Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly(proflavine) Deposited from Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Influence Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
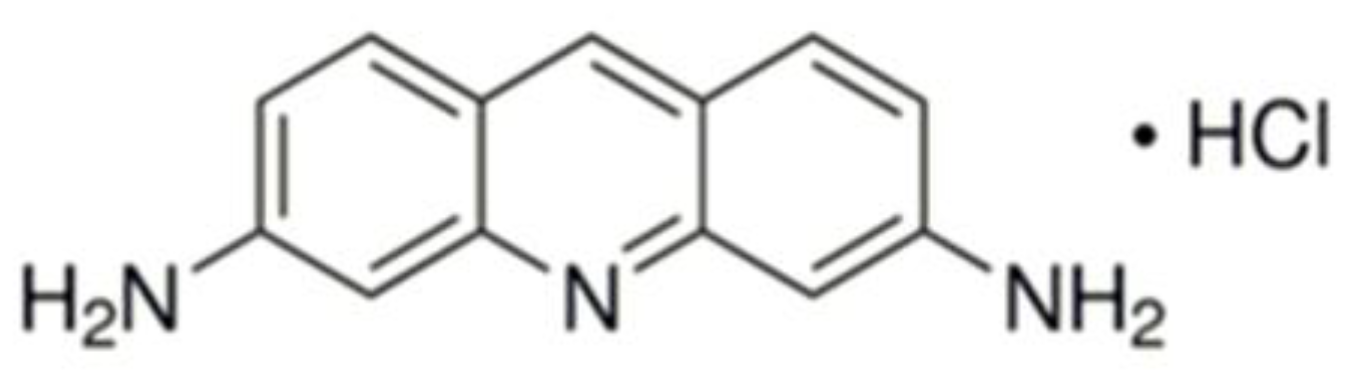
2.3. Proflavine Electropolymerization and DNA Sensor Assembling
2.4. Antioxidative Effect Assessment and Real-Sample Analysis
3. Results
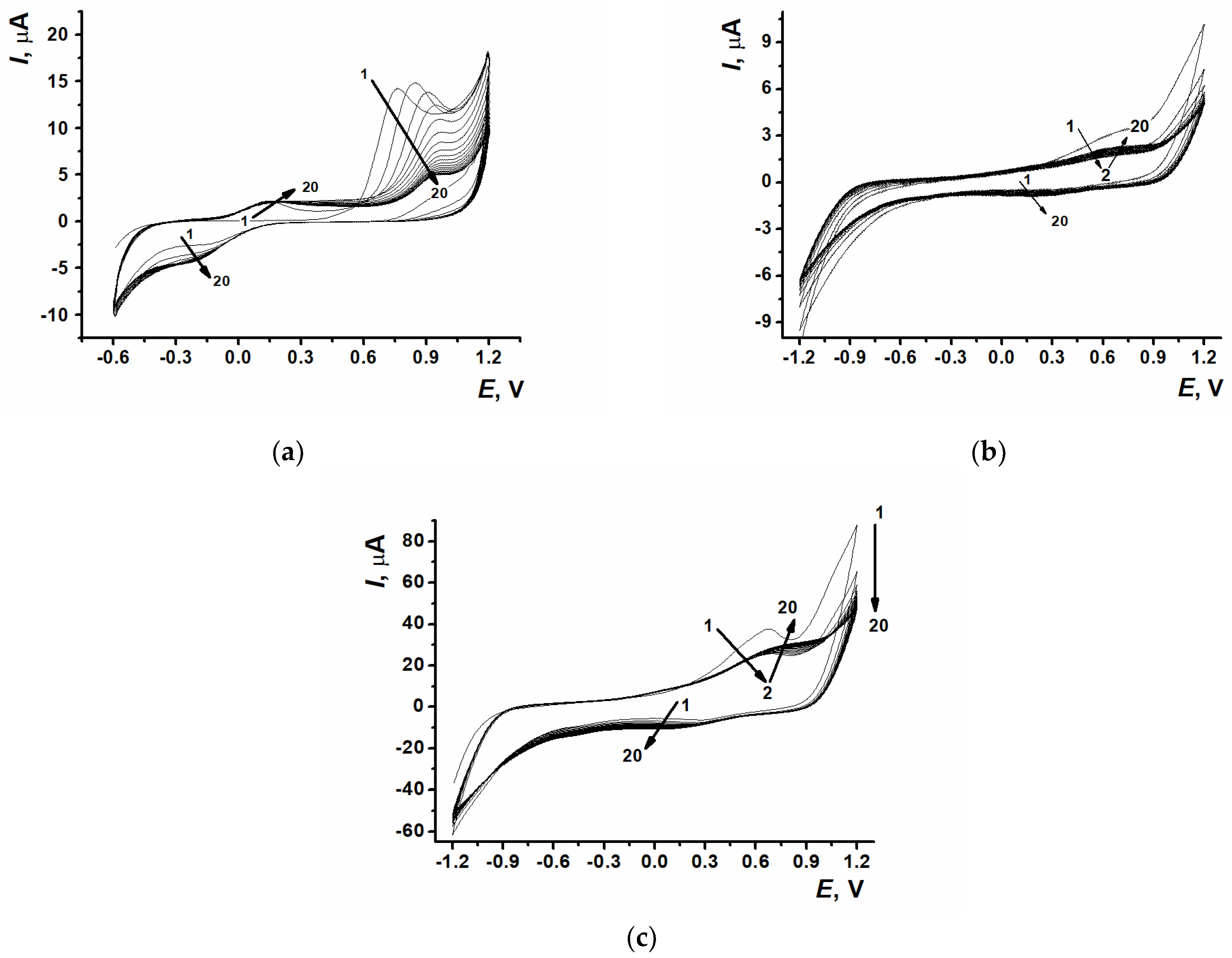
3.1. Electropolymerization of Proflavine and Estimation of Poly(proflavine) Electrochemical Characteristics
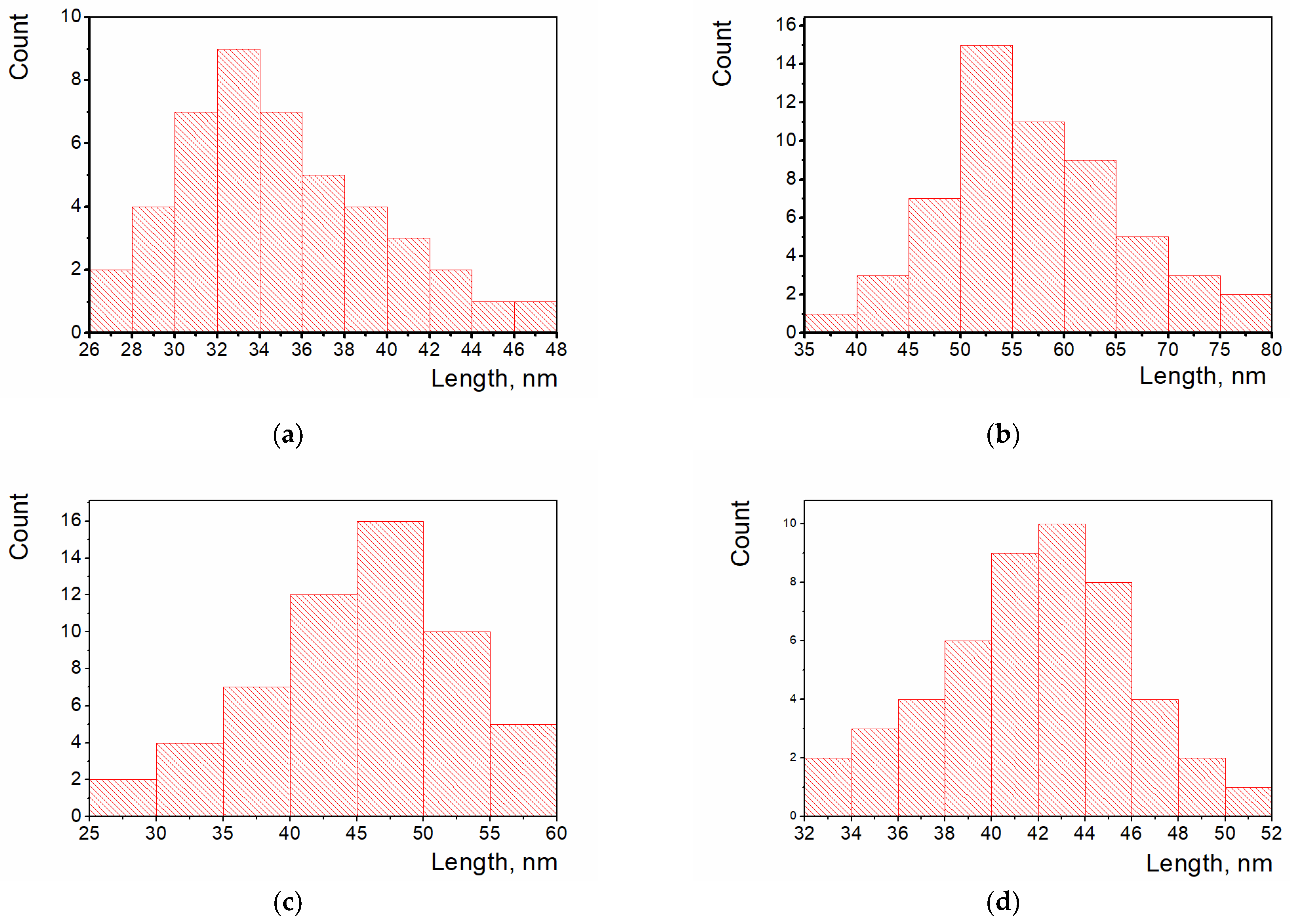
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Particle Size Evaluation
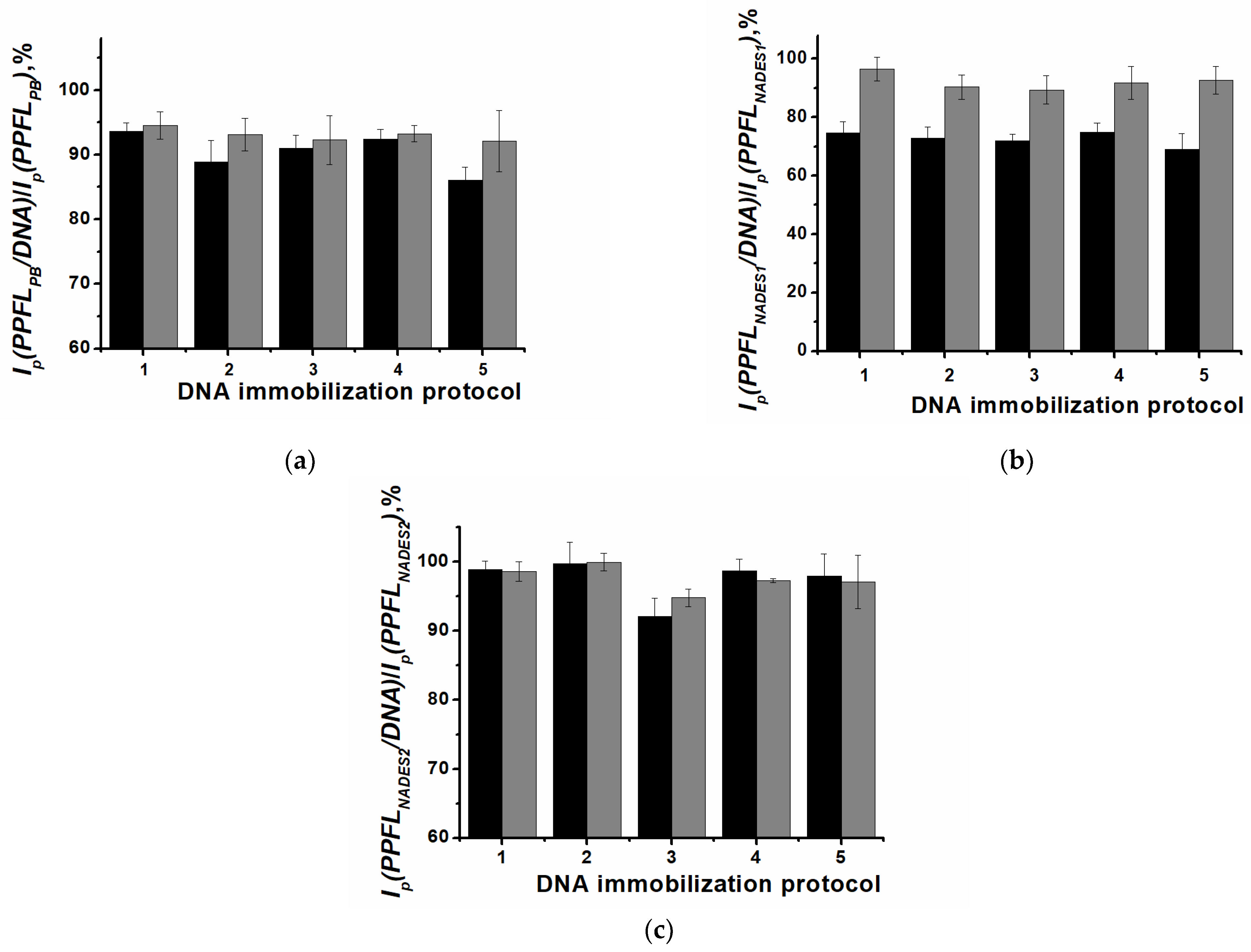
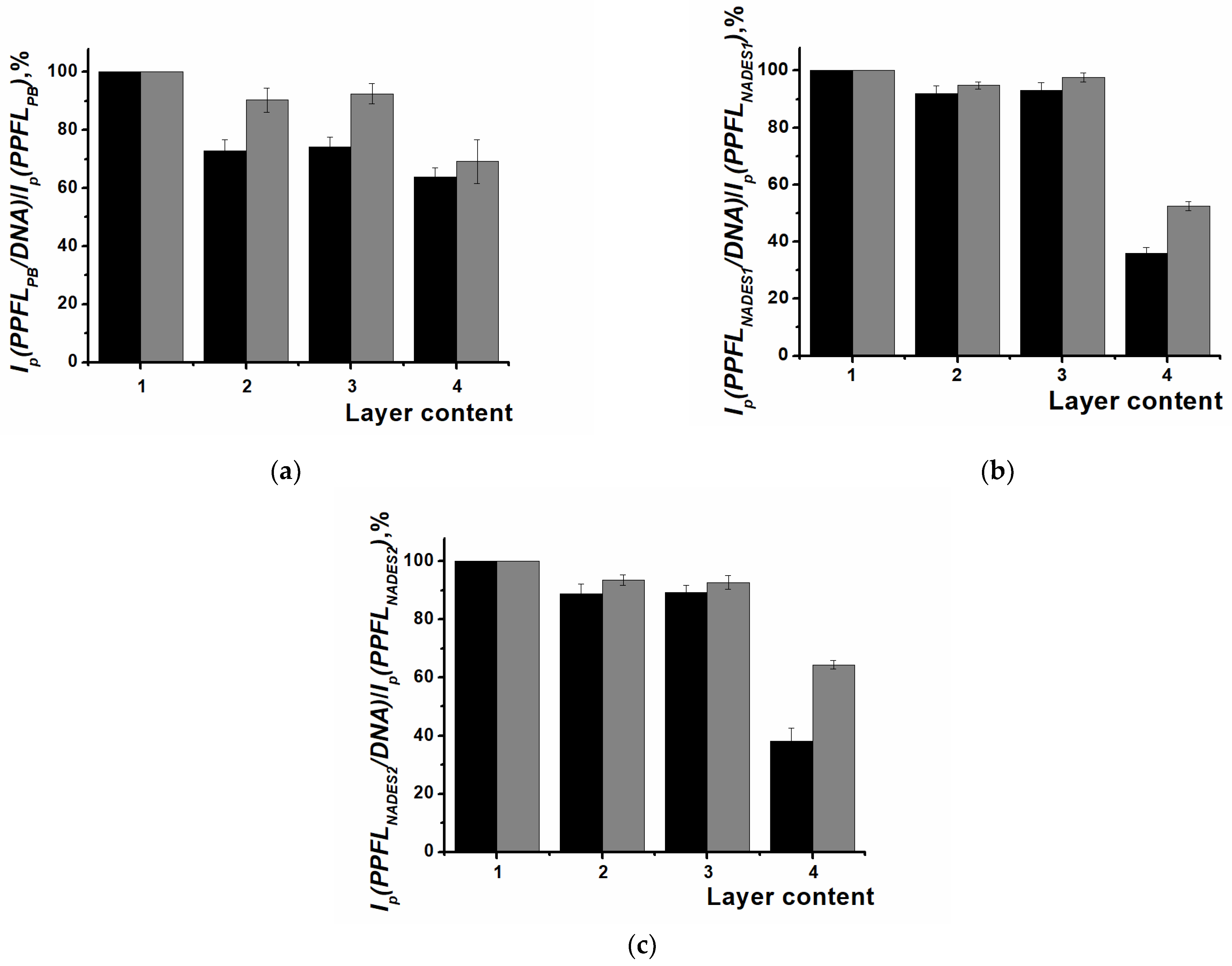
3.3. DNA Implementation in Surface Layers
3.4. Voltammetric Detection of Oxidative DNA Damage
Cu+ + H2O2 → Cu2+ + OH− + ∙OH
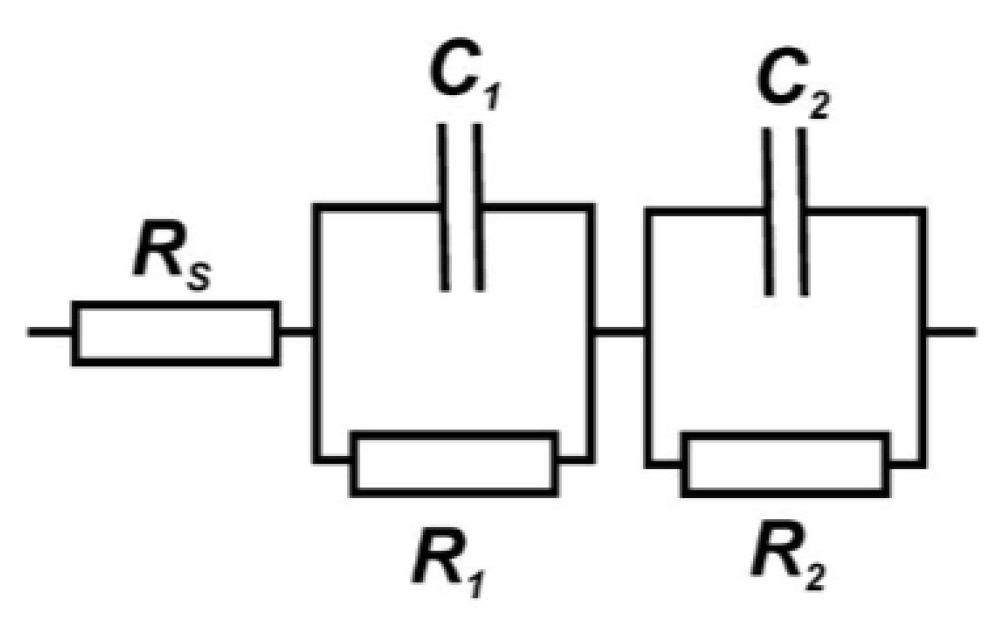
3.5. Electrochemical Impedance Detection of DNA Damage
3.6. Sensor-to-Sensor Repeatability, Stability, and Selectivity Assessment
3.7. Evaluation of Antioxidant Influence and Real-Sample Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Svitková, V.; Labuda, J. Construction of electrochemical DNA biosensors for investigation of potential risk chemical and physical agents. Monatsh. Chem. 2017, 148, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz Morales, K.; Alarcón-Angeles, G.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterial-based sensors for the study of DNA interaction with drugs. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, U.S.; Tan, B.W.Q.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Jeyasekharan, A.D. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radstake, W.E.; Parisi, A.; Miranda, S.; Gautam, K.; Vermeesen, R.; Rehnberg, E.; Tabury, K.; Coppes, R.; van Goethem, M.