Abstract
The detection of bifenthrin is closely related to the adsorption of SERS substrates. In this study, superparamagnetic Fe3O4@Au MNPs coated with GO were used to detect the adsorption and enrichment of bifenthrin molecules with benzene rings. Firstly, the thermal solvent method synthesized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) with a particle size of ~250 nm. Next, polyethylene imide (PEI) was used as an intermediate layer to modify the surface of Fe3O4 to form a positively charged ultra-thin polymer middle layer. Next, the gold shell was developed by adsorption of ~20 nm AuNPs, without affecting the magnetic properties. Then, the additional amount of colloidal gold and GO on SERS performance was systematically studied. Using crystal violet (CV) as the probe, we investigated the SERS performance of composite nanomaterials. The lowest detected concentration reached 10−8 mol/L, confirming that the composite functional material had good SERS activity and magnetic properties. Finally, the substrate was used to detect bifenthrin in an acetone solution, and the lowest detection concentration was 10−8 mol/L. These results showed that the prepared GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs were efficient SERS substrates that could detect bifenthrin pesticide residue with high sensitivity.
1. Introduction
The problem of pesticide residues has attracted more and more attention with the mass production and widespread use of pesticides. Pyrethroids are widely used in agricultural production because of their high efficiency, low amounts of residue, easy degradation, and crop safety. They replace organophosphorus and other pesticides, which are toxic and do not degrade easily. However, as a spectral insecticide, bifenthrin is widely used in vegetables, tea, and other crops, leading to a high risk of residue. In addition, this pesticide can cause specific harm to skin and mucosa [1], the nervous system [2], and the digestive system [3] through direct contact, inhalation via the respiratory tract, or intake via the digestive tract [4,5]. Therefore, how to detect bifenthrin pesticide residues accurately, quickly, and effectively has become a topic of concern to researchers. Currently, bifenthrin is mainly detected by conventional gas chromatography [6] and liquid chromatography [7], which require expensive equipment and a cumbersome sample pretreatment process. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a rapid detection method for bifenthrin.
Compared with rapid detection methods such as enzyme inhibition and immunoassay methods, which have long preparation periods and low sensitivity, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) [8], as a non-destructive testing technology, has low detection cost [9], simple sample preparation [10], fast detection speed [11], and high sensitivity [12]. There is little existing research on pyrethroid pesticide detection based on SERS. Hidayah et al. used Au@Ag colloidal nanoparticles as the substrate to detect deltamethrin pesticides in tea soup. The results showed that deltamethrin’s minimum concentration (LOD) was 0.01 mg/L [13]. Pham et al. used a laser-assisted photochemical method to grow and deposit silver (Ag) nanodendrites at the core end of the multi-mode fiber for the detection of permethrin pesticides in the concentration range of 0.1 mg/L to 20 mg/L, which verified the potential of this method for the rapid detection of permethrin [14]. Tianhui Jiao et al. used plasma oscillation produced by ZnO semiconductors and precious metals to improve the Raman signal of deltamethrin and the least partial square algorithm to simulate deltamethrin prediction. The detection limit (LOD) of the method was 0.16 μg/kg, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) was 5% [15]. In another study calculating the Raman spectra of bifenthrin using the density functional theory (DFT), the results showed that the vibration modes of bifenthrin were many, and the characteristic peaks were difficult to identify [16]. Due to the complex molecular interaction and interaction between groups, the Raman peak complex can lead to a specific deviation in the spectrum. It also illustrates that the SERS detection method of bifenthrin has a particular difficulty [17,18]. At present, there are relatively few Raman spectroscopic studies on bifenthrin. However, due to the vast and massive application of bifenthrin, the problem of detection of bifenthrin pesticide residues has attracted much attention. SERS spectroscopic bifenthrin surveys will help the rapid qualitative and quantitative detection and analysis of the pesticide residues. In general, the adsorption of pyrethrin pesticide on common gold and silver SERS substrates was weak, so it was necessary to enhance the SERS signal with other methods [19]. Therefore, developing a substrate with strong adsorption of pyrethroids is helpful to perform SERS detection of bifenthrin pesticides.
Combining precious metals with magnetic materials and active substances can give new the substrate new abilities to detect substances that are difficult to detect with conventional noble metals [20,21]. Graphene material has been proven to be a promising SERS substrate due to its strong chemical enhancement effect [22]. Graphene can reduce the SERS background, quench molecular fluorescence, and improve the Raman signal-to-noise ratio [23]. In addition, the large surface area and interconnected SP2 network of graphene or GO enable π-π stacking and charge transfer with aromatic molecules [24], thus significantly enhancing its absorption capacity for benzene ring pesticides. Compared to graphene, GO has sufficient reactive oxygen sites and a high surface negative charge, which can substantially improve its electrostatic adsorption [25,26,27]. The oxidation and p-doping of graphene can increase the chemical strength of aromatic dye molecules by 104 times [28].
