Abstract
This present review article considers the rapid development of miniaturized handheld near-infrared spectrometers over the last decade and provides an overview of current instrumental developments and exemplary applications in the fields of material and food control as well as environmentally relevant investigations. Care is taken, however, not to fall into the exaggerated and sometimes unrealistic narrative of some direct-to-consumer companies, which has raised unrealistic expectations with full-bodied promises but has harmed the very valuable technology of NIR spectroscopy, rather than promoting its further development. Special attention will also be paid to possible applications that will allow a clientele that is not necessarily scientifically trained to solve quality control and authentication problems with this technology in everyday life.
1. Introduction
For more than ten years, we have been closely following the process of the miniaturization of vibrational spectrometers (Raman, mid-/near-infrared (MIR/NIR)). Five decades ago, Raman and FT-IR spectrometers were room-filling instruments, and since the introduction of NIR spectroscopy as a long/short wavelength attachment to UV/VIS and IR instruments, respectively, this technology has evolved very rapidly with stand-alone instruments. Although the introduction of optical fibers, special probes, and chemometric evaluation techniques have brought the technology out of the laboratory and into the processes, strictly speaking, it has always been operated by scientific personnel only. The development of miniaturized and handheld NIR spectrometers over the past decade has not only expanded the application range of NIR technology to include on-site and in-the-field measurements, but it is also expected that these instruments will be used in non-traditional user environments in the not-too-distant future.
When the first handheld Raman and mid-IR spectrometers came on the market, they were used by the military much more quickly than industry for the on-site control of chemical quality and homeland security processes. Since then, other major public services, such as emergency services, law enforcement, environmental agencies, and food control facilities, have also recognized the potential of handheld spectrometers. Most of the above applications are primarily concerned with the rapid and secure on-site classification of unknown substances—sometimes hazardous or toxic—or authentication of the correct origin of goods by trained users—but not necessarily scientists [1,2,3,4]. Therefore, it seems that the realization has taken hold that vibrational spectroscopy—and as will be explained in more detail below, specifically handheld NIR instruments—can make a significant contribution to improving safety and general standards in everyday areas of life [5,6,7,8,9,10,11].
One of the most important goals in miniaturizing an analytical instrument is to ensure that the reduction in size does not come at the expense of measurement performance. Therefore, handheld spectrometers will only have a real impact on quality control if their spectra can provide comparable analytical results to larger benchtop instruments. However, with respect to this issue, we have demonstrated in numerous feasibility studies in recent years (including the test of miniaturized and benchtop spectrometers to solve the same analytical problem) that equivalent results can be obtained for both qualitative and quantitative applications [7,9,12].
While the weight of most Raman and MIR spectrometers is still in the range of 1 kg, miniaturization of NIR spectrometers has progressed down to ~100 g, and developments are underway to integrate them into cell phones [13]. In addition, Raman and MIR handheld spectrometers are still in the tens of thousands price range (USD) because, despite miniaturization, they offer a variety of add-ons and accessories, such as orbital raster scanning (ORS), surface-enhanced spectroscopy (SERS), Sequentially Shifted Excitation (SSE™), and dual laser excitation (DuoLASERTM) [14], for the Raman technique and various measurement modes for the FT-IR technique, such as attenuated total reflection (ATR) and diffuse/regular reflection. In contrast, miniaturized NIR systems have already reached price levels of USD < 1000 in some cases. Given these differences, the acquisition of Raman and MIR instruments will be limited to the aforementioned public institutions, whereas NIR systems will become affordable for private use in everyday-life applications by a non-expert user community in the near future because of further cost reductions resulting from the possibility of large-scale manufacturing.
NIR spectroscopy is primarily based on the absorption bands of overtone and combination vibrations of C-H, O-H, N-H, C=O, and C=C functionalities [15,16]. These signals occur at 10–100 times lower intensity compared to fundamental vibrations in the MIR [17]; however, with increasing sample thickness and in combination with chemometric evaluation models, the NIR technique has proven to be an excellent tool for qualitative and quantitative analysis with comparable chemical specificity and sensitivity to Raman and MIR spectroscopy. Due to the simplicity of sample presentation (measurements are predominantly performed in diffuse reflection or transflection without sample preparation), the advantages of miniaturization, and the affordability mentioned above, NIR spectroscopy has surpassed the other vibrational spectroscopic techniques as a handheld tool [18]. This review article, therefore, focuses primarily on the different design principles and the performance of commercially available, modern handheld NIR spectrometers and discusses their potential use in relation to selected on-site applications for materials and food testing.
2. Instrumentation
Generally, the main building blocks of a handheld NIR spectrometer are similar to a benchtop instrument. Thus, the light source of handheld NIR spectrometers is also based on tungsten-halogen lamps in analogy to benchtop instruments (but taking into account the thermal stability of the light source for a miniaturized system), and several variants are available for the wavelength selector and (depending on this) for the detection system [19].
In view of the rapid instrumental developments, several articles [2,5,19,20,21,22] have dealt with miniaturized and handheld NIR spectrometers in recent years. In the present work, we bring this topic up to the very latest level for the interested readers.
Miniaturization of NIR spectrometers has progressed primarily through the use of MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical) and MOEMS (Micro-Opto-Electro-Mechanical) systems [23,24]. Usually, portable NIR spectrometers are divided into two categories according to the type of detector: array detectors and single detector devices. In the NIR wavelength range, indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) is the preferred material for manufacturing detectors. Compared with array detectors, the price of a single-detector system is much lower [25]. Thus, for the design of new instruments it is the preferred alternative for the reduction of hardware costs.
As for the wavelength selector, at present the equipment can be divided into the following types:
- (a)
- Linear-variable filter instruments with array detectors.
- (b)
- MEMS-based FT-NIR instruments with an opto-electro-mechanical structure.
- (c)
- Spectrometers with Texas Instruments’ digital micro-mirror device (DMD™) as wavelength selector.
- (d)
- Spectrometers with a Fabry-Perot etalon acting as a tunable wavelength filter.
- (e)
- NIR grating micro spectrometers.
- (f)
- Individual NIR scanner based on 16 organic solar cells as detectors, that absorb only a limited wavelength range in the NIR and does not require a monochromator.
In Figure 1, the different types of selected, commercially available, handheld NIR spectrometers are summarized with their simplified building principles and the most important performance parameters. An in-depth discussion of the individual monochromator/detector principles can be found in a recent publication [21]. As far as the performance of different handheld instruments is concerned, a high S/N ratio and a wide range of available wavelengths/wavenumbers are generally beneficial for the prediction performance. In a trade-off situation, a high S/N ratio can compensate for the shortcomings of a narrow wavelength range.

Figure 1.
Handheld NIR spectrometers with different monochromator/detector principles and their performance parameters: (a) linear variable filter instruments (trinamiX GmbH, Ludwigshafen, Germany; VIAVI Solutions Inc., Santa Rosa, CA, USA); (b) digital micro-mirror device (DMD™) spectrometers (Texas Instruments, Dallas, TX, USA; Innospectra Corp., Xinzhu, Taiwan, China); (c) Fabry Perot tunable filter instrument (Spectral Engines, Helsinki, Finland); (d) MEMS FT-NIR spectrometers (Si-Ware Systems, Cairo, Egypt; Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu city, Japan; Southnest Technology, Hefei, Anhui, China); (e) grating microspectrometers (Insion GmbH, Obersulm, Germany; OrO Photonics, Xinzhu, Taiwan, China) (f) NIR scanner with 16 solar cell detectors (Senorics GmbH, Dresden, Germany). Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [21].
Regardless of instrument performance, simplification of sample presentation also plays a major role in the ease of use of handheld NIR spectrometers. Most applications for on-site or in-the-field measurements focus on the investigation of solids where the NIR scanner window is brought into direct contact or only a short distance from the sample and the spectra are recorded in diffuse reflection. A very interesting development, which is also suitable and highly recommended for the measurement of heterogeneous solid samples, has recently been launched by SiWare Systems. In Figure 2b, this hardware add-on is shown in use for the bottom-up measurement of soil samples in comparison to the conventional manual diffuse-reflection approach (Figure 2a). Due to the rotation of the turntable and the bottom-up measurement through a glass bottom, on the one hand, a very easy sample preparation is guaranteed and, on the other hand, an extensive exclusion of the influence of the heterogeneity of the sample is ensured. For measurements of liquid samples, either special hardware add-ons (see the example of oil measurements in the Applications section) or the NIR spectrometer with transflectance mode must be used.

Figure 2.
Examples of sample presentation for diffuse-reflection measurements of soil: (a) manual operation with an LVF NIR scanner (trinamiX, Ludwigshafen, Germany); and (b) rotating-dish accessory of the MEMS FT-NIR scanner (Si-Ware Systems, Cairo, Egypt).
3. Applications
Numerous articles are currently devoted to the quality control of agricultural products and foodstuffs [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37], pharmaceuticals [12,38,39,40,41,42,43], polymers [7,44], and forensic investigations [45,46,47] with handheld NIR spectrometers. In a very recent literature review, Bec et al. summarized the applications of this technique to the analysis of food, including milk and dairy products, meat, fish, fruits and vegetables, beverages, and syrups [5].
Unfortunately, fraud and adulteration have recently become frequent issues ranging from life science to everyday life materials, such as foods and textiles. The previously mentioned progress in miniaturization and increasing affordability of handheld NIR spectrometers make them an attractive quantitative analysis and authentication tool for customer protection by on-site and in-the-field measurements. The application examples listed below not only demonstrate the general potential of handheld NIR spectrometers for the analysis of materials but also illustrate the impact for quality control in everyday life. As part of the description of these application examples, efforts to develop robust calibration models, including the use of external validation sample sets, replicate measurements of samples, choices of variable selection algorithms, and spectral preprocessing algorithms, will also be discussed.
The following application examples refer either to recently published papers or to feasibility studies performed in our laboratories. In the former case, only the results are briefly summarized, while in the latter case, both the measurements, spectra pretreatment, and evaluation are described in some detail. The evaluation of the measured spectra was always carried out with the aid of chemometric evaluation models, both for qualitative analysis and for quantitative determinations. Various commercial or specially developed evaluation programs were available for this purpose.
3.1. Textiles
3.1.1. Qualitative Analysis
Textiles are extremely important materials for daily life, whether for use as simple body coverings or beauty and decoration purposes. Although their quality and price vary widely, it is difficult for the general population to identify and distinguish the material purely visually. Thus, there is an urgent need for a simple tool to quickly verify the correct identity of purchased textiles to protect consumer rights. With this in mind, we have investigated the potential of portable near-infrared spectrometers for textile authentication and identification [48].
