Abstract
Previous studies have reported the development of a taste sensor using a surface modification approach to evaluate umami taste, specifically substances like monosodium L-glutamate (MSG) and monosodium L-aspartate. The sensor was modified with 2,6-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (2,6-DHTA). However, the mechanism underlying umami substance detection in the 2,6-DHTA- treated sensor remains unidentified, as does whether the specific detection is due to an intermolecular interaction between the modifier and the analyte. In this study, 1H-NMR measurements were conducted for a variety of modifiers and analytes in terms of structures, along with taste sensor measurements. By comparing the 1H-NMR spectra and the results of the taste sensor, we suggested that both modifiers and analytes need to meet certain molecular structure conditions to produce intermolecular interactions. The modifier needs to possess intramolecular H-bonds and have carboxyl groups in the para position of the benzene ring, i.e., two carboxyl groups. In conclusion, we validated that the response mechanism of the taste sensor for umami substance measurement proposed in previous studies is reasonable and predicted the binding form of 2,6-DHTA and MSG.
1. Introduction
Over a century ago, the first umami compound, monosodium L-glutamate (MSG), was extracted by Ikeda from seaweed broth [1]. Unlike the other four well-defined tastes qualities (sourness, bitterness, saltiness, sweetness), umami qualities exhibit a meaty, mouth-filling, rich taste [2,3]. Umami qualities not only serve as food additives to enhance the taste of food, but also play a significant role in health. Studies have indicated that umami, as a flavor enhancer in food, can reduce the risk of diseases such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases due to excessive consumption of salt [4,5,6]. In addition, umami has been reported to stimulate saliva secretion, promoting the appetite of patients with impaired taste and smell functions, resulting in decreased saliva production, and improving their overall health [4,7,8]. Some studies also suggest that continuous intake of MSG can improve the nutritional status of hospitalized elderly patients and the cognitive abilities of patients diagnosed with dementia [9,10].
Based on its unique taste presentation and health-promoting functions, umami has received much attention [2]. Chemical sensors, i.e., odor sensing systems and taste sensing systems, have been developed to reproduce the sense of humans or animals [11]. Odor sensing systems use various transducers such as carbon nanotubes [12,13] and carbon black composites [11]. Taste sensing systems, also known as the electronic tongue, comprise various sensing methodologies, such as potentiometry [14,15,16,17], triboelectric fingerprint signals [18], biomimetic biosensing [19,20,21], and enzymatic methods [22,23]. Among them, the potentiometric taste sensors developed by Toko and co-workers can detect five basic tastes, including umami, with excellent reproducibility [24,25,26]. An example of the commercialized machine is TS-5000Z (Intelligent Sensor Technology, Inc., Kanagawa, Japan). This instrument features sensor electrodes with lipid/polymer membranes designed based on the ionic and/or hydrophobic (or hydrophilic) properties of taste substances. Using such lipid/polymer membranes in taste sensors can classify and quantify the five basic tastes [15].
The taste sensors for detecting umami substances employ phosphoric acid di(2-ethylhexyl) ester (PAEE) as one of the lipids [15]. Due to the phosphate groups in lipid PAEE having a lower dissociation constant compared to the carboxyl group of MSG, protons dissociate from the phosphate groups of the lipid, leading to a negative change in membrane potential [27]. Nonetheless, the membranes containing the lipid PAEE exhibit a response to alkaline substances such as NaOH and NaHCO3, closely resembling the response to MSG [27]. This implies that the sensor may not effectively differentiate between responses to MSG or alkaline substances, as the reaction is not based on the membrane’s molecular recognition of the chemical structure of MSG. Instead, it is caused by the transfer of H+ from PAEE to the carboxyl group of MSG.
Recently, researchers have developed a novel taste sensor employing lipid/polymer membranes for detecting umami substances (e.g., MSG, monosodium L-aspartate (MSA)) using a surface modification method [28]. The lipid/polymer membranes of the taste sensor were immersed in the modifier solution to adsorb modifiers onto the lipid/polymer membranes for sample measurement [29]. Such a method was also employed to detect non-charged bitter substances like caffeine [30]. The response value of umami substances was compared by employing various structurally different modifiers, such as 2,6-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (2,6-DHTA) and 2,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid (2,6-DHBA). It was concluded in a previous report [28] that modifiers capable of detecting umami substances should meet two conditions: possess intramolecular H-bonds and have carboxyl groups in the para position, i.e., two carboxyl groups. In [28], it was thus inferred that the detection mechanism for umami substances involves the intermolecular interaction between the umami substance and the modifier. This interaction influences the formation of intramolecular H-bonds within the modifier, thereby influencing the dissociation state of the carboxyl groups of the modifier. This change in the dissociation state of the carboxyl groups results in a return of H+ on the membrane surface, altering the surface charge density of the membrane and ultimately generating a positive response. However, this intermolecular interaction, involving multisite binding between MSG and modifiers, has yet to be verified at the molecular level.
