Abstract
The simulation of human sensory functions is a key trend in the field of sensor development. In taste sensing, taste biosensors emulate taste perception using biorecognition elements that participate in taste transduction, such as taste receptors, cells, tissues, etc. This approach obtains high selectivity and a wide detection range of human taste perception, making taste biosensors widely used in food analysis and taste perception studies. By combining biorecognition elements with suitable data processing and analysis techniques, the taste information generated during the process of taste transduction, obtained by the sensing elements of the sensor, can be accurately captured. In this paper, we explore current available solutions to stability and sensitivity, and other challenges in taste biosensors using taste receptors, cells, and tissues as sensing elements. We also outline the applied signal processing techniques based on the signal characteristics from different types of taste biosensors. Finally, it is proposed that the development of taste biosensing sensors will further promote the application of intelligent sensory evaluation and human perception analysis systems in food, medicine, and other fields.
1. Introduction
Taste sensors, which detect taste substances, can be classified based on their sensing elements into categories such as the lipid/polymer membranes-based taste sensor, enzymes-based taste sensor, receptors-based taste sensor, cells-based taste sensor, buds-based taste sensor, metalloporphyrins-based sensor, ion-sensitive electrodes-based taste sensor, and others [1,2,3,4]. These sensors are widely used in food analysis and taste perception studies due to their response to relevant taste substances and their correlation status with human perception data. Among them, taste biosensors using biorecognition elements such as taste receptors, taste cells, taste bud tissues, and others as sensitive materials form a particular class of all taste sensors [5,6,7]. This unique class of taste biosensors is characterized by their high selectivity for taste substances, and signal states similar to real perception.
By common definition, taste biosensors are instruments consisting of one or more biosensors that mimic the perception mechanism of the mammalian gustatory system. They use the specific interaction between the biorecognition elements and the taste substances to obtain measurable and relevant taste information [8,9]. This information is typically in the form of electrical or optical signals converted by transducers, which contain information about the quality, intensity, and duration of the taste substances. These signals can be effectively interpreted after a series of signal processing steps, such as feature extraction, qualitative/quantitative analysis, etc. [10,11]. The target substances detected by taste biosensors include inorganic ions, organic acids, sugars and polysaccharides, amino acids and peptides, glycosides, and alkaloids [12]. The differences between these substances are expressed perceptively in the five basic tastes: umami (e.g., inosine-5′-monphosphate(IMP), monosodium L-glutamate(MSG)), bitter (e.g., quinine, denatonium), sweet (e.g., sucrose, saccharin), salty (e.g., potassium chloride (KCl), sodium chloride(NaCl)), and sour (e.g., acetic acid, vinegar). Among these, the perception of umami, sweet, and bitter tastes is mediated by G-protein coupled receptors, while ion channel-type receptors mediate sour and salty flavors [13]. The inherent specificity of biorecognition elements for these taste substances makes taste biosensors an excellent detection tool.
Research on the application of biorecognition elements in taste biosensors began in the late 20th century, a period marked by the discovery of numerous taste receptor types [14]. Research on taste and olfaction perception mechanisms provides a solid biological foundation for subsequent sensor development [15,16,17]. As biological science advanced, the application of biorecognition elements, such as taste receptors, cells, and tissues, has become widespread [18,19,20,21]. Advances in technologies such as micro/nanomaterials, genetic engineering, and cellular engineering are driving the development of new ways to apply biorecognition elements, including the customization, functionalization, and integration of biological substances. The processing of sensing signals has also evolved gradually with the development of neural pathways, multivariate data analysis techniques, and artificial neural networks. This evolution has shifted from simple statistical methods or empirical models for signal parsing to multimodal fusion and parsing at the level of neural transduction. Figure 1 is a brief summary of the content of this paper.
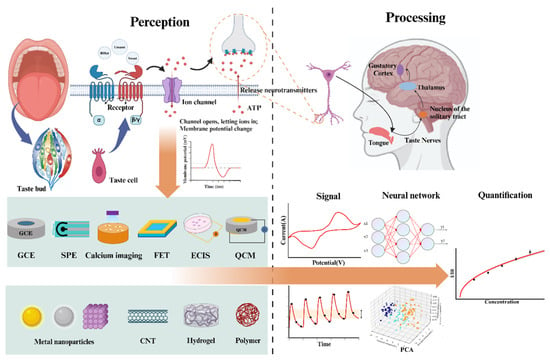
Figure 1.
Summary of biosensory technology.
On the one hand, the construction of the sensors mimics the signal acquisition state of the mammalian gustatory system (MGS). This type of research focuses on using sensing platforms, novel materials, and other technology to better acquire and amplify signals from specific biorecognition elements [22,23,24,25,26]. It improves the sensor’s sensitivity, specificity, and stability, expanding its potential application capabilities. On the other hand, the analysis and processing of sensor signals mimics the brain signal processing pathways. Signal processing technology can help identify and interpret complex signal patterns, overcoming issues such as noise and signal drift. This enhances the sensor detection accuracy and stability, making them more applicable in real-world detection scenarios [27,28].
This review describes the current state of research on bio-taste sensing in terms of both simulation of taste transduction and signal analysis. Firstly, the principles and performance of taste biosensors applying these biorecognition elements are analyzed, according to the different taste transduction stages in which they are involved. Then, based on the characteristics of the output signals of various types of sensors, the processes and techniques for analyzing these signals are presented. Finally, the challenges and future trends of biorecognition elements and signal-processing techniques are discussed.
2. Biorecognition Elements Based Taste-Biosensors
In taste sensing, research on biorecognition elements has received significant attention due to their crucial role as sensing elements in taste biosensors. This review defines the biorecognition element as bioactive substances with taste functionality that include or partially include taste transduction mechanisms [9,29,30,31]. This includes taste receptors, cells, buds, and epithelial tissues [32]. Specific taste perception involves the taste buds in the epithelial tissue of the tongue, which contain a variety of taste cells. These cells are classified into different types according to their functions and morphologies, such as type I (dark cells), type II (light cells), type III (intermediate cells), and type IV (basal cells) [33,34,35]. Taste receptors on cell membranes are a class of large transmembrane proteins, including the transmembrane heptahelical domain, the Venus Flytrap module (the ligand-binding locus), and the carboxy-terminal tail [36,37]. When these receptors interact with taste substances, they trigger an intracellular signaling cascade, causing the cell to release neurotransmitters. After interactions between multiple cells in the taste buds, the transmitters stimulate the gustatory neural pathway, transmitting taste information to the cerebral cortex, where taste perception is produced [38]. As a result, based on the biorecognition elements involved in different taste transduction stages, taste biosensors employing these elements can be classified into the following three categories: receptor-based taste biosensors, cell-based taste biosensors, and tissues-based or MGS-based taste biosensors [39].
2.1. Receptor-Based Taste Biosensors
Receptor-based taste biosensors respond quickly to taste stimuli and exhibit stability under suitable conditions [40]. These sensors are generally constructed using bitter taste receptors, sweet taste receptors, and umami taste receptors expressed by mammals or insects as sensing elements, combined with sensing platforms such as field-effect transistors (FETs), quartz crystal microbalances (QCMs), and glassy carbon electrodes (GCEs), which convert the binding events of the analyte and the receptor into an analyzable signal output. This construction strategy of using taste receptors as sensing elements allows these sensors to specifically detect taste substances, eliminating the interference from multiple receptor expressions or cellular metabolism that occurs when using tissues or cells to prepare taste sensors [6,41].
