Analytical Tool for Quality Control of Irrigation Waters via a Potentiometric Electronic Tongue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Samples
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of the Ion-Selective Electrodes
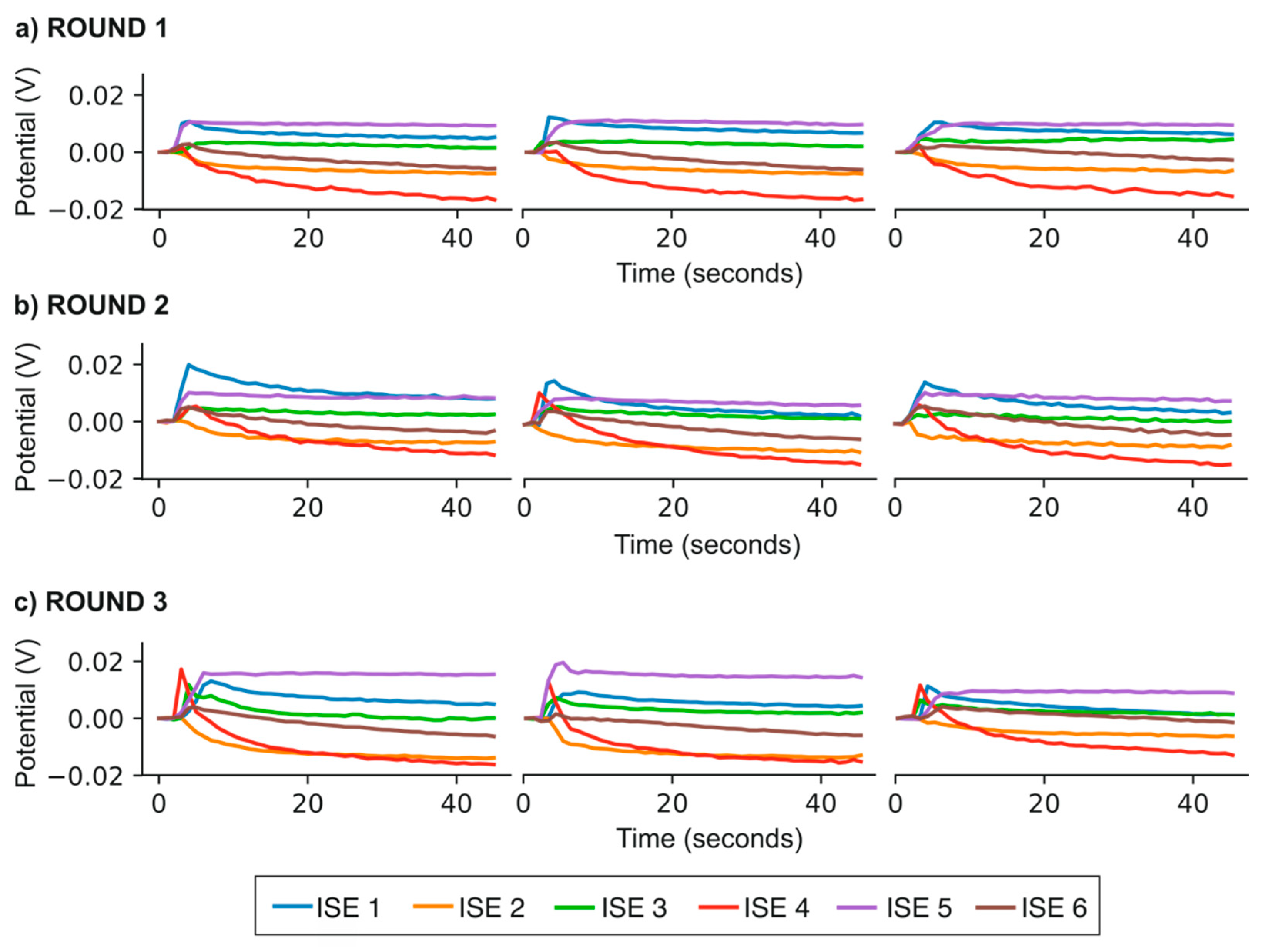
2.4. Procedure for the Analysis of the Samples
3. Results
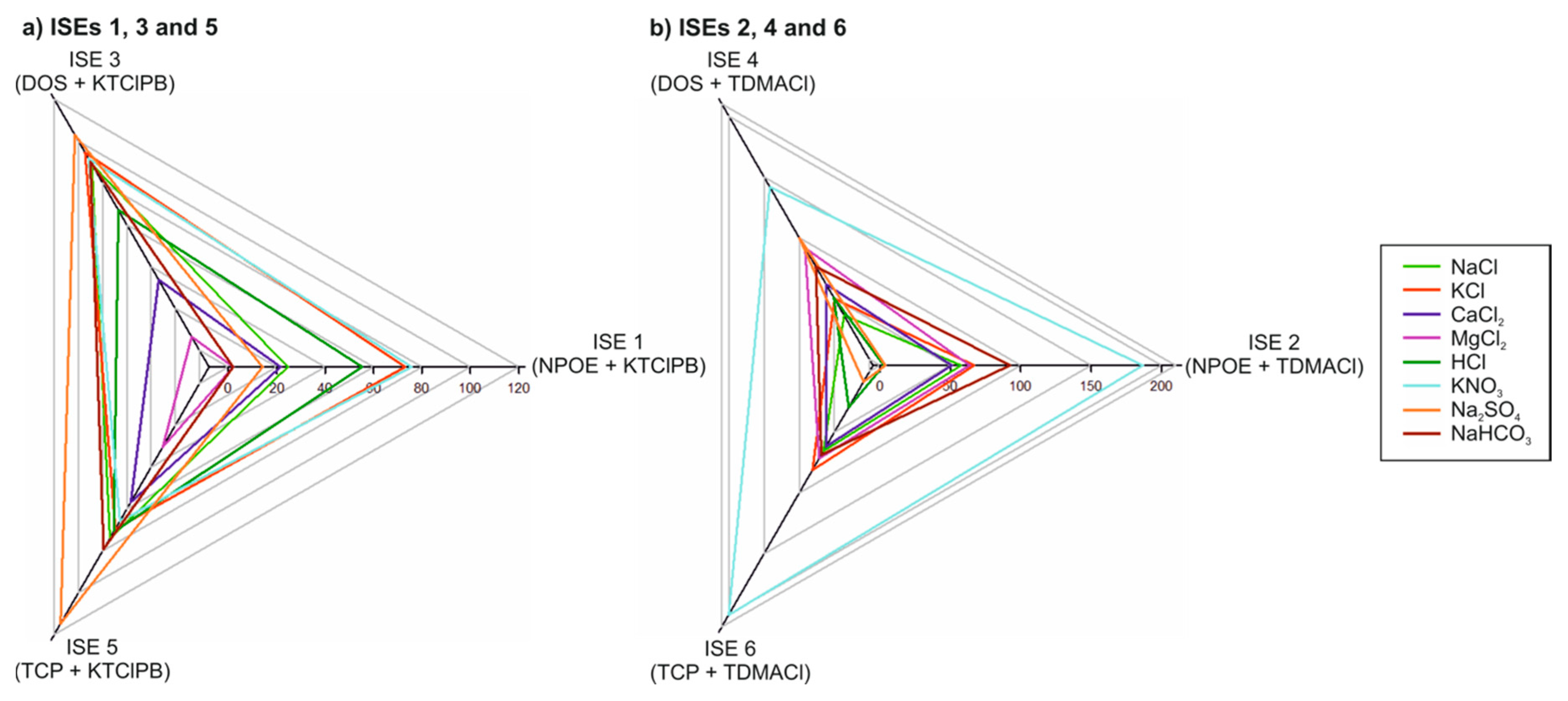
3.1. Potentiometric Response of Each Electrode in the Electronic Tongue towards the Major Ions Present in Irrigation Water Samples
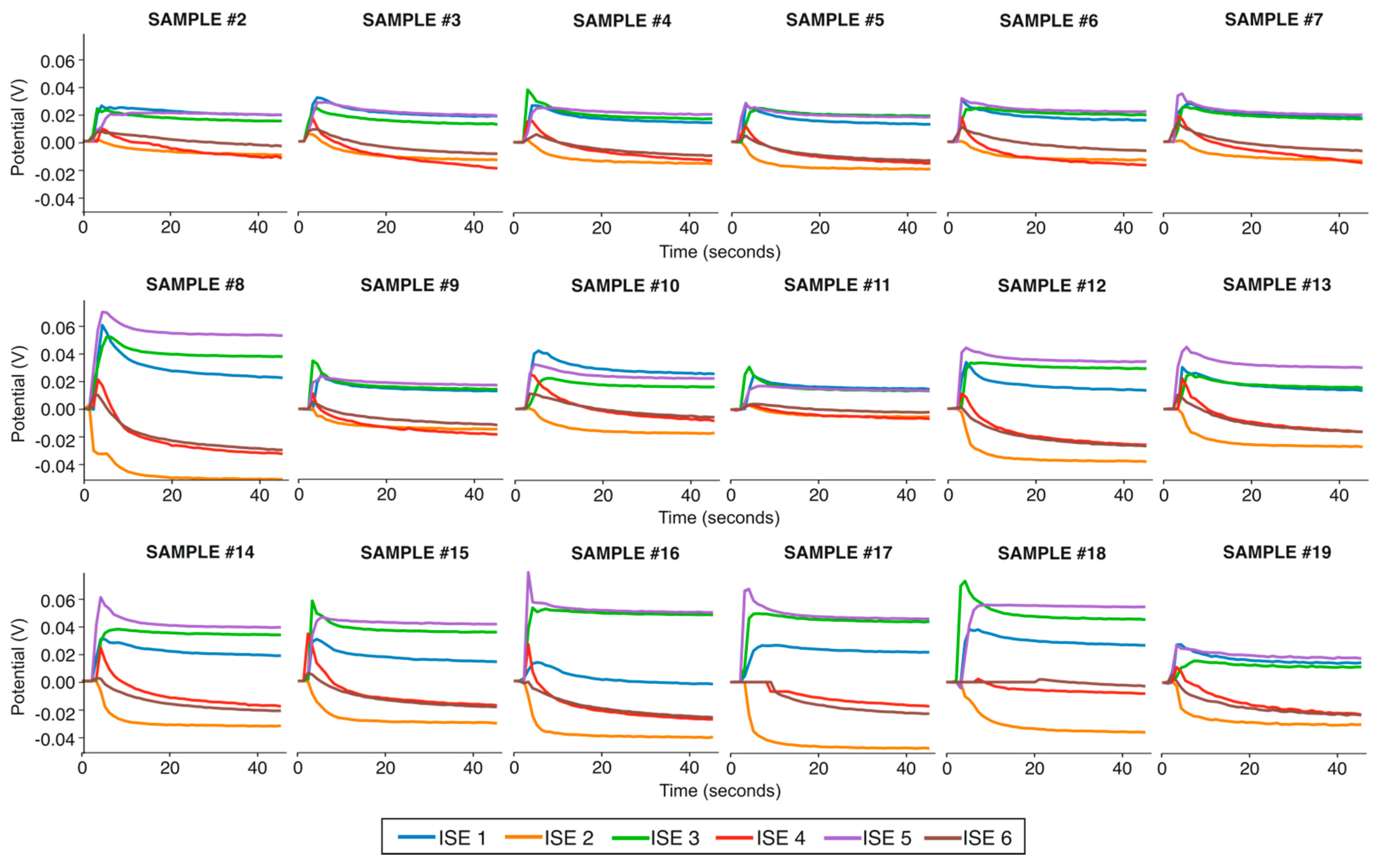
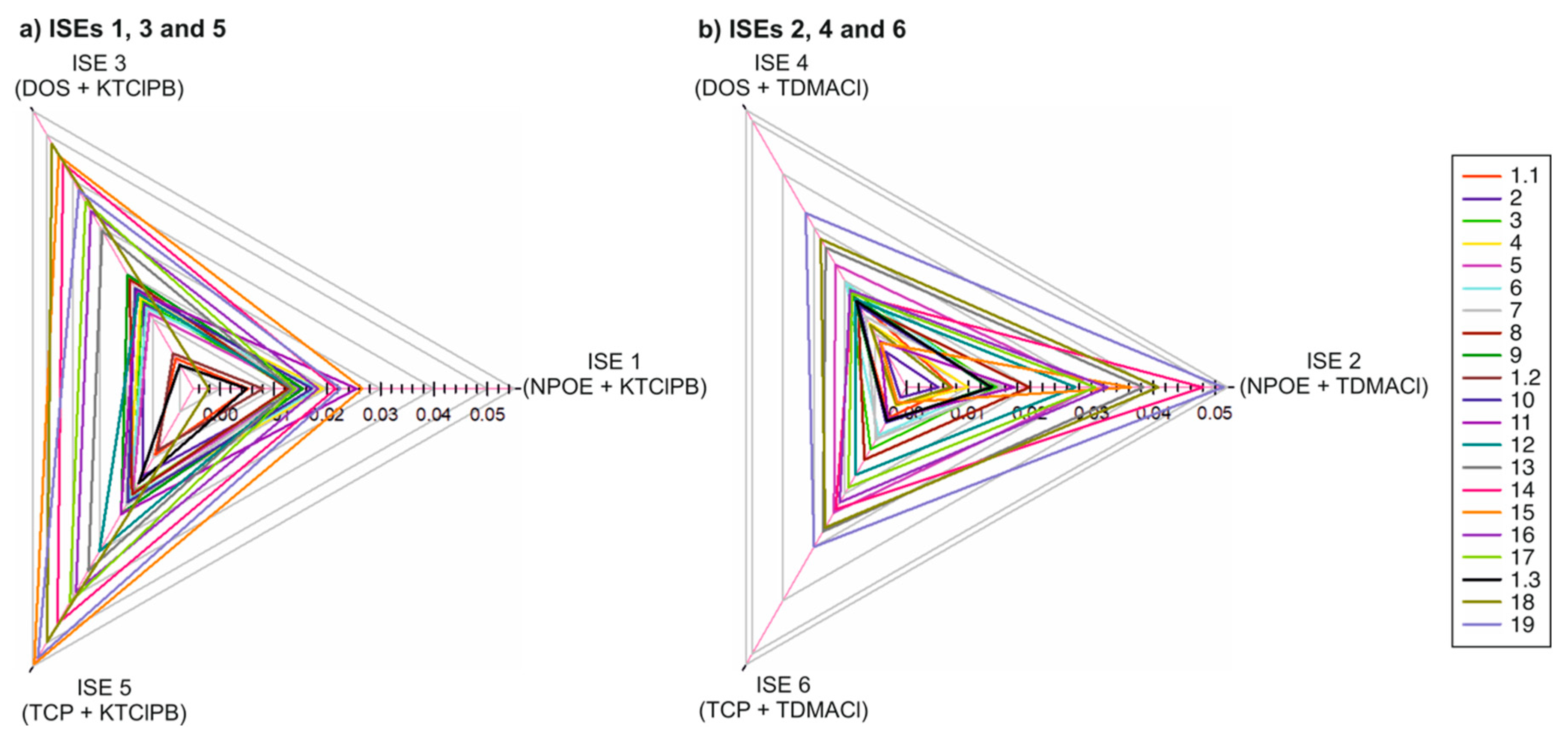
3.2. Potentiometric Response of Each Electrode in the Electronic Tongue towards 19 Samples of Irrigation Waters
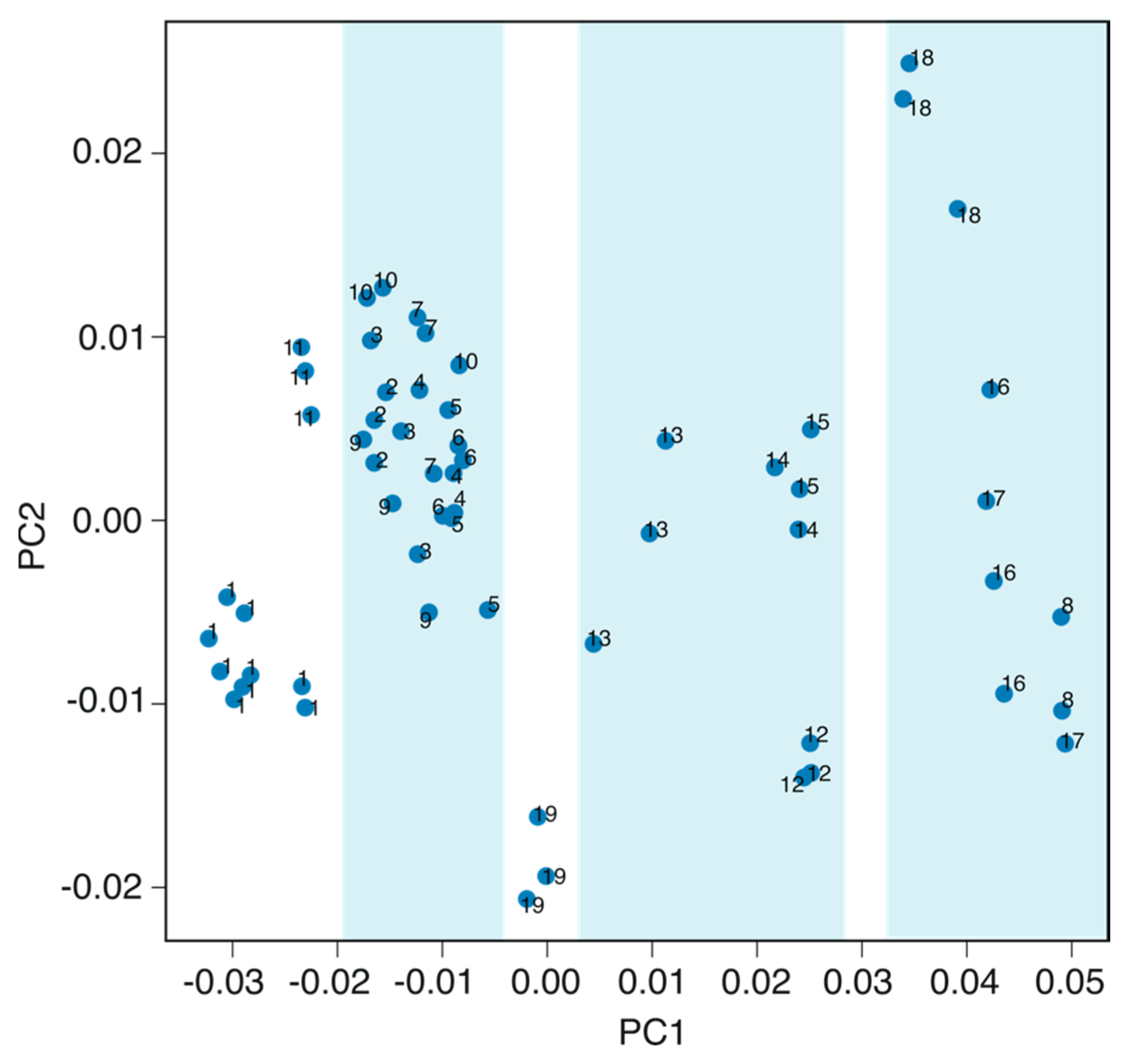
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0016/324610/Health-2020-Agriculture-and-health-through-food-safety-and-nutrition-en.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Antonacci, A.; Arduini, F.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Scognamiglio, V. Nanostructured (Bio)sensors for smart agriculture. TrAC 2018, 98, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- García-Tejero, I.F.; Durán-Zuazo, V.H.; Muriel-Fernández, J.L.; Rodríguez-Pleguezuelo, C.R. Water and Sustainable Agriculture; SpringerBriefs in Agriculture Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S.; Saha, N.