Thus, in this study, AuNPs produced a vast electromagnetic enhancement by directly coating Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanoparticles with a small amount of GO. AuNPs are used to create a substantial electromagnetic enhancement. On the other hand, GO promotes hybridization, increases absorption of aromatic molecules, and provides additional charge transfer enhancement without overpowering the molecule’s signal to be measured, resulting in a low signal-to-noise ratio.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Ferric chloride (FeCl3), ethylene glycol (EG), Anhydrous sodium acetate (NaAc), sodium citrate (C6H5Na3O7·2H2O), polyethylene imine (PEI, MW 10000, 99%), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP, MW 40000), and crystal violet (CV) from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Bifenthrin was obtained at Shanghai Pesticide Research Institute Co., Ltd. Graphite and potassium permanganate were bought at Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. Hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid were purchased at Huadong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Hydrochloric acid and anhydrous ethanol were obtained at Zhejiang Sanying Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. They can be used without further purification. All aqueous solutions were prepared with deionized water and purified by the Millipore Milli-Q system (18.2 MΩ/cm).
2.2. Synthesis of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs
2.2.1. Preparation of High-Quality Fe3O4 Magnetic Particles
Fe3O4 magnetic particles were synthesized via the solvothermal method reported by Li [29]. FeCl3 (0.65 g, 4.0 mmol) was dissolved in ethylene glycol (20 mL), and the solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer until it turned orange and transparent. Next, the above solution was added to trisodium citrate (Na3Cit.H2O, 0.30 g, 0.51 mmol) and stirred intensely for 60 min. Next, NaAc (1.20 g) was added and stirred intensely for 40 min. A suspension was obtained and then heated at 200 °C for 10 h in a stainless-steel autoclave lined with polytetrafluoroethylene (50 mL capacity). After cooling to room temperature, the prepared Fe3O4 was enriched magnetically and washed with pure water and ethanol three times. Finally, the enriched Fe3O4 was dried at 60 °C for 6 h in a vacuum oven, and Fe3O4 microspheres of ~250 nm were obtained.
2.2.2. Preparation of PEI-Modified Fe3O4 Magnetic Particles
PEI-modified Fe3O4 magnetic particles were prepared according to the following procedure: Firstly, a 5 mg/mL PEI solution was prepared. Secondly, a 10 mg/mL Fe3O4 solution was prepared by dissolving 100 mg of Fe3O4 microspheres in 10 mL of deionized water and sonicating for 10 min to thoroughly disperse the mixture. Then, the above Fe3O4 and PEI solutions were diluted at a volume ratio of 1:1 and sonicated for 10 min. Finally, the PEI-modified Fe3O4 was enriched in a magnetic field washed five times with deionized water to remove the residual PEI. The final product of PEI-modified Fe3O4 magnetic particles was stored in 10 mL of deionized water for later use.
2.2.3. Preparation of GO/Fe3O4@Au Magnetic Nanoparticles
An amount of 99 mL ultrapure water and 1 mL 1% chloroauric acid aqueous solution were successfully put into a 250 mL conical flask, heated to 100 °C, and stirred vigorously. After the solution reached the set temperature, 1.5 mL 1% trisodium citrate aqueous solution was added quickly and heated and stirred for another 15 min. In the process, the color of the solution changed from light yellow to wine red. After the reaction, the solution was cooled naturally to room temperature for later use. The final size of the Au nanoparticles prepared was about 20 nm.
A GO was prepared according to a previous method [30]: 0.8 g of graphite powder was added to a 250 mL beaker, followed by 50 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid and then 4 g of potassium permanganate, with continuous mixing for 2 min. The next step was magnetic stirring for 4 h at a speed of 1500 rpm. Then, 100 mL of deionized water and 4 mL of hydrogen peroxide (30%) were gradually added to the beaker after mixing and shaken ultrasonically for 30 min. The solution was then transferred into a 50-mL centrifuge tube and centrifuged for 10 min at 8000 rpm. Next, the supernatant was poured out, and pH test paper was used to test the acidity and alkalinity. Next, deionized water and 3% hydrochloric acid were added to clean the centrifuged sediment, and the solution was centrifuged again. The above centrifugation and cleaning steps were repeated until the solution’s pH was 7. Finally, it was put into the vacuum drying oven for 6 h, at a temperature of 60 °C. After drying, it was weighed again. A 5 mg/mL GO solution was thus prepared for later use.
