Femtosecond Direct Laser Writing of Silver Clusters in Phosphate Glasses for X-ray Spatially-Resolved Dosimetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Glass Sample
2.2. Infrared Femtosecond Direct Laser Writing (DLW) of Pristine Glasses
2.3. X-ray Irradiations of Pristine and Laser-Inscribed Glasses
2.4. Absorption Spectroscopy
2.5. Radio-Photoluminescence Micro-Spectroscopy
2.6. Micro-Absorption Spectroscopy
2.7. Phase Imaging Microscopy and Local Refractive Index Change Measurement
2.8. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study of Non-Inscribed Samples Exposed to X-rays
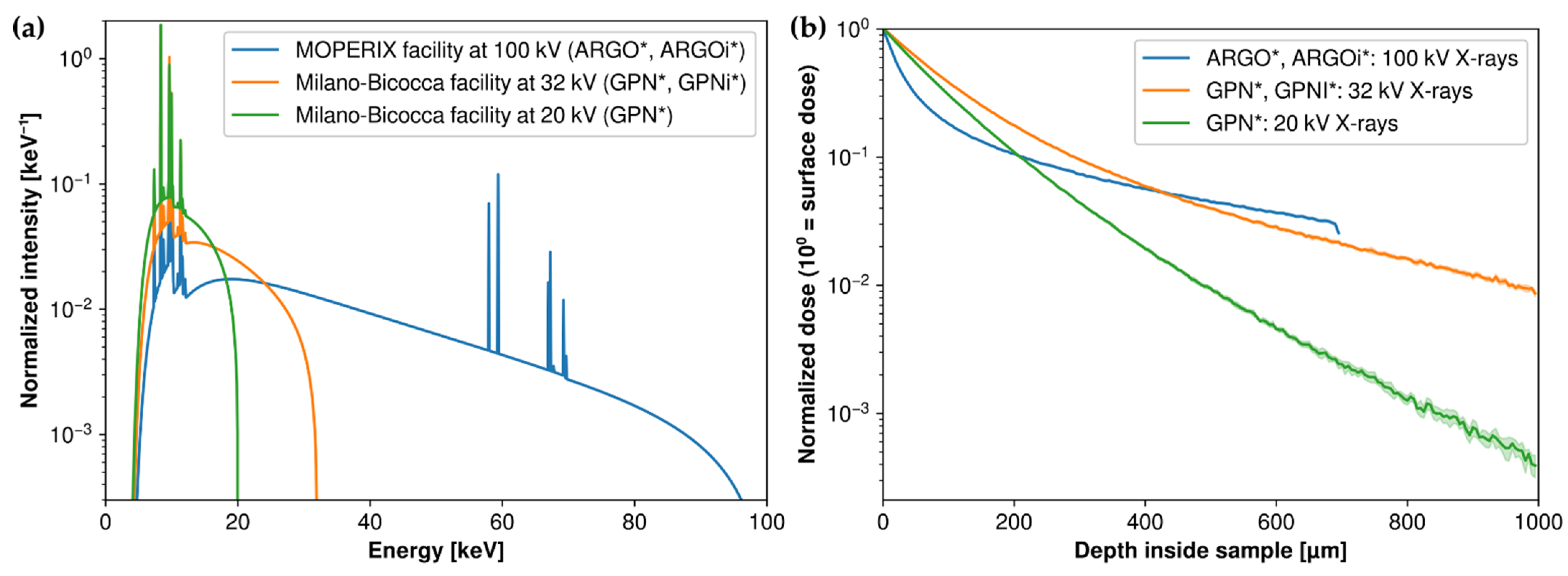
3.2. Simulation Model for Energy Spectrum and Depth-Deposited Dose
3.3. Study of Silver Clusters Inscribed by DLW Exposed to X-ray Irradiation
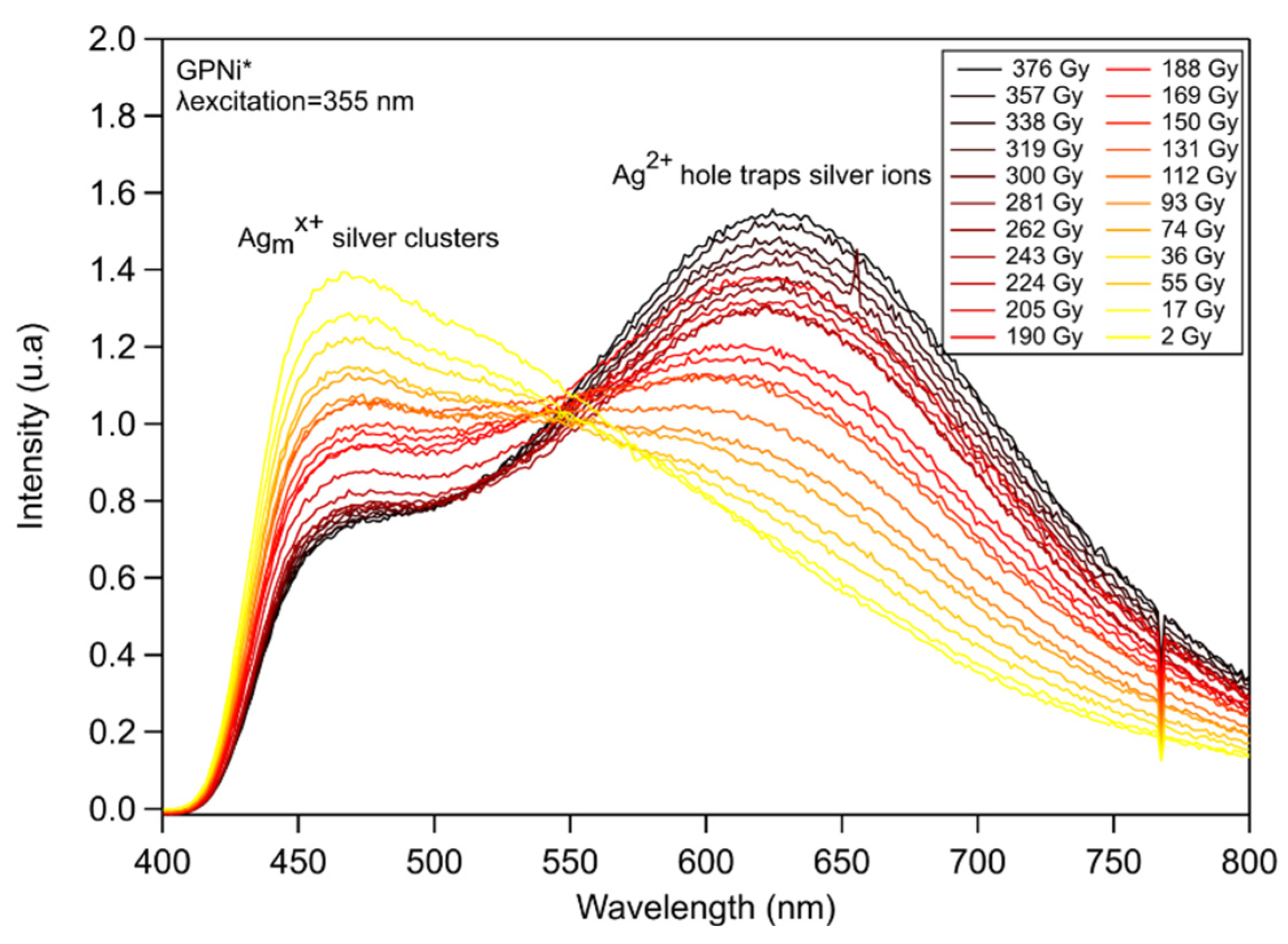
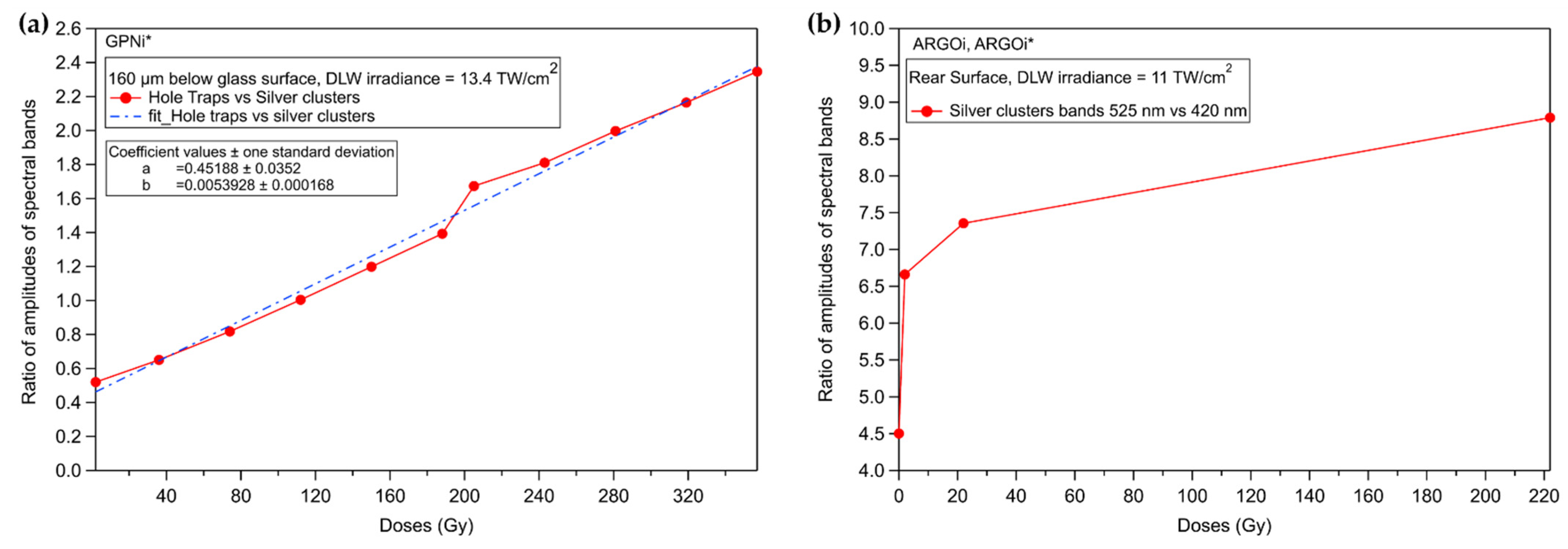
3.3.1. Silver Containing Sodo-Gallophosphate Glass (GPNi)
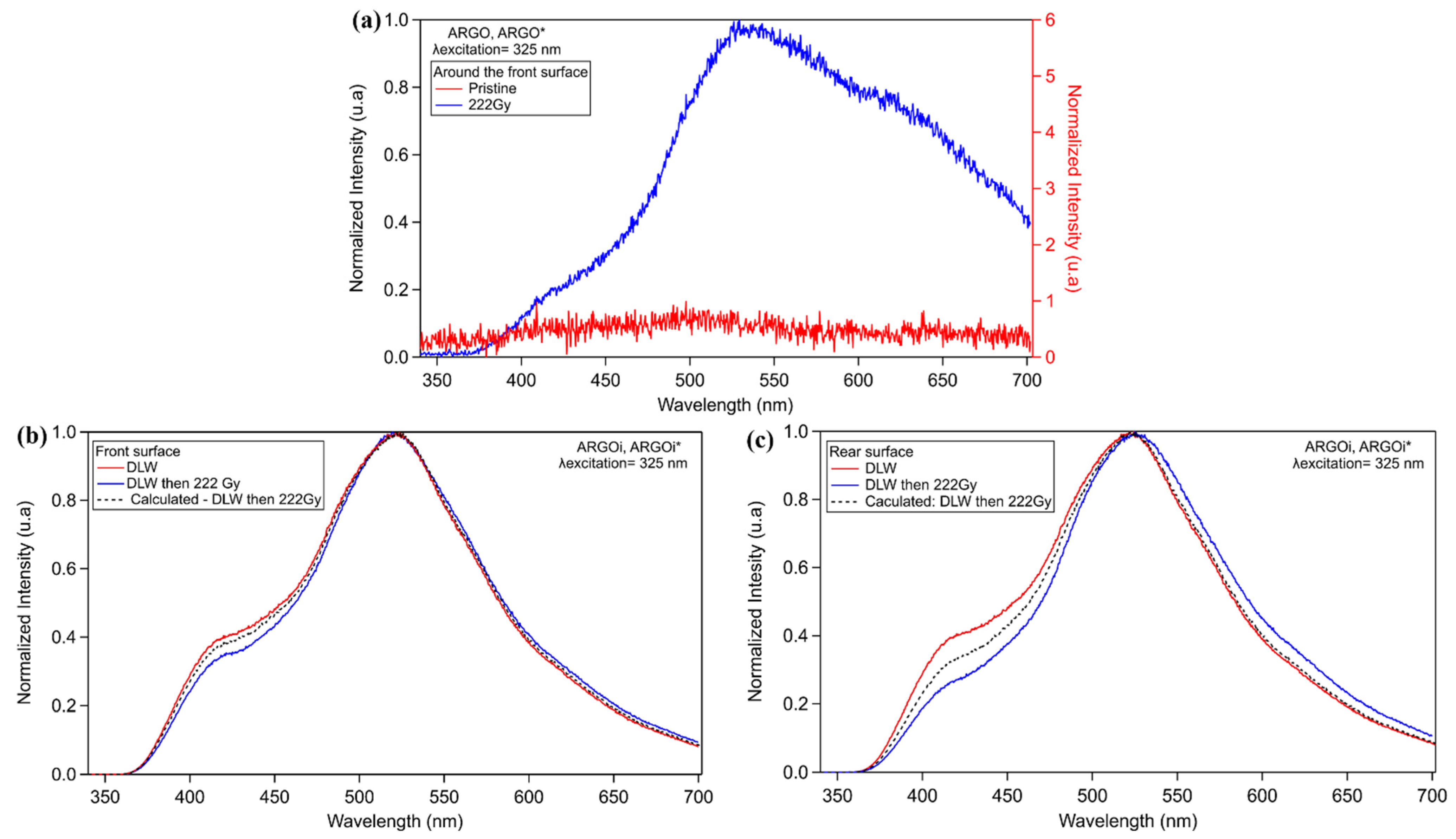
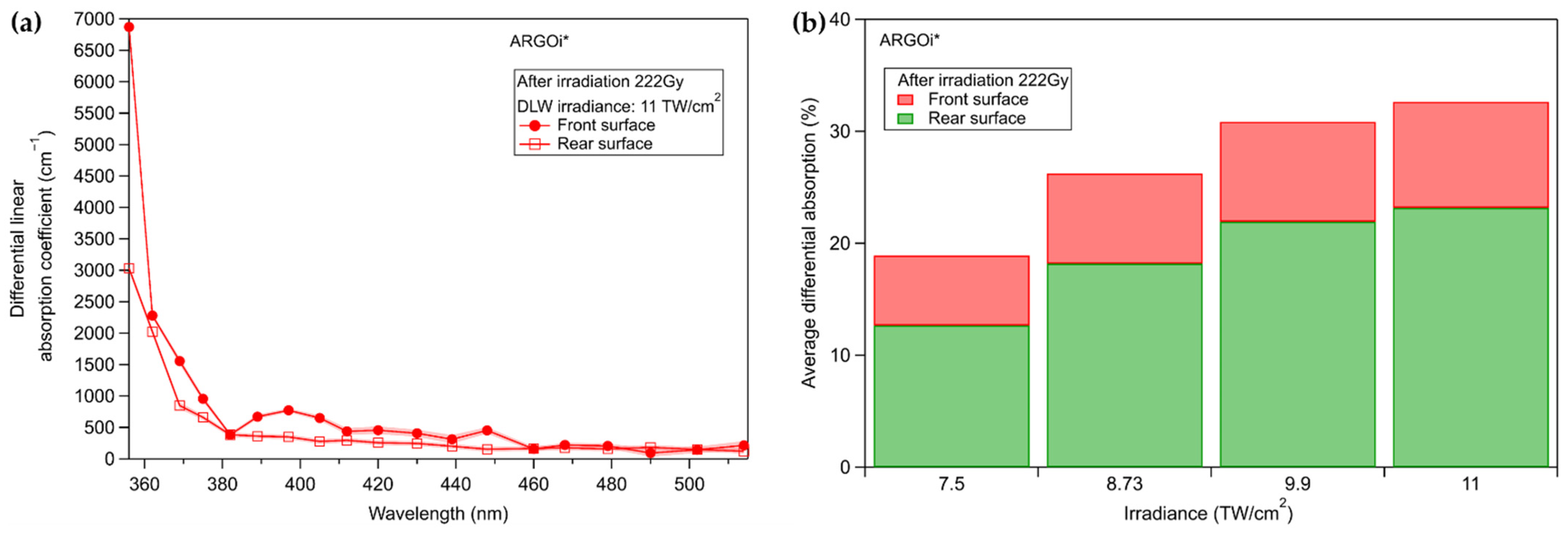
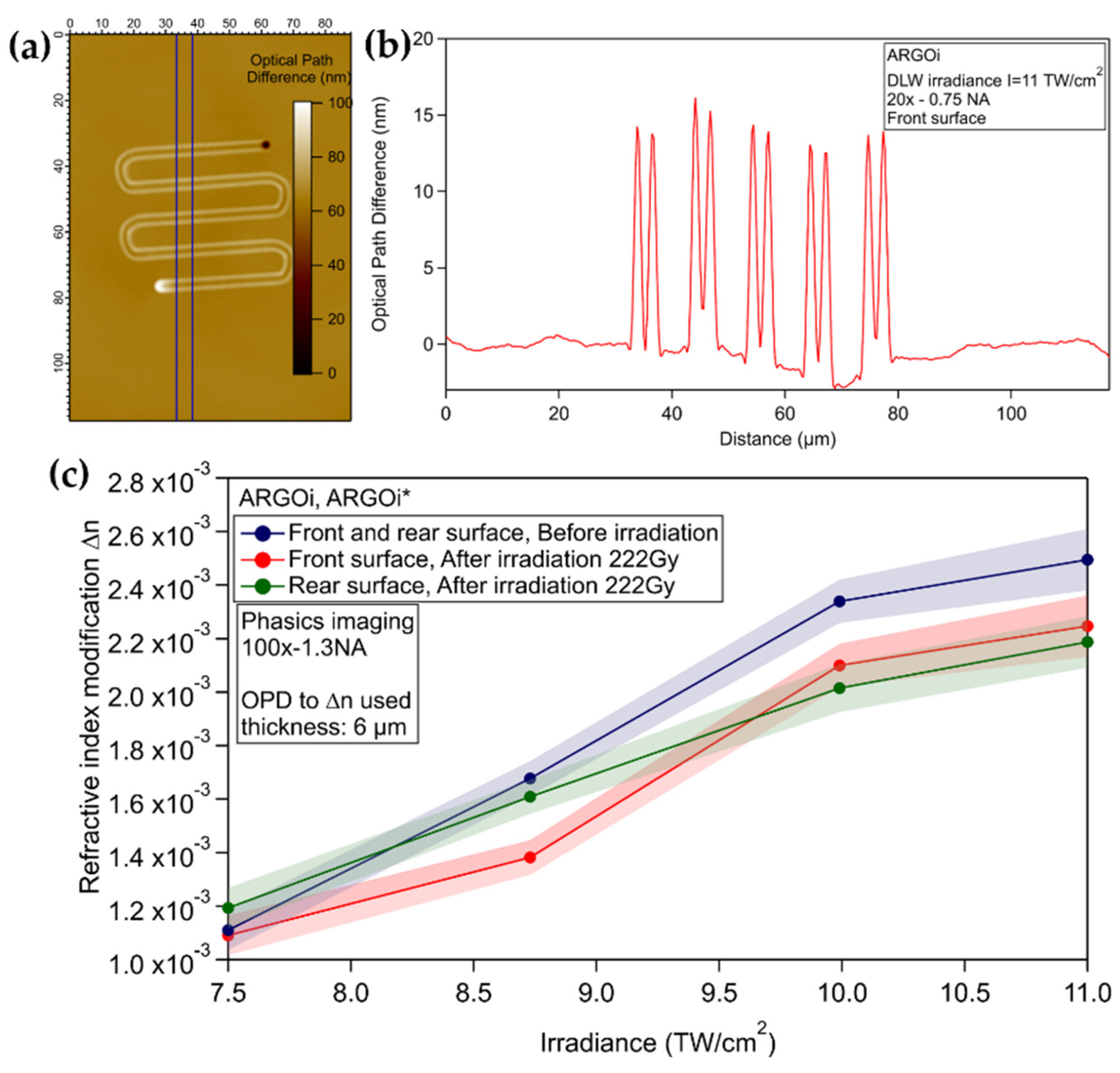
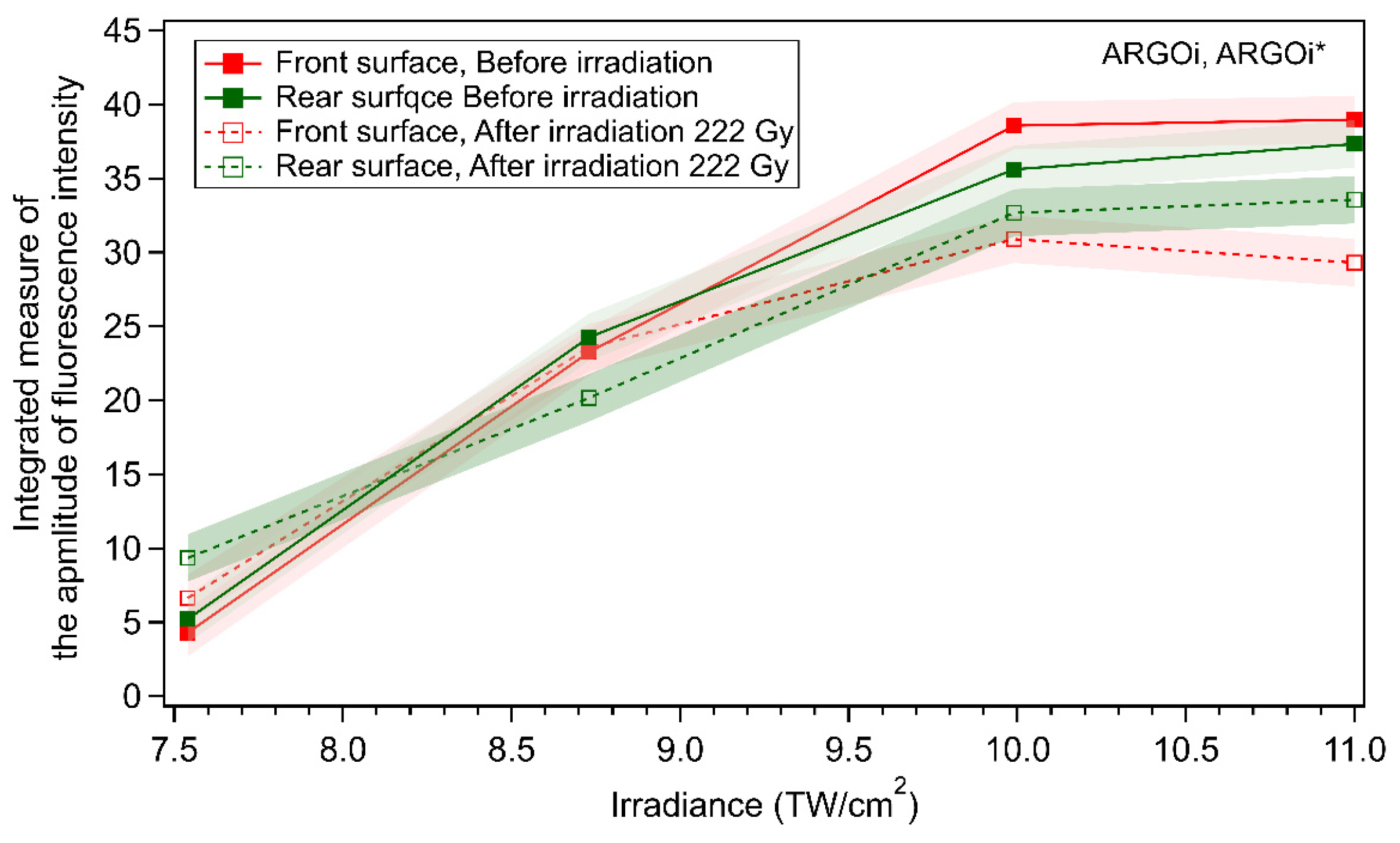
3.3.2. Commercial Argolight Glass (ARGOi)
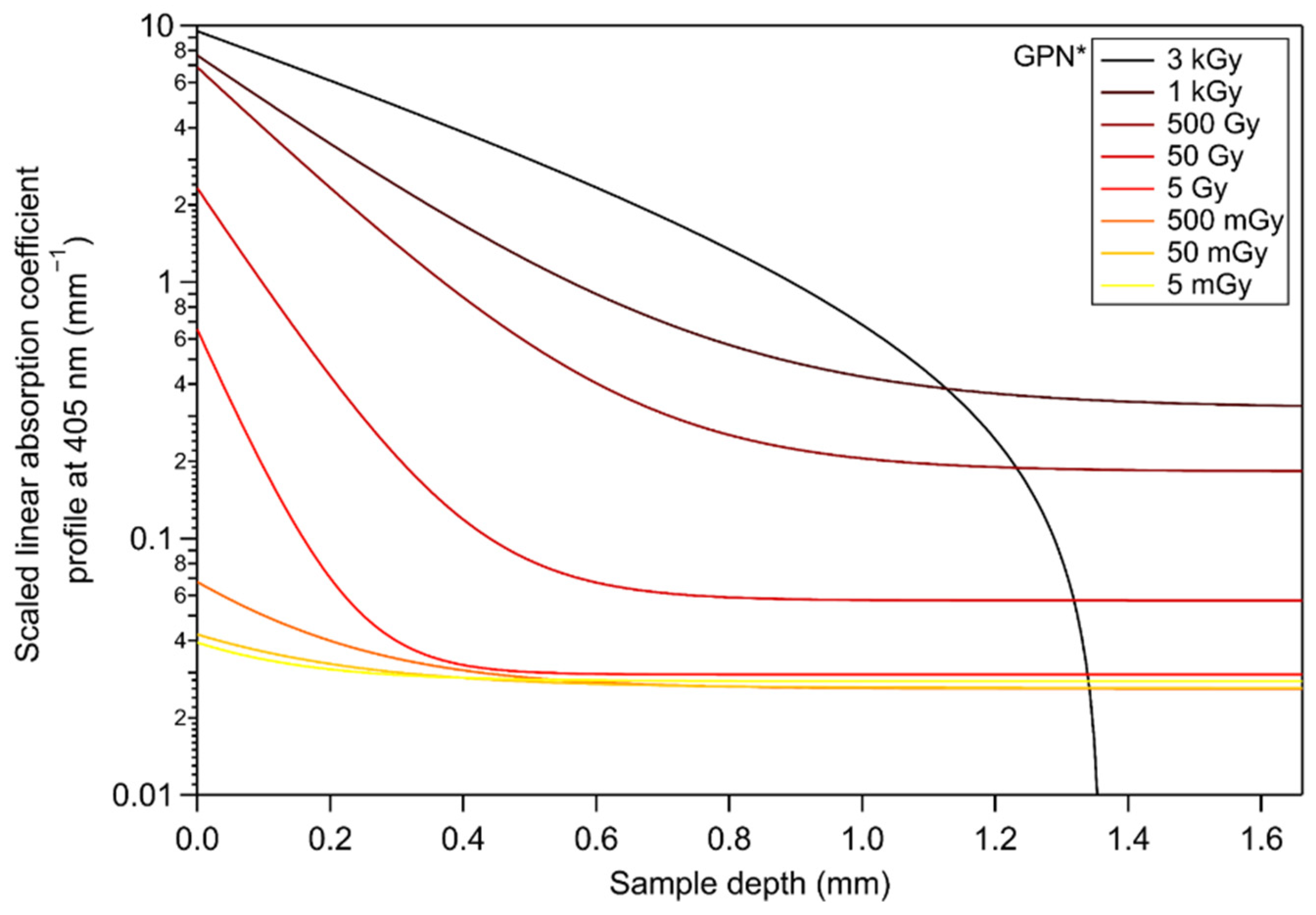
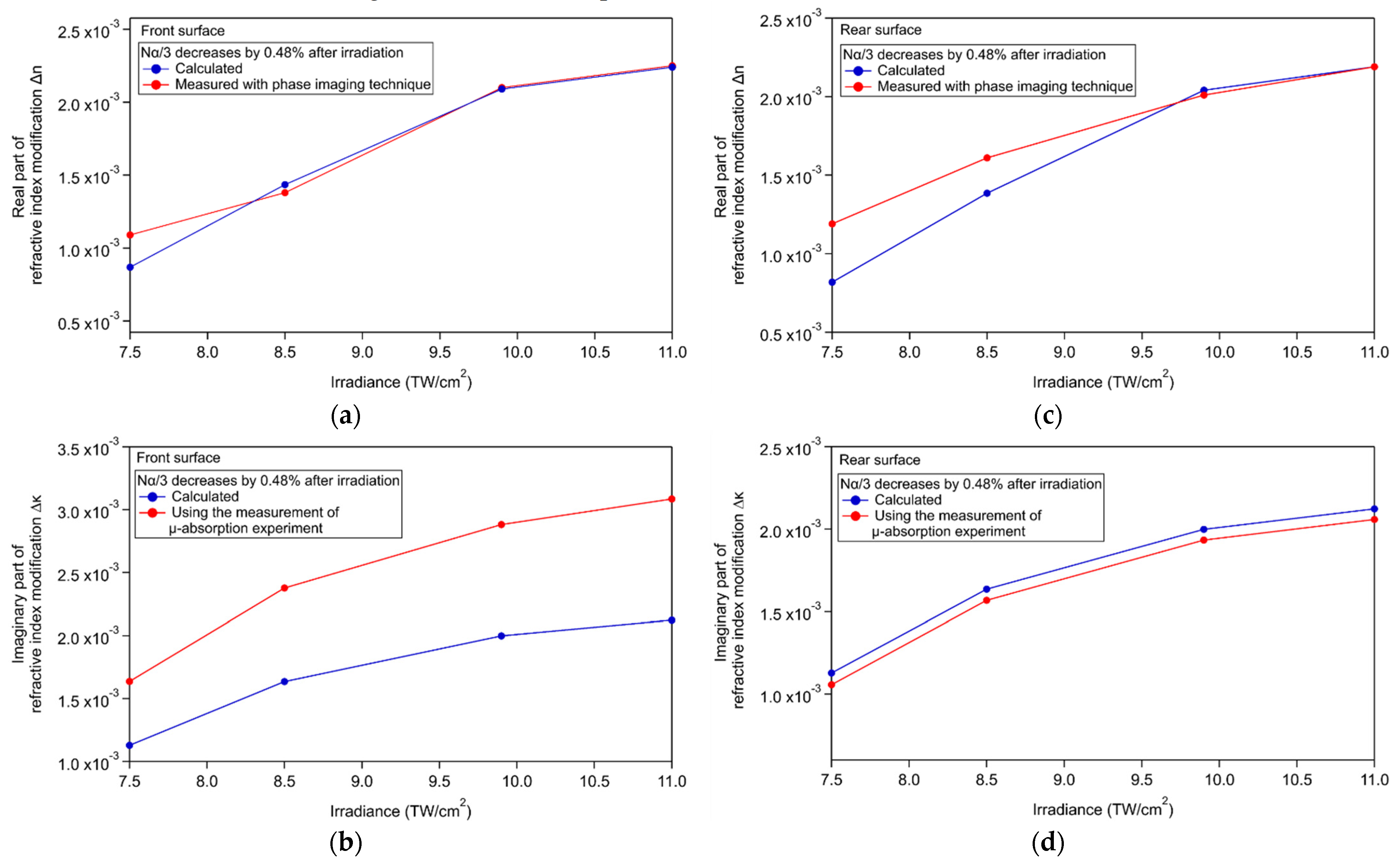
3.4. Inscribed Glasses with Silver Clusters for Application to X-ray Dosimetry
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Calculation of the Estimated Depth-Dependent Profiles in Absolute Values of the Linear Absorption Coefficient at 405 nm
Appendix B. Calculation of the Local Differential Linear Absorption Coefficient
References
- Schulman, J.H.; Ginther, R.J.; Klick, C.C.; Alger, R.S.; Levy, R.A. Dosimetry of X-rays and Gamma-rays by Radiophotoluminescence. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.H.; Shurcliff, W.; Ginther, R.J.; Attix, F.H. Radiophotoluminescence dosimetry system of the U.S. NAVY Radiophotoluminescence Dosimetry System of the U.S. Nucleon (U.S.) Ceased Publ. 1953, 5, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Piesch, E.; Burgkhardt, B. Photoluminescence Dosimetry: The Alternative in Personnel Monitoring. Radioprotection 1994, 29, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piesch, E.; Burgkhardt, B. One-Element Phosphate Glass Dosimetry Systems for the Simultaneous Indication of Different Dose Quantities in Individual and Area Dosimetry. Radioprotection 1986, 17, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.A. RPL Dosimetry. Radiophotoluminescence in Health Physics. In Medical Science Series; Adam Hilger: Bristol, UK, 1987; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T. RPL Dosimetry: Principles and Applications. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2011; Volume 1345, pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodaira, S.; Yanagida, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Kitamua, H.; Kurani, M.; Ogura, K. Note: Complementary Approach for Radiation Dosimetry with Ag+-Activated Phosphate Glass. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, S.W.W.; Sholom, S.; Shrestha, N.; Klein, D.M. An In-Situ, Fiber-Optic System for Sub-Surface, Environmental Dose Measurements Using Radiophotoluminescence from Ag-Doped Alkali-Phosphate Glass. Radiat. Meas. 2020, 132, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Takei, Y.; Nanto, H.; Kurobori, T.; Konnai., A.; Yanagida., T.; Yoshikawa., A.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Sakakura, M.; Miura, K.; et al. Radiophotoluminescence from Silver-Doped Phosphate Glass. Radiat. Meas. 2011, 46, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobori, T. Performance Characterisation of a Real-Time Fiber Dosimetry System Using Radiophotoluminescent Glasses. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, S.W.W.; Sholom, S.; Shrestha, N.; Klein, D.M. Build-up of Radiophotoluminescence (RPL) in Ag-Doped Phosphate Glass in Real-Time Both during and after Exposure to Ionizing Radiation: A Proposed Model. Radiat. Meas. 2020, 132, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.M.; Yeh, S.H.; Lin, M.S.; Chen, W.L. Comparison on Characteristics of Radiophotoluminescent Glass Dosemeters and Thermoluminescent Dosemeters. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2006, 119, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, Y.; Kishi, A.; Kada, W.; Sato, F.; Kato, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Iida, T. Acompact System for Measurement of Radiophotoluminescence of Phosphate Glass Dosimeter. Radiat. Meas. 2008, 43, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranogajek-Komor, M. Ranogajec-Komor, M. Passive solid state dosimeters in environmental monitoring. In New Techniques for the Detection of Nuclear and Radioactive Agents; Aycik, G.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bourhis, K.; Royon, A.; Papon, G.; Bellec, M.; Petit, Y.; Canioni, L.; Dussauze, M.; Rodriguez, V.; Binet, L.; Caurant, D.; et al. Formation and Thermo-Assisted Stabilization of Luminescent Silver Clusters in Photosensitive Glasses. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobori, T.; Zheng, W.; Miyamoto, Y.; Nanto, H.; Yamamoto, T. The Role of Silver in the Radiophotoluminescent Properties in Silver-Activated Phosphate Glass and Sodium Chloride Crystal. Opt. Mater. 2010, 32, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobori, T.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, C. Silver-Activated Radiophotoluminescent Glass: Band Assignments and a Novel Readout System Using a Modulated UV Laser Diode. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, S.W.W.; Sholom, S.; Shrestha, N. Observations Regarding the Build-up Effect in Radiophotoluminescence of Silver-Doped Phosphate Glasses. Radiat. Meas. 2019, 123, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitryuk, A.V.; Paramzina, S.E.; Perminov, A.S.; Solov’eva, N.D.; Timofeev, N.T. The Influence of Glass Composition on the Properties of Silver-Doped Radiophotoluminescent Phosphate Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 202, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, R.; Imagawa, H. Radiophotoluminescent Centers in Silver-Activated Phosphate Glass. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 23, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Koyama, S.; Takei, Y.; Nanto, H.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Sakakura, M.; Miura, K.; Hirao, K. Emission mechanism of radiophotoluminescence in Ag-doped phosphate glass. Radiat. Meas. 2010, 45, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Kurobori, T. Assignments and Optical Properties of X-ray-Induced Colour Centres in Blue and Orange Radiophotoluminescent Silver-Activated Glasses. J. Lumin. 2011, 131, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, D.; Nagai, T.; Sato, F.; Kato, Y.; Iida, T. Microscopic Dose Measurement with Thin Radiophotoluminescence Glass Plate. Radiat. Meas. 2011, 46, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, C.; Cardinal, T.; Canioni, L.; Treguer, M.; Videau, J.J.; Choi, J.; Richardson, M. Luminescence Properties of Silver Zinc Phosphate Glasses Following Different Irradiations. J. Lumin. 2009, 129, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobori, T.; Itoi, H.; Yanagida, T.; Chen, Y.Q. Time Resolved Dose Evaluation in an X-and Gamma-ray-Irradiated Silver-Activated Glass Detector for Three-Dimensional Imaging Applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2015, 793, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Ohno, T.; Takei, Y.; Nanto, H.; Kurobori, T.; Yanagida, T.; Yoshikawa, A.; Nagashima, Y.; Yamamoto, T. Optical properties in Ag+ Doped Phosphate Glass Irradiated with X-rays and α particles. Radiat. Meas. 2013, 55, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquestaut, N.; Petit, Y.; Royon, A.; Mounaix, P.; Cardinal, T.; Canioni, L. Three-Dimensional Silver Nanoparticle Formation Using Femtosecond Laser Irradiation in Phosphate Glasses: Analogy with Photography. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5824–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellec, M.; Royon, A.; Bousquet, B.; Bourhis, K.; Treguer, M.; Cardinal, T.; Richardson, M.; Canioni, L. Beat the Diffraction Limit in 3D Direct Laser Writing in Photosensitive Glass. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Khalil, A. Direct Laser Writing of a New Type of Optical Waveguides and Components in Silver Containing Glasses. Ph.D. Thesis, Bordeaux University, Bordeaux, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bellec, M.; Royon, A.; Bourhis, K.; Choi, J.; Bousquet, B.; Treguer, M.; Cardinal, T.; Videau, J.J.; Richardson, M.; Canioni, L. 3D Patterning at the Nanoscale of Fluorescent Emitters in Glass. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15584–15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cremer, G.; Coutino-Gonzalez, E.; Roeffaers, M.B.J.; De Vos, D.E.; Hofkens, J.; Vosch, T.; Sels, B.F. In Situ Observation of the Emission Characteristics of Zeolite-Hosted Silver Species During Heat Treatment. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2010, 11, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cremer, G.; Coutino-Gonzalez, E.; Roeffaers, M.B.J.; Moens, B.; Ollevier, J.; Vander Auweraer, M.; Schoonheydt, R.; Jacobs, P.A.; De Schryver, F.C.; Hofkens, J.; et al. Characterization of Fluorescence in Heat-Treated Silver-Exchanged Zeolites. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.J.; Tikhomirov, V.K.; Chibotaru, L.F.; Cuong, N.T.; Kuznetsov, A.S.; Rodríguez, V.D.; Nguyen, M.T.; Moshchalkov, V.V. Energy Level Diagram and Kinetics of Luminescence of Ag Nanoclusters Dispersed in a Glass Host. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 13582–13591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Khalil, A.; Lalanne, P.; Bérubé, J.P.; Petit, Y.; Vallée, R.; Canioni, L. Femtosecond Laser Writing of Near-Surface Waveguides for Refractive-Index Sensing. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 31130–31143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Khalil, A.; Bérubé, J.P.; Danto, S.; Desmoulin, J.C.; Cardinal, T.; Petit, Y.; Vallée, R.; Canioni, L. Direct Laser Writing of a New Type of Waveguides in Silver Containing Glasses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, Y.; Danto, S.; Guérineau, T.; Abou Khalil, A.; Le Camus, A.; Fargin, E.; Duchateau, G.; Bérubé, J.P.; Vallée, R.; Messaddeq, Y.; et al. On the Femtosecond Laser-Induced Photochemistry in Silver-Containing Oxide Glasses: Mechanisms, Related Optical and Physico-Chemical Properties, and Technological Applications. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2018, 7, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, P. Nanostructuration des Propriétés Optiques Linéaires et Non-Linéaires d’Un Verre Photosensible Par Laser Femtoseconde. Ph.D. Thesis, Bordeaux University, Bordeaux, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Royon, A.; Bourhis, K.; Béchou, L.; Cardinal, T.; Canioni, L.; Deshayes, Y. Durability Study of a Fluorescent Optical Memory in Glass Studied by Luminescence Spectroscopy. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérineau, T.; Cova, F.; Petit, Y.; Abou Khalil, A.; Fargues, A.; Dussauze, M.; Danto, S.; Vedda, A.; Canioni, L.; Cardinal, T. Silver Centers Luminescence in Phosphate Glasses Subjected to X-rays or Combined X-rays and Femtosecond Laser Exposure. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2019, 11, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérineau, T.; Loi, L.; Petit, Y.; Danto, S.; Fargues, A.; Canioni, L.; Cardinal, T. Structural Influence on the Femtosecond Laser Ability to Create Fluorescent Patterns in Silvercontaining Sodium-Gallium Phosphate Glasses. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 3748–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, K. Photostructuration Par Laser Infrarouge Femtoseconde de Verres Photosensible de Phosphate de Zinc, d’Argent et de Gallium. Ph.D. Thesis, Bordeaux University, Bordeaux, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Desmoulin, J.C.; Petit, Y.; Canioni, L.; Dussauze, M.; Lahaye, M.; Magallanes Gonzalez, H.; Brasselet, E.; Cardinal, T. Femtosecond Laser Structuring of Silver-Containing Glass: Silver Redistribution, Selective Etching, and Surface Topology Engineering. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 213104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royon, A.; Bourhis, K.; Bellec, M.; Papon, G.; Bousquet, B.; Deshayes, Y.; Cardinal, T.; Canioni, L. Silver Clusters Embedded in Glass as a Perennial High Capacity Optical Recording Medium. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5282–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershov, B.G.; Ionova, G.V.; Kiseleva, A.A. Silver Clusters: Calculations of Optical Transmissions and of the Formation and Properties of “Magic” Positively Charged Clusters. Rus. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 69, 239. [Google Scholar]
- Harb, J.; Petit, Y.; Guérineau, T.; Cardinal, T.; Canioni, L. Direct Laser Writing in Photosensitive Glasses: Application to Optical Systems for the Creation of High-Sensitivity Dosimeters. In Proceedings of the OPAL 2021 Conference, Corfu, Greece, 13–15 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alhelou, N. Etude de Verres Pour La Dosimétrie Fibrée de Rayonnements Ionisants. Ph.D. Thesis, Lille University, Lille, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kahan, T. Discussion de Formules et Courbes Theoriques Relatives Aux Rayons. J. Phys. Radium 1939, 10, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poludniowski, G.; Omar, A.; Bujila, R.; Pedro, A. Technical Note: SpekPy v2.0—A Software Toolkit for Modeling X-ray Tube Spectra. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 3630–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujila, R.; Artur, O.; Poludniowski, G. A Validation of SpekPy: A Software Toolkit for Modelling X-ray Tube Spectra. Phys. Med. 2020, 75, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.; Amako, K.; Apostolakis, J.; Arce, P.; Asai, M.; Aso, T.; Bagli, E.; Bagulya, A.; Banerjee, S.; Barrand, G.; et al. Recent Developments in GEANT4. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2016, 835, 186–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streltsov, A.M.; Borrelli, N.F. Study of Femtosecond-Laser-Written Waveguides in Glasses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2002, 19, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
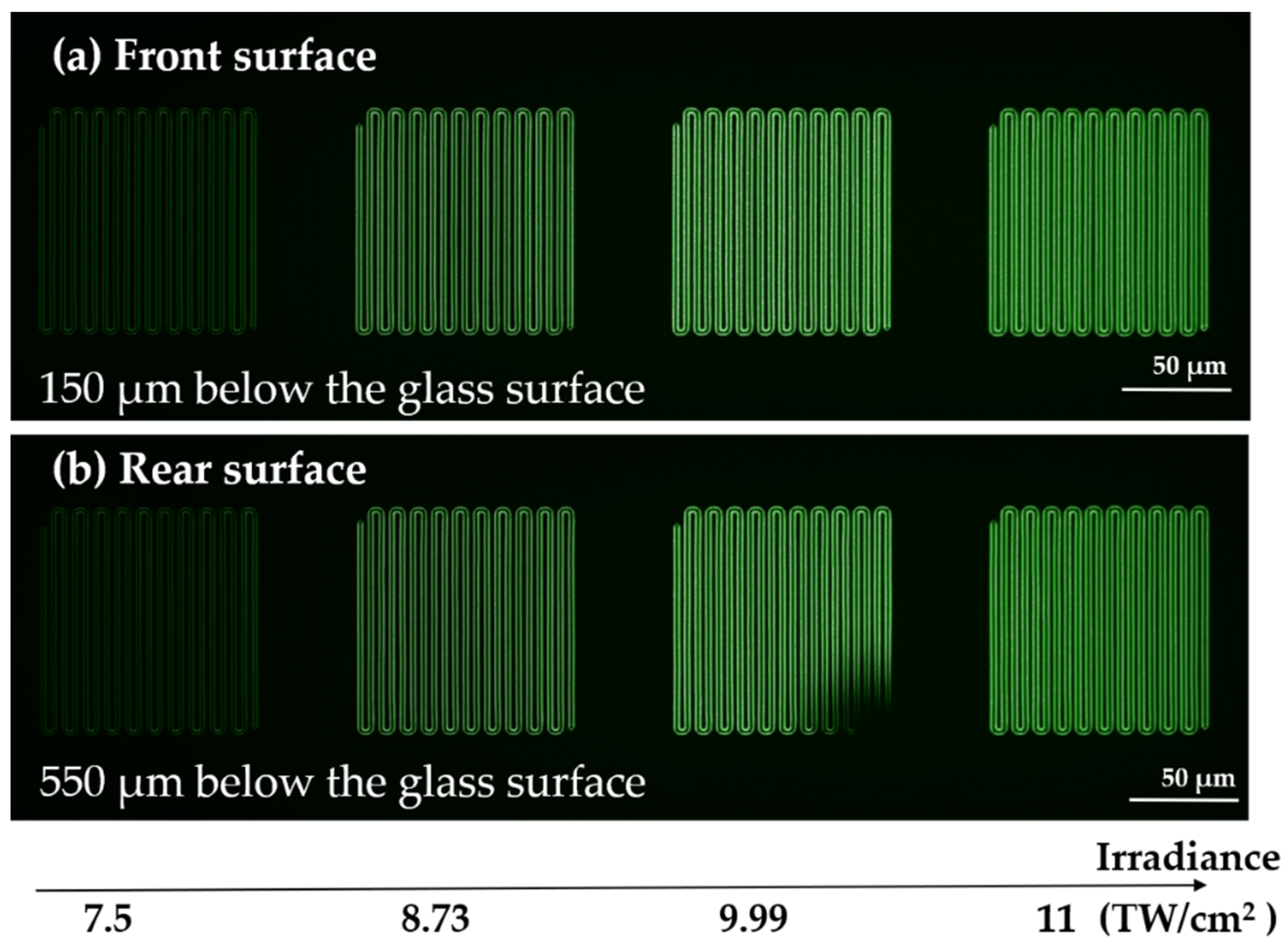
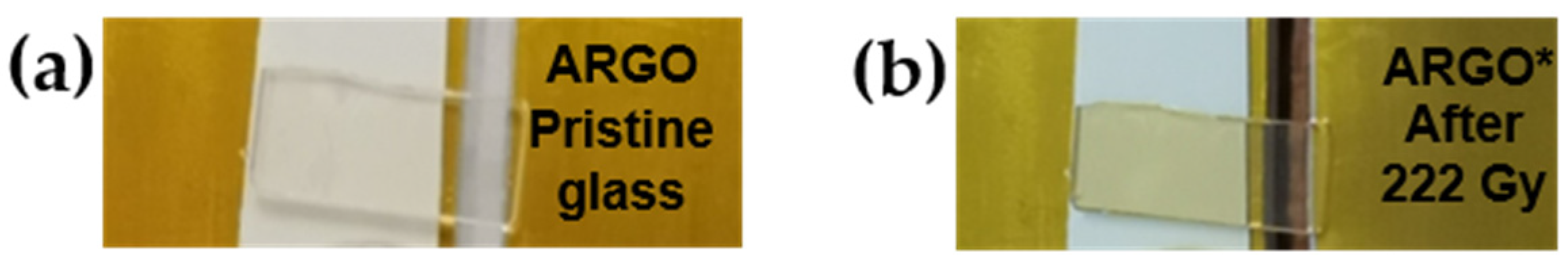
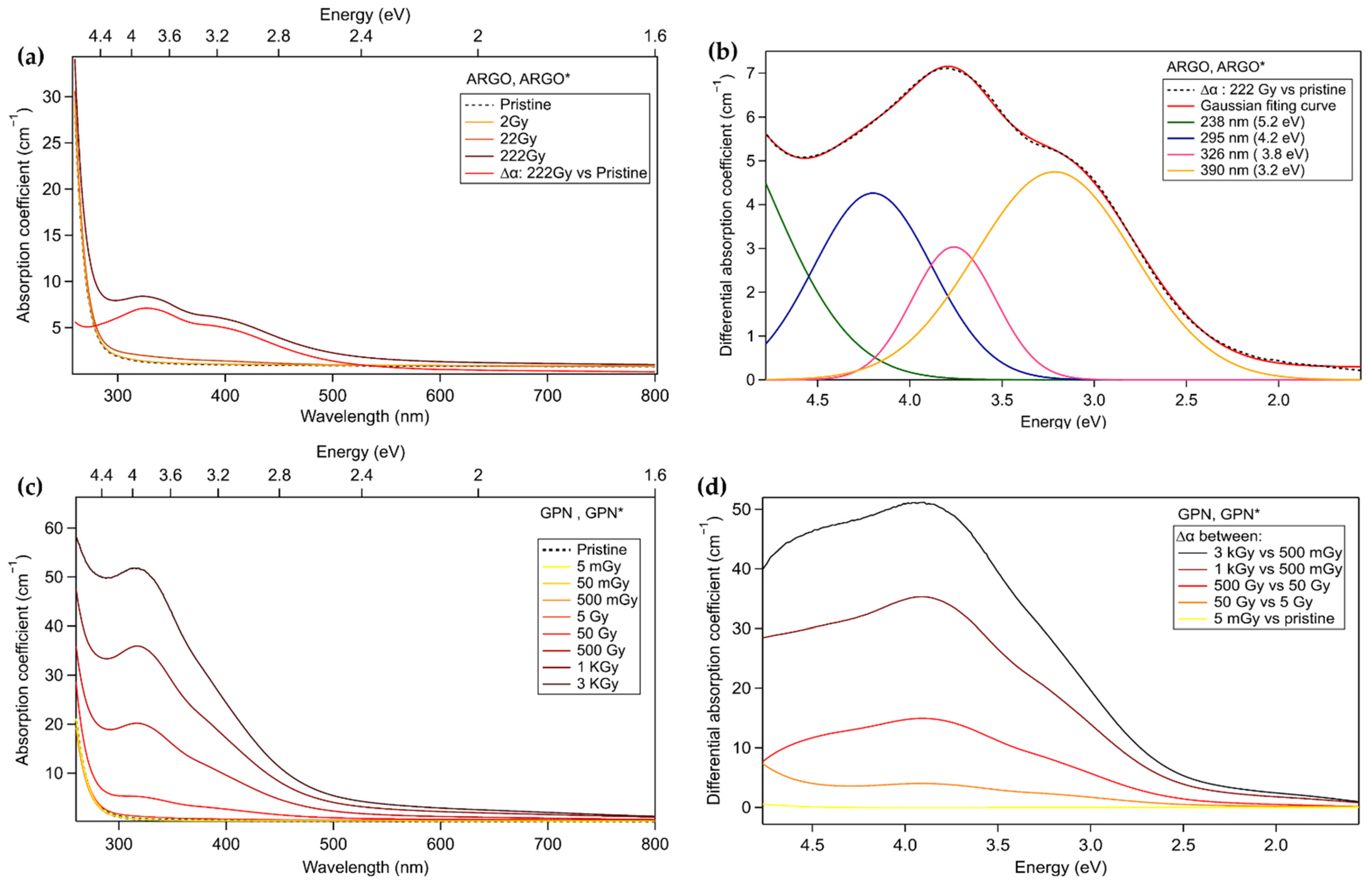
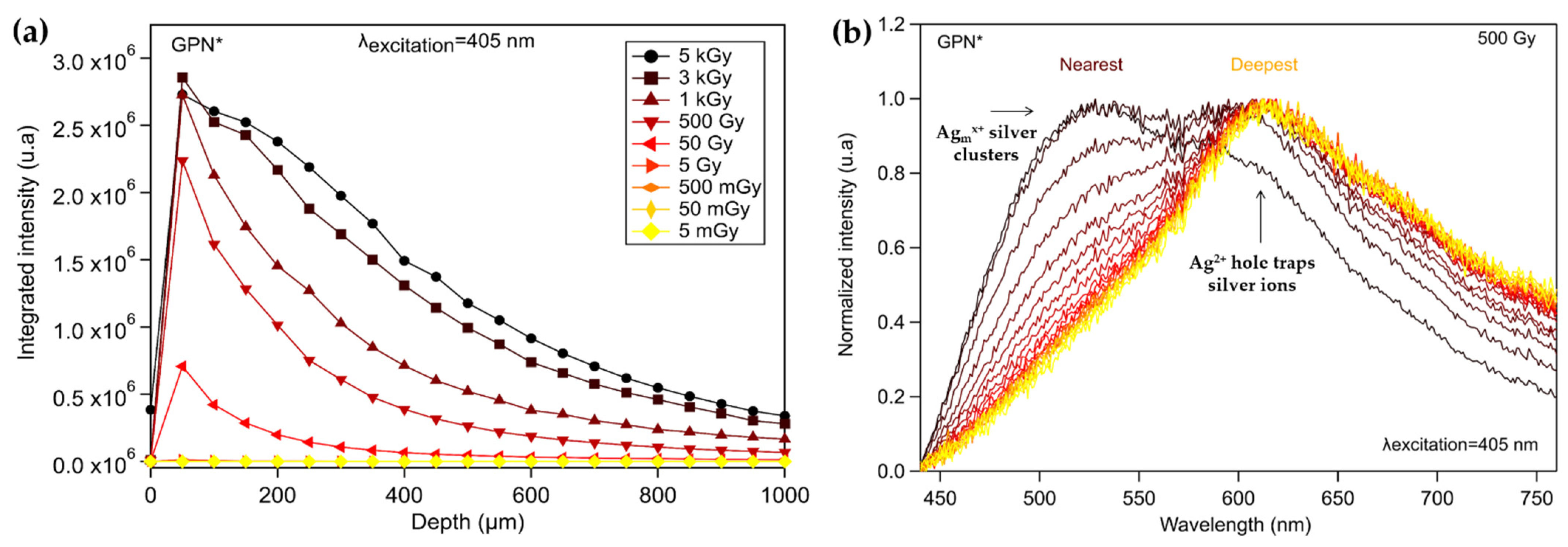
| Acronym | Nominal Cationic Composition (mol %) | n589 (±0.002) | Temperature of Glass Transition Tg (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARGO | 39.0P2O5-53.8ZnO-5.8Ag2O-1Ga2O3 * | 1.611 | 375 |
| GPN | 56.0P2O5-28.0Ga2O3-14.0Na2O-2.0Ag2O | 1.566 | 497 |
| λ (nm) | Refractive Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Before irradiation | Front irradiated surface | Rear irradiated surface | |
| 589 | 1.611 ± 0.002 | 1.608 ± 0.002 | 1.608 ± 0.002 |
| Glass Sample | Maximum Dose at Surface | Silver Clusters Depth [µm] | Maximum Dose in Silver Clusters [Gy (Material)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARGOi* | 222 Gy ± 10% (H2O) | 150 (Front) | 57 ± 10% |
| 550 (Rear) | 18 ± 10% | ||
| GPNi* | 357 Gy ± 10% (quartz) | 160 (Front) | 76 ± 10% |
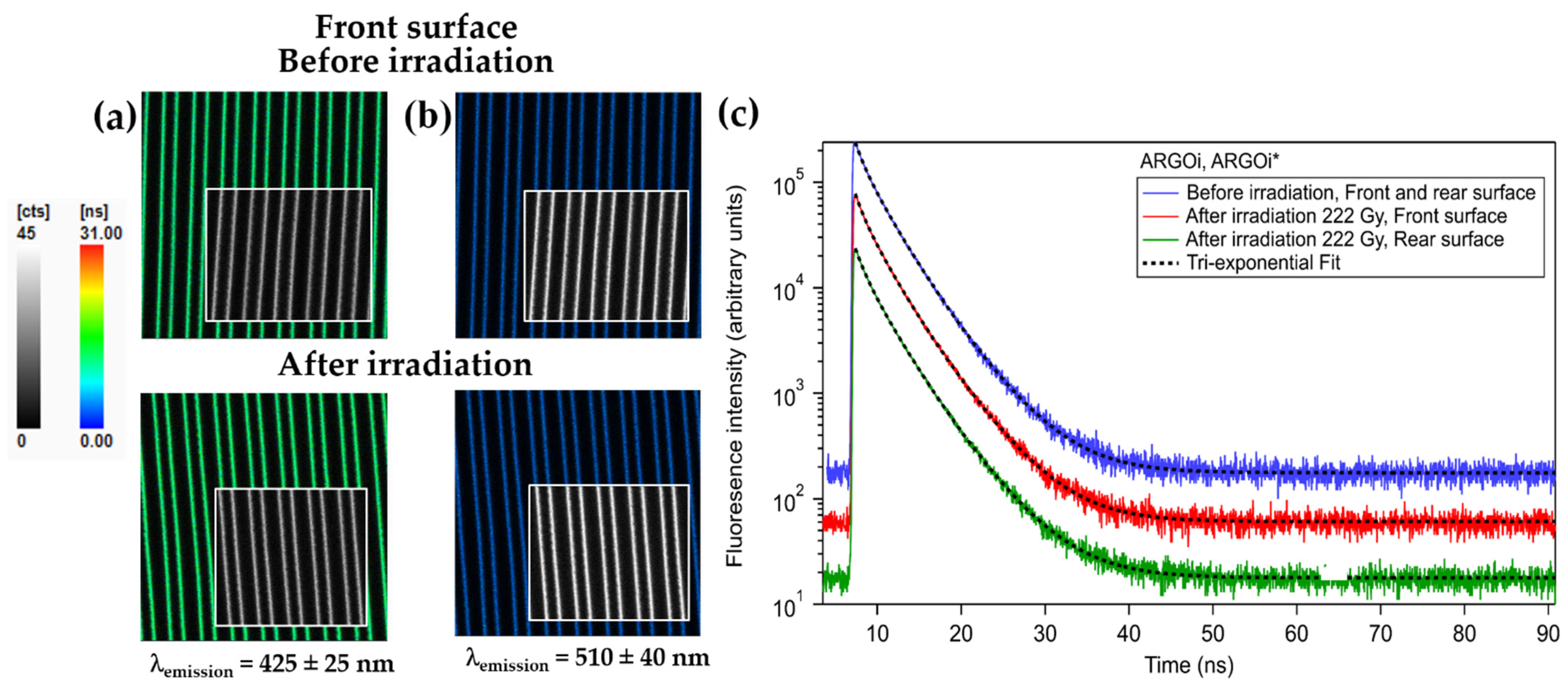
| Fluorescence Decay | Associated Amplitude (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λemission | ARGOi | ||||||
| 425 ± 25 nm | Before Irradiation * | 0.9; 0.1 | 2.9; 0. 2 | 5.1; 0. 5 | 28; 2 | 56; 4 | 16; 3 |
| After irradiation, Front surface * | 0.9; 0.1 | 2.8; 0.16 | 5.2; 0.5 | 32; 4 | 52; 12 | 16; 8 | |
| After irradiation, Rear surface * | 0.9; 0.1 | 2.8; 0.2 | 5.0; 0.6 | 34; 3 | 51; 3 | 15; 7 | |
| 510 ± 40 nm | Before Irradiation * | 1.8; 0.2 | 4.3; 0.2 | 7.5; 0.5 | 28; 3 | 57; 3 | 15; 3 |
| After irradiation, Front surface * | 1.9; 0.2 | 4.5; 0.2 | 7.7; 0.4 | 29; 3 | 56; 3 | 15; 3 | |
| After irradiation, Rear surface * | 1.9; 0.3 | 4.4; 0.3 | 7.4; 0.5 | 30; 5 | 53; 5 | 17; 5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harb, J.; Guérineau, T.; Morana, A.; Meyer, A.; Raffy, G.; Guerzo, A.D.; Ouerdane, Y.; Boukenter, A.; Girard, S.; Cardinal, T.; et al. Femtosecond Direct Laser Writing of Silver Clusters in Phosphate Glasses for X-ray Spatially-Resolved Dosimetry. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030110
Harb J, Guérineau T, Morana A, Meyer A, Raffy G, Guerzo AD, Ouerdane Y, Boukenter A, Girard S, Cardinal T, et al. Femtosecond Direct Laser Writing of Silver Clusters in Phosphate Glasses for X-ray Spatially-Resolved Dosimetry. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(3):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarb, Joelle, Théo Guérineau, Adriana Morana, Arnaud Meyer, Guillaume Raffy, André Del Guerzo, Youcef Ouerdane, Aziz Boukenter, Sylvain Girard, Thierry Cardinal, and et al. 2022. "Femtosecond Direct Laser Writing of Silver Clusters in Phosphate Glasses for X-ray Spatially-Resolved Dosimetry" Chemosensors 10, no. 3: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030110
APA StyleHarb, J., Guérineau, T., Morana, A., Meyer, A., Raffy, G., Guerzo, A. D., Ouerdane, Y., Boukenter, A., Girard, S., Cardinal, T., Petit, Y., & Canioni, L. (2022). Femtosecond Direct Laser Writing of Silver Clusters in Phosphate Glasses for X-ray Spatially-Resolved Dosimetry. Chemosensors, 10(3), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030110









