by the PDMS mold method (a microfabrication technique for replicating microneedle structures using polydimethylsiloxane molds), which could be used for the detection of thiophanate in agricultural products [107] (the detection principle and device are shown in Figure 4c). The experimental data confirmed that the prepared PVA-HA-MNs could efficiently detect target pesticide residues on the inner and outer surfaces of agricultural products, and the detection limits of thiophanate reached 10−7 and 10−8, respectively. The unique stepped structure of the microneedles significantly increases their specific surface area, which provides sufficient sites for the uniform distribution of silver (Ag) nanoparticles and the effective capture of pesticide molecules, thereby significantly improving the detection sensitivity of the sensor [121,122,123].
Although MN-based agricultural sensing technology is moving from the laboratory to the field, and although it shows great potential in plant physiological monitoring and precision agriculture with its advantages such as minimally invasive and in situ detection, there are certain shortcomings in material selection: the metal MNs commonly used at present are susceptible to soil corrosion, and the metal ions produced by acid treatment are difficult to degrade. In the future, MN materials need to make breakthroughs in the direction of biocompatibility, degradability, and functional responsiveness to help smart agriculture transform to efficiency and sustainability.
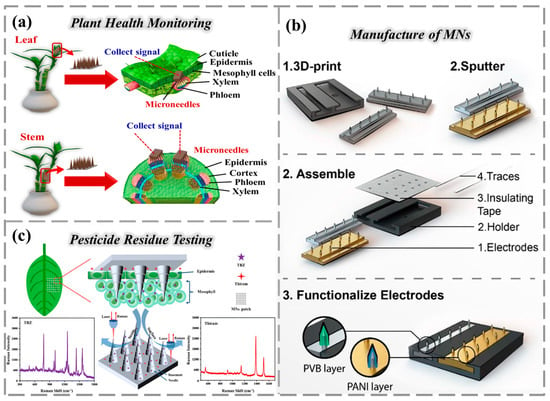
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic diagram of MNs and their application in agriculture, monitoring plant health by inserting MNs into the surface of leaves and stems. Reproduced from Ref. [107]. (b) Schematic diagram of the fabrication of an MN device for portable continuous pH monitoring. Microneedle arrays are fabricated using low-cost 3D printing technology, sputtered with thin metal layers, and arranged on novel MN electrode configurations for functionalization with PVB and PANI. Reproduced from Ref. [112]. Copyright (2024), with permission from RSC. (c) Schematic diagram of the detection of pesticide residues in agricultural products using MN technology. Reproduced from Ref. [107].
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic diagram of MNs and their application in agriculture, monitoring plant health by inserting MNs into the surface of leaves and stems. Reproduced from Ref. [107]. (b) Schematic diagram of the fabrication of an MN device for portable continuous pH monitoring. Microneedle arrays are fabricated using low-cost 3D printing technology, sputtered with thin metal layers, and arranged on novel MN electrode configurations for functionalization with PVB and PANI. Reproduced from Ref. [112]. Copyright (2024), with permission from RSC. (c) Schematic diagram of the detection of pesticide residues in agricultural products using MN technology. Reproduced from Ref. [107].
3.2. Nanosensor Technology
The rapid development of nanotechnology is driving a profound transformation of traditional food and agriculture. Various nanosensors based on the research and development of novel nanomaterials are playing an irreplaceable key role in improving food quality and safety, optimizing crop growth management, and accurately monitoring environmental conditions. Nanosensors are a class of nanoscale selective sensing devices with. Currently, various types of nanosensors have been used in the field of plant monitoring, including Förster resonant energy transfer (FRET)-based nanosensors, electrochemical nanosensors, and mechanical nanosensors.
3.2.1. FRET-Based Nanosensors
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based nanosensors are a special class of optical sensors that have been widely used to study protein–protein interactions, small molecule–protein interactions, and cellular content parameters. This type of sensor uses photosensitive fluorescent molecules as signal units to realize its function by detecting the energy transfer process between molecules [124]. The essence of FRET is the non-radiative transfer of excited-state energy, which is achieved through a dipole–dipole coupling mechanism between fluorophores when the distance between two fluorophores is in the nanoscale range [125,126,127]. When the analyte of interest is bound to the sensor, the spatial conformation of the sensor is altered (folded, stretched, or assembled/unassembled), causing the distance or orientation of the donor to the recipient to deviate from the “FRET range”, resulting in a decrease (manifested by enhanced donor fluorescence and decreased receptor fluorescence) or increase (manifested as reduced donor fluorescence and enhanced receptor fluorescence) in FRET efficiency [128,129,130]. Qualitative and quantitative detection of the target analyte can be achieved by detecting characteristic changes in the fluorescence signal (intensity ratio, fluorescence lifetime) [131,132,133].
Plants themselves can express fluorescent proteins (FPs) through genetic coding, providing a natural signaling unit for FRET-based nanosensors [134]. These nanosensors can use proteins, protein domains, nanoparticles, or molecular ligands to precisely adjust the distance between the two fluorophores of the donor and recipient. When the donor is excited, part of the energy is transferred to the receptor fluorophore through resonant energy transfer, which stimulates the receptor to produce characteristic fluorescence [124] (Figure 5a). By monitoring the ratio of emission peak intensity between donor and recipient, it is possible to detect the ratio of target substances in plants, such as hormone level determination and metabolite analysis. For example, FRET-based sugar sensors monitor relative changes in sugar levels in subcellular compartments, enabling the detection and analysis of sucrose and glucose in plants [135].
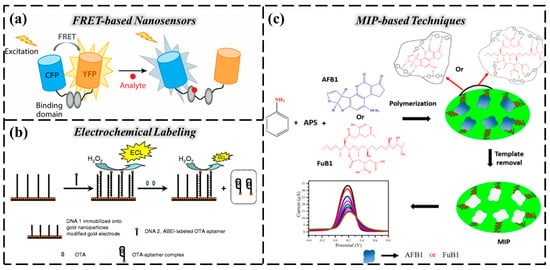
Figure 5.
(a) A typical FRET sensor consisting of two spectral variants of fluorescence proteins (CFP and YFP) whose conformations change when binding to analytes, causing FRET. Reproduced from Ref. [124]. (b) Functionalized GO-based electrochemically labeled aptasensor for AFB1 detection, employing an MB-labeled aptamer as the signaling fragment. Reproduced from Ref. [136]. (c) MIP-based techniques for the evaluation of the mycotoxins AFB1 and FuB1. Reproduced from Ref. [136].
Figure 5.
(a) A typical FRET sensor consisting of two spectral variants of fluorescence proteins (CFP and YFP) whose conformations change when binding to analytes, causing FRET. Reproduced from Ref. [124]. (b) Functionalized GO-based electrochemically labeled aptasensor for AFB1 detection, employing an MB-labeled aptamer as the signaling fragment. Reproduced from Ref. [136]. (c) MIP-based techniques for the evaluation of the mycotoxins AFB1 and FuB1. Reproduced from Ref. [136].
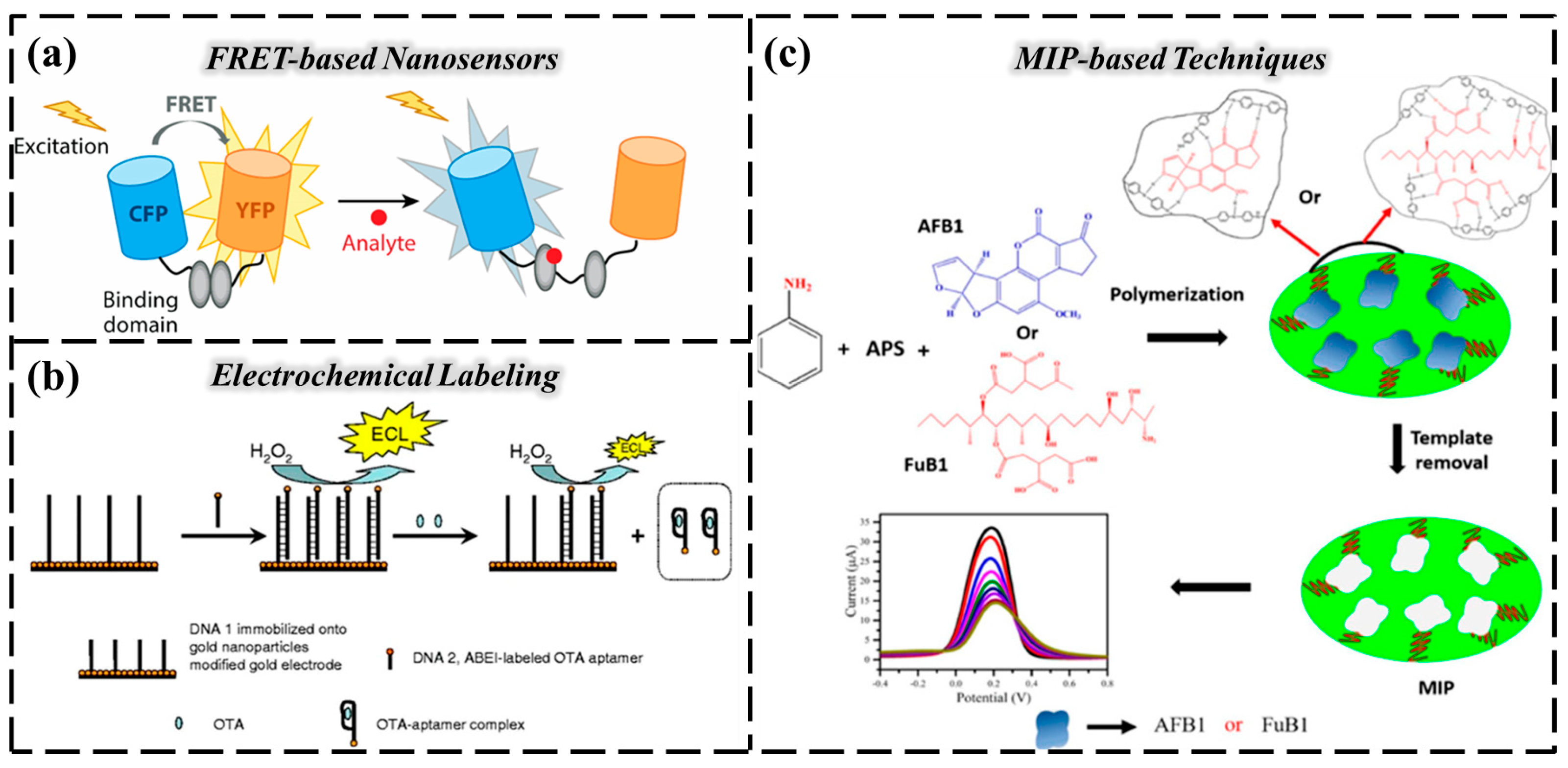
Recently, Chiang et al. reported a FRET-based sucrose sensor constructed using invertase–nanogold clusters embedded in the inner epidermal membrane of onions [137]. Onion membrane was chosen as a platform for fixing enzymes due to its good substrate and product permeability and excellent mechanical strength. In experiments, glucose transporters have been found in the inner coating of vacuoles and plastids, indicating that steady-state glucose levels are jointly regulated by transplasma membrane flux, metabolic rate, and compartmentalization. It can be seen that FRET glucose nanosensors have been successfully applied in plant research to analyze glucose concentrations in the cytoplasm of plant roots and leaves, and the results show that the cytosolic steady glucose levels of leaves and roots depend on external supply.
3.2.2. Electrochemical Nanosensors
Electrochemical nanosensors are widely used in many fields due to their excellent adaptability and ultra-high sensitivity. These sensors enable the accurate detection and quantification of trace biomolecules and other chemical analytes in samples. Their working principle is to capture the changes in electrical properties (such as voltage or current fluctuations) generated when the target analytes (ions, molecules, biomolecules, etc.) interact with the sensor surface through redox reactions, ion exchange, or charge transfer on the electrode surface, and to convert these changes into quantifiable analytical signals, thereby achieving accurate determination of the contents of target molecules in the sample [138,139]. Thanks to their high sensitivity and strong selectivity, electrochemical nanosensors are particularly widely used in biomedical research and diagnostics. For example, they can be used to detect disease biomarkers and monitor drug levels in patients—the core mechanism is to accurately measure the electrical properties of analytes in solution with electrodes, thereby providing reliable data support for clinical diagnosis and research.