Prices of textiles (natural materials—cashmere, silk, cotton, etc.; or synthetic materials—polyamide, acrylic, polyester, etc.) vary widely, and fraudsters often sell low-quality materials to gullible customers at unreasonably high prices. For example, mercerized cotton, which has a shiny feel, is used to make fake silk carpets, quilts, and scarves. However, this deception can be easily avoided using handheld NIR spectroscopy by simply comparing reference spectra with the spectrum of the material tested on-site (Figure 3). Therefore, even non-expert users can quickly identify or authenticate products of interest by handheld NIR spectroscopy in combination with an easy-to-use evaluation model for specific materials.
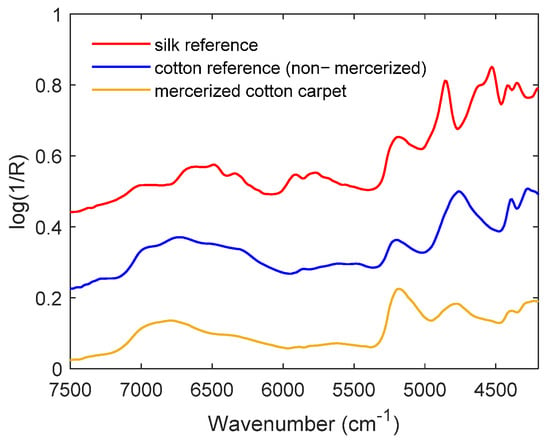
Figure 3.
Rapid identification of the actual material utilized for a carpet (yellow spectrum) based on visual inspection of NIR spectra recorded with a handheld NIR instrument.
For the identification of more textile materials, a proof-of-concept study was conducted [48]. Forty-eight samples were collected from nine different categories of natural and synthetic materials (cotton, wool/cashmere, silk, acrylic, Kevlar, elastane, polyester, Nomex, and polyamide-6/polyamide-66). NIR spectra were measured in diffuse reflection using four different handheld scanners (DLP NIRscan Nano EVM, Si-Ware Systems FT-NIR, Spectral Engines NR 2.0-W, and Viavi MicroNIR 1700). Principal component analysis (PCA) was combined with soft independent modelling of class analogies (SIMCA) and mean Euclidean distances in the PCA score plot were evaluated to build a classification model for textiles whose performance was validated with 24 external samples. In Figure 4, the covered wavenumber ranges of the four spectrometers are compared based on the spectra of two textiles (cashmere wool and silk). Due to the coverage of the largest and most important spectral range (blue spectra in Figure 4a,b), the best classification capability was demonstrated by the MEMS FT-NIR (Si-Ware Systems) instrument.
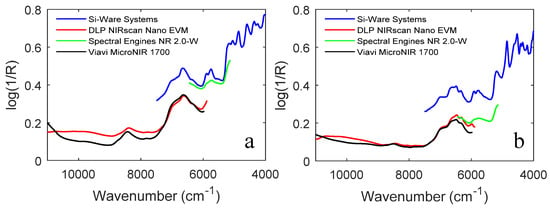
Figure 4.
NIR spectra of two selected representatives of the investigated textile species ((a) cashmere wool, (b) silk) recorded with the four different handheld NIR spectrometers. Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [48].
3.1.2. Quantitative Analysis
Due to its exceptional chemical, physical, aesthetic, and tribological properties, silk is a popular material for the manufacturing of clothing, blankets, and carpets. It is often blended with cotton, polyester, or other materials to achieve a different look and feel [49]. This leads to strong price fluctuations and because the distinction of silk blends from pure silk is difficult for the ordinary consumer, this situation is often used in tourist centres or on-line sales to deceive customers [50,51].
To document the suitability of handheld NIR spectrometers for detecting such deception, the rapid elucidation of the composition of silk–cotton blends using miniaturized NIR scanners is demonstrated as a first quantitative example. Five different handheld NIR spectrometers, trinamiX spectrometer (trinamiX GmbH, Ludwigshafen, Germany), NeoSpectra Scanner (Si-Ware Ltd., Cairo, Egypt), Viavi MicroNIR 1700 (Santa Rosa, CA, USA), Spectral Engines NR 2.0-W (Helsinki, Finland), and SenoCorder Solid (Dresden, Germany), were used to detect the cotton content in silk–cotton blends [9], and their performance was compared with the Thermo Antaris II reference spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Madison, WI, USA). Eighty-one blended samples with cotton content from 0.00 to 100.00% (w/w) were prepared, and a partial least squares (PLS) model was constructed. Twenty samples (3.00%~98.00% (w/w)) were prepared as a test set for external validation. The sample presentation for the measurements with the different instruments and the corresponding spectra of pure silk and cotton are shown in Figure 5. The results showed that the root mean square error (RMSE) of the calibration model established by the laboratory benchtop NIR spectrometer was about 1.9% (w/w), while the corresponding values for handheld instruments ranged from 2.5 to 4.0% (w/w). Notwithstanding these slight RMSE variations, all handheld spectrometers in this comparative study were considered suitable tools for detecting intentional fraud in silk–cotton blends, thus enabling customers to protect themselves against adulteration.
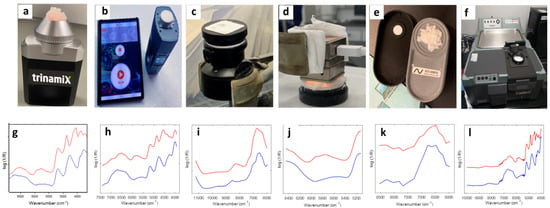
Figure 5.
Sample presentation for spectra recording with the different NIR instruments. Top row: (a) trinamiX scanner, (b) NeoSpectra scanner, (c) Viavi MicroNIR 1700, (d), Spectral Engines NR 2.0-W, (e) SenoCorder Solid, and (f) Thermo Antaris II benchtop instrument. Bottom row: (g–l) the spectra of pure cotton (blue) and pure silk (red) recorded with the corresponding instruments above. Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [9].
As pointed out above, for the performance of handheld instruments, a high S/N ratio and a large wavelength/wavenumber range typically have beneficial effects on the predictive performance. In addition, a high S/N ratio can always compensate for the shortcomings of a narrow wavelength range.
In a similar application example, the silk was blended with polyester [52]. Based on a PLS calibration with 65 reference samples and 34 test samples of known content (silk/polyester blends in the concentration range 100/0–50/50 % (w/w)), a NIR spectroscopic technique for testing with a handheld instrument (MicroNIR 1700) was developed, which allows a rapid estimation of the silk content with a root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) of about 2% (w/w) directly at the point of purchase (Figure 6).
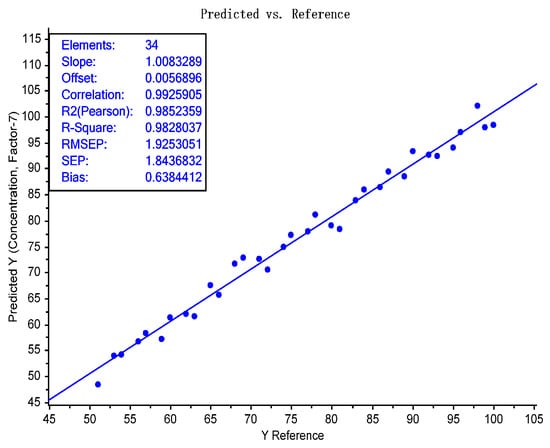
Figure 6.
Actual/predicted plot of 34 test samples demonstrating the feasibility of an NIR spectroscopic on-site test for the determination of the silk content in quilts.
3.2. Polymers
Recycling the most common polymers, such as poly(ethyleneterephthalate) (PET), polyethylene (PE), poly(vinylchloride) (PVC), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS), is an extremely important issue for the sustainable use of raw materials and environmental protection. In the following application example, two handheld spectrometers (NeoSpectra and NIR One) based on different monochromator principles and different wavelength/wavenumber ranges (see also Figure 1) were used for the development of a classification model for the aforementioned polymers.
Forty-three polymer samples in different morphologies (plates, pellets, powders, films, and fibres) were collected and measured in diffuse reflection with the two spectrometers. Some samples contained small amounts of additives, pigments, or dyes (however, no carbon black), which had no significant impact on the NIR spectra. Then, 29 samples were randomly selected as a PCA calibration set for modelling, while the other 14 samples were used for the validation of the PCA model performance.
The diffuse reflection spectra (averaged triplicates) were pre-treated by the second derivative and SNV algorithms. The effect of pre-treatment based on the raw spectra of the five different polymers measured with the NeoSpectra scanner is shown in Figure 7.
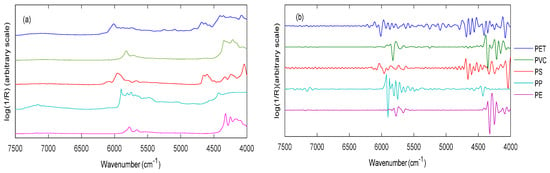
Figure 7.
Comparison of the original spectra (a) of selected representatives of the five polymers measured using the NeoSpectra scanner and (b) the corresponding spectra after pre-treatment by 2nd derivative and SNV. Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [7].
Figure 8a1,b1 shows the PCA score plots for the first three PCs of the five polymer commodities measured by the two spectrometers. In Figure 8a2,b2, the same score plots with the inclusion of the test samples (cyan dots) are shown. It is demonstrated that the MEMS based FT-NIR spectrometer (NeoSpectra) with a large wavenumber range can clearly distinguish the five polymers and successfully assigns the test samples to the correct clusters. However, the Fabry Perot tuneable filter instrument (NIR One) failed to separate PE and PVC (Figure 8b1,b2, red and magenta dots) because of its limited wavenumber range and reduced significant spectral features.
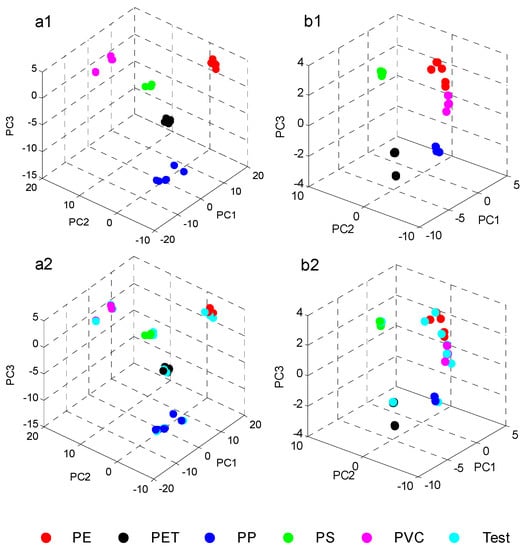
Figure 8.
