Abstract
This work deals with the development of water-soluble optical sensors based on ruthenium(II) tris(diimine) complexes that exhibit high molar absorptivity and are emissive in aqueous media. Palladium-catalyzed arylation of polyamines with 3-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline (Brphen) and [Ru(bpy)2(Brphen)](PF6)2 (bpy = 2,2’-bipyridine) was explored to prepare Ru2+ complexes with 1,10-phenanthrolines (phen) substituted by linear polyamines (PAs) at position 3 of the heterocycle ([Ru(bpy)2(phen–PA)](PF6)2). The most convenient synthetic pathway leading to the target molecular probes includes the preparation of phen–PA ligands, followed by ruthenium complexation using cis-Ru(bpy)2Cl2. Complexes bearing a polyamine chain directly linked to phenanthroline core are emissive in aqueous media and their quantum yields are comparable to that of parent [Ru(bpy)3](PF6)2. Their structure can be easily adapted for detection of various analytes by modification of amine groups. As an example, we prepared the emissive complex Ru(N2P2phen) which is suitable for the dual channel (spectrophotometry and luminescence (ON–OFF probe)) selective detection of Cu2+ ions at the physiological pH levels with limits of detection (LOD) by spectrophotometry and fluorescence spectroscopy equal to 9 and 6 μM, respectively, that is lower than the action level in drinking water for copper as prescribed by the US Environmental Protection Agency.
1. Introduction
The design and synthesis of abiotic molecular systems capable of signaling various guest molecules or ions by changing optical properties has spurred tremendous research efforts [1]. Being optimized, these molecular probes have many advantages, such as real-time and rapid colorimetric response, and/or beneficially exploit the high sensitivity and environmental versatility of photoluminescence spectroscopy. However, many chemosensors already reported suffer from various drawbacks such as slow response, poor chemical or photostability, irreversibility, short lifetimes, low solubility, and/or low quantum yields in aqueous media. While most analytical applications concern aqueous solutions, the optical sensoring techniques in this media are still underdeveloped, because the synthesis of water-soluble receptors is generally laborious and their solubility in aqueous medium is not easily predictable. A common strategy to increase water solubility of aromatic molecules, which consists of the introduction of charged functional groups, such as carboxylates, sulfonates, or ammonium [2,3], is only of limited value for developing chemosensors, in particular for metal ions, because these donor groups can serve as alternative ligand sites for ions that strongly deteriorates selectivity.
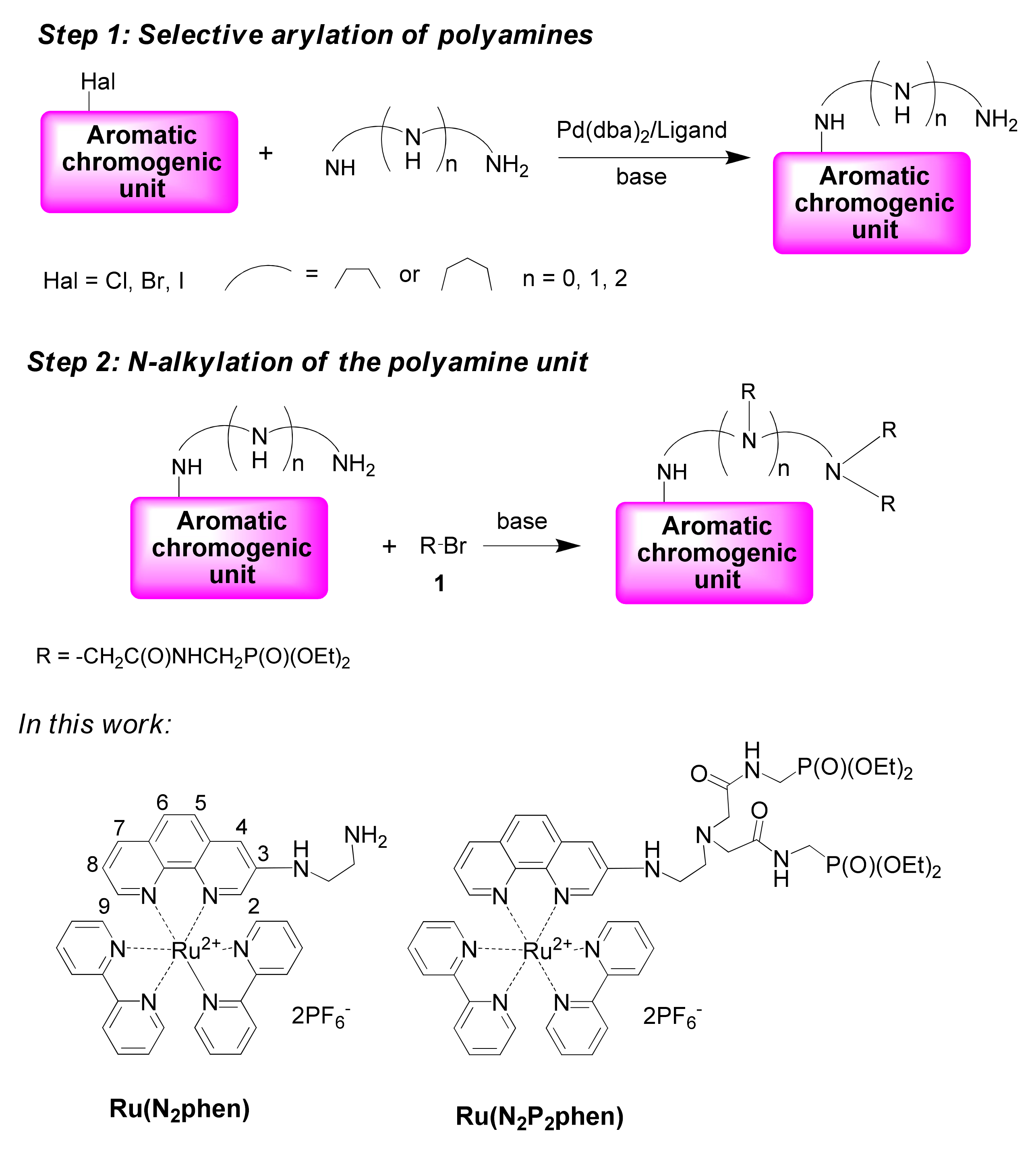
Recently, water-soluble polyamine ionophores incorporating hydrophilic diethoxyphosphoryl-substituted amide moieties were developed by our groups (Scheme 1) [4]. The synthetic approach to these chromogenic chelators involves the selective Pd-catalyzed amination reaction (step 1) followed by their N-alkylation with alkyl halides bearing diethoxyphosphoryl moieties such as [(2-bromoacetylamino)methyl]phosphonic acid diethyl ester (1) (step 2). This strategy could be expected to be useful for a variety of chromogenic units due to the wide substrate scope of both steps involved in the reaction sequence. In this work, we report on the synthesis of chemosensors bearing mixed ligand ([Ru(bpy)2(phen)]2+-type complexes as signaling groups.