Table 1 summarizes the recent developments in taste sensors based on taste receptors. The data from Table 1 demonstrates that advances in receptor-based taste biosensors have primarily focused on the design of sensor structures, utilization of novel materials, and modification of receptor proteins. The receptor-based taste biosensor has been effectively improved in sensitivity, stability, and other properties. Various optical and electrical transduction methods play pivotal roles in this process. For example, field-effect transistors (FETs) serve as transducers, and the FET-based biosensors are adept at detecting neutral or charged substances [42]. When combined with nanomaterials, they further enhance the sensitivity of detection devices. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) biosensors, known for their label-free detection capability, offer benefits such as quick response and user-friendly operation, excelling particularly in the detection of low concentrations [43]. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is an optical sensing technique widely used in biosensing and gas detection. The binding of receptors to a ligand on the metal film surface causes a change in the refractive index of the metal film [44,45]. By measuring these changes in surface refractive index, molecular interactions can be detected in real-time with high sensitivity.

Table 1.
Taste biosensors-based receptor.
Taste receptors are key components in taste perception, and their binding to taste substances involves complex interactions with multiple metabolites and ion channels [53,54,55]. In plain words, various types of taste transduction. For example, when a taste substance binds to T1Rs or T2Rs receptors, it activates heterotrimeric G proteins, releasing the Gβγ subunit, which subsequently stimulates phospholipase cβ2. This activation ultimately results in the production of intracellular messengers, triggering the gating of the taste transduction channel [18].
In the above transduction pathways, the binding of taste receptors to taste substances serves as the starting point of taste transduction and is a highly specific and dynamic process. The reactions induced by this binding, such as the binding or breaking of ionic bonds and receptor conformational changes, produce subtle electrical or chemical signals. Therefore, sensors with high sensitivity are required to detect these signals accurately [56,57,58]. To address this issue, common approaches are using high specific surface area nanomaterials such as graphene, nanowires, or single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), applying nanochannel-type sensing structures, and using highly conductive sensing platforms such as field-effect tubes (FETs). These methods can detect weak changes in electrical currents and amplify the signals generated by receptor–ligand binding [59]. SWCNT has a high specific surface area, providing a larger effective reaction interface and improving the efficiency of intermolecular reactions. Additionally, the electron-permeable network formed by carbon nanotubes facilitates electron transport, effectively amplifying the electrical signals generated by receptor-taste substance binding, thereby enhancing the sensor’s sensitivity [60,61]. Considering the biocompatibility of biomaterials and the binding issues with the electrode surface when applying SWCNTs, chitosan-carbon nanotube composites are an ideal choice. In this nanocomplex, the noncovalent complexation of chitosan (CS) with SWCNTs resulted in a well-dispersed state of SWCNTs in the matrix, constructing an ideal conductive network [62,63]. Additionally, CS itself has excellent film-forming properties and abundant surface functional groups, enabling effective immobilization with electrodes and providing covalent binding sites for biorecognition elements [64]. Figure 2a shows the construction of an electrochemical umami sensor by combining T1R1-VFT, SWCNTs, and PB on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). The higher reactive interface of the SWCNTs increases the binding efficiency of T1R1 to the taste substances, while the co-electrodeposition of Prussian blue (PB) and the combination of T1R1-VFT with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) further enhance the signal amplification [50]. Finally, the differential pulse method is used to detect four representative umami substances with high specificity and sensitivity.
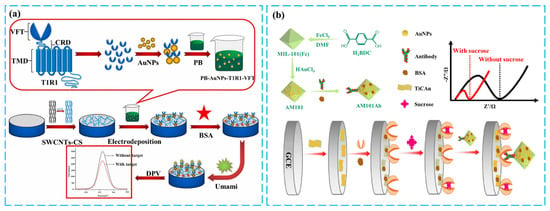
Figure 2.
Illustration of various solutions for enhancing the sensitivity of receptors-based taste biosensors: (a) Production of SWCNTs-CS/PB/AuNPs/T1R1-VFT/GCE sensor and fresh flavor detection. Reproduced with permission from [50]. Copyright 2021 Elsevier. (b) Production of electrochemical sweet taste sensor based on T1R2-VFT and immune amplification with nanomaterial carriers. Reproduced with permission [59]. Copyright 2024 Elsevier.
Another notable technique to improve sensor sensitivity was proposed by Jing Ye’s team, which utilizes immune competition to amplify the signal at the binding level of the receptor to the taste substance. The spatial hindrance and negative charge of the AM101Ab antibody cause repulsion of the electrochemical indicator, resulting in an increase in impedance. Conversely, the competitive interaction between the sweet substance and the antibody reduces the binding of the receptor and antibody, thereby decreasing the impedance value. Thus, the strong binding signal of protein and protein is correlated with the binding event between taste substances and receptors, achieving highly sensitive sweetness detection. The detection of sweetness with a low detection limit of 5.1 pM is achieved [59]. The preparation of this sensor is shown in Figure 2b. The EIS technique used in this study is widely employed in biosensing. It involves measuring the change in impedance of the system at different frequencies of AC voltage and building equivalent circuits related to electrode/electrolyte interface and redox reaction processes. This technique allows for analyzing interface reaction processes associated with biomolecular recognition events and surface modifications on the electrode.
In addition to improving sensor sensitivity, realizing the effective binding of receptors to the sensing platform to obtain the desired signal is also a current challenge. The integration of taste receptors generally involves purifying and immobilizing them on secondary transducers, such as FETs and QCM. However, some receptors’ complex structures and properties make them difficult to prepare and immobilize effectively with the transducers. For example, the typical transmembrane structural domains of bitter taste receptors TAS2Rs show that they are members of the GPCR families with complex peptide chain structures and are hydrophobic. This results in the heterologous overexpression and purification of bitter taste receptors exhibiting low efficiency [65,66]. Figure 3a illustrates a solution to this problem by using a cell-free protein expression system to express the bitter taste receptor directly. The cell-free protein expression system’s high-precision synthesis of proteins and reconstruction in a hydrophobic environment enables the purification and functional expression of bitter taste receptors for sensing functions [6,67]. Customization of the receptor can insert a His6-tag at the C-terminus of the bitter receptor molecule, which binds to an anti-His6 aptamer on the surface of the QCM. This not only effectively immobilizes the receptor but also allows for the efficient removal of irrelevant proteins by using detergents. The QCM can convert the mass change resulting from the interaction of the functional layer with bitter substances into a change in crystal resonant frequency, thereby enabling the detection of representative bitter substances such as quinine.
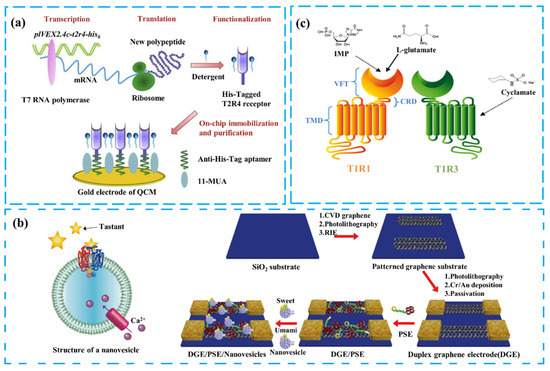
Figure 3.