-J.; Brandenburg, S.; et al. Radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in cortisol exposed fibroblasts as quantified with the novel foci-integrated damage complexity score (FIDCS). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Kondo, T.; Tachibana, K.; Feril, L.B. Ultrasound-induced DNA damage and cellular response: Historical review, mechanisms analysis, and therapeutic implications. Radiat. Res. 2022, 197, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, P.; Ostad, S.N.; Heydari, A.; Aliebrahimi, S.; Montazeri, V.; Foroushani, A.R.; Monazzam, M.R.; Ghazi-Khansari, M.; Golbabaei, F. Effect of heat stress on DNA damage: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2022, 66, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron-Carrasco, J.P.; Jacquemin, D. Electric field induced DNA damage: An open door for selective mutations. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7578–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, R.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Biomarkers of oxidative damage in human disease. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, B.M.; Srinivasan, S.; Ezhilan, M.; Nesakumar, N. Nucleic acid-based electrochemical biosensors. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 559, 119715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Scaloni, A.; Giustarini, D.; Cavarra, E.; Tell, G.; Lungarella, G.; Colombo, R.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A. Proteins as biomarkers of oxidative/nitrosative stress in diseases: The contribution of redox proteomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 55–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokni, M.; Tlili, A.; Khalij, Y.; Attia, G.; Zerrouki, C.; Hmida, W.; Othmane, A.; Bouslama, A.; Omezzine, A.; Fourati, N. Designing