Three-dimensional PCA score plots based on the calibration spectra of the five polymer commodities measured with the two different handheld spectrometers: (a1) NeoSpectra Scanner; (b1) NIR One; (a2,b2) corresponding score plots with the inclusion of the test samples (cyan points). Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [7].
Incidentally, the result found via PCA of a better identification trend of the polymer clusters with the data from the instrument with a wider wavelength/wavenumber range (NeoSpectra scanner) was also confirmed by soft-independent-modelling-class analysis (SIMCA) in the work described.
In the PCA, the clustering state has a significant influence on the classification ability. Usually, the larger the Euclidean distance between two classes, the stronger the ability to classify them [53], which provides a way to compare the ability to distinguish and recognize spectra measured on different spectrometers. Table 1 clearly reflects that using the NeoSpectra scanner can achieve larger distances.

Table 1.
The Euclidian distances between each two polymers of the 3D score plots based on the spectra measured with the two different instruments (the bottom line shows the mean values over all values for the respective spectrometer). Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [7].
3.3. Food
In no other material sector (except for pharmaceutical products) are adulteration and deception as widespread and associated with negative health consequences for the consumer as in the food sector. In the following sections, we discuss, by way of example—but certainly not comprehensively—some applications of food authentication and discrimination and food fraud detection using portable NIR spectroscopy.
3.3.1. Edible Oil
Edible oil is an important food ingredient and numerous studies have been conducted to develop methods for its quality control by handheld NIR spectrometers, including the detection of adulteration, identification, and quantitative analysis of quality indicators.
Qualitative Analysis
In several articles, promising results regarding the quality control of oil by handheld NIR spectroscopy are reported. Herein, we selected the detection of adulteration of palm oil, copaiba oil, olive oil, and others. Regarding palm oil adulteration, the NIRScan Nano spectrometer was used to discriminate pure palm oil from palm oil adulterated with recycled cooking oil in varying concentrations. In this study, it was demonstrated that palm oil samples adulterated with recycled cooking oil at a concentration of 15% (w/w) and above could be classified with 100% accuracy [54]. For the authenticity identification of copaiba oil, the handheld VIAVI MicroNIR 1700 spectrometer was used in combination with DD-SIMCA, and the results showed that the specificity related to samples not belonging to the target class was 97.3%, and the average efficiency of the model was 92.3%, revealing it to be very promising for quality control and authenticity testing applications [55]. Olive oil contains a high concentration of unsaturated fatty acid, which is very beneficial to the human body. Therefore, it is often adulterated with low-price oil. Yan et al. examined the spectral features of olive oils with the NIR Pro 1700ES spectrometer (JDSU, Milpitas, CA, USA) to explore the technology’s capability to distinguish extra virgin olive oil from lower grade oils. The results demonstrated that the handheld NIR spectroscopic technique is promising for the rapid screening of olive oil grades. In these investigations, especially the 1350–1570 nm wavelength range, proved very sensitive for the distinction of the oils [56]. The NeoSpectra scanner (Si-Ware Systems, Inc., Cairo, Egypt) provides an effective tool for the rapid in situ identification with 100% accuracy of the oil type used for potato chips. The spectra have also been used to predict the major fatty acid composition (palmitic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid) with a strong correlation (Rval > 0.97) and low standard error of prediction (SEP = 1.08–3.55%(w/w)) [57].
As a final example, peony oil shall be discussed here [58]. The beautiful peony flower has not only a high ornamental value but also a high nutritional and health care function. It is a pure natural yellow edible oil (Figure 9a), in which the total content of unsaturated fatty acids, including α-linolenic acid (ω-3 fatty acid), linoleic acid, and oleic acid, is >90.0%(w/w). In addition, it contains abundant healthy active substances, such as squalene, flavonoids, and polyphenol compounds [59,60,61]. Thus, it enjoys great popularity, but to avoid fraud by fake products, a rapid identification analytical technique by handheld NIR spectroscopy was investigated.
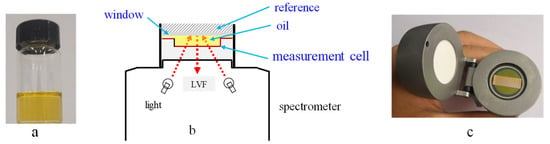
Figure 9.
MicroNIR 1700 handheld spectrometer with a liquid-sample accessory for measuring oil samples (a), schematic diagram of the measurement (b), and the liquid-sample accessory (c). Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [58].
A MicroNIR 1700 instrument (Figure 9b) was used to record the spectra for the development of a calibration model to rapidly discriminate peony oil from other oil species. Eighteen peony seed oil and nineteen other oil samples (olive, sunflower, blended, corn, and sesame), collected from different oil factories, were used as the calibration set to build a model. A test set consisting of 9 peony seed oils and 10 other oil samples was collected for the external validation of the model performance.
The spectra were pre-treated by SNV, and then a PCA was carried out. Additionally, a SIMCA model was used to test the identification capability for the spectra of the test set. In Figure 10A, the 3D-PCA score plot based on the first three PCs is shown for the calibration samples. The peony seed oil was clearly discriminated from the other oil species and the test samples were assigned to the correct clusters. The SIMCA classification result is represented in a Coomans plot and, in the present case, the peony seed oil identity can be achieved if the spectra of the unknown test samples were assigned to the relevant quadrant defined by the SIMCA model. In Figure 10B, the Coomans plot (5% significance) represents the unambiguous discrimination of peony and non-peony oil samples by assigning the spectra of the test set correctly to the corresponding quadrants. Thus, it has been clearly proved by this feasibility study that handheld NIR spectroscopy can be utilized for the discrimination of peony oil from other oil samples.
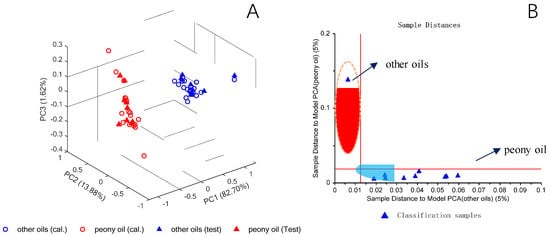
Figure 10.
3D-PCA score plot for the calibration samples (open symbols) and test set samples (closed symbols) of peony seed oil and other oil species (A) and Coomans plot for the spectra of test samples of peony seed oil and other oil species (B). Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [58].
Quantitative Analysis
As stated further above, the quality of oil crops and oil adulterated with other substances are one of the research focuses of handheld NIR spectroscopy. For canola oil quality, for example, the NIR models developed with the MicroNIR OnSite-W instrument (Viavi Solutions Inc, Santa Rosa, CA, USA.) for the content of oil, protein, oleic acid, and iodine value showed excellent stability and predictive power with R2 values of 0.94–0.99 and low standard errors of prediction (SEPs) for external validation sample sets [62].
For in-the-field quality evaluation of the oil content in olive drupes, the portable and comparatively cheap Vis/NIR (500–1000 nm) device Jaz (OceanOptics Inc., Dunedin, FL, USA) was used, and the results showed that the R2CV and RMSECV were 0.67 and 3.58%(w/w), respectively. However, the prediction accuracy was low, compared to a benchtop instrument [63]. For palm oil, Sudan IV dye is often added to improve the appearance for a higher price. With reference to this issue, an identification study was conducted, and it was demonstrated that palm oil samples adulterated with Sudan IV dye in the concentration range of 0.002–0.10 % (w/w) can be certified rapidly and nondestructively by using the short-wave handheld NIR spectrometer (740–1024 nm) SCIOTM (model CP-SC006). The best PLS results (R2C of 0.91, R2P of 0.90, RMSEC of 0.0841% (w/w), and RMSEP of 0.0868%(w/w)) were achieved with SNV preprocessing [64].
Another very important research area is oil composition, including normal components (fatty acid content) and harmful components (peroxide value, etc.).
For the determination of fatty acid composition, a handheld NIR spectrometer (MicroNIR OnSite, VIAVI Solutions Inc., Monza, Italy) was used for on-site determination of the fatty acid’s (FAs) composition of industrial fish oils from fish byproducts. Evaluation of the external test set in models for saturated fatty acids (SFAs), monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and omega-3 showed promising results, with R2 values of 0.98, 0.97, 0.97, and 0.99, respectively; RMSEPs (%(w/w)) of 0.94, 1.71, 1.11, and 0.98, respectively; and bias (%(w/w)) values of 0.78, 0.12, 0.80 and 0.67, respectively [65].
During the storage of oil, some intermediate products are produced, which are very unstable and continue to decompose into aldehydes, ketones, and other oxides, which further deteriorate the oil [66]. The degree of oxidation of oils and fatty acids is reflected by the peroxide value (PV). Long-term consumption of food with a high PV is harmful to human health [67]. Therefore, a fast detection method for the PV of oil is an everyday life requirement for common people. For this purpose, a MicroNIR 1700 instrument combined with a liquid-sample accessory (Figure 9b,c) was applied to investigate the feasibility of identification. Fifty-four oil samples were collected as the calibration set for the development of the calibration models, and twenty-seven samples were collected as the test (or prediction) set to externally validate the prediction capability of the calibration models. The spectra were pre-treated by SNV scatter correction and the wavelength variables were optimized by three kinds of wavelength selection algorithms: competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS), random frog (RF), and genetic algorithm (GA). The results showed that CARS has the best performance with the lowest RMSEC of 0.76 mmol/kg. The calibration performance was also validated by the test samples [68].
3.3.2. Flour
Flour is obtained by milling a variety of different grains (wheat, barley, corn, oat, rye, potato, and rice) and is used as raw material for a wide variety of food products [69,70,71,72], including bread, pasta, cake, and dumplings. Due to different kinds of flour having different prices, the authentication and quality assurance of this basic food product are of great public importance.
Adulteration
Since almond (Prunus dulcis) flour is highly nutritious and has a high price, it has become a candidate for adulteration to increase the profit by lowering the product cost. Netto et al. [73] used three different portable NIR instruments (DLPR NIRscanTM Nano, MicroNIR™ 1700, and NeoSpectra FT-NIR) to identify the authenticity of almond flours. The classification results achieved 100% sensitivity and more than 95% specificity for samples with an adulterant concentration of 5% (w/w) or above, and the PLS models showed R2 values greater than 0.90 for all models and RMSEP values between 3.2 and 4.8% (w/w) for purity. For the detection of quinoa flour adulteration, portable near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRscan™ Nano) was used to detect adulteration in the range of 0–51% (w/w). The PLS model had an R2P of 0.98, RMSEP of 1.60%(w/w), RPD of 7.71, and RER of 22.56, which demonstrated the potential of portable NIRS as a rapid, low-cost and non-destructive analytical tool for adulteration detection in this product [74].
