Can Nano Yield Big Insights? Oligonucleotide-Based Biosensors in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
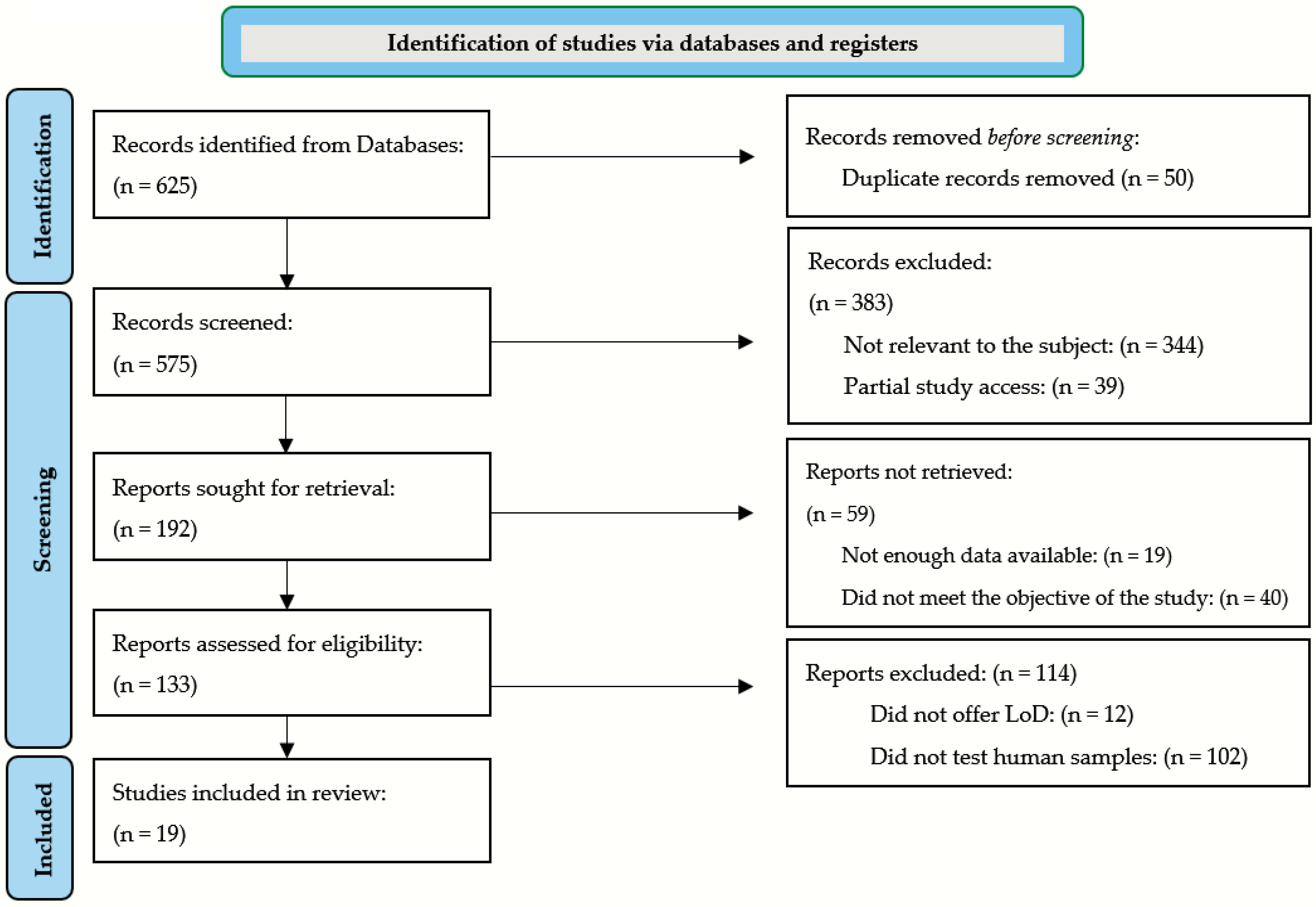
2. Methods
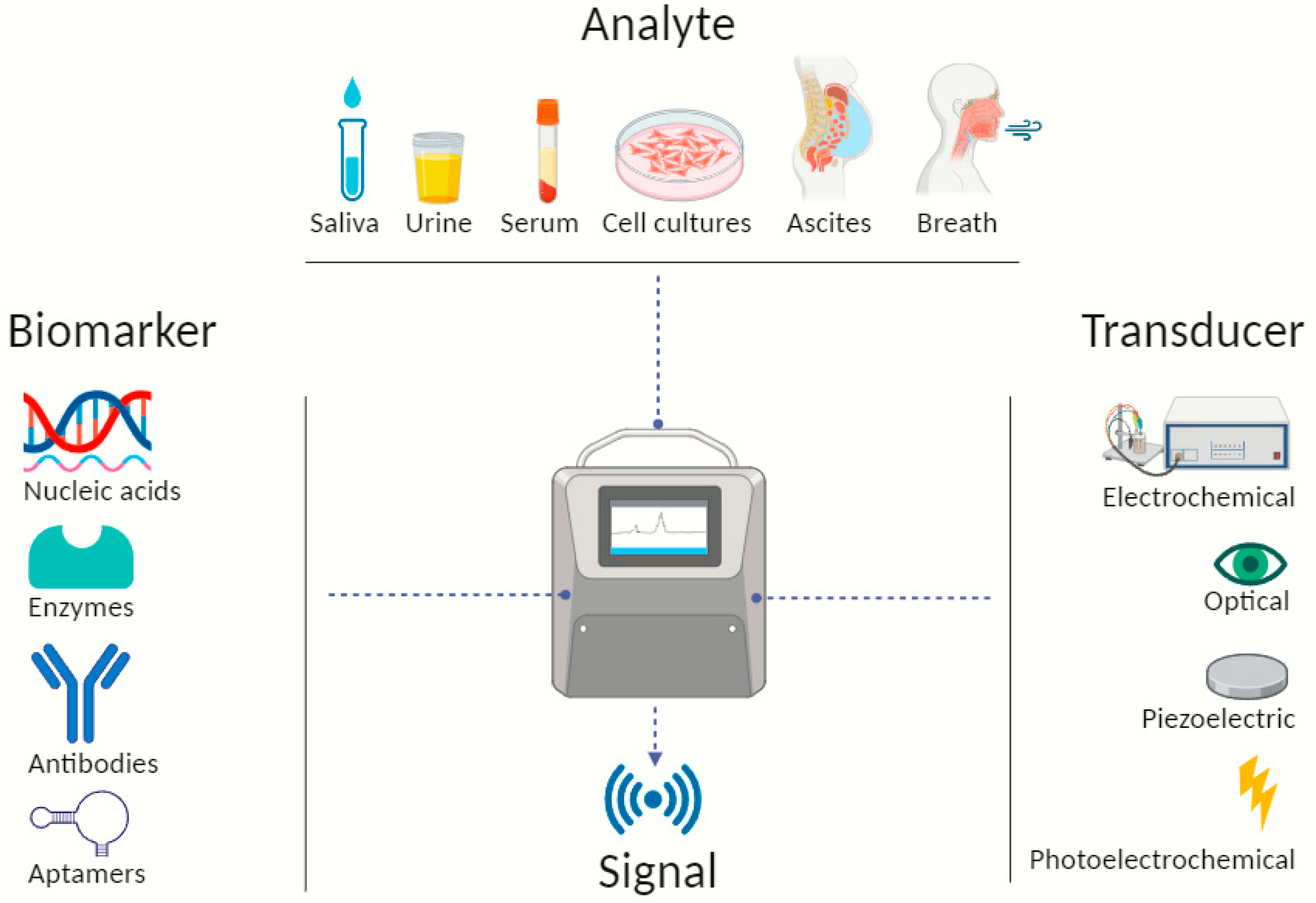
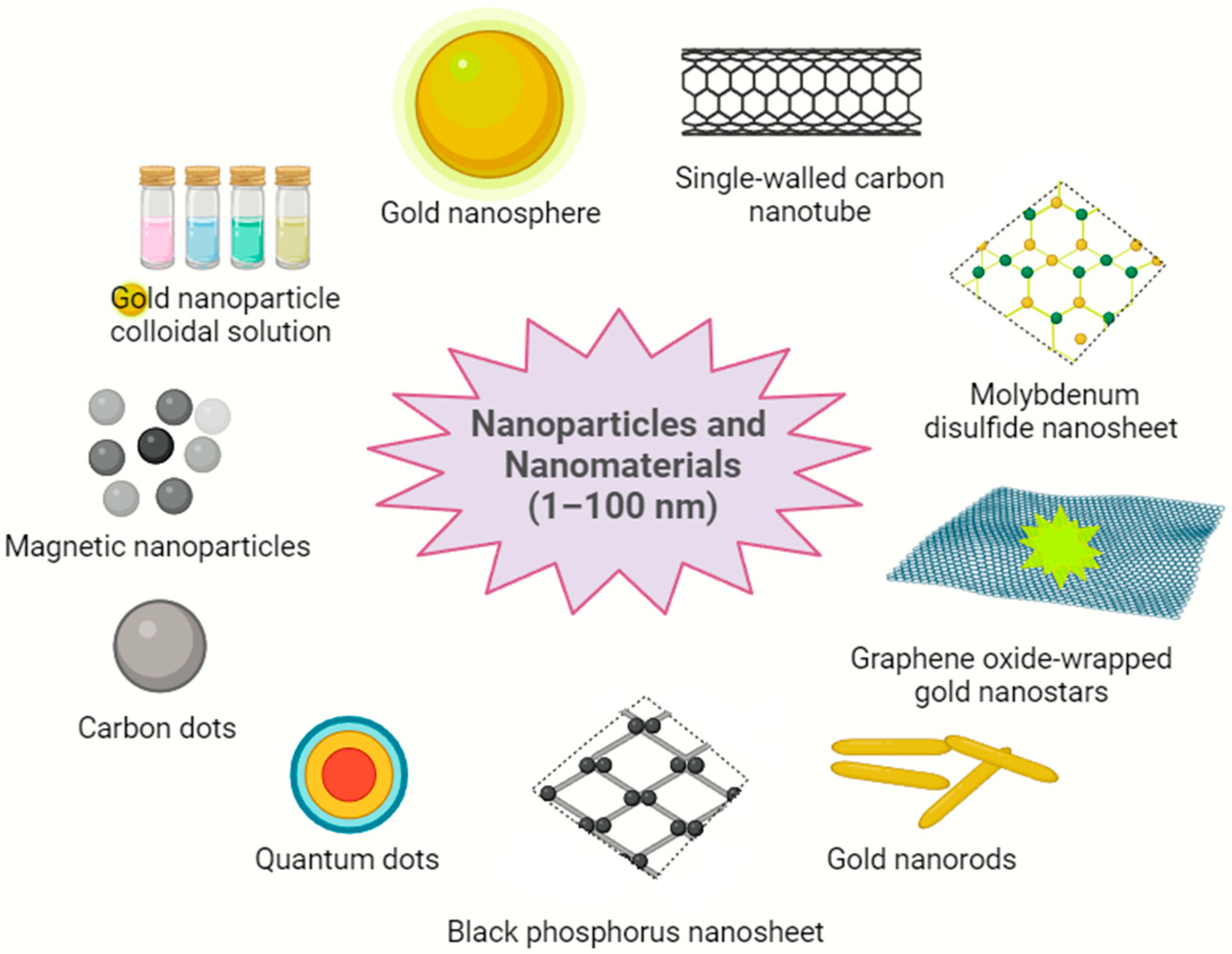
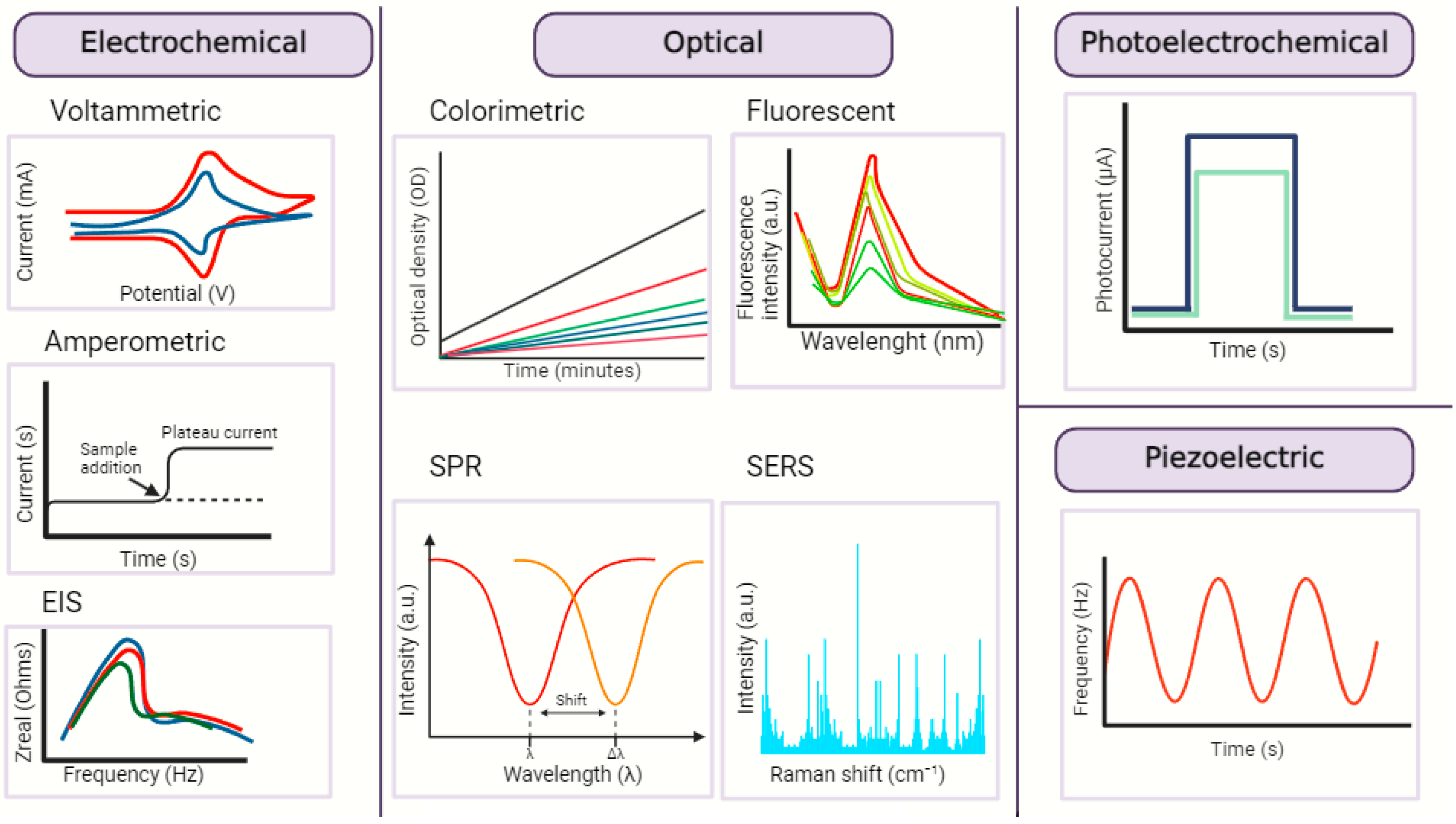
3. Nanobiosensors—Sensing Mechanism and Attributes
4. DNA Nanobiosensors in GC
| Sensing Platform | Transducer | Biomarker | Human Sample | LoD | Takeaways | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-density “hot spot” AuNPs@SiO array substrate with RCA strategy | Optical (SERS) | M.SssI | Serum | 2.51 × 10−4 U mL−1 | Simple preparation, high biocompatibility, uniformity, reproducibility, stability | [56] |
| Polymeric l-arginine and rGO-AuNSs on glass electrode | Electrochemical (CV) | PIK3CA ctDNA | 1.0 × 10−20 M | Label-free, desirable stability, wide dynamic response | [57] | |
| SWCN DMEJ with DNA–gold urchin | Electrochemical (IDE) | SOX-17 | 1 aM | High performance, efficiency, biocompatibility, no cross-reactivity | [58] | |
| Nitrophenyl-functionalized black phosphorus nanosheets and FAM labelling | Optical (fluorescence) | PIK3CA E542K ctDNA | Tumor cell lines | 50 fM | Enzyme-free, long-term stability, simple manufacturing process, good discrimination ability of interferences | [59] |