Electrochemical nanosensors can also detect key indicators in agricultural production quickly and accurately. With the development of agriculture towards “precision and intelligence”, the application of electrochemical nanosensors in agriculture has attracted great attention [140,141,142,143]. Electrochemical nanosensors can reflect plant growth and environmental conditions by detecting a variety of biomolecules [144,145,146]. For example, by detecting the contents of plant hormones such as ethylene and auxin [147], the metabolic process of plant growth can be assessed. At the same time, reactive oxygen species (ROS) [148] and related products in plants can be monitored, which could reflect the metabolome characteristics, stress response, and environmental conditions of plants. Nguyen et al. [149] reported an electrochemical impedance biosensor based on a special aptamer for AFM 1 assay [150] for the detection of mycotoxin content in wheat samples (Figure 5b). In soil testing, in view of the problem that heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury endanger food safety through crop accumulation, electrodes modified with materials such as carbon nanotubes can trigger current or potential changes through the specific adsorption of heavy metal ions [151] on the electrode surfaces to achieve trace detection. At the same time, they can also accurately measure the contents of nutrient ions [152] in the soil, providing data support for optimizing crop yields.
3.2.3. Biomimetic Nanosensors
Nanosensor devices have become the core carrier of technological breakthroughs, with their ability to accurately identify specific molecules, biological transducers, and environmental states. Among the various detection methods, biosensors stand out for their unique advantages of both portability and precision [153,154]. These devices can generate clear systematic data in quantitative or semi-quantitative ways by integrating biologically derived identification elements and signal conversion units, enabling efficient evaluation of targets. As an advanced form of biosensor, biomimetic nanosensors further integrate the dual characteristics of “biomimetic recognition” and “nanomaterial enhancement”, and they achieve ultra-high specificity and sensitive detection of target substances by simulating the perception mechanisms of biological systems, combined with the excellent properties of nanomaterials (such as high specific surface area and quantum effect) [155,156,157]. This innovative technology has shown great application potential in the agricultural field, greatly simplifying the detection process of key indicators such as pesticide residues [158,159,160], veterinary drug residues [161,162,163], foodborne pathogenic microorganisms [164,165,166,167], toxic pollutants, and heavy metal ions [168,169,170], which not only breaks through the dependence of traditional methods on complex equipment and professional operations but also significantly improves the detection accuracy and efficiency, and provides strong technical support for agricultural product safety supervision, environmental monitoring of production areas, and agricultural production risk prevention and control [171].
Bionic nanosensors for agricultural applications primarily rely on three bionic recognition mechanisms, each tailored to specific detection targets [172]. Enzyme-mimetic catalytic mechanisms achieve specific binding and catalysis of target analytes by mimicking the structure of natural enzyme active sites, such as acetylcholinesterase and transaminase. For instance, nanocomposites constructed by immobilizing enzyme-mimetic materials—such as metal porphyrins or Cu2+ loaded onto metal–organic frameworks (MOFs)—on carbon nanotubes can detect organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. The most representative example of the antibody/receptor model mechanism is molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) [173]. By incorporating template molecules—functionally modified monomers that act as “artificial antibodies”—and combining them with nanomaterials, their performance in agricultural applications can be significantly enhanced. Furthermore, the biofilm selective permeation simulation mechanism achieves rapid detection of pesticide residues on fruit surfaces by simulating the lipid bilayer structure of the biofilm, enabling selective permeation of target molecules such as small-molecule pesticides and nutrient ions [174].
With their rich and diverse characteristics, nanoparticles have widespread application potential in sensing structures based on electrochemical phenomena, laying the foundation for the integration of bionic nanosensors and electrochemical technology. At present, electrochemical biosensors with cholinesterase as the core have become the preferred solution for detecting pesticide residues, especially for the detection of carbamate and organophosphate pesticides [175]. This is due to their high sensitivity, strong selectivity, and simple preparation process, providing a significant advantage in the field of pesticide residue detection.
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) [176,177] are multifunctional biomimetic molecular receptors that act as an “artificial antibody”, greatly improving the detection performance of sensors on targets in agricultural environments by simulating the specific recognition mechanism of biomolecules and synergizing with nanomaterials (such as carbon nanotubes, gold nanoparticles, quantum dots, etc.) [178,179]. For aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), fumonisin B1 (FuB1) [180], and other toxic substances of fungal origin, Kavitha Lakavath et al. proposed a high-sensitivity electrochemical sensing platform based on MIP-A/ITO and MIP-F/ITO for the specific detection of these two toxins [136] (Figure 5c). The platform uses a simple chemical oxidation polymerization method to prepare polyaniline (PANI)-based sensing arrays, in which MIP-A/ITO uses AFB1 as the template molecule and MIP-F/ITO uses FuB1 as the template molecule [181]. This array design of the sensor has excellent sensitivity, reliable detection performance, and convenient operation characteristics, providing a practical solution for the efficient detection of mycotoxins.
In summary, protein complex-based nanosensors enable in situ dynamic intracellular detection through fluorescent proteins such as CFP and YFP. These fluorescent proteins can be directly introduced into plants via genetic encoding and exhibit high specificity toward trace target molecules—such as sucrose and glucose at the subcellular level—thus precisely meeting the core requirement for real-time monitoring of plant physiological states in precision agriculture.
3.3. Wireless Sensor Networks
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) rely on the collaborative operation of a large number of microsensor nodes to build a closed loop of real-time perception, transmission, and analysis of key information such as farmland environment, crop growth, and resource status [182,183,184]. The monitoring network formed by multi-node interconnection can not only achieve real-time dynamic monitoring of a large area but also support cross-node data fusion and sharing, which not only greatly expands the breadth and depth of data collection but also provides accurate and three-dimensional data support for the dynamic assessment of complex agricultural environmental systems [185] (Figure 6).
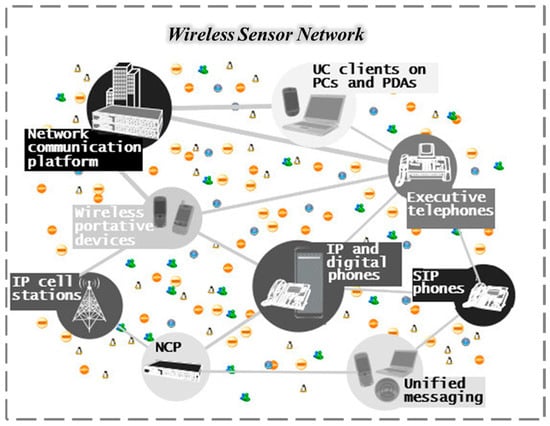
Figure 6.
Wireless mesh sensor network. Reproduced from Ref. [185]. Copyright (2022), with permission from the IEEE.
Specifically, a large number of microsensor nodes are distributed in farmland, greenhouses, orchards, and other scenarios to undertake the task of collecting key agricultural production data. The aggregation node serves as the core transit station of the network, receives the data of each sensor, completes the preliminary processing (such as compression and screening), and then uploads the aggregated data to the upper platform through wireless or wired methods [17,186]. The gateway is responsible for converting the aggregated data into a standardized format and transmitting it to a cloud server, while the cloud platform stores and analyzes the data in depth (such as predicting crop growth trends or pest and disease risks, combined with AI algorithms [187]) and, finally, generates accurate decision-making recommendations. Users can view data in real time, receive early warnings, or remotely control agricultural equipment through mobile phones, computers, and other terminals to achieve intelligent management of the whole process [188,189].
The emergence of WSNs has greatly alleviated the problems of “difficult information acquisition and extensive management” in traditional agriculture and provided data-driven and accurate solutions for agricultural production. Their low power consumption, self-organization, and anti-interference characteristics [190] make them suitable for complex farmland environments. Their application in scenarios such as environmental monitoring, water and fertilizer management, and early warning of pests and diseases directly promotes the improvement of agricultural production efficiency and resource conservation.
4. Applications of Agricultural Sensors
Smart agriculture is the development direction of modern agriculture around the world, and sensor technology plays an increasingly important role in the construction of smart agriculture. By deploying sensors, various agricultural production links can be effectively monitored and controlled. At present, the mainstream agricultural sensors can be mainly divided into environmental, soil, and crop sensors, and different technical principles cover the main links, such as crop sowing and growth. The specific applications can be divided into drought detection, soil detection, and crop detection.
4.1. Agricultural Drought Detection
In the context of global climate change, agricultural drought has a significant impact on crop yield and food security, so strengthening the detection and monitoring of agricultural drought has become a core work that needs to be promoted urgently [191]. Agricultural drought refers to the abnormal drought state that hinders crop growth due to severe water shortage, and the severity and frequency of crop water deficit are the core indicators of agricultural drought detection. Water utilization in the process of crop growth is mainly achieved through transpiration and metabolic consumption. When agricultural drought occurs, soil water deficit will directly lead to a decrease in soil evaporation [192,193] and insufficient water absorption by crop roots, making it difficult for the plants to maintain their own water balance, and weakening leaf transpiration. As droughts continue to intensify, crop leaves and stems will wilt and yellow. If water stress is not alleviated, plant dehydration will cause leaf and stem cell structures to disintegrate, which will eventually lead to plant death and significant decreases in yield [194]. Although agricultural management measures such as precision irrigation and crop variety improvement have significantly increased food production in recent years, agricultural drought remains a potential risk to food security. In this context, sensor technology can be applied to accurately monitor the dynamics of agricultural drought, analyze its spatiotemporal distribution characteristics, and provide data support for the formulation of scientific and effective disaster prevention and mitigation measures.
Humidity sensors are commonly used to monitor soil moisture. For example, capacitive humidity sensors are able to capture small fluctuations in air humidity due to their high accuracy, making them a perfect fit for the stringent standards of humidity monitoring in high-end agricultural farming. At the same time, they respond quickly to the dynamic changes in humidity in the agricultural environment, providing strong support for timely regulation and control. In the field of agricultural production, they have outstanding performance in the greenhouse cultivation of moisture-sensitive crops such as strawberries and orchids, and they can accurately monitor humidity in real time and provide a reliable basis for precise control [195,196]. In the modern intelligent greenhouse, they can be seamlessly linked with humidifiers, dehumidifiers, and other equipment to strictly control the humidity in the best range for crop growth, thereby effectively improving the quality and yield of crops [52,197]. However, the manufacturing costs and later maintenance costs of capacitive humidity sensors are relatively high, and how to effectively improve the economic benefits under the premise of ensuring their performance advantages is still an urgent problem to be solved.
Resistive moisture sensors can also monitor soil moisture in the crop root zone for agricultural drought protection, triggering timely irrigation. For specific applications, choose probe sensors matching crops’ root depths (e.g., 15–30 cm probes for wheat, 30–50 cm probes for fruit trees, prioritizing corrosion-resistant materials), and plan sampling points according to field types. Precise deployment follows, converting resistance signals into soil volumetric water content through real-time data collection. This data is compared against crop drought thresholds (e.g., wheat: below 12% indicates mild drought, below 10% indicates severe drought) to assess drought severity. Subsequently, initiate tiered protective actions: mild drought triggers drip irrigation with frequent, small-volume watering; severe drought activates sprinkler irrigation for rapid replenishment. Simultaneously monitor watering effectiveness to achieve end-to-end management from drought detection to proactive mitigation.