NMR measurement involves applying radiofrequency pulses to nuclei in a strong magnetic field to detect their resonance frequencies, providing detailed information about their molecular structure, chemical environment, and dynamics [31,32]. The resonance frequency of a nucleus or chemical shift (δ, ppm) is affected by the electron distribution in its chemical bonds, with the specific resonance frequency determined by the molecule’s structure [33]. Thus, by analyzing changes in the chemical shift phenomenon, NMR spectroscopy can examine intermolecular interactions between substances at the molecular level.
In this study, we used modifiers with different structures for sensor surface modification. Sensors were employed to measure analytes with different structures. We analyzed the influence of the structures of the modifiers and analytes on the response values of the taste sensors. Additionally, we employed 1H-NMR measurements to investigate the intermolecular interactions between the modifier (e.g., 2,6-DHTA and aniline) and umami substances (e.g., MSG and MSA). The 1H-NMR spectra were analyzed to validate the intermolecular interaction between the modifiers and the analytes. Thus, we compared the 1H-NMR spectra with the detection data from the taste sensors to identify the response mechanism of umami taste detection in taste sensors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Tetradodecylammonium bromide (TDAB) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Dioctyl phenyl-phosphonate (DOPP) was purchased from Dojindo Molecular Technologies (Kumamoto, Japan). Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), 2,6-DHBA, aniline, and MSA were purchased from FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Osaka, Japan). 2,6-DHTA was purchased from BLDpharm (Shanghai, China). MSG, L-glutamine (Gln), potassium chloride (KCl), and tartaric acid were purchased from Kanto Chemical Co. (Tokyo, Japan). Figure 1 shows the structural formula of 2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, aniline, MSG, MSA, and Gln. D2O (99.8 atom% D) was purchased from Acros Organics (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). 3-Trimethylsilyl-1-propanesulfonic acid-d6 (DSS-d6, 98.0 atom% D) was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA).
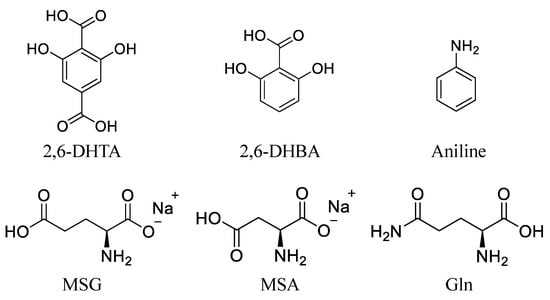
Figure 1.
The structural formula of 2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, aniline, MSG, MSA, and Gln.
2.2. Fabrication of Lipid/Polymer Membrane
In this study, we prepared the sensor electrodes with a lipid/polymer membrane. The lipid/polymer membrane comprises TDAB as the lipid, DOPP as the plasticizer, and PVC as the supporting material. In a cleaned and dried screw tube bottle, 0.01 mmol TDAB was dissolved in 10 mL THF. A total of 1.5 mL DOPP and 800 mg PVC were added sequentially. The resulting mixture was stirred thoroughly and then spread onto a clean Petri dish (90 mm φ). The lipid/polymer membrane was formed through the evaporation of THF. Then, the obtained lipid/polymer membrane was cut and placed onto the sensor electrode.
2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, and aniline were employed for surface modification. Following the same method as in a previous study [28], a group of sensor units was immersed into a 0.03 wt% 2,6-DHTA solution for 72 h. Similarly, surface modification for two additional groups of sensor units was conducted using 0.03 wt% solutions of 2,6-DHBA and aniline, respectively. Each group of sensor units comprises eight electrodes.
2.3. Measurement of Umami Substances by Fabricated Taste Sensors
The taste sensor measurements were conducted using a commercial taste sensing system (TS-5000Z, Intelligent Sensor Technology, Inc., Kanagawa, Japan). Both the sensor and reference electrodes, as depicted in Figure 2, utilize a Ag wire coated with a AgCl layer and are filled with an inner solution containing 3.33 M KCl and saturated AgCl.
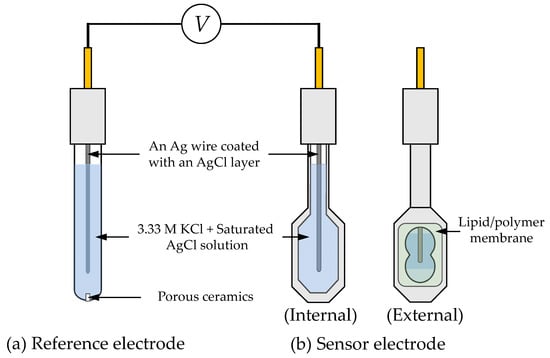
Figure 2.
