Abstract
The detection of iodide ions (I−), despite challenges due to low concentrations and potential masking, is crucial for studying physiological processes and diagnosing diseases. A colorimetric sensor was developed to improve I− ion monitoring and facilitate on-site detection based on filter paper, which is a cost-effective platform. The sensor observed color changes in response to the exposure of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), from colorless to yellowish brown. The sensor demonstrated a detection limit of 0.125 × 10−6 M for I− ions in a relatively wide range of 0.01 to 15 × 10−6 M under optimized conditions including gel concentration, temperature, incubation time, TMB and H2O2 concentration, and pH. Furthermore, the proposed sensor was successfully employed in a variety of applications, such as biological (urine and blood serum), food (egg yolk and snacks), and environmental samples (tap water). The study established effective recoveries in complex media for visual on-site I− ion monitoring, indicating the developed assay as a potent, affordable, and practical platform.
1. Introduction
Iodine is a crucial micronutrient for metabolism and human growth [1]. Iodine plays an essential role in the healthy functioning of the thyroid gland and is necessary for normal human development [2]. The World Health Organization advises a regular iodide intake of 150 μg/day [3]. Iodide deficiency, also known as hypothyroidism [4], affects millions of people worldwide and may also result in spontaneous abortion, mental defects, and an increase in infant mortality. In contrast, hyperthyroidism [5] refers to an excess of iodine in our bodies. Hypo- and hyperthyroidisms can cause anxiety, goiter, confusion, weight loss, nervous agitation in dementia, and circulatory system disorders [6]. An excess or deficiency of I− ions in the human body and environmental samples have certain consequences, and therefore screening for I− ions via a simple approach with good sensitivity and selectivity is critical for both biological and environmental impacts [7].
Many approaches based on various principles have been suggested to determine low concentration levels of I− ions, including electrostatic ion chromatography [8], capillary electrophoresis [9], chemiluminescence [10], atomic absorption spectrometry [11], etc. Every technique has a unique set of benefits and drawbacks, and they are frequently designed to meet environmental and analytical needs. To better meet the needs of diverse applications across fields, scientists have worked to improve upon current techniques and create new ones through ongoing research and development. These optical sensors have opened new avenues for the investigation of simple, safe, quick, and distant mechanisms. They are especially well-suited for applications needing real-time monitoring in a variety of fields due to their flexibility and adaptability, i.e., industrial processes, biomedical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring [12].
A crucial aspect of the current global health strategy is the development of portable diagnostic tools for infectious and chronic illnesses [13]. Testing platforms that are quick and affordable are critical for efficiently managing the commencement, development, and spread of disease. Compared to other optical sensor approaches, the colorimetric assay has the advantage of being able to detect analytes with the naked eye [14]. The visible color change that indicates the existence or concentration of a target analyte is easily observed visually or, in more specialized cases, using ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy [15]. Colorimetric detection offers a practical and approachable solution for a wide range of analytical needs, including clinical diagnostics and environmental monitoring [16]. Recently, efforts have focused on developing smartphone-based methods for quantitative readouts of optical signals in an attempt to lower costs and simplify real-time biomarker analysis [17].
To account for the catalytic influence of enzyme mimics on the oxidation-reduction reaction of iodide, several innovative colorimetric reaction systems have also been reported and employed for I− ion detection. These approaches may be candidates for a simple and quick colorimetric method for determining I− ions [15]. It is important to note that many ions can modify or change the activity of nanozymes, highlighting their importance in ion sensing. Consequently, leveraging their inhibitory or enhancing effects on nanozyme activity, ions such as copper (Cu2+) [18], mercury (Hg2+) [19], sulfide (S2−) [20], and cyanide (CN−) [21] have been effectively detected and discerned. However, they still have several disadvantages, such as a complex preparation process and high detection limits. The development of analytical techniques for ion detection is crucial to enhance sensitivity, selectivity, and accuracy without the need for costly or complex instrumentation [22,23]. Optodes are a notable technological development in the modern world. They have demonstrated a high level of practical dependability, as an accessible and useful alternative to certain conventional analytical methods [24]. Different colorimetric methods have been reported for the detection of I− ions; for example, Muniyandi Maruthupandi et al. studied iodide detection by using polymer-capped silver nanoparticles. Although the detection limit of this method was commendable, but required expensive instrumentation and involved time-consuming procedures [25]. On the other hand, the study carried out by the Yasomasa Fukoshima group presented a different method for identifying I− ions in aqueous medium. These methods have several benefits, including affordability and ease of use, etc. Notably, absorption spectroscopy produced an even lower limit of detection at 1.31 µM, while visual observation (naked eye) yielded a 30 µM limit of detection. Colorimetric detection is useful for sensing I− ions and has real-world applications in various fields due to its enhanced availability and sensitivity [26]. Jung-Hwa Cho reported the colorimetric detection of I− ions in water [27]; however, the limit of detection was determined to be sufficiently sensitive. Sustained refinement and optimization of the methodology might result in solutions to these challenges, increasing its viability and applicability in a variety of analytical scenarios.