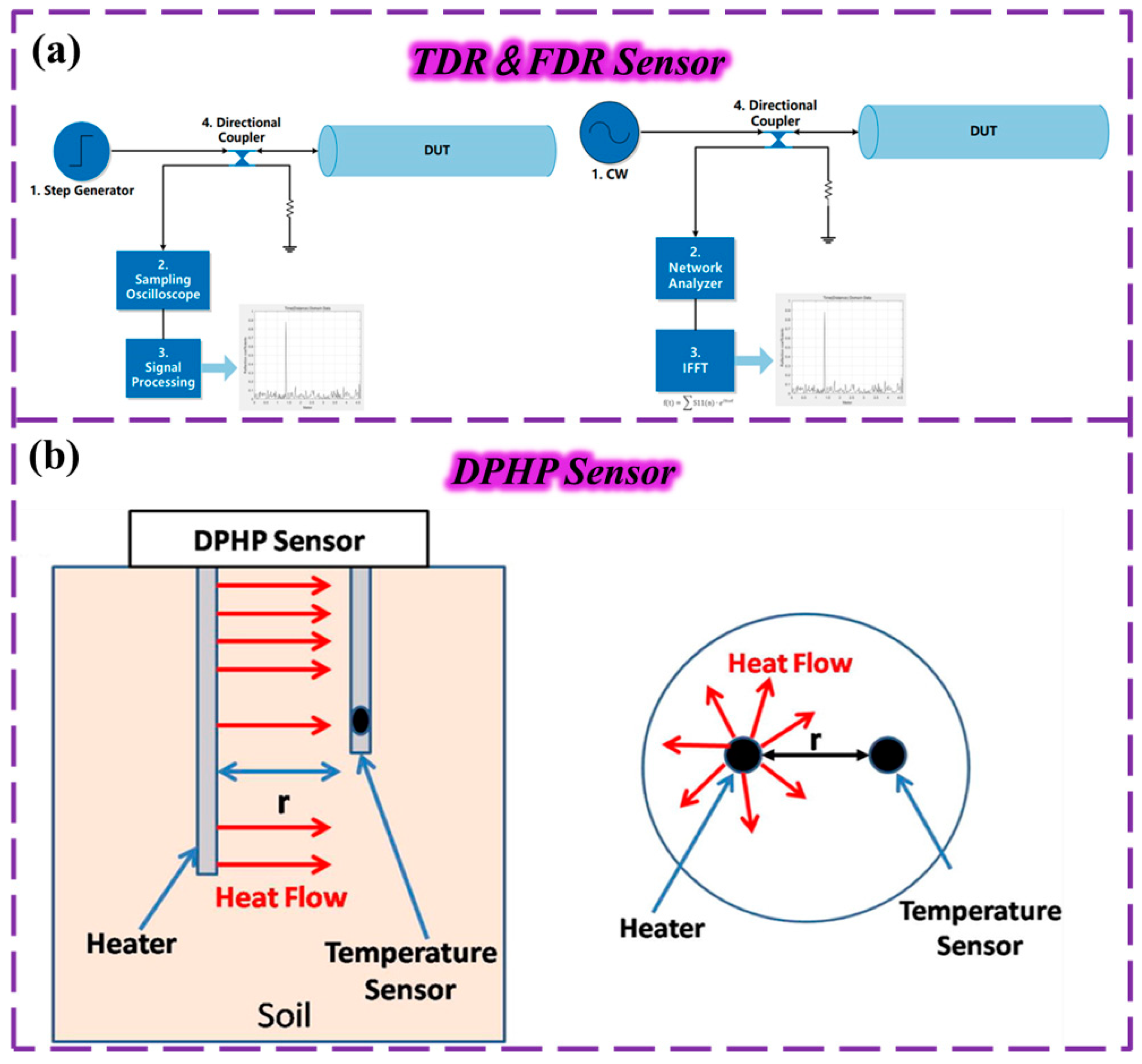
In addition to the capacitive and resistive sensors mentioned above, several novel types of soil moisture sensors are gaining widespread attention. Soil conductivity (EC) sensors and dielectric constant sensors are two types of commonly used soil moisture monitoring equipment, each with their own characteristics in principle and performance. Soil conductivity sensors indirectly estimate volumetric water content (VMC) by measuring the conductivity of the soil between two metal electrodes [198]. Because conductivity is susceptible to interference by soil texture (e.g., sand-to-clay ratio) and salinity (e.g., soluble ion content), the measurement accuracy of these sensors fluctuates greatly, and the error can increase significantly in saline–alkali or complex soils. In contrast, soil dielectric constant sensors rely on the significant difference in dielectric constant between water and other transducers of the soil (solid particles, air) (the dielectric constant of water is much higher than the latter two) and measure by time-domain reflectometry (TDR) [199,200] or frequency-domain reflectometry (FDR) [201] (Figure 7a). TDR emits electromagnetic waves along the waveguide and calculates the soil VMC by recording the return velocity of the signal. The principle of FDR is similar, but the water content is derived by measuring changes in signal frequency. These sensors offer the advantages of high portability and fast readings (far superior to traditional gravimetric methods), and although they are also limited by soil texture and other factors, they can be calibrated to greatly improve accuracy and output accurate data in most soil types, making them more widely used [202].
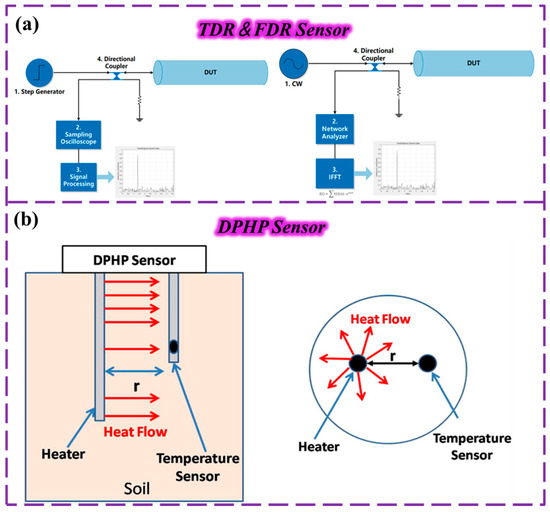
Figure 7.
(a) Schematic diagram of TDR technology and FDR technology. TDR: A broadband transmitter is used to send a fast step or shock excitation signal to the transmission line under test, and when there is a fault point or impedance discontinuity point on the transmission line, part or all of the excitation signal is reflected back to the broadband receiver. FDR: A broadband transmitter is used to send a fast step or shock excitation signal to the transmission line under test, and when there is a fault point or impedance discontinuity point on the transmission line, part or all of the excitation signal is reflected back to the broadband receiver. (b) Schematic diagram of a traditional DPHP sensor. By applying a voltage, a heat stream is generated from the heater probe. Reproduced from Ref. [203]. Copyright (2017), with permission from Elsevier.
In agricultural production, soil temperature can change greatly over different periods of time, affecting the response of soil moisture sensors. Faced with this problem, dual-probe thermal pulse (DPHP) sensors are another economical solution for soil moisture measurement. Vinay S. Palaparthy et al. used a low-power DPHP sensor [203] to analyze the influence of temperature in different soils under laboratory conditions, constructed a temperature compensation model, and carried out temperature compensation experiments on the DPHP sensor based on this. At the same time, they designed and developed a sustainable field measurement system that simultaneously collects soil moisture and temperature through DPHP sensors and benchmarks them using temperature-compensated soil moisture sensors (Figure 7b).
4.2. Soil Testing
Soil is the core carrier of agricultural production, and its physical and chemical properties, nutrient composition, and health directly affect the growth quality, resource utilization efficiency, and even the sustainability of the ecological environment. Therefore, soil testing has irreplaceable strategic value and far-reaching significance in the development of modern agriculture. From building a solid foundation for food security to protecting ecological barriers, from improving production efficiency to building a solid food safety defense line, its value has long transcended a single agricultural production link and has become a key link connecting food security and ecological protection. As the evolution of smart agriculture is accelerating, the popularization and deepening of soil testing technology will surely inject a steady stream of momentum into the high-quality development of agriculture.
4.2.1. Soil Temperature Testing
The rapid development of smart agriculture has become unstoppable, and self-powered sensing technology with sustainable and stable operation characteristics is gaining more and more attention. In a greenhouse environment, too high or too low soil temperature will directly affect the normal growth of crops. If the soil temperature of the greenhouse cannot be monitored in real time, it will lead to a decrease in crop yield at best, and to a wilting of plants at worst, bringing significant losses to agricultural production [204,205]. Therefore, effective monitoring of soil temperature in greenhouses is the key basis for ensuring the normal growth of crops. At present, the soil temperature management of greenhouses still relies on manual experience, but this method not only requires farmers’ experience and judgment ability to be extremely high but also wastes a lot of manpower and time due to insufficient temperature control accuracy, which indirectly causes significant economic losses [206,207]. In order to achieve precise regulation of soil temperature, research on various temperature sensors has been gradually carried out.
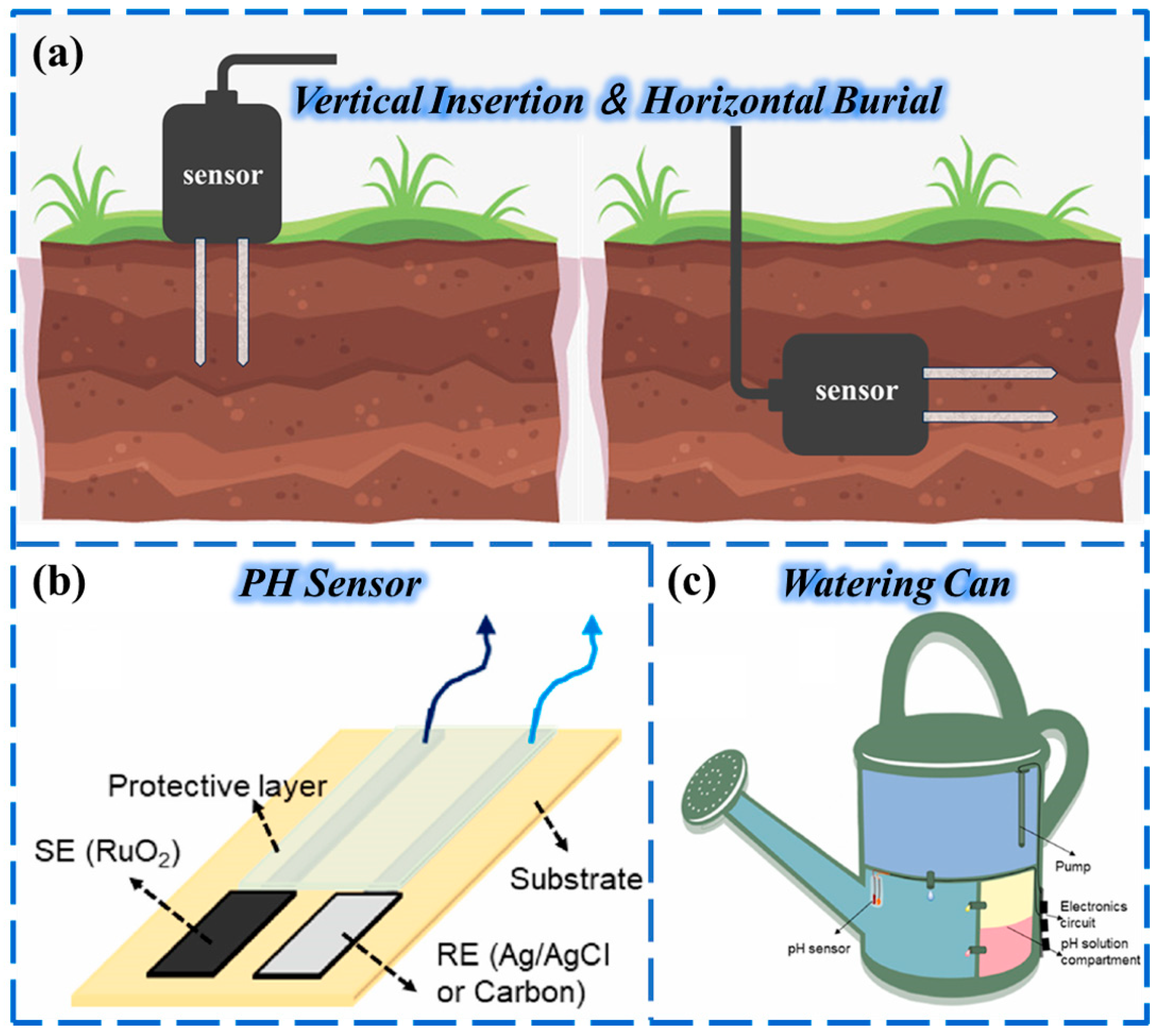
The installation of soil temperature sensors mainly adopts two methods: vertical insertion and horizontal burial. Vertical insertion is suitable for monitoring layered temperatures at different depths, and the probe needs to be inserted into the soil in a vertical direction to ensure that the entire temperature sensing area [208] (usually 5~10 cm at the front end) is completely buried to avoid exposure to air. Horizontal burial [209] is used for horizontal temperature distribution monitoring at specific depths, such as dense root layers. Shallow trenches need to be excavated at preset depths, and the sensors should be placed horizontally, backfilled with soil, and gently compacted to ensure close contact with the soil to reduce thermal resistance interference (Figure 8a).