The structure of the reference electrode and the sensor electrode.
The detection process of the taste sensors can be divided into four steps. Initially, the sensor and reference electrodes are immersed in a reference solution, which contains 3.33 M KCl and 0.3 mM tartaric acid, for 30 s to obtain the reference potential (Vr). Subsequently, they are immersed in the test sample solution for 30 s to obtain a sample potential (Vs). The relative response values of the test samples is calculated by taking the difference between Vs and Vr. Finally, the membrane surface is refreshed by applying a water-based solution consisting of 10 mM KOH, 100 mM KCl, and 30 vol% EtOH for the next measurement cycle. To ensure the reliability of the experimental data, the detection process was conducted five times, and the data from the last three measurements were used for analysis.
MSG, MSA, and Gln were utilized as the test samples and were dissolved in the reference solution. The concentrations of the test samples were 1, 10, and 100 mM. MSG and MSA are umami substances and were used as umami substance samples in our previous experiments. For Gln, a previous study suggested [34] that the taste profile of Gln is primarily characterized by sweetness, although it demonstrates subtle umami attributes at higher concentrations. It is noteworthy that Gln is not an umami substance. Gln’s side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide group. Based on its structural similarity, we utilized Gln as a control group sample in our experiments to further confirm the specific recognition conditions of umami substances MSG and MSA. We prepared solutions of these three samples at different concentrations to test the response of the taste sensor. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated from 24 (8 electrodes × 3 rotations) sets of electrical response values. Three types of taste sensors, i.e., sensors modified with 2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, or aniline, were used for measuring these samples.
2.4. Measurement of Umami Substances and Modifiers by 1H-NMR
To confirm whether there were intermolecular interactions between the prepared modifiers and umami substances, we conducted 1H-NMR measurements. All 1H-NMR spectra were obtained using an ECS-400 spectrometer (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). The investigated modifiers were 2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, and aniline. Although aniline does not meet the structural criteria for modifiers established in our previous studies, it was included for comparison with the other two modifiers as a negative control. The test samples included the umami substances MSG and MSA, as well as Gln, which is a non-umami substance with a structure similar to that of MSG. We prepared mixed solutions of the modifiers and test samples in five different molar ratios, 0:1, 0.5:1, 1:1, 2:1, and 3:1, using D2O as the solvent. Additionally, to mimic the conditions of the taste sensor measurements, which utilized the KCl electrolyte solution as the solvent, we also employed 1 mM KCl-containing D2O solution as the solvent for the test samples.
An aliquot of the test sample containing DSS-d6 as a reference compound (d at 0.00 ppm) was placed into a 5 mm NMR sample tube (Nihonseimitsu Scientific Co., Tokyo, Japan). 1H-NMR spectra were acquired by a single-pulse sequence under the following conditions: acquisition time, 2.73 s; scans, 16; relaxation delay, 12 s; auto-gain and spinning at 15 Hz.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Detection of Umami Substances Using Taste Sensors Treated with 2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, and Aniline
A previous study [28] indicated that the taste sensor, after surface modification with 2,6-DHTA, demonstrated a significant potential response to umami substances, i.e., MSG and MSA. Based on these understandings, in this experiment, we used 2,6-DHTA as a modifier and employed 2,6-DHBA and aniline as control group modifiers. 2,6-DHBA and 2,6-DHTA both contain two hydroxyl groups, and the hydroxyl groups on the benzene ring can form intramolecular H-bonds with the neighboring carboxyl groups [35,36,37]. Compared to 2,6-DHBA, 2,6-DHTA has an additional carboxyl group in the para position of the benzene ring. In contrast to 2,6-DHBA and 2,6-DHTA, aniline has only one amide on the benzene ring and cannot form intramolecular H-bonds. By comparing the response values of sensors modified with different modifiers to the test sample, we aim to verify the most suitable modifier for test sample detection and summarize the characteristics of the modifiers.
Figure 3a–c show the taste sensors’ response to MSG, MSA, and Gln solutions at different concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 mM. According to Figure 3a,b, sensors treated with 2,6-DHTA exhibited significant responses to MSG and MSA, with the response increasing with the increase in umami substance concentration. These results were consistent with our previous experimental findings [28].
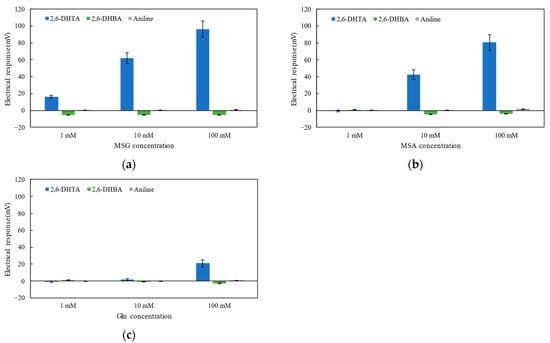
Figure 3.