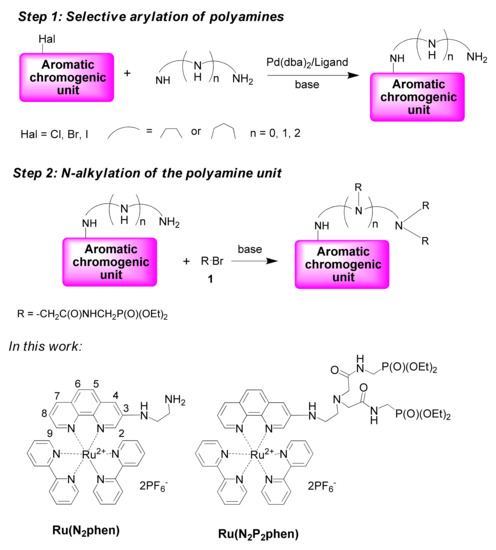
Scheme 1.
Synthetic approaches to chemosensors with polyamine ionophores and the structures of complexes investigated in this work.
The stable and biocompatible ruthenium(II) tris(diimine) complexes (diimine = bpy, phen, terpyridine) have attracted considerable attention as luminophores and been explored in labeling, sensing, and imaging of various gases (dioxygen [5], nitric oxide [6], and carbon monoxide [7]), biological analytes (DNA, sugars, methylglyoxal, thiols, and amino acids) [8,9,10], and anions [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. In contrast to most organic dyes, these complexes can exhibit a high brightness [20] in aqueous media, in part due to the electrostatic repulsive interactions that prevent the aggregation of these charged species in aqueous media. Nevertheless, structure/sensing efficiency relationships in this series of indicators are still less well understood compared to common organic dyes, in part because these compounds are hardly accessible. For most of the reported complexes with phen ligands, the ionophore unit is located at the most reactive positions of the heterocycle, namely, 4/7 and 5/6, and attached to the signaling group by C=O, –CH=N–, or imidazole linkers.
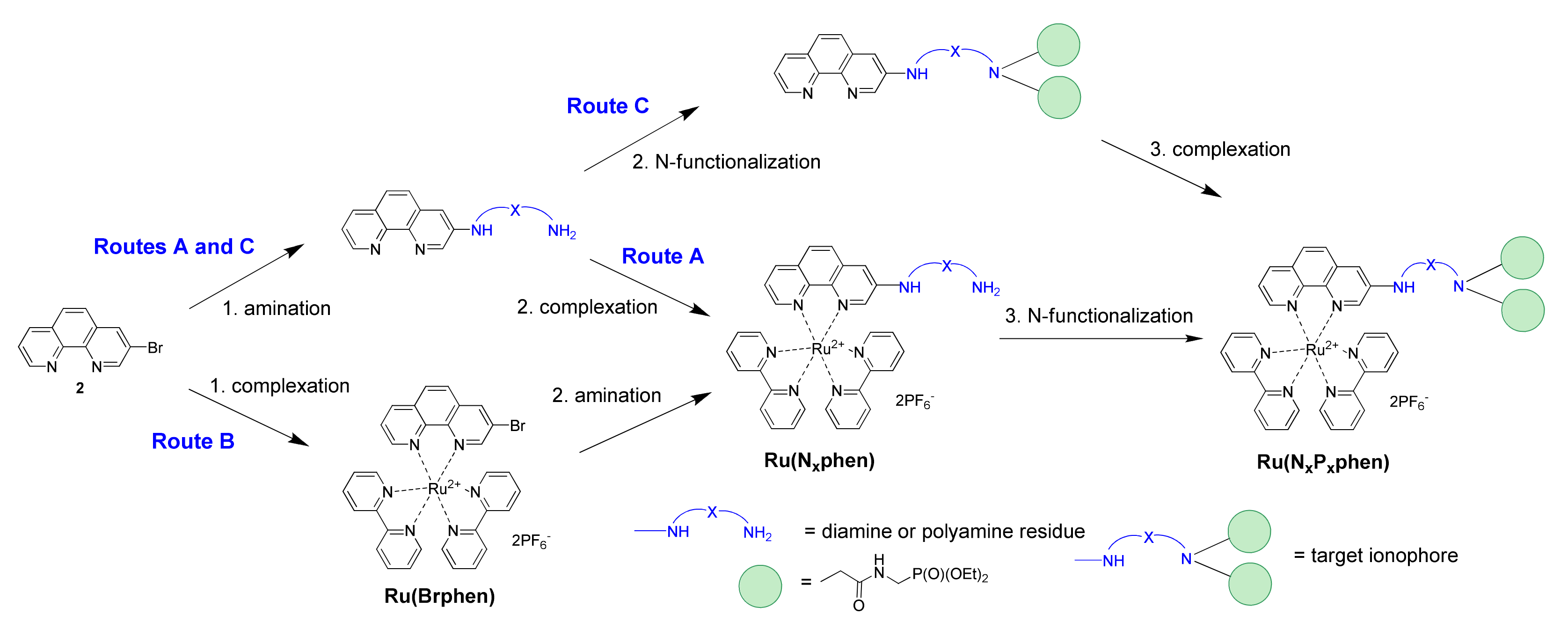
1,10-Phenanthrolines, which bear ionophores directly connected to the aromatic scaffold, are promising ligands for development of chemosensors, as analyte uptake could be expected to exert a strong impact on both the photophysical and electrochemical properties of the corresponding ruthenium(II) complexes, thus allowing for multichannel detection of analytes. The only reported examples of such chelators are the complexes containing mixed-donor (N, O, S) macrocycles (i.e., crown-ether-type receptors fused at the central six-membered ring via positions 5 and 6 or attached at positions 4 and 7 of the heterocycle, or azacrown-type derivatives bearing two macrocycles attached at positions 4 and 7 of the phenanthroline ring) [21,22]. On the other hand, the emissive properties of ruthenium(II) tris(diimine) complexes with aminophenanthroline ligands are strongly dependent on the position of the amino-substituent attached to the heterocycle, and emission quantum yields of complexes involving 4-substituted phen ligands are expected to be low [23,24]. This could be detrimental for the sensibility of chemosensors. In contrast, the introduction of the amino substituents in the 3- or 5-position of the 1,10-phenanthroline ring results only in a small decrease in luminescence quantum yields compared to that of the parent complex [Ru(bpy)2(phen)](PF6)2, while the brightness of the complexes with the 3-substituted ligands is comparable to that of the parent complex. In these Ru2+ complexes, the signaling and receptor units are directly connected, and HOMO is localized on the aminophenanthroline ligand [24]. As a consequence, analyte binding by the nitrogen atom of the substituent should strongly affect the HOMO energy, leading presumably to significant modulation of the absorption and emission properties. We were interested in preparing complexes bearing polyamine ionophores, which are widely used in detection and are efficient for binding both cationic and anionic analytes depending on the degree of their protonation and can be easily adapted to the analyte structure using functionalization of amino groups. Various synthetic approaches were investigated to propose a reliable approach to the preparation of these molecular probes (Scheme 2).