In this research work, the detection of I− ions was carried out in the presence of TMB and H2O2 through a simple colorimetric assay. The sensitivity was achieved under optimized experimental conditions like gel concentration, H2O2 and TMB concentration, incubation time (min), and pH. TMB was used, which is a widely utilized substrate in peroxidase-based detection systems because of its ability to yield solvent oxidized products and outstanding absorption coefficients, which allow for detectable color distinction that is visible to the human eye. The selectivity was carried out to check the potential of the proposed sensor in the presence of interfering species. The stability of the proposed sensor was also tested, and the sensor was successfully employed for applications in biological (blood serum and urine), food (egg yolk and snacks), and environmental samples (tap water) for detecting I− ions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), potassium iodide (KI) (≥99%), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (30%), and sodium alginate (NaC6H7O6) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Deionized water was prepared using the Milli-Q ultrapure water system (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany). The eggs for the real sample analysis were bought directly from local market. The snacks were carried directly from KIMS Food Industrial Estate Hattar, Haripur, Pakistan, whereas urine, blood, and water samples were collected from Ayub Teaching Hospital Abbottabad KPK, Pakistan.
2.2. Software Used
Image J software (version 1.54g) was used to calculate the RGB values by taking averages. Origin software (version 2022) was used for plotting the optimization graphs. End note X8.0.2 was used for the citation of articles. The filter paper images were taken with the help of a mobile phone camera, which was suitable to achieve better-quality images.
Image J was specifically chosen for colorimetric analysis due to its ease of use and broad applicability in image processing. Image J consists of the primary colors, red, blue, and green, providing a simple but reliable platform for obtaining quantitative data from the color changes on the filter paper. Its selection for the color analysis was further justified by its adaptability and experience with image display in LCD screens and computers, which assured a smooth transition into the experimental workflow and enabled the precise interpretation of the sensor output.
2.3. Designing a Filter-Paper-Based Colorimetric Sensor
The first step in the sensor fabrication process was to make a sol–gel solution, which was 0.3 g per 6 mL and was carefully prepared to obtain the best possible consistency and performance. The 0.6 mm diameter of filter paper substrate was cautiously coated with the sodium alginate gel, which was spread very carefully to produce a perfectly even surface. The prepared filter paper was first treated with 10 µL of a 25 µM solution of H2O2 and 16 mM solutions of TMB. These substrates were carefully dispensed onto the paper, and then 10 µL of a 1 mM iodide solution was added onto the filter paper. Careful series of additions assured the creation of a sensor platform for iodide detection at the highest possible sensitivity and reliability. After that, the analysis was undertaken using the advanced imaging capabilities of a high-resolution smartphone camera that was placed at a consistent distance of 10 cm from the sensor surface to quantify color and evaluate intensity. This methodological approach made it easier to measure and assess color changes accurately, which allowed a more accurate and reproducible quantification of iodide concentration.
2.4. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions for Iodide Detection
The experiment was optimized using different optimization parameters to obtain an accurate, reliable, and more sensitive output signal. Gel concentration, measurement time after reagent addition, H2O2, pH, and TMB concentration were the optimization parameters which affected the colorimetric response.
2.5. Selectivity of the Iodide Assay
To assess the selectivity of the proposed method, different potential interfering species were tested. For this purpose, 10 µL of each interfering compound solution such as Br−, Cl−, F−, CN−, Na+, Al3+, Zn2+, Cu2+, and Mg2+ were incubated with modified filter paper strips in the presence of 25 µM of H2O2 and 16 mM of TMB, respectively. The color shift of these mixtures was recorded using software to calculate the intensity of the photographs taken.