In another application example, a low-cost, ultra-compact, and handheld MicroNIR 2200 spectrometer (JDSU, Santa Rosa, CA, USA) with a spectral wavelength range of 1150–2150 nm was used to detect the adulteration of wheat flour by eight varieties of cassava flour at five concentration levels of 5, 10, 20, 30, and 40%(w/w). The prediction accuracies of the 2-class discriminant models were all over 95.00% in separating the pure and adulterated wheat flour. However, the highest overall accuracy of a 6-class (0, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 40%(w/w)) discriminant model was only 75.31% [75].
The examples cited above demonstrate that the technique of handheld NIR spectroscopy is a very valuable tool for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of flours and their derivatives.
Quantitative Analysis
The main ingredient for staple food products, such as bread, pasta, dumplings, and noodles, is wheat [72]. Due to the environmental and various climate influences, the protein, wet gluten, moisture, ash, sedimentation, and further physical and chemical properties of flour, milled from wheat of different origin, vary greatly, which directly affects the scope of its applications [76,77,78,79]. For noodles, high protein content in the flour is needed, while, on the contrary, low content is suitable for biscuits. Many people use a variety of wheat flours to prepare different kinds of food, and a handheld NIR spectrometer would be a welcome and affordable tool to rapidly test the flour in use for its qualification to produce a specific food, such as high-quality bread, pita bread, baguette, cakes, hand-pulled noodles, dumplings, etc. To develop a solution approach to this problem, 187 samples of wheat flour, belonging to the 405, 1050, 700, and 550 types, were collected as the calibration set, and five parameters of protein, moisture, wet gluten, ash, and sedimentation were chosen as the prediction indicators. Three kinds of handheld NIR spectrometers, Spectral Engines NR 2.0-W (Helsinki, Finland), Viavi MicroNIR 1700 (Santa Rosa, CA, USA), and Si-Ware Systems (Cairo, Egypt), were used to measure the samples, and PLS calibration models were developed. Additionally, the prediction performance of the calibration models was validated by 48 test samples [80]. Furthermore, the feasibility study provided the following conclusions: (1) the basic parameters of wheat flour can be rapidly determined by using the different handheld NIR spectrometers; (2) protein yielded the highest calibration accuracy, followed by ash, wet gluten, moisture, and sedimentation; (3) for the performance comparison of the Si-Ware Systems and Viavi MicroNIR 1700 spectrometers, there is competition with reference to wavenumber range and signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio; and (4) as shown for other applications, the lower calibration performance of the Spectral Engines instrument is due to the narrow spectral wavelength/wavenumber range of its spectra.
3.3.3. Hazelnut
Hazelnuts are widely used in the food industry for the production of butter, chocolate, ice-cream, dairy products, confectionary and baking, and can also be added to yoghurts, breads, cereals, and liquors. Besides the food industry, hazelnuts can also be used as additives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations [81]. Thus, the hazelnut crops have increased in many countries in recent years, and the hazelnut market is projected to reach a CARG (Compound Annual Rate of Growth) of 10% during the forecast period (2022–2027) [82].
The oxidation process is the main degradation factor in food containing oil and fat. Since hazelnuts are rich in mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids [83], the control of storage, shelf life, and annual harvest has shown enormous importance both in the industrial production chain and in supplier analysis.
To test the feasibility of discrimination between hazelnuts harvested in two successive years of cultivation, the trinamiX spectrometer (trinamiX GmbH, Ludwigshafen, Germany) was used in conjunction with a Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) model. Twenty samples (ten from the 2021 crop and ten from the 2022 crop) were ground to obtain homogeneous samples and minimize the physical effect of different particle size.
The powdered samples were placed in petri dishes and the spectrometer was positioned to measure top-down while maintaining a maximum distance of 1–2 mm between the scanner window and the sample surface (Figure 11A). Spectra were collected every 2s in the wavenumber range of 4080–6896 cm−1 with a spectral resolution of 8 cm−1. Triplicates were measured at different positions of the sample and the average of these spectra (Figure 11B) was utilized to develop the PLS-DA model. The raw average spectra were preprocessed by the 2nd derivative (window 9, polynomial 3) and the wavenumber ranges 4080–4200 cm−1 and 6896–6200 cm−1 were truncated (Figure 11C) before further processing. Slight differences can be found in the spectral profile between 4200 and 4500 cm−1, which can be attributed to combination bands of ν(C-H) and ν(C-C) of lipids and ν(O-H) and ν(C-O) and ν(C-H) and δ(CH2) of polysaccharides [17].
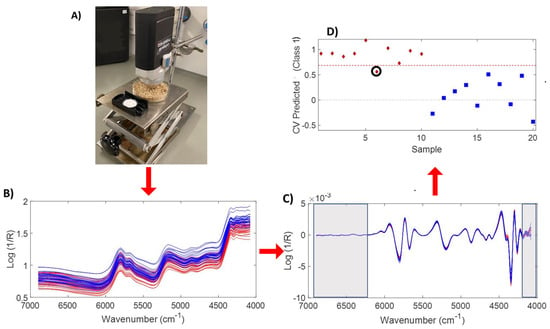
Figure 11.
The whole analysis process, experimental set-up of hazelnut-powder measurement (A), spectral processing (B,C), and PLS-DA results (red: 2021 crop, blue: 2022 crop) (D).
An exploratory PLS-DA model was built using leave-one-out cross-validation and the results are shown in Figure 11A. The threshold for discrimination of the old and the new crop is shown by the dashed red line (Figure 11D). Samples above the threshold are attributed to the 2021 crop, while the samples below the limit are assigned to the 2022 crop. Only one sample of the old crop (circled in black) was erroneously attributed to the new crop. The sensitivity value of new samples was 90%, while their specificity was 100%. On the other hand, samples of the old crop reached values of 100% and 90% for sensitivity and specificity, respectively.
To develop a robust model, further samples will be added to the model and an external validation set will be tested. Notwithstanding further improvements, the achieved preliminary results demonstrate the potential of this application for the differentiation of different crops.
3.3.4. Bread Staling
In the preceding examples, applications of general, practical value to consumers have been discussed first and foremost. In the following study of bread—the most widely consumed food—it will be demonstrated that data measured with a hand-held NIR scanner can also be used as a basis for a sophisticated, advanced research application.
According to the 2021 Food Waste Index [84], global food waste has been estimated at 931 million tons per year. Unfortunately, bread is also one of the most wasted products because of loss of taste and other negative aging characteristics. The reason is the so-called staling process, which is based on the two critical factors: retrogradation (recrystallization) of starch [85] and the decrease of water content by evaporation and diffusion from core to crust. Therefore, in a lengthy feasibility study, based on time-dependent NIR measurements of a fresh bread surface in diffuse reflection, we analyzed the chemical process of staling by applying a Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy (2D-COS) analysis [86] and a Multivariate Curve Resolution—Alternating Least Squares (MCR-ALS) model [87,88] to the spectroscopic data.
Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy (2D-COS)
Many techniques have been applied for the investigation of the staling process, such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) [89], nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) [90], rheological studies [91], and mid-infrared spectroscopy [92]. To demonstrate the potential of handheld NIR spectroscopy, the present investigation was carried out with the NeoSpectra FT-NIR Scanner of Si-Ware Systems (Cairo, Egypt), which operates on the basis of a monolithic MEMS single-chip Michelson interferometer.
To elucidate which chemical functionalities of starch and water are sensitive to the staling process and to propose a possible sequence of structural changes based on the intensity variations, 2D-COS analysis was applied as the first step. The surface of fresh baguette was monitored in this work in total over a period of 48 hours. However, only the 2D-COS results of the most important structural changes of the first 6 h are discussed here in a condensed version. The complete analysis and discussion of the 48 h interval can be found in Neves et al. [93].
Three replicate spectra were recorded in the wavenumber range of 4000–7400 cm−1 from a Ø 10 mm sample spot with a scan time of 10 s at a spectral resolution of 66 cm−1 (at 1550 nm). As a reference, a 99% Spectralon reflectance standard (Labsphere Inc., North Sutton, NH, USA) was used. The spectra were stored by wireless connectivity via Bluetooth on a Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (Seoul, Republic of Korea) tablet. The average spectra of the replicate measurements were calculated and an extended multiplicative scatter correction (EMSC) [94] was applied to the dataset. In the final preprocessing step, the spectral range was truncated to the wavenumber range of 6000–4000 cm−1. In Figure 12a,b the structural schematic of retrogradation and the measurement set-up are shown.
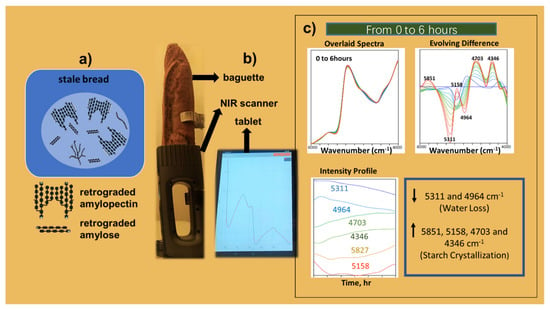
Figure 12.
The whole analysis process, structural schematic of bread staling (a), experimental set-up of the NIR measurements (b), and overlaid evolving difference spectra and intensity profiles for the time interval from 0 to 6 h (after scatter correction and truncation to 6000–4000 cm−1) (c). Reprinted with permission from ref. [93]. 2023 Elsevier.
To rapidly visualize the spectral variations, the evolving difference spectra were calculated by using the spectrum at time zero as reference for subtraction from the subsequent spectra. As a result, a graphic with bands pointing up or down resulted (Figure 12c), which could be related to specific functionalities of water and starch.
Due to water evaporation and diffusion from core to crust, the bands pointing down at 5311 cm−1 and 4964 cm−1 in the evolving difference plot are related to the ν(OH) + δ(OH) combination bands of weakly and strongly hydrogen-bonded water, respectively. The bands pointing up at 5851 cm−1 (2xν(CH2), 1st overtone), 5158 cm−1 (ν(OH)+ δ(OH) combination), 4703 cm−1 (ν(OH) + ν(C-O) combination), and 4346 cm−1 (ν(CH2) + δ(CH2) combination) are related to absorption bands that represent the crystallization of starch during the aging process.