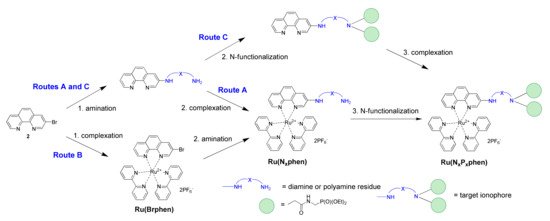
Scheme 2.
The three tested synthetic routes for the preparation of Ru(NxPxphen).
After preparing Ru(N2P2phen) and Ru(N2phen) in reasonable yield, the optical properties of these chromophores in aqueous media were investigated followed by studies of their proton sensitivity and sensing properties towards metal ions. It was demonstrated that despite a high brightness of both complexes, only Ru(N2P2phen) allows for dual channel optical detection of Cu2+ ions in aqueous media including tap water.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals and starting materials were obtained commercially from Acros (via Fisher Scientific, Illkirch, France) and Aldrich–Sigma Co. (via Merck Co., Darmstadt, Germany) and used without further purification. Preparative column chromatography was carried out using silica gel 60 (40–63 µm) from Merck Co. (Darmstadt, Germany). Dioxane was distilled successively over NaOH and sodium under argon, CH2Cl2 and CH3CN were distilled over CaH2, chloroform was distilled over P2O5, and MeOH was used freshly distilled. [(2-Bromoacetylamino)methyl]phosphonic acid diethyl ester (1) was obtained according to a known procedure [25]. Pd(dba)2 was synthesized according to a known method [26] and used without recrystallization. 3-Bromo-1,10-phenanthroline (2) was synthesized according to the procedure in [27] and purified by column chromatography followed by recrystallization from boiling acetone. N1,N1’-(ethane-1,2-diyl)diethane-1,2-diamine (5e) was prepared by treatment of tetraethylenepentamine dihydrochloride with 2.5 M solution of KOH in methanol. The starting complex, cis-Ru(bpy)2Cl2, was synthesized from RuCl3·3H2O according to a known method [28].
2.2. Apparatus
The pH measurements were carried out using Mettler Toledo apparatus with a combined electrode LE438. The electrode was calibrated with commercial buffers (pH = 4.01 and 7.00). UV–Vis spectra were registered with an Agilent Cary 60 device in quartz cuvette (Hellma, l = 1 cm). Fluorescence spectra were obtained with a Horiba Jobin Yvon Fluoromax-2 apparatus in quartz cuvette (Hellma, l = 1 cm). Luminescence quantum yields were determined relative to Ru(bpy)3(PF6)2 in aerated acetonitrile according to a standard procedure [29].
1H, 31P, and 13C NMR spectra were registered with a Bruker Avance-400 spectrometer in chloroform-d1, methanol-d4, or acetonitrile-d3 using the residual signals of chloroform, CHD2OD, or acetonitrile-d2 as internal standards. 13C spectra of Ru(II) complexes were not collected due to the rather low solubility of these compounds. Accurate mass measurements (ESI-HRMS) were performed with a Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Elite high-field orbitrap hybrid mass spectrometer. MALDI-TOF mass spectra were registered on a Bruker Daltonics Autoflex II mass spectrometer in the positive ion mode with a dithranol matrix and polyethyleneglycols as internal standards. FTIR spectra were registered on Nicolet iS 5 and Bruker Vector 22 spectrophotometers. Micro-ATR accessory (Pike) was used in order to register the FTIR spectra of polycrystalline solid complexes. The limit of detection (LOD) of Cu(II) ions was determined by UV–Vis and fluorescence spectroscopies using the 3σ method [30].
2.3. Synthesis
Synthetic procedures, characterization of the compounds, and their IR and NMR spectra are given in the Supplementary Materials.
2.4. Protonation and Complexation Studies
Protonation and complexation studies were performed at room temperature. The solutions were prepared with double-deionized high-purity water (18.2 MΩ cm) obtained from a Millipore Simplicity apparatus. Solution concentrations and other experiment conditions are given in the corresponding figures and tables. Protonation studies were conducted in a glass beaker equipped with magnetic stirrer and pH-electrode adding HCl (4 or 0.01 M) or KOH (5 or 0.01 M) to the solutions of complexes. Metal-binding experiments were conducted by a manual addition of the aliquots of metal salt solutions by a Hamilton syringe to a solution of chemosensor placed in a quartz cuvette. All metal salts used were perchlorates of general M(ClO4)n·xH2O formula. Caution: although no problems were experienced, perchlorate salts are potentially explosive when combined with organic ligands and should be manipulated with care and used only in very small quantities.