2.6. Application to Real Samples
To evaluate the sensor’s performance in practical applications, the egg yolk samples were procured straight from the local market. The urine, blood, and water samples were taken from Ayub Teaching Hospital in Abbottabad, KPK, Pakistan, while the snacks samples were bought from KIMS Food Industrial Estate Hattar, Haripur, Pakistan. Egg yolk samples were prepared by carefully separating the yolks from the whites, homogenizing them in a blender, and then diluting the homogenized yolk with deionized water. Following that, homogenized egg yolks, blood serum, urine, and snacks (crushed) were centrifuged for 10 min at 3000 rpm to remove particles and dilute them with deionized water. After that, the clear supernatant was transferred into a fresh container. The pH ranges for the samples mentioned above were between 6 and 7 and the assay conditions were the same as those mentioned above for detecting iodide.
3. Results
3.1. The Mechanism and Principle of the Iodide Detection Assay
The sensor demonstrated a remarkable colorimetric response; this was due to its exceptional characteristics, which enabled the efficient detection of I− ions in the presence of TMB and H2O2. The complex process that underlies this response, as shown in Figure 1, provided an insight into the basic working of the modified filter paper-based sensor. With TMB acting as a substrate for chromogenic peroxidase, the sensor effectively detected iodide by utilizing its built-in sensitivity. As shown in Figure 1, I− ions and H2O2 combined to form a catalytic reaction in which I− ions oxidized H2O2, thereby serving as a catalytic oxidizing agent. The color of the filter paper substrate changed significantly from being colorless to yellowish-brown due to the catalytic process.
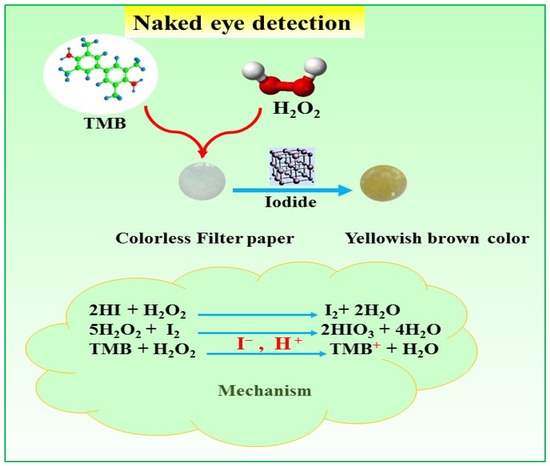
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanism for I− ion detection.
This mechanistic pathway’s clarification highlights the sensor’s reliable operation and usefulness as an adaptable instrument for optical sensing applications. Target analytes can be detected quickly and sensitively to translate molecular interactions into visually perceptible signals, which is made possible by the synergistic interaction of key components such as iodide ions, TMB, and hydrogen peroxide. Our sensor stimulated the chromogenic reaction of H2O2 and TMB, enhancing the system’s colorimetric effect and suggesting that the proposed sensor was more intrinsically peroxidase-biomimetic and could be used to develop a sensor for iodide detection. I− ions were oxidized to IO−3 in the presence of H2O2, while TMB was oxidized to a colored product [28].
3.2. Optimization of Experimental Parameters
For the sensitive detection of I− ions using the proposed assay, several key parameters (gel concentration, H2O2 concentration, TMB concentration, time, and pH) were systematically investigated to determine the optimum reaction conditions to obtain maximum efficiency, enhance the sensitivity (the capability to detect low concentrations of the analyte) and specificity (the capability to differentiate the analyte from interference substances), and ensure reproducibility.
3.2.1. Effect of Gel Stability and Time
To optimize various experimental conditions, gels of five different concentrations (0.1 to 0.5 g) in 6 mL of distilled water were prepared. A 0.3 g/6 mL gel sample was found to be most suitable because of the smooth pattern, as upon the increased concentration of sodium alginate, the gel became hardened, became lower in porosity, and it became challenging to provide a proper colorimetric reaction, as shown in Figure S1a. The gel patterns turned out to be liquid-based while reducing the sodium alginate concentration and were incompatible on the filter paper, which was in good agreement with the previous study [29]. As a result, a 0.3 g/6 mL concentration was chosen for further optimization and experimentation.