The response to (a) MSG, (b) MSA, and (c) Gln solutions with three types of sensors: the sensor modified with 2,6-DHTA, 2,6-DHBA, and aniline, respectively. Error bars indicate the SD of the data; n = 8 (electrode) × 3 (rotation) = 24 values.
By comparing the data from sensors treated with different modifiers, as depicted in Figure 3a–c, it is evident that sensors treated with 2,6-DHBA and aniline exhibited negligible responses (less than 10 mV) to MSG, MSA, and Gln. This result indicates that the sensor modified with aniline or 2,6-DHBA cannot induce a significant response to MSG and MSA. Aniline lacks the structural condition of intramolecular H-bonds. Although 2,6-DHBA contains two intramolecular H-bonds, it lacks the structural factor of having carboxyl groups in the para position on the benzene ring. These findings further indicate that modifiers used to test sensors’ response to MSG and MSA should possess specific structural factors: intramolecular H-bonds and carboxyl groups in the para position on the benzene ring, i.e., two carboxyl groups.
In Figure 3c, we also noticed that the 2,6-DHTA-treated sensor exhibited a slight response to the 100 mM Gln solution (approximately 20 mV), but it showed negligible potential changes for 1 mM and 10 mM Gln solutions. This agrees with the fact [34] that Gln shows umami properties at high concentrations.
Additionally, by comparing the results between Figure 3a,b, this sensor showed a lower response to MSA. Thus, we infer that the analytes should also possess certain structural conditions: the structure of MSG. For instance, MSG has carboxyl groups at both sides of its carbon chain; MSA has one less carbon chain compared to MSG, making it shorter in length, and the sensor’s response to MSA is lower than that to MSG. Due to the amide group in Gln, the sensor modified with 2,6-DHTA exhibits negligible membrane potential changes at low concentrations of Gln.
In general, for effective detection by taste sensors utilizing surface modification, both the modifier and the umami substance should possess specific structural conditions. We infer that the structural factors between the sensor’s modifier and the target substance induce bidirectional molecular interactions which may effectively cause changes in the membrane surface potential of the taste sensor, thereby enabling selective measurement of the umami substance. To confirm whether such a molecular interaction exists between the modifier and the umami substance (analyte), we conducted an 1H-NMR measurement at the molecular level.
3.2. Investigation of the Interaction between Modifiers and Umami Substances by 1H-NMR
To further analyze the molecular interactions between the modifiers and the test samples, we conducted 1H-NMR measurements. Figure 4 shows the 1H-NMR spectra for each modifier and MSG in D2O solution containing 1 mM KCl. The chemical shift varied with the mixing ratio of each substance. The chemical shift change is very sensitive to structural changes and can be measured very accurately, meaning that almost any genuine binding interaction will produce the chemical shift change [38,39]. Figure 5 was plotted to demonstrate the variations in chemical shift clearly. The horizontal axis represents the molar ratio of the mixed solution, while the vertical axis represents the change in chemical shift. According to Figure 5a, it can be clearly observed that as the concentration of MSG increased, the chemical shift of 2,6-DHTA changed to high magnetic fields. Moreover, according to Figure S1a–c in the Supplementary Materials, the chemical shifts on the MSG side also changed with the varying molar ratio of the mixed solution. In the mixed solution of 2,6-DHTA and MSG, the chemical shift changes were observed in both 2,6-DHTA and MSG molecules as the concentration of MSG increased. This suggests the occurrence of bidirectional intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG.
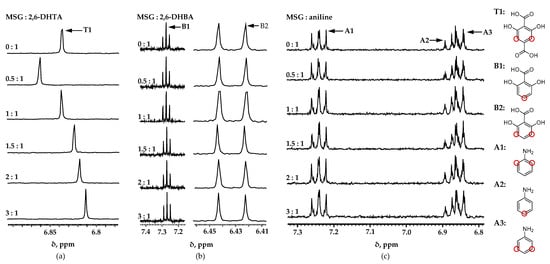
Figure 4.
1H-NMR spectra for each modifier and MSG: (a) 2,6-DHTA, (b) 2,6-DHBA, and (c) aniline. Chemical shifts (δ) changed with increases in molar ratio in 2,6-DHTA only.
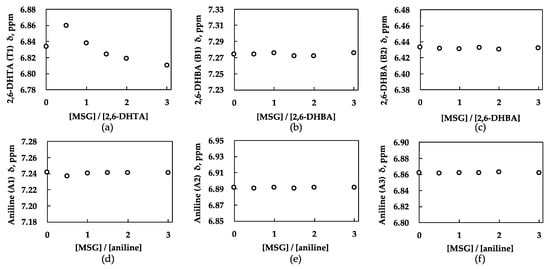
Figure 5.