Illustration of various solutions to the integration challenges of taste receptors with sensing platforms: (a) Schematic of a chip synthesizing and purifying bitter receptors using a cell-free expression system. Reproduced with permission [6]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier. (b) Combination of nanovesicles and a graphene sensing platform. Reproduced with permission [68]. Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society. (c) Schematic of the umami ligand-binding domain (VFT). Reproduced with permission [69]. Copyright 2018 Elsevier.
In addition to bitter taste receptors, applying taste receptors, such as T1R1/T1R3 and T1R2/T1R3 heterodimers as sensing elements for taste detection, is also part of the research in bio-taste sensing. The traditional solution is to bind cytochalasin B-induced nanovesicles to the sensing platform, after expressing the receptor in a heterologous cell system. The nanovesicles are secreted from the cells and encapsulate the taste receptor in a bilayer lipid membrane, maintaining the essential active state of the taste receptor [70]. In the study shown in Figure 3b, the researchers combined nanovesicles containing sweet receptors T1R2/T1R3 with those containing umami receptors T1R1/T1R3 on G-FETs [68], creating a dual-channel taste sensor for umami and sweet flavors. The sensor’s sensing performance was analyzed, and it was discovered that the sweet substance cyclamate (CYC) enhances the response of the umami channel [71]. The nanovesicles provided a conducive environment for the receptors, shielding them from external factors and improving sensor stability. When the receptors on the nanovesicles are activated, the ion channels on the cell membrane are opened, which causes a change in the Ga2+ concentration. This change affects the charge carrier density of the semiconductor channel material, which changes the conductance and measured current of the device [72]. However, the complex structure and large size of this type of taste receptor led to its low efficiency of heterologous expression and difficulty in binding to the sensing platform [51,52]. Nanovesicles have limitations, such as the complex preparation process and difficulties in measuring time signals due to the lack of ion pumps to maintain ion concentration [42].
To address these issues, researchers have attempted to modify the sensitive materials to reduce structural complexity. Figure 3c shows the overall structure of the T1R1/T1R3 heterodimer receptor. The VFT domain, responsible for recognizing taste substances [36], can achieve functional expression in a heterologous cell system [73]. Compared to the heterodimer, the VFT domain has a simpler structure, while retaining good selectivity and sensitivity to taste substances. The VFT can be immobilized on the sensing platform surface using a chemically stable peptide bond formed by the reaction of an amine residue in the VFT protein with a carboxyl group on the modifying substance [69]. Figure 4a presents the construction of a biomimetic nanochannel system based on the T1R1-VFT domain of the human umami receptor. The T1R1-VFT was immobilized on the inner wall of the nanochannel using an amidation reaction between amine residues in T1R1-VFT and abundant carboxylate groups in the PET membrane. Synthetic nanopores have electrochemical properties similar to biological channels. Conformational changes from the binding of VFTs to taste substances produce charge changes that alter the electric field within the nanopore, increasing ionic flux through the nanochannels. This sensor has high sensitivity, specificity, and stability, and can effectively measure electrical signal changes to detect four representative umami substances [46]. Jin Young’s team constructed a sweetness sensor using T1R2 VFT, the ligand-binding domain of the sweetness receptor, as the sensing element. This sensor was combined with a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNTFET) as the transducer. The reversible binding of the T1R2-VFT to the sweet substance allows the sensor to be used repeatedly for detection [26].
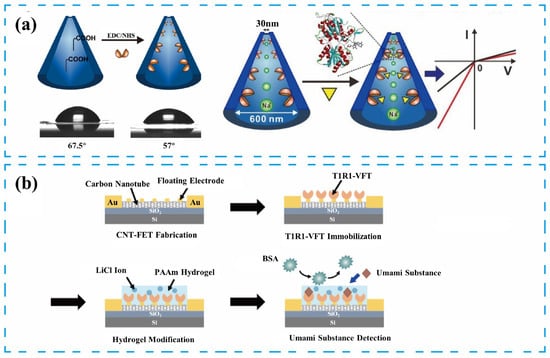
Figure 4.
Illustration of various solutions for enhancing the stability of receptors-based taste biosensors: (a) Preparation of the umami sensor based on the nanochannel structure and T1R1-VFT/AuNPs sensing elements. Reproduced with permission [46]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier. (b) Preparation of the umami sensor using PAAm conductive hydrogel membranes and T1R1-VFT/AuNPs sensing elements. Reproduced with permission [25]. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society.
Considering the preservation of the overall function of the taste receptor and avoiding the complex structure that causes difficulty in functional expression, mimicking insect taste may be another potential solution [74]. Yoonji Choi’s team proposed the application of the honeybee’s sweetness receptor, AmGr1, as the sensing element to achieve sweet taste detection [48]. This biorecognition element’s monomer or mono-dimer form enabled its functional expression in a heterologous cellular system. Notably, AmGR1 achieves the distinction between natural and artificial sweeteners. The possible reason is that receptor-ligand interactions and allosteric coupling determine recognition specificity [75]. Distinctions between receptor functions due to natural selection may provide a basis for developing additional biorecognition components.
In recent years, receptor-based taste biosensors’ stability and reproducibility have been effectively improved, primarily due to the development of novel materials and the enhancement of biorecognition elements. Specifically, biorecognition elements of the receptor flytrap structural domain type and the introduction of novel materials such as hydrogels and Prussian blue have played significant roles in this process [26,76,77,78]. Notably, novel materials like hydrogels exhibit excellent biocompatibility and adjustable pore structures, enable effective immobilization of biorecognition elements, and provide a favorable environment for biomaterials to maintain their activity [79]. Additionally, the adjustable porosity of the hydrogel’s three-dimensional scaffold structure allows for the controlled diffusion and reaction of macromolecules, thereby improving sensor stability [80]. In Figure 4b, the sensor adsorbs a polyacrylamide conducting hydrogel film onto its surface, which excludes interfering factors present in actual samples while inhibiting the non-specific adsorption of non-target molecules on the sensor surface, maintaining the stability of the receptor protein structure [40,81]. The signal of the sensor changed by only 5% over a storage time of up to 4 weeks. This sensor can achieve detection sensitivity as low as 1fM and has a detection range of 10−15~10−2 M for monosodium glutamate (MSG) and disodium inosinate (IMP), reaching the threshold value for human umami recognition [25,40].
2.2. Cell-Based Taste Biosensors
The construction of cell-based taste biosensors typically involves using cells that are either endogenous cells or heterologous cells as sensing elements [37]. These cells are immobilized on sensing platforms that have been modified with biological or chemical materials, such as microelectrode arrays (MEAs), light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPSs), glassy-carbon electrode (GCE), and electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) [82]. When cells are stimulated by taste substances, they undergo a series of intracellular cascade reactions, resulting in changes in electrochemical signals. These changes can be captured by the sensing platform and converted into effective signal outputs. Table 2 summarizes recent advancements in cell-based taste sensors.

Table 2.
Taste biosensors-based cell.
In cell-based taste sensing research, the detection of taste substances is often achieved by monitoring changes in membrane potential, transmitter release, and other information generated by cells during normal taste transduction. This information reflects, in part, the strategies of taste encoding at the cellular level and provides a basis for studying intracellular cascade reactions [91]. The mechanism behind changes in membrane potential involves the activation of taste receptors, leading to calcium ion signaling, which subsequently opens ion channels in the cell membrane. This results in membrane depolarization and the formation of an action potential, followed by the release of ATP [92]. Figure 5a illustrates a taste sensor constructed using mouse taste cells as sensing elements. A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) is used as the working electrode to detect the membrane potential changes of taste cells stimulated by MSG. The GCE, modified with Poly-L-lysine (PLL) and gold nanoparticles, exhibits excellent biocompatibility, sensitivity, and chemical stability. After effectively immobilizing taste cells, this sensor demonstrates high sensitivity and rapid response to MSG [83]. Another approach involves detecting both membrane potential changes and ATP release. Light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS) are extremely sensitive to changes in surface potential and can measure external potential changes in taste cells on a silicon chip. When using electrodes functionalized with ATP-sensitive DNA aptamers, ATP release detection can be achieved by recording the shift of the bias-photocurrent curve in discrete mode [84], as shown in Figure 5b. The results of testing with bitter substances indicate that cell-based taste sensors can effectively detect taste substances and observe parts of the taste signal transduction process.