The Hg(ClO4)2 solution was prepared in acetonitrile (HPLC, Merck) to avoid hydrolysis of the salt. Aqueous solutions of metal perchlorates were prepared with concentrations approximately 1000-fold of that of the ligands in order to decrease the influence of the medium changes on the spectra of the studied solutions. Stability constants were calculated using nonlinear least squares analysis by means of HYPERQUAD software [31] after factor analysis of the combined data sets [32]. The goodness of fit was assessed through the scaled standard deviation of the residuals (s), which has an expectation value of unity in the absence of systematic errors assuming a correct weighting scheme. The results were checked by plotting calculated molar extinction graphs (Figure S15). The calculated species distribution diagram for the Ru(N2P2phen)/Cu2+ system in water is shown in Figure S16.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
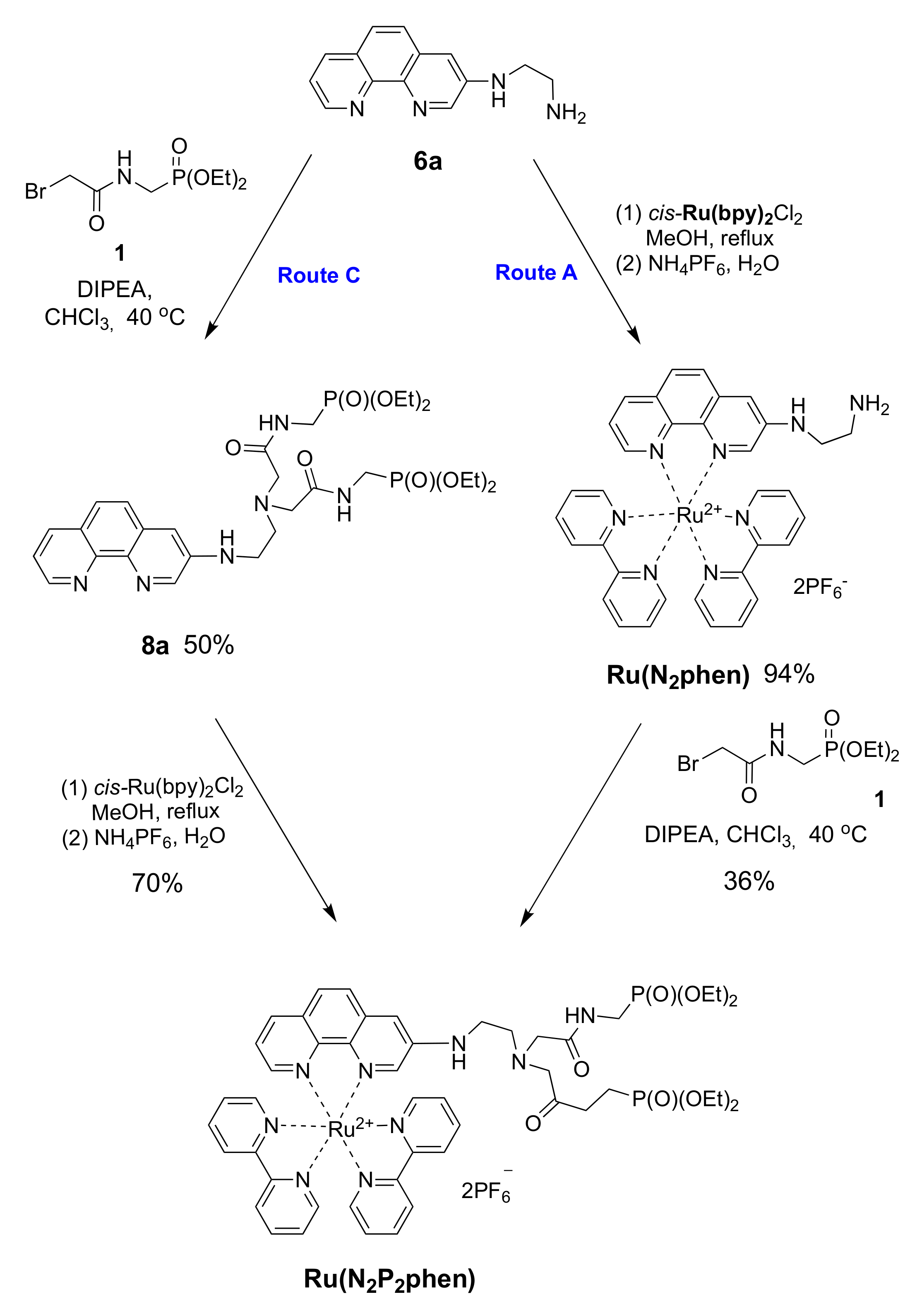
The molecular probe Ru(N2P2phen) can be obtained from available 3-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline (2) according to a three-step reaction sequence involving (i) the nucleophilic substitution of the bromine atom by a polyamine; (ii) the complexation of the phen chelator by cis-Ru(bpy)2Cl2; (iii) the N-alkylation of this compound by bromide 1. These reactions can be performed in various orders (Scheme 2). The amination can be placed before (Routes A and C) or after (Route B) the complexation of the phen ligand by ruthenium(II). Moreover, the N-functionalization can occur before the complexation (Route C) or in the last step of the synthetic scheme (Routes A and B).
The substitution of the bromine atom of the 1,10-phenanathroline ring by a polyamine is a challenging step in all of these synthetic approaches due to the rather low reactivity of such bromides in the nucleophilic substitution reactions. Palladium or copper catalyst is often required to perform these reactions, but both 1,10-phenantroline and polyamines are known to form stable complexes with these metals that can interrupt the catalytic cycle.