Figure S1b depicts the effect of time on I− ion concentration and the color intensity was measured after adding 15 × 10−6 M of I− ions at various time intervals. The color started to change from 1 to 4 min and then became intense at 12 min. Because the color was observed to be quite dark after 12 min, making it difficult to identify accurately [30], 12 min was determined to be the optimum incubation duration for the subsequent experimentation.
3.2.2. Effect of TMB and H2O2 Concentration
The optimum concentration of TMB, a crucial component of the colorimetric reaction mechanism, was determined through a methodical investigation in order to optimize the sensor’s performance. It was observed that an increase in TMB concentration was accompanied by an increase in color intensity. A quantitative correlation between TMB concentration and color intensity is demonstrated in Figure S1c, which offers a clear illustration of this phenomena. Following a comprehensive evaluation, it was concluded that 16 mM would be the optimal TMB concentration for further experimentation.
The impact of varying H2O2 concentrations was also examined with a fixed concentration of 10 µL of I− ions and H2O2 values ranging from 2 to 50 µM. After 2 µM, the color began to change from colorless to yellow, with the color intensity gradually increasing as the H2O2 concentration increased. The color reached its maximum intensity after 25 µM. As shown in Figure S1d, a noticeable color intensity was identified with a concentration of 25 µM, which was chosen for further experimentation because after 25 µM, the color intensity was not as accurate for consideration.
3.2.3. Effect of pH
We investigated the impact of pH on I− ion detection in the presence of TMB and H2O2. Figure S1e demonstrates that the catalytic oxidation rate of TMB by H2O2 in the presence of I− ions was significantly higher in slightly acidic medium compared to neutral and basic mediums. In the somewhat acidic solution, the reaction rate increased with increasing H2SO4 concentration up to 0.1 M and then decreased at higher concentrations. The creation of IO−3 may oxidize TMB to a colorful product, depending on the presence of H2O2 and H+. The presence of H+ ions promoted the reaction by stabilizing the iodine production process between I− ions and peroxide. Consequently, pH 5 was determined to be the optimal pH for further experimentation. At neutral and alkaline pHs, H2O2 can still oxidize I− ions, although it may not be as effective as it would be in an acidic conditions. Though reaction kinetics may be slower and total color intensity may be lower than in basic circumstances, TMB oxidation to its colored product might be reduced.
3.2.4. Detection of Iodide under Optimized Conditions
The quantitative detection of iodide was carried out under optimized conditions. Initially, the color intensity was increased steadily as the concentration of I− ions increased, and a significant intensification was observed after the addition of 4 µM of iodide, as shown in Figure 2. The sensing performance of the proposed sensor was observed in a broad linear range of 0.01 to 15 × 10−6 M and the limit of detection for I− ions was found to be as low as 0.125 × 10−6 M and could be compared well with the already-reported literature, as displayed in Table S1. The LOD of an analyte was calculated using the formula given,
where SD = Standard Deviation. The LOD is vital for determining the minimum concentration or amount of I− ions. This assessment is important for evaluating the sensitivity of the method, and particularly its ability to detect trace levels of the I− ions with certainty. The linear curve demonstrated a good linear relationship between I− ions with a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.999. This indicates the reliability of the proposed sensor and suggests that the concentration of I− ions can be accurately determined based on the observed response.
LOD = 3.3 SD/Slope
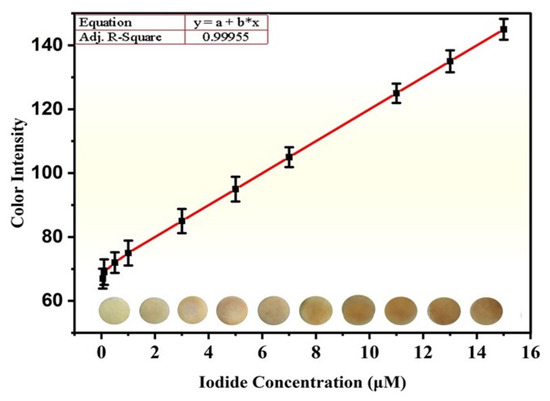
Figure 2.
Detection of I− ions under optimal conditions.