Chemical shift (δ) with increasing molar ratio for each modifier: (a) 2,6-DHTA (T1); (b) 2,6-DHBA (B1); (c) 2,6-DHBA (B2); (d) aniline (A1); (e) aniline (A2); (f) aniline (A3). Chemical shift of 2,6-DHTA (T1) changed. Chemical shift of 2,6-DHBA and aniline did not change. Changes in chemical shifts indicate interaction occurs between modifier and MSG.
Figure 5b depicts the chemical shift changes on the 2,6-DHBA side in the mixed solution of 2,6-DHBA and MSG as the concentration of MSG increases. Evidently, 2,6-DHBA presented no significant chemical shift changes, although pronounced shifts were observed on the MSG side, as indicated by Figure S1d–f in the Supplementary Materials. Similarly, in Figure 5c and Supplementary Figure S1g–i, both aniline and MSG exhibit no remarkable chemical shift changes. Drawing on the experimental data and the structural features of different modifiers, we suggest that 2,6-DHBA and aniline have difficulty forming bidirectional molecular interactions with MSG because their structural configurations do not meet the specific criteria outlined in Section 3.1. 2,6-DHBA, lacking a carboxylic group, and aniline, which lacks intramolecular hydrogen bonding, present obstacles to the formation of bidirectional interactions with MSG.
We confirmed the presence of intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG through chemical shift changes observed in 1H-NMR measurements. To further identify that the test substance should possess specific structural conditions, we also conducted 1H-NMR measurements using the same sample substances, i.e., MSA and Gln, as those used in the taste sensor measurements.
Figure 6 shows the 1H-NMR spectra and the chemical shift plots of the 2,6-DHTA modifier and the analytes (MSA and Gln) in D2O solution containing 1 mM KCl. According to Figure 6c, the chemical shift of 2,6-DHTA changes with increasing MSA concentration. Although the magnitude of this chemical shift change is not as significant as that observed in the mixed solution of 2,6-DHTA and MSG, it can be confirmed that the chemical shift of 2,6-DHTA changes with the concentration of MSA. According to Supplementary Figure S2a,b, the chemical shift of MSA also changes with the increase in MSA concentration in the mixed solution. This further suggests that there are bidirectional intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSA, although these interactions are weaker compared to those between 2,6-DHTA and MSG. This is evident from the lower response in taste sensor measurements and the less significant chemical shift changes observed in the 1H-NMR experiments.
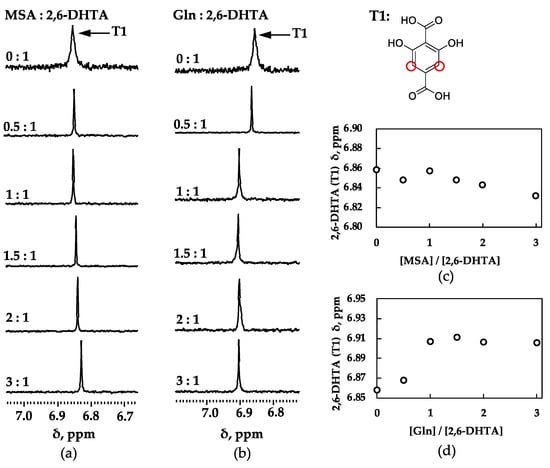
Figure 6.
1H-NMR spectra for 2,6-DHTA and analytes: (a) MSA; (b) Gln. Chemical shift (δ) with increasing molar ratio for 2,6-DHTA and analytes: (c) MSA; (d) Gln. Chemical shift of 2,6-DHTA (T1) changed. Changes in chemical shifts indicate interaction occurs between modifier and analytes.
According to Figure 6d, although the chemical shift of 2,6-DHTA undergoes significant changes at low concentrations of Gln compared to no addition of Gln, there is no significant change in chemical shift at the high concentration of Gln. Additionally, according to Supplementary Figure S2c–e, despite the increase in Gln concentration, the measured chemical shift of Gln shows almost no significant change. Moreover, some studies indicate that when some protons are close to amide groups, they undergo chemical shifts due to the anisotropic distributions of electrons in amide groups [38]. We inferred that the chemical shift changes at low concentrations of Gln were caused by its amide group. Unlike MSG and MSA, as the concentration of Gln increases in the mixed solution, no continuous and significant chemical shift changes are observed for either Gln or 2,6-DHTA. Based on the structure of Gln, which has a carboxyl group at one end and an amide at the other, we speculated that Gln’s structure cannot effectively form bidirectional intermolecular interactions with the modifier 2,6-DHTA.