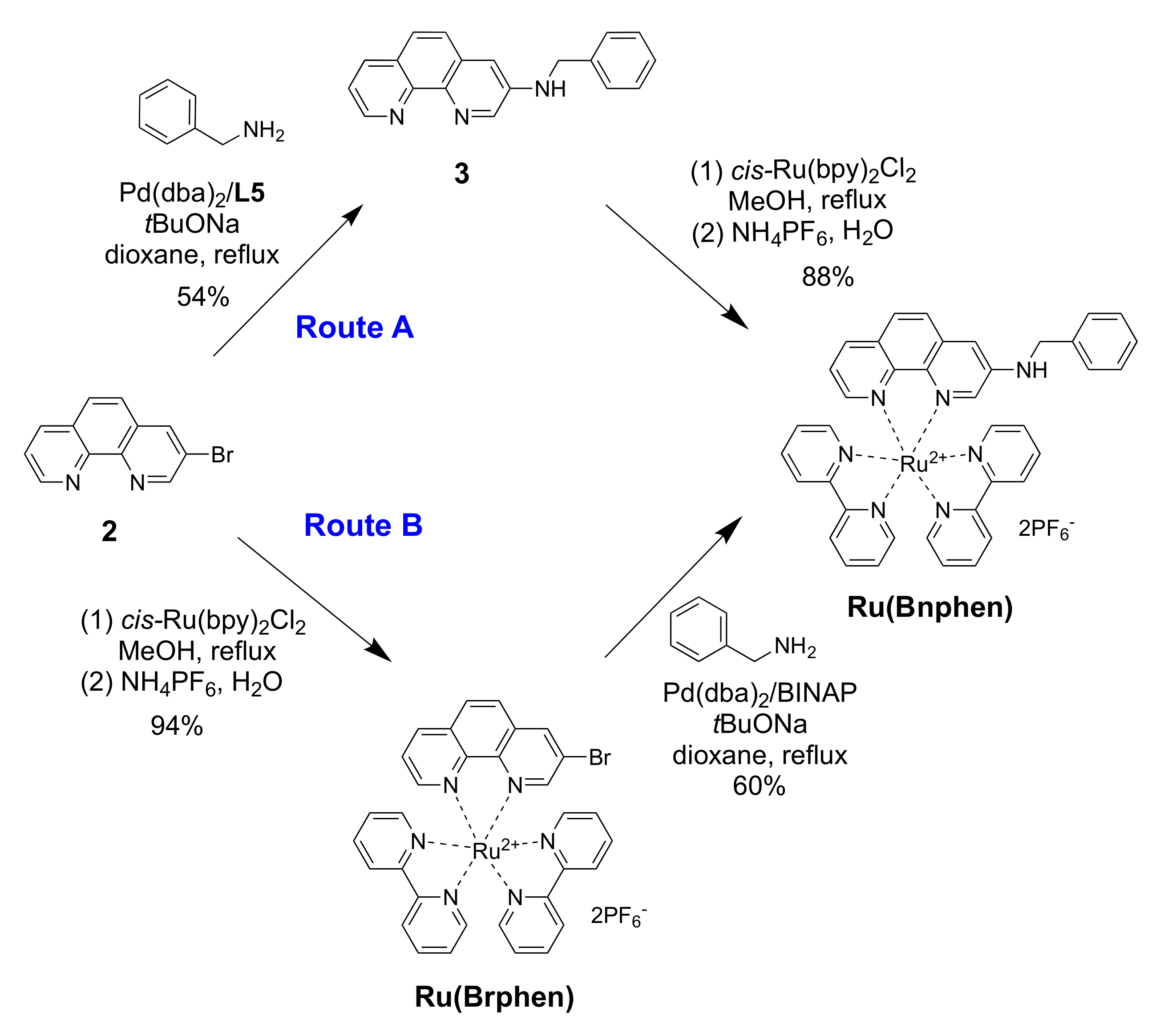
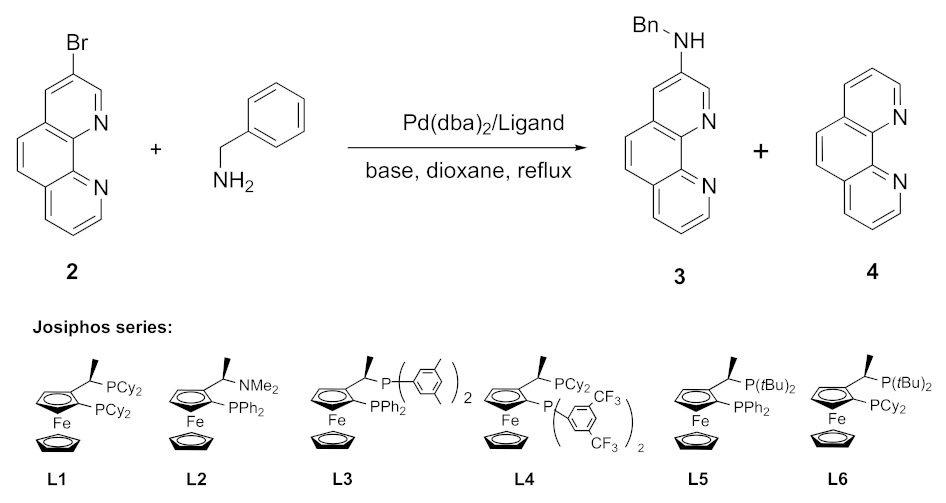
Preliminary experiments were performed using a more reactive and non-chelating primary amine, benzylamine (Scheme 3). The results of amination of 3-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline (2) (Route A, step 1) are summarized in Table 1.
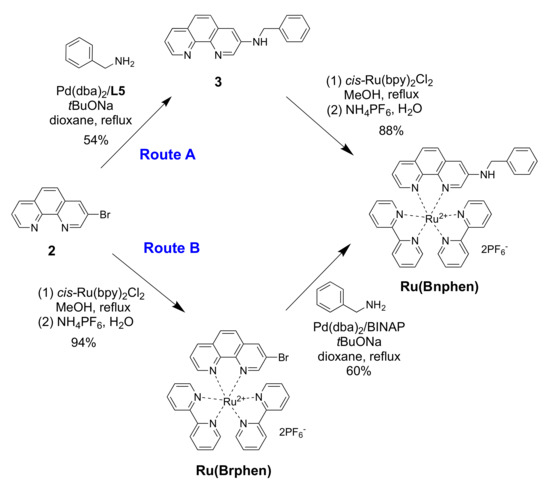
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of the aminophenanthroline-ruthenium complex Ru(Bnphen).

Table 1.
Amination of 3-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline (2) with benzylamine 1.
As expected, compound 2 did not react with benzylamine in DMF at 140 °C (entry 1), in contrast to the more reactive 1,10-phenanthrolines bearing halogen substituents at positions 4 or 7, which do react with amines under these conditions [33,34]. Copper- and palladium-catalyzed amination of 3-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline (2) were reported, but only for a few nucleophiles with enhanced NH acidity such as imidazole, carbazole, phenoxazine, or diarylamines [35,36,37,38]. Addition of CuI [36,39] in the reaction under study afforded exclusively the dehalogenated product, phen (4) (entry 2). Catalysis with palladium complexes under standard conditions (Pd(dba)2/BINAP, tBuONa, dioxane, and reflux) [40,41,42,43,44] also gave only this dehalogenated product (entry 3), and even a huge excess of ligand failed to suppress this reduction (entries 3 and 4), which is commonly observed as a side reaction in palladium-catalyzed C–N coupling [45,46]. Chelation of palladium with phen is likely to interfere, as it may hamper proper control of the coordination shell of the metal by the diphosphine ligand. Noteworthy is the fact that the more sterically hindered bromo-substituted 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenantrolines in the reactions with primary amines did not cause such problems [47].
Meanwhile, increasing the Pd(dba)2 loading up to 10 mol% resulted in the formation of target compound 3, though only as a minor product in 28% yield (entry 5). Further experiments in which the base and the solvent were varied along with increasing amounts of the amine and BINAP failed to provide any essential improvements (entries 6–9). Among many ligands tested (listed in Table 1 and Table S1), only some of the expensive ones belonging to the Josiphos family, like L5 and L6, afforded the desired coupling product 3 (entries 10–15) in reasonable yields (50–54%; Table 1, entries 14 and 15). Fortunately, further complexation of aminophenanthroline 3 to cis-Ru(bpy)2Cl2 was straightforward and gave the target complex Ru(Bnphen) in 88% yield (Scheme 3, Route A).
We also explored an alternative procedure (Route B in Scheme 3) consisting of the prior preparation of complex [Ru(Brphen)(bpy)2](PF6)2 (Ru(Brphen)) followed by the amination reaction. In this case, the phen chelator could not compete with the diphosphine ligand in the catalytic cycle, as it was engaged in a stable Ru complex.
The Ru(Brphen) complex was prepared in 94% yield and introduced in the amination reaction with benzylamine using the relatively cheap Pd(dba)2/BINAP catalytic system. This coupling was also accompanied by the reductive debromination leading to the [Ru(phen)(bpy)2](PF6)2 complex. The target compound, Ru(Bnphen), was isolated in 60% yield following this approach, which was twice as much as the yield obtained for the amination of bromide 2 using BINAP (Table 1, entry 5) and slightly better than the results obtained with the best L5 and L6 ligands (Table 1, entries 14 and 15). Nevertheless, the separation of the two highly polar complexes by column chromatography turned out to be laborious, especially in a scaled-up synthesis where the pure compounds were obtained only after three consecutive chromatographic runs. Thus, Route A, involving the amination of the ligand, was chosen for the preparation of polyamine derivatives.
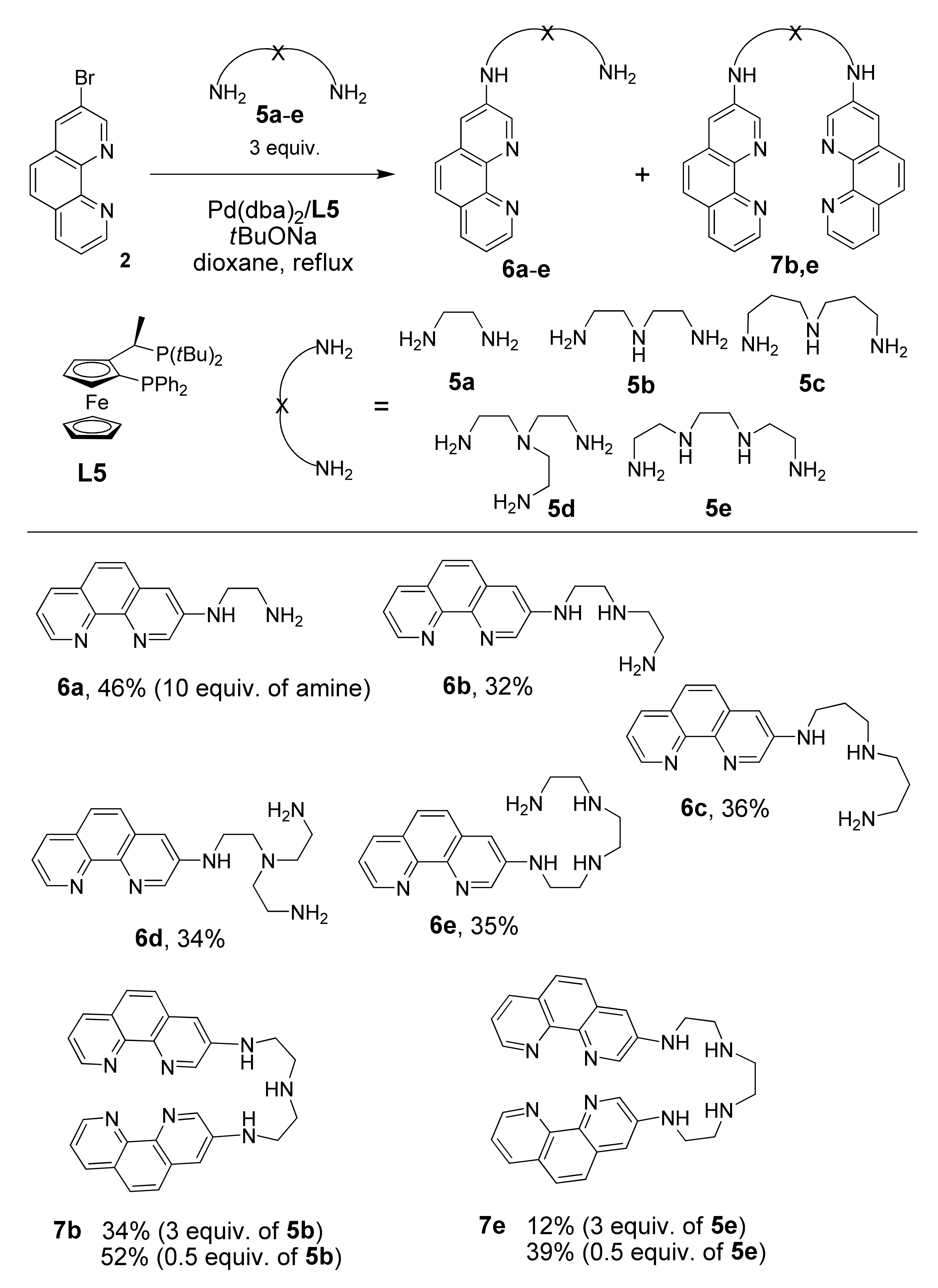
Bromide 2 was reacted with unprotected polyamines because the reactions of linear primary and secondary polyamines with aryl halides are known to be chemoselective and lead to the N-functionalization of only the primary amino groups [48]. The catalytic reactions of bromide 2 by chelating polyamines 5a–e, which differ by the number of nitrogen atoms and by length of the alkyl chains, were performed using the most efficient ligand, L5, by increasing the amount of the polyamines 5a–e up to 3 equivalents (and even to 10 equivalents in the case of volatile diaminoethane 5a) to diminish the consecutive coupling reactions leading to N,N’-bis(heteroaryl)-substituted products 7 (Scheme 4).
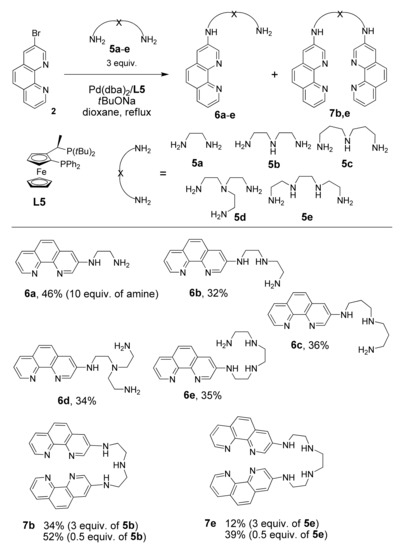
Scheme 4.
Pd-catalyzed synthesis of 1,10-phenanthroline-polyamine chelators 6a–e and 7b,e.
For all studied amines 5a–e, the complete conversion of starting bromide 1 was achieved within 24 h when the reaction was performed with 10 mol% of Pd(dba)2 and tBuONa in dioxane at reflux. However, the target products 6a–e were isolated in only moderate yields (32–46%) due to the competing reduction and amination of the second primary amino group of 6a–e, which produced polyamines 7. To diminish the yields of bisheteroarylated products, the amount of starting polyamine 5b–e was increased up to 5 equivalents Unfortunately, separation of the product from an excess of polyamine was much more complicated under these conditions in comparison with the reactions described above, and several consecutive chromatographic columns were required resulting in product loss. Only for 6b did we managed to increase the isolated yield up to 55% under these conditions.
Noteworthy was that the diarylated polyamines 7b and 7e could be obtained in good yields (52% and 39%, respectively) conducting the coupling reactions with 0.5 equivalents of the corresponding polyamines. This novel type of ambidentate bis(phenanthroline)–polyamine triads hold promise for development of sensors and supramolecular coordination polymers, which have recently attracted increasing interest [49].
Next, the N-alkylation of amine 6a with diethyl ((bromoacetylamino)methyl)phosphonate (1) was investigated. This reaction can also be performed using either the free chelator 6a or the corresponding ruthenium(II) complex (Scheme 5). The N-alkylation of amines (Route C) is a classical method of synthesis, although it is well known for its rather poor selectivity and the undesired formation of quaternary ammonium salts due to the fact of overalkylation. Moreover, in our case, a competitive alkylation of the aromatic amino group was also observed as a side reaction. After optimization of the reaction conditions, the target product 8a was obtained in 50% yield in chloroform at 40 °C using DIPEA as a base. The yield of Ru(N2P2phen) prepared from this chelator and cis-Ru(bpy)2Cl2 was only 70% due to the losses incurred from the high solubility of complex 8a in all organic solvents and aqueous media.
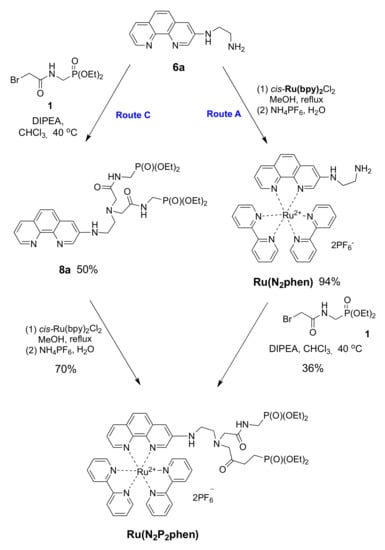
Scheme 5.
Synthesis of chemosensor Ru(N2P2phen).
Therefore, we tried to increase the selectivity of the N-alkylation by conducting the reaction with the Ru(N2phen) precursor, assuming a reduced nucleophilicity of the aromatic amino group compared to that exhibited by the free phenanthroline derivative as a consequence of electronic and steric effects (Route A). The complex Ru(N2phen) was prepared in 71% yield by reacting phenanthroline 6a with cis-(bpy)2RuCl2 before converting the reaction product with bromide 1 in the presence of DIPEA in chloroform. Unfortunately, the desired complex, Ru(N2P2phen), was obtained in 36% yield only after tedious chromatographic purification.
Thus, the insertion of a metal atom at the last step (Route C, Scheme 1) was the least resource- and time-consuming procedure among those explored, though comparable product yields can be obtained using other routes. It is worth noting that this synthetic pathway can be readily adapted for the synthesis of various visible light-active transition metals (RuII, IrIII, ReII, OsII, FeII, CoII, and PtII), if screening of chromogenic molecular probes would be needed.
The examples of the functionalization of Ru2+ complexes reported in this work unambiguously demonstrate that synthetic strategies based on introduction of the target substituent in the pre-formed Ru2+ complexes (“chemistry-on-the-complex”) [50] are of limited scope and hardly applicable to the preparation of complexes bearing ligands with any polar functional groups if the chromatographic purification of target product is required in the synthesis. According to our experience, the synthetic post-modification of the already assembled Ru2+ precursor could be of practical use only when the involved transformations are selective enough to afford the desired ruthenium complex after its precipitation from the reaction mixtures.
3.2. Optical Properties of Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen)
Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) are soluble in water at pH 0.5–12 and in 0.03 M HEPES solution under physiological conditions (pH = 7.4). Their spectroscopic data in aqueous media are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Photophysical data for Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen).
The electronic absorption spectra of both compounds in pure water were similar and typical for mixed ligand Ru(bpy)2(phen)-type complexes. For both compounds, the π-π* ligand-centered electronic transitions gave rise to intense bands in the 250–300 nm range [51,52]. The spectra also displayed characteristic broad absorption bands in the visible region that were assigned to the overlapping spin-allowed metal-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) and to interligand bpy/phen-based charge transfer (LLCT) transitions. The shape of the visible absorption bands was more complicated than that observed for [Ru(bpy)3](PF6)2. Their broadening was likely the result of an increased number of MLCT and LLCT transitions in these unsymmetrical heteroleptic complexes [23]. An additional absorption maximum appearing in the 300–350 nm region presumably corresponded to ligand-ligand π-π* transitions involving bipyridine and the aminated phenanthroline ligands [53]. As shown in Table 2, all bands were quite intensive which is welcome in view of further use in optical sensing.
Similar to many related ruthenium complexes [54], Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) are bright luminophores (Table 2). In aerated HEPES solutions, the emission spectrum for each complex showed a broad band extending over approximately the 500–700 nm range with a maximum at 601 nm. The shape of the absorption and emission bands as well as the quantum yields were concentration independent within the limits of the experimental method, which is indicative of the absence of significant aggregation in solution. The luminescence quantum yields of 4% and 3% for Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen), respectively, are roughly the same as those reported elsewhere for the parent [Ru(bpy)3]2+ chromophore in aqueous media (4.2%) [54] and aerated acetonitrile (3.2%) [55].
Both of the complexes studied have proton sensitive sites at the periphery of phenanthroline ring. Such complexes attracted constant interest as potential working elements of pH sensors. A wide range of new applications with specific demands justifies the development of novel pH-sensing concepts. The complexes with bipyridine ligands bearing hydroxy, sulfonic, and carboxylic groups or involving pyridine, imidazole, or calix [4] arene residues were investigated as luminescent molecular probes of pH levels [56,57]. Some of them were also successfully used in the development of photochemical-sensing devices [58,59,60]. To our knowledge, the reported Ru(II) complexes with phenanthroline ligands bearing the proton sensitive sites are limited to coordination compounds with 5-amino- [61] and 4,7-dihydroxy-1,10-phenanthrolines [62]. While the emission of the first compound is almost independent of pH, the luminescence of the hydroxy-substituted derivative varied in a wide pH range that was used to develop optical pH sensor devices for pH measuring in an unusually broad range of acidity levels [58].
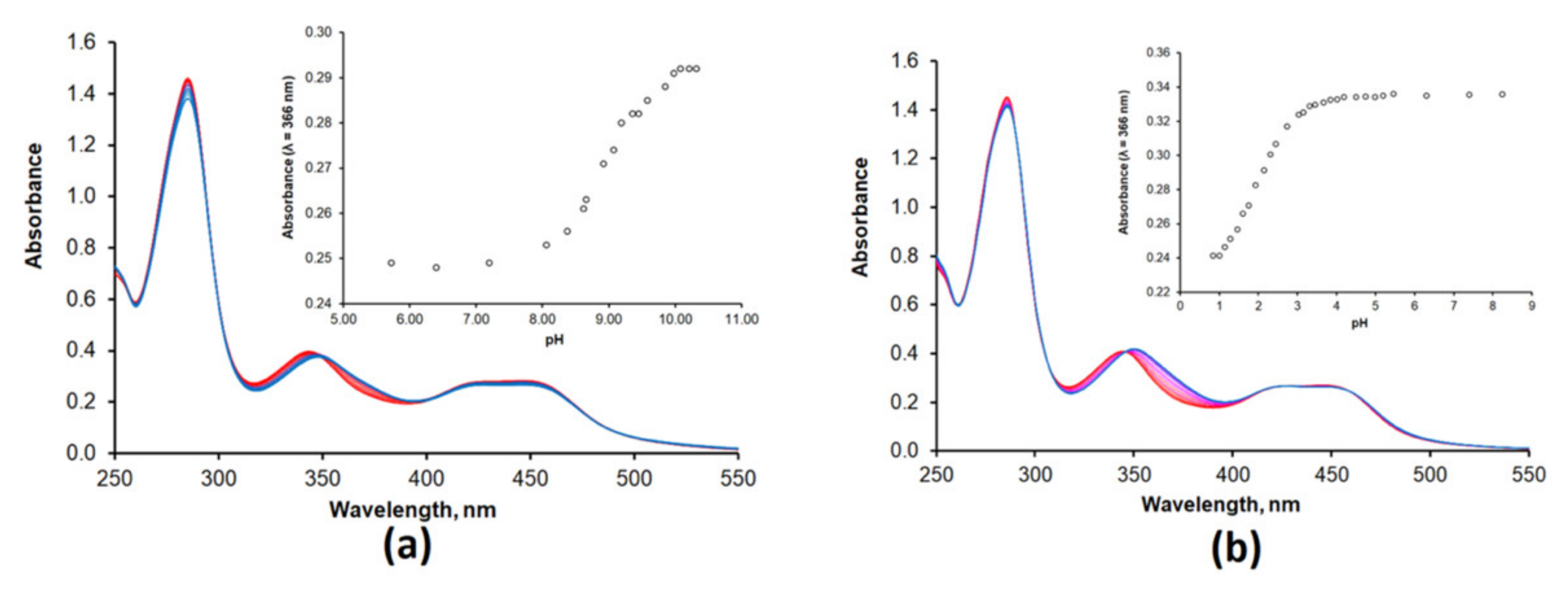
We briefly investigated the acid–base behavior of Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) by performing UV–Vis and luminescence titrations of these complexes in the range of pH 1–12 (Figure 1 and Figures S1–S8).
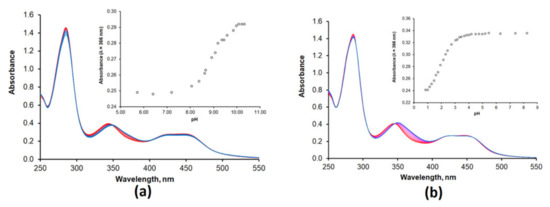
Figure 1.
Evolution of the electronic absorption spectra of the compound Ru(N2phen) ([Ru(N2phen)]tot = 33 μM) (a) and Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)]tot = 21 μM) (b) as a function of pH. The range of pH 1–12 was investigated for both complexes, but only the region of pH changing (see insets) are shown in the figure. Insets show the pH dependence of the absorbance at λabs = 336 nm.
The protonation of the nitrogen atom separated from the light absorbing aromatic moiety by a saturated NCH2CH2 linker had a rather weak influence on the light absorption by the complexes Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) despite the presence in the linker of the nitrogen atom directly bonded to chromogenic unit and capable of the intramolecular hydrogen binding of protonated sites. Surprisingly, in the electronic absorption spectra of both complexes, only the band with the maximum at 350 nm was progressively blue-shifted from 350 to 346 nm upon gradual addition of hydrochloric acid. In contrast, the bands presumably corresponding to the lowest-energy MLCT transitions in the visible region (400–550 nm) were almost independent on pH. Similar changes in electronic adsorption spectra were reported for {Ru(bpy)2[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,2’-bipyridine]}(PF6)2 and tentatively explained assuming that the pH-sensitive site is not attached to the ligand involved in formation of the ground and exited states [63]. To obtain deeper insight into the electronic properties of our complexes, basic DFT computations were performed (Figure 2).
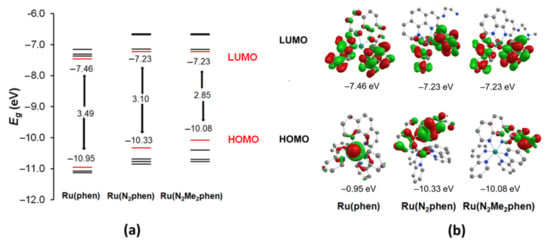