An amount of 1 mL Fe3O4@PEI (2 mg/mL) was added to 2 mL, 4 mL, 6 mL, 8 mL, and 10 mL of AuNPs for ultrasonic reaction for 30 min. The excess colloidal gold solution was removed by magnet adsorption, and cleaned with deionized water three times.
Amounts of 0.15 mL, 0.2 mL, 0.25 mL, 0.5 mL, and 1 mL of 0.5 mg/mL GO and the optimized Fe3O4@Au were taken over 15 min; transferred into the centrifugal tube; stirred; adsorbed on the silent agitator for 6 h; and stored at 4 °C for later use.
2.2.4. Preparation and Detection of Bifenthrin
A bifenthrin stock solution of 10−2 mol/L was prepared with acetone. The stock solutions was diluted with acetone to prepare analytes in different concentrations (from 10−4 mol/L to 10−10 mol/L) for each use. For the measured SERS, 100 μL of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs and 100 μL of bifenthrin solution were mixed and incubated in a silent mixer for 0.5 h to enhance the adsorption effect. Then, 50 μL was dropped onto a special tapered glass plate, with a matching magnet placed under the glass plate for magnetic enrichment, and put on the sample platform of the Raman spectrometer for detection.
2.3. Instruments and Measurements
Size and morphological analyses were conducted using a scanning electron microscope (HITACHI, SU8010 FE-SEM). A 200 nm–800 nm UV-vis spectrophotometer was used to obtain UV-vis spectra (FIG-1901, Purkinje, China). Surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra (SERS) of all samples were captured using a confocal Raman microscopy system (Horiba). The diameter of the laser was 5 mm; its excitation wavelength was 633 nm, and it illuminated the test substrate vertically.
GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs prepared under different growth conditions were dropped into a CV solution (10−4 mol/L) for the SERS test. The substrate was combined with the CV concentration of 10−4 mol/L–10−8 mol/L, and SERS detection was carried out through magnetic enrichment to obtain the SERS spectrum of CV at 5 s per scan and 1% of maximum laser power. The results were recorded on the confocal Raman microscope system. Cumulative scanning was performed on the preferred substrate to obtain SERS spectra of the bifenthrin concentration gradient; each scanning time was 20 s, each scan was at 10% of maximum laser power, and the results were recorded on a confocal Raman microscope system (Horiba). All measurements were randomly performed three times.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation Principle and Optimization of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs
3.1.1. Preparation Principle of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs
As shown in the schematic diagram in Figure 1, by modifying PEI, Fe3O4 MNPs with a particle size of ~250 nm were aminated [31]. Colloidal gold prepared by the sodium citrate method had strong electronegativity, enabling Fe3O4@PEI to adsorb gold nanoparticles under ultrasonic conditions so that gold nanoparticles with a particle size of 20 nm had a SERS-enhanced effect on the surface modification of magnetic beads. The magnetic beads were then wrapped with a small amount of GO lamellar structure to obtain a GO/Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanosubstrate. AuNPs were used to generate substantial electromagnetic augmentation, where folds formed by the GO lamellae structure promote the absorption of aromatic molecules and provide additional charge transfer augmentation [32].
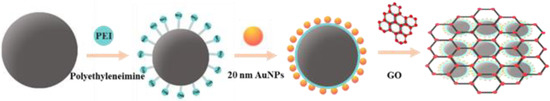
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of GO/Fe3O4@Au magnetic SERS substrate.
3.1.2. Effect of Colloidal Gold Volume with 20 nm Particle Size on GO/Fe3O4@Au MNP Synthesis
Firstly, the critical parameters for preparing GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs were optimized. Then, by adding different volumes of 20 nm AuNPs into the Fe3O4@PEI magnetic beads, the maximum loading of AuNPs on the Fe3O4 surface and the effect of the AuNPs on the SERS-enhanced effect of graphene-coated, gold-shelled magnetic beads were studied. As shown in Figure 2a, 2 mL, 4 mL, 6 mL, 8 mL, and 10 mL of colloidal gold were ultrasonically reacted with 1 mL 2 mg/mL of Fe3O4@PEI for 30 min, respectively, and GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs were prepared. When the colloidal gold volume was 8 mL, the SERS spectral intensity of the magnetic beads was the highest. However, when the volume of colloidal gold was further increased to 10 mL, the SERS intensity decreased significantly. As SERS enhancement was derived from the high-intensity local electric field in the gap between noble metal nanoparticles, when AuNPs were further adsorbed on the surface of magnetic beads, the “hot spots” formed between AuNPs were covered, resulting in a significant decrease in signal instead of an enhancement. Additionally, the complex substrate structure can be seen in Figure 2b, which shows the UV absorption spectrum. When the colloidal gold volume is less than 10 mL, the electron energy level transition is accompanied by a variety of vibrational and rotational energy level transitions, which causes the broader absorption peak of the UV-vis spectrum. However, when the colloidal gold volume is 10 mL, the absorption peak becomes significantly narrower, indicating that many redundant AuNPs are dispersed in the solution, indicating that the adsorption AuNPs on the magnetic bead surface have reached saturation. Therefore, the colloidal gold dosage of 8 mL is the optimal colloidal gold volume for further experiments with GO/Fe3O4@Au.