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Shen, S.; Bodrud-Doza, M.D. Evaluation of Water Quality for Sustainable Agriculture in Bangladesh. Water Air Soil Poll. 2017, 228, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.D. Crop and irrigation management strategies for saline-sodic soils and waters aimed at environmentally sustainable agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 323, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L. Irrigation Water Quality. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.J.; Oster, J.D.; Sposito, G. Potassium and magnesium in irrigation water quality assessment. Agri. Water Manag. 2015, 157, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrigation Water Quality Criteria. Available online: https://itc.tamu.edu/files/2018/05/00506.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Bagordo, F.; Migoni, D.; Grassi, T.; Serio, F.; Idolo, A.; Guido, M.; Zaccarelli, N.; Fanizzi, F.P.; De Donno, A. Using the DPSIR framework to identify factors influencing the quality of groundwater in Greca Salentina (Puglia, Italy). Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2016, 27, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, T.G.; Arain, M.B.; Jamali, M.K.; Jalbani, N.; Afridi, H.I.; Sarfraz, R.A.; Baig, J.A.; Shah, A.Q. Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, M.; Mutavdzic, B.; Srdevic, Z.; Srdevic, B. Irrigation water fitness assessment based on Bayesian network and FAO guidelines. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 71, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westcot, D.W.; Ayers, R.S. Irrigation Water Quality Criteria. In Irrigation with Reclaimed Municipal Wastewater—A Guidance Manual; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cuartero, M. Electrochemical sensors for in-situ measurement of ions in seawater. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2021, 334, 129635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://hispagua.cedex.es/en/instituciones/confederaciones/segura (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Sghaier, K.; Barhoumi, H.; Maaref, A.; Siadat, M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Characterization and Classification of Groundwater from Wells Using an Electronic Tongue (Kairouan, Tunisia). J. Water Res. Prot. 2011, 3, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.S.; Ortuno, J.A.; Albero, M.I.; Cuartero, M. Application of a trazodone-selective electrode to pharmaceutical quality control and urine analyses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, M.; Ruiz, A.; Galian, M.; Ortuno, J.A. Potentiometric Electronic Tongue for Quantitative Ion Analysis in Natural Mineral Waters. Sensors 2022, 22, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Franco, J.A.; Ruiz, A.; Ortuno, J.A. Dynamic Potentiometry with an Ion-Selective Electrode: A Tool for Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Inorganic and Organic Cations. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Buhlmann, P.; Pretsch, E. The phase-boundary potential model. Talanta 2004, 63, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morf, W.E.; Pretsch, E.; de Rooij, N.F. Theory and computer simulation of the time-dependent selectivity behavior of polymeric membrane ion-selective electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 614, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morf, W.E.; Pretsch, E.; de Rooij, N.F. Memory effects of ion-selective electrodes: Theory and computer simulation of the time-dependent potential response to multiple sample changes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 633, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, V.V.; Novakovskii, A.D.; Zdrachek, E.A. Modeling of the effect of diffusion processes on the response of ion-selective electrodes by the finite difference technique: Comparison of theory with experiment and critical evaluation. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 72, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.V.; Novakovskii, A.D.; Zdrachek, E.A. An Interface Equilibria-Triggered Time-Dependent Diffusion Model of the Boundary Potential and Its Application for the Numerical Simulation of the Ion-Selective Electrode Response in Real Systems. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambly, B.; Guzinski, M.; Pendley, B.; Lindner, E. Kinetic Description of the Membrane–Solution Interface for Ion-Selective Electrodes. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokalski, T.; Lingenfelter, P.; Lewenstam, A. Numerical Solution of the Coupled Nernst−Planck and Poisson Equations for Liquid Junction and Ion Selective Membrane Potentials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokalski, T.; Lewenstam, A. Application of Nernst–Planck and Poisson equations for interpretation of liquid-junction and membrane potentials in real-time and space domains. Electrochem. Commun. 2001, 3, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample# | Conductivity (mS/cm) | Cl− (ppm) | NO3− (ppm) | SO42− (ppm) | HCO3− (ppm) | Ca2+ (ppm) | K+ (ppm) | Mg2+ (ppm) | Na+ (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.28 | 13 | 9 | 5 | 191 | 58 | 1.0 | 8 | 7 |
| 2 | 1.13 | 183 | ND | 355 | 191 | 123 | 5.5 | 54 | 102 |
| 3 | 1.86 | 233 | ND | 487 | 766 | 244 | 4.2 | 106 | 149 |
| 4 | 1.97 | 336 | ND | 547 | 377 | 134 | 7.6 | 120 | 214 |
| 5 | 2.01 | 222 | ND | 745 | 482 | 152 | 15.2 | 133 | 220 |
| 6 | 2.04 | 266 | ND | 748 | 482 | 135 | 13.5 | 105 | 270 |
| 7 | 2.13 | 166 | ND | 635 | 940 | 176 | 14.3 | 153 | 223 |
| 8 | 6.14 | 1386 | 89 | 2227 | 343 | 576 | 20.4 | 269 | 734 |
| 9 | 0.87 | 197 | ND | 148 | 125 | 54 | 4.6 | 28 | 121 |
| 10 | 2.44 | 164 | ND | 1485 | 255 | 509 | 9.2 | 98 | 142 |
| 11 | 0.65 | 245 | ND | ND | 37 | 13 | 4.7 | 8 | 133 |
| 12 | 3.83 | 1070 | 175 | 453 | 321 | 113 | 14.6 | 124 | 601 |
| 13 | 3.64 | 735 | 71 | 904 | 267 | 257 | 8.2 | 143 | 472 |
| 14 | 4.98 | 1253 | 91 | 1081 | 235 | 274 | 14.4 | 199 | 672 |
| 15 | 5.77 | 1504 | 94 | 1145 | 318 | 253 | 12.8 | 247 | 765 |
| 16 | 5.88 | 1657 | 28 | 1219 | 237 | 382 | 15.7 | 236 | 698 |
| 17 | 4.13 | 860 | 103 | 1238 | 414 | 341 | 16.6 | 191 | 498 |