In a further step, the dataset was subjected to a 2D-COS analysis and the synchronous and asynchronous 2D-COS maps were developed for the time interval of 0–6 h (Figure 13). The strongest peaks were selected for both synchronous and asynchronous maps, and the analysis of these signals with reference to their peak signs (+/−) and the conclusions regarding their sequence are summarized in Table 2.
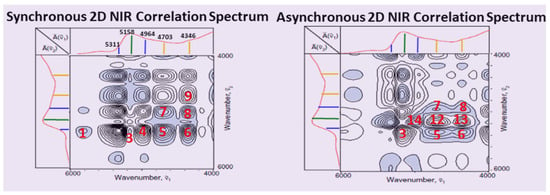
Figure 13.
Synchronous and asynchronous 2DCOS maps for the aging time interval of 0–6 h. The strongest peaks in both maps were selected and numbered in red for interpretation of the sequential spectral changes in Table 2 (open and grey-shaded signals are positive and negative, respectively). Reprinted with permission from ref. [93]. 2023 Elsevier.

Table 2.
Peaks selected from the synchronous and asynchronous maps, their signal assignment, and sequence related to the segmented dataset for the time interval of 0–6 h. Reprinted with permission from ref. [93]. 2023 Elsevier.
From Table 2 and the 2DCOS interpretation rules [86], the following sequence of spectral variations can be proposed for the most intense cross peaks: cm−1.
Thus, in conclusion, for the first six hours of white bread staling, the sequence of events is: diffusion and evaporation of strongly hydrogen-bonded water > reorganization of starch OH-functionalities > evaporation of weakly hydrogen-bonded water and partial conversion to strongly hydrogen-bonded species > crystallization of amylopectin.
Multivariate Curve Resolution—Alternating Least Squares (MCR-ALS)
For the MCR-ALS analysis the NIR spectra measured during the total aging time interval of 0–48 h, truncated to the 6000–4000 cm−1 range and scatter corrected by EMSC, were used. Two components were selected to initialize the MCR-ALS algorithm [95,96]: the first component is the first spectrum of the system, mainly related to amorphous starch and water, and the second component is the last spectrum of the system, mainly related to crystalline starch. The constraint non-negativity was applied to the spectral profiles since the NIR spectra have only positive values after the EMSC scatter correction.
The optimized spectral profiles (ST) obtained by decomposition of the instrumental dataset (X) are shown in Figure 14A, and the corresponding concentration profiles (C) of the two components are shown in Figure 14B.
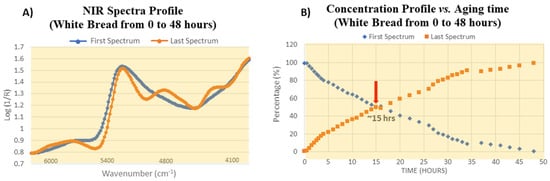
Figure 14.
NIR spectra profiles of the first and last component (A) and concentration profiles for the first and last spectrum obtained from MCR-ALS (B). The steady state occurs at approximately 15 h (red arrow). Reprinted with permission from ref. [93]. 2023 Elsevier.
The crossover point (represented by the red arrow in Figure 14B) indicates that the system contains 50% of each component, viz. 50% amorphous starch plus water and 50% crystallized starch. Since the second component strongly resembles the spectrum of crystalline starch, the crossover points specifically, and the orange trace in general, may be associated with a “tentative degree of crystallinity” of the system under investigation.
By 2D-COS analysis, the structural changes for the investigated time interval of aging are emphasized. Thus, in the initial phase, between (0–6 h) the crystallization of starch, it was highlighted as the first process, followed by the depletion of weakly hydrogen-bonded and subsequently strongly hydrogen-bonded water.
MCR-ALS analysis, on the other hand, provided practically valuable concentration profiles of the initial components (amorphous starch and water) and the final aging product (crystalline starch) as a function of aging time. From the crossover point of the two concentration profiles, the 50% degree of starch crystallization could be derived.
3.3.5. Grapes
Precision viticulture drives the observed growth in automation and monitoring with the objective to improve several aspects, such as grape and wine quality, optimize crop management, comply with legal regulations, and decrease operating costs.
The key point in viticultural operation targeting to “grow grapes to specifications” is the possibility for the winegrower to have access to the metabolic information of the vine, i.e., the composition of the grape, enabling management of the maturation and consequent quality of the wine. The lack of a non-destructive technology that can directly or indirectly measure a high number of vine and grape metabolic parameters has made it difficult to implement advanced management strategies using process analytical technology and bioinformatics existing in other areas of agro-industrial biotechnology [97].
The implementation of an analytical on-site tool for managing the quality of the grapes requires the development of a “Smart Sensor” fit for decision making. This tool should support the following features:
- (a)
- Automate the processing of spectroscopic data in the database.
- (b)
- Integrate the information collected in the field and in the laboratory in the field image, using augmented reality techniques.
- (c)
- Visualize, based on the image of the field, the different classifications of the quality of the grape, and the chemical composition of the grape obtained either based on an estimate or based on laboratory analysis.
- (d)
- Visualization of the results of the various wine management strategies.
The analytical technique of in-the-field spectra acquisition must contemplate the collection of information about (i) variation of the spectrum collected in each shot; (ii) spectral variation of the bunch; (iii) spectral variation of bunches in different plants; (iv) variation and definition of spatial resolution; as well as (v) definition of temporal resolution.
Materials and Methods
In this study, grapes from the same cultivar (Palato do Côa, Portugal) and harvest year were collected at three different maturation stages: pre-harvest, harvest, and post-harvest. The grape varieties used in this study were Touriga Nacional and Touriga Franca. Spectra were collected using the handheld NIR spectrometer, NIR-M-R2, in the wavelength range of 900–1700 nm (InnoSpectra Corp., Zhubei City, Taiwan) with a digital resolution of 228 points, exposure time of 1.27 ms, and 15 scans to average. A precise place of the grape was chosen for analysis to ensure consistent results. For each grape, juice was collected using a manual press and the sugar content level (Brix) was measured using a Pallete Atago (Tokyo, Japan). All measurements were carried out in the lab, on the same day as the harvest, and in a temperature-controlled environment.
In total, the dataset is composed of 218 different samples. The sugar content level of the grapes ranged from 7 to 26°. The dataset was split into a calibration set (152 samples) and an external test set (66 samples), maintaining the same proportion between brix values.
For the initial sugar PLS calibration, we preprocessed the data using a combination of algorithms, such as retaining wavelength variables between 930 and 1450 nm, Standard Normal Variate (SNV), and first derivative using a Savitzky-Golay filter, with a window size of nine and 2nd order polynomial. The cross-validation method used was 5-fold random subsets. After choosing the latent variables, this model was applied to the external dataset, to validate the performance of the model (RMSEP).
To make this model robust to external parameters, such as temperature, the same experimental design proposed by J.-M. Roger in 2003 [98] was applied. Briefly, a new dataset was created featuring five distinct grapes. These grapes were evaluated under four varying temperature conditions (20 °C, 25 °C, 35 °C, and 50 °C), and their spectra were measured in various positions across the grape. Utilizing this dataset, we then orthogonally corrected the calibration model using two established methods: the External Parameter Orthogonalization (EPO) [98] and the Error Removal by Orthogonal Subtraction (EROS) [99].
Results and Discussion
- (1)
- Building the Base Calibration
The comparison between the raw and preprocessed data is shown in Figure 15. Calibration set (a) without preprocessing; (b) preprocessed with truncation, SNV, and first derivative using Savitzky–Golay. It is worth noting the presence of four peaks in the preprocessed data.
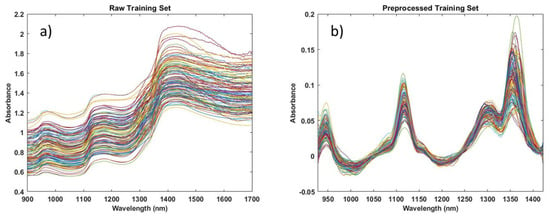
Figure 15.
Calibration set (a) without preprocessing and (b) preprocessed with truncation, SNV, and first derivative using Savitzky–Golay.
The PLS regression was used to model the relationship between the NIR spectra and a set of response variables Y (e.g., ºBrix). To choose the best number of latent variables, we evaluated the calibration error (RMSEC) and the cross-validation error (RMSECV) as a function of the number of latent variables between 1 and 20 (Figure 16). From this figure, it can be derived that for a number of latent variables bigger than five, the RMSEC continues to decrease, but the RMSECV does not follow this trend. Thus, the best balance between RMSEC and RMSECV is five latent variables.
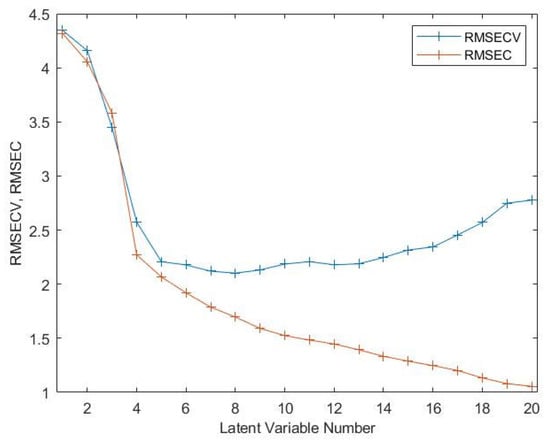
Figure 16.
Choice of the number of latent variables by the plot of RMSEC and RMSECV as a function of latent variables (see text).
The base calibration has a RMSEC and RMSECV of 2.06 and 2.20 units of ºBrix, respectively (Figure 17a). When the external dataset is predicted, an RMSEP of 2.75 ºBrix has been obtained (Figure 17b).
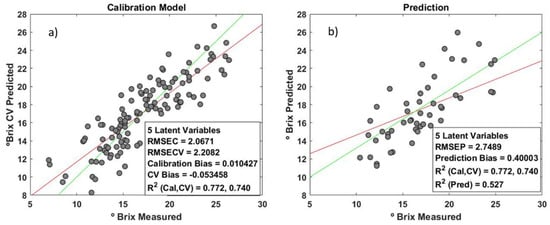
Figure 17.
The plot of reference values vs. prediction values for the calibration set and prediction set. (a) Calibration model of Brix. (b) External samples predicted by the model (the red lines represent the ideal regression, and the green lines are the linear fit between predicted and real values).
