Abstract
Carbon dots (CDs) are a new class of carbon-based luminescence materials with fascinating properties. They have been given great expectations on superseding traditional semiconductor quantum dots due to their good dispersity and stability, relatively low toxicity, superior resistance to photobleaching, and excellent biocompatibility. The diversified luminescence properties of CDs are largely due to the synthetic strategies and precursors. In view of those described above, this study has explored the possibility to establish a facile one-step hydrothermal method for the one-pot synthesis of folic acid-modified cerium-doped CDs (Ce-CDs-FA), which could be further utilized as a sensitive fluorescent nanoprobe for biosensing. This investigation demonstrates that the Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites have nice biocompatibility and bright fluorescent properties, which can be readily utilized to detect cancer cells through recognizing overexpressing folate receptors by virtue of folic acid. Meanwhile, it is noted that the Fe3+ ion can actualize a specific and hypersensitive quenching effect for these Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites, which can be further explored for special ion recognition, including iron ions. It raises the possibility that the as-prepared Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites could be extended as a dual fluorescence sensor for targeted cell imaging and Fe3+ ion detection.
1. Introduction
Carbon dots (CDs) are a new type of luminescent material and a new member of carbon nanostructures with unique structural and photophysical properties, which were accidentally discovered in 2004 [,]. They have similar photoluminescence (PL) properties to semiconductor quantum dots as well as low toxicity with organic dye molecules. Therefore, tremendous attention has been given to sundry CDs as promising upgrading tools for exploitation in bioimaging and sensor fields to supersede semiconductor quantum dots []. Generally, CDs can be readily synthesized by two synthetic categories, “top-down” and “bottom-up” approaches, and hydrothermal treatment is one of the most effective and popular methods to prepare CDs [,]. A variability of precursor materials and procedures can be utilized to produce CDs by “bottom-up” synthetic routes, which can lead to the distinctive properties of various CDs [,]. Thus, the structure and function of CDs could be readily regulated by synthesis and post-modificatory processing. Nevertheless, there are still some controversies about the PL mechanism of CDs, which have become the focus of extensive investigations. Recently, Yang′s group have summarized the theoretical structure models of CDs [] and divided CDs into three categories: graphene quantum dots (GQDs), carbon quantum dots (CQDs), and carbonized polymer dots (CPDs), depending on the core structures and surface states [,]. According to the structure model theory, the fluorescence characteristics of CDs are mainly caused by hybridization and synergy effects between the carbon core and surface chemical groups [,].
CDs represent an emerging subset of promising nanomaterials for various possible applications. More recently, much attention has been focused on the extensive applications of some CDs in bioimaging [,,,], sensing and detection [,,,,,,,,], phototherapy [,,], drug delivery [,,], light-emitting diodes (LEDs) [,,], and catalysis [,,], etc., due to their excellent biocompatibility, tunable emission wavelength, and high stability. Owing to the characteristics of low cost, simple, and high efficiency, CD-based sensors have essential roles in metal ion detection and biomolecule sensing by quenching or enhancing the effect on the CDs’ fluorescence, which is the most commonly studied in terms of CD research []. These mechanisms are reported as static quenching, dynamic quenching, photoinduced electron transfer (PET), energy transfer (ET), and the inner filter effect (IFE) [,]. The efficient sensing and detection of ferric ion have a great importance for health risk assessment. Ferric ions have been the most commonly detected ions in the literature by using quantum dots (QDs) as fluorescent probes due to the presence of the amino, carboxyl, and hydroxyl functional groups on the surface [,]. Zulfajri et al. synthesized CDs by a green precursor Volvariella volvacea and used it as a fluorescent sensor to detect Fe3+ and Pb2+ ions in water samples with good spike recoveries []. Fruit peels can be turned into CDs via a hydrothermal-carbonization route and utilized for detection of ferric ion in an aqueous medium by fluorescent quenching [].
Surface passivation and heteroatom doping are critical factors to efficiently tune the intrinsic PL properties of CDs [,]. Most obtained CDs have a relatively low emission efficiency compared to the conventional semiconductor quantum dots []. The doping of the heteroatom can introduce holes or electrons into the CDs and create disorders within the carbon backbone by the formation of conjugated carbon clusters, which distinctly improve the physicochemical features, PL and chemical activity [,]. The quantum yield and PL properties of the heteroatom-doped CDs are closely related to the electronegativity values of the heteroatoms [,]. Doping with high electronegative atoms usually cause blue-shifted PL emission and low electronegative atoms have the reverse effect []. The CDs with heteroatoms can be acquired by undergoing dehydration and carbonization reactions using heteroatom substituted organic molecules as precursors. The passivation and functionalization through surface chemistry with heteroatom-contained molecules are also common methods to obtain heteroatom-doped CDs. Although both metals and non-metal heteroatoms have been introduced into the carbon skeleton matrices and chemical structures, non-metal-based doping is the most adopted strategy due to the facile and efficient doping process []. To date, various non-metal atoms, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, boron, selenium, tellurium, silicon, and halogens (F/Cl/Br/I), have been reported to effectively dope into CDs and widely investigated for applications [,]. N, P, and S can increase the electron concentration of CDs while B and Si can generate a large number of active sites. Se-doped CDs can protect the cells from excessive ROS and F-doped CDs can initiate magnetism [,]. Te-doped CDs can specifically trace superoxide anion in vivo and I-doped CDs give a strong X-ray attenuation in CT diagnosis imaging [,].