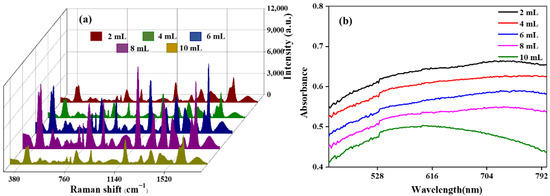
Figure 2.
SERS effect of CV detected by 1 mL 2 mg/mL GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs prepared with different volumes of colloidal gold (a) and UV-vis absorption spectrum (b).
3.1.3. Effect of Different GO Volumes on GO Fe3O4@Au MNP Synthesis
The amount of GO coating significantly influenced the SERS performance of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs. If the GO coating was too thick, AuNPs could not form surface plasmons with the target molecules, so achieving a good enhancement effect was not easy. Therefore, by adding different volumes of GO solution to the Fe3O4@Au magnetic beads, the impact of the amount of GO coating on the aggregation of magnetic beads and SERS-enhanced effect was studied. The findings are displayed in Figure 3a–f: SEM images of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs created for various GO volumes. The gold-shelled magnetic beads aggregated visibly when GO was 0.15 mL, but the surfaces of the magnetic beads were not uniformly coated. The concentration of gold-shelled magnetic bead increased when the amount of GO was greater than 0.2 mL. The figure shows that the GO lamellae on the surface are excessively thick, and AuNPs are concealed beneath the GO film. When the GO concentration was increased to 1 mL, the magnetic beads with the gold shell were covered entirely with GO, and the gold shell was no longer visible. As shown in Figure 3f, SERS intensity rose as GO increased when GO was lower than 0.2 mL. However, SERS intensity quickly dropped as the GO concentration increased, which was consistent with the SEM findings.
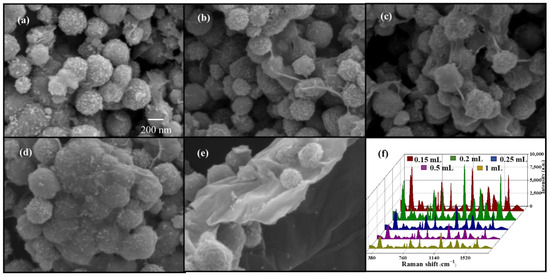
Figure 3.
SEM (a–e) and SERS effect (f) of CV detected by 1 mL 2 mg/mL GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs prepared with different volumes of GO.
3.2. GO/Fe3O4@Au MNP Characterization
The growth process of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs was measured by UV-vis spectroscopy (Figure 4a). The magnetic Fe3O4 microspheres had an absorption peak at 500 nm, which showed a slight red shift after PEI modification. Fe3O4@Au shows a new peak (blue curve) at 545 nm. The red shift of the absorption peak indicates the successful adsorption of AuNPs on Fe3O4. After wrapping Fe3O4@Au with GO, enhanced absorbance was observed at ~250 nm (green curve), suggesting the presence of GO [33]. However, the peak value of AuNPs still exists, but it is slightly redshifted and widened compared with Fe3O4@Au, indicating that the Fe3O4@Au composite has a specific aggregation after interacting with GO. Such aggregation may generate more SERS hot spots, which is crucial for the effective electromagnetic enhancement of the SERS signal. These results confirm the formation of Fe3O4@Au and GO-coated Fe3O4@Au MNPs.
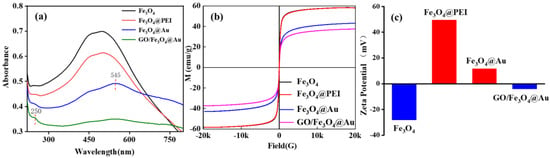
Figure 4.