a simple electrochemical genosensor for the detection of urinary PCA3, a prostate cancer biomarker. Micromachines 2024, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.W.; Nobusawa, K.; Yamashita, I. Anomalous enhancement of electrochemical charge transfer by a Ru complex ion intercalator. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güngör, M.A.; Alev, O.; Kaya, H.K.; Arslan, L.Ç.; Büyükköse, S.; Öztürk, Z.Z.; Kuralay, F. Atomic layer deposited zinc oxide thin film on pencil graphite for DNA sensor applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtugyn, G.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical DNA sensors and aptasensors based on electropolymerized materials and polyelectrolyte complexes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebala, M.; Stoica, L.; Neugebauer, S.; Schuhmann, W. Label-free detection of DNA hybridization in presence of intercalators using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girousi, S.; Kinigopoulou, V. Detection of short oligonucleotide sequences using an electrochemical DNA hybridization biosensor. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfireva, A.V.; Goida, A.I.; Rogov, A.M.; Evtugyn, G.A. Impedimetric DNA sensor based on poly(proflavine) for determination of anthracycline drugs. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; Si, L.; Jung, D.J.; Calderón, A.I. Application of eco-friendly natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) in HPLC for separation of complex natural products: Current limitations and future directions. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 244, 116102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.A. Perspectives for the use of deep eutectic solvents in the preparation of electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2024, 45, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjuna, K.; Ilangeswaran, D. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis in newly formed ternary deep eutectic solvent media, characterization and their antifungal activity. Curr. Nanomater. 2023, 8, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Yüksek, A.G.; Elik, A.; Altunay, N. Rapid and safe determination of vitamin B1 in dairy products, fruits, nuts and vitamin tablets: Combination of natural deep eutectic solvents, experimental design and artificial intelligence. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 131, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simamora, A.; Timotius, K.H.; Setiawan, H.; Saputri, F.A.; Putri, C.R.; Aryani, D.; Ningrum, R.A.; Mun’im, A. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of xanthorrhizol from Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb. Rhizomes by natural deep eutectic solvents: Optimization, antioxidant activity, and toxicity profiles. Molecules 2024, 29, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfireva, A.; Goida, A.; Evtugyn, V.; Evtugyn, G. Impedimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polythionine from deep eutectic solvent for epinephrine determination. Green Anal. Chem. 2024, 9, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goida, A.; Rogov, A.; Kuzin, Y.; Porfireva, A.; Evtugyn, G. Impedimetric DNA sensors for epirubicin detection based on polythionine films electropolymerized from deep eutectic solvent. Sensors 2023, 23, 8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Niu, H.; Zhang, N.; Hou, T.; Guan, P.; Hu, X. Facile fabrication of electrochemically reduced graphene oxide/polythionine-methylene blue and its use as a platform for detection of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in the artificial urine sample. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 425, 140715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfireva, A.; Begisheva, E.; Evtugyn, V.; Evtugyn, G. Electrochemical DNA sensor for valrubicin detection based on poly(Azure C) films deposited from deep eutectic solvent. Biosensors 2023, 13, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsan, M.M.; Pinto, E.M.; Brett, C.M.A. Electrosynthesis and electrochemical characterisation of phenazine polymers for application in biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3973–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shang, J.; Mao, Z.; Yang, C. Measurement methods of particle size distribution in emulsion polymerization. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, T.N.; Porfireva, A.V.; Shamagsumova, R.V.; Evtugyn, G.A. Voltammetric sensor with replaceable polyaniline-DNA layer for doxorubicin determination. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2284–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Cui, D.; Zhai, S.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, G. A label-free electrochemical impedimetric DNA biosensor for genetically modified soybean detection based on gold carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Salah, K.M.; Ansari, A.A.; Alrokayan, S.A. DNA-based applications in nanobiotechnology. BioMed Res. Int. 2010, 2010, 715295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickoloff, J.A.; Sharma, N.; Taylor, L.; Allen, S.J.; Hromas, R. Nucleases and co-factors in DNA replication stress responses. DNA 2022, 2, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Villani, R.M.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Villani, R.M.; Wang, H.; Simpson, M.J.; Roberts, M.S.; Tang, M.; Liang, X. The role of cellular reactive oxygen species in cancer chemotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, H.; Halliwell, B. Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem. J. 1996, 313, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Takada, K. Reactive oxygen species in cancer: Current findings and future directions. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoewe, R.; Prütz, W.A. Copper-catalyzed DNA damage by ascorbate and hydrogen peroxide: Kinetics and yield. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1987, 3, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzin, Y.; Ivanov, A.; Evtugyn, G.; Hianik, T. Voltammetric detection of oxidative DNA damage based on interactions between polymeric dyes and DNA. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangruwa, N.; Srivastava, M.; Mishra, D. CISS-based label-free novel electrochemical impedimetric detection of UVC-induced DNA damage. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 37705–37713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Kazemnadi, N.; Amini, M.; Rezaei, B. Impedimetric DNA-biosensor for the study of dopamine induces DNA damage and investigation of inhibitory and repair effects of some antioxidants. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 104, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F. Evolution of dietary antioxidants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2003, 136, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, D.G.; Clifford, M.N. Critical reviews produced within the EU Concerted Action ‘Nutritional Enhancement of Plant-based Food in European Trade’ (NEODIET). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 793–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezová, V.; Polovka, M.; Staško, A. The influence of additives on beer stability investigated by EPR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2002, 58, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önem, A.N.; Başkan, K.S.; Apak, R. Voltammetric measurement of antioxidant activity by prevention of Cu (II)-induced oxidative damage on DNA bases using a modified electrode. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5103–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfireva, A.; Plastinina, K.; Evtugyn, V.; Kuzin, Y.; Evtugyn, G. Electrochemical DNA sensor based on poly(Azure A) obtained from the buffer saturated with chloroform. Sensors 2021, 21, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghian-Grosan, C.; Biris, A.R.; Coros, M.; Pogacean, F.; Pruneanu, S. Electrochemical and spectroscopic studies of ssDNA damage induced by hydrogen peroxide using graphene based nanomaterials. Talanta 2015, 138, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S.; Bao, L.; Shi, H.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Ma, Q.; Shi, X. Electrochemical biosensor based on ds-DNA/N-G@CS/GCE for highly sensitive and rapid measurement of antioxidant activity. ECS Adv. 2023, 2, 026501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. Electrochemical evaluation of total antioxidant properties in red wine. Food Meas. 2023, 17, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S.L.; Rede, D.; Ramalhosa, M.J.; Correia, M.; Santos, M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Moreira, M.M.; Soares, C.; Barroso, M.F. Assessment of the antioxidant capacity of commercial coffee using conventional optical and chromatographic methods and an innovative electrochemical DNA-based biosensor. Biosensors 2023, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar]