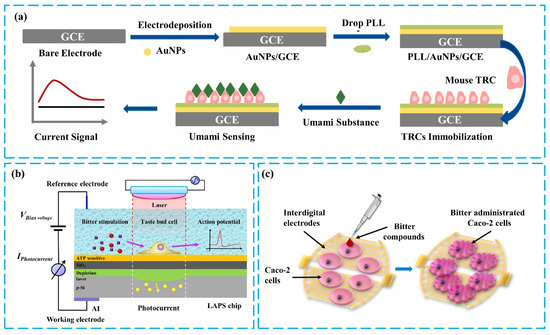
Figure 5.
(a) Fabrication of umami sensors based on GCE/TRs. Reproduced with permission [83]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (b) Mechanism of detecting bitter stimuli in single taste bud cells using LAPS. Reproduced with permission [84]. Copyright 2018 Elsevier. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (c) Detection of bitterness based on membrane potential and shrinkage signals of Caco-2 cells. Reproduced with permission [93]. Copyright 2019 Elsevier.
Remarkably, due to the widespread expression of some taste receptors and advancements in cell transfection technology, certain non-taste cells can also be used for the detection of taste substances. This is achieved by recording the electrical signals of gustatory stimuli through the sensing platform for the detection of taste substances [94,95]. Because these sensors utilize cells with single receptor expression, they can achieve highly specific recognition of taste substances. Thus, taste biosensors have been constructed by using non-taste cells, such as rat cardiomyocytes, human embryonic kidney cells (HEK-293), male mouse germ cells, and human intestinal cells (Caco-2), as sensing elements [85,90,94,96]. The Chunlian Qin team constructed a bitter taste sensor using Caco-2 cells that endogenously express the T2R38 receptor. ECIS was used to detect the cellular morphological changes induced by receptor activation [93], enabling the quantitative evaluation of bitter substances such as phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) and propylthiouracil (PROP). This research combined information on impedance changes caused by cellular morphology alterations and changes in fluorescence intensity from calcium imaging due to increased Ca2+ during taste transduction. By integrating multiple data, the identification of bitter substances and the screening of T2R38 agonists were achieved, as shown in Figure 5c.
From the research described above, which uses changes in cell morphology to identify taste substances, it can be inferred that more methods for detecting taste-related information have been developed. In addition to detecting signals in the taste transduction process, the responses of cells stimulated by taste substances, such as mechanical beating, acidification, and morphological changes, have also been used to identify or assist in identifying taste substances, providing new ideas for cell-based bio-taste sensing research [97]. The study in Figure 6a developed a method for detecting different types of bitter compounds. This method uses Caco-2 cells expressing the T2R38 receptor and SH-SY5Y cells expressing the T2R16 receptor as biorecognition elements [85]. Upon activation by their respective ligands, T2Rs increase intracellular Ca2+ levels through the typical inositol triphosphate/diacylglycerol (IP3/DAG) pathway, leading to the release of neurotransmitters and subsequent morphological changes in the cells, such as cell shrinkage. Since the ligands for T2R38 and T2R16 are different, the impedance changes of mixtures of Caco-2 and SH-SY5Y cells in response to various bitter compounds can be detected, using ECIS technology, allowing for the differentiation of ligands for different bitter taste receptors. Another mechanism is the inhibitory effect of bitter substances on the mechanical beating(MB) of mouse cardiomyocytes. Based on this, the study in Figure 6b used rat cardiomyocytes expressing bitter taste receptors as the main sensing element and recorded extracellular field potential (EFP) and mechanical beating (MB) changes in cardiomyocytes, after the binding of taste substances to the receptors [98]. By correlating these signals with the parameters of the bitter taste substance and monitoring different signal patterns, bitter substances can be identified [87,88]. Metabolic perturbations caused by the stimulation of cells by taste substances serve as a mechanism that can be used to indirectly detect the interaction of bitter compounds with the receptor. Activation of the bitter taste receptor hT2R4 expressed in Escherichia coli induces changes in cellular metabolism, altering the rate of extracellular acidification (solution pH) caused by its production of acid. Detection of changes in the pH of the cell suspension can be achieved by Capacitance-voltage (C-V) or detection of potential changes at constant capacitance [86]. Then, the measurement of bitter substances is achieved. It is necessary to propose that either a change in solution pH or a conformation change, resulting from the activation of the recognition element, results in a change in capacitance, which is caused by a change in the surface charge of the electrode.
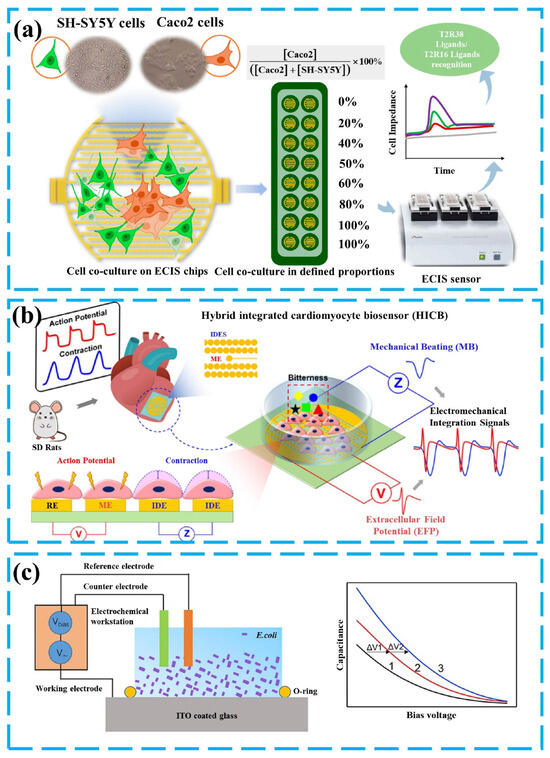
Figure 6.
(a) Preparation of the bitterness sensor based on HEK-293 cells and human Caco-2 cells. Reprinted from Ref [85]. (b) Detection of bitter substances based on mechanical beating (MB) and extracellular field potential (EFP). Reproduced with permission [98]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (c) Schematic diagram of electrochemical bitterness sensing based on Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) electrode and Escherichia coli cells. Reproduced with permission [86]. Copyright 2019 Elsevier.
2.3. Tissue-Based and MGS-Based Taste Biosensors
Taste sensors using taste bud tissue and MGS as sensing elements can respond to a variety of taste stimuli in real-time, and the sensor detection process is similar to the taste perception process. These sensors have high biocompatibility, and the application of the taste transduction mechanism involved in taste buds or MGS is generally done by directly obtaining the response of biorecognition elements to taste stimuli through transducers or electrodes. The molecular mechanism that results in this response is not clear. Sensor construction is mostly aimed at the study of taste perception mechanisms. Table 3 summarizes recent research in tissue-based and MGS-based taste sensors.