| Nanoplasmonic, nanogold-linked sorbent assay | Optical (FOPPR and FONLISA) | Methylated SOCS-1 | Tumor tissue and cell lines | 0.81 fM | PCR- and amplification-free, label- and sequencing-free; superior to PCR and other assays | [60] |
5. RNA Nanobiosensors in GC
| Sensing Platform | Transducer | Biomarker | Human Sample | LoD | Takeaways | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackberry-like magnetic DNA/FMMA nanospheres on gold stir-bar using CHA-HCR and RAFT amplification | Electrochemical (V) | miR-106a | Serum | 0.68 aM | Enzyme-free, simple nanomaterials, acceptable storage stability, RNA extraction-free, sample pretreatment-free technique, high recovery | [74] |
| Gold–magnetic NPs single-strand (ss) probe 1 (P1) | Electrochemical (EIS, CV, DPV) | miR-106a | Serum | 0.3 fM | Great performance, stability, simplicity, reproducibility, agreeable storage stability | [75] |
| AuNPs and CdSe@CdS QDs-contained magnetic nanocomposites labels with polythiophene/rGO-modified carbon electrodes | Electrochemical (CV, DPV) | miR-106a let-7a | Plasma | 0.06 fM (miR-106a) 0.02 fM (let-7a) | Multiplexing, good recovery, reproducibility, appropriate storage stability | [76] |
| AgNRs array coated by the mF-MoS2 NSs, dual mode detection assay | Optical (SERS) and electrochemical (SWV) | miR-106a | Serum | 67.44 fM 248.01 fM | In situ, stability, reliability, reproducibility, minimal interference | [77] |