The results achieved in this preliminary study are satisfactory and comparable to reports in the literature [100,101,102]. We believe that the moderate results are due to the small spectral region covered by the handheld sensor, which also has a relatively low S/N ratio (see Figure 1). Although this calibration model is not yet ready to go to the field and needs further improvements regarding robustness against external effects, such as temperature and acquisition location, the applied sensor has the great advantage that it can be used directly in the vineyard.
- (2)
- Building the Orthogonally Corrected Calibration
To orthogonally correct the temperature effect, two matrices D were created from the second dataset. Subsequently, the matrices P were calculated to EPO and EROS [103].
Comparing the EPO and EROS results, there are no significant differences between the two methods (Figure 18). Furthermore, comparing the orthogonally corrected models with the base model, no significant differences can be observed. Regarding the two chosen methods for orthogonal correction, we opted for EPO, because although the RMSEPs are identical, the D matrix contains more information about the external parameters (Figure 19). However, it is necessary to carry out further tests with grapes at different temperatures to definitely state that there are differences.
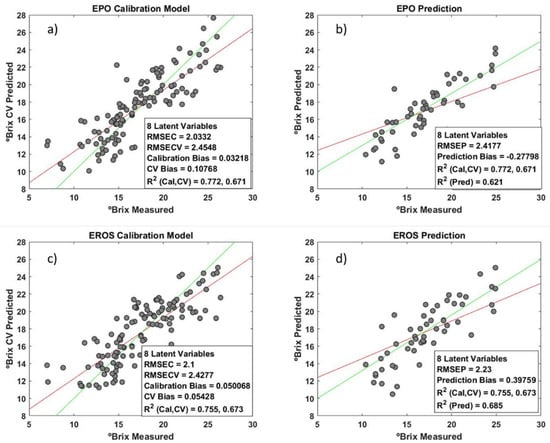
Figure 18.
The performance of calibration and validation with two different algorithms: (a) calibration model using the EPO algorithm; (b) external samples predicted by EPO model; (c) calibration model using EROS algorithm; and (d) external samples predicted by EROS model (the red lines represent the ideal regression, and the green lines are the linear fit between predicted and real values).
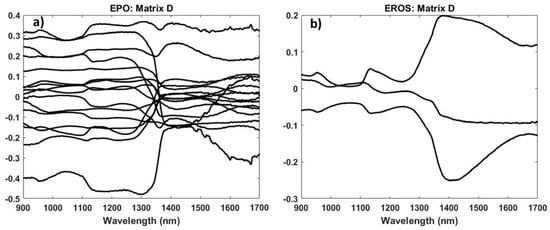
Figure 19.
Detrimental space (a) of EPO and (b) of EROS.
Once the Brix models are created, they must be integrated into a data architecture that allows curation, prediction, and distribution of data in real-time. This flexibility of the data permits the creation of new digital tools, such as digital twins of vineyards, helping the winegrower’s decision making. These digital twins make it possible to better understand the behavior of the vines during maturation, thereby optimizing the harvest.
In conclusion, the development of a Smart Grape Sensor (SGS) using handheld NIR spectroscopy has shown to be a valuable tool for precision viticulture in determining the quality of grapes and optimizing their crop management. By combining the data collected in the field with laboratory analysis, the SGS system was able to predict the sugar content level (Brix) of the grapes. The use of PLS regression in combination with the orthogonal correction algorithm allowed the development of a robust calibration model for use under varying temperature conditions.
Handheld sensors allow the integration of augmented reality techniques and visualization of the data provides an innovative and user-friendly interface for decision-making in the vineyard. The results of this study highlight the potential for an SGS system to improve the quality of grapes and wine production, while reducing operating costs and enabling product segmentation.
3.4. Environmental and Exploration Studies
In the following final section, the use of handheld NIR spectrometers for soil investigations is discussed regarding two aspects:
- (a)
- Soil investigations in remote sites for the exploration of bauxite deposits.
- (b)
- Soil testing to quantify the total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) content for exploration purposes and to determine decontamination measures.
In both cases, the desirable use of handheld equipment is easily understood to avoid the time-consuming sending of soil samples to distant analytical laboratories. The desirable homogeneity of the soil samples for the NIR spectroscopic investigations can be realized relatively easily on-site by sieving and/or pretreating with a small hand mill.
3.4.1. Detection of Bauxite Deposits
Bauxite occurs in three different modifications: Gibbsit (Hydrargillit) γ-Al(OH)3, Böhmit γ-AlO(OH), and Diaspor α-AlO(OH). This means that in the present case, the analyte aluminum has to be determined via the NIR footprint of the OH functionalities of the different modifications, because the metal has no absorption band of its own in the NIR spectrum.
This situation is illustrated by the spectra sections in Figure 20. While the large spectral range corresponds to the spectra measured on a benchtop instrument (VECTOR 22N, Bruker Optik GmbH, Germany) of two samples containing no aluminum and 53.6%(w/w) aluminum, respectively, the inset contains the spectra of the same samples measured on the handheld spectrometer VIAVI MicroNIR (see Figure 1a). The very sharp absorption bands of the benchtop spectrum of the aluminum-rich sample in the wavenumber range of 7000–7500 cm−1 can be assigned to 2 × ν(OH) overtone vibrations of OH-functionalities in different hydrogen-bonding states. Although the fine structure of this 2 × ν(OH) band complex is lost in the spectrum measured with the handheld spectrometer, the RMSE values of the corresponding PLS calibration show only a slight deterioration compared to the PLS calibration based on the data of the benchtop instrument (see below).
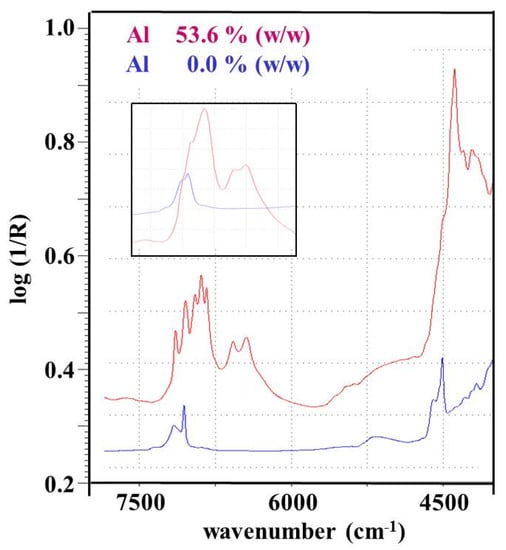
Figure 20.
NIR spectra of two soil samples with different aluminum content measured with a benchtop and a handheld (inset) spectrometer. Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [58].
Based on 83 and 82 calibration spectra for the benchtop instrument and the handheld spectrometer, respectively, PLS calibration models were developed, and the most important preprocessing and performance parameters are reproduced in Table 3. In summary, a prediction accuracy (RMSECV) of about 4.5% (w/w) was obtained with the handheld NIR spectrometer compared to the superior RMSECV value of 3.9% (w/w) achieved with the calibration of the benchtop data. However, with regard to the use of the handheld device in the context of an on-site analytical technique, the achieved accuracy can be considered perfectly adequate for a rapid screening method.

Table 3.
Comparison of the calibration processing and performance parameters obtained with the benchtop and handheld spectrometers for the determination of the aluminum content.
3.4.2. Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) in Soil
For successful soil remediation and hydrocarbon exploration operations, determining the TPH content of soils [104] is an indispensable process step. Thus, for rapid decisions for exploration work or for environmental site assessment projects, a quick—preferably on-site—determination of the extent and magnitude of TPH content is desirable. Preceding studies by another research group favored a handheld FT-MIR spectrometer in diffuse reflection measurements for the quantitative determination of TPH in soils [105]. They claimed not only detection limits in the range of a few 100 ppm TPH but also the development of a global, site-independent calibration model. However, because of the strong overlap of the water absorption with the CH bands of the hydrocarbons in the MIR spectrum, we view these research results rather critically. Even in a pure two-phase system of potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) and water, the LOD for KHP obtained with a benchtop NIR spectrometer equipped with a fiber optic cable attachment is approximately 150 ppm [106]. In view of the much better separation of the water and hydrocarbon absorptions in the NIR spectrum, in the following section, selected results of our recent study [107] on the NIR spectroscopic determination of TPH content in soil samples using the NeoSpectra NIR scanner (Figure 1d) will be briefly presented for comparison.
For the development of PLS calibration models, diffuse-reflection NIR spectra were recorded from 162 soil samples from two different sites (Site#1: 98 samples; Site#2: 64 samples) with varying TPH reference values ranging from 350 to 30,000 ppm, as determined by capillary gas chromatography and flame ionization detection. These sample sets were further split into a calibration and a test set for the development of the calibration models and for external validation, respectively (Table 4).

Table 4.
Description of the investigated sample sets of different origin. Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [107].
In addition to site-specific calibration models, the study also attempted to use the LW-PLS [108] to develop a site-independent calibration model of the combined sample sets from both sites without significant penalty in calibration performance. Due to the importance of global calibrations for samples of different origin and nature, in what follows, only the conservative PLS model based on the NIR spectra of both sites is compared to the application of the LW-PLS model applied to the same sample set. Here, the obvious improvement of the calibration parameters of the LW-PLS model can be seen impressively in the comparison of the two models in Figure 21. Thus, not only the results achieved with the PLS calibration (RMSEC/RMSECV and R2C/R2CV values of 3007/3058 ppm and 0.755/0.747) improved dramatically by the application of the LW-PLS model (RMSEC/RMSECV and R2C/R2CV values of 687/959 ppm and 0.987/0.975) but also the average prediction error of the test samples ∅(Δ|P-R|) decreased almost by an order of magnitude from 2475 to 703 ppm (Figure 21a,b). Finally, the RMSE and R2 values of the LW-PLS approach differ only insignificantly from the parameters of the conservative PLS models for the site-specific calibrations. In conclusion, this study confirms the ability of next-generation portable NIR spectrometers to predict low-TPH levels in various soil types of different geographical origin to become rapid screening tools in the field.
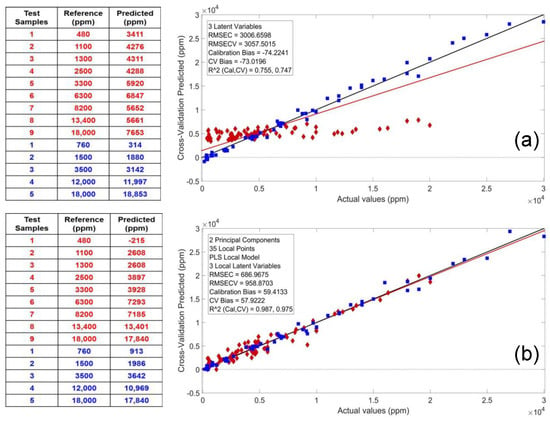
Figure 21.