The metallic and transition metallic dopants can chelate to the functional groups and modulate the band structures in the carbonization and dehydration processes of precursors []. Several metal atoms, such as Cu, Mg, Zn, Gd, Cr, Co, Mn, Ge, etc. are employed to create metal atom-doped CDs []. In addition, some research efforts have recently studied the effect of rare earth element doping for CDs [,,]. Doping with Tb3+ and Eu3+ can improve the PL quantum yield of CDs by causing the energy transfer from CDs to the rare-earth metal ions []. The substitution of carbon atoms with cerium can energize a variety of biomedicine functions of CDs, such as mimetic phosphatases activity [], antibacterial activity [], and radical scavenging activity [], for the degradation of organophosphorus pesticide, accelerating wound healing and enhancing antioxidants, respectively. The doping of Mn(II) and Gd(III) can render magnetic properties to CDs for an MRI modality [,]. Li et al. synthesized chromium(III)-doped carbon dots (Cr-CDs) by a hydrothermal approach []. Tris(2, 4-pentanedionato) chromium(III) and polyethyleneimine were used as precursors. This Cr-CDs have low cytotoxicity with a 20% quantum yield, and excitation-independent emissions. Cr-CDs can be used as a fluorescence probe for insecticide metabolite p-nitrophenol (p-NP) in human urine. Subsequently, they exploited manganese(III) acetylacetonate (Mn(C5H7O2)3) as the single precursor and achieved manganese oxide-doped CDs (MnOx-CDs) []. The multifunctional MnOx-CDs can be used as a sensitive thermometer in living cells, restrain the migration of HepG2 cancer cells for liver cancer adjuvant treatment and detect Fe3+ and biothiols with high reliability and accuracy as fluorescence probes.
In the present investigation, the folic acid-modified cerium-doped CDs (Ce-CDs-FA) nanocomposites were explored and fabricated by a facile one-step hydrothermal synthetic route in which polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-K30), cerium acetate (Ce(Ac)3), and folic acid (FA) were mixed and heated to 160 °C to induce carbonization. UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy, PL spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrum, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS) analyses were conducted to characterize the formation and properties of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites. The use of folic acid (FA) molecules as precursors could render the nano Ce-CDs-FA as a potential targeted imaging agent for specific bio-recognition and selectively staining of cancer cells expressing folate receptors on cell surfaces. Furthermore, the luminescence of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites can be selectively quenched by the Fe3+ ion, which makes it possible for the as-prepared Ce-CDs-FA to be applied as a dual fluorescence sensor for cancer cell recognition and Fe3+ ion detection.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Reagents
The polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-K30) was obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). FA was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Ce(Ac)3 was produced by Nanjing Chemlin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Dulbecco′s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) was acquired from Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The fetal bovine serum (FBS) was supplied by Hyclone Co., Ltd. (Logan, UT, USA). The trypsin and penicillin–streptomycin solutions were bought from Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was purchased from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). All metal ions, in the form of nitrate or chloride salts, were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and were dissolved in ultrapure water to prepare the stock solutions (100 mM). Ultrapure water (18.2 MΩ·cm, Millipore Simplicity, USA) was used throughout the experiment.
2.2. Characterization
The morphology of the as-prepared Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites was characterized by a JEM-2100F transmission electron microscope (JEOL Co., Ltd., Akishima, Japan). The particle size distribution of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites was measured by the DLS on a Zetasizer Nano ZS90 (Malvern Co., Ltd., Malvern, UK). The UV-vis absorption spectra were obtained on an Evolution 260 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific Co., Ltd. Waltham, MA, USA). The fluorescence spectra were recorded with a Shimadzu RF-5301 PC spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan). The FT-IR spectra were carried out on a Nicolet iS50 FT-IR spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA). The XRD measurement was performed on a SmartLab-3 KW X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). XPS was recorded with an Ulvac Phi Quantera II scanning XPS microscope (ULVAC Co., Ltd. Chigasaki, Japan). The Fe3+ concentrations of blood samples were measured by an Agilent 7700 Series inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The in vitro bioimaging was performed by a Nikon ECLIPSE Ti2-C2 confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) (Nikon Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
2.3. Preparation of Ce-CDs-FA Nanocomposites
Initially, 0.15 g PVP-K30, 0.1 g FA, and 0.05 g Ce(Ac)3 were dissolved in 15 mL ultrapure water with ultrasonication for 10 min. Then the solution was poured into a 20 mL Teflon-lined stainless-steel reactor and treated at 160 °C for 24 h. After that, the solution was cooled to room temperature and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min to remove impurities and large particles. The supernatant was collected and kept in the refrigerator at 4 °C as the stock solution for further study. The final FA-modified cerium-doped carbon-dots (Ce-CDs-FA) powder was obtained by drying under vacuum at 60 °C or lyophilized in a freeze-dryer. For comparison, the nano Ce-CDs were synthesized by the same procedure without FA.