UV-vis spectra (a), hysteresis regression curves (b), and Zeta potential (c) of Fe3O4, Fe3O4@PEI, Fe3O4@Au, and GO/Fe3O4@Au.
The magnetic properties of Fe3O4, Fe3O4@PEI, Fe3O4@Au, and GO/Fe3O4@Au at room temperature are depicted in Figure 4b. Hysteresis loops can be seen in the curves, and the corresponding magnetic saturation strengths are 58.5 emu/g, 58.1 emu/g, 43.0 emu/g, and 37.3 emu/g, respectively. The rise in the percentage of non-magnetic components in magnetic particles is responsible for the decrease in magnetic saturation intensity. All curves intersect the origin at room temperature, indicating that all products are superparamagnetic. It can be seen from the M-H curve that the decrease in the value is limited, and the magnetic response is weakened by about 30%. The GO/Fe3O4@Au nanocomposites still have a high magnetic saturation strength value, indicating that these particles all show superparamagnetism [34]. The magnetic saturation intensity after the modification of AuNPs was smaller than that of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@PEI because the change in AuNPs led to the increase in particle size of magnetic beads and the gold shell formed covered the surface of the magnetic beads. When covered with GO, the magnetic saturation intensity decreases to 5.7 emu/g, indicating that a small amount of GO can improve the adsorption capacity of benzene ring molecules in the magnetic bead adsorption band without affecting the magnetic response capacity of the magnetic bead.
Figure 4c shows the Zeta potentials of Fe3O4, Fe3O4@PEI, Fe3O4@Au, and GO/Fe3O4@Au. Fe3O4 modified the amino group on its surface via PEI-mediated modification, giving the magnetic particles a positive charge on their surfaces (Zeta potential changed from −28.2 mV to 49.6 mV). AuNPs prepared by citric acid reduction were modified by Fe3O4@PEI to form Fe3O4@Au (Zeta potential = 11.6 mV) by electrostatic interaction. The composite was mixed with GO suspension to generate GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs (Zeta potential = −4.1 mV) via electrostatic interaction.
Crystal violet (CV) containing benzene rings was used as a SERS probe molecule to detect the SERS adsorption and enhancement effect of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNP substrate. Figure 5 show the SERS spectral results and linear regression curves of CV detected by GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs at different concentrations. As can be seen from the Figure 5a, when the concentration of CV was 10−8 mol/L, GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs still had a noticeable enhancement effect. According to the literature, the primary SERS peak CV sources detected by GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs were assigned [35]. The (C+-benzene) bending that occurred out-of-plane caused the peak at 441 cm−1. The C-H bending vibration may be responsible for the Raman peak at 810 cm−1. The radial benzene ring skeleton vibration is responsible for the 920 cm−1 Raman signal. The Raman peaks at 1178 cm−1, 1371 cm−1, and 1618 cm−1 can be attributed to in-plane C-H bending vibration, N-benzene stretching vibration, φ-N stretching, and C-C stretching vibration. The CV characteristic peak at 1178 cm−1 was taken as a reference, and the molecular concentration-peak intensity correction curve was obtained by linear fitting, as shown in Figure 5b. The correlation coefficient of the fitting curve reached 96.412%. These results demonstrate that the gold-shelled magnetic beads coated with GO have good adsorption and enhancement ability for aromatic molecules containing benzene rings.
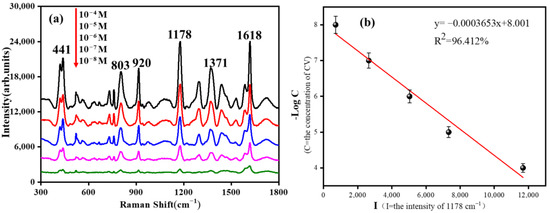
Figure 5.
(a) SERS spectra of CV with different concentrations on GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs; (b) SERS peak strength linear fitting curve of different concentrations of CV at 1178 cm−1.
3.3. FDTD Simulation Results of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs
In addition to the experimental study, a finite difference time domain (FDTD) simulation of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNP substrate was carried out using Lumerical FDTD Solutions software to further analyze its electric field distribution [36,37]. First, we simulated a GO/Fe3O4@Au single-sphere model and two adjacent GO/Fe3O4@Au two-sphere models. As shown in Figure 6a,b. The core of Fe3O4 was 250 nm, the diameter of the gold shell was 20 nm, and the graphene structure was directly above the single-sphere model. The graphene structure of the double-sphere model was placed in the middle of the two spheres, and the excitation wavelength was 633 nm. The theoretical enhancement factor script provided by The Official Website of FDTD [38] shows that the enhancement factor of the GO/Fe3O4@Au single sphere model was 16932900 and that of the Fe3O4@Au MNPs without GO was 17933400, demonstrating that GO had almost no effect on SERS enhancement of precious metal substrate.