Comparison of the calibration and prediction results for the soil samples of the two investigated sites using the ordinary PLS model (a) and the LW-PLS model (b). Reproduced (CC-BY 4.0 license) from [107].
4. Conclusions
The objective of this review is to turn the interested readers’ attention to the realistic potential of state-of-the-art handheld NIR spectrometers for qualitative and quantitative quality control. The large number of examples from extremely different application areas impressively demonstrates the state of development of handheld NIR spectroscopy for use in the quality control of materials and for authentication in the food sciences. Further advances in miniaturization will adapt these instruments for on-site use, e.g., by integrating spectrometer hardware into mobile phones, and further development of calibration software will make evaluation faster, more user-friendly, and more reliable, even for complex systems.
Vendors have succeeded in considerably reducing the manufacturing costs of handheld NIR spectrometers and are making great efforts to bring these instruments closer to a public non-expert user community for everyday life applications. Notwithstanding this progress, the technical background of new, elaborately advertised “NIR scanners of the future with cloud evaluation of big data”—especially for food and life science applications—should be critically scrutinized.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.W.S., H.Y., M.D.G.N., I.N., A.C.S.F. and G.M.G.; methodology, H.Y., M.D.G.N., I.N., A.C.S.F., G.M.G., F.P., X.C. and H.W.S.; validation, H.Y., M.D.G.N., I.N., A.C.S.F. and X.C.; formal analysis, H.W.S., H.Y., M.D.G.N., A.C.S.F. and G.M.G.; investigation, H.Y., M.D.G.N., I.N., F.P., X.C., A.C.S.F. and G.M.G.; resources, H.W.S.; data curation, H.Y., M.D.G.N., I.N., A.C.S.F., G.M.G., F.P. and X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W.S., H.Y., M.D.G.N. and A.C.S.F.; writing, reviewing, and editing, H.W.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work for the section “Environmental and Exploration Studies” was funded by ALCOA of Australia Ltd. and CHEVRON U.S.A. Inc.; the section “textiles” was funded by the earmarked fund for CARS-18.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the following instrument companies: trinamiX GmbH, Ludwigshafen, Germany; VIAVI Solutions Inc., Santa Rosa, CA, USA; Spectral Engines, Helsinki, Finland; Si-Ware Systems, Cairo, Egypt; Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu city, Japan; and Senorics GmbH, Dresden, Germany. Furthermore, the supply of samples (including reference values) by S. Kasanmascheff (Altum Solutions GmbH, Erlangen, Germany), M. Nunes (ALCOA of Australia Ltd., Kwinana, Western Australia, Australia), and T. Miao, N. Sihota (CHEVRON Technical Center, Richmond, CA, USA) are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sorak, D.; Herberholz, L.; Iwascek, S.; Altinpinar, S.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W. New developments and applications of handheld Raman, mid-infrared, and near-infrared spectrometers. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2012, 47, 83–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocombe, R.A. Portable spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 1701–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodionova, O.Y.; Titova, A.V.; Pomerantsev, A.L. Discriminant analysis is an inappropriate method of authentication. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 78, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantsev, A.L.; Rodionova, O.Y. New trends in qualitative analysis: Performance, optimization, and validation of multi-class and soft models. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bec, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Miniaturized NIR Spectroscopy in Food Analysis and Quality Control: Promises, Challenges, and Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedjoah, R.-C.A.-A.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, M.; Yan, H. Fast monitoring total acids and total polyphenol contents in fermentation broth of mulberry vinegar using MEMS and optical fiber near-infrared spectrometers. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2021, 260, 119938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Siesler, H.W. Identification Performance of Different Types of Handheld Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectrometers for the Recycling of Polymer Commodities. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Xu, Y.-C.; Siesler, H.W.; Han, B.-X.; Zhang, G.-Z. Hand-Held Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Authentication of Fengdous and Quantitative Analysis of Mulberry Fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, Z.-N.; Yan, H.; Siesler, H.W. Fast detection of cotton content in silk/cotton textiles by handheld near-infrared spectroscopy: A performance comparison of four different instruments. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jia, B.; Dai, J.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Yan, H.; Han, B. Qualitative classification of Dendrobium huoshanense (Feng dou) using fast non-destructive hand-held near infrared spectroscopy. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2022, 30, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Han, B.; Siesler, H.W. Handheld Near-Infrared Spectrometers: Reality and Empty Promises. Spectroscopy 2020, 35, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Siesler, H.W. Quantitative analysis of a pharmaceutical formulation: Performance comparison of different handheld near-infrared spectrometers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinig, P.; Grüger, H.; Knobbe, J.; Pügner, T.; Meyer, S. Bringing NIR spectrometers into mobile phones. In MOEMS and Miniaturized Systems XVII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzi, F.; Basso, E.; Rizzo, A.; Cesaratto, A.; Tague, T.J., Jr. Evaluation and optimization of the potential of a handheld Raman spectrometer: In situ, noninvasive materials characterization in artworks. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, J.; Weyer, L. Practical Guide and Spectral Atlas for Interpretive Near-Infrared; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Siesler, H.W. Near Infrared Spectra, Interpretation. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 3rd ed.; Lindon, J.C., Tranter, G.E., Koppenaal, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Siesler, H.; Ozaki, S.K.; Heise, H. Near Infrared Spectroscopy; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki, Y.; Huck, C.; Tsuchikawa, S.; Engelsen, S.B. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory, Spectral Analysis, Instrumentation, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Principles and applications of miniaturized near-infrared (NIR) spectrometers. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 1514–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, C. Near infrared spectroscopy: A mature analytical technique with new perspectives—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1026, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Siesler, H.W.; Huck, C.W. Handheld near-infrared spectrometers: Where are we heading? NIR News 2020, 31, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Siesler, H.W. Hand-held near-infrared spectrometers: State-of-the-art instrumentation and practical applications. NIR News 2018, 29, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antila, J.; Tuohiniemi, M.; Rissanen, A.; Kantojärvi, U.; Lahti, M.; Viherkanto, K.; Kaarre, M.; Malinen, J. MEMS-and MOEMS-based Near-Infrared Spectrometers; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, L.P.; Milne, J.S.; Dell, J.M.; Faraone, L. MEMS-based microspectrometer technologies for NIR and MIR wavelengths. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 133001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Cui, P.; Lei, H.; Yan, H. Detection of the alcohol fermentation process in vinegar production with a digital micro-mirror based NIR spectra set-up and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemair, V.; Huck, C.W. Evaluation of the performance of three hand-held near-infrared spectrometer through investigation of total antioxidant capacity in gluten free grains. Talanta 2018, 189, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qian, Z.; Shi, B.; Medlicott, J.; East, A. Evaluating the performance of a consumer scale SCiO (TM) molecular sensor to predict quality of horticultural products. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 145, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; He, Y. SeeFruits: Design and evaluation of a cloud-based ultra-portable NIRS system for sweet cherry quality detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 152, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Casiraghi, E.; Alamprese, C. Handheld NIR device: A non-targeted approach to assess authenticity of fish fillets and patties. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, G.F.; Cardoso Andrade, S.A.; da Silva, V.H.; Honorato, F.A. Multivariate Classification of UHT Milk as to the Presence of Lactose Using Benchtop and Portable NIR Spectrometers. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Parra, H.A.; Pustjens, A.; Hettinga, K.; Mongondry, P.; van Ruth, S.M. Evaluation of portable near-infrared spectroscopy for organic milk authentication. Talanta 2018, 184, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.M.; Tosato, F.; Domingos, E.; Rodrigues, R.R.T.; Aquino, L.F.M.; Filgueiras, P.R.; Lacerda, V., Jr.; Romao, W. Portable near infrared spectroscopy applied to quality control of Brazilian coffee. Talanta 2018, 176, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, N.; Pawluczyk, O.; Dugan, M.E.R.; Aalhus, J.L. A Review of the Principles and Applications of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Characterize Meat, Fat, and Meat Products. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 1403–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malegori, C.; Nascimento Marques, E.J.; de Freitas, S.T.; Pimentel, M.F.; Pasquini, C.; Casiraghi, E. Comparing the analytical performances of Micro-NIR and Ft-NIR spectrometers in the evaluation of acerola fruit quality, using PLS and SVM regression algorithms. Talanta 2017, 165, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, K.N.; Hussain, M.N.; Bakar, J.; Sharif, Z.; Khir, M.F.A.; Zoolfakar, A.S. Classification and quantification of palm oil adulteration via portable NIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2017, 173, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento Marques, E.J.; de Freitas, S.T.; Pimentel, M.F.; Pasquini, C. Rapid and non-destructive determination of quality parameters in the ‘Tommy Atkins’ mango using a novel handheld near infrared spectrometer. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killeen, D.P.; Andersen, D.H.; Beatson, R.A.; Gordon, K.C.; Perry, N.B. Vibrational Spectroscopy and Chemometrics for Rapid, Quantitative Analysis of Bitter Acids in Hops (Humulus lupulus). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2014, 62, 12521–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.K.; Kaur, H.; Allan, E.L.; Lozama, A.; Bell, D. A New Handheld Device for the Detection of Falsified Medicines: Demonstration on Falsified Artemisinin-Based Therapies from the Field. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, H.; Wickstrom, H.; Desai, D.; Preis, M.; Sandler, N. Application of a handheld NIR spectrometer in prediction of drug content in inkjet printed orodispersible formulations containing prednisolone and levothyroxine. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemain, A.; Degardin, K.; Roggo, Y. Performance of NIR handheld spectrometers for the detection of counterfeit tablets. Talanta 2017, 165, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.H.; da Silva, J.J.; Pereira, C.F. Portable near-infrared instruments: Application for quality control of polymorphs in pharmaceutical raw materials and calibration transfer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 134, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zontov, Y.V.; Balyklova, K.S.; Titova, A.V.; Rodionova, O.Y.; Pomerantsev, A.L. Chemometric aided NIR portable instrument for rapid assessment of medicine quality. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hsiung, C.; Pederson, C.G.; Zou, P.; Smith, V.; von Gunten, M.; O’Brien, N.A. Pharmaceutical Raw Material Identification Using Miniature Near-Infrared (MicroNIR) Spectroscopy and Supervised Pattern Recognition Using Support Vector Machine. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.; Zumba, J.; Fortier, C. Measurement comparison of cotton fiber micronaire and its components by portable near infrared spectroscopy instruments. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.d.S.; Honorato, R.S.; Honorato, F.A.; Pereira, C.F. Authenticity assessment of banknotes using portable near infrared spectrometer and chemometrics. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 286, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risoluti, R.; Gregori, A.; Schiavone, S.; Materazzi, S. “Click and Screen” Technology for the Detection of Explosives on Human Hands by a Portable MicroNIR-Chemometrics Platform. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4288–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.Q.; Silva, C.S.; Vieira, M.J.L.; Pimentel, M.F.; Braz, A.; Honorato, R.S. Evaluation and identification of blood stains with handheld NIR spectrometer. Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Siesler, H.W. Identification of textiles by handheld near infrared spectroscopy: Protecting customers against product counterfeiting. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2018, 26, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, M.; Matsuura, N.; Li, H.; Ohisa, N.; Amano, T.; Ogawa, N. Application of a portable near infrared spectrometer for the manufacturing of noodle products. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2004, 12, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guifang, W.; Hai, M.; Xin, P. Identification of varieties of natural textile fiber based on Vis/NIR spectroscopy technology. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 19–20 December 2015; pp. 585–589. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yan, L.; Xie, Y.; Xu, J. Determination of Fiber Contents in Blended Textiles by NIR Combined with BP Neural Network. ISRN Text. 2013, 2013, 546481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Shen, Y.; Siesler, H.W. Nah-Infrarot-Spektrometer für Alltagsanwendungen. GIT Labor Fachz. 2020, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W. Evaluating the molecular interaction of organic liquid mixtures using near-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Irfan, U.; Pui, L.P.; Solihin, M.I. Feasibility Study of Detecting Palm Oil Adulteration with Recycled Cooking Oil Using A Handheld NIR Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Electronic Devices, Systems and Applications (ICEDSA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28–29 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira Moreira, A.C.; Batista Braga, J.W. Authenticity Identification of Copaiba Oil Using a Handheld NIR Spectrometer and DD-SIMCA. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; van Stuijvenberg, L.; van Ruth, S.M. Handheld Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Distinction of Extra Virgin Olive Oil from Other Olive Oil Grades Substantiated by Compositional Data. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1900031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Aykas, D.P.; Rodriguez-Saona, L. Rapid Authentication of Potato Chip Oil by Vibrational Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis. Foods 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Siesler, H.W. Handheld Near-Infrared Spectrometers: On-Site Quality Control and Protection Against Product Counterfeiting. Available online: https://www.etextonline.org/articlepdfs/Handheld-Near-Infrared-Spectrometers:-On-Site-Quality-Control-and-Protection-Against-Product-Counterfeiting.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. A review of chemical composition and nutritional properties of minor vegetable oils in China. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Du, X.; Yang, L.; Zu, Y.; Yang, F. Simultaneous synergistic microwave–ultrasonic extraction and hydrolysis for preparation of trans-resveratrol in tree peony seed oil-extracted residues using imidazolium-based ionic liquid. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Li, X. Progress in peony seed oil and comprehensive utilization value of oil peony. China Oils Fats 2017, 42, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Barthet, V.J.; Petryk, M.W.P.; Siemens, B. Rapid Nondestructive Analysis of Intact Canola Seeds Using a Handheld Near-Infrared Spectrometer. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Jolayemi, O.S.; Giovenzana, V.; Tugnolo, A.; Squeo, G.; Conte, P.; De Bruno, A.; Flamminii, F.; Casiraghi, E.; Alamprese, C. Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Green Technology for the Quality Prediction of Intact Olives. Foods 2021, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.L.; Teye, E.; Darkwa, S. Predicting adulteration of Palm oil with Sudan IV dye using shortwave handheld spectroscopy and comparative analysis of models. Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 110, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Ortega, S.; Olabarrieta, I.; Saitua, E.; Arana, G.; Foti, G.; Melado-Herreros, A. Improvement of Oil Valorization Extracted from Fish By-Products Using a Handheld near Infrared Spectrometer Coupled with Chemometrics. Foods 2022, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Wen, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Sagymbek, A.; Yu, X. Analytical methods for determining the peroxide value of edible oils: A mini-review. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, R.R.; Susanti, E.; Hidayati, L.; Wahab, R.A. Analysis of Peroxide Value, Free Fatty Acid, and Water Content Changes in Used Cooking Oil from Street Vendors in Malang; AIP Publishing LLC.: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2231, p. 040057. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Yan, H.; Siesler, H. Rapid Determination of the Peroxide Value of Edible Oil by Handheld NIR Spectroscopy in Combination with Wavelength Variables Selection and PLS Calibration. Spectroscopy 2022, 37, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, L.; Schäfe, W.; Freund, W. A Compendium of Flour Improvement; Agrimedia GmbH, ERLING Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Clence, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Myhrvold, N.; Migoya, F. Modernist Bread; Phaidon Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Atwell, W.A.; Finnie, S. Wheat Flour, 2nd ed.; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hamelman, J. Bread: A Baker’s Book of Techniques and Recipes; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, J.M.; Honorato, F.A.; Celso, P.G.; Pimentel, M.F. Authenticity of almond flour using handheld near infrared instruments and one class classifiers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Kamruzzaman, M. Portable NIR spectroscopy and PLS based variable selection for adulteration detection in quinoa flour. Food Control 2022, 138, 108970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Liu, L.; Kucha, C.; Ngadi, M. Rapid and non-destructive detection of cassava flour adulterants in wheat flour using a handheld MicroNIR spectrometer. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 203, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanell, E.; Minarro, B.; Carrasco, N. Detection of low-level gluten content in flour and batter by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS). J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.R.; Maghirang, E.B.; Xie, F.; Dowell, F.E. Comparison of dispersive and Fourier-transform NIR instruments for measuring grain and flour attributes. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2006, 22, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, F.M.; Walker, C.E. Grain, flour and bread-making properties of eight Pakistani hard white spring wheat cultivars grown at three different locations for 2 years. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, O.M.; Fraga, J.M.G.; Jimenez, A.I.; Jimenez, F.; Arias, J.J. Characterization of toasted cereal flours from the Canary Islands (gofios). Food Chem. 2014, 151, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Siesler, H.W.; Yan, H. Rapid analysis of wheat flour by different handheld near-infrared spectrometers: A discussion of calibration model maintenance and performance comparison. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2021, 252, 119504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, F.D.; Adrar, N.; Bolling, B.W.; Capanoglu, E. Valorisation of hazelnut by-products: Current applications and future potential. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2022, 38, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intelligence, M. Hazelnut Market—Rowth, Trends, COVID-19 Impact, and Forecasts (2023–2028). Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/global-hazelnut-market (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Shafiei, G.; Ghorbani, M.; Hosseini, H.; Sadeghi Mahoonak, A.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Jafari, S.M. Estimation of oxidative indices in the raw and roasted hazelnuts by accelerated shelf-life testing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Food Waste Index; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chinachoti, P.; Vodovotz, Y. Bread Staling; Chinachoti, P., Vodovotz, Y., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy: Applications in Vibrational and Optical Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jaumot, J.; Gargallo, R.; De Juan, A.; Tauler, R. A graphical user-friendly interface for MCR-ALS: A new tool for multivariate curve resolution in MATLAB. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2005, 76, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaumot, J.; de Juan, A.; Tauler, R. MCR-ALS GUI 2.0: New features and applications. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 140, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, C.G.; Correa, M.J.; Ferrero, C. Kinetic study of staling in breads with high-amylose resistant starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curti, E.; Carini, E.; Cobo, M.; Bocher, T.; Vittadini, E. The use of two-dimensional NMR relaxometry in bread staling: A valuable tool? Food Chem. 2017, 237, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Karboune, S. A review of bread qualities and current strategies for bread bioprotection: Flavor, sensory, rheological, and textural attributes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1937–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringsted, T.; Siesler, H.W.; Engelsen, S.B. Monitoring the staling of wheat bread using 2D MIR-NIR correlation spectroscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.D.G.; Noda, I.; Siesler, H.W. Investigation of bread staling by handheld NIR spectroscopy in tandem with 2D-COS and MCR-ALS analysis. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afseth, N.K.; Kohler, A. Extended multiplicative signal correction in vibrational spectroscopy, a tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 117, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, A.C.; Omidikia, N. Initialization effects in two-component second-order multivariate calibration with the extended bilinear model. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1125, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazivila, S.J.; Santos, J.L. A review on multivariate curve resolution applied to spectroscopic and chromatographic data acquired during the real-time monitoring of evolving multi-component processes: From process analytical chemistry (PAC) to process analytical technology (PAT). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Xu, W.; Yan, T.; Yan, J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, C. Application of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Machine Learning Algorithms for Quality Inspection of Grape: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, J.-M.; Chauchard, F.; Bellon-Maurel, V. EPO–PLS external parameter orthogonalisation of PLS application to temperature-independent measurement of sugar content of intact fruits. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2003, 66, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fearn, T.; Samuel, D.; Dhar, A.; Hameed, O.; Bown, S.G.; Lovat, L.B. Error removal by orthogonal subtraction (EROS): A customised pre-treatment for spectroscopic data. J. Chemom. J. Chemom. Soc. 2008, 22, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.; Guesalaga, A.; Agosin, E. Shortwave–near infrared spectroscopy for non-destructive determination of maturity of wine grapes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraín, M.; Guesalaga, A.R.; Agosín, E. A multipurpose portable instrument for determining ripeness in wine grapes using NIR spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urraca, R.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Tardaguila, J.; Diago, M.P. Estimation of total soluble solids in grape berries using a hand-held NIR spectrometer under field conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, J.M.; Boulet, J.C. A review of orthogonal projections for calibration. J. Chemom. 2018, 32, e3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennadiev, A.; Pikovskii, Y.I.; Tsibart, A.; Smirnova, M. Hydrocarbons in soils: Origin, composition, and behavior. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.T.; Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Kirk, J.; Janik, L.J.; Forrester, S.T.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Stewart, R.J. Rapid prediction of total petroleum hydrocarbons in soil using a hand-held mid-infrared field instrument. Talanta 2016, 160, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, T.; Watanabe, T.; Tsuchikawa, S. The effect of path length, light intensity and co-added time on the detection limit associated with NIR spectroscopy of potassium hydrogen phthalate in aqueous solution. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, T.; Sihota, N.; Pfeifer, F.; McDaniel, C.; De Gea Neves, M.; Siesler, H.W. Rapid determination of the total petroleum hydrocarbon content of soils by handheld Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2023. in print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnoff, M.; Metz, M.; Roger, J.M. Comparison of locally weighted PLS strategies for regression and discrimination on agronomic NIR data. J. Chemom. 2020, 34, e3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).