| 18 | 4.29 | 729 | 68 | 1103 | ND | 484 | 15.7 | 174 | 497 |
| 19 | 1.56 | 206 | 104 | 487 | 448 | 271 | 0.5 | 59.9 | 97 |
| Membrane | Components | ISE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC (wt.%) | Plasticizer | Ion Exchanger | ||||
| Compound | (wt.%) | Compound | (wt.%) | |||
| 1 | 33.1 | NPOE | 66.4 | KTClPB | 0.5 | 1 |
| 2 | 32.9 | NPOE | 66.6 | TDMACl | 0.5 | 2 |
| 3 | 32.9 | DOS | 66.6 | KTClPB | 0.5 | 3 |
| 4 | 32.8 | DOS | 66.7 | TDMACl | 0.5 | 4 |
| 5 | 31.6 | TCP | 67.9 | KTClPB | 0.5 | 5 |
| 6 | 32.7 | TCP | 66.8 | TDMACl | 0.5 | 6 |
| Slope (mV/dec) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt | ISE 1 | ISE 2 | ISE 3 | ISE 4 | ISE 5 | ISE 6 |
| NaCl | 37.9 | −36.5 | 56.5 | −39.1 | 54.9 | −43.2 |
| KCl | 47.9 | −40.0 | 54.1 | −42.3 | 52.9 | −47.3 |
| CaCl2 | 11.2 | −37.5 | 45.2 | −41.5 | 26.3 | −41.9 |
| MgCl2 | – | −41.1 | 36.6 | −45.3 | 25.0 | −42.6 |
| HCl | 55.9 | −56.7 | 72.3 | −60.3 | 71.2 | −60.9 |
| KNO3 | 48.2 | −53.4 | 54.0 | −53.1 | 52.2 | −56.0 |
| Na2SO4 | 29.9 | −1.3 | 50.7 | −23.7 | 50.3 | −0.4 |
| NaHCO3 | 57.1 | −57.1 | 65.9 | −24.9 | 65.5 | −41.1 |
| Parameter | ISE 1 | ISE 2 | ISE 3 | ISE 4 | ISE 5 | ISE 6 | Offset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | –72.65 | –26.63 | 47.06 | 3.67 | 52.72 | –3.53 | –0.175 |
| Cl− (ppm) | –20,855.3 | –6553.5 | 14,343.8 | 374.6 | 13,634.3 | –3064.0 | 3.33 |
| NO3− (ppm) | 1443.2 | –1773.5 | –627.3 | –343.1 | –281.4 | –2745.0 | –39.71 |
| SO42− (ppm) | 29,121.5 | –16,409.0 | –9655.8 | –18,257.7 | 25,536.4 | 20,067.4 | –633.0 |
