Abstract
Extensive research shows that there is a close correlation between a disease diagnostic and the patient’s exhale breath gas composition. It has been demonstrated, for example, that patients with a diabetes diagnosis have a certain level of acetone fume in their exhale breath. Actually, symptoms from many other diseases could be easily diagnosed if appropriate and reliable gas sensing technologies are available. The COVID-19 pandemic has created demand for a cheap and quick screening tool for the disease, where breath biomarker screening could be a very promising approach. It has been shown that COVID-19 patients potentially present a simultaneous increase in ethanal (acetaldehyde) and acetone in their exhale breath. In this paper, we explore two different sensing approaches to detect ethanal/acetone, namely by colorimetric markers, which could for example be integrated into facemasks, and by a breathalyzer containing a functionalized quartz crystal microbalance. Both approaches can successfully detect the presence of a biomarker gas on a person’s breath and this could potentially revolutionize the future of healthcare in terms of non-invasive and early-stage detection of various diseases.
1. Introduction
1.1. Breath Analysis and Diseases
Breath biomarker screening has shown to be an efficient approach to achieve early indication prior to the diagnosis of a certain disease [1,2,3,4,5]. Since the discovery from Pauling that human breath contains hundreds of volatile organic compounds (VOC) [6] several studies and correlations between VOC presence in breath and diseases have been performed [7,8,9,10,11]. The range of diseases and metabolic disorders which can be detected via monitoring of VOCs in breath is very wide. Patients with breast cancer, for example, have the presence of formaldehyde in their breath, while patients with lung cancer exhale a significant number of alkanes [6].
For instance, the presence of isoprene in human breath is related to blood cholesterol levels, and patients with Type 1 diabetes have excess acetone in their breath [6]. Such knowledge suggests that breath analysis is useful for human disease diagnosis and/or metabolic status monitoring. The main challenges in the application of breath biomarkers for early diagnostics regards the low concentrations and large quantity of different compounds in exhaled breath. That requires sensing techniques with sufficient sensitivity and selectivity to the specific target gases. The gold standard for exhale breath analysis is gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). This method has a routine detection sensitivity of ppb to ppt and can analyze multiple compounds simultaneously and selectively; yet, GC-MS requires complicated procedures for sample collection and pre-concentration and also has high instrument costs [5,6,7,8].
1.2. Gas Sensing Techniques
Colorimetric sensing is a simple and cheap approach with demonstrated applications within the field of gas sensing [12,13]. Although its output is qualitative and therefore with limitations regarding gas levels quantification, techniques involving image recognition and application of artificial intelligence can be a useful tool in converting colorimetric sensing into a powerful tool for gas sensing [14,15]. Colorimetric sensors can be tuned to react only to specific gases, reaching desired selectivity. Therefore, colorimetric sensors are a good candidate for portable and cheap gas sensing solutions, including detection of breath biomarkers.
Another sensitive technique for gas sensing with perspectives for miniaturization and portable gas sensing solutions consists of piezoelectric resonators, including cantilevers, membranes and quartz crystals. Demonstrations of portable gas sensing solutions for selected targets have been demonstrated [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24], and selectivity can be achieved by applying a selective binder to the surface of the piezoelectric resonator. When the target molecules bind to the sensor surface, changes in mass can be measured as changes in the resonance frequency/impedance of the sensor. Other methods which could achieve the same sensitivity and be used as sensing platforms are optical methods such as spectroscopy or plasmonic sensing, piezoresistive transducers or electrochemical sensors. In this paper we have investigated piezoelectric resonators due to the group’s expertise within this field.
1.3. Selected Disease for Demonstration: COVID-19
The Corona virus (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic has affected the entire world, bringing unmeasurable health and economic problems, which puts humanity few steps back on fulfilling the UN sustainability goals. The world was clearly not prepared for epidemics, and therefore we have reached the global pandemic level. Several reports show that the virus was already present in Europe in the middle of 2019. If we were equipped with advanced pandemic monitoring systems, we might have identified the threat well in advance to handle it before it became a pandemic. This virus is not the first and will not be the last to cause a pandemic. Human history has witnessed many such pandemics in the past and the possibilities of new pandemics in the future due to the onset of new viruses having mutation and deadly infection capabilities cannot be ignored. The lesson learned from all this is that we need to invest in pandemic risk monitoring and prediction in order to take early measures to avoid such catastrophes.
Due to a great effort, vaccines against the new corona virus are becoming available for a growing number of people around the world. Unfortunately, along with the positive vaccine spread, new variants and mutations of the virus are emerging and will continue to emerge across the world. It is still unknown if the vaccines can cover the growing number of viral mutations, and therefore, better viral outbreak monitoring and continuous protective measures are in high demand.
When the world was caught by the COVID-19 pandemics, extensive lockdowns were implemented across the whole world. Though lockdown was the most efficient tool to control the viral spread, the consequences of this approach are still echoing in the socio-economic situation of the current world [25]. If a quick disease screen technique was available then, it could have been a very useful tool during the pandemic [26].
Several approaches for quick disease screening have been developed since then, most of them based on antigen tests [27]. A few studies mention the possibilities for ultra-fast screening [26,27,28] but the options considering breath biomarkers to identify COVID-19 are still quite limited [29]. In a recent study, the breath biomarker fingerprint of patients who tested negative and positive for COVID-19 was determined by gold standards (gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry), and a simultaneous increase in ethanal (acetaldehyde) and acetone was observed in the breath of infected patients [30]. There are still many reports of tentative breath VOC biomarkers for COVID-19, and in some of them, a decrease in breath-borne acetone is reported [31], indicating that further studies are necessary. We therefore study two biomarkers whose concentration variation (increase or decrease) is interesting as a baseline to demonstrate the approach. Upon new discoveries of relevant biomarkers, the method can be rapidly adapted to address these. Pathogens which are responsible for big pandemics cause certain infections in the affected persons. These infections lead to the production of certain specific volatile compounds on the infected person’s breath. A simple and cheap indication to which mask user might be infected could be a simple colorimetric sensor which is sensitive to specific materials. In a second phase, an online real-time breath monitor integrated directly into protective clothing has the potential to be the key for achieving early alerts and the prevention of pandemics. Here, special smart fabric integrated into clothing could identify if the user is carrying an infective disease by real-time monitoring the breath gas composition. The integrated sensors can send reliable electrical data to an artificial intelligence platform which will be able to instantaneously evaluate local viral outbreaks and send alarm signals to relevant persons.
1.4. Intelligent Healthcare Products
There are several intelligent healthcare products with integrated real-time sensing and instantaneous notification to the user, such as the smart incontinence product Abena Nova [32], which sends caretakers warnings when the products contain urine and should be replaced. The Japanese C-Face Mask aims to improve communication between persons wearing masks, while the Intelligent Mask Face prediction system was proposed in 2018 as a tool to identify biometric features, and Air+ commercializes masks with integrated ventilation systems [33].
Regarding facemasks which could notify the users if a virus has been in contact with the mask, there are alternative approaches, such as the one used by the Bioengineering group at Harvard and MIT, where a face mask which lights up when in contact with a virus has been demonstrated [34]. Another approach, from the University of California, makes use of a colorimetric sensor for gas biomarkers which indicate viral infection. If the user is suffering from a viral infection, the biomarker gases react with the mask, which changes color upon activation (mobile antibodies need to be released) [35]. Another approach consists of a fiber gas sensor-integrated smart face mask for room-temperature distinguishing of target gases. Flexible fiber gas sensors with carbon nanotubes and ZnO quantum dot-decorated sensing elements could be operated at room temperature to detect target gases with good sensitivity and recovery time. Such face masks have great potential applications on the Internet of Things and wearable electronics [36].
1.5. Our Approach
Our hypothesis is that by functionalizing sensing platforms with solutions that are sensitive to ethanal and acetone, one can quickly detect these biomarkers in a person’s breath. This would offer an indication of a potential infection, and the patient could then conduct a viral specific test to confirm or disregard the indication. The scope of this paper is to demonstrate sensing platforms to screen potential infections by detection of breath biomarkers. Ethanal and acetone are the chosen gases due to reports from an independent study from breath biomarkers experts for COVID-19 patients. If other potential biomarkers should be reported to present higher sensitivity, the flexibility of the proposed methods could rapidly address the new biomarkers.
In this study we explore two methods which upon confirmation of breath biomarkers for COVID-19, will potentially allow for cheap and fast COVID-19 disease screening using the method described in the hypothesis. The first one makes use of ethanal and acetone sensitive colorimetric solutions, which change color when exposed to the gases. We have demonstrated how the solutions could be integrated into facemasks, and in that case could offer a color change indication to the facemask user of a potential infection. The second method makes use of resonant quartz crystal microbalance sensors which are functionalized with an ethanal binding solution. The sensors, electronics and mechanical design are integrated into a breathalyzer which resembles a routine driving alcohol test. The solutions have been tested by observing a clear color change when exposed to the breath of COVID-19 patients (n = 3), while the color change was absent when exposed to persons who tested negative to COVID-19 (n = 5).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gas Biomarker Sensitive Solutions Preparation
Ethanal-sensitive colorimetric solutions were prepared by dissolving Methyl Red (0.8 g), Methyl Red sodium salt (0.7 g), and NaOH (4.75 g) in a mixed solvent (methanol (10 mL): water (10 mL)) [12].
Acetone-sensitive colorimetric solutions were prepared by dissolving 100 mg of hydroxylamine sulfate and 2 mg of thymol blue in a solvent mixture containing methanol, water, and glycerol (volume ratio of 6.5:3:0.5) [13].
Ethanal-sensitive molecular binding solutions were prepared by dissolving 1.2 mM Methyl Red (0.12 g), 1.2 mM Methyl Red sodium salt (0.13 g), and 8 mM NaOH (0.1 g) in a mixed solvent (methanol (250 mL): water (250 mL)).
2.2. Application to Surgical Facemasks
The solutions were drop-casted on medical surgical masks and left to dry under the fume-hood for 2 h. The color change intensity study was performed by exposing the facemasks to a chamber with an ethanal atmosphere (created by the presence of ripe bananas) or acetone atmosphere (created by the presence of a Becker with acetone). The selectivity study was performed by exposing the facemasks to ethanol, water vapor, ethanal and acetone. The color change was quantified by making use of a color recognition algorithm using the Hue color appearance parameter. The Hue value (H) can be calculated by extracting RGB (Red-Green-Blue) measurements from the image and applying it to the following equation [14]:
Hue values are defined as the corresponding angle of location of a certain color within the Hue spectrum and can be visualized in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The values vary from 0 to 360, where both values correspond to a red color.
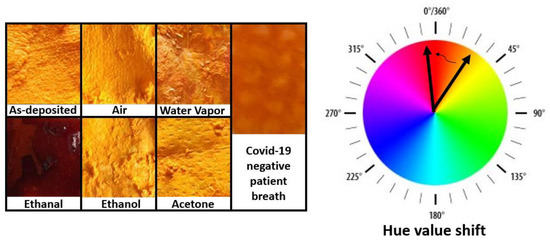
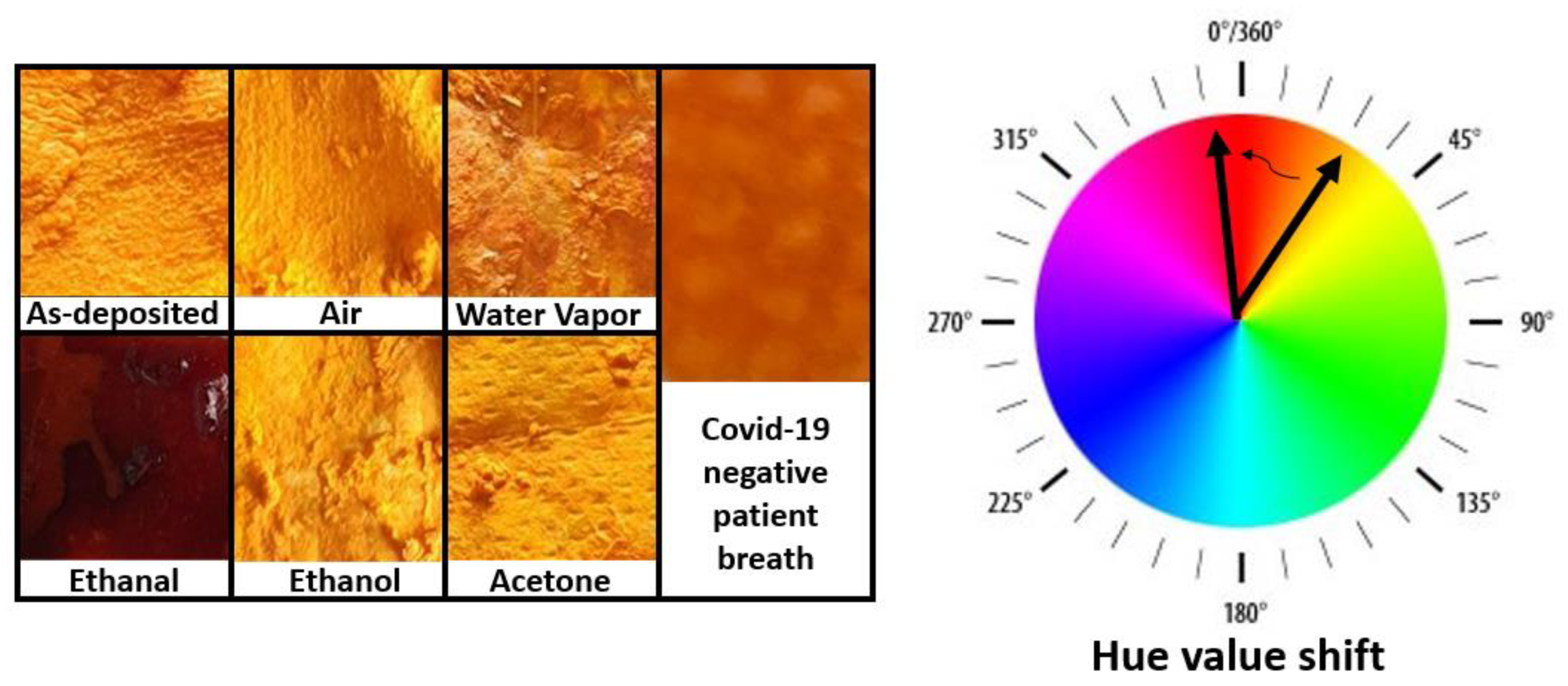
Figure 1.
Images of facemask fabrics covered with ethanal-sensitive colorimetric solutions. The masks were exposed to several gases for 8 h. A clear change in color is exclusively observed upon exposition to ethanal.
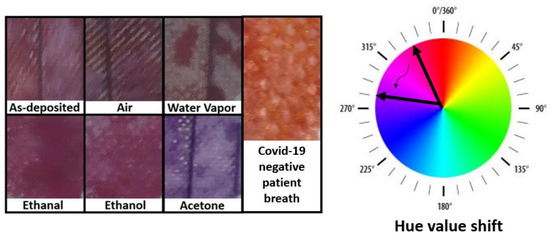
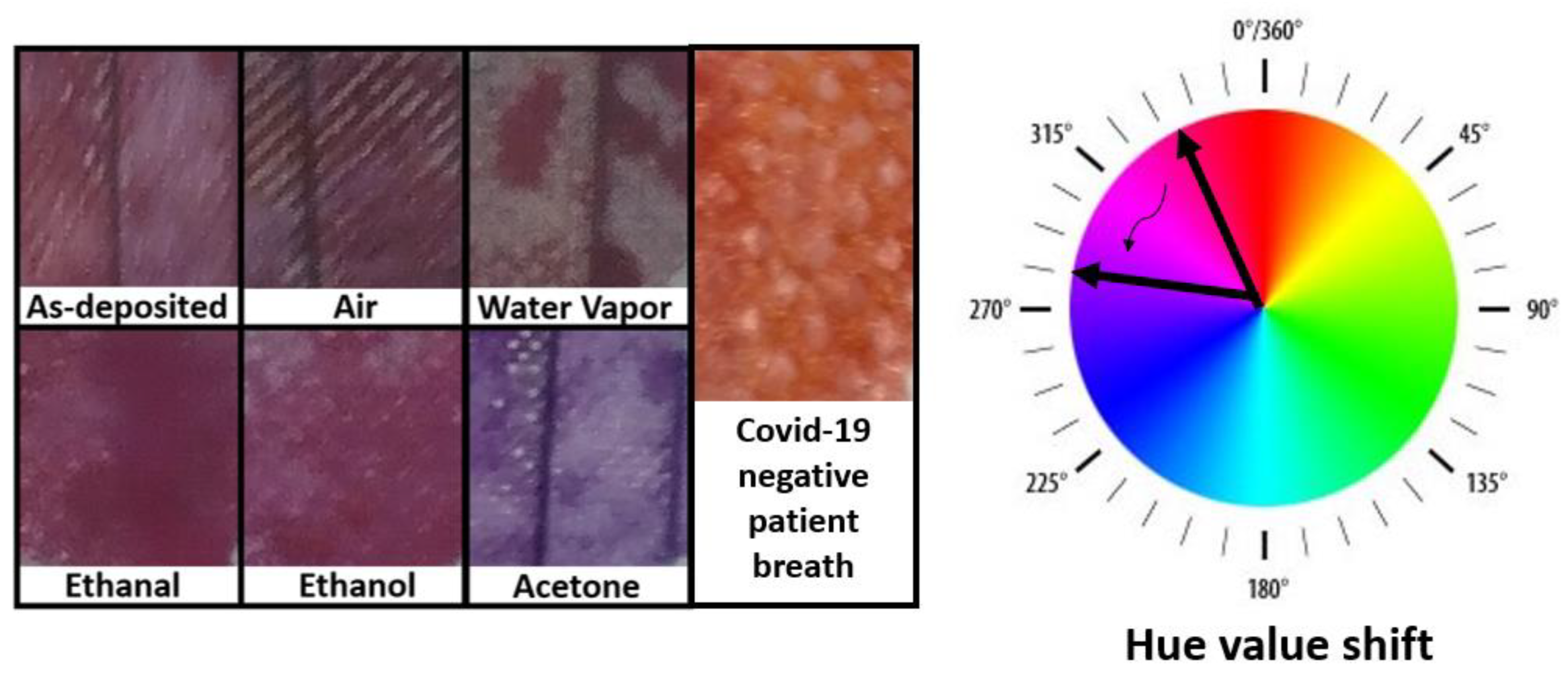
Figure 2.
Images of facemask fabrics covered with acetone-sensitive colorimetric solutions. The masks were exposed to several gases for 8 h. A clear change in color is exclusively observed upon exposition to acetone.
Furthermore, plastic bags with pieces of facemasks containing dots of the colorimetric ethanal-sensitive solutions were delivered to 3 COVID-19 positive patients (2 female and 1 male, ages 32, 28, and 38 years old) and to 5 COVID-19 negative patients (2 female and 3 male, ages 37, 38, 43, 3, and 7 years old). All patients blew into the bag, creating a person’s exhale breath atmosphere in the bag. The color change of the dotted facemasks over time were carefully recorded by multiple photographs.
2.3. Breathalyzer
Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensors with a resonance frequency of 3 MHz were purchased from QCM sensors. The sensors consist of a 14 mm diameter quartz crystal with optically polished surfaces. They have wrap around electrode geometry for one-side contacting. The electrodes are made of 5 nm Ti + 100 nm Au.
Following, the ethanal-sensitive colorimetric solutions (prepared as described above) were drop-cased on the quartz membranes. An investigation of several solutions leads to a uniform film with about 700 nm thickness. The resonance frequency shifts were measured by the indigenously developed electronics interface developed. The frequency sweep was created by the waveform generator AD5932. This waveform generator has been selected since it outputs each frequency in the range of interest for a defined length of time and then steps to the next frequency in the scan range. The length of time the device outputs a particular frequency is preprogrammed, and the device increments the frequency automatically. The frequency scan profile is initiated, started, and executed by toggling the CTRL pin. The most appealing features were the frequency range up to 25 Mhz, single pin control, power supply range from 2.3 V to 5.5 V and low power solution consuming only 6.7 mA. The whole system was controlled by a programmable Teensy 4.1 microcontroller, which can read and save the frequency peaks in a memory card. If a frequency peak shift exceeds 50 Hz, a signal turns on a red LED indicator, which indicates the presence of ethanal gas.
Resonance frequencies, impedance and phase shifts were measured with a calibrating desktop impedance analyzer upon exposure to ethanal atmosphere. The atmosphere was created by exposing the coated sensors to the atmosphere in a box with ripe bananas, which are a natural source of ethanal. The ethanal molecules bind to the functional layer on the sensor, leading to an increase in mass on the piezoelectric resonator. The change in mass reflects a change in resonance frequency, impedance, and phase, which can be measured via the developed breathalyzer and outputted to the user via LED indicators.
Ethanal is a gas compound which is also present in healthy persons’ breath (25 ± 17 ppb) [37]. However, recent studies [30] indicate that there is a significant increase in ethanal on the breath of persons with a COVID-19 infection. Therefore, our sensor should detect down to 1 ppm concentrations of ethanal, which can be simulated by exposure to 100 g of bananas [38]. A clear change in the electronic parameters can be observed and the signal is processed and sent to the output indicator LED which turns red in the presence of ethanal gas.
The mechanical design accommodates the sensors and electronics necessary for operation. The prototype was 3D printed, checked, and validated carefully.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solutions Reactivity and Selectivity
Figure 1 contains images of fabric surfaces upon drop-casting with ethanal-sensitive colorimetric solutions. As it can be seen from the image, the as-deposited fabric presents an intense orange color (Hue 38). The fabric pieces were exposed to ambient air, acetone, ethanol, and to a healthy person´s breath, and did not present significant color changes within 8 h (Hue ambient air 31, Hue Acetone 36, Hue Ethanol 33). The samples exposed to water vapor or healthy person´s breath presented a slightly darker orange color (Hue water vapor 32, Hue breath 29), but the samples exposed to ethanal vapors presented a significant change towards a brown color (Hue 356).
These results indicate a good selectivity of the solution to ethanal gas. The exposure to the breath of a healthy person also serves as a reference since the breath will contain all regular fingerprints of relevant gases which could influence the measurement, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen. It also demonstrated the solution application to facemask fabrics by simple drop-casting methods.
The next step was to repeat the experiments with the acetone-sensitive solution. Figure 2 illustrates how the color changes for fabrics coated with the solution. In this case, the samples exposed to control gases present a Hue value around 330, which is shifted to around 270 upon exposure to acetone fumes. The exposure to a healthy person´s breath also promoted a color change to a Hue value around 10, indicating that the solution reacts also with other gases on a person´s breath.
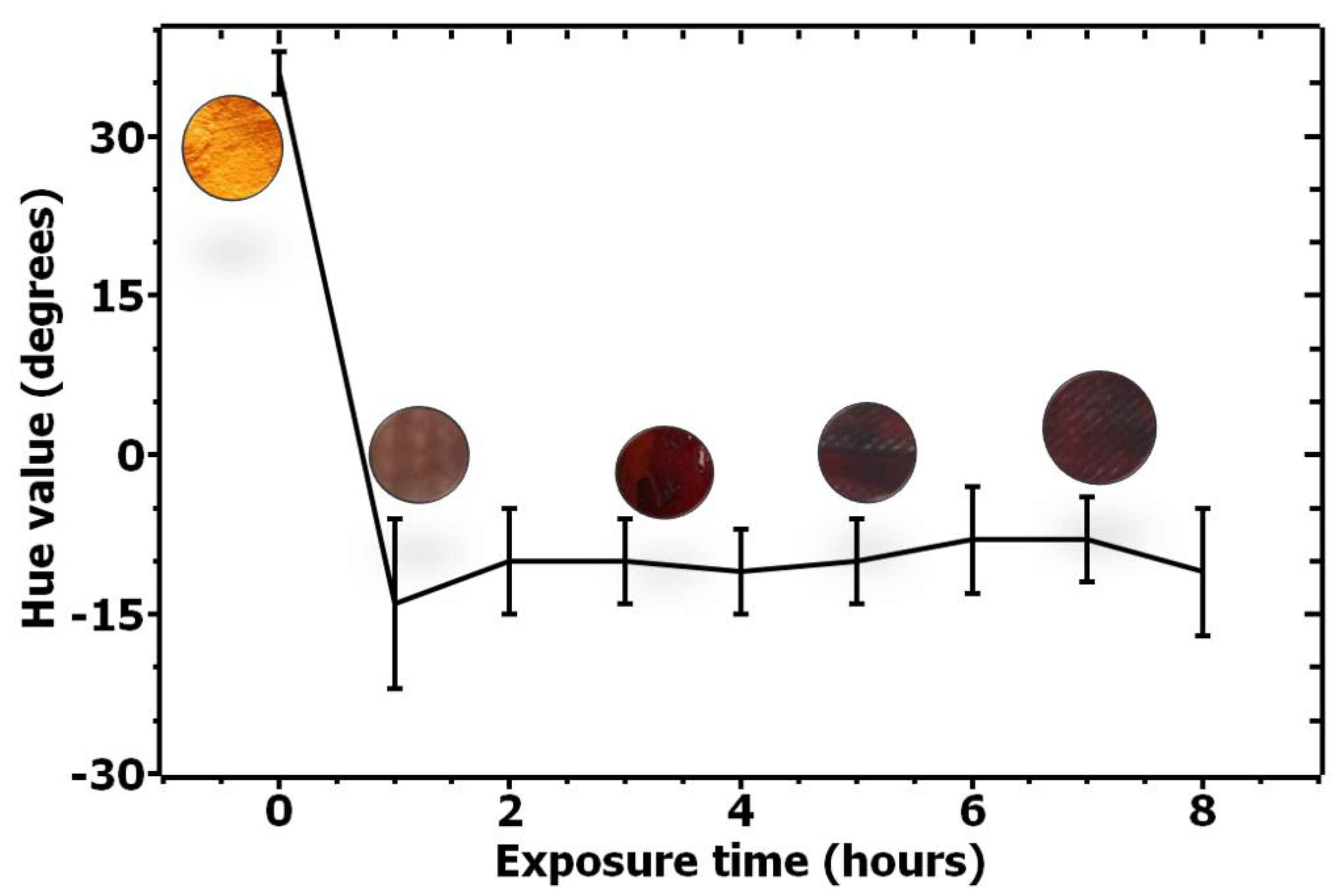
Based on the satisfactory results for solutions reactivity and selectivity, a systematic and quantitative recording of the color change over time was performed. Figure 3 quantifies the color change for the ethanal-sensitive solution over time by monitoring the changes on the Hue value over time for six samples. As can be seen from the image, a significant change on the H value occurs over time, quantifying the color change.
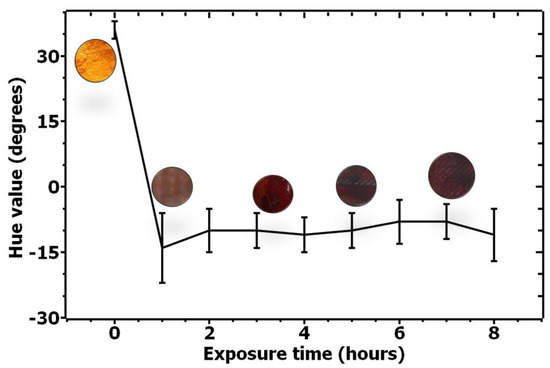
Figure 3.
Quantification of color change for ethanal-sensitive solution upon exposure to ethanal from 0 to 8 h.
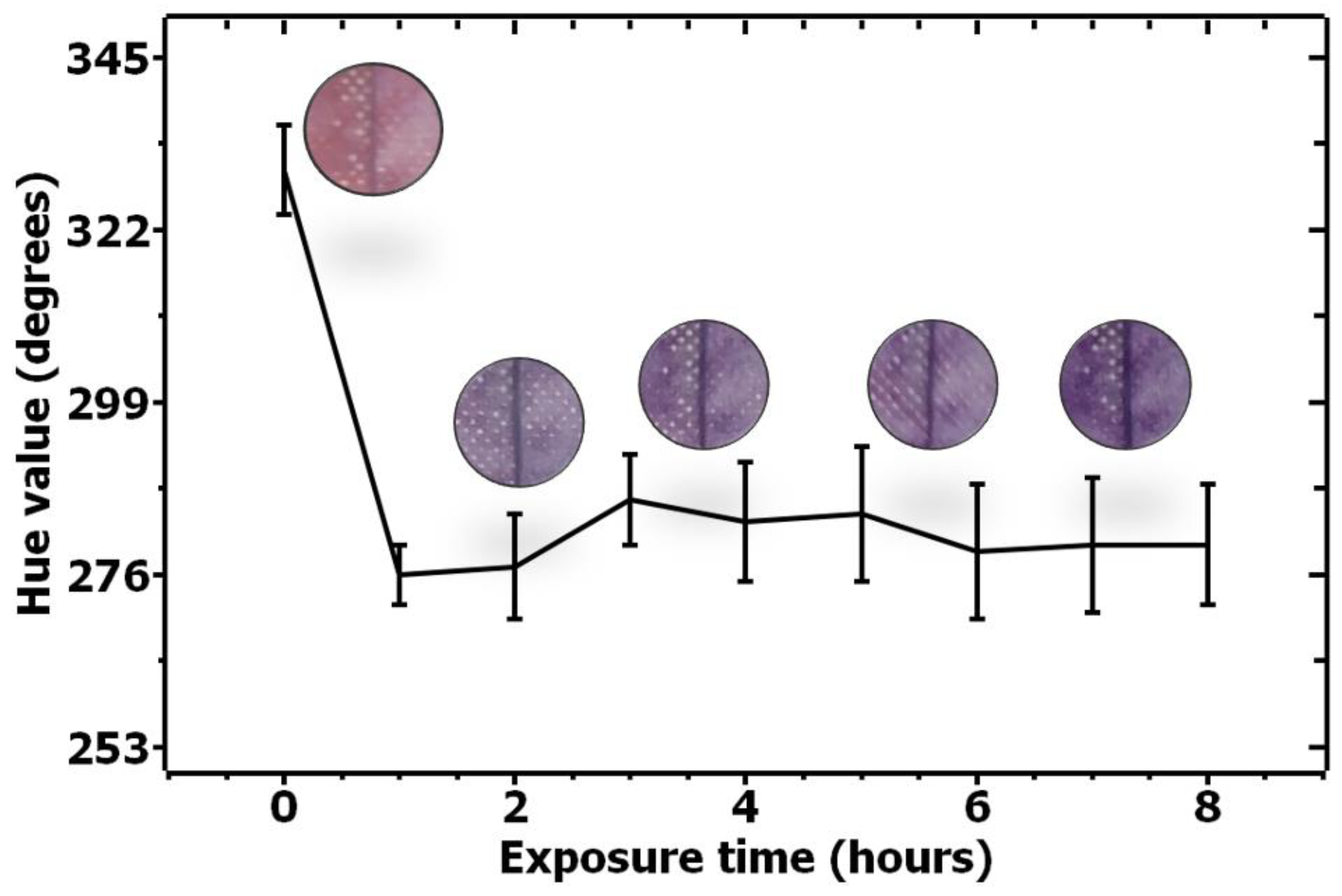
In order to evaluate the color change for the acetone-sensitive solution, a similar quantification experiment was performed, and the results are shown in Figure 4.
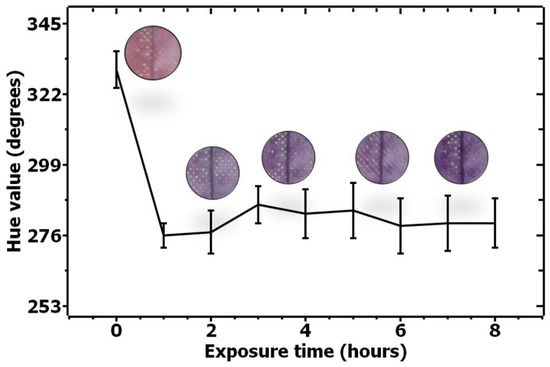
Figure 4.
Quantification of color change for acetone-sensitive solution upon exposure to acetone from 0–8 h.
3.2. COVID-19 Patients Breath Exposure
In order to explore the possibility of integration of colorimetric markers on facemasks for indication of COVID-19 infection, solution coated masks were delivered to persons who tested positive to COVID-19. The persons were asked to blow into a plastic bag containing the mask fabric and to register the color change over time. Control experiments with persons who tested negative to COVID-19 were also performed with an identical method. Figure 5 illustrates how the ethanal-sensitive solution reacted with the positive and negative breath exposure. A clear change of color towards dark brown is observed for patients who tested positive. A color change is also observed when reacting to the breath of negative-tested patients; however, the color change is not as intense as the results of the positive persons. This reflects the color change observed upon exposure to water vapor in Figure 1. Further investigation on the limit of detection of this method needs to be conducted, by determining the actual ethanal concentration versus color change, but these results are a qualitative indication of the applicability of the method.
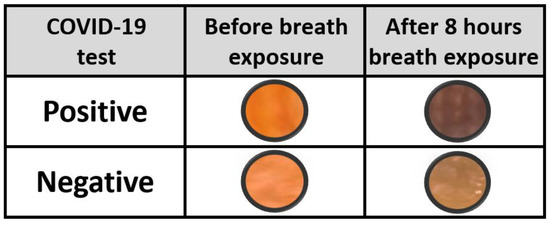
Figure 5.
Ethanal-sensitive solution color change reactivity upon exposition to COVID-19 negative and positive tested persons’ breath.
3.3. Technological Outlook: Facemasks with Infection Indicators
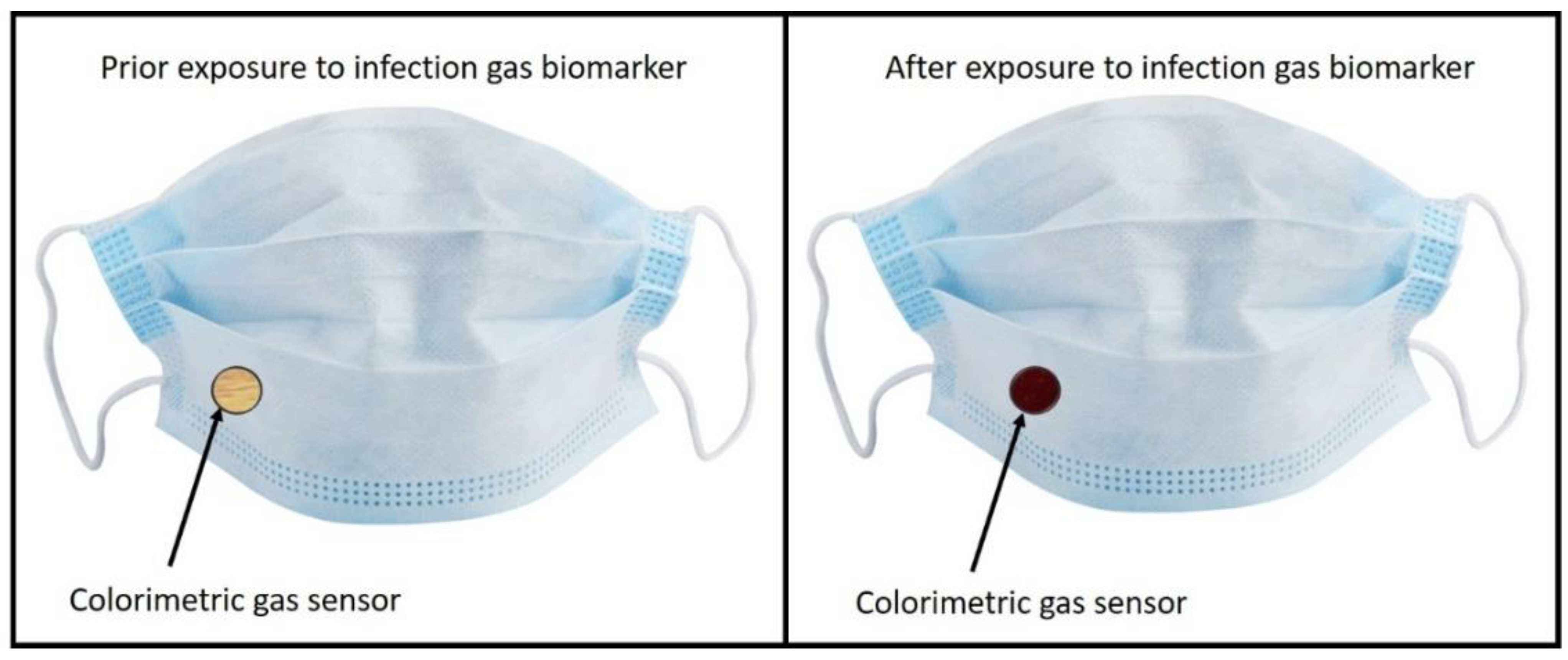
Colorimetric sensing is a cheap and fast sensing method, and the demonstration of a method to detect breath biomarkers in COVID-19 patients have been explored. Future applications of this technology could be the implementation of these colorimetric markers into healthcare facemasks, as shown in Figure 6.
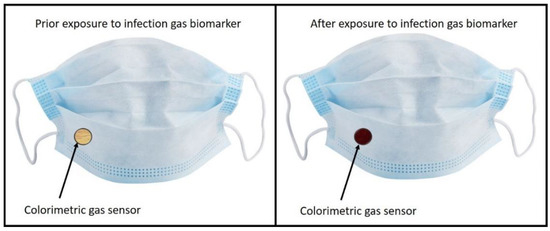
Figure 6.
Example of potential technological outlook for the explored sensing method.
3.4. Technological Outlook: Breathalyzer
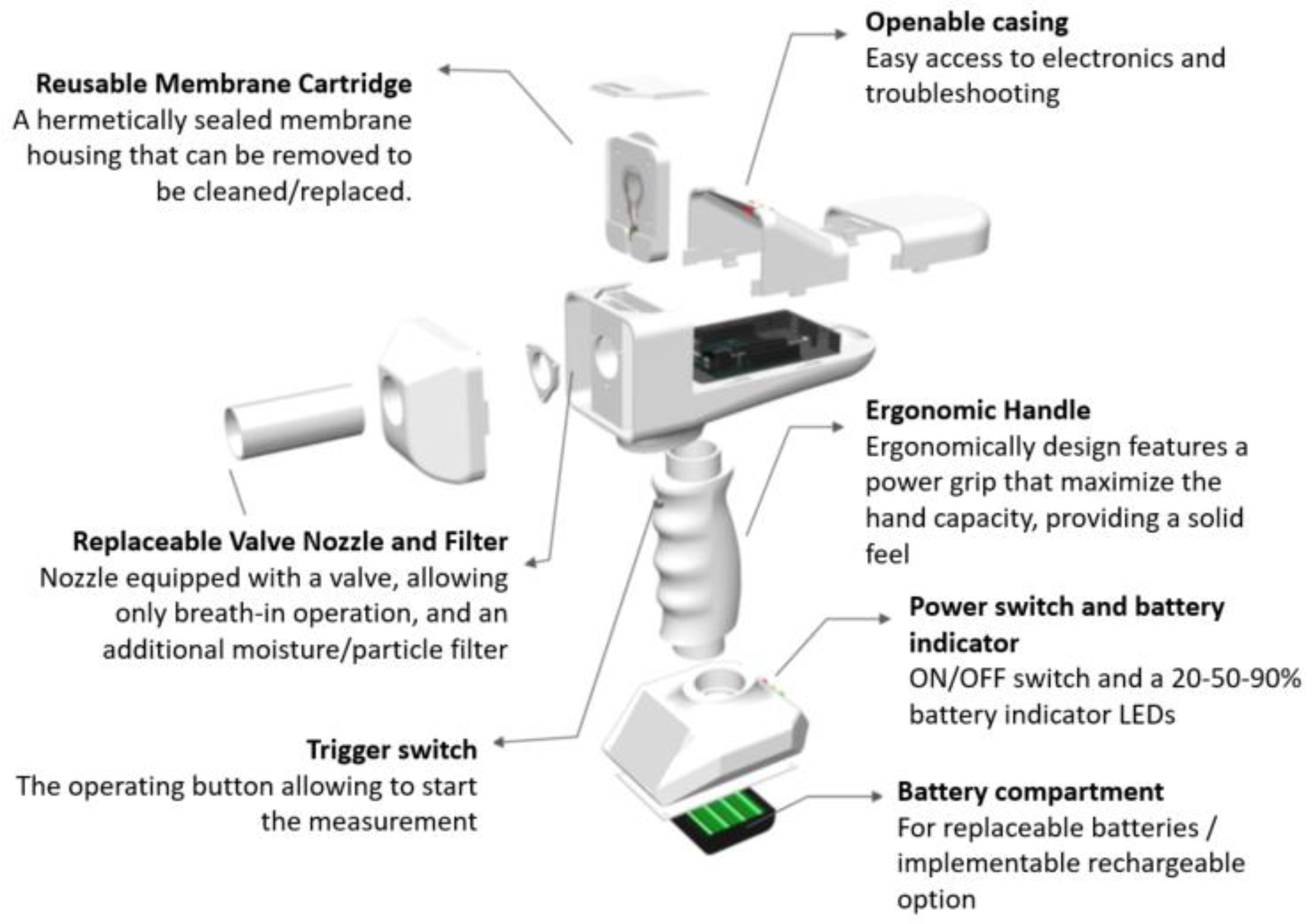
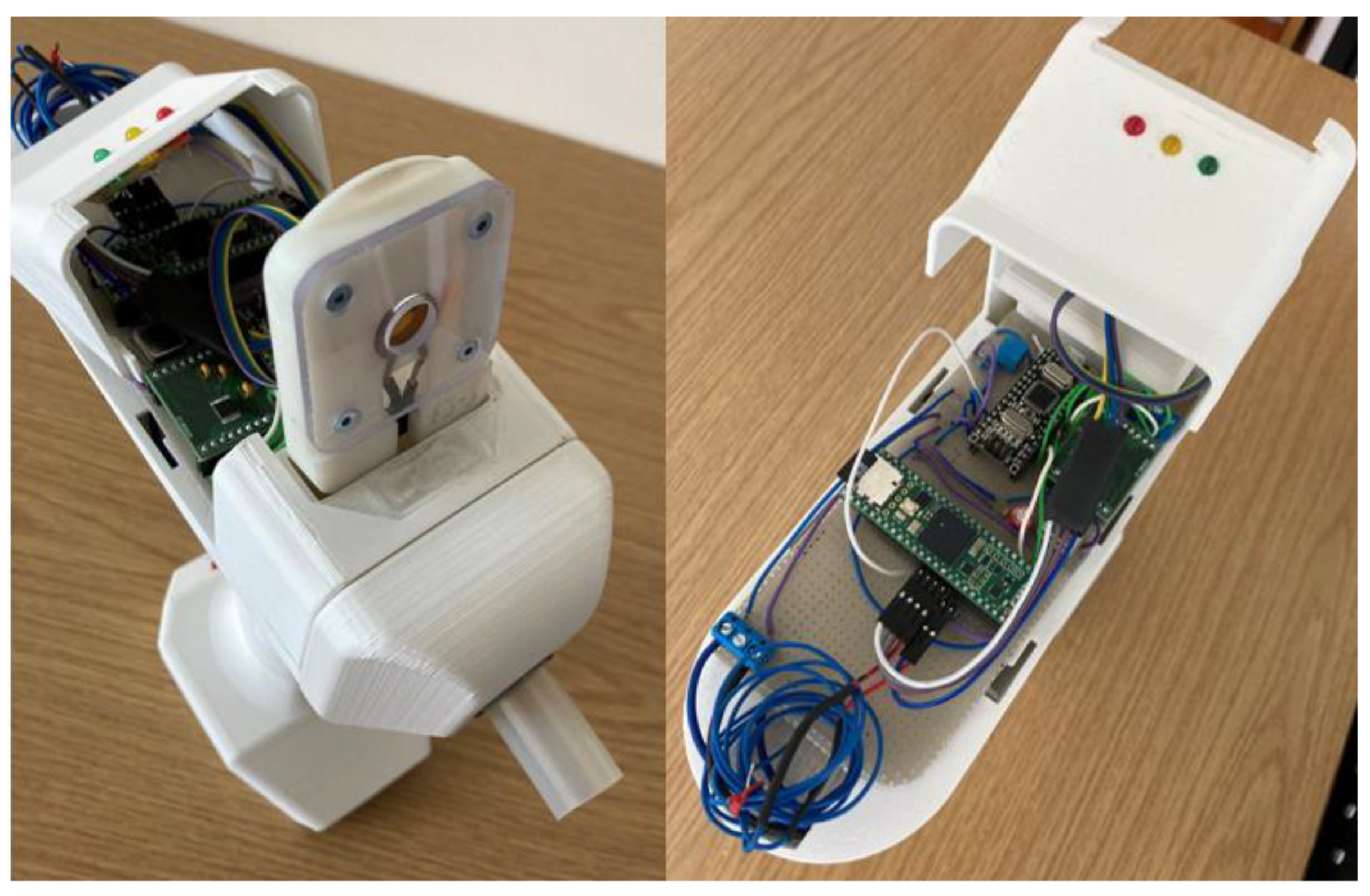
A breathalyzer is a device for estimating blood alcohol content or to detect viruses or diseases from a breath sample. Working principles of commercial breathalyzers are mostly based on electrochemical reactions [15]. We have demonstrated the application of ethanal sensing in breath by developing a breathalyzer device containing a quartz crystal microbalance as sensing element, as illustrated in Figure 7. The device was designed and built in house.
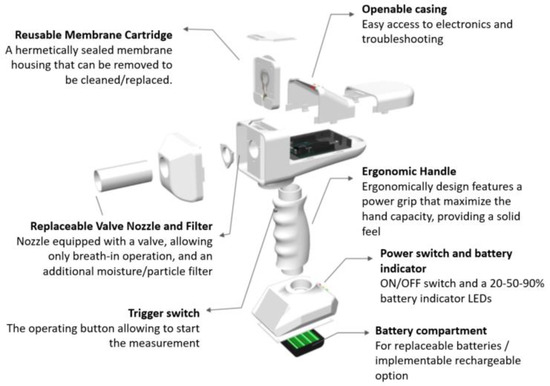
Figure 7.
Overview of the breathalyzer prototype with sensing elements, electronics, microprocessor and mechanical casing.
A person is subjected to quick potential COVID-19 screening by blowing into the device in a similar method as the blood alcohol test content in the replaceable valve nozzle. The sensing element is mounted on a reusable membrane cartridge and coated with a slightly modified ethanal-sensitive solution as described in the methodology section. The sensing element is connected to signal collection and processing by customized electronics and microprocessing.
Upon binding of ethanal to the sensing element, a clear shift in resonance frequency, impedance and phase can be measured by the processing unit and the signal is displayed via a green or red LED indication, where a red indication stands for ethanal content detection on the breath—and potential COVID-19 infection.
3.5. Microscopic Investigation of Coated Sensing Element upon Ethanal Exposition
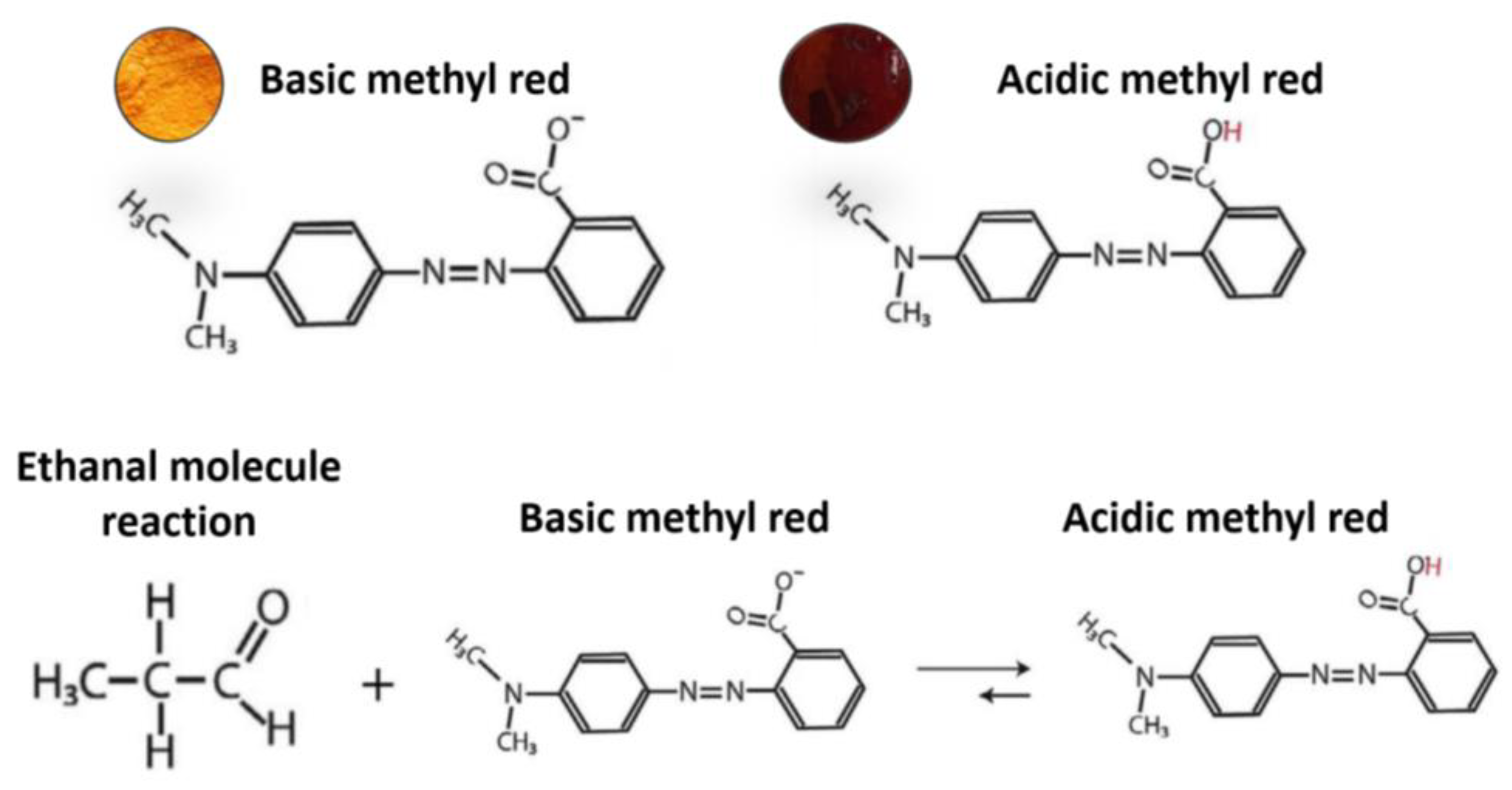
In order to achieve proper ethanal binding and sensitivity, the ethanal-sensitive solution has been modified from the previously color-sensitive solution. The ethanal molecules suffer a chemical reaction and when in contact with Methyl Red, decrease the substance’s PH. As Methyl Red is a colorimetric PH indicator, the solution color is strictly connected to its PH. The reaction is shown in Figure 8 and has been adapted from [12]. For the breathalyzer application, we are mostly interested on the molecular binding between the coated surface and the ethanal molecules. Therefore, a solution for ethanal-sensitive molecular binding was prepared as described in the methodology section. Figure 9 shows optical microscopy images of coated surfaces with the colorimetric and with the molecular binding solutions before and after exposure to ethanal gas.
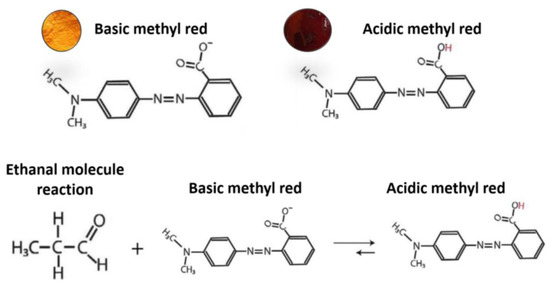
Figure 8.
Scheme illustrating the chemical reaction responsible for the color change (adapted from [23].
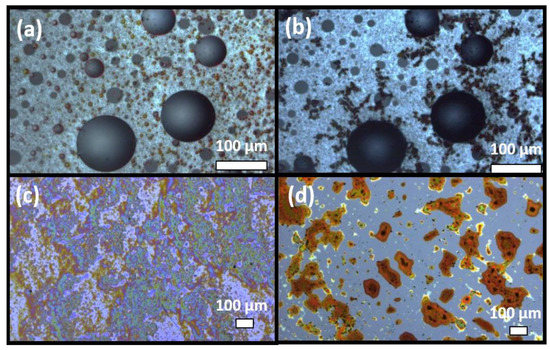
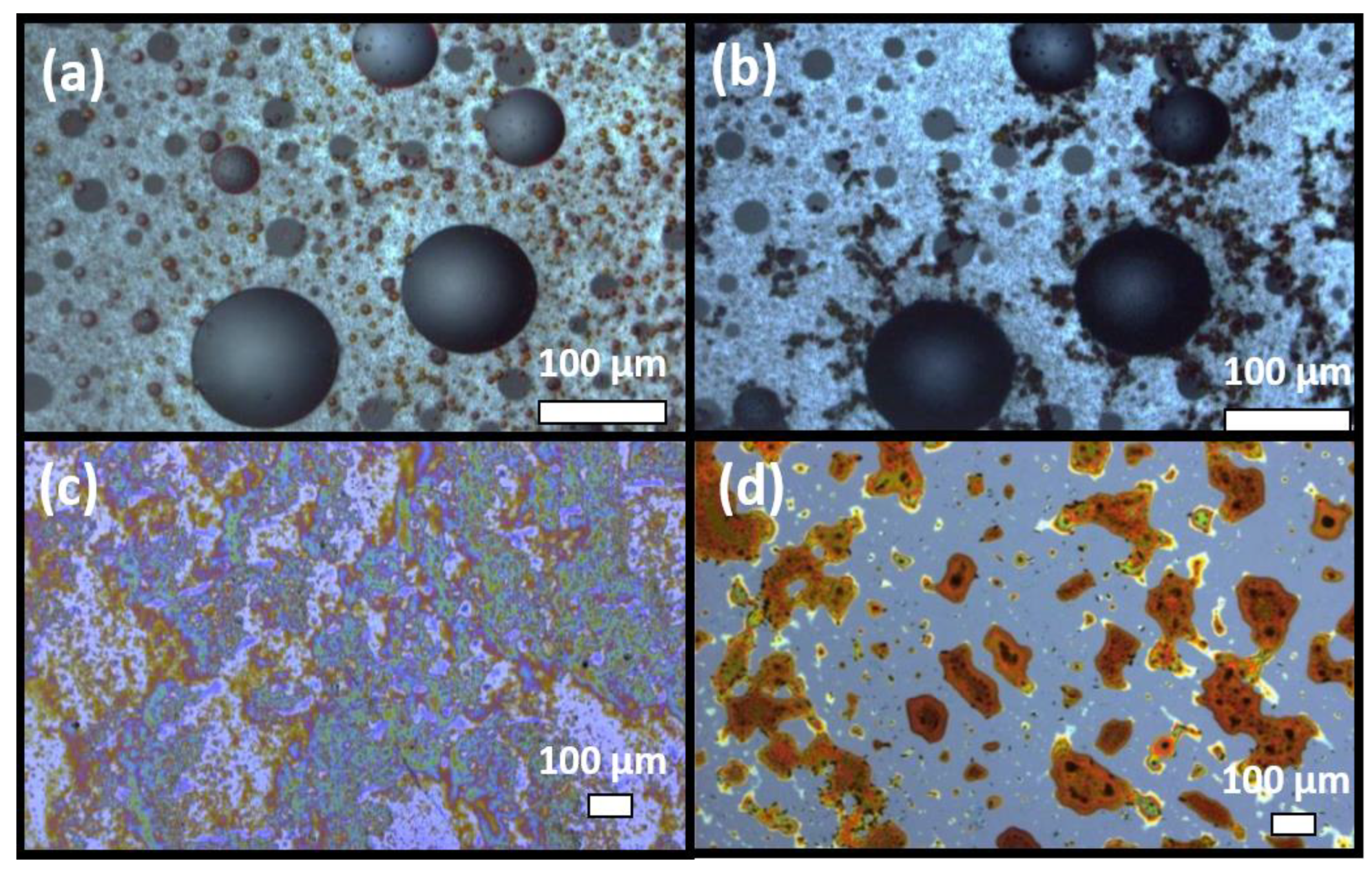
Figure 9.
Microscopic images of the colorimetric ethanal-sensitive solution before (a) and after (b) exposure to ethanal gas for 8 s and of the molecular-binding ethanal-sensitive solution before (c) and after (d) exposure to ethanal gas for 8 s.
As it can be observed from the images, both solutions present significant morphological changes upon ethanal exposure, demonstrating molecular binding. However, the molecular-binding tuned solutions (c) and (d) present a more significant change and better homogeneity which are more suitable for application in a sensing element whose response is based on added molecular weight.
3.6. Breathalyzer Electronic Response to Ethanal Exposition
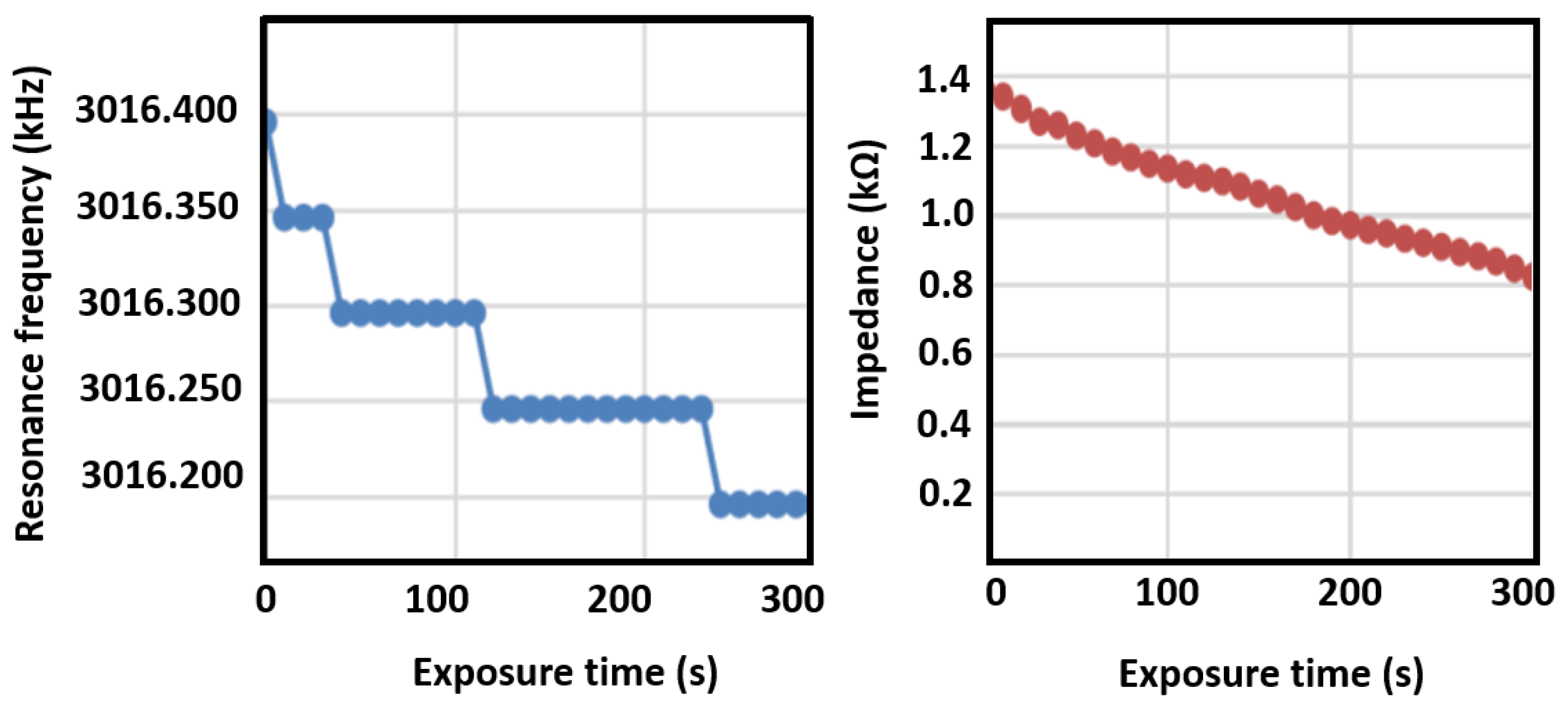
The resonance frequency shift and impedance shift of the sensing elements were measured as a function of exposure time to ethanal gas, as shown in Figure 10, which were obtained by connecting the sensor to an impedance analyzer. The membrane sensor is able to detect a 50 Hz shift when exposed to 1 ppm of ethanal, leading to a sensitivity of 0.02 ppm/Hz. The breath of a healthy person (negative to COVID-19) did not present any changes on resonance frequency. The moisture filter is an important feature to hinder reaction of the solution with moisture. Furthermore, non-functionalized sensors were exposed to ethanal, but did not present any changes in electrical response, demonstrating the response selectivity to ethanal.
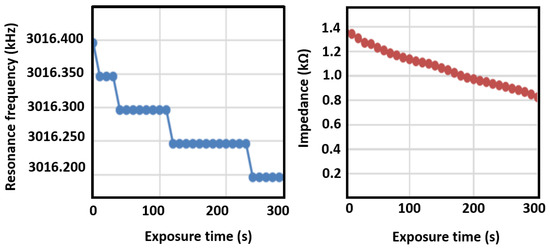
Figure 10.
Changes in quartz crystal microbalance resonance frequency and impedance upon exposure to ethanal.
As it can be seen from the data, a decrease in resonance frequency due to increased molecular weight is clearly observed, as well as a linear decrease in element impedance. The sensor was also exposed to water vapor and the shift was not observed in that case, indicating good sensor selectivity. The breathalyzer device’s electronics are programmed to read the frequency shift, and to turn on the red LED indicator upon a shift larger than 50 Hz. Additionally, by tuning the signal processing electronics, it is possible to detect the impedance shift after a few seconds of gas exposure, demonstrating the application of this method as a breathalyzer device. Figure 11 is a picture of the breathalyzer prototype, with the electronics, sensor cartridge, and LED indicators.
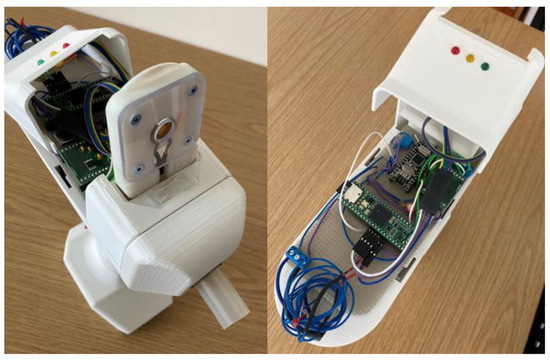
Figure 11.
Pictures of the breathalyzer device showing the removable sensor cartridge (left) and the reading electronics and LED indicators (right).
4. Conclusions
In summary, the scope of new gas sensing-based approaches toward non-invasive disease identifications have been presented. We have investigated solutions which are sensitive to breath biomarkers and could thus work as potential early-stage disease indicators; COVID-19 as an example, has been demonstrated here. The solutions were applied into two distinct sensing platforms and evaluated in terms of gas reactivity and selectivity. The obtained results are promising and offer a good approach for quick screening of diseases, such as cancer and COVID-19, and could be easily extended to many other diseases. The proposed breathalyzer-based sensing platform could be very helpful in early-stage diagnosis of various developing diseases, and thus could become an important future healthcare tool.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.d.O.H.; Data curation, R.d.O.H.; Formal analysis, Y.K.M. and R.d.O.H.; Funding acquisition, H.-G.R. and R.d.O.H.; Investigation, Z.-M.T. and A.F.B.; Methodology, Z.-M.T., A.F.B., K.K., C.G.M.G.d.T. and L.N.; Resources, H.-G.R. and R.d.O.H.; Supervision, L.N. and R.d.O.H.; Validation, L.N. and R.d.O.H.; Visualization, R.d.O.H.; Writing—original draft, R.d.O.H.; Writing—review and editing, Y.K.M. and H.-G.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Regional Development Fund Interreg Deutschland-Danmark under project number 096-1.1-18 (Access and Acceleration) and by a grant from the Fabrikant Mads Clausen Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Arune Lapinskaite, Boris Kacer, Cadence Andersen, Lucas Weber, Oskar Skoczylas, Richard Jenis, and Tobias Schult for developing and building the breathalyzer prototype.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cao, W.; Duan, Y. Breath analysis: Potential for clinical diagnosis and exposure assessment. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K.; Noeldge-Schomburg, G.F.E. Diagnostic potential of breath analysis—Focus on volatile organic compounds. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 347, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M. Breath tests in medicine. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Herrera, J.; Krishnan, S.; Zain, M.; Greenberg, J.; Cataneo, R.N. Variation in volatile organic compounds in the breath of normal humans. J. Chromatogr. B 1999, 729, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Chowdhury, B.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Magnussen, H.; Page, C.P.; Postma, D.; Saetta, M. Pulmonary biomarkers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sahay, P. Breath Analysis Using Laser Spectroscopic Techniques: Breath Biomarkers, Spectral Fingerprints, and Detection Limits. Sensors 2009, 9, 8230–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindicci, C.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Ito, M.; Elliott, M.W.; Hogg, J.C.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Nitric oxide synthase isoenzyme expression and activity in peripheral lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krisher, S.; Riley, A.; Mehta, K. Designing breathalyser technology for the developing world: How a single breath can fight the double disease burden. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2014, 38, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisco, F.; Aprea, E.; Lembo, V.; Fogliano, V.; Vitaglione, P.; Mazzone, G.; Cappellin, L.; Gasperi, F.; Masone, S.; De Palma, G.D.; et al. Rapid “breath-print” of liver cirrhosis by proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry. A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59658. [Google Scholar]
- Arasaradnam, R.P.; Covington, J.A.; Harmston, C.; Nwokolo, C.U. Review article: Next generation diagnostic modalities in gastroenterology--gas phase volatile compound biomarker detection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fens, N.; van der Schee, M.P.; Brinkman, P.; Sterk, P.J. Exhaled breath analysis by electronic nose in airways disease. Established issues and key questions. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Jin, S.Y.; Park, J.S. Non-destructive monitoring of apple ripeness using an aldehyde sensitive colorimetric sensor. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Prabhakar, A.; Qin, X.; Forzani, E.S.; Tao, N. Colorimetric Sensor for Online Accurate Detection of Breath Acetone. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebralidze, I.; Laschuck, N.; Poisson, J.; Zenkina, O. Colorimetric Sensors and Sensor Arrays. Nanomaterials Design for Sensing Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 978-0-12-814505-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bihar, E.; Deng, Y.; Miyake, T.; Saadaoui, M.; Malliaras, G.G.; Rolandi, M. A Disposable paper breathalyzer with an alcohol sensing organic electrochemical transistor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, A.; Dohn, S.; Keller, S.S.; Schmid, S.; Tenje, M. Cantilever-like micromechanical sensors. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2011, 74, 036101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preumont, A. Vibration Control of Active Structures: An Introduction; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, M.I. MEMS Linear and Nonlinear Statics and Dynamics; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Korsa, M.; Domingo, J.M.C.; Nsubuga, L.; Hvam, J.; Niekiel, F.; Lofink, F.; Rubahn, H.-G.; Adam, J.; de Oliveira Hansen, R. Optimizing piezoelectric cantilever design for electronic nose applications. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexi, N.; Hvam, J.; Lund, B.L.W.; Nsubuga, L.; Hansen, R.D.; Lofink, F.; Byrne, D.; Leisner, J. Cadaverine as a freshness indicator of microbial and Quality Index Method (QIM) quality of chilled Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares) steaks: The potential of novel biosensor technology for shelf life prediction. Food Control 2020, 125, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.B.; Grazhdan, D.; Fiutowski, J.; Nebling, E.; Blohm, L.; Lofink, F.; de Oliveira Hansen, R. Meat and fish freshness evaluation by functionalized cantilever-based biosensors. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 26, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sobolewska, E.K.; Fiutowski, J.; Rubahn, H.G.; de Oliveira Hansen, R.; Albers, J.; Hansen, R.D.O. Functionalizing micro-cantilevers for meat degradation measurements. In Proceedings of the 2016 Symposium on Design, Test, Integration and Packaging of MEMS and MOEMS, Budapest, Hungary, 30 May—2 June 2016; pp. 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Costa CA, B.; Sobolewska, E.K.; Fiutowski, J.; Brehm, R.; Albers, J.; de Oliveira Hansen, R. Micro-cantilevers for optical sensing of biogenic amines. Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 24, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamou, D.; Nsubuga, L.; Lisboa Marcondes, T.; Høegh, S.O.; Hvam, J.; Niekiel, F.; Lofink, F.; Rubahn, H.-G.; de Oliveira Hansen, R. Surface Modification Enabling Reproducible Cantilever Functionalization for Industrial Gas Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.F.; Ma, B.; Shahzad, L. A brief review of socio-economic and environmental impact of COVID-19. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, A.; Ranjan, P.; Sanghi, S.; Srivastava, A.; Khan, R. Point-of-Care Biosensor-Based Diagnosis of COVID-19 Holds Promise to Combat Current and Future Pandemics. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 11, 7326–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Bal, J.; Seo, S.K.; Chong, C.-K.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H. Development and Clinical Evaluation of an Immunochromatography-Based Rapid Antigen Test (GenBody™ COVAG025) for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Viruses 2021, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.; He, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, F.; Lai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; et al. A new and rapid approach for detecting COVID-19 based on S1 protein fragments. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhitano, Y.; Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Saviano, A.; Persiano, T.; Leo, M.; Piccioni, A.; Betti, M.; Maconi, A.; Pindinello, I.; et al. Single-Breath Counting Test Predicts Non-Invasive Respiratory Support Requirements in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruszkiewicz, D.M.; Sanders, D.; O’Brien, R.; Hempel, F.; Reed, M.J.; Riepe, A.C.; Bailie, K.; Brodrick, E.; Darnley, K.; Ellerkmann, R.; et al. Diagnosis of COVID-19 by analysis of breath with gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry—A feasibility study. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Yao, M. COVID-19 screening using breath-borne volatile organic compounds. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 047104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: www.abenanova.com (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Available online: www.donutrobotics.com/c-mask (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Nowrin, A.; Afroz, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Mahmud, I.; Cho, Y.-Z. Comprehensive Review on Facemask Detection Techniques in the Context of COVID-19. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 106839–106864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: www.medgadget.com/2021/01/face-mask-sensor-to-detect-covid-19.html (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Gao, Z.; Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Jiang, K.; Fu, Z.; Han, W.; Shen, G. Fiber gas sensor-integrated smart face mask for room-temperature distinguishing of target gases. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.; Spanel, P.; Smith, D. A longitudinal study of ethanol and acetaldehyde in the exhaled breath of healthy volunteers using selected-ion flow-tube mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebelacker, M.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Quantitative Determination of Acetaldehyde in Foods Using Automated Digestion with Simulated Gastric Fluid Followed by Headspace Gas Chromatography. J. Autom. Methods Manag. Chem. 2011, 2011, 907317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).