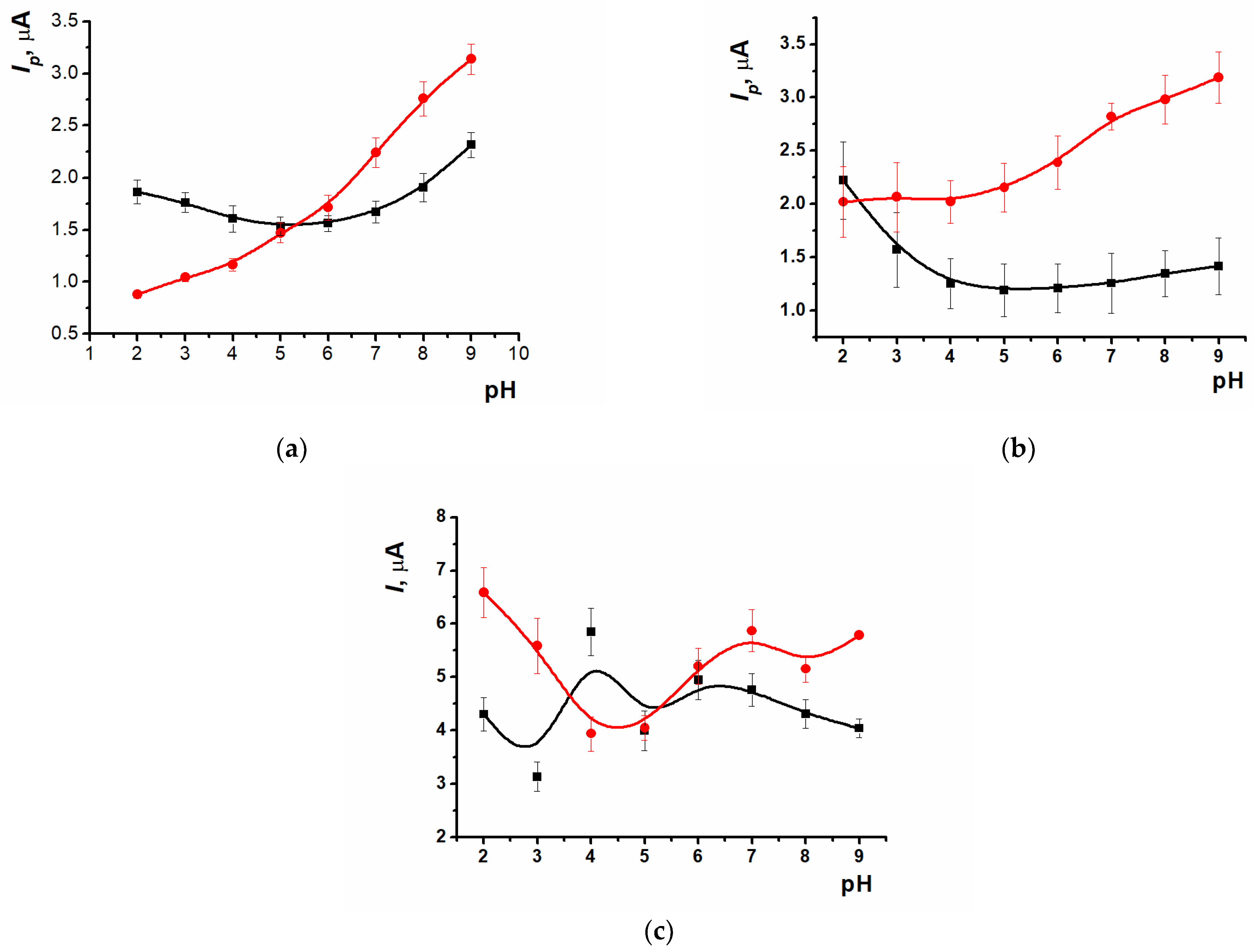



| Coating | Slope dEm/dpH, V/pH |
|---|---|
| PPFLPB | −0.064 ± 0.002 |
| PPFLNADES1 | −0.068 ± 0.001 |
| PPFLNADES2 | −0.057 ± 0.001 |
| Real Sample | R1, kΩ | Recovery, % |
|---|---|---|
| Ascorbic acid in sachets | 1.16 ± 0.06 | 103 ± 6 |
| Ascorbic acid in tablets | 1.24 ± 0.11 | 110 ± 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porfireva, A.; Goida, A.; Evtugyn, V.; Mozgovaya, M.; Krasnova, T.; Evtugyn, G. Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly(proflavine) Deposited from Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Influence Assessment. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100215
Porfireva A, Goida A, Evtugyn V, Mozgovaya M, Krasnova T, Evtugyn G. Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly(proflavine) Deposited from Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Influence Assessment. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(10):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100215
Chicago/Turabian StylePorfireva, Anna, Anastasia Goida, Vladimir Evtugyn, Milena Mozgovaya, Tatiana Krasnova, and Gennady Evtugyn. 2024. "Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly(proflavine) Deposited from Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Influence Assessment" Chemosensors 12, no. 10: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100215
APA StylePorfireva, A., Goida, A., Evtugyn, V., Mozgovaya, M., Krasnova, T., & Evtugyn, G. (2024). Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly(proflavine) Deposited from Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Influence Assessment. Chemosensors, 12(10), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100215