| Perovskite–graphene oxide nanocomposite on an electrode, genosensing assay | Electrochemical (chronoamperometry) | miR-21 | Cell lines | 2.94 fM | Label-free, reproducibility, reusability, stability, versatility, robustness | [78] |
| Ratiometric strategy using CDs with triple function and FAM-labeled ssDNA | Optical (fluorescence) | miR-21 | Plasma | 1 pM | Reproducibility, reliability, simplicity, strong anti-interference ability, excellent performance | [79] |
| Two-stage cyclic enzymatic amplification with T4 RNA ligase 2 and T7 exonuclease and AuNPs | Electrochemical (DPV) | miR-21 | Serum | 0.36 fM | Convenience, reproducibility, excellent performance, stability | [80] |
| MXene-derivative QDs (Mo2TiC2 QDs) and SnS2 nanosheets/lipid bilayer | Electrochemical and optical (voltammetry and fluorescence) | miR-27a-3p | Ascites | 1 fM | Reproducibility, low background noise, wide dynamic range, good stability, minimal interference | [81] |
| “Hot spot” bismuth nano-nest/Ti3CN QD- SPC-ECL | Electrochemical and optical (voltammetry and fluorescence) | miR-421 | Ascites | 0.3 fM | Improved luminescence and catalytic activity, stability, controllability | [82] |
| Dual-response–single-amplification nanomachine | Optical (fluorescence) | miR-5585-5p & PLS3 mRNA | Serum | 1.19 fM (miR-5585-5p) 16.37 fM (PLS3) | Enzyme-free, extraction-free, high recovery, great performance | [83] |
| CPs/AuNP-AuE with DSN | Electrochemical (chronoamperometry and CV) | miR-100 | Serum | 100 aM | Enzyme-free, reliability, controllability, effectiveness | [84] |
6. Exosomes-Based Nanobiosensors in GC
| Sensing Platform | Transducer | Biomarker | Human Sample | LoD | Takeaways | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2 QDs-MXene heterostructure and AuNPs@biomimetic lipid layer | Electrochemical and optical (V and fluorescence) | Exosomal miR-135b | Ascites | 10 fM | Versatility, reproducibility, reliability, low background noise, high accuracy; large surface area, excellent flexibility and superior conductivity of substrates, excellent antifouling property | [92] |
| “Hot spot” AuNSs-decorated MoS2 nanocomposite (MoS2-AuNSs) aptasensors | Optical (SERS) | CD63 of exosomes | Serum | 17 particles μL−1 | Reliability, reproducibility, good stability long term, excellent Raman enhancement effect and generability in bioanalysis | [14] |
7. Bench to Clinic: Trials
- Limited sample size;
- Lack of an independent sample set for blind validation before building DFA models;
- The nanomaterial-based sensors are typically more sensitive to certain classes of VOCs and less sensitive to other classes;
- Absence of histology data;
- Exclusion criteria included medication for gastric upset (common in this population)
- The origin of other VOCs cannot yet be easily understood;
- Cautious interpretation, particularly for the VOCs in room air samples below the limit of quantification.