3.2.5. Selectivity of Iodide Assay
Achieving high chemical selectivity is an essential goal for any sensing platform, especially in situations where possible interference could exist and make detection difficult. As can be seen from Figure 3, except for I− ions, none of the ions tested produced a noticeable color change. Moreover, this response was selective and consistent with what is known about the behavior of halide ions during catalytic oxidation; I− ions are more catalytically active than fluoride (F−), chloride (Cl−), bromide (Br−), cyanide (CN−), sodium (Na+), aluminum (Al3+), magnesium (Mg2+), copper (Cu2+), and zinc (Zn2+) ions. I− ions are superior reducing agents because they are larger in size and have a greater tendency to donate electrons. Iodide functions as a reducing agent in the reaction between oxidized TMB and iodide ions, causing the oxidized TMB to return to its original state while the iodide itself oxidizes to produce iodine (I2).
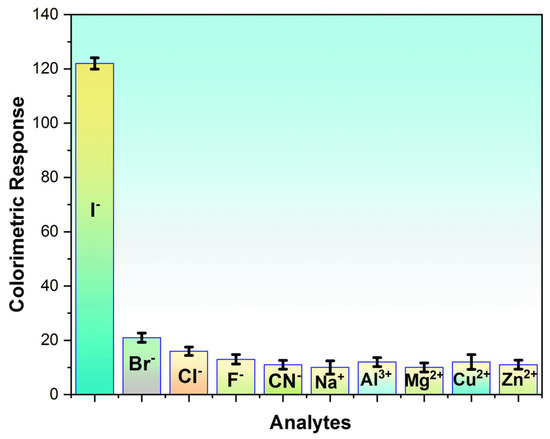
Figure 3.
Specificity against the interfering compounds.
In comparison, other halogens are poor reducing agents and they are smaller in size, and less likely to donate electrons in a redox reaction due to their high electronegativity. Because of differences in their chemical reactivity, metals like Na+, Mg2+, and others usually do not react immediately with TMB or H2O2. Highly electropositive cations, such as Na+ and Mg2+ ions, are able to donate electrons with ease to form stable ionic bonds with negatively charged ions or molecules. The minimal reaction induced by the inspected interferants highlighted the exceptional specificity of the suggested sensor to I− ions, thus validating its significant potential for implementation in intricate media encountered in industrial, medicinal, or food sample examination.
3.2.6. Stability Test for the Proposed Sensor
Stability makes an assay feasible and economical by guaranteeing its precision, sensitivity, repeatability, and reliability. Reliable data from stable colorimetric detection systems is necessary for environmental, medical, and scientific applications. The stability of the proposed sensor was evaluated by observing changes in the intensity of the color over a period of seven days under already-optimized conditions. The proposed sensor (Figure 4) revealed minimal performance changes, signifying its reasonable stability with an RSD value of less than 5%.
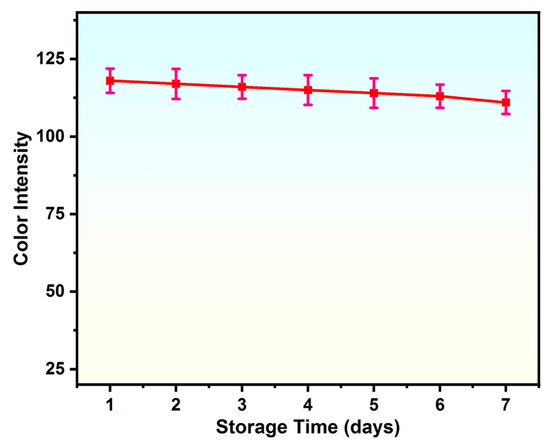
Figure 4.
Stability test of the proposed sensor.
3.2.7. Real Sample Analysis
Over the course of the study, an accurate assessment of the potential and reliability of the suggested sensing platform was carried out, taking into account a variety of real-world samples including biological samples like blood serum and urine, food samples like egg yolks and snacks, and tap water. As indicated in Table 1, to evaluate the sensor selectivity in real mediums, these samples were spiked with a known amount of I− ions. The suggested sensing platform was shown to be highly efficient in detecting I− ions based on the good range of percentage recoveries from these investigations (91.2% to 101.1%). This impressive recovery rate shows the sensor’s precision and durability in monitoring I− ion concentrations across a range of sample matrices, confirming its suitability for practical applications.