In soil temperature monitoring, thermistor and thermocouple sensors are the two mainstream types of equipment. Thermistor sensors measure temperature based on the resistance-temperature characteristics of conductors or semiconductors: Metal thermal resistors (such as PT100) have a positive temperature coefficient [210,211], and the resistance changes linearly with temperature, with an accuracy of up to ±0.1 °C, which is suitable for high-precision scenarios. Semiconductor thermistors (such as metal oxide materials) have a negative temperature coefficient, and the resistance changes exponentially with temperature, with high sensitivity but nonlinear compensation, and its signal is converted into a voltage signal through the Wheatstone bridge and then processed and output. This type of sensor adapts to the soil environment through a corrosion-resistant housing such as stainless steel and a needle-like probe design, and the advantages of stability and sensitivity in the room-temperature area make it the first choice for field monitoring [212]. The thermocouple sensor is based on the Seebeck effect, using a closed loop composed of two metals to measure the temperature of the electromotive force generated by the temperature difference, and needs to eliminate the ambient temperature interference through cold end compensation, although it has the advantage of a wide temperature range of −270~1800 °C, but due to the weak EMF signal, the need for high gain amplification will lead to high power consumption [213].
Both types of sensors have theoretical limitations: thermistors require continuous power supply, thermocouple power consumption is high, and both are single-point measurement equipment, making is difficult to cover wide-area soil temperature changes. However, their mature heat–electricity conversion mechanism and environmental adaptability are still the core tools for capturing temperature dynamics in smart agriculture and soil thermal properties research.
4.2.2. Soil PH Value Testing
Soil pH is of significant importance, as it determines the form of essential nutrients that plants can absorb by influencing ion solubility and chemical reactions. For example, macroelements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are most effective at pH values of 6.5–7.5 [214], and excessive acidity or alkalinity can reduce nutrient availability. At the same time, it will also affect the activity and diversity of soil microbial communities, which, in turn, affect the soil’s colloidal charge characteristics, aggregate stability, and water retention capacity. Soil’s pH value is also closely related to crop adaptability, growth performance, and yield. Different crops have specific needs for pH; the ideal range is mostly 5.5–7.2 [215], and pH incompatibility can lead to root stunting, disease resistance, and other problems, even directly inhibiting growth.
The soil pH sensor determines the acidity and alkalinity by measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in the soil, and its working principle is mainly based on glass electrodes, ion-selective electrodes, and metal electrodes. The metal electrode sensor completes the measurement by measuring the total soil conductivity (EC) between two metal surfaces separated by an insulator. This type of sensor can be directly inserted into the soil without on-site sampling, and the cost is lower than that of glass electrode sensors, but the sensitivity is insufficient, and it is difficult to accurately measure soil pH to meet the needs of field evaluation [216,217]. The glass electrode is usually composed of hydrogen-sensitive glass membrane balls. The former reacts with hydrogen ions in the soil, and the latter measures the total EC, which can obtain accurate readings of 0.01 pH units by analyzing the conductivity values of the two, with high pH sensitivity, as well as good stability and repeatability. Ion-selective electrodes use the change in potential generated by the ion-sensitive film on the semiconductor surface to measure the pH value, which is highly sensitive to hydrogen ions and can be integrated with other sensors to facilitate miniaturized applications, but the maintenance cost is relatively high, and it is difficult to use in high-humidity environments. These sensors facilitate precise regulation of soil fertility and can monitor soil pH changes based on optimal crop growth conditions, thereby improving crop yield and quality.
There are significant differences in the requirements of different plants for soil pH and nutrient availability. To meet the personalized growth needs of crops, several novel sensing systems have been applied to the estimation of soil pH in agricultural scenarios. However, other chemicals in the soil due to the presence of various nutrients can interfere with the performance of the pH sensors [198,218]. Therefore, systems with integrated multi-sensor probes are an advanced solution. They can monitor multiple parameters simultaneously, allowing for more accurate data analysis. In this context, Anika Rabak et al. [219] developed a thick-film potentiometric pH sensor that can monitor the pH value of soil and irrigation water in real time, which is made of a screen-printed RuO2-based sensitive electrode and a thick-film Ag/AgCl reference electrode (Figure 8b). In addition, they designed a novel smart kettle that monitors water pH and dynamically adjusts by controlling the addition of acidic/alkaline solutions (Figure 8c).
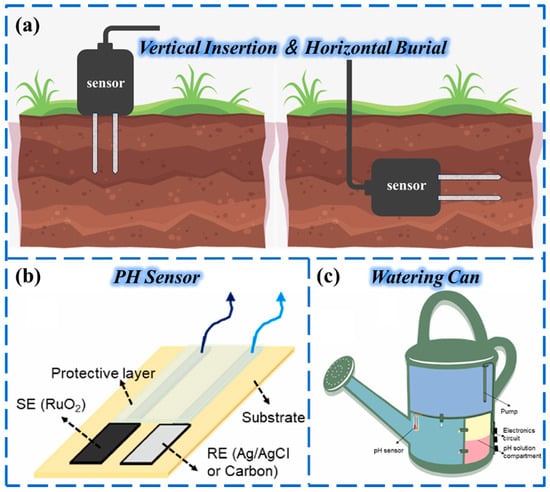
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic diagram of two different methods for measuring soil temperature with sensors: vertical insertion and horizontal embedding. (b) Schematic of potentiometric pH sensor. Reproduced from Ref. [219]. Copyright (2023), with permission from Elsevier. (c) Schematic representation of the watering can with sensors and circuits for controlling the pH value of water. Reproduced from Ref. [219]. Copyright (2023), with permission from Elsevier.
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic diagram of two different methods for measuring soil temperature with sensors: vertical insertion and horizontal embedding. (b) Schematic of potentiometric pH sensor. Reproduced from Ref. [219]. Copyright (2023), with permission from Elsevier. (c) Schematic representation of the watering can with sensors and circuits for controlling the pH value of water. Reproduced from Ref. [219]. Copyright (2023), with permission from Elsevier.
4.3. Quality Testing of Agricultural Products
The quality and safety of agricultural products lie at the core of ensuring the health of the food supply chain, and their ingredients and trace elements are directly related to quality and nutritional value. As a result, the need for technology for the fast and accurate analysis of agricultural composition is becoming more critical. Traditional quality assessment relies on sensory inspection or large laboratory instruments, suffering from drawbacks such as high subjectivity, lengthy testing cycles, and unfeasibility of on-site application. Sensor technology enables end-to-end precision monitoring “from farm to fork” by capturing the physical properties, chemical signals, and biomarkers of agricultural products in real time.
The spoilage process of meat is accompanied by protein decomposition, lipid oxidation, and microbial metabolism, producing characteristic chemicals that serve as targets for sensor detection [220]. In the distribution and storage of meat products, freshness serves as the core indicator for assessing quality and safety, and sensor technology offers an efficient and precise monitoring solution. The core principle of this technology involves using specific sensors to capture volatile organic compounds (VOCs) generated by microbial activity and chemical changes during meat spoilage in real time—these compounds act as key “markers” of declining meat freshness. For instance, microbial breakdown of proteins produces trimethylamine (TMA), with a fishy odor, and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), with a rotten egg smell, while oxidative deterioration of fats in meat releases characteristic substances like hexanal [221,222,223]. Sensors rapidly identify and quantify concentration changes in these VOCs, converting them into intuitive real-time data. Analysis of this data not only instantly reflects the current freshness level of meat but also provides a scientific basis for adjusting storage conditions, planning transport timelines, and optimizing preservation strategies [220]. This empowers businesses and retailers to precisely control meat quality throughout the supply chain, minimizing spoilage-related losses.
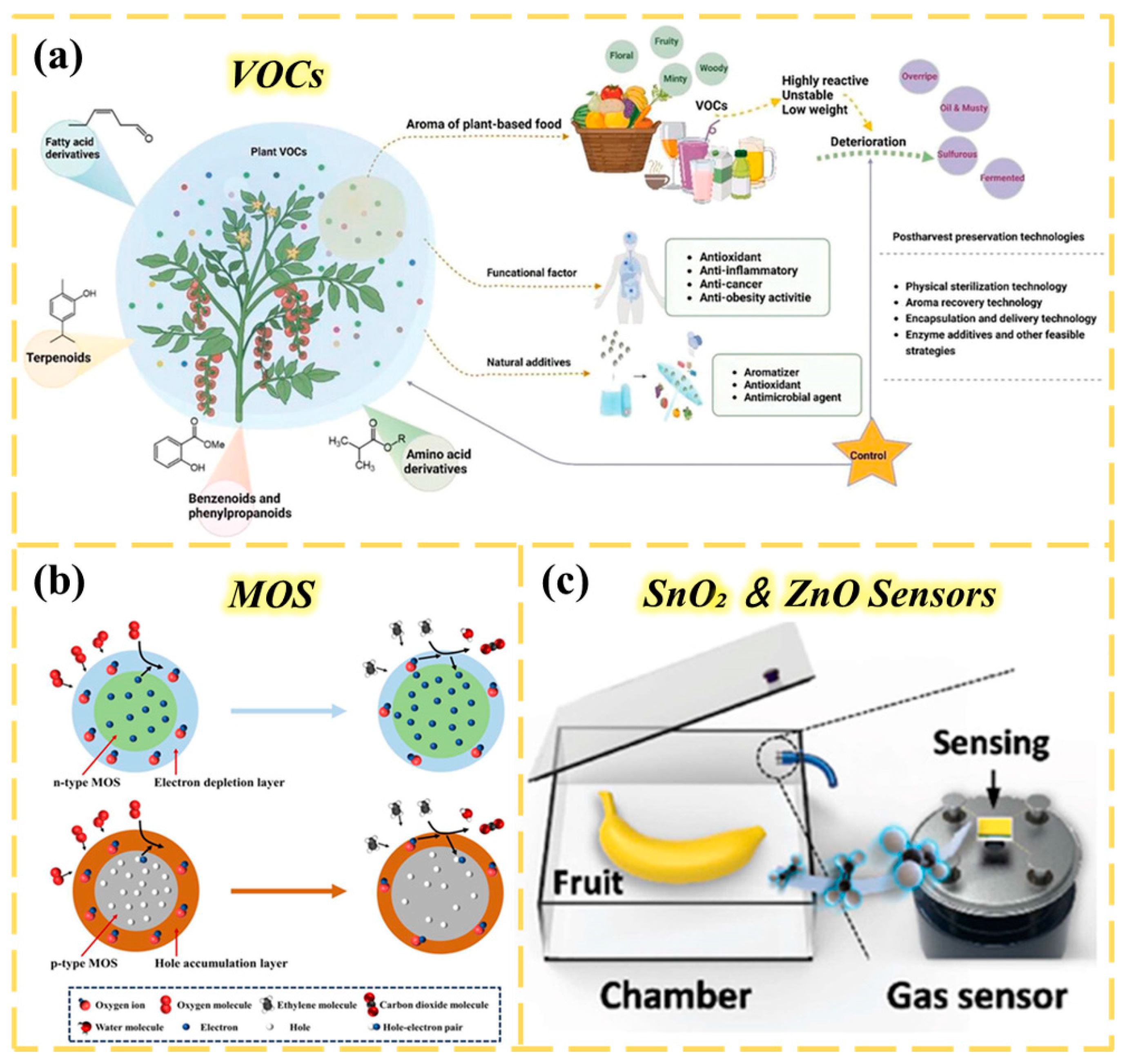
The freshness of agricultural products such as fruits and flowers can be assessed by their shape, surface luster, and color. Among these methods, odor detection is highly favored for its direct and efficient nature [224,225,226]. Similar to monitoring methods for meat products, this detection technology analyzes VOCs to directly determine the ripeness or spoilage level of agricultural products using “odor” signals [227] (Figure 9a). As one of these VOCs, ethylene is an important plant hormone that plays a key role in plant growth and fruit and vegetable ripening [228]. As a typical ripening agent, excessive ethylene will cause rapid deterioration and economic losses in the transportation and storage of agricultural products. Ethylene is mainly derived from plants and agricultural products themselves, and the synthesis pathway and maturation regulatory mechanism of ethylene in fruits and other ornamental cut flowers have been extensively studied [229,230]. Therefore, it is necessary to precisely regulate ethylene levels in the environment to maintain the freshness of agricultural products. Kongcan Hu et al. systematically reviewed the materials, preparation, application in agriculture, and sensing mechanisms of MOS chemical resistance sensors [231] (Figure 9b). They designed two metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS)-based chemical resistance sensors—SnO2 and ZnO—for the real-time monitoring of ethylene gas content in agricultural scenarios, thereby accurately determining the ripeness of fruits after harvest (Figure 9c). These MOS-based chemical resistance sensors offer significant performance advantages: They are extremely sensitive and can capture subtle changes in low concentrations of ethylene. They also have fast response and recovery speed, enabling them to provide real-time feedback on gas concentration dynamics. At the same time, they have the characteristics of low cost, simple structure, and strong stability, making them easy to deploy in large-scale production and actual scenarios. These characteristics give them great application potential in agricultural production, and they can provide efficient and economical technical support for maturity control in the post-harvest processing, warehousing, and transportation of fruit.