8. Discussion—The Other Side of the Coin
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Stomach. Globocan. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/7-Stomach-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Xu, Z.-Q.; Broza, Y.Y.; Ionsecu, R.; Tisch, U.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.; Song, Q.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Xiong, F.-X.; Gu, K.-S.; et al. A nanomaterial-based breath test for distinguishing gastric cancer from benign gastric conditions. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdecchia, A.; Francisci, S.; Brenner, H.; Gatta, G.; Micheli, A.; Mangone, L.; Kunkler, I.; EUROCARE-4 Working Group. Recent cancer survival in Europe: A 2000–2002 period analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, L.; Jiang, X.; Luo, D.; Yang, D. Non-invasive detection of gastric cancer relevant d -amino acids with luminescent DNA/silver nanoclusters. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 19367–19373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roukos, D.H. Current status and future perspectives in gastric cancer management. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2000, 26, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necula, L.; Matei, L.; Dragu, D.; I Neagu, A.; Mambet, C.; Nedeianu, S.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Chivu-Economescu, M. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrift, A.P.; El-Serag, H.B. Burden of Gastric Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.; Peleteiro, B.; Malvezzi, M.; Bosetti, C.; Bertuccio, P.; Levi, F.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Lunet, N. Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1330–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmarcher, T.; Lindgren, P. Cost of All Digestive Cancers in Europe Exceeds 40 Billion Euro. Digestive Cancers Europe, 14 October 2020. Available online: https://digestivecancers.eu/new-study-cost-of-all-digestive-cancers-in-europe-exceeds-40-billion-euro/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- The Economic Burden of Digestive Cancers in Europe. Digestive Cancers Europe. 2020. Available online: https://europacolonpolska.pl/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/DICE_WhitePaper_HealthEcoStudy_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Li, M.; Jiang, F.; Xue, L.; Peng, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, C.; et al. Recent Progress in Biosensors for Detection of Tumor Biomarkers. Molecules 2022, 27, 7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta-Melo, A.R.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Libânio, D.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M. Missing rate for gastric cancer during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincze, Á. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment in gastric cancer: Current evidence and new perspectives. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1122454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Dong, Y.; Gong, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, C.; Ge, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chao, J.; Su, S.; et al. Sensing gastric cancer exosomes with MoS2-based SERS aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 215, 114553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rød, A.M.K.; Harkestad, N.; Jellestad, F.K.; Murison, R. Comparison of commercial ELISA assays for quantification of corticosterone in serum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.P. Double-Contrast Barium Meal and Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A Comparative Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 101, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fu, Z.; Yan, F.; Ju, H. Biomedical and clinical applications of immunoassays and immunosensors for tumor markers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jin, W.; Wan, C.; Zhu, C. Diagnostic value of combined detection of CA72-4, CA19-9, and carcinoembryonic antigen comparing to CA72-4 alone in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.-M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Lee, Y.-C.; Sheu, B.-S.; Sugano, K.; Cheng, H.-C.; Yeoh, K.-G.; Hsu, P.-I.; Goh, K.-L.; Mahachai, V.; et al. Screening and eradication of Helicobacter pylori for gastric cancer prevention: The Taipei global consensus. Gut 2020, 69, 2093–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.J.; Kim, B.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Jang, M.S.; Kim, K.-M. PD-L1 expression in paired biopsies and surgical specimens in gastric adenocarcinoma: A digital image analysis study. Pathol.—Res. Pract. 2021, 218, 153338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, S.I.; Ko, G.H.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Hong, S.C.; Ha, W.S. CD44 Variant 9 Serves as a Poor Prognostic Marker in Early Gastric Cancer, But Not in Advanced Gastric Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 48, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Umapathy, V.R.; Natarajan, P.M.; Swamikannu, B.; Moses, J.; Jones, S.; Chandran, M.P.; Anbumozhi, M.K. Emerging Biosensors for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis—A Review Unravelling Their Role in Past and Present Advancements in the Field of Early Diagnosis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, W.; He, Y.; Xu, L.; Fu, F. A microfluidic chip-based fluorescent biosensor for the sensitive and specific detection of label-free single-base mismatch via magnetic beads-based ‘sandwich’ hybridization strategy. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ai, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, S.; Guan, W. Nanotechnology-based strategies for gastric cancer imaging and treatment. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35392–35407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T. Nanotechnology in cancer diagnosis: Progress, challenges and opportunities. J. Hematol. Oncol. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Biosensors applications in medical field: A brief review. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Guleria, P. Application of DNA-Nanosensor for Environmental Monitoring: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, R.; Fatima, I.; Sargazi, S.; Rahdar, A.; Karamzadeh-Jahromi, M.; Pandey, S.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Bilal, M. Novel Perspectives towards RNA-Based Nano-Theranostic Approaches for Cancer Management. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.A.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Recent Advances in the Development and Analytical Applications of Biosensing Probes. C R C Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1988, 20, 149–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, D.; Francia, G.; Natale, C.; Neri, G.; Seeber, R.; Tajani, A. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors in Italy: A Review of the 2015 Literature. Sensors 2017, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical–Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2019, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Payam, A.F. Opportunities and Challenges for Biosensors and Nanoscale Analytical Tools for Pandemics: COVID-19. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7783–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M. Design, Optimization and Application of Small Molecule Biosensor in Metabolic Engineering. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Jiang, K.; Jiang, X.; Pan, J.; Wen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Weng, S.; Lan, S.; Nie, K.; Zheng, Z.; Ji, S.; et al. Current Evidence and Future Perspective of Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Application for Early Gastric Cancer Diagnosis With Endoscopy: A Systematic and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 629080. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2021.629080 (accessed on 18 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Car, L.T.; Papachristou, N.; Urch, C.; Majeed, A.; El–Khatib, M.; Aylin, P.; Atun, R.; Car, J.; Vincent, C. Preventing delayed diagnosis of cancer: Clinicians’ views on main problems and solutions. J. Glob. Health 2016, 6, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Gastric Cancer in Young Adults: A Different Clinical Entity from Carcinogenesis to Prognosis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 9512707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaza, A.; Josué, B.M.; Gloire, B.; Ganywamulume, B.; Justin, M.; Désiré, A.M. Gastric cancer for young adults: Case series of three cases. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2023, 110, 108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, W. Primary care system outdated and inconvenient for many millennials. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2018, 190, E1430–E1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, K.B.; Oosthuizen, F.; Bonsu, A.B. Cancer awareness among community pharmacist: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomers, V.L.M.N.; Lidington, E.; Sirohi, B.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Darlington, A.-S.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; Husson, O. The Prolonged Diagnostic Pathway of Young Adults (Aged 25–39) with Cancer in the United Kingdom: Results from the Young Adult Cancer Patient Journey Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subasinghe, D.; Mahesh, P.K.B.; Wijesinghe, G.K.; Sivaganesh, S.; Samarasekera, A.; Lokuhetty, M.D.S. Delay in diagnosis to treatment and impact on survival of gastric adenocarcinoma in a low income setting without screening facility. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Early cancer diagnosis saves lives, cuts treatment costs. Saudi Med. J. 2017, 38, 328–329. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, E.C.; Powell, J.M.; Clevinger, T.B.; Fairman, A.E.; Shukla, A. Advances in Biosensors and Diagnostic Technologies Using Nanostructures and Nanomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Suh, Y.D.; Lee, J.; Lee, P.; Han, S.; Hong, S.; Yeo, J.; Lee, H.; Ko, S.H. Recent progress in silver nanowire based flexible/wearable optoelectronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7445–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, J.; Zhu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Z.; Luo, K. Recent advances in development of dendritic polymer-based nanomedicines for cancer diagnosis. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 13, e1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, G.; Bütün, I.; Muganlı, Z.; Kozalak, G.; Namlı, I.; Sarraf, S.S.; Ahmadi, V.E.; Toyran, E.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Koşar, A. Biomedical Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amperometric Biosensors. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/13201 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Ma, W.; Du, H.; Zhang, M.; Mori, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. One-Step Synthesis of Tunable Zinc-Based Nanohybrids as an Ultrasensitive DNA Signal Amplification Platform. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electrochemical Biosensors—An overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/electrochemical-biosensors (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Guy, O.J.; Walker, K.-A.D. Chapter 4—Graphene Functionalization for Biosensor Applications. In Silicon Carbide Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Saddow, S.E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 85–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwen, L.; Zhang, S.; Chao, J. Recent Advances in DNA Nanotechnology-Enabled Biosensors for Virus Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, M.; Wasowicz, B.; Rymaszewska, A. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): The Better Sibling of PCR? Cells 2021, 10, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Ran, M.; Mao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Cao, X. A novel DNA biosensor for the ultrasensitive detection of DNA methyltransferase activity based on a high-density ‘hot spot’ SERS substrate and rolling circle amplification strategy. Analyst 2021, 146, 5326–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Niu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhou, C.; Tang, N.; Jin, H.; Cui, D. Electrochemical Biosensor Based on l -Arginine and rGO-AuNSs Deposited on the Electrode Combined with DNA Probes for Ultrasensitive Detection of the Gastric Cancer-Related PIK3CA Gene of ctDNA. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 5094–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Anbu, P. Single-walled carbon nanotube-gold urchin nanohybrid for identifying gastric cancer on dimicroelectrodes junction. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 121, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Cui, H.; Wu, L.; Yang, N.; Zhou, W.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, X.-F. Sensitive and selective ctDNA detection based on functionalized black phosphorus nanosheets. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthula, L.S.; Yeh, K.-T.; Huang, W.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Huang, C.-J.; Chau, L.-K.; Chan, M.W.; Lin, S.-H. Quantitative and amplification-free detection of SOCS-1 CpG methylation percentage analyses in gastric cancer by fiber optic nanoplasmonic biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 214, 114540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpu, Y.; Cordelier, P.; Cho, W.C.; Torrisani, J. DNA Methylation and Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15029–15058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammann, R.H.; Richter, A.M.; Jiménez, A.P.; Woods, M.; Küster, M.; Witharana, C. Impact of Natural Compounds on DNA Methylation Levels of the Tumor Suppressor Gene RASSF1A in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.M.; Managò, S.; Mangini, M.; De Luca, A.C. Biosensing Using SERS Active Gold Nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jiménez, A.I.; Lyu, D.; Lu, Z.; Liu, G.; Ren, B. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Benefits, trade-offs and future developments. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4563–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ge, S.; Hua, W.; Zhou, X.; Lu, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Qian, Y. A pump-free and high-throughput microfluidic chip for highly sensitive SERS assay of gastric cancer-related circulating tumor DNA via a cascade signal amplification strategy. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Su, L.; Qian, C. Circulating tumor DNA: A promising biomarker in the liquid biopsy of cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48832–48841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquid Biopsy: The Value of Different Bodily Fluids—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35073730/ (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Dang, D.K.; Park, B.H. Circulating tumor DNA: Current challenges for clinical utility. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittla, P.; Kaur, S.; Sojitra, V.; Zahra, A.; Hutchinson, J.; Folawemi, O.; Khan, S. Exploring Circulating Tumor DNA (CtDNA) and Its Role in Early Detection of Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e45784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, S.; Xie, H.; Peng, X.; Yin, W.; Tao, Y.; et al. miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayi, M.; Farjami, Z.; Hosseini, Z.S.; Ebrahimi, N.; Abouzari-Lotf, E. MicroRNA-based Biosensors for Early Detection of Cancers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 24, 4675–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Su, X. Sensing of circulating cancer biomarkers with metal nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 22152–22171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radfar, S.; Ghanbari, R.; Isfahani, A.A.; Rezaei, H.; Kheirollahi, M. A novel signal amplification tag to develop rapid and sensitive aptamer-based biosensors. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 145, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshpour, M.; Omidfar, K.; Ghanbarian, H. A novel electrochemical nanobiosensor for the ultrasensitive and specific detection of femtomolar-level gastric cancer biomarker miRNA-106a. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshpour, M.; Karimi, B.; Omidfar, K. Simultaneous detection of gastric cancer-involved miR-106a and let-7a through a dual-signal-marked electrochemical nanobiosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, H.; Peng, Q.; Gan, H.; Su, S.; Yuwen, L.; Song, C. SERS/electrochemical dual-mode biosensor based on multi-functionalized molybdenum disulfide nanosheet probes and SERS-active Ag nanorods array electrodes for reliable detection of cancer-related miRNA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 368, 132245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi-Derakhshi, P.; Mahmoudi, E.; Majidi, M.M.; Sohrabi, H.; Amini, M.; Majidi, M.R.; Niaei, A.; Shaykh-Baygloo, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. An Ultrasensitive miRNA-Based Genosensor for Detection of MicroRNA 21 in Gastric Cancer Cells Based on Functional Signal Amplifier and Synthesized Perovskite-Graphene Oxide and AuNPs. Biosensors 2023, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Hao, X.; Miao, C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, X.; Weng, S. Ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on carbon dots as internal reference signal and T7 exonuclease-assisted signal amplification strategy for microRNA-21 detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1103, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, F.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, W.; Yin, H.; Ai, S.; Zhang, X. Two-stage cyclic enzymatic amplification method for ultrasensitive electrochemical assay of microRNA-21 in the blood serum of gastric cancer patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Ma, Q. A novel bimetallic MXene derivative QD-based ECL sensor for miRNA-27a-3p detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 228, 115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Liang, Z.; Wang, D.; Nie, Y.; Ma, Q. Bismuth Nano-Nest/Ti3CN Quantum Dot-Based Surface Plasmon Coupling Electrochemiluminescence Sensor for Ascites miRNA-421 Detection. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9706–9713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tong, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Luan, D.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Du, L.; et al. The Dual-Response–Single-Amplification Fluorescent Nanomachine for Tumor Imaging and Gastric Cancer Diagnosis. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 16553–16564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Wan, H.; Zhang, X. Electrochemical detection of miRNA-100 in the sera of gastric cancer patients based on DSN-assisted amplification. Talanta 2021, 225, 121981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.-J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zheng, J.-N.; Pei, D.-S. MiR-106a: Promising biomarker for cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5373–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Yeo, J.-S. On-chip plasmonic detection of microRNA-106a in gastric cancer using hybridized gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, M.R.M.; Parhizkar, J. Au nanoparticles/g-C3N4 modified biosensor for electrochemical detection of gastric cancer miRNA based on hairpin locked nucleic acids probe. Nanomedicine Res. J. 2020, 5, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, D.; Krishnan, R.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Rajasekaran, B.; Islam, V.I.H.; Sekar, P. Significance of microRNA 21 in gastric cancer. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2016, 40, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Schwarz, H.; Nanda, H.S.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Exosomes, a New Star for Targeted Delivery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 751079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Fu, K.; Zhang, Q. Advances of exosomes-based applications in diagnostic biomarkers for dental disease and dental regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 229, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Nie, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Ma, Q. MoS2 QDs-MXene heterostructure-based ECL sensor for the detection of miRNA-135b in gastric cancer exosomes. Talanta 2023, 259, 124559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- cfDNA Assay Prospective Observational Validation for Early Cancer Detection and Minimal Residual Disease (CAMPERR). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05366881?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=14&rank=136 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Early Detection of Five Common Cancers Using the ctDNA Analysing Test (K-DETEK). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05227261?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=11&rank=103 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Preliminary Experimental Study on Key Technologies for Early Screening of Gastric Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05991947?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=5&rank=48 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Gastric Cancer Early Detection by Multi-dimensional Analysis of cfDNA. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05668910?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=4&rank=40 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Early Detection of Gastric Cancer Using Plasma Cell-free DNA Fragmentomics. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05269056?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=4&rank=36 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Gastric Cancer Screening and Alarm Symptoms in Early Gastric Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01659632?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=5&rank=43 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- OLGA Stage Is More Appropriate in Predicting Early Gastric Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02562976?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=3&rank=28 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Methylation Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA in Gastric Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04511559?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=3&rank=27 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Screening for Early Gastric Cancer in Shaanxi Province. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05291728?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=3&rank=23 (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- The EpiGASTRIC/EDGAR Project: New Strategies for the Early Detection and Prevention of Gastric Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05551416?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=2&rank=15 (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Detection of Methylated Reprimo in Plasma for Asymptomatic Gastric Cancer (DEMRAC). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01774266?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=2&rank=14 (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- BLI for the Diagnosis of Precancerous Conditions and Cancerous Lesions. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04768218?cond=Early%20Gastric%20Cancer&term=Diagnosis&page=2&rank=13 (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Study of the Exhaled Breath and Salivary Metabolites of Patients with Malignant or Benign Gasctric Lesions (DGLES2013). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01420588?cond=NCT01420588&rank=1 (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- Amal, H.; Leja, M.; Funka, K.; Skapars, R.; Sivins, A.; Ancans, G.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Kikuste, I.; Lasina, I.; Haick, H. Detection of precancerous gastric lesions and gastric cancer through exhaled breath. Gut 2016, 65, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discriminant Factor Analysis of 31P NMR Spectroscopic Data in Myopathies—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2314212/ (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Xiang, L.; Wu, S.; Hua, Q.; Bao, C.; Liu, H. Volatile Organic Compounds in Human Exhaled Breath to Diagnose Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 606915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demonstrating the Diagnostic Power of an Electronic Nose: Study on Exhaled Air Samples (OLFADIAG). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03721042?cond=Gastric%20Cancer&term=nano&rank=4 (accessed on 4 November 2023).
- Krishnamoorthy, S. Nanostructured sensors for biomedical applications—A current perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 34, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, H.; Shao, H.; Park, Y.I.; Peterson, V.M.; Castro, C.M.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inci, F.; Tokel, O.; Wang, S.; Gurkan, U.A.; Tasoglu, S.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Nanoplasmonic Quantitative Detection of Intact Viruses from Unprocessed Whole Blood. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4733–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Plasmonic Chip for Biomarker Discovery and Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.dbproxy.umfiasi.ro/25038825/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Zavaleta, C.L.; Garai, E.; Liu, J.T.C.; Sensarn, S.; Mandella, M.J.; Van de Sompel, D.; Friedland, S.; Van Dam, J.; Contag, C.H.; Gambhir, S.S. A Raman-based endoscopic strategy for multiplexed molecular imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2288–E2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar-Lopez, F.J. Recent Progress in Micro- and Nanotechnology-Enabled Sensors for Biomedical and Environmental Challenges. Sensors 2023, 23, 5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasooly, A. Moving biosensors to point-of-care cancer diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| GC—Non-Malignant Gastric Conditions | Early-Stage GC vs. Late-Stage GC | GC vs. OLGIM III-IV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [2] | [106] | [2] | [106] | |
| Accuracy | 90% | 92% | 91% | 90% |
| Sensitivity | 89% | 73% | 89% | 93% |
| Specificity | 90% | 98% | 94% | 80% |
| Trial | Number of Patients | Compound | LoD (ppb) | Less Severe Condition Concentration Range (ppb) | Gastric Ulcer Concentration Range (ppb) | GC Concentration Rage (ppb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [2] | 130 | 2-propene-nitrile | 1.34 | 2.62 ± 0.57 | 3.65 ± 1.06 | 4.24 ± 1.28 |
| furfural | 1.37 | 1.88 ± 0.18 | 2.09 ± 0.17 | 2.32 ± 0.22 | ||
| 6-methyl-5- | 1.88 | 4.12 ± 0.98 | 6.03 ± 1.50 | 6.05 ± 1.18 | ||
| [106] | 484 | 2-propene-nitrile | 1.3 | 7.5 ± 6.2 | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 13.2 ± 13.7 |
| hexadecane | 2.3 | 4.2 ± 4.0 | 3.0 ± 2.1 | 10.7 ± 12.3 | ||
| 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene | 2.7 | 11.6 ±7.7 | 12.0 ±7.8 | 20.0 ± 13.6 | ||
| 2-butanone | 2.9 | 90 ± 43.1 | 89.5 ±83.0 | 68.3 ± 49.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avanu, A.E.; Ciubotariu, A.M.; Dodi, G. Can Nano Yield Big Insights? Oligonucleotide-Based Biosensors in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12030044
Avanu AE, Ciubotariu AM, Dodi G. Can Nano Yield Big Insights? Oligonucleotide-Based Biosensors in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvanu, Alexandra E., Alexandra M. Ciubotariu, and Gianina Dodi. 2024. "Can Nano Yield Big Insights? Oligonucleotide-Based Biosensors in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer" Chemosensors 12, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12030044
APA StyleAvanu, A. E., Ciubotariu, A. M., & Dodi, G. (2024). Can Nano Yield Big Insights? Oligonucleotide-Based Biosensors in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. Chemosensors, 12(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12030044