Table 3.
Taste biosensors based on taste buds and MGS.
Taste buds are distributed in large numbers on the tongue and have different shapes depending on their location, including fungiform papillae, circumvallate papillae, and foliate taste papillae [105]. Taste buds are connected to neurons, and after a series of signal transduction in taste cells, the activation of receptors produces an electrochemical signal [106,107,108], which is transmitted through the interaction of cells within the taste buds to form the output of the taste bud tissue. GCE, MEA, and other sensing platforms can convert this output into an analyzable electrical signal, which more accurately represents the response of real taste perception to taste [109]. At the same time, the 50 to 150 elongated cells contained in the taste buds and the different taste receptors they express provide the basis for studying the mechanism of taste perception [110]. These include the kinetic study of taste receptors and the antagonistic or synergistic action study between different taste substances, among others [89,101]. The research in Figure 7a isolated different taste receptor regions from the tongue. A three-electrode system was constructed using pig taste bud tissue as the sensing element. The chronoamperometry method was employed to measure the response of various regions of pig tongue epithelium to MSG and IMP and to investigate the synergistic effects between umami substances [99]. Chunlian Qin et al. constructed a taste biosensor that combines mouse taste epithelium and MEA. Based on the encoded information obtained from taste buds after taste stimulation, it quantitatively analyzed the interaction between sour and sweet tastes and explored the taste perception process of sour and sweet tastes in taste bud tissues [102,111]. During signal acquisition, the advantages of the MEA sensing platform, such as high-throughput transmembrane electrical recording and high temporal resolution, enable the effective acquisition of action potentials of cells, as shown in Figure 5b [112,113].
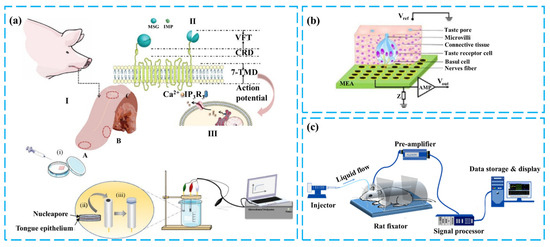
Figure 7.
(a) Construction of the three-layered pig taste bud sensory function layer and umami detection. Reproduced with permission [99]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier. (b) Salty taste sensor based on mouse taste buds and MEA. Reproduced with permission [112]. Copyright 2013 Elsevier. (c) Schematic of detection based on the overall gustatory system of mice. Reproduced with permission [103]. Copyright 2019 IEEE.
For biorecognition elements such as the MGS, which include the complete taste transduction process, measuring its signal can capture the whole perception state of taste stimulation [104]. As a result, the taste sensing system based on a brain–computer interface (BCI) and MGS can obtain the ability of mammals to perceive taste substances, achieving rapid, high-sensitivity, and wide-range detection. Figure 7c illustrates a method for detecting gustatory cortex (GC) neuron responses, using an invasive brain–computer interface. The taste perception system of mice is utilized as the sensing element of a taste biosensor. This system identifies and classifies sweet substances by decoding the brain’s electrical signal response patterns induced by the sweet taste perceived by the mouse [103]. This type of sensor exhibits a short response time, quick recovery, and rapid detection.
3. Analysis of Signals from Taste Biosensors
In taste biosensors, the binding event between the sensing element and taste substances triggers a series of taste transduction processes. The resulting changes can be captured by detection technologies and converted into analyzable signals. These signals vary in form depending on the detection method employed, such as amperometry, voltammetry, potentiometry, or calcium ion imaging. Signal processing techniques play a crucial role in translating complex or ambiguous sensor data into easily interpretable information [114]. This section discusses the analysis of signals obtained from taste biosensors, focusing on two distinct types of signals.
3.1. Low-Dimensional Signal from Taste Sensors Using Taste Receptors and Cells
The first type of taste sensor uses taste receptors and cells as sensing elements. The detection mechanism for taste sensors that use taste receptors and cells involves the binding of the receptor to the taste substance, which causes an accumulation of electrical charge or a change in the ion concentration of the cell. This affects the potential, conductivity, or fluorescence intensity of the transducer, enabling effective detection of the signal change [26,69]. This detection mechanism is characterized by the simplicity of the signal state, minimal noise, and the feasibility of establishing response curves for different target substance concentrations through simple univariate calibration. However, variations between different biorecognition elements and transducer devices can result in differing current changes during detection. To address this issue, signal normalization is often the first step in signal processing. The ratio of the change in response to the initial response level better represents the sensor’s response value. This includes ∆I/I0, ∆F/F0, ∆G/G0, etc., which eliminate changes under different experimental conditions. Another type of parameter, normalized sensitivity (∆I/Imax), indicates the sensor or detection system’s ability to respond to stimulus changes, with higher values representing greater sensitivity. This feature was used to analyze the dose-dependent response of a duplex bioelectronic tongue (DBT) to commercially available artificial flavorings and its ability to perceive different sweet substances, showing lower threshold concentrations and a wider detection range [68].
3.2. High-Dimensional Signal from Taste Sensors Using Taste Epithelium or MGS
The second type of taste sensor uses taste epithelium or MGS as the sensitive material. After the taste cells are stimulated by the taste substance, the membrane potential changes and neurotransmitters are released, forming a response encoded by the retained taste transduction process. This response can be detected by sensors such as microelectrode arrays (MEAs) or brain–computer interfaces (BCI). These sensors have high sensitivity and can detect small changes in electrical signals. Multi-channel data acquisition allows signals to have high spatial and temporal resolution, including the response of the recognition element to the taste substance and the noise generated by cellular metabolic activity [115].
The characteristics of these signals necessitate advanced analysis beyond simple regression methods. Feature extraction is crucial, followed by employing signal processing techniques for effective interpretation. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a qualitative technique converting high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional format, facilitating the discovery of primary patterns and structures within the data [116]. The Xinwei Wei team utilized MEA to measure heart muscle responses to bitter and umami stimuli, identifying key spike signal features, such as initial potential, primary peak, valley point, and secondary peak [88]. By combining these features of the signal in both time and frequency domains [117], PCA enabled clustering analysis of different bitter substances. Importantly, due to similarities with EEG signals, these approaches suggest potential applications for additional techniques like wavelet transformations [118], spike template matching [111,119], and deep learning [120]. Research by Zhen Qin’s team explored correlations between local field potential (LFP) oscillations in different frequency bands and concentration levels. They found that for low-gamma oscillations, post-stimulation power spectral densities (PSDs) exhibited a linear relationship with denatonium benzoate (Dena) concentration, demonstrating stable and sensitive performance down to at least 0.076μM of bitter substances [104]. Wavelet transformation further aids in separating signals across different frequency bands.
Beyond these techniques, signal processing methods offer insights for sensor data analysis. For instance, taste nerve pathways leverage computational models based on taste nerve conduction mechanisms to enhance sensing signals by transforming them into spike signals akin to EEG patterns [121,122,123]. Mathematical modeling then facilitates detailed analysis. Research results show that this computational model can be effectively applied to analyze e-tongue data and achieve classification [124], with detection rates of 96.0% and 96.7% in beer and tea identification [125]. Cloud models represent another approach, where taste sensors provide quantitative or qualitative detection results for food but lack the intuitive expression of taste information as in human subjective evaluation. These models utilize sensor data to construct human-like fuzzy evaluation models, using membership cloud concepts and feature matrices to convert quantitative descriptions into understandable evaluation language [126].