| HCO3− (ppm) | 13,031.1 | 3584.7 | 1315.3 | –16,430.8 | –5422.6 | 729.0 | 73.12 |
| Ca2+ (ppm) | 9770.9 | –9432.7 | –8532.1 | 936.9 | 9995.4 | 6369.6 | –130.0 |
| K+ (ppm) | 62.05 | 22.65 | 245.4 | –148.3 | 138.6 | 129.9 | –0.713 |
| Mg2+ (ppm) | 464.0 | –704.8 | 2134.4 | –431.2 | 2068.3 | 329.2 | –11.18 |
| Na+ (ppm) | –4718.6 | –2909.1 | 7196.2 | –182.1 | 6407.7 | –1145.5 | –25.46 |
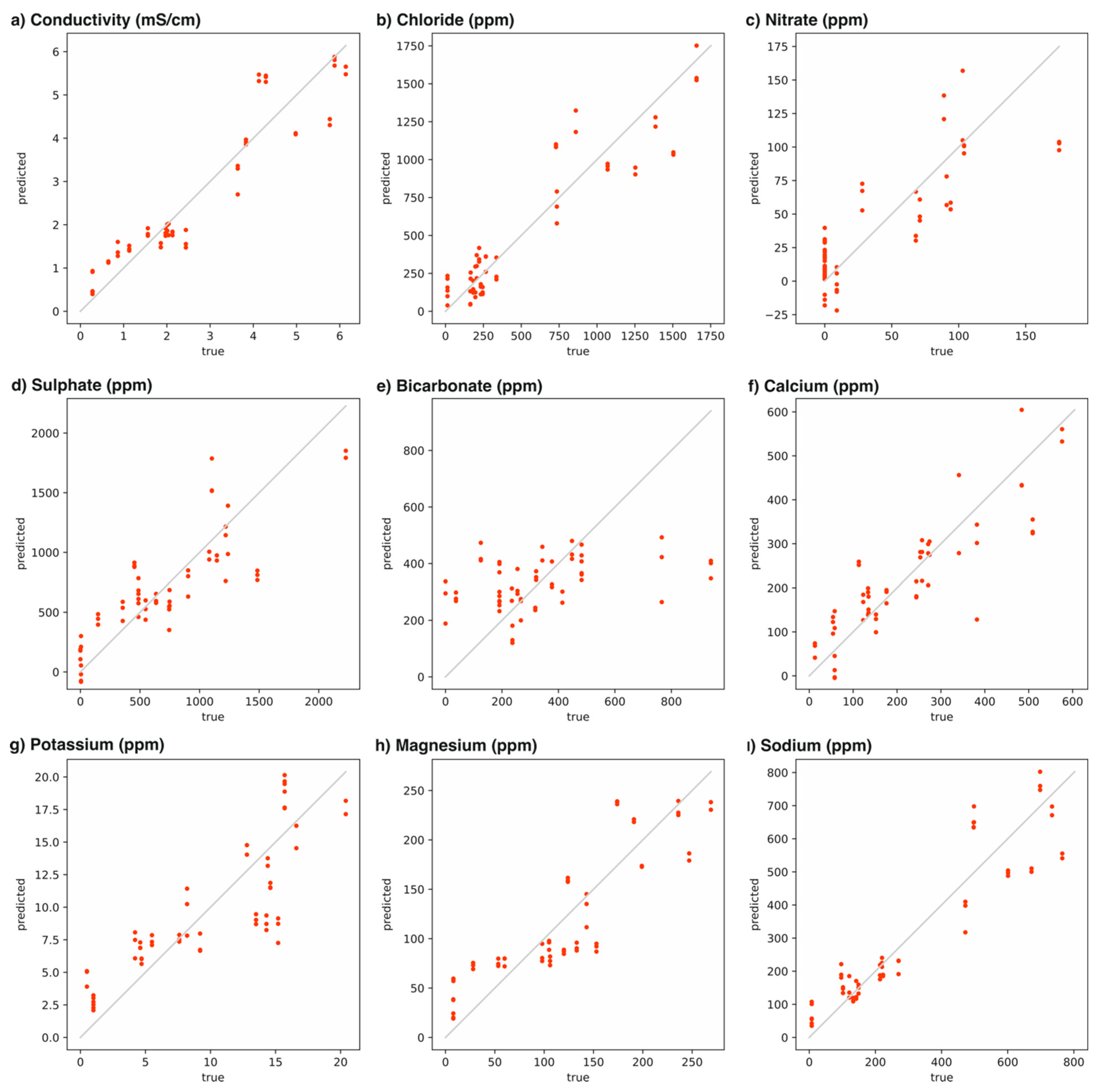
| Calibration | Cross-Validation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | R2 | CC | R2 | CC |
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | 0.89 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.91 |
| Cl− (ppm) | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.88 |
| NO3− (ppm) | 0.69 | 0.83 | 0.28 | 0.63 |
| SO42− (ppm) | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.22 | 0.57 |
| HCO3− (ppm) | 0.15 | 0.38 | −0.27 | −0.03 |
| Ca2+ (ppm) | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.24 | 0.58 |
| K+ (ppm) | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.49 | 0.72 |
| Mg2+ (ppm) | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.64 | 0.81 |
| Na+ (ppm) | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.88 |
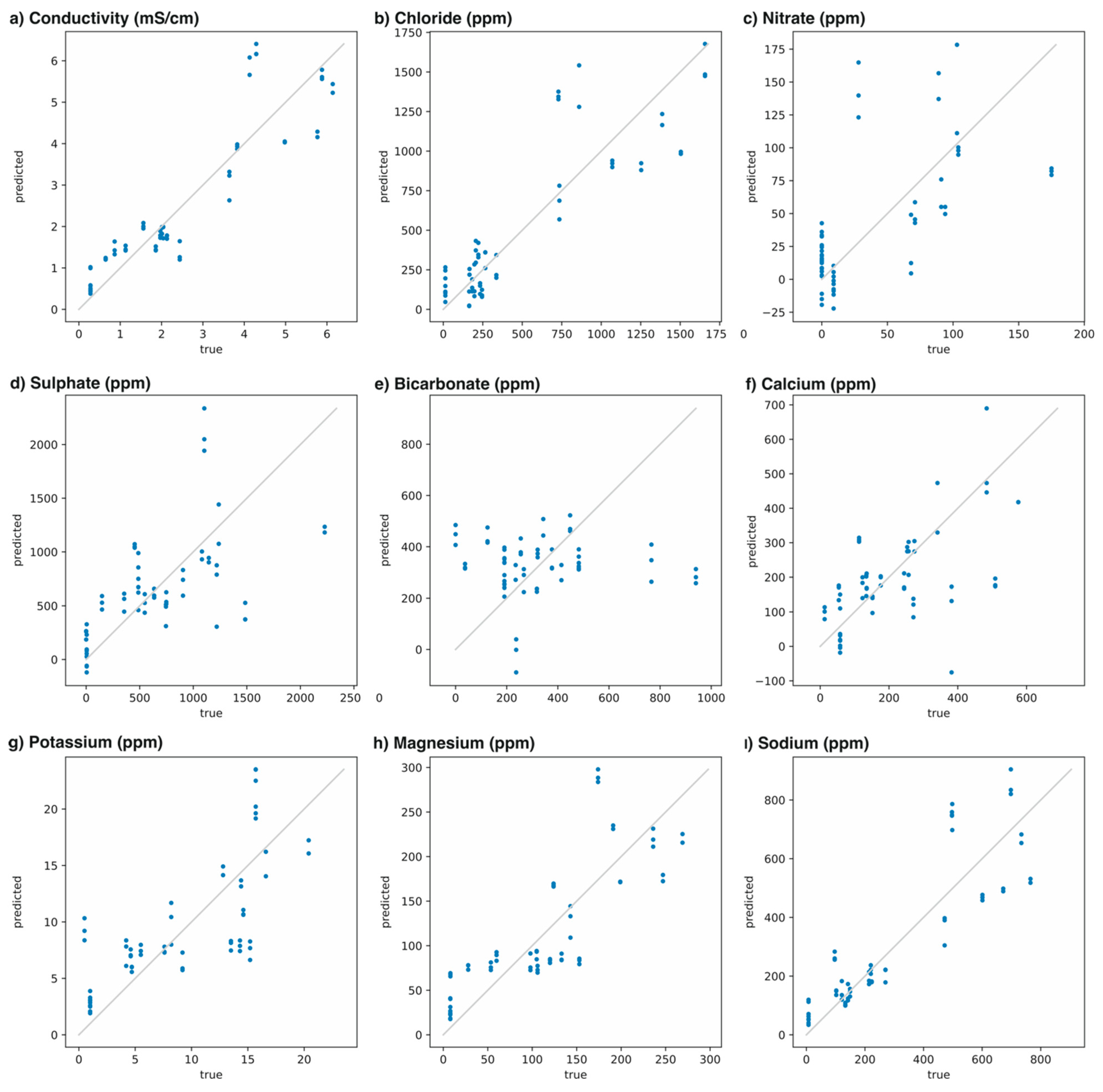
| Parameter | Model | Cross-Validated R2 | CC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | −0.58 + 118.3 ISE5 | 0.77 | 0.89 |
| Cl– (ppm) | −24,502.3 ISE1 + 33,680.8 ISE5 | 0.73 | 0.86 |
| NO3– (ppm) | −23.7 − 1610.3 ISE2 − 2285.0 ISE6 | 0.33 | 0.66 |