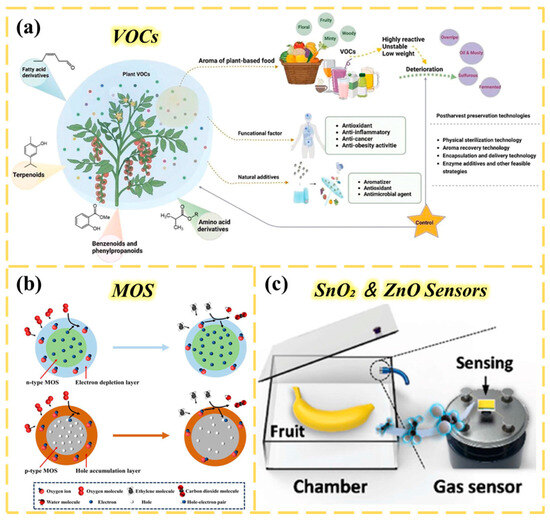
Figure 9.
(a) The process of aroma release by crops and its manual detection. Reproduced from Ref. [228]. Copyright (2024), with permission from John Wiley and Sons. (b) Sensing mechanism of chemical resistance ethylene sensor based on n-type and p-type MOS. The ethylene concentration is determined by resistance changes, and when exposed to atmospheric conditions, oxygen molecules are chemically adsorbed on the surface of the MOS sensing layer. By trapping electrons in the conduction band, oxygen molecules are converted into chemically adsorbed negatively charged oxygen. Reproduced from Ref. [231]. (c) Schematic diagram of the detection scenario of Cr2O3 customized SnO2 and ZnO sensors for fruit ripeness detection. Reproduced from Ref. [231].
5. Conclusions and Prospects
In this review, we introduced the current mainstream types of agricultural sensors and novel sensor technologies, and we illustrated the application of sensor technology in agricultural production, with specific examples. From the perspective of classification and characteristics, agricultural sensors are mainly classified according to monitoring parameters, including humidity sensors, light sensors, gas sensors, pressure sensors, nutrient sensors, and other emerging types. Each type of sensor has its own unique working principle and application scenarios: Humidity sensors achieve “water vapor-electrical signal conversion”, among which capacitive sensors have high accuracy, suitable for high-end greenhouse cultivation, but with high manufacturing and maintenance costs, while resistive sensors have low cost and a simple structure, and they are suitable for large-scale scenarios with low accuracy requirements. Light sensors rely on photoelectric conversion; photoresistors are low-cost, suitable for greenhouse light regulation, while photodiodes have excellent temperature stability and are suitable for harsh environments. Gas sensors target specific gases (e.g., CO2 sensors based on infrared spectroscopy, NH3 sensors based on electrochemical methods) to monitor crop photosynthesis and livestock and poultry health. In terms of emerging technologies, microneedle-based sensing technology can achieve minimally invasive, in situ, real-time monitoring of plant physiology and pesticide residues, with high sensitivity but challenges such as material corrosion and poor degradability. Nanosensors (based on FRET, electrochemical, and biomimetic sensors) have achieved ultra-high-sensitivity detection of trace substances (such as mycotoxins and heavy metals), but their stability and scalability still need to be improved. Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) enable large-area dynamic monitoring through multi-node collaboration, breaking through the limitations of traditional single-point measurements, but still need to be optimized in terms of interference resistance and energy efficiency. In practical applications, agricultural sensors have shown clear scenario-specific applicability: in greenhouses, capacitive humidity sensors, CdS photoresistors, and MOS-based ethylene sensors (SnO2, ZnO) regulate growth environments and post-harvest storage; in laboratories, FRET-based nanosensors, MIP-modified electrochemical sensors, and microneedle sensors (e.g., Ag-PVA-HA-MNs) conduct precise analysis of plant metabolites, mycotoxins, and pesticide residues (overcoming the complexity of traditional GC/HPLC methods). However, despite its significant contribution to agriculture, sensor technology still faces significant contradictions. High-precision sensors are difficult to promote on a large scale due to their high cost, and low-cost sensors struggle to meet the accuracy requirements of precision agriculture. Emerging technologies have great potential, but there is still a lot of room for improvement due to material properties and technological maturity.
We believe that the future development of agricultural sensors will solve current limitations through material technology innovation, moving towards intelligence, integration, and sustainability; for example, the development of biocompatible, degradable materials, combined with advanced materials such as MOFs and nanocomposites to improve stability and resistance to harsh environments. Integrating multiple sensing units into a single probe reduces deployment complexity and improves data correlation to further improve inspection efficiency. The introduction of AI algorithms enables real-time data fusion, dynamic prediction, and intelligent decision-making.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and S.W.; methodology, J.L.; validation, J.L., S.W.; formal analysis, S.W.; investigation, J.L.; resources, J.L.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, S.W.; visualization, S.W.; supervision, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no funding.
Data Availability Statement
All of the data required are available within the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adesipo, A.; Fadeyi, O.; Kuca, K.; Krejcar, O.; Maresova, P.; Selamat, A.; Adenola, M. Smart and Climate-Smart Agricultural Trends as Core Aspects of Smart Village Functions. Sensors 2020, 20, 5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.F.; Yuan, W.S.; Li, G.H.; Petropoulos, E.; Xue, L.X.; Feng, Y.F.; Xue, L.H.; Yang, L.Z.; Ding, Y.F. Deep fertilization with controlled-release fertilizer for higher cereal yield and N utilization in paddies: The optimal fertilization depth. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 5027–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Chen, L.W.; Zhang, Z.Y. A Study on the Utilization Rate and Influencing Factors of Small Agricultural Machinery: Evidence from 10 Hilly and Mountainous Provinces in China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Shabbir, H.; Naqvi, S.R.; Peng, L. Smart Agriculture: Current State, Opportunities, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 144456–144478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Ahmad, W.; Hassan, M.M.; Zareef, M.; Viswadevarayalu, A.; Arslan, M.; Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S. Landing microextraction sediment phase onto surface enhanced Raman scattering to enhance sensitivity and selectivity for chromium speciation in food and environmental samples. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy Maddikunta, P.K.; Hakak, S.; Alazab, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Khan, W.Z.; Pham, Q.-V. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Smart Agriculture: Applications, Requirements, and Challenges. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 17608–17619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Guo, X.P.; Wang, Z.C.; Chen, S.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Javed, Q. Response of Fertigation Under Buried Straw Layer on Growth, Yield, and Water-fertilizer Productivity of Chinese Cabbage Under Greenhouse Conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.K.; Karim, S.; Zeadally, S.; Nebhen, J. Recent Trends in Internet-of-Things-Enabled Sensor Technologies for Smart Agriculture. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 23583–23598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Wu, J.; Zhu, N. Scale measurement and economic effect evaluation of smart agriculture in China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2025, 99, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.K.; Huang, X.Y.; Aheto, J.H.; Zhang, D.J.; Feng, F. Detection of Beef Adulterated with Pork Using a Low-Cost Electronic Nose Based on Colorimetric Sensors. Foods 2020, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Lee, J.J.; Shin, J.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, S. Resistive Water Level Sensors Based on AgNWs/ PEDOT:PSS-g-PEGME Hybrid Film for Agricultural Monitoring Systems. ACS omega 2022, 7, 15459–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorissen, L.; Konrad, K.; Turnhout, E. Sensors and sensing practices: Shaping farming system strategies toward agricultural sustainability. Agric. Hum. Values 2025, 42, 1477–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollo, A.; Cameron, J.; Dias, J.D.F.; Cichocki, R.; Synkiewicz-Musialska, B.; Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Kettle, J. Hybrid Agricultural Monitoring System with Detachable, Biodegradable, and Printed pH Sensors with a Recyclable Wireless Sensor Network for Sustainable Sensor Systems. Acs Appl. Electron. Mater. 2025, 7, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.P.; Du, X.X.; Yan, Y.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Ma, G.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.Y.; Shi, Q. Highly sensitive detection of daminozide using terahertz metamaterial sensors. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, M.E. Enhancing sensor network sustainability with fuzzy logic based node placement approach for agricultural monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. Sensors key to advances in precision agriculture. Sens. Rev. 2017, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, Y.E.M.; Msallam, M.M. Smart heterogeneous precision agriculture using wireless sensor network based on extended Kalman filter. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 5653–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jayakumar, K.; Wen, Y.; Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Duan, X.; Xu, J. Recent advances in metal-organic framework (MOF)-based agricultural sensors for metal ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Fan, B.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Seglah, P.A.; Gao, C. Analysis of the Development Status and Prospect of China’s Agricultural Sensor Market under Smart Agriculture. Sensors 2023, 23, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Digital Development Strategy of Agricultural Planting and Breeding Enterprises Based on Intelligent Sensors. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 6495191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Yonet-Tanyeri, N.; Vander Ende, E.; Henry, A.-I.; White, B.E.P.; Mrksich, M.; Van Duyne, R.P. Plasmonic Microneedle Arrays for in Situ Sensing with Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS). Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6862–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Leong, V.; Alagappan, G.; Krivitsky, L. Enhancing Optical Readout from Diamond AFM Tips for Quantum Nanosensing. ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 4244–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhong, A. Resource Allocation in Wireless Powered Virtualized Sensor Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 40327–40336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.A.G.; Sousa, R.H.V. Looking for a systemic concept and physiological diagnosis of a plant stress state. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2024, 36, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Cai, D.; He, L.; Zhong, N.; Wen, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. A Facile Approach To Remediate the Microenvironment of Saline-Alkali Soil. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lv, C.; Liu, J. Quality and safety traceability system of agricultural products based on Multi-agent. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 35, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbers, R.; Adamchuk, V.I. Precision Agriculture and Food Security. Science 2010, 327, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Bartzanas, T. Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring of Agricultural Structures. Sensors 2021, 21, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, Y.K.K.; Timoshenkov, S.P.; Simonov, B.M.; Riabyshenkov, A.C. Analysis of the Suspension Elements for the Sensitive Element of a Micromechanical Accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Seminar on Electron Devices Design and Production (SED), Prague, Czech Republic, 27–28 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, L.; Ren, W.; Liu, W.; Gou, Y.; Ren, X. Research on the Output Characteristics of Energy Conversion Elements under External Excitation. Micromachines 2023, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fulginiti, I.; Mendl, C.B. Reducing mid-circuit measurements via probabilistic circuits. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–20 September 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, T.A.; Eksperiandova, L.P.; Belikov, K.N. Recent trends of ceramic humidity sensors development: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulliani, J.-M.; Inserra, B.; Ziegler, D. Carbon-Based Materials for Humidity Sensing: A Short Review. Micromachines 2019, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Lopez, F.; Briand, D.; de Rooij, N.F. All additive inkjet printed humidity sensors on plastic substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Huang, M.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Feng, Z.S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.J.; Xu, Z.Q.; Liu, H.G.; Wang, Y. Printing assembly of flexible devices with oxidation stable MXene for high performance humidity sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.T.; Tan, R.Q.; Feng, M.X.; Shen, W.F.; Lv, D.W.; Song, W.J. Humidity Sensing Using Polymers: A Critical Review of Current Technologies and Emerging Trends. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Yin, F.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Kan, H.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wang, C. Ultrafast-response/recovery capacitive humidity sensor based on arc-shaped hollow structure with nanocone arrays for human physiological signals monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liang, J.-G.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.-C.; Bai, B.; Meng, F.-Y.; Zou, D.-Q.; Ali, L.; Jing, C.-Q.; Zhao, M.; et al. Target properties optimization on capacitive-type humidity sensor: Ingredients hybrid and integrated passive devices fabrication. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 340, 129883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetti, E.; Pantalei, S.; Pecora, A.; Valletta, A.; Maiolo, L.; Minotti, A.; Macagnano, A.; Fortunato, G.; Bearzotti, A. Design and optimization of an ultra thin flexible capacitive humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Xu, W.X.; Leng, J.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Ding, H.N.; Zhou, J.F.; Cui, L.F. Review and Research Prospects on Additive Manufacturing Technology for Agricultural Manufacturing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A. Using additive manufacturing applications for design and development of food and agricultural equipments. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2019, 58, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ocana, I.; Fernandez Delgado, N.; Molina, S.I. Biomass waste from rice and wheat straw for developing composites by stereolithography additive manufacturing. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvailo, A.; Xing, Y.; Hines, J.; Borguet, E. Thin polymer film based rapid surface acoustic wave humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harito, C.; Utari, L.; Putra, B.R.; Yuliarto, B.; Purwanto, S.; Zaidi, S.Z.J.; Bavykin, D.V.; Marken, F.; Walsh, F.C. Review—The Development of Wearable Polymer-Based Sensors: Perspectives. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Chen, A.N.; Su, J.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhou, S.X.; He, J.H.; Cao, Z.W.B.; Shi, Y.S.; et al. An overview on ceramic multi-material additive manufacturing: Progress and challenges. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2025, 7, 042005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.; Jayan, H.; Gao, S.P.; Zhou, R.Y.; Yosri, N.; Zou, X.B.; Guo, Z.M. Recent and emerging trends of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-based sensors for detecting food contaminants: A critical and comprehensive review. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.X.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y.; Huang, X.W.; Liu, C.; et al. Rapid detection of cadmium ions in meat by a multi-walled carbon nanotubes enhanced metal-organic framework modified electrochemical sensor. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Yan, X.; Lu, G. Enzyme-Engineered Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Construction of Organophosphorus Pesticide Biosensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2309383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetya, N.; Okur, S. Investigation of the free-base Zr-porphyrin MOFs as relative humidity sensors for an indoor setting. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2024, 377, 115713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, G.T.; Chen, J.B.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, H.; Sun, L.N. Upconversion Luminescent Humidity Sensors Based on Lanthanide-Doped MOFs. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butova, V.V.; Pankin, I.A.; Burachevskaya, O.A.; Vetlitsyna-Novikova, K.S.; Soldatov, A.V. New fast synthesis of MOF-801 for water and hydrogen storage: Modulator effect and recycling options. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2021, 514, 120025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Humidity Sensors Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.Q.; Zhang, X.A.; Li, W.T.; Liang, N.N.; Hu, X.T.; Xiao, J.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y. An intrinsic dual-emitting fluorescence sensing toward tetracycline with self-calibration model based on luminescent lanthanide-functionalized metal-organic frameworks. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 133995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.; Arslan, M.; Hu, X.T.; Zhang, X.A.; Li, Z.H.; Shi, J.Y.; Zou, X.B. Ratiometric Fluorescent Metal-Organic Framework Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Acrylamide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10065–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Syed, A.; Akhtar, F.H.; Shevate, R.; Singh, S.; Peinemann, K.-V.; Baran, D.; Wu, T. Giant Humidity Effect on Hybrid Halide Perovskite Microstripes: Reversibility and Sensing Mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29821–29829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlknecht, J.; Wuzella, G.; Lammer, H.; Khalifa, M. A smart functional surfactant activated conductive polymer coated on paper with ultra-sensitive humidity sensing characteristics. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1804–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajt, T.; Jasinski, G.; Chachulski, B. Electrical properties of polymer humidity sensor based on polyethyleneimine. In Optoelectronic and Electronic Sensors V; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, S.A.; Gunlycke, D. Analysis of Correlated Dynamics in the Grotthuss Mechanism of Proton Diffusion. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.K.; Zhao, L.; Luo, X.; Guo, J.X.; Liu, X.J. Perceptual Soft End-Effectors for Future Unmanned Agriculture. Sensors 2023, 23, 7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, S.A. Facile synthesis of cerium doped Co-Mn-FeO nano ferrites as highly sensitive and fast response humidity sensors at room temperature. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamry, A.; Lu, T.Q.; Chen, H.R.; Adiraju, A.; Nasraoui, S.; Brahem, A.; Bajuk-Bogdanovic, D.; Weheabby, S.; Pasti, I.A.; Kanoun, O. Ultra-Sensitive and Fast Humidity Sensors Based on Direct Laser-Scribed Graphene Oxide/Carbon Nanotubes Composites. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailov, S.J.; Ding, H.M.; Szabo, K.; Hnatovsky, C.; Walker, R.B.; Lu, P.; De Silva, M. High Sensitivity Fiber Bragg Grating Humidity Sensors Made With Through-the-Coating Femtosecond Laser Writing and Polyimide Coating Thickening. Ieee Sens. Lett. 2024, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, H.G.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y. Designing High Performance Carbon/ZnSn(OH)6-Based Humidity Sensors. Sensors 2024, 24, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, S.G.; Bouvet, M. Effects of Visible Light on Gas Sensors: From Inorganic Resistors to Molecular Material-Based Heterojunctions. Sensors 2024, 24, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.B.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.C.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, H. Actuators and Sensors for Application in Agricultural Robots: A Review. Machines 2022, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Sarkar, S.; Tsuda, T.; Chae, S.; Knapp, A.; Nitschke, M.; Das, A.; Wiessner, S.; König, T.A.F.; Fery, A. Plasmonic Photoresistor Based on Interconnected Metal-Semiconductor Grating. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennel, Z.; McGeehan, M.; Ong, K.G. An Optoelectronics-Based Compressive Force Sensor with Scalable Sensitivity. Sensors 2023, 23, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C. Intelligent Environmental Control in Plant Factories: Integrating Sensors, Automation, and AI for Optimal Crop Production. Food Energy Secur. 2025, 14, e70026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, H.O.; Kim, C.G. A Study on the Possibility of Measuring Sludge Sedimentation Using Contrast Detection Characteristics of CdS Photoresistors. Energies 2021, 14, 7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Yi, F.T. Fabrication and photosensitivity of ZnO/CdS/silica nanopillars based photoresistor. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 11326–11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, E.; Simon, J.C. The effect of crystal composition and environment on the color Doppler ultrasound twinkling artifact. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 035021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.P.; Natrella, M.; Lin, X.L.; Graham, C.; Renaud, C.C.; Seeds, A.J. Photodiodes for Terahertz Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2022, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, B.; Schneider-Hornstein, K.; Zimmermann, H. Ultra-Low Capacitance Spot PIN Photodiodes. IEEE Photonics J. 2023, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.T.; Zhang, X.P.; Sharawi, M.S.; Kashyap, R. Advances in High-Speed, High-Power Photodiodes: From Fundamentals to Applications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, T.; He, P.H.; Ding, Y.H.; Chen, Q.S. Rapid measurement of fatty acid content during flour storage using a color-sensitive gas sensor array: Comparing the effects of swarm intelligence optimization algorithms on sensor features. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, J.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.T.; Gong, Y.Y.; Zou, X.B. A Novel Gas Sensor for Detecting Pork Freshness Based on PANI/AgNWs/Silk. Foods 2022, 11, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.M.; Jayan, H.; Cai, J.R.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Guo, Z.M.; Zou, X.B. Spoilage Monitoring and Early Warning for Apples in Storage Using Gas Sensors and Chemometrics. Foods 2023, 12, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, K.S.V.; Ahamed, N.N.N. Greenhouse Gas Sensors Fabricated with New Materials for Climatic Usage: A Review. Chemengineering 2018, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, A.S.; Bien, D.C.S.; Lee, H.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lee, M.W. In-Situ Grown Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube on Interdigitated Electrodes for Carbon Dioxide Sensing. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 14, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Honeycutt, W.T.; Ley, M.T.; Materer, N.F. Precision and Limits of Detection for Selected Commercially Available, Low-Cost Carbon Dioxide and Methane Gas Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chachuli, S.A.M.; Ying, W.H.; Shamsudin, N.H.; Coban, O. Real-time Monitoring of Carbon Dioxide with IoT ThingSpeak using TiO2 Thick Film Gas Sensor. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2024, 56, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, O.S. Detection of Carbon Dioxide Using Cucurbit[6]uril-Functionalized Gold Nanorod Gas Sensor Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 2021, 30, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Zhang, T. An Overview: A Design Strategy for Dioxide Carbon QCM Gas Sensor Based on MOFs or COFs. Adv. Sens. Res. 2025, 4, 2400170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumjun, P.; Kim, S.; Kwak, C.H.; Shanmugam, K.R.; Kyu, H.Y.; Cho, Y.; Suk, H.Y. Visual colorimetric detection of ammonia under gaseous and aqueous state: Approach on cesium lead bromide perovskite-loaded porous electrospun nanofibers. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 97, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobelets, K.; Panteli, C.; Sydoruk, O.; Li, C. Ammonia sensing using arrays of silicon nanowires and graphene. J. Semicond. 2018, 39, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshayedi, A.J.; Khan, A.S.; Hu, J.D.; Nawaz, A.; Zhu, J.X. E-Nose-Driven Advancements in Ammonia Gas Detection: A Comprehensive Review from Traditional to Cutting-Edge Systems in Indoor to Outdoor Agriculture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, G.Q.; Wang, B.; Yu, X.H. Progress and perspectives of self-powered gas sensors. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Soppera, O.; Chen, L.-Y.; Meng, H.-F.; Zan, H.-W. Two-Minute Onsite Detection of Agricultural Water Nitrogen Pollution with an Ammonia Gas Sensing System. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Stockler, A.H.; Feilberg, A.; Kamp, J.N. Investigation of non-target gas interferences on a multi-gas cavity ring-down spectrometer. Atmos. Environ.-X 2024, 22, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, B.; Alessi, E.; Krol, D.; Morton, P.A.; Daly, K. Application of metal oxide semiconductor for detection of ammonia emissions from agricultural sources. Sens. BIO-Sens. Res. 2022, 38, 100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenarsari, A.E.; Vitton, S.J.; Beard, J.E. Tactile Pressure Sensors to Measure Ground Pressure from Tractor Tire Loads. Geotech. Test. J. 2018, 41, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Xie, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, H.; Zeng, W.; Wei, N.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Y. Supercapacitive brophene-graphene aerogel as elastic-electrochemical dielectric layer for sensitive pressure sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 601, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Cai, L.; Fang, H.; Chen, H. Fruit recognition and classification based on tactile information of flexible hand. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2024, 370, 115224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, P.; Sugeru, H.; Wibowo, E.P. Wireless Sensor Networks for Precision Agriculture: A Review of NPK Sensor Implementations. Sensors 2024, 24, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nifong, R.L.; Taylor, J.M. Vegetation and Residence Time Interact to Influence Metabolism and Net Nutrient Uptake in Experimental Agricultural Drainage Systems. Water 2021, 13, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, V.; Hinck, S.; Peiter, E.; Ruckelshausen, A. Handling of Ion-Selective Field-Effect Transistors (ISFETs) on Automatic Measurements in Agricultural Applications Under Real-Field Conditions. Electronics 2024, 13, 4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidhof, M.J. Precision livestock feeding: Matching nutrient supply with nutrient requirements of individual animals. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.; Phairatana, T.; Jeerapan, I. Tackling the challenges of developing microneedle-based electrochemical sensors. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Esser, L.; Easton, C.D.; Cadarso, V.J.; Voelcker, N.H. Wearable microneedle array-based sensor for transdermal monitoring of pH levels in interstitial fluid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowers, S.A.N.; Freeman, D.M.E.; Rawson, T.M.; Rogers, M.L.; Wilson, R.C.; Holmes, A.H.; Cass, A.E.; O’Hare, D. Development of a Minimally Invasive Microneedle-Based Sensor for Continuous Monitoring of β-Lactam Antibiotic Concentrations in Vivo. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Narayan, R.J.; Polsky, R. Microneedle-based sensors for medical diagnosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Li, L.; Regmi, S.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S. Microneedle-Based Glucose Sensor Platform: From Vitro to Wearable Point-of-Care Testing Systems. Biosensors 2022, 12, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.; Zheng, Y.; Haick, H. Protocol to fabricate wearable stretchable microneedle-based sensors. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, G.; Haick, H.; Zhang, M. Wearable Clinic: From Microneedle-Based Sensors to Next-Generation Healthcare Platforms. Small 2023, 19, 2207539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, F.; Tortolini, C.; Bollella, P.; Antiochia, R. Microneedle-based electrochemical devices for transdermal biosensing: A review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Tehrani, F.; Mahato, K.; Wang, J. Lab under the Skin: Microneedle Based Wearable Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2002255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Talreja, N.; Chauhan, D.; Ashfaq, M. Microneedle (MN)-based sensing technology: An innovative solution for agriculture. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 8745–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Park, K.D.; Cho, S. Review-In Vivo and In Vitro Microneedle Based Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Continuous Glucose Monitoring Biosensors. Ecs J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, Q3159–Q3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, K.; Dalton, C. Recent Developments in Microneedle Biosensors for Biomedical and Agricultural Applications. Micromachines 2025, 16, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.P.; Luo, X.L.; Lv, S.P. Advances in microneedles for transdermal diagnostics and sensing applications. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, M.; Gao, B.B. A Review of Recent Advances in Microneedle-Based Sensing within the Dermal ISF That Could Transform Medical Testing. Acs Sens. 2024, 9, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Halima, H.; Lakard, B.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Microneedle-Based Sensors for Wearable Diagnostics. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortolini, C.; Cass, A.E.G.; Pofi, R.; Lenzi, A.; Antiochia, R. Microneedle-based nanoporous gold electrochemical sensor for real-time catecholamine detection. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes-Ramirez, G.; Li, Y.-C.; Kim, J.; Jia, W.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Nunez-Flores, R.; Miller, P.R.; Wu, S.-Y.; Narayan, R.; Windmiller, J.R.; et al. Microneedle-based self-powered glucose sensor. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 47, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, L.; Yin, Y.H.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Dai, Y.T.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.Y.; Qiu, F.X. Lamellar Ti 3 C 2 MXene composite decorated with platinum-doped MoS 2 nanosheets as electrochemical sensing functional platform for highly sensitive analysis of organophosphorus pesticides. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.Z.; Zhou, R.Y.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Yi, Y.H.; Zhu, G.B. Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of paraoxon ethyl in water and fruit samples based on defect-engineered graphene nanoribbons modified electrode. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Haruna, S.A.; Ahmad, W.; Wu, J.Z.; Chen, Q.S.; Ouyang, Q. Tunable multiplexed fluorescence biosensing platform for simultaneous and selective detection of paraquat and carbendazim pesticides. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floare-Avram, C.V.; Molnar, C.; Covaciu, F.-D. Integrated UHPLC-PDA and GC-ECD approaches for detecting pesticide residues in frozen fruits and vegetables: Unveiling contaminants and assessing health risks. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 145, 107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chen, D.; Yan, X.; Kang, C.; Tian, W.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, T.; Long, Y. Dynamic visual monitoring of triazole pesticide residues and penetration behavior in fruits and vegetables by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Microchem. J. 2025, 214, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, C. Novel Microneedle Patch-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Sensor for the Detection of Pesticide Residues. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Xu, Y.; He, P.H.; Zareef, M.; Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S. Simultaneous determination of benzimidazole fungicides in food using signal optimized label-free HAu/Ag NS-SERS sensor. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Li, H.H.; Ahmad, W.; Zareef, M.; Wang, J.J.; Xie, S.C.; Wang, P.Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, Q.S. Au@Ag nanostructure based SERS substrate for simultaneous determination of pesticides residue in tea via solid phase extraction coupled multivariate calibration. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 105, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.A.; Huang, X.W.; Zou, X.B.; Li, Z.H.; Wei, R.C. Facile synthesis of Au@Ag core-shell nanorod with bimetallic synergistic effect for SERS detection of thiabendazole in fruit juice. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.-Y.; Wong, M.H.; Lew, T.T.S.; Bisker, G.; Lee, M.A.; Kaplan, A.; Dong, J.; Liu, A.T.; Koman, V.B.; Sinclair, R.; et al. Nanosensor Technology Applied to Living Plant Systems. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 10, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.S.; Honeychurch, K.C. Nanosensor Applications in Plant Science. Biosensors 2022, 12, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.H.; Lu, B.; Wu, M.M.; Dai, C.X. Grade Identification of Tieguanyin Tea Using Fluorescence Hyperspectra and Different Statistical Algorithms. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Arumugam, S.S.; Sabarinathan, D.; Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S. Metal organic framework based fluorescence sensor for detection of antibiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 1002–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.Y.; Lv, R.Q.; Huang, X.Y.; Chen, Q.S.; Dong, Y.N. Rapid quantitative assessment of lipid oxidation in a rapeseed oil-in-water (o/w) emulsion by three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Mao, H.P.; Wu, X.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Gao, H.Y. Identification of pesticide residue level in lettuce based on hyperspectra and chlorophyll fluorescence spectra. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Han, Y.F.; Ling, L.; Deng, N.N.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y. Development of Quantum Dots-Labeled Antibody Fluorescence Immunoassays for the Detection of Morphine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrin, G.; Ahmad, M.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Ahmad, A. Conversion of Cytochrome P450 2D6 of Human Into a FRET-Based Tool for Real-Time Monitoring of Ajmalicine in Living Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.Z.; Nie, C.; Wei, Y.L.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Z.L.; Xiang, P. FRET-based innovative assays for precise detection of the residual heavy metals in food and agriculture-related matrices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 469, 214676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Xu, J.L.; Qiu, Y.L.; Li, P.; Liu, B.B.; Yang, L.F.; Barnych, B.; Hammock, B.D.; Zhang, C.Z. Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody and Sensitive Quantum Dot Beads-Based Fluorescence Immunochromatographic Test Strip for Tebuconazole Assay in Agricultural Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9096–9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, H.; Ambrin, G.; Okla, M.K.; Alamri, S.A.; Soufan, W.H.; Ibrahim, E.I.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A.; Ahmad, A. FRET-Based Genetically Encoded Nanosensor for Real-Time Monitoring of the Flux of α-Tocopherol in Living Cells. ACS omega 2021, 6, 9020–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, R.; Okla, M.K.; Fatima, U.; Mohsin, M.; Soufan, W.H.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A.; Ahmad, A. Designing and Development of FRET-Based Nanosensor for Real Time Analysis of N-Acetyl-5-Neuraminic Acid in Living Cells. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 621273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakavath, K.; Kafley, C.; Sajeevan, A.; Jana, S.; Marty, J.L.; Kotagiri, Y.G. Progress on Electrochemical Biomimetic Nanosensors for the Detection and Monitoring of Mycotoxins and Pesticides. Toxins 2024, 16, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal-Kestwal, D.; Kestwal, R.M.; Chiang, B.H. Invertase-nanogold clusters decorated plant membranes for fluorescence-based sucrose sensor. J. Nanobiotechnology 2015, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Marty, J.L.; Yang, X. Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of Ochratoxin A using unmodified gold nanoparticles indicator. Biosens Bioelectron 2011, 26, 2724–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.C.; Guo, W.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.C.; Qiu, J.; Peng, J.B. A Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Graphene Oxide Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles-Molecular Imprinted Polymers for Determination of Sunset Yellow in Soft Drinks. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.H.; Zou, X.B.; Xu, Y.W.; Xu, X.C. A smart-phone-based electrochemical platform with programmable solid-state-microwave flow digestion for determination of heavy metals in liquid food. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, M.-W.; Lee, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chao, L.-C.; Huang, K.-C.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Thanachayanont, C. Custom-Designed Portable Potentiostat and Indirect Cyclic Voltammetry Index Analysis for Rapid Pesticide Detection Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, C.L.A.; Govan, J.E. Machine Learning Techniques for Improving Nanosensors in Agroenvironmental Applications. Agronomy 2024, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Su, X.; Li, L.; Lew, T.T.S.; Wu, C. Wearable electrochemical bioelectronics for agriculture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 22396–22416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, X.X.; Gao, C.B.; Gai, Z.Q.; He, Y.X.; Qian, Z.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Lei, H.T.; Sun, Y.M.; Xu, Z.L. Development of a highly sensitive and selective electrochemical immunosensor for controlling of rhodamine B abuse in food samples. Food Control 2022, 133, 108662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Lin, Z.; Qian, J.; Wang, F.; Qu, L.; Zou, B. Research Progress on the Application of Nanoenzyme Electrochemical Sensors for Detecting Zearalenone in Food. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejigu, A.; Tefera, M.; Guadie, A. Electrochemical detection of pesticides: A comprehensive review on voltammetric determination of malathion, 2,4-D, carbaryl, and glyphosate. Electrochem. Commun. 2024, 169, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Du, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Passerini, S.; Wu, Y. High-Entropy Approach vs. Traditional Doping Strategy for Layered Oxide Cathodes in Alkali-Metal-Ion Batteries: A Comparative Study. Energy Storage Materials 2025, 79, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirizadeh, N.; Shekari, Z.; Nazari, A.; Tabatabaee, M. Fabrication of a novel electrochemical sensor for determination of hydrogen peroxide in different fruit juice samples. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evtugyn, G.; Porfireva, A.; Sitdikov, R.; Evtugyn, V.; Stoikov, I.; Antipin, I.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Determination of Ochratoxin A at the Au Electrode Modified with Ag Nanoparticles Decorated with Macrocyclic Ligand. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Qian, J.; Jiang, L.; Yan, Y.T.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K. Ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor for ochratoxin A based on two-level cascaded signal amplification strategy. Bioelectrochemistry 2014, 96, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J.; Wen, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J.; Ding, W. Novel highly selective fluorescent sensor based on electrosynthesized poly(9-fluorenecarboxylic acid) for efficient and practical detection of iron(III) and its agricultural application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.; Patra, S.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Simultaneous determination of heavy metals in biological samples by a multiple-template imprinting technique: An electrochemical study. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 56690–56700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, P.; Kaushik, R.; Shiva Swaraj, V.J.; Kumar, N. Organophosphorus pesticides residues in food and their colorimetric detection. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Pandey, V.; Sharma, M.M.M.; Patra, A.; Singh, B.; Mehta, S.; Husen, A. A Review on Biosensors and Nanosensors Application in Agroecosystems. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Z.; Feng, L.; Yan, Y. Biomimetic metalloporphyrin oxidase modified carbon nanotubes for highly sensitive and stable quantification of anti-oxidants tert-butylhydroquinone in plant oil. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.W.; Zhu, A.F.; Adade, S.; Ali, S.; Chen, Q.M.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.M.; Jiao, T.H.; Chen, Q.S. Ag@Au core-shell nanoparticle-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering coupled with chemometrics for rapid determination of chloramphenicol residue in fish. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 138026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.W.; Zou, X.M.; Song, S.H.; Chen, G.H. Quantum Dots Applied to Methodology on Detection of Pesticide and Veterinary Drug Residues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, D.J.; Pattanaik, K.P.; Kulabhusan, P.; Naik, S.; Mahanty, A.; Mohapatra, S.D.; Adak, T. Microfluidic paper-based devices for efficient and sensitive pesticide detection: A review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 142, 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, L. Applications and Challenges of Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Pesticide Residues in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 4982–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Q. Improved Detection of Veterinary Drug Residues: Advancing Analytical Techniques to Ensure Food Safety. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 19, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldra, F.; Reig, M. Methods for rapid detection of chemical and veterinary drug residues in animal foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.X.; Chen, G.H.; Fang, R.; Zhang, L.; Yi, L.X.; Meng, H.L. Analysis of Six β-Lactam Residues in Milk and Egg by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography with Large-Volume Sample Stacking and Polarity Switching. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3456–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J.W. Fabricating a Novel Raman Spectroscopy-Based Aptasensor for Rapidly Sensing Salmonella typhimurium. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenyorege, E.A.; Ma, H.L.; Ayim, I.; Zhou, C.S. Ultrasound decontamination of pesticides and microorganisms in fruits and vegetables: A review. J. Food Saf. Food Qual.-Arch. Fur Leb. 2018, 69, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huan, X.Y.; Yi, R.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R.; Golly, M. Electronic nose classification and differentiation of bacterial foodborne pathogens based on support vector machine optimized with particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, S.; Du, Q.; Yang, S.