These advancements underscore the interdisciplinary nature of taste sensor research, combining biorecognition elements with sophisticated signal processing techniques to enhance sensor performance and expand applications in food detection and beyond. It is foreseeable that Artificial Intelligence will have a good combination with taste biosensing in the signal processing part of taste biosensing. On the one hand, the research on Artificial Intelligence for processing small sample data coincides with the state of data acquisition by taste biosensing sensor detection. On the other hand, there is still scope for progress in the stability of the sensor response signal and the acquisition of complex information in multi-taste, in which Artificial Intelligence can play a good role in assisting.
4. Conclusions and Prospect
In conclusion, the application and design of various biorecognition elements have not only enhanced the performance of taste biosensors in detecting taste substances but also made them an effective tool for studying the gustatory encoding mechanism of various biorecognition elements. Sensing elements with taste transduction mechanisms enables such sensors to have an objective, standardized evaluation output for taste substances. Comparing various biorecognition elements, taste biosensors based on taste receptors can specifically recognize various taste substances, and combining various novel materials further improves this ability. Multi-sensor arrays and similar sensor construction strategies can help achieve recognition of multiple taste substances. Cell-based taste biosensors can detect a variety of taste substances and explore the response mechanisms of more cells to taste stimuli. The difference between some heterologous expression taste receptor cells and the real perception state is still a problem that needs to be considered. Tissue-based taste biosensors capture signals that are close to biological taste perception, and effective signal processing techniques enable real-time responses of biorecognition elements to taste substances. The mechanism by which tissues and MGS transduce taste signals is still a black box. Such sensors can provide practical tools for exploring the mechanism of action of cells in taste buds, or the perception mechanism of the brain in the future, further improving the performance of taste biosensors. The analysis and processing of the signals from these sensors is currently limited to the interpretation of the data, such as normalization or clustering. To further improve the detection ability of the sensor for complex foods, the enhancement of data characteristics, multi-modal data fusion, and other technologies may be directions to consider in the future.
It is foreseeable that the design and application of biorecognition elements in bio-taste sensing research will continue. Further exploration of taste perception transduction will also help to exploit more biorecognition elements with taste functionality. However, there are still a number of challenges in enabling taste biosensors to truly move towards practical applications, which include the stability, reproducibility, and response speed of biomaterials in long-term detection. The application of composite nanomaterials, as well as hydrogel materials in bio-taste sensing, will hopefully improve the detection lifetime of biorecognition elements and achieve multiple reliable detections of taste biosensors. The development of biomaterials with more response mechanisms, as well as optical, electrochemical, and other detection modalities, will help improve the stability of biorecognition elements during long-term in vitro detection. The signal calibration, feature enhancement, and other processing techniques are expected to help dimensionally stabilize the response output of sensors under long-term operating conditions. When the simulation of human sensory perception becomes fully realized, it will provide a standardized evaluation system for the food industry. This advancement will enable better product optimization and offer precise simulations and assessments of drug taste characteristics for the pharmaceutical industry. As a result, it will significantly advance drug development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L., Z.W. and S.J.; investigation, J.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z., Y.C., S.L., Y.L. and L.Q.; supervision, J.L. and J.M.; funding acquisition, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [31871882].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [31871882].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hayashi, N.; Chen, R.; Ikezaki, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Maruyama, D.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ujihara, T.; Kohata, K. Techniques for universal evaluation of astringency of green tea infusion by the use of a taste sensor system. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2006, 70, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toko, K.; Tahara, Y.; Habara, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ikezaki, H. Taste Sensor. In Essentials of Machine Olfaction and Taste, 4th ed.; Nakamoto, T., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 87–174. ISBN 9781118768495. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Toko, K. Taste sensor: Electronic tongue with lipid membranes. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toko, K.; Akiyama, H.; Chishaki, K.; Ezaki, S.; Iyota, T.; Yamafuji, K. Detection of taste substances using impedance change in lipid/polymer membranes. Sens. Mater. 1997, 9, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, M.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Huang, Z.; Yin, L.; Gao, L. A cell-based electrochemical taste sensor for detection of Hydroxy-α-sanshool. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Chen, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, P.; Wu, C.; Wang, P. A biomimetic taste biosensor based on bitter receptors synthesized and purified on chip from a cell-free expression system. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 312, 127949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Jiao, L.; Pang, G.; Xie, J. A novel pungency biosensor prepared with fixing taste-bud tissue of rats. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to selecting a biorecognition element for biosensors. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.P.; Arulanandam, B.P.; Matta, L.L.; Weis, A.; Valdes, J.J. Biosensor recognition elements. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2008, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xia, X.; Shi, Y.; Men, H. CMTP-TCE: A Data Augmentation Method of Electronic Tongue Combined with Dot-Product Attention Mechanism and Residual Network for Food Quality Classification. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 21652–21660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S.D. Encoding Taste: From Receptors to Perception. In The Pharmacology of Taste; Palmer, R.K., Servant, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2022; pp. 53–90. ISBN 978-3-031-06450-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann, B. Receptors and transduction in taste. Nature 2001, 413, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouzet, S.M.; Busch, N.A.; Ohla, K. Taste quality decoding parallels taste sensations. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, S.D.; Chaudhari, N. Taste buds: Cells, signals and synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurot, C.; Brenet, S.; Buhot, A.; Barou, E.; Belloir, C.; Briand, L.; Hou, Y. Highly sensitive olfactory biosensors for the detection of volatile organic compounds by surface plasmon resonance imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzotto, F.; Khalife, M.; Hou, Y.; Chaix, C.; Lagarde, F.; Scaramozzino, N.; Vidic, J. Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors for food control. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herness, M.S.; Gilbertson, T.A. Cellular mechanisms of taste transduction. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 873–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Hoon, M.A.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nature 2006, 444, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, T.R.; Stone, L.M.; Margolskee, R.F.; Kinnamon, S.C. Immunocytochemical evidence for co-expression of Type III IP 3 receptor with signaling components of bitter taste transduction. BMC Neurosci. 2001, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Matsunami, H. Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels and taste sensation. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannilli, E.; Gudziol, V. Gustatory pathway in humans: A review of models of taste perception and their potential lateralization. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y. A novel umami electrochemical biosensor based on AuNPs@ ZIF-8/Ti3C2 MXene immobilized T1R1-VFT. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, U.K.; Jang, J.; Park, T.H. Human Taste Receptor-Functionalized Field Effect Transistor as a Human-Like Nanobioelectronic Tongue. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-K.; Park, S.-C.; Yu, J.-M.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-K. A bioinspired artificial gustatory neuron for a neuromorphic based electronic tongue. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 5244–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cha, Y.K.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.-E.; Wang, G.; Zhao, S.; Park, T.H.; Liu, Y.; Hong, S. Hydrogel-based Bioelectronic Tongue for the Evaluation of Umami Taste in Fermented Fish. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 2750–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-Y.; Cha, Y.K.; Ahn, S.R.; Shin, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, T.H.; Hong, S. Ultrasensitive bioelectronic tongue based on the Venus flytrap domain of a human sweet taste receptor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Valle, M. Electronic tongues employing electrochemical sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, R.-I.; Staden, J.F.v.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Electrochemical sensor arrays. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1999, 29, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ye, X.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tan, M.