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytotoxicity assay of the Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites was performed by using the CCK-8 on the L02 and cancer cell lines. Generally, L02 cells or cancers cells were seeded into a 96-well plate at a density of 0.8 × 104–1.0 × 104 cells per well and incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in a humidified atmosphere. The DMEM was supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 100 U/mL penicillin. The medium was changed every other day until 80% confluence had been reached. Then different concentrations of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites were added in the wells. After 24 h incubation, 10 μL CCK-8 solution was added to each well and removed 1–4 h later. Then the absorbance of each individual well was measured by an automatic enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analyzer at 450 nm. The cell viabilities were obtained by a simple calculation with a control group (100%).
2.5. Cellular Bioimaging
The targeted fluorescence bioimaging performance of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites was evaluated in vitro on the L02 and Hela cell lines by using the CLSM. The Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites were dissolved in DMEM at a final concentration of 250 µg/mL and several incubated with the two cell lines for 24 h. The unmodified Ce-CDs were simultaneously incubated and implemented on CLSM as control group. The blank group without any treatment was conducted in parallel. After treatment, the cells were rinsed twice with PBS and changed into fresh medium to remove the non-internalized nanoparticles before fluorescence bioimaging to evaluate the in vitro targeted imaging validity.
2.6. Detection of Fe3+ Ion
Different metal ions of K+, Na+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Al3+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Co2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ and Ce3+ were offered for the detection. The Ce-CDs-FA stock solution was diluted up to 50 μg/mL and appraised as a metal ion sensor through titration. In short, the highly dilute solution of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites was added into a quartz photometric cuvette and the fluorescence emission spectra were acquired as control. The PL intensity of the control was noted as F0. A certain volume (20 μL) of metal ion solution (10 mm) was dropped into the Ce-CDs-FA solution and incubated for 1 min. The PL intensity in the presence of metal ions was noted as F. The PL intensity ratios (F/F0) of Ce-CDs-FA solution were calculated. Multiple dropping proceeded once there was a significant quenching effect. All the experimental procedures were carried out under the same conditions. The relationship of different concentrations of metal ions and the PL intensity of the relevant Ce-CDs-FA was explored by using linear line fitting.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
The optical properties of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites were characterized by UV-Vis spectra and fluorescence spectra, as shown in Figure 1A. The characterization of a relevant UV-Vis absorption peak around 290 nm was observed, while at 350 nm excitation the fluorescence emission of the Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites covered almost the entire visible light range (400~650 nm). High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) was performed to confirm the formation of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites. Figure 1B shows the TEM and HRTEM images of the as-prepared Ce-CDs-FA, which demonstrates a spherical in shape and good monodispersity. The relevant crystalline lattice displays a width of 0.34 nm, which closely matches the graphite lattice parameters ((002) crystal planes) []. The particle size distribution was further counted by the DLS spectrum. The result in Figure 1C reflects that the average particle size distribution is estimated to be 3.8 nm by a single peak. The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) was carried out over the range of 10~80° (2θ) to investigate the crystalline characteristics and particle size of the Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites. A typical broad peak appears in Figure 1D around 25° in a pattern indexed to the (002) diffractions of carbon [,], which verifies the existence and amorphous property of carbon, in agreement with HRTEM observations.
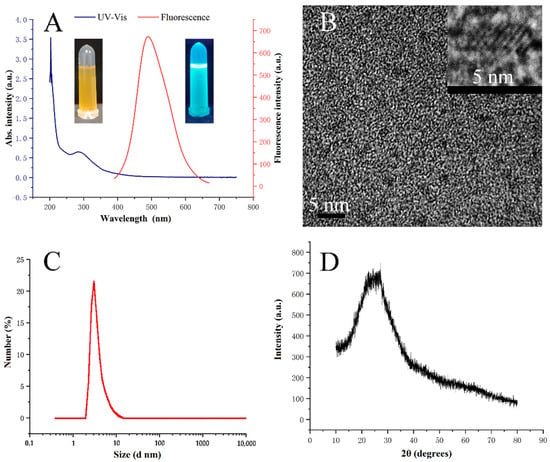
Figure 1.
(A) UV-Vis spectra and fluorescence spectra of Ce-CDs-FA (inset: photographs of 1 mg/mL Ce-CDs-FA solution under natural light and 365 nm UV lamp). (B) TEM photograph (inset: HRTEM image). (C) DLS measurement. (D) XRD analysis.