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Lin, H. Dual-signal enhanced lateral flow immunoassay with nanobody-functionalized magnetofluorescent nanoprobes for multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1369, 344360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, K.; Akhtar, S.; Gong, Y.Y.; Routledge, M.N.; Ismail, A.; Oliveira, C.A.F.; Iqbal, S.Z.; Ali, H. Evaluation of the impact of activated carbon-based filtration system on the concentration of aflatoxins and selected heavy metals in roasted coffee. Food Control 2021, 121, 107583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, C.T.; Bao, Q.H.; Zheng, J.; Deng, D.; Duan, Y.Q.; Shen, L.Q. The physicochemical characterization, equilibrium, and kinetics of heavy metal ions adsorption from aqueous solution by arrowhead plant (Sagittaria trifolia L.) stalk. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sikaily, A.; Ghoniem, D.G.; Ramadan, O.; El-Nahrery, E.M.; Shahat, A.; Hassan, R.Y.A. Highly selective detection of heavy metal ions in food and water using a 5-BHAHS@NC/MnO2-based electrochemical sensor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2025, 216, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K. Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. South Afr. J. Bot. 2010, 76, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, A.; Ong, Y.R.; Schirhagl, R.; Tahir, M.A.; Khan, W.S.; Bajwa, S.Z. Nanosensors for diagnosis with optical, electric and mechanical transducers. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 6793–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, P. Micro- and Nanosensors for Medical and Biological Measurement. Sens. Mater. 2012, 24, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Yin, H.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in Nanosensors for Motion Detection. Acs Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Gao, J.; Jiang, Y. Acetylcholinesterase/chitosan-transition metal carbides nanocomposites-based biosensor for the organophosphate pesticides detection. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 128, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Surya, S.G.; Beduk, T.; Vijjapu, M.T.; Lamaoui, A.; Durmus, C.; Timur, S.; Shekhah, O.; Mani, V.; Amine, A.; et al. Metal-Organic Frameworks Meet Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Insights and Prospects for Sensor Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49399–49424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.X.; Pan, J.M.; Yan, Y.S.; Zhang, X.F. A precise and efficient detection of Seta-Cyfluthrin via fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymers with ally fluorescein as functional monomer in agricultural products. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, H.Y.; Han, Y.F.; Yu, F.F.; Shi, X.M. Development of a biomimetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on molecularly imprinted polymers on paper for the detection of carbaryl. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, X.M.; Yu, F.F.; Quan, Y. Preparation of dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on dextran-modified magnetic nanoparticles Fe3O4 for the selective detection of acrylamide in potato chips. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmandoust, M.; Erk, N.; Naser, M.; Soylak, M. Molecularly imprinted polymer film loaded on the metal–organic framework with improved performance using stabilized gold-doped graphite carbon nitride nanosheets for the single-step detection of Fenamiphos. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Song, Y.; Tu, J.; Mukasa, D.; Ye, C.; Xu, C.; Heflin, N.; McCune, J.S.; et al. A wearable electrochemical biosensor for the monitoring of metabolites and nutrients. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaccan, C.N.; Cruz, F.R.G.; Agulto, I.C. Wireless Sensor Network for Agricultural Environment using Raspberry Pi based Sensor Nodes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 9th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (IEEE Hnicem), Manila, Philippines,, 1–3 December 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, N. Research on Integration of WSN and RFID Technology for Agricultural Product Inspection. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Control and Electronics Engineering (ICICEE), Xi’an, China, 23–25 August 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Sreeram, V.; Zhao, D.A.; Duan, S.L.; Jiang, J.M. A wireless sensor network-based monitoring system for freshwater fishpond aquaculture. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurlan, Z.; Zhukabayeva, T.; Othman, M.; Adamova, A.; Zhakiyev, N. Wireless Sensor Network as a Mesh: Vision and Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H. Low-Power Intelligent Wireless Sensor Network for Precision Agriculture Oriented Agricultural Greenhouse Management System. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 34865–34876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.; Galelyuka, I.; Antonova, H.; Kovyrova, O.; Hrusha, V.; Voronenko, O. Application of Wireless Sensor Networks for Digital Agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems—Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Metz, France, 18–21 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zhu, Y. Environment Monitoring System for Precise Agriculture Based on Wireless Sensor Network. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 475, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Chikangaise, P.; Shi, W.D.; Chen, W.H.; Yuan, S.Q. Review of intelligent sprinkler irrigation technologies for remote autonomous system. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, T. Understanding the continuous usage in wireless sensor networks of wisdom agriculture. Int. J. Mob. Commun. 2019, 17, 422–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.H.; Al-Yaari, A.; Yilmaz, M.T. Comparative Evaluation of Microwave L-Band VOD and Optical NDVI for Agriculture Drought Detection over Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.; Zohaib, M.; Kim, U.; Aadil, M.; Choi, M. Agricultural drought assessment based on multiple soil moisture products. J. Arid. Environ. 2019, 167, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Sagan, V.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ren, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; et al. Optical and Thermal Remote Sensing for Monitoring Agricultural Drought. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, M.M.; Sanchez, N.; Piles, M.; Ruscica, R.; Gonzalez-Zamora, A.; Roitberg, E.; Martinez-Fernandez, J. The Added-Value of Remotely-Sensed Soil Moisture Data for Agricultural Drought Detection in Argentina. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6487–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.M.; Liu, Q.; Manthar, A.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.L. Surface Acoustic Wave Humidity Sensor: A Review. Micromachines 2023, 14, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustaffa, S.N.; Rashid, A.R.A.; Jin, T.S.; Menon, P.S.; Ab Razak, M.Z.; Markom, A.M.; Haris, H.; Saad, I.; Muhammad, A.R. Metal Oxide Coated Optical Fiber for Humidity Sensing Application: A Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 126568–126600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.; Wang, D.; Tipparaju, V.V.; Tsow, F.; Xian, X.J. Mitigation of Humidity Interference in Colorimetric Sensing of Gases. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheberl, L.; Scharenbroch, B.C.; Werner, L.P.; Prater, J.R.; Fite, K.L. Evaluation of soil pH and soil moisture with different field sensors: Case study urban soil. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplowitz, M.D.; Machemer, P.; Pruetz, R. Planners’ experiences in managing growth using transferable development rights (TDR) in the United States. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hua, S.; Timlin, D.; Kojima, Y.; Lu, S.; Sun, W.; Fleisher, D.; Horton, R.; Reddy, V.R.; Tully, K. Time Domain Reflectometry Waveform Interpretation With Convolutional Neural Networks. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobriyal, P.; Qureshi, A.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A. A review of the methods available for estimating soil moisture and its implications for water resource management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 458, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapilaratne, R.G.C.J.; Lu, M. Automated general temperature correction method for dielectric soil moisture sensors. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaparthy, V.S.; Singh, D.N.; Baghini, M.S. Compensation of temperature effects for in-situ soil moisture measurement by DPHP sensors. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 141, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banon, S.; Ochoa, J.; Banon, D.; Ortuno, M.F.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J. Assessment of the Combined Effect of Temperature and Salinity on the Outputs of Soil Dielectric Sensors in Coconut Fiber. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Li, W.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Li, W.G.; Song, R.; Liu, C.C. Comparative Evaluation of Land Surface Temperature Images from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Satellite Observation for Agricultural Areas Using In Situ Data. Agriculture 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavanne, X.; Frangi, J.-P. A Sensor to Monitor Soil Moisture, Salinity, and Temperature Profiles for Wireless Networks. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2024, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehingia, B.; Lahkar, R.; Dey, B.; Kalita, H. Tunable Sensitivity in Graphene-Based Soil Moisture Sensors via Controlled Vapor Phase Reduction Method. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024, 8, 1502604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Khaparde, P.; Patle, K.S.; Bhaliya, C.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, M.V.; Palaparthy, V.S. Environmental and Soil Parameters for Germination of Leaf Spot Disease in the Groundnut Plant Using IoT-Enabled Sensor System. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2023, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, B.; Ali, N.; Dong, Y. Methods to correct temperature-induced changes of soil moisture sensors to improve accuracy. Methodsx 2025, 14, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Yu, D. Research on highly sensitive Fabry-Perot cavity sensing technology in frozen soil. Optoelectron. Lett. 2023, 19, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlbauer, L.K.K.; Zavattoni, G.; Virtanen, R.; Grube, M.; Weber, B.; Clark, A.T. Arduinos in the wild: A novel, low-cost sensor network for high-resolution microclimate monitoring in remote ecosystems. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2023, 4, e12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liopa-Tsakalidi, A.; Kalorizou, H.; Gana, V.; Thomopoulos, V.; Giannaros, A. Integrating sensor technology in organic table olive cultivation: A case study. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 11, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyono, S.; Telaumbanua, M.; Mulyani, Y.; Yulianti, T.; Amin, M.; Haryanto, A. Desain of soil temperature and Moisture Sensors for Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Cultivation Controlling System. Agritech 2018, 38, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, M.A.; Dhamu, V.N.; Paul, A.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Espial: Electrochemical Soil pH Sensor for In Situ Real-Time Monitoring. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamilla, S.; Zahid Yousuf, S.; Mohan Avulapati, M.; Ahmad-Al-Mallahi, N.V.L.; Narasimha Murty, N.V.L. A Low-Cost, Reusable All-Solid-State TiN-Based EGFET Soil pH Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 4184–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merl, T.; Rasmussen, M.R.; Koch, L.R.; Sondergaard, J.V.; Bust, F.F.; Koren, K. Measuring soil pH at in situ like conditions using optical pH sensors (pH-optodes). SOIL Biol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; Akshaya, A.V.; Joseph, J. An In-Situ Soil pH Sensor With Solid Electrodes. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2022, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, K.; Kan, T.; Onoe, H. Entirely Biodegradable Wireless pH Sensor with Split-Ring Resonators for Soil pH Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabak, A.; Uppuluri, K.; Franco, F.F.; Kumar, N.; Georgiev, V.P.; Gauchotte-Lindsay, C.; Smith, C.; Hogg, R.A.; Manjakkal, L. Sensor system for precision agriculture smart watering can. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, X.L.; Du, L.; Yang, L.P.; Jiao, Y.N.; Jiang, D.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, T.L.; Gao, X.B. Heavy metals in meat products from Shandong, China and risk assessment. Food Addit. Contam. Part B-Surveill. 2024, 17, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Wei, J.T.; Chiu, H.Y. Analysis of veterinary drug residue monitoring results for commercial livestock products in Taiwan between 2011 and 2015. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiuk, M.; Zakhodym, M.; Borkovska, V.; Balla, I. The Monitoring of the Livestock Product Market for the Formation of Food Security. Econ. Ecol. Socium 2023, 7, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, P.; Trymers, M.; Chajecka-Wierzchowska, W.; Tkacz, K.; Zadernowska, A.; Modzelewska-Kapitula, M. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Context of Animal Production and Meat Products in Poland-A Critical Review and Future Perspective. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Hu, Y.G.; Buttar, N.A.; Mahmood, A. X-ray computed tomography for quality inspection of agricultural products: A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.H.; Yu, P.P.; Huang, Y.R.; Zhang, G.; Lu, C.L.; Jiang, X.P. Application Status and Prospect of Impedance Spectroscopy in Agricultural Product Quality Detection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Suo, C.; Xiong, L. Impact of agricultural digital transformation on the quality of exported agricultural products. J. China Agric. Univ. 2025, 30, 274–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X. Detection Strategies for Volatile Fragrance Released from Agricultural Products: Progress and Prospects. Adv. Sens. Res. 2024, 3, 2400044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, F. Regional VOCs Gathering Situation Intelligent Sensing Method Based on Spatial-Temporal Feature Selection. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wang, F.; Liang, W.; Shi, G.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Liang, D.; Feng, Y.; Russell, A.G. Implications for ozone control by understanding the survivor bias in observed ozone-volatile organic compounds system. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Jin, Z.; Lu, S.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, K.; Xie, S. Emission factors and source profiles of volatile organic compounds from the automobile manufacturing industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xian, J.; Zhang, C. A Review on Metal Oxide Semiconductor-Based Chemo-Resistive Ethylene Sensors for Agricultural Applications. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).