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, M.; Luo, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, X. Recent advancements in the taste transduction mechanism, identification, and characterization of taste components. Food Chem. 2023, 433, 137282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chale-Rush, A.; Burgess, J.R.; Mattes, R.D. Evidence for human orosensory (taste?) sensitivity to free fatty acids. Chem. Senses 2007, 32, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta Banik, D.; Medler, K.F. Taste Receptor Signaling. In The Pharmacology of Taste; Palmer, R.K., Servant, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2022; pp. 33–52. ISBN 978-3-031-06450-0. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, R.O.; Kare, M.R.; Cagan, R.H. Distribution of taste buds on fungiform and circumvallate papillae of bovine tongue. Anat. Rec. 1979, 195, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, E.; Hoon, M.A.; Mueller, K.L.; Chandrashekar, J.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell 2000, 100, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Murabe, N.; Mizuta, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Nagai, T. Bioelectrical signal associated with sweet taste transduction in humans is a hyperpolarizing potential on the lingual epithelium. Chem. Senses 2021, 46, bjab040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Staszewski, L.; Xu, H.; Durick, K.; Zoller, M.; Adler, E. Human receptors for sweet and umami taste. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4692–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pin, J.-P.; Galvez, T.; Prézeau, L. Evolution, structure, and activation mechanism of family 3/C G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Hu, P.; Jia, J.; Ni, J.; Jiang, T.; Yang, H.; Bai, J.; Tian, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, Q. Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for sensing sweetness. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 177, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikut-Ligaj, D.; Trzcielińska-Lorych, J. How taste works: Cells, receptors and gustatory perception. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2015, 20, 699–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.-k.; Zhang, H.-t. Function and structure of bradykinin receptor 2 for drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ahmed, S.; Sun, B.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chuang, W.-T.; Chan, Y.-H.; Gupta, D.; Wu, P.-W.; Lin, H.-C. Self-healable and anti-freezing ion conducting hydrogel-based artificial bioelectronic tongue sensing toward astringent and bitter tastes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 198, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Park, T.; Ahn, B.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.; hun Lee, J.; Oh, U.; Jang, Y. Rapid quantitative analysis of tobacco smoking in saliva using a TRPA1 ion channel-mediated bioelectronic tongue inspired by the human sensory system. Sens. Actuators B 2023, 393, 134149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.; Cha, Y.K.; Kim, S.-o.; Cho, S.; Ko, H.J.; Park, T.H. FET-based nanobiosensors for the detection of smell and taste. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, construction, and biosensing applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, M.; Farre, C.; Lagarde, F.; Mathey, R.; Buhot, A.; Vidic, J.; Léguillier, V.; Hou, Y.; Chaix, C. Investigation of the Affinity of Aptamers for Bacteria by Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Using Nanosomes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 29645–29656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, R.L.; Myszka, D.G. Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensor analysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, N.; Cui, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Li, M.; Lu, W.; Qing, G.; Liu, Y. Biomimetic ion nanochannels for sensing umami substances. Biomaterials 2022, 282, 121418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Meng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J. Bimetallic bionic taste sensor for perception of the synergistic effect of umami substances. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 234, 115357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.; Kwon, H.W. Bioelectronic Tongues Mimicking Insect Taste Systems for Real-Time Discrimination between Natural and Artificial Sweeteners. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 3682–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Seo, S.E.; Nam, Y.; Jwa, S.; Yang, I.; Park, T.H.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, S.H. Bioelectronic Tongue for Identifying and Masking Bitterness Based on Bitter Taste Receptor Agonism and Antagonism. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Yang, F.; Dong, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, G.; Fan, Y. Human-like performance umami electrochemical biosensor by utilizing co-electrodeposition of ligand binding domain T1R1-VFT and Prussian blue. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Shu, G.; Sun, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, M. Development of sensitive and stable electrochemical impedimetric biosensor based on T1R1 receptor and its application to detection of umami substances. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Research on sensing characteristics of three human umami receptors via receptor-based biosensor. Flavour Fragr. J. 2020, 35, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.; Landin, A.M.; Roper, S.D. A metabotropic glutamate receptor variant functions as a taste receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, O.; Drago, F. Pharmacological significance of extra-oral taste receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, P.; Zhou, L.; Qin, Z.; Gao, K.; Yao, J.; Li, C.; Wang, P. A biomimetic bioelectronic tongue: A switch for On-and Off-response of acid sensations. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, N.; Roper, S.D. Review series: The cell biology of taste. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, I.S.; DeSimone, J.A. Otopetrin-1: A sour-tasting proton channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taruno, A.; Vingtdeux, V.; Ohmoto, M.; Ma, Z.; Dvoryanchikov, G.; Li, A.; Adrien, L.; Zhao, H.; Leung, S.; Abernethy, M. CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes. Nature 2013, 495, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lin, C.-T.; Zhang, D. A novel biomimetic electrochemical taste-biosensor based on conformational changes of the taste receptor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 249, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Song, H.S.; Park, T.H.; Jang, J. Conducting nanomaterial sensor using natural receptors. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 36–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Jin, H.J.; Ahn, S.R.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, U.-K.; Simons, C.T.; Hong, S.; Park, T.H. Bioelectronic tongue using heterodimeric human taste receptor for the discrimination of sweeteners with human-like performance. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9781–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozarkar, S.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. Improved dispersion of carbon nanotubes in chitosan. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Du, C.; Zou, Z.; Li, X.; Akins, D.L.; Yang, H. A biosensing platform based on horseradish peroxidase immobilized onto chitosan-wrapped single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, L.; Kelly-Brown, C.; Stewart, M.; Oki, A.; Regisford, G.; Luo, Z.; Bakhmutov, V.I. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–carbon nanotube composites. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, M.; Ziegler, F. Structure-function analyses of human bitter taste receptors—Where do we stand? Molecules 2020, 25, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Bader, M.L.; Drew, D.; de Gier, J.-W. Rationalizing membrane protein overexpression. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, A.D.; Karim, A.S.; Jewett, M.C. Cell-free gene expression: An expanded repertoire of applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.R.; An, J.H.; Song, H.S.; Park, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, J.; Park, T.H. Duplex bioelectronic tongue for sensing umami and sweet tastes based on human taste receptor nanovesicles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7287–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.R.; An, J.H.; Jang, I.H.; Na, W.; Yang, H.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Song, H.S.; Jang, J.; Park, T.H. High-performance bioelectronic tongue using ligand binding domain T1R1 VFT for umami taste detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Oh, E.H.; Park, J.; Hong, S.; Park, T.H. Ion-channel-coupled receptor-based platform for a real-time measurement of G-protein-coupled receptor activities. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Son, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.T.; Moon, H.; Kim, M.J.; Misaka, T.; Rhyu, M.-R. Modulation of sweet taste by umami compounds via sweet taste receptor subunit hT1R2. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novodchuk, I.; Bajcsy, M.; Yavuz, M. Graphene-based field effect transistor biosensors for breast cancer detection: A review on biosensing strategies. Carbon 2021, 172, 431–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Sekiyama, N.; Otsu, M.; Shimada, Y.; Sato, A.; Nakanishi, S.; Jingami, H. Expression and purification of the extracellular ligand binding region of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13089–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liman, E.R.; Zhang, Y.V.; Montell, C. Peripheral coding of taste. Neuron 2014, 81, 984–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.V.; Singh-Bhagania, S.; Cenci, M.; Chacon Cordon, C.; Singh, M.; Butterwick, J.A. The molecular basis of sugar detection by an insect taste receptor. Nature 2024, 629, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Cho, A.-N.; Jin, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.-W. Bio-artificial tongue with tongue extracellular matrix and primary taste cells. Biomaterials 2018, 151, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, V.; Dékány, I. Synthesis and stabilization of Prussian blue nanoparticles and application for sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiao, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, K.; Li, L.; Fan, Y.; Hu, L. A hydrogel-based biosensor for stable detection of glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 221, 114908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Kalambate, P.K.; Mugo, S.M.; Kamau, P.; Chen, J.; Jain, R. Polymer hydrogel interfaces in electrochemical sensing strategies: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Chu, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, W. A review on recent advances of Protein-Polymer hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 162, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.; Choe, A.; Lim, S.; Lee, Y.; Na, S.; Ko, H. Soft and ion-conducting hydrogel artificial tongue for astringency perception. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Du, L.; Zou, L.; Zhao, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, P. Recent advances in taste cell-and receptor-based biosensors. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 201, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Umami taste evaluation based on a novel mouse taste receptor cell-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 237, 115447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, P. Dual functional extracellular recording using a light-addressable potentiometric sensor for bitter signal transduction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1022, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, M.; Jiang, N.; Zhuang, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, P. A Cell Co-Culture Taste Sensor Using Different Proportions of Caco-2 and SH-SY5Y Cells for Bitterness Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kong, S.; Chen, F.; Chen, W.; Du, L.; Cai, W.; Huang, L.; Wu, C.; Zhang, D.-W. A bioelectronic taste sensor based on bioengineered Escherichia coli cells combined with ITO-constructed electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1079, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Jiang, D.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Qin, C.; Yuan, Q.; Xue, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N. Hybrid integrated cardiomyocyte biosensors for bitter detection and cardiotoxicity assessment. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Qin, C.; Gu, C.; He, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, L.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. A novel bionic in vitro bioelectronic tongue based on cardiomyocytes and microelectrode array for bitter and umami detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, C.; Qin, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N.; Yuan, Q.; Duan, Y.; Liu, M.; Wei, X.; Yu, Y. Mimicking the biological sense of taste in vitro using a taste organoids-on-a-chip system. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xu, J.; Qin, Z.; Hu, N.; Zhou, M.; Huang, L.; Wang, P. Detection of bitterness in vitro by a novel male mouse germ cell-based biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 223, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M. Taste perception and coding in the periphery. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2006, 63, 2000–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hoon, M.A.; Chandrashekar, J.; Mueller, K.L.; Cook, B.; Wu, D.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J. Coding of sweet, bitter, and umami tastes: Different receptor cells sharing similar signaling pathways. Cell 2003, 112, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Qin, Z.; Zhao, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Wan, H.; Di Pizio, A.; Malach, E.; Niv, M.Y.; Huang, L. A bioinspired in vitro bioelectronic tongue with human T2R38 receptor for high-specificity detection of N-C=S-containing compounds. Talanta 2019, 199, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.-H.; Mi, S.-S.; Deng, S.-P. Sweet and bitter tastants specific detection by the taste cell-based sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolskee, R.F.; Dyer, J.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Salmon, K.S.; Ilegems, E.; Daly, K.; Maillet, E.L.; Ninomiya, Y.; Mosinger, B.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15075–15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Wang, T.; Jing, Y.; Fernandes, V.S.L. The novel mechanism of bitter taste receptors attenuating rat ventricular contractility. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 839.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Reddy, V.S.; Gao, S.; Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Niu, L.; Zhang, D.; Ramakrishna, S.; Zou, X. Recent advances in electrochemical cell-based biosensors for food analysis: Strategies for sensor construction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 248, 115947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Yuan, Q.; Han, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Ping, J.; Xu, L. Biomimetic integrated gustatory and olfactory sensing array based on HL-1 cardiomyocyte facilitating drug screening for tachycardia treatment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 223, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Shu, G.; Wang, R.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, M. Kinetics of a new porcine taste-bud tissue biosensor for the detection of umami substances and their synergistic effect. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Study on the distribution of umami receptors on the tongue and its signal coding logic based on taste bud biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qiao, L.; Pang, G.; Xie, J. A kinetic study of bitter taste receptor sensing using immobilized porcine taste bud tissues. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Q.; Jiang, N.; Liu, M.; Duan, Y.; Wan, H.; Li, R.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, P. Biohybrid tongue for evaluation of taste interaction between sweetness and sourness. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 6976–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Qin, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. An in vivo bioelectronic tongue for sweetness detection using rat gustatory perception based on brain-computer interface. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Fukuoka, Japan, 26–29 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Hu, L.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. A novel bioelectronic tongue in vivo for highly sensitive bitterness detection with brain–machine interface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. The tongue map and the spatial modulation of taste perception. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, S.D. Signal transduction and information processing in mammalian taste buds. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2007, 454, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, L.A. Progress and renewal in gustation: New insights into taste bud development. Development 2015, 142, 3620–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S.D. Taste buds as peripheral chemosensory processors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 24, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabadaj, M.; Szuplewska, A.; Balcerzak, M.; Chudy, M.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P. Ion chromatographic fingerprinting of STC-1 cellular response for taste sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, P.; Xie, J.; Pang, G. The investigation of allosteric regulation mechanism of analgesic effect using SD rat taste bud tissue biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, P.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Du, L.; Wu, C. A Taste Bud Organoid-Based Microelectrode Array Biosensor for Taste Sensing. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Hsia, K.J.; Wang, P. Bioelectronic tongue of taste buds on microelectrode array for salt sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.; Hu, N.; Hsia, K.J.; Wang, P. Extracellular potentials recording in intact taste epithelium by microelectrode array for a taste sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, M.; Romero, N.; Cetó, X.; Valle, M.d. Optimization of sensors to be used in a voltammetric electronic tongue based on clustering metrics. Sensors 2020, 20, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, G.; Qin, Y.; Freeman, W.J. A pattern recognition method for electronic noses based on an olfactory neural network. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 125, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordella, C.B. PCA: The basic building block of chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2012, 47, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takekawa, T.; Isomura, Y.; Fukai, T. Spike sorting of heterogeneous neuron types by multimodality-weighted PCA and explicit robust variational Bayes. Front. Neuroinform. 2012, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, R.Q.; Nadasdy, Z.; Ben-Shaul, Y. Unsupervised spike detection and sorting with wavelets and superparamagnetic clustering. Neural Comput. 2004, 16, 1661–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, M.H.; Hurwitz, C.; Sorbaro, M. Scaling spike detection and sorting for next-generation electrophysiology. Adv. Neurobiol. 2019, 22, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wu, B.; Blank, I.; Yu, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. TastePeptides-EEG: An Ensemble Model for Umami Taste Evaluation Based on Electroencephalogram and Machine Learning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 13430–13439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Tan, G.; Zou, L. Research on the relation of EEG signal chaos characteristics with high-level intelligence activity of human brain. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2010, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K.; Matsuno, T.; Yamafuji, K. Chaotic processes in taste recognition. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 1997, 12, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Men, H.; Shi, Y.; Ying, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Computational model of taste pathways: A biomimetic algorithm for electronic tongue based on nerve conduction mechanism. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 6859–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Xia, X.; Ying, Y.; Men, H. A data processing method for electronic tongue based on computational model of taste pathways and convolutional neural network. Measurement 2022, 205, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Lian, X.; Li, X.; Low, S.S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Xu, N. Taste analog perception system based on impedance spectrum sensor array and human-like fuzzy evaluation cloud model. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19513–19523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).