Table 1.
Real samples’ analysis and their recovery percentages obtained with the designed sensor.
The accuracy and reliability of the suggested sensor makes it an excellent tool for addressing significant challenges in environmental management, industrial quality control, and healthcare sectors.
4. Conclusions
The system’s colorimetric response significantly improved as a result of the proposed sensor’s successful catalysis of the chromogenic reaction between TMB and H2O2. This result highlighted the intrinsic biomimetic peroxidase-like activity of the sensor, suggesting that it may be a flexible and dependable analytical instrument. Several factors, such as pH, reaction time, gel concentration, H2O2 concentration, and TMB concentration, were carefully adjusted in order to maximize the sensor’s performance for the best results. The sensor was critical for its broad range of linear detection, with a low limit of detection. The sensor’s high accuracy and sensitivity in detecting target analytes showed a wide range of applications. Its remarkable sensitivity and selectivity allowed it to accurately identify I− ions in a variety of samples including biological specimens, food matrices, and environmental samples. Validation experiments with good recovery percentages ranging from 91.2% to 101.1% exhibited consistent performance and the potential use of the sensor for onsite monitoring.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors12060102/s1, Figure S1. Colorimetric reaction under various experimental conditions: (a) gel, (b) time, (c) TMB and (d) H2O2 optimization, and (e) pH; Table S1. Comparison of LODs of different reported sensors with the proposed sensor [25,31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
Author Contributions
A.K.: Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. H.A.: Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. A.Y.: Data curation, Methodology. A.T.J.: Software, data curation. S.J.: Writing, Visualization, Software: D.H.: Software, formal analysis, N.A.: Data curation, Validation, Writing—Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Program for Universities (NRPU-14816), and the Raid Technology Transfer Grant (RTTG-70) under the Higher Education Commission, HEC, Pakistan and the World Bank.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, J. Reverse flow injection spectrophotometric determination of iodate and iodide in table salt. Talanta 2004, 63, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. A highly selective and sensitive colorimetric sensor for iodide detection based on anti-aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Progress towards the Elimination of Iodine Deficiency Disorders (IDD); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; Volume 1, p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W. Age-specific thyrotropin references decrease over-diagnosis of hypothyroidism in elderly patients in iodine-excessive areas. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, K.; Sato, K.; Fujikawa, M.; Bandai, S.; Ikenoue, H.; Kitazono, T. Iodide-sensitive Graves’ hyperthyroidism and the strategy for resistant or escaped patients during potassium iodide treatment. Endocr. J. 2022, 69, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, E.; Berg, G.E.; Jansson, S.K.; Torring, O.; Valdemarsson, S.V. Thyroid Disease in Adults; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.-L.; Sung, Y.-M.; Wu, C.-H.; Wu, S.-P. Colorimetric sensing of iodide based on triazole-acetamide functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yang, P.-J.; Hasebe, K.; Haddad, P.R.; Tanaka, K. Rapid and direct determination of iodide in seawater by electrostatic ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 956, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Ichihara, T.; Zhuo, H.; Kumamoto, K.; Timerbaev, A.R.; Hirokawa, T. Determination of trace iodide in seawater by capillary electrophoresis following transient isotachophoretic preconcentration: Comparison with ion chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 497, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Mohammadzai, I.U.; Inoue, H.; Kumamaru, T. Chemiluminescence determination of iodide and/or iodine using a luminol–hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride reversed micelle system following on-line oxidation and extraction. Analyst 2000, 125, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, M.; Cespon, R. Indirect automatic determination of iodide by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 405, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, Q.; Ajab, H.; Farooq, M.; Shahzad, S.A.; Yaqub, A. Fabrication of colorimetric sensor using Fe3O4@Musa paradisiaca L. nanoparticles for detecting hydrogen peroxide: An application in environmental and biological samples. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 2841–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, P.; Domingo, G.J.; Gerdes, J. Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Yaqub, A.; Haq, M.Z.U.; Ajab, H.; Jafry, A.T.; Khan, M.K. Sensitive and cost-effective colorimetric sensor based on enzyme mimic MoS2@CoTiO3 nanocomposite for detection of hydrogen peroxide in milk and tap water. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 124, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liang, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Smartphone-based colorimetric sensor array using gold nanoparticles for rapid distinguishment of multiple pesticides in real samples. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, G.; Jafry, A.T.; Malik, S.; Shah, S.F.; Nishat, S.; Awan, F.R. Multifunctional rotational active valve for flow control in paper-based microfluidic devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 378, 133142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbach, S.; Jiang, N.; Moreddu, R.; Dong, X.; Kurz, W.; Wang, C.; Dong, J.; Yin, Y.; Butt, H.; Brischwein, M. Smartphone-based colorimetric detection system for portable health tracking. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, W.; Gao, H.-W.; Solin, N.; Hu, Z.; Uvdal, K. Selective colorimetric detection of copper (II) by a protein-based nanoprobe. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 252, 119462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasurya, S.; Syed, A.; Thomas, A.M.; Marraiki, N.; Al-Rashed, S.; Elgorban, A.M.; Raju, L.L.; Das, A.; Khan, S.S. Colorimetric detection of mercury ions from environmental water sample by using 3-(Trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate functionalized Ag NPs-tryptophan nanoconjugate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanikandan, R.; Ilanchelian, M. Simple smartphone merged rapid colorimetric platform for the environmental monitoring of toxic sulfide ions by cysteine functionalized silver nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2022, 174, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, T.; Ilanchelian, M. Colorimetric and visual detection of cyanide ions based on the morphological transformation of gold nanobipyramids into gold nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 4713–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Xie, W. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric sensor for H2O2 and Hg2+ detection based on homogeneous iodide with high peroxidase-mimicking activity. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhao, C.; Pan, C.; Li, F. Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric detection of iodide based on anti-aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichev, A.V.; Zieger, S.E.; Koren, K. Optical sensors (optodes) for multiparameter chemical imaging: Classification, challenges, and prospects. Analyst 2023, 149, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthupandi, M.; Chandhru, M.; Rani, S.K.; Vasimalai, N. Highly selective detection of iodide in biological, food, and environmental samples using polymer-capped silver nanoparticles: Preparation of a paper-based testing kit for on-site monitoring. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11372–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, Y.; Aikawa, S. Colorimetric detection of iodide ion by a nuclear fast red-based Hg2+ complex in aqueous media. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 67, 152877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Ahn, I.-H.; Sessler, J.L.; Cho, D.-G. Colorimetric iodide detection in water: A new photo-activated indicator system. Supramol. Chem. 2011, 23, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhu, L.; Lai, C.; Wang, H.; Zou, W.; Li, H. An easy and cost-effective colorimetric assay of hydrogen peroxide based on iodide-catalyzed oxidation of 3, 3′, 5, 5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 13100–13107. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Ajab, H.; Yaqub, A.; Ayub, K.; Yar, M.; Ullah, H. An experimental and theoretical aided 2D MoS2 nanoflowers strategy for rapid visual sensing of Gallic acid in food and clinical matrixes. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 20, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzdar, M.; Yaqub, A.; Hayat, A.; Haq, M.Z.U.; Khan, A.; Ajab, H. Paper based colorimetric sensor using novel green magnetized nanocomposite of pinus for hydrogen peroxide detection in water and milk. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, H.; Bui, B.; Wang, L.; Xing, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Hu, Z.; Chen, W. Nitrogen-doped fluorescence carbon dots as multi-mechanism detection for iodide and curcumin in biological and food samples. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1541–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, G.; Bessiere, J.; Walcarius, A. Cuprite-modified electrode for the detection of iodide species. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 59, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Colorimetric iodide recognition and sensing by citrate-stabilized core/shell Cu@ Au nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3911–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niaz, A.; Bibi, A.; Zaman, M.I.; Khan, M.; Rahim, A. Highly selective and ecofriendly colorimetric method for the detection of iodide using green tea synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-C.; Hsu, P.-H.; Lee, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-C. Selective detection of iodide and cyanide anions using gold-nanoparticle-based fluorescent probes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, L. Carbon dot/gold nanocluster-based fluorescent colorimetric paper strips for quantitative detection of iodide ions in urine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 9760–9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bian, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.; Zhang, J.; Huo, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Gel-sol and colorimetric dual-modal sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of iodide ions based on gelatin fabricated AuNPs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).