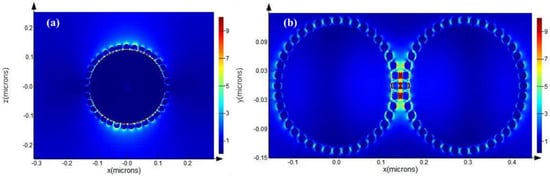
Figure 6.
Digital FDTD simulation: (a) SERS effect simulation of single GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs; (b) SERS effect simulation of two GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs at D = 1 nm (graphene was placed between the two spheres).
Then, we calculated the theoretical enhancement factor of two adjacent GO/Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles, which was 1356758. The above simulation results proved that the GO/Fe3O4@Au structure had an excellent SERS-enhanced effect, and SERS-enhanced hot spots could be formed between the gold sphere and two gold-shelled magnetic beads on the surface of a single particle.
3.4. Detection of Different Concentrations of Bifenthrin
It can be seen from Figure 7a that there are two benzene rings in the molecular structure of bifenthrin. Raman spectra of bifenthrin were obtained by direct detection of bifenthrin solid powder. The results are shown in Figure 7b. Due to the complex molecular structure of bifenthrin, there are many peak sites in the spectrum, among which the main peak sites are 656 cm−1, 991 cm−1, 1288 cm−1, and 1650 cm−1. Then, a magnetic enrichment detection method was used to detect bifenthrin in acetone with GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs as the substrate. The corresponding peak positions between the SERS characteristic peak and the solid Raman characteristic peak are marked in red.
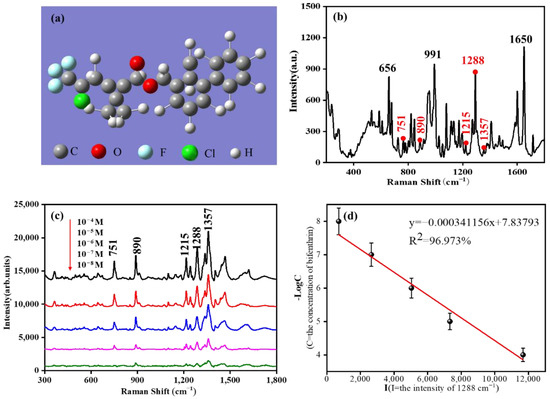
Figure 7.
(a) The 3D molecular structure model of bifenthrin; (b) Bifenthrin solid-state Raman spectroscopy; (c) SERS spectra of different concentrations of bifenthrin detected by GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs; (d) SERS peak strength linear fitting curve at 1288 cm−1.
In contrast, the strong solid Raman characteristic peaks are marked in black. The results are shown in Figure 7c. Its characteristic peak was still clearly visible when the solution concentration was 10−8 mol/L. It was proven that the GO/Fe3O4@Au MNP substrate had excellent bifenthrin SERS adsorption detection ability. Among them, the signals of the five spectrum peaks at 751 cm−1, 890 cm−1, 1215 cm−1, 1288 cm−1, and 1357 cm−1 were evident in the SERS spectrum of bifenthrin. Due to the conformation change in molecules during the SERS and conventional Raman tests, the polarization angle of the laser, and many other factors, the excitation peak was not the original prominent peak. Corresponding peak locations have been marked in Figure 7b. The characteristic peak positions of SERS peak locations were attributed to C-Cl stretching vibration at 751 cm−1, C-O-C stretching vibration at 890 cm−1, C-H bending vibration at 1215 cm−1, C-H stretching vibration at 1288 cm−1, and benzene ring stretching vibration at 1357 cm−1. In Figure 7d, the correlation curve between the peak intensity of 1288 cm−1 and the concentration of bifenthrin is Y = −0.000341156x + 7.83793, and the correlation coefficient (R2) is 96.973%, indicating that there is an excellent linear relationship between the peak intensity and concentration.
Furthermore, as shown in Figure S1, we detected bifenthrin and its structural analogues using GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs as a SERS substrate. It can be quickly concluded that only bifenthrin exhibited the distinguishable characteristic peak. At the same time, the other analogues could not excite good characteristic peaks, which proves the excellent specificity of the SERS substrate for the detection of bifenthrin. In addition, we calculated the limit of detection (LOD) [39], and the details are in the supporting information. The LOD of bifenthrin is as low as 7.122 μg/kg. Therefore, it was proven that GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs could be used as an effective SERS adsorption-enhanced substrate for bifenthrin.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we reported a preparation method for graphene-coated, gold-shelled magnetic beads of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNP as a SERS substrate, which increased the adsorption and SERS-enhanced effect and was used to detect residues of bifenthrin pesticide. The method can be divided into four steps: the preparation of magnetic microspheres, PEI modification of the magnetic microspheres, gold shell growth, and GO coating. By optimizing the two steps of gold shell growth and GO coating, we prepared GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs in a controlled manner. Using CV as the probe molecule, we evaluated the enhanced effect of the magnetic beads under different growth conditions, and obtained the SERS gradient and linear regression curve. It has been proven that the prepared substrate has good uniformity of size and shape, high magnetic responsiveness, and SERS activity. Based on the adsorption of graphene to molecules with a benzene ring and the enrichment ability of the magnetic substrate, the detection of bifenthrin with this substrate achieved its lowest concentration of 10−8 mol/L. These results showed that GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs can be used as SERS substrates for the rapid, convenient, and highly sensitive detection of bifenthrin pesticide residues.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors11020073/s1, Figure S1: SERS spectra of bifenthrin and its structural analogues based on GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs.
Author Contributions
Y.S. and K.X. contributed to this article equally. Z.Y. and P.L. designed the experiment and wrote this article. Y.S., K.X. and Q.C. carried out the experiment. X.Z. (Xiubing Zhang) conducted the data collation and analysis. W.C. participated in the substrate preparation and characterization of gold material. Z.Y. and D.Z. performed the SERS test. X.Z. (Xiaodong Zhang) conducted a pesticide test experiment. D.N. made valuable suggestions for this work; he polished and checked this manuscript before submission. P.L. guided the whole research process with Z.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFD1000401) and the Hubei Provincial Water Resources Key Research Project (Grant No. HBSLKJTG202001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dar, M.A.; Khan, A.M.; Raina, R.; Verma, P.K.; Wani, N.M. Effect of bifenthrin on oxidative stress parameters in the liver, kidneys, and lungs of rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9365–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammon, D.W.; Liu, Z.W.; Chandrasekaran, A.; El-Naggar, S.F.; Kuryshev, Y.A.; Jackson, S. Pyrethroid neurotoxicity studies with bifenthrin indicate a mixed Type I/II mode of action. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Xi, F.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Du, R.; et al. Bifenthrin induces fat deposition by improving fatty acid uptake and inhibiting lipolysis in mice. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 14048–14055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Park, S.; Lim, W.; Song, G.H. Bifenthrin reduces pregnancy potential via induction of oxidative stress in porcine trophectoderm and uterine luminal epithelial cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, N.X.; Wang, C.L. Toxicity of the pyrethroid bifenthrin insecticide. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.M.G.; Botelho, A.F.M.; Silva, R.H.S.; Almeida, S.S.F.; Ferreira, E.R.; David, L.C.; Lima, D.A.F.; Silva, T.C.E.; Cunha, P.H.J.; Antoniosi, N.R. Identification of cattle poisoning by Bifenthrin via earwax analysis by HS/GC-MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2021, 35, e5017. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, R.; Singh, R.; Singh, M.; Mogha, N.K.; Kumari, P.; Paliwal, G.; Singh, P.P.; Das, M. LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of pyriproxyfen and bifenthrin and their dissipation kinetics under field conditions in chili and brinjal. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.K.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Brolo, A.G. A review on recent advances in the applications of surface-enhanced Raman scattering in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1097, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhu, C.; Meng, G.; Wu, N. Review—Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensors for Food Safety and Environmental Monitoring. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B3098–B3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.R.; Tian, X.D.; Liu, S.Y.; Yun, Z.; Li, J.F. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy solution and solid substrates with built-in calibration for quantitative applications. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.M.; Li, X.; Zou, S.; Zhang, D. Quantitative Comparison of Raman Activities, SERS Activities, and SERS Enhancement Factors of Organothiols: Implication to Chemical Enhancement. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 3, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.I.; Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R.P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayah, A.N.; Triyono, D.; Herbani, Y.; Saleh, R. Liquid Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Sensor-Based Au-Ag Colloidal Nanoparticles for Easy and Rapid Detection of Deltamethrin Pesticide in Brewed Tea. Crystals 2022, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.B.; Hoang, T.H.C.; Pham, V.H.; Nguyen, V.C.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vu, D.C.; Pham, V.H.; Bui, H. Detection of Permethrin pesticide using silver nano-dendrites SERS on optical fibre fabricated by laser-assisted photochemical method. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, T.H.; Mehedi Hassan, M.; Zhu, J.J.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, W.; Wang, J.J.; Lv, C.X.; Chen, Q.S.; Li, H.H. Quantification of deltamethrin residues in wheat by Ag@ZnO NFs-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupling chemometric models. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, S.; Chen, B.; Gu, Y.F.; Song, C.; Lei, J.J.; Gao, X. The Study of Raman Spectroscopy of Bifenthrin Molecular. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2020, 40, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, R.D.; Phan, H.T.; Gibbons, S.N.; Haes, A.J. Quantitative Surface-Enhanced Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2022, 73, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Biswas, N.; Malkar, V.V.; Mukherjee, T.; Kapoor, S. Studies on adsorption of carnosine on silver nanoparticles by SERS. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 491, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, T.; Pu, H.B.; Sun, D.W. Functionalization techniques for improving SERS substrates and their applications in food safety evaluation: A review of recent research trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Wang, Y.; Deng, R.; Yang, L.Y.; Yu, S.H.; Xu, S.P.; Xu, W.Q. Fe3O4@Graphene Oxide@Ag Particles for Surface Magnet Solid-Phase Extraction Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SMSPE-SERS): From Sample Pretreatment to Detection All-in-One. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14160–14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Jing, C. Preparation of Thiol Modified Fe3O4@Ag Magnetic SERS Probe for PAHs Detection and Identification. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2011, 115, 17829–17835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D. Preparation of Graphene Oxide and Its Application as Substrates for SERS. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 8050524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Lee, Y.H.; Pedireddy, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.X.; Ling, X.Y. Graphene oxide and shape-controlled silver nanoparticle hybrids for ultrasensitive single-particle surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensing. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4843–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, X.; Moura, L.G.; Pimenta, M.A.; Zhang, J. Charge-Transfer Mechanism in Graphene-Enhanced Raman Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25112–25118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.S.; Shang, S.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Z.; Sheng, Y.Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Qiu, H.W.; Huo, Y.Y.; Jiang, S.Z. An optical fiber SERS sensor based on GO/AgNPs/rGO sandwich structure hybrid films. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 81750–81756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liang, A.H.; Jiang, Z.L. SERS quantitative analysis of trace ferritin based on immunoreaction regulation of graphene oxide catalytic nanogold reaction. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 263, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.J.; You, X.R.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.L.; Dhinakar, A.; Liu, S.H.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.M. Development of graphene oxide-wrapped gold nanorods as robust nanoplatform for ultrafast near-infrared SERS bioimaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4349–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasztelan, M.; Sloniewska, A.; Gorzkowski, M.; Lewera, A.; Palys, B.; Zoladek, S. Ammonia modified graphene oxide—Gold nanoparticles composite as a substrate for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 554, 149060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Li, X.L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.P.; Li, Y.D. Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2782–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.J.; Ni, D.J.; Yu, Z.; Liang, P. Preparation of SERS-active substrates based on graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites for rapid zdetection of L-Theanine. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Yang, X.B.; Zhang, D.; Zou, Y.Q.; Ni, D.J.; Ye, J.M.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Jin, S.Z.; et al. Fabrication of Fe3O4@Ag magnetic nanoparticles for highly active SERS enhancement and paraquat detection. Microchem. J. 2022, 173, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Xiong, X. Free-standing paper-like heat spreading films based on graphene oxide-aromatic molecule composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 3050–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Zhu, S.F.; Luo, X.P.; Zou, M.; Huang, S.H. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy of graphene oxides. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 032146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Obata, S.; Niwa, M. Simulation of the Magnetic Hysteresis Loop in Ferrimagnetism. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, S.Z.; Huo, Y.Y.; Ning, T.Y.; Liu, A.H.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Wang, M.H.; Li, C.H.; Man, B.Y. 3D silver nanoparticles with multilayer graphene oxide as a spacer for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy analysis. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5897–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liang, P.; Tang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Dong, Q.; Huang, J.; He, P. Synergistic effects of semiconductor substrate and noble metal nanoparticles on SERS effect both theoretical and experimental aspects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Yang, Z.L.; Meng, L.Y.; Sun, Y.D.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.B.; Liu, J.H.; Tian, Z.Q. Three-Dimensional and Time-Ordered Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Hotspot Matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5332–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.P.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Z.L.; Shi, Z.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Du, L.T. Highly Sensitive and Reproducible SERS Substrates Based on Ordered Micropyramid Array and Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29222–29229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).