Cleavage Reaction Lateral Flow Assays for Salivary Pepsin Measurement Using a Pepsin-Susceptible Peptide Substrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
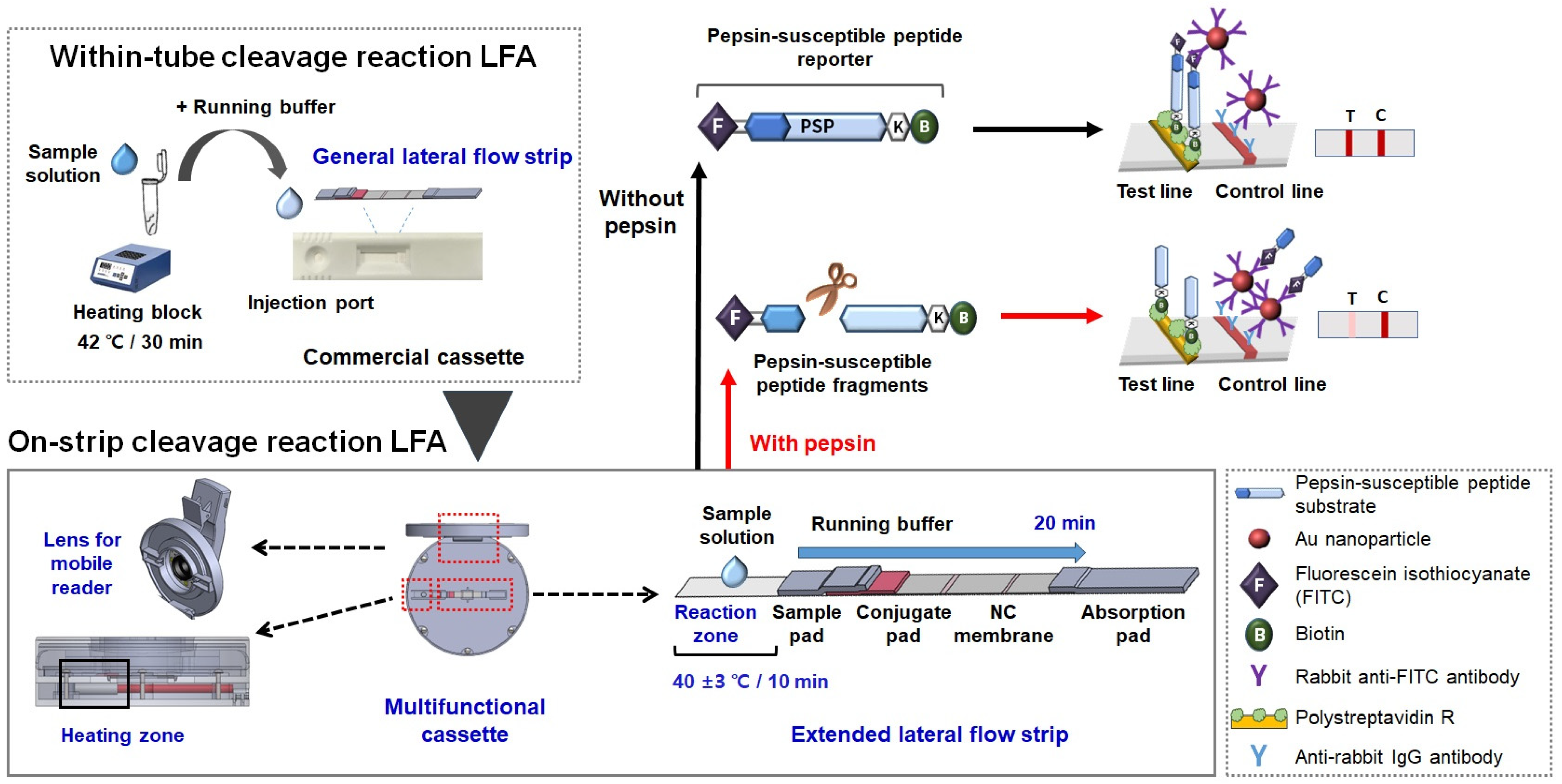
2.2. Preparing the Two Types of Lateral Flow Strips
2.3. Detecting Pepsin Using the Within-Tube Cleavage Reaction LFAs
2.4. Fabricating the Multifunctional Strip Cassette Integrated with a Heating Pad and Mobile Reader
3. Results and Discussion
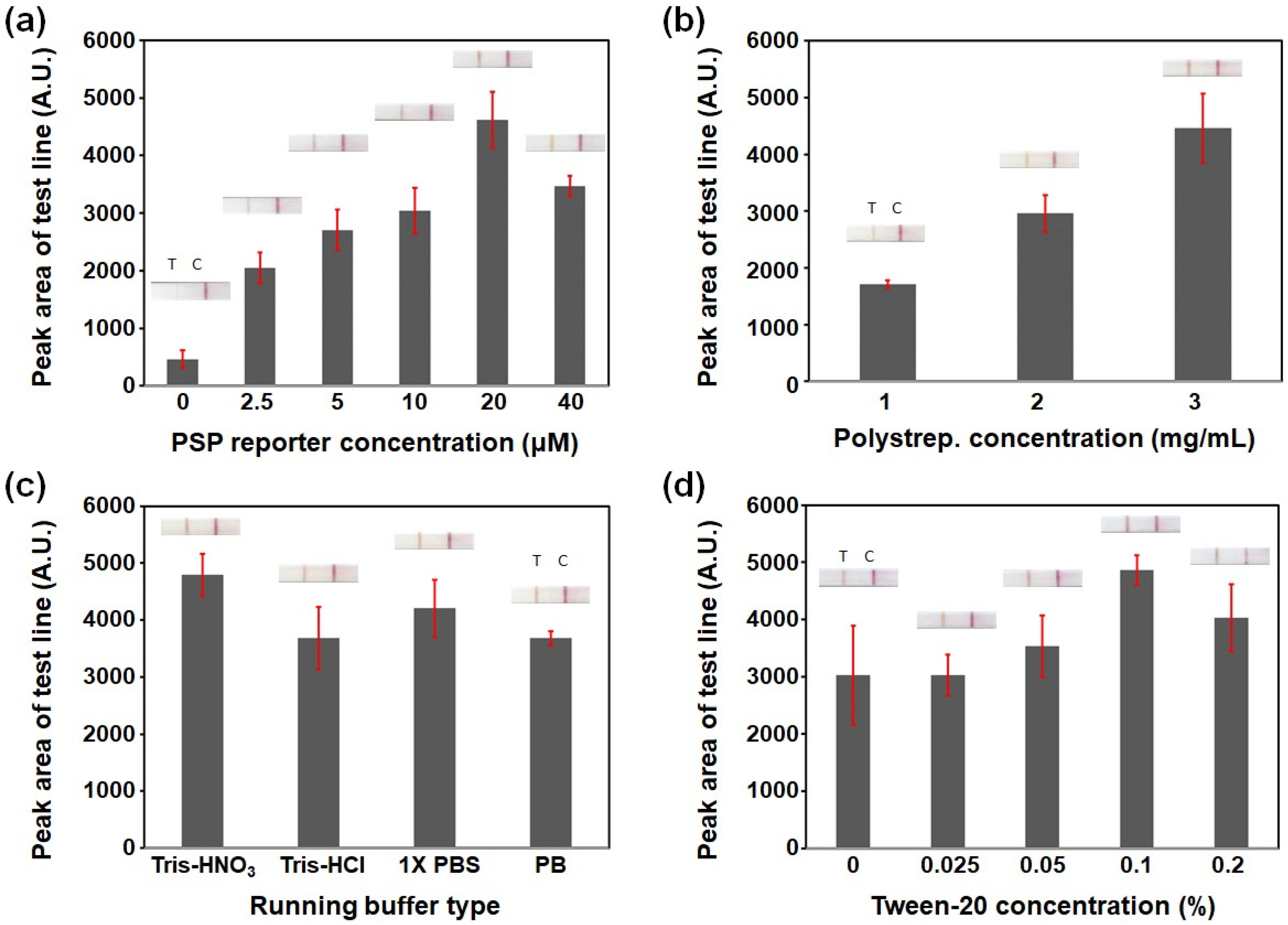
3.1. Optimizing the PSP-Based Cleavage Reaction LFA Conditions: pSA and PSP Reporter Concentrations and Running Buffer Composition
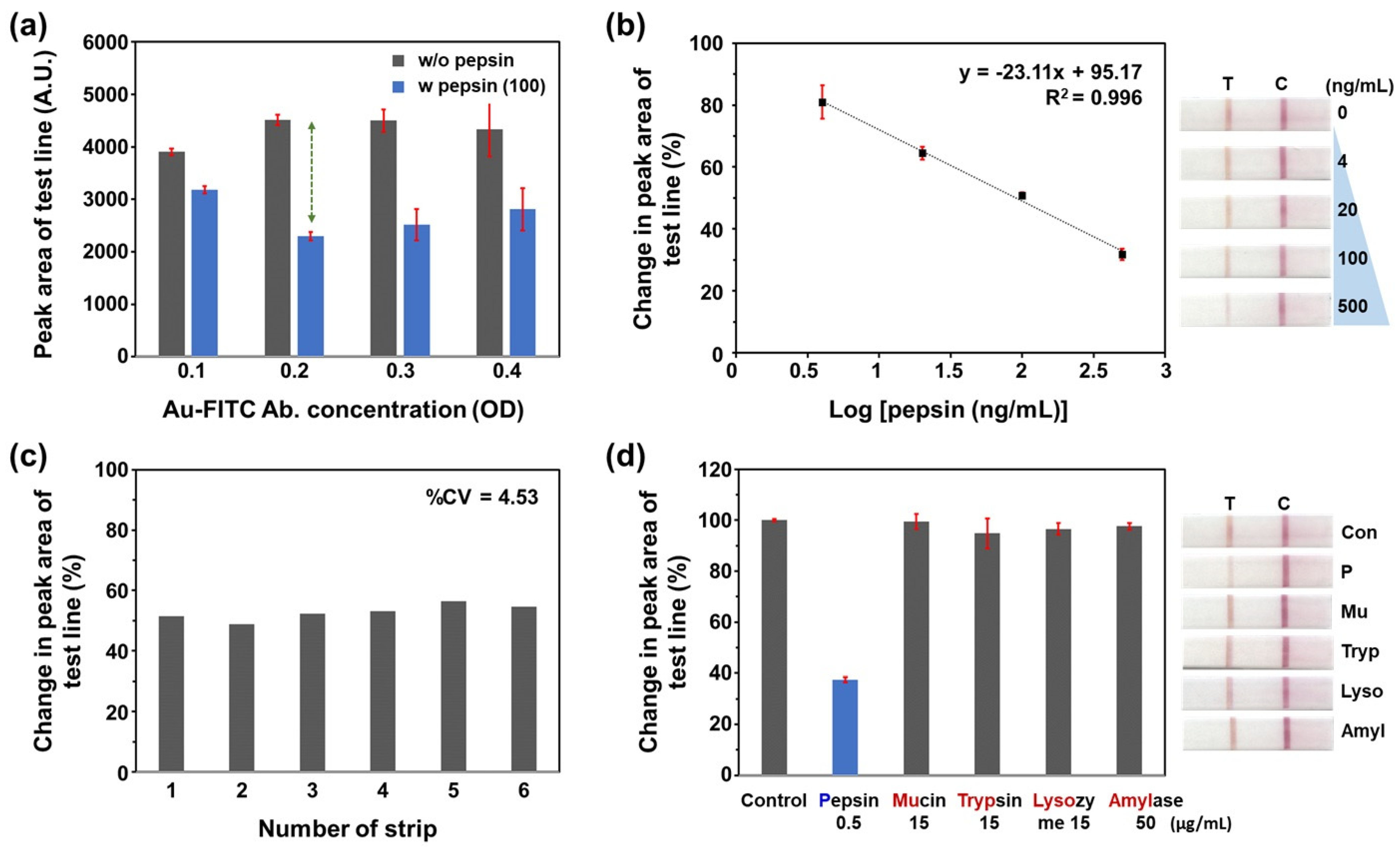
3.2. Analytical Performance of the PSP-Based Within-Tube Cleavage Reaction LFA for Pepsin Detection
3.3. Comparison with a Commercially Available Dipstick Assay for Pepsin Detection
3.4. Evaluation of On-Strip Cleavage Reaction LFA with a Multifunctional Strip Cassette
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samuels, T.L.; Johnston, N. Pepsin as a marker of extraesophageal reflux. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.M.; Hussey, D.J.; Woods, C.M.; Watson, D.I.; Carney, A.S. Biomarkers and laryngopharyngeal reflux. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 125, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, N.; Dettmar, P.W.; Bishwokarma, B.; Lively, M.O.; Koufman, J.A. Activity/stability of human pepsin: Implications for reflux attributed laryngeal disease. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Lang, X.Q.; Wu, D.; He, Y.Q.; Lan, C.H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, B.; Zou, D.W.; Wu, J.M.; Zhao, Y.B.; et al. Salivary Pepsin as an Intrinsic Marker for Diagnosis of Sub-types of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-related Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakaran, S.; Rajendran, S.; Thomas, R.M.; Jacob, J.; Kurien, M. Laryngopharyngeal rReflux: Symptoms, signs, and Presence of Pepsin in Saliva—A Reliable Diagnostic Triad. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 25, e273–e278. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kwon, J.; Shin, S.; Eun, Y.G.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, G.J. Opti mization of Saliva Collection and Immunochromatographic Detection of Salivary Pepsin for Point-of-Care Testing of Laryn gopharyngeal Reflux. Sensors 2020, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.Y.; Kwon, O.E.; Lee, Y.C.; Eun, Y.G. Optimal timing of saliva collection to detect pepsin in patients. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2270–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C. The Role of Salivary Pepsin in the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Evaluated Using High-Resolution Manometry and 24-Hour Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-pH Monitoring. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e927381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, F.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhang, C.; Tang, J. The diagnostic value of pepsin detection in saliva for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: A preliminary study from China. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Nhari, R.M.H.; Muhammad Zailani, A.N.; Khairil Mokhtar, N.F.; Hanish, I. Detection of porcine pepsin in model cheese using polyclonal antibody-based ELISA. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess 2020, 37, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C. Salivary peptest for laryngopharyngeal reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Medicine 2021, 100, e26756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strugala, V.; Woodcock, A.D.; Dettmar, P.W.; Faruqi, S.; Morice, A.H. Detection of pepsin in sputum: A rapid and objective measure of airways reflux. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Bobin, F. Diagnostic Value of Fasting and Bedtime Saliva Pepsin Measurements in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebke, K.E.; Samuels, T.L.; Johnston, N. The Role of Pepsin in LPR: Will It Change Our Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach to the Disease? Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2016, 4, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, M.; Yosef, T.M.; Mahmoud, A.M.; George Michael, T.M.A. Fasting salivary pepsin level as a reliable non-invasive method of screening for laryngopharyngeal reflux in Egyptian patients. Egypt. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 34, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y.; Lu, R.; Wei, Z.; Huang, K.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Portable and Rapid Fluorescence Turn-On Detection of Total Pepsin in Saliva Based on Strong Electrostatic Interactions. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 18303–18308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Luo, C.; Mehdi, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, S. A bovine serum albumin and squaraine dye assembly fluorescent probe for pepsin detection. Microchem. J. 2023, 186, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; Wang, L.; He, Z. Scissor-based fluorescent detection of pepsin using lysozyme-stabilized Au nanoclusters. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 6789–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Noh, J.K.; Woo, S.R.; Kang, S.W.; Eun, Y.G.; Lee, G.J. Determination of pepsin in human saliva using pepsin-susceptible peptide reporter and colorimetric dipstick assay: A prospective, crosssectional study. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domfe, T.; Njengele-Tetyana, Z.; Mhlanga, N.; Tetyana, P.; Skepu, A.; Ngila, J.C.; Sikhwivhilu, L.M. Development of a Versatile Half-Strip Lateral Flow Assay toward the Detection of Rift Valley Fever Virus Antibodies. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2019-2, 20190109; Standards and Specifications for Utensils, Containers and Packages. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea: Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2019; Part II. p. 208.
- Jacinto, M.J.; Trabuco, J.R.C.; Vu, B.V.; Garvey, G.; Khodadady, M.; Azevedo, A.M.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Chang, L.; Kourentzi, K.; Litvinov, D.; et al. Enhancement of lateral flow assay performance by electromagnetic relocation of reporter particles. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0186782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yrad, F.M.; Castañares, J.M.; Alocilja, E.C. Visual Detection of Dengue-1 RNA Using Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Qin, Z.; Sackrison, J.; Bischof, J.C. Ultrasensitive and highly specific lateral Flow assays for point-of-care diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3593–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, G.M.S.; Filippini, D.; Nielen, M.W.F.; Salentijn, G.I.J. Unraveling the Hook Effect: A Comprehensive Study of High Antigen Concentration effects in Sandwich lateral Flow immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15587–15595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallerbach, K.; Khederlou, K.; Wentland, L.; Senten, L.; Brentano, S.; Keefe, B.; Fu, E. Protein-Based Anchoring Methods for Nucleic Acid Detection in Lateral Flow Format Assays. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.; Goikoetxea, G.; Alday, E.; Jiménez, T.; Arias-Moreno, X.; Hernandez, F.J.; Hernandez, L.I. Ultra-Sensitive and Specific Detection of S. aureus Bacterial Cultures Using an Oligonucleotide Probe Integrated in a Lateral Flow-Based Device. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzendorfer, M.; Antoniou, S.A.; Schredl, P.; Witzel, K.; Weitzendorfer, I.C.; Majerus, A.; Emmanuel, K.; Koch, O.O. Pepsin and oropharyngeal pH monitoring to diagnose patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Zhao, J.; Tang, S.; Shen, W.; Lee, H.K. Logarithmic Data Processing Can Be Used Justifiably in the Plotting of a Calibration Curve. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 12156–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverniers, I.; De Loose, M.; Van Bockstaele, E. Trends in quality in the analytical laboratory. II. Analytical method validation and quality assurance. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena-Torralba, A.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Parolo, C.; Piper, A.; Merkoç, I. Toward Next Generation Lateral Flow Assays: Integration of Nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 14881–14910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puangpila, C.; Anukulkich, N.; Chiapleam, S.; Intajan, B.; Jakmunee, J.; Pencharee, S. Development of lectin-based lateral flow assay for fucosylated alpha-fetoprotein. J. Cell Biochem. 2023, 124, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbaji, A.; Heidari-Bafroui, H.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Faghri, M. A New Paper-Based Microfluidic Device for Improved Detection of Nitrate in Water. Sensors 2021, 21, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Geng, W.C.; Li, H.B.; Guo, D.S. Sensitive fluorescence detection of saliva pepsin by a supramolecular tandem assay enables the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Supramol. Chem. 2021, 33, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, Y.J.; Eun, Y.G.; Lee, G.J. Label-free detection of salivary pepsin using gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified screen-printed Electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kwak, C.H.; Heo, N.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, G.W.; Ezhil Vilian, A.T.; Han, Y.K.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Rapid and label-free bioanalytical method of alpha fetoprotein detection using LSPR chip. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 469, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Feng, F.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Bai, Y.-F.; Guo, F.-F.; Wu, F.-Y.; Zhou, G. Sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen using surface plasmon resonance biosensor with gold nanoparticles signal amplification. Talanta 2015, 140, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, O.; Ravalli, A.; Lo Piccolo, G.M.; Cristea, C.; Sandulescu, R.; Marrazza, G. Smartphone-based immunosensor for CA125 detection. Talanta 2017, 166, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Salimi, A.; Hamd-Ghadareh, S.; Fathi, F.; Soleimani, F. A FRET immunosensor for sensitive detection of CA 15-3 tumor marker in human serum sample and breast cancer cells using antibody functionalized luminescent carbon-dots and AuNPs-dendrimer aptamer as donor–acceptor pair. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 557, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, X.-H.; Hahm, E.; Huynh, K.-H.; Son, B.S.; Kim, H.-M.; Jun, B.-H. Sensitive colorimetric detection of prostate specific antigen using a peroxidase-mimicking anti-PSA antibody coated Au nanoparticle. BioChip J. 2020, 14, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, S.Y.; Shukla, S.; Hong, S.B.; Heo, N.S.; Bajpai, V.K.; Chun, H.S.; Jo, C.-H.; Choi, B.G.; Huh, Y.S.; et al. Heteroassembled gold nanoparticles with sandwich-immunoassay LSPR chip format for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fishlock, S.; Sharpe, P.; McLaughlin, J. Development of colorimetric lateral flow assays with gold nanostructures for Cystatin C detection. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100121. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.-W.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.-C.; Eun, Y.-G.; Lee, G.-J. Cleavage Reaction Lateral Flow Assays for Salivary Pepsin Measurement Using a Pepsin-Susceptible Peptide Substrate. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12110241
Kang S-W, Lee YJ, Lee J-C, Eun Y-G, Lee G-J. Cleavage Reaction Lateral Flow Assays for Salivary Pepsin Measurement Using a Pepsin-Susceptible Peptide Substrate. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(11):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12110241
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sung-Woong, Young Ju Lee, Jae-Chul Lee, Young-Gyu Eun, and Gi-Ja Lee. 2024. "Cleavage Reaction Lateral Flow Assays for Salivary Pepsin Measurement Using a Pepsin-Susceptible Peptide Substrate" Chemosensors 12, no. 11: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12110241
APA StyleKang, S.-W., Lee, Y. J., Lee, J.-C., Eun, Y.-G., & Lee, G.-J. (2024). Cleavage Reaction Lateral Flow Assays for Salivary Pepsin Measurement Using a Pepsin-Susceptible Peptide Substrate. Chemosensors, 12(11), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12110241