3.3. Discussion of Experimental Results from Taste Sensors and 1H-NMR Measurements
To identify the mechanism underlying the detection of umami substances by employing taste sensors with surface modification, we have conducted taste sensor measurements on three different structural modifiers and samples with different structures.
Table 1 summarizes the responses of the taste sensors and 1H-NMR measurements for various modifiers. By comparing the results of taste sensors and 1H-NMR measurements, we have found that only the combination of 2,6-DHTA and MSG can yield a significant sensor response and clear chemical shift changes. Moreover, both the modifier itself and MSG exhibit chemical shift changes. This indicates that this specific combination is effective in forming bidirectional intermolecular interactions.

Table 1.
Summary of taste sensor results and 1H-NMR results for MSG.
Regarding the combination of 2,6-DHBA and MSG, although in 1H-NMR measurements, chemical shift changes were detected on the MSG side when 2,6-DHBA acted as the modifier in 1H-NMR measurements, no significant chemical shift changes were observed on the 2,6-DHBA side. Additionally, as Figure 3a shows, using 2,6-DHBA as a modifier did not lead to noticeable membrane potential changes in MSG detection. Therefore, it is concluded that bidirectional intermolecular interactions were not formed between 2,6-DHBA and MSG.
Moreover, aniline did not induce significant membrane potential changes in MSG in taste sensor measurements, and no significant chemical shift changes were observed for aniline and MSG in 1H-NMR measurements. Consequently, it is determined that intermolecular interactions between aniline and MSG do not exist.
By comparing the different structural characteristics of the three modifiers, we indicated that the prerequisites for modifiers are the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonds and carboxylic groups on the para position of the benzene ring.
To understand why the 2,6-DHTA-treated taste sensor showed the most significant response to MSG, we discussed the prerequisites for analytes with 2,6-DHTA-treated sensor detection. The results of the taste sensor and 1H-NMR measurements are summarized in Table 2. Chemical shift changes were observed in 1H-NMR measurements for both 2,6-DHTA and MSA. MSA has one less carbon chain compared to MSG, making it shorter, and the potential changes in the taste sensor are weaker than those of MSG. On the other hand, no notable chemical shift changes of Gln were observed in the 1H-NMR measurements. Additionally, the taste sensor treated with 2,6-DHTA only detected potentials far lower than MSG in high concentrations (100 mM) of Gln solution. By comparing the results of the taste sensor and 1H-NMR measurements, we further confirmed that the structure and length of MSG provide the optimal conditions for its detection by the taste sensor with 2,6-DHTA as the modifier. Therefore, we inferred that it is the structural conditions met by both MSG and 2,6-DHTA molecules, forming effective bidirectional intermolecular interactions, that ultimately cause the changes in membrane surface potential.

Table 2.
Summary of taste sensor results and 1H-NMR results for 2,6-DHTA.
3.4. Prediction of the Binding Form and Response Mechanism between 2,6-DHTA and MSG
By comparing the results of the taste sensor and the 1H-NMR measurements, we confirmed the presence of intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG. Furthermore, these intermolecular interactions require specific structural factors in both the modifier and the test sample. According to the chemical shift plots of the 2,6-DHTA side (Figure 5a) and the MSG side (Figure S1a–c), it is evident that the T1 position of 2,6-DHTA and the M2′ position of MSG show significant chemical shift changes as the molar ratio increases. This indicates that the electron density around the hydrogen atoms at these sites undergoes noticeable changes, suggesting the presence of hydrogen bonding interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG.
Based on these results, we can infer the form of the intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG, as illustrated in Figure 7. The results from the 1H-NMR measurements delineate the positions with the most significant chemical shifts for both 2,6-DHTA and MSG. The carboxyl groups of these molecules can act as proton donors or acceptors, enabling various H-bond interactions [40]. One of the most classic examples is the H-bond of carboxyl dimers [41,42]. Considering the results from the 1H-NMR measurements and molecular structure, we speculated that the carboxyl groups of MSG may form two intermolecular H-bonds with the carboxyl group at the para position on the benzene ring of 2,6-DHTA. The formation of intermolecular H-bonds needs the participation of H+ in the MSG sample solution, which results in the return of H+ on the membrane surface. The return of H+ can change the membrane surface charge density, resulting in a positive response for MSG. Based on the intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG, the detection principle for umami substances using the taste sensors that we proposed in our previous study [28] is reasonable.
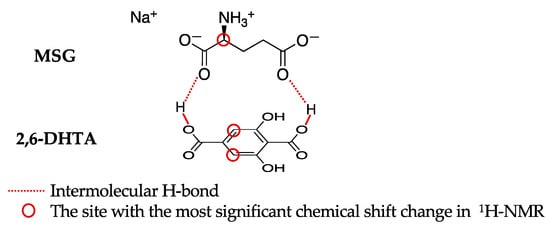
Figure 7.
The prediction of the binding forms of 2,6-DHTA and MSG. These binding forms were predicted from the information of the chemical shift changes provided by the 1H-NMR measurements.
4. Conclusions
Previous studies have documented the sensitivity and selectivity of taste sensors treated with 2,6-DHTA for umami substance (MSG and MSA) measurements. In this study, we used taste sensors and 1H-NMR measurements to analyze the mechanisms underlying the detection of umami substances by taste sensors with surface modification. Most notably, in the mixed solution of 2,6-DHTA and MSG, significant chemical shift changes were observed in both substances with increasing MSG concentration through 1H-NMR measurements. This demonstrated the existence of the bidirectional intermolecular interactions between 2,6-DHTA and MSG. By comparing the results of the taste sensors and the 1H-NMR spectra, we found that the modifiers and analytes need to meet certain structural factors to generate bidirectional intermolecular interactions. Considering the results from the 1H-NMR measurements and the presence of carboxyl groups in both molecules, which can act as H-bond donors and acceptors, we speculate that intermolecular H-bonds are formed between the two molecules. The H+ involved in forming H-bonds eventually alters the membrane surface charge density. However, there are still some limitations in the field of detecting umami substances using the taste sensors reported here. For example, taking into consideration molecular distance as a benchmark, further exploration of new modifier structures, such as isophthalic acid structural modifiers, can be undertaken to enhance the sensitivity of taste sensors to umami substances. Additionally, for other structurally different umami substances, such as IMP (inosine monophosphate) and GMP (guanosine monophosphate), novel binding modes can be investigated based on membrane surface modification methods for detection by taste sensors. This approach will thereby broaden the recognition range, sensitivity, and selectivity of this novel umami sensor for various umami substances.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors12080146/s1, Figure S1: Chemical shift (δ) of MSG changes with increasing molar ratio in a mixed solution containing; Figure S2: Chemical shift (δ) of MSA and Gln changes with increasing molar ratio in a mixed solution containing.
Author Contributions
The work presented here was carried out as a collaboration among all authors. W.Y., H.I., Z.Z., M.K., S.K., T.M. and K.T. defined the research theme; W.Y. and Z.Z. carried out the experiments of the taste sensors and analyzed the data; H.I. and M.K. carried out the experiments of 1H-NMR; W.Y., M.K. and Z.Z. interpreted the results and wrote the paper; K.T., T.M. and S.K. provided directions for the experimental methods, the analysis of data, the interpretation of the results, and the writing of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI, grant number JP21H05006.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nakamura, E. One Hundred Years since the Discovery of the “Umami” Taste from Seaweed Broth by Kikunae Ikeda, Who Transcended His Time. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Characterization and Evaluation of Umami Taste: A Review. TrAC Trends Analyt. Chem. 2020, 127, 115876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, I.E.T.; Kringelbach, M.L.; Rolls, E.T.; Hobden, P. Representation of Umami Taste in the Human Brain. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 90, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepeveen, J.; Moerdijk-Poortvliet, T.C.W.; van der Leij, F.R. Molecular Insights into Human Taste Perception and Umami Tastants: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, R.; Ohta, M.; Hayabuchi, H.; Fujitani, S.; Yoshida, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Tsuchihashi, T. Quantitative Verification of the Effect of Using an Umami Substance (L-Glutamate) to Reduce Salt Intake. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Pinto-e-Silva, M.E.M.; Simoni, N.K. Can Umami Taste Be an Adequate Tool for Reducing Sodium in Food Preparations? Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 5315–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uneyama, H.; Kawai, M.; Sekine-Hayakawa, Y.; Torii, K. Contribution of Umami Taste Substances in Human Salivation during Meal. J. Med. Investig. 2009, 56, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasano, T.; Satoh-Kuriwada, S.; Shoji, N. The Important Role of Umami Taste in Oral and Overall Health. Flavour 2015, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kouzuki, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Nagano, M.; Nakamura, S.; Katsumata, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Urakami, K. Effect of Monosodium L-Glutamate (Umami Substance) on Cognitive Function in People with Dementia. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoe, M.; Inoue, Y.; Sanbe, A.; Toyama, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Komatsu, T. Clinical Trial of Glutamate for the Improvement of Nutrition and Health in the Elderly. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1170, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatabe, R.; Shunori, A.; Wyszynski, B.; Hanai, Y.; Nakao, A.; Nakatani, M.; Oki, A.; Oka, H.; Washio, T.; Toko, K. Odor Sensor System Using Chemosensitive Resistor Array and Machine Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, A.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Meyyappan, M. A Sensor Array for the Detection and Discrimination of Methane and Other Environmental Pollutant Gases. Sensors 2016, 16, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaw, J.M.; Sevilla, F.B. Discrimination of Wood Species Based on a Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composite Chemiresistor Array. Holzforschung 2018, 72, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K. A Taste Sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Toko, K. Taste Sensor: Electronic Tongue with Lipid Membranes. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, G.; Muszynski, M.; Ruch, P.W. A Reconfigurable Integrated Electronic Tongue and Its Use in Accelerated Analysis of Juices and Wines. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Aveiro, Portugal, 29 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Ghosh, A. An Improved Fractional-Order Circuit Model for Voltammetric Taste Sensor System with Infused Tea as Analyte. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7792–7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, B.; Cao, X.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Dual-Sensory Fusion Self-Powered Triboelectric Taste-Sensing System towards Effective and Low-Cost Liquid Identification. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Umami Taste Evaluation Based on a Novel Mouse Taste Receptor Cell-Based Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 237, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A Novel Umami Electrochemical Biosensor Based on AuNPs@ZIF-8/Ti3C2 MXene Immobilized T1R1-VFT. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Research on Sensing Characteristics of Three Human Umami Receptors via Receptor-Based Biosensor. Flavour Fragr. J. 2020, 35, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauliukaite, R.; Zhylyak, G.; Citterio, D.; Spichiger-Keller, U.E. L-Glutamate Biosensor for Estimation of the Taste of Tomato Specimens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kong, L.; Dong, Y.; Shu, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, M. Multienzyme-Mediated Dual-Channel Magnetic Relaxation Switching Taste Biosensor (D-MRSTB) for Simultaneous Detection of Umami Compounds and Synergistic Enhancement in Food. ACS Sens. 2023, 9, 1820–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Ismail, I.; Joo, S.T. Identification of Umami Taste in Sous-Vide Beef by Chemical Analyses, Equivalent Umami Concentration, and Electronic Tongue System. Foods 2020, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Chen, R.; Ikezaki, H.; Ujihara, T. Evaluation of the Umami Taste Intensity of Green Tea by a Taste Sensor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7384–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woertz, K.; Tissen, C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Breitkreutz, J. A Comparative Study on Two Electronic Tongues for Pharmaceutical Formulation Development. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, S.; Kuga, H.; Ezaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Toko, K. Peculiar Change in Membrane Potential of Taste Sensor Caused by Umami Substances. Sens. Actuators 55B Chem. 2003, 91, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Kimura, S.; Toko, K. Development of Taste Sensor with Lipid/Polymer Membranes for Detection of Umami Substances Using Surface Modification. Biosensors 2024, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Kimura, S.; Onodera, T.; Toko, K. Molecular Structure Underlying the Allosteric Mechanism of Caffeine Detection in Taste Sensor. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, J.; Toko, K.; Tahara, Y.; Ishida, M.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Kojima, H.; Ikegami, S.; Yoshida, M.; Uchida, T. Development of Taste Sensor to Detect Non-Charged Bitter Substances. Sensors 2020, 20, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edison, A.S.; Colonna, M.; Gouveia, G.J.; Holderman, N.R.; Judge, M.T.; Shen, X.; Zhang, S. NMR: Unique Strengths That Enhance Modern Metabolomics Research. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 478–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, R.A. Basic Principles. In In Vivo NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, H. The Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectra of Organic Molecules-Chemical Shift and Spin-Spin Coupling. In NMR Spectroscopy: Basic Principles, Concepts and Applications in Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; pp. 29–66. ISBN 978-3-527-67477-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, M.; Sekine-Hayakawa, Y.; Okiyama, A.; Ninomiya, Y. Gustatory Sensation of L-And D-Amino Acids in Humans. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Li, K. Influence of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bond of Templates on Molecular Recognition of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2001, 450, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.E.; Kung, F. Effect of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding on Ionization Constants of Substituted Salicylic Acids. Can. J. Chem. 1996, 44, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, P.; Böhm, S.; Kulhánek, J.; Exner, O. Acidity of Ortho-Substituted Benzoic Acids: An Infrared and Theoretical Study of the Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.P. Using Chemical Shift Perturbation to Characterise Ligand Binding. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2013, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, V.; Young, K.; Maudsley, A.A. Proton NMR Chemical Shifts and Coupling Constants for Brain Metabolites. NMR Biomed. 2000, 13, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žagar, E.; Grdadolnik, J. An Infrared Spectroscopic Study of H-Bond Network in Hyperbranched Polyester Polyol. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 658, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiserowitz, L. Molecular Packing Modes. Carboxylic Acids. Acta. Cryst. 1976, 32, 775–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggirala, N.K.; Wood, G.P.F.; Fischer, A.; Wojtas, Ł.; Perry, M.L.; Zaworotko, M.J. Hydrogen Bond Hierarchy: Persistent Phenol⋯Chloride Hydrogen Bonds in the Presence of Carboxylic Acid Moieties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 4341–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).