| SO42– (ppm) | −462.6 + 22,310.4 ISE1 − 28,551.2 ISE3 + 52,715.5 ISE5 | 0.34 | 0.64 |
| HCO3– (ppm) | 18,837.6 ISE1 | <0 | 0.01 |
| Ca2+ (ppm) | −156.8 + 8436.1 ISE1 − 14,265.8 ISE3 + 20,363.0 ISE5 | 0.51 | 0.73 |
| K+ (ppm) | 2.1 + 345.5 ISE3 | 0.49 | 0.73 |
| Mg2+ (ppm) | 4354.0 ISE5 | 0.63 | 0.80 |
| Na+(ppm) | −3651.9 ISE1 + 16,730.3 ISE3 | 0.73 | 0.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miras, M.; Cuartero, M.; García, M.S.; Ruiz, A.; Ortuño, J.Á. Analytical Tool for Quality Control of Irrigation Waters via a Potentiometric Electronic Tongue. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070407
Miras M, Cuartero M, García MS, Ruiz A, Ortuño JÁ. Analytical Tool for Quality Control of Irrigation Waters via a Potentiometric Electronic Tongue. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(7):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070407
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiras, Marina, María Cuartero, María Soledad García, Alberto Ruiz, and Joaquín Ángel Ortuño. 2023. "Analytical Tool for Quality Control of Irrigation Waters via a Potentiometric Electronic Tongue" Chemosensors 11, no. 7: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070407
APA StyleMiras, M., Cuartero, M., García, M. S., Ruiz, A., & Ortuño, J. Á. (2023). Analytical Tool for Quality Control of Irrigation Waters via a Potentiometric Electronic Tongue. Chemosensors, 11(7), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070407