Meanwhile, FTIR and XPS analyses were carried out to investigate the as-prepared Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites. The relevant FT-IR spectra are illustrated in Figure 2A and Table 1, presenting the appearance of varied functional groups. The observed broad absorption peaks around 3500 cm−1 and 3200 cm−1 can be ascribed to the O-H and N-H stretching vibration bonds [,]. The relevant peak at 2900 cm−1 symbolizes a stretching vibration of C-H [,]. The peaks at 1670 cm−1 and 1220 cm−1 correspond to the C=O stretching motion and C–H stretching motion [], respectively. After the formation of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites, the peak at 1640 cm−1 could be attributed to carboxyl groups O-H bending vibrations while the C=O peak has become less obvious. Three peaks at 1420 cm−1, 1283 cm−1, and 1020 cm−1 can be attributed to the C-H bending vibrations and stretching vibrations of C-N and C-O, respectively []. The peak at 1562 cm−1 demonstrates the stretching vibrations of C=C from benzene in FA [].
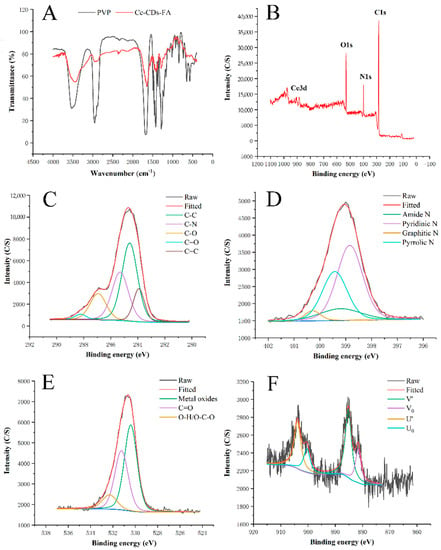
Figure 2.
(A) FT-IR spectra of PVP and Ce-CDs-FA. (B) XPS spectrum of Ce-CDs-FA. (C) C 1s zone. (D) N 1s zone. (E) O 1s zone. (F) Ce 3d zone.

Table 1.
FT-IR data of the Ce-CDs-FA.
Moreover, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was further explored to acquire the elemental information. The raw XPS data were corrected with reference to the C1s line at 284.6 eV before analysis. As shown in Figure 2B, the XPS data indicate that the Ce-CDs-FA primarily consist of four elements: carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and cerium. The C 1s spectrum in Figure 2C shows five different bonding energy peaks at 283.9 eV, 284.6 eV, 285.2 eV, 286.8 eV, and 288.2 eV, corresponding to the C=C (benzene), C-C, C-N, C-O, and C=O groups [], respectively. The N 1s spectrum of the Ce-CDs-FA in Figure 2D is represented by four peaks at 398.8 eV, 399.2 eV, 399.4 eV, and 400.3 eV, associated with pyridinic N, amide N, pyrrolic N and graphite N [], respectively. The O 1s region of Ce-CDs-FA in Figure 2E has three peaks at 530.4 eV, 531.2 eV, and 532.3 eV, symbolizing metal oxides, C=O, and O-H/O-C-O [,], respectively. The Ce 3d spectra are shown in Figure 2F. The four peaks at 881.4 eV, 885.2 eV, 900 eV, and 903.9 eV originated from Ce(III) oxide [].
3.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
The CCK-8 assay was applied to assess the cytotoxicity of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites. The graded concentrations (62.5, 125, 250, 500, and 1000 µg/mL) of Ce-CDs-FA were incubated with L02 and Hela cells for 24 h. An encouraging cytotoxicity result was shown in Figure 3. The trend lines exhibited that the L02 and Hela cells had different responses for the same concentration of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites. These data indicate that Ce-CDs-FA was biocompatible for cells even though the concentration was up to 1000 µg/mL. It could be a potential multicolored fluorescence agent in the field of bioimaging application.
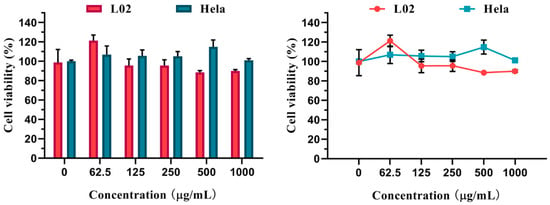
Figure 3.
Cytotoxicity of different Ce-CDs-FA concentrations on L02 and Hela cells.
3.3. Targeted Multicolored Bioimaging
The capabilities of targeted cell imaging were studied on Hela and L02 cell lines by CLSM. The experimental group was incubated with Ce-CDs-FA and the control group was incubated with Ce-CDs simultaneously. The cells in the blank group proliferated naturally without any treatment. The cell fluorescence imaging could reflect the internalization level of Ce-CDs-FA and Ce-CDs into Hela and L02 cells. The multicolored fluorescence of the Hela experimental group could be clearly visible (Figure 4), which indicated that the Ce-CDs-FA was imbibed into the cytoplasm. The obvious difference of fluorescence intensity on Hela cells between the control groups and experimental groups indicated that Ce-CDs-FA and Ce-CDs could produce different degrees of internalization. This consequence displays a cooperative effect of FA and Ce-CDs. Meanwhile, the notable differences in cell internalization between Ce-CDs-FA and Ce-CDs have not been observed in L02 cells (Figure 5). This demonstrated the diverse internalization mechanism of Ce-CDs-FA on Hela and L02 cells. Since FA served as the major contributor to rapid cell internalization, this could be attributed to the abundant folate receptors on the surface of Hela cells. It is evident that the cell imaging studies by CLSM demonstrated the specific cancer cell recognition of Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites.
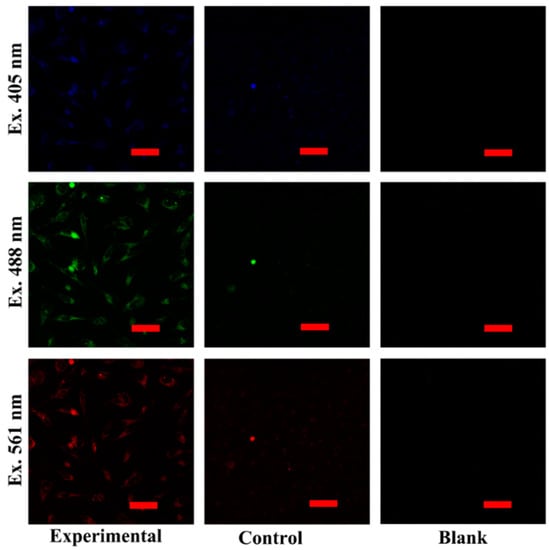
Figure 4.
The multicolor bioimaging of Ce-CDs-FA and Ce-CDs on Hela cell lines. The scale bar is 50 μm.
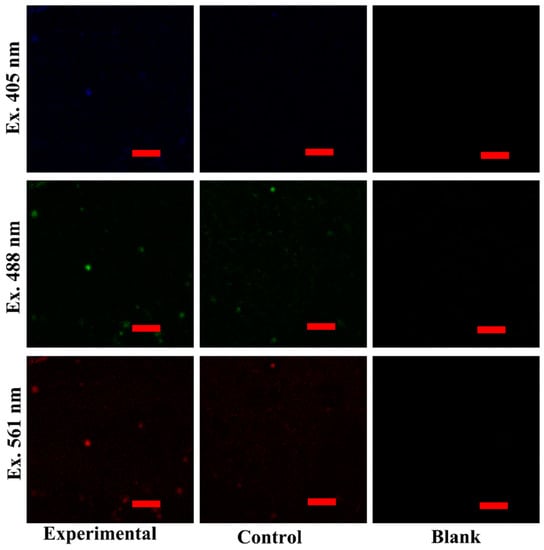
Figure 5.
The multicolor bioimaging of Ce-CDs-FA and Ce-CDs on L02 cell lines. The scale bar is 50 μm.
3.4. Detection of Fe(III)
Various metal ion solutions with identical concentrations (10 mm) were added to the Ce-CDs-FA dilute solution several times to check out the quenching degree correlated with the type and valence of metal ions. K+, Na+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Al3+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Co2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Ce3+ ions were inspected and the results were exhibited by the PL intensity ratios (F/F0) in Figure 6. It was obvious that Ce-CDs-FA was highly specific and hypersensitive to the Fe3+ ion compared to any other metal ion.
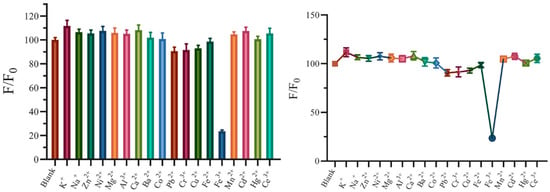
Figure 6.
The quenching effect of metal ions to Ce-CDs-FA.
The quenching effect has made it inescapably clear that the Ce-CDs-FA could be developed as a fluorescence sensor for Fe3+ detection. So, further measurement was performed to ascertain the linear range by the titrimetric method. Figure 7A shown that the fluorescence intensity of the Ce-CDs-FA quenched gradually with increasing the concentration of Fe3+ ions between 0 to 2 mm. The F/F0 declined with the increase in Fe3+ concentration and an exponential equation (y = 99.747e−0.707x) was fitted, with a regression coefficient R2 = 0.9941 (Figure 7B). Thus, the Ce-CDs-FA was available for Fe3+ ions detection as a fluorescence probe.
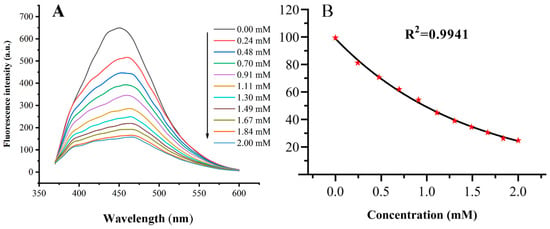
Figure 7.
(A) The Fe3+ detection of Ce-CDs-FA by specific quenching with standard solution. (B) The curve-fitting analysis of Fe3+ detection by Ce-CDs-FA with standard solution. The error bars are not visible as they are obscured by the data point (the red pentagram symbols).
The whole blood samples were used as actual specimens to appraise the potency of Ce-CDs-FA as an Fe3+ fluorescence sensor. The EDTA-K2-anticoagulated whole blood was diluted with ultrapure water 20 times and fragmented by ultrasonic disruption for 1 h. After centrifugation for 5 min at 8000 rpm, the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filtration membrane before analysis. The final solution was analyzed by 50 µg/mL Ce-CDs-FA aqueous solutions for Fe3+ detection. These samples were digested several times via concentrated nitric acid, filtered with 0.22 μm filtration membranes, and detected with ICP-MS. The calculation result of the Fe3+ concentration was compared with the standard ICP-MS method. The comparison results between the ICP-MS method and fluorescence method are shown in Figure 8 and Table 2. Meanwhile, the fluorescence method shows a relatively good consistency with the ICP-MS method. Thus, the fluorescence analysis was a simple and convenient alternative method for effective Fe3+ detection in blood samples, and thus has enormous potential.
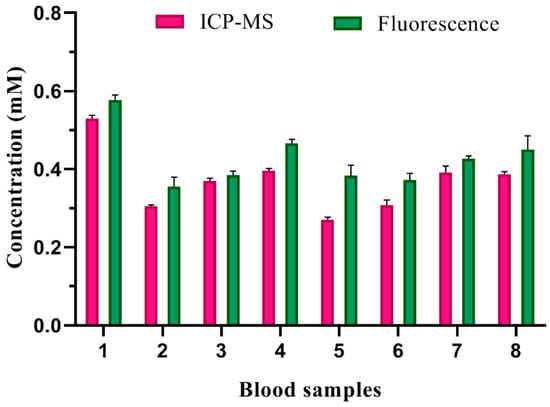
Figure 8.
The Fe3+ detection of blood samples by ICP-MS method and fluorescence method.

Table 2.
The Fe3+ analysis of blood samples.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have synthesized cerium-doped carbon dots modified with folic acid by a simple one-pot procedure. The as-prepared Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites have unique properties, including commendable biocompatibility, low toxicity, multicolor luminescence, and low cost. More importantly, it possible to be used as a dual fluorescence sensor for the identification of cancer cells expressing the folate receptors and the detection of Fe3+ ions. It is evident that the Ce-CDs-FA nanocomposites could be explored as a promising powerful fluorescent probe for multicolored bioimaging and ion detection.
Author Contributions
Data curation, J.L., Z.G., T.L., J.Z. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, J.L.; funding acquisition, H.J. and X.W.; investigation, J.L.; methodology, J.L.; resources, L.Y. and X.W.; software, J.L. and Z.G.; supervision, X.L., H.J. and X.W.; validation, J.L. and F.Y.; visualization, J.L.; writing—original draft, J.L.; writing—review and editing, X.L., H.J. and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82061148012, 82027806, 91753106) and the Key R&D Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BE2019716).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of BE2019716.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflict to declare.
References
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, M.; Bilal, M.; Rahdar, A.; Barani, M.; Arshad, R.; Behl, T.; Brisc, C.; Banica, F.; Bungau, S. Nanomaterials for Diagnosis and Treatment of Brain Cancer: Recent Updates. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lei, F.; Chen, H.; Yin, L.; Shi, Y.; Xie, J. One-step hydrothermal synthesis and optical properties of self-quenching-resistant carbon dots towards fluorescent ink and as nanosensors for Fe3+ detection. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8290–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zulfajri, M.; Liu, K.; Pu, Y.; Rasool, A.; Dayalan, S.; Huang, G.G. Utilization of Carbon Dots Derived from Volvariella volvacea Mushroom for a Highly Sensitive Detection of Fe3+ and Pb2+ Ions in Aqueous Solutions. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, T. Photoluminescence tuning in carbon dots: Surface passivation or/and functionalization, heteroatom doping. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7797–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.; Sun, H.; Yang, B. One-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Conjugated Carbonized Polymer Dots with 31% Efficient Red Emission for In Vivo Imaging. Small 2018, 14, 1703919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yuan, T.; Sui, L.; Wang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Tan, Z.; Chen, A.; et al. Engineering triangular carbon quantum dots with unprecedented narrow bandwidth emission for multicolored LEDs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yong, X.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Theoretical Understanding of Structure-Property Relationships in Luminescence of Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 7671–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, P.Y.; Graham, R.M.; Pandey, R.R.; Chusuei, C.C.; Mintz, K.J.; Zhou, Y.; Harper, J.K.; Wu, W.; Wikramanayake, A.H.; Vanni, S.; et al. Carbon Nitride Dots: A Selective Bioimaging Nanomaterial. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakocak, B.B.; Laradji, A.; Primeau, T.; Berezin, M.Y.; Li, S.; Ravi, N. Hyaluronan-Conjugated Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Use. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Gao, J.; Cong, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Yao, J. Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Carbon Dots for Bioimaging. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Yan, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Su, W. Orange-red to NIR emissive carbon dots for antimicrobial, bioimaging and bacteria diagnosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, A.H.; Sofer, Z.; Bousa, D.; Ulbrich, P.; Bonanni, A.; Pumera, M. Carboxylic Carbon Quantum Dots as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for DNA Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, W.; Hao, A. Fluorescent carbon dots based sensing system for detection of enrofloxacin in water solutions. Spectroc. Acta Pt. A-Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2019, 219, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Chao, D.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L. Preparation and characterisation of dual sensing carbon dots for water and Cu2+ detection. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 198, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qin, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Hou, J. Bioinspired Carbon Dots as an Effective Fluorescent Sensing Platform for Tetracycline Detection and Bioimaging. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Huang, J.; Gao, W.; Lu, X.; Shi, X. Carbon Dots Fluorescence-Based Colorimetric Sensor for Sensitive Detection of Aluminum Ions with a Smartphone. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Kishore, S.C.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Vinodh, R.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Babu, R.S.; Alagan, M.; Lee, Y.R. Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots as a Potential Fluorescence Probe for Selective Sensing of Ferric Ions in Aqueous Solution. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.C.P.; Correia, A.S.; Duarte, D.; Brandão, A.T.S.C.; de Yuso, M.D.V.M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Vale, N.; Pereira, C.M.; Algarra, M.; Pinto Da Silva, L. An Active Surface Preservation Strategy for the Rational Development of Carbon Dots as pH-Responsive Fluorescent Nanosensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chang, H. Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe of Vesicle-like Carbon Dots and Gold Clusters for Quantitation of Cholesterol. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Review-Intracellular Sensors Based on Carbonaceous Nanomaterials: A Review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 37540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowley, C.; McHale, A.P.; McCaughan, B.; Fraix, A.; Sortino, S.; Callan, J.F. Carbon quantum dot-NO photoreleaser nanohybrids for two-photon phototherapy of hypoxic tumors. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, R.; Singh, R.; Marappan, G.; Kushwaha, G.; Gupta, N.; Meena, R.; Gupta, J.P.; Agarwal, R.R.; Fahmi, N.; Kushwaha, O.S. Fluorescent carbon dots driven from ayurvedic medicinal plants for cancer cell imaging and phototherapy. Heliyon 2019, 5, e2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, T.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S. Carbon Dots with Absorption Red-Shifting for Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Tumor Tissue pH and Synergistic Phototherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35365–35375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, R.; Liang, L.; Teng, P.; Zheng, H. Hollow luminescent carbon dots for drug delivery. Carbon 2013, 59, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.K.; Wongso, V.; Sambudi, N.S.; Isnaeni. Biowaste-derived carbon dots/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite as drug delivery vehicle for acetaminophen. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 93, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Guo, R.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L. Red-Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots for Nuclear Drug Delivery in Cancer Stem Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, R.; Liang, X.; Xiang, W. Intense enhancement of yellow luminescent carbon dots coupled with gold nanoparticles toward white LED. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 140, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X. Preparation of N-doped carbon dots based on starch and their application in white LED. Opt. Mater. 2018, 86, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. High-efficient, spherical and thermal-stable carbon dots@silica fluorescent composite as rare earth-free phosphors for white LED. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 14706–14712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailotto, S.; Mazzaro, R.; Enrichi, F.; Vomiero, A.; Selva, M.; Cattaruzza, E.; Cristofori, D.; Amadio, E.; Perosa, A. Design of Carbon Dots for Metal-free Photoredox Catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 40560–40567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, G.A.M.; Reuillard, B.; Martindale, B.C.M.; Caputo, C.A.; Lockwood, C.W.J.; Butt, J.N.; Reisner, E. Carbon Dots as Versatile Photosensitizers for Solar-Driven Catalysis with Redox Enzymes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16722–16730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahato, D.; Kharwar, Y.P.; Ramanujam, K.; Haridoss, P.; Thomas, T. S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots decorated TiO2 and supported with carbon for oxygen reduction reaction catalysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 21549–21565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafranko, S.; Goman, D.; Stanković, A.; Medvidović-Kosanović, M.; Moslavac, T.; Jerković, I.; Jokić, S. An Overview of the Recent Developments in Carbon Quantum Dots-Promising Nanomaterials for Metal Ion Detection and (Bio)Molecule Sensing. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, G.L.; Bartoli, M.; Giorcelli, M.; Rovere, M.; Tagliaferro, A. A Review on the Use of Biochar Derived Carbon Quantum Dots Production for Sensing Applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots and Their Applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2019, 2, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Vinodh, R.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Babu, R.S.; Lee, Y.R. Leftover Kiwi Fruit Peel-Derived Carbon Dots as a Highly Selective Fluorescent Sensor for Detection of Ferric Ion. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Jiang, S.; Park, S.; Meng, L. A review: Recent advances in preparations and applications of heteroatom-doped carbon quantum dots. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 6915–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, L. Effects of elemental doping on the photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 91225–91232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Kuang, T.; Liu, Y.; Cai, L.; Peng, X.; Sreenivasan Sreeprasad, T.; Zhao, P.; Yu, Z.; Li, N. Heteroatom-doped carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization, properties, photoluminescence mechanism and biological applications. J. Mat. Chem. B 2016, 4, 724–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, D.; Xu, H. Non-Metal-Heteroatom-Doped Carbon Dots: Synthesis and Properties. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. J. Mat. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6553–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, T.; Sun, C.; Xia, J.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, H. Selenium-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Free-Radical Scavenging. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2017, 56, 9910–9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Ye, Q.; Huang, Z. Novel Synthesis of Slightly Fluorinated Graphene Quantum Dots with Luminescent and Paramagnetic Properties through Thermal Cutting of Fluorinated Graphene. Materials 2018, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Tang, B. Te-containing carbon dots for fluorescence imaging of superoxide anion in mice during acute strenuous exercise or emotional changes. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Ju, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gong, A.; Wu, C.; Du, F. Engineering iodine-doped carbon dots as dual-modal probes for fluorescence and X-ray CT imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6943–6953. [Google Scholar]
- John, V.L.; Nair, Y.; Vinod, T.P. Doping and Surface Modification of Carbon Quantum Dots for Enhanced Functionalities and Related Applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2021, 38, 2100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, R.; Shan, X.; Chen, Q.; Sun, G.; Liu, J. Facile Preparation of Double Rare Earth-Doped Carbon Dots for MRI/CT/FI Multimodal Imaging. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2544–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Yao, D.; Chen, J.; Yu, M.; Su, L. Detection of Hg2+ by a Dual-Fluorescence Ratio Probe Constructed with Rare-Earth-Element-Doped Cadmium Telluride Quantum Dots and Fluorescent Carbon Dots. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 10735–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Xu, L.; Dong, B.; Song, H. Facilely prepared carbon dots and rare earth ion doped hybrid composites for ratio-metric pH sensing and white-light emission. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61468–61472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Kuzmanoski, A.; Goessl, D.M.; Popescu, R.; Gerthsen, D.; Feldmann, C. Polyol-mediated C-dot formation showing efficient Tb3+/Eu3+ emission. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7503–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Qi, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Fan, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhuo, S.; Zhu, C. Fabrication of highly active phosphatase-like fluorescent cerium-doped carbon dots for in situ monitoring the hydrolysis of phosphate diesters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41551–41559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhai, X.; Ma, T.; Huang, Y.; Yan, C.; Du, Y. Multifunctional cerium doped carbon dots nanoplatform and its applications for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Xiao, L.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Ju, H.; Sun, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Z.; Du, F. Fabrication of cerium doped carbon dots with highly radical scavenging activity alleviates ferroptosis-induced oxidative damage. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 395605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, L.; Gu, W. Microwave-assisted polyol synthesis of gadolinium-doped green luminescent carbon dots as a bimodal nanoprobe. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10933–10939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Zheng, X.; Chen, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P. A Magnetofluorescent Carbon Dot Assembly as an Acidic H2O2-Driven Oxygenerator to Regulate Tumor Hypoxia for Simultaneous Bimodal Imaging and Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, H.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Chromium(III)-doped carbon dots: Fluorometric detection of p-nitrophenol via inner filter effect quenching. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qin, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Manganese oxide doped carbon dots for temperature-responsive biosensing and target bioimaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yin, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Constructing hollow graphene nano-spheres confined in porous amorphous carbon particles for achieving full X band microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 142, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for Multicolor Patterning, Sensors, and Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Minh, T.P.; Gul, A.R.; Thi, N.L.; Kim, M.W.; Kailasa, S.K.; Oh, K.T.; Park, T.J. One-pot synthesis of carbon dots with intrinsic folic acid for synergistic imaging-guided photothermal therapy of prostate cancer cells. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 5187–5196. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmi, M.Z.; Sholihah, N.F.; Wibrianto, A.; Sakti, S.C.W.; Firdaus, F.; Chang, J. Simple and fast design of folic acid-based carbon dots as theranostic agent and its drug release aspect. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 267, 124596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakier, Y.M.; Ghali, M.; Zahra, W.K. Highly sensitive fluorescent detection of pyridine using small size carbon quantum dots derived from folic acid. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 405103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Chiu, T. Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Selective and Sensitive Probes for Cupric Ions and Cell Imaging. Molecules 2019, 24, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G.; Tan, H.; Wu, K.; Song, F.; Mechler, A.K.; Schleker, P.P.M.; Lu, Q.; et al. Overall Oxygen Electrocatalysis on Nitrogen-Modified Carbon Catalysts: Identification of Active Sites and In Situ Observation of Reactive Intermediates. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2021, 60, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, D.R.; Overbury, S.H.; Huntley, D.R. Electron spectroscopy of single crystal and polycrystalline cerium oxide surfaces. Surf. Sci. 1998, 409, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.K.; Maity, A.R.; Nandi, S.; Stepensky, D.; Jelinek, R. Imaging Cancer Cells Expressing the Folate Receptor with Carbon Dots Produced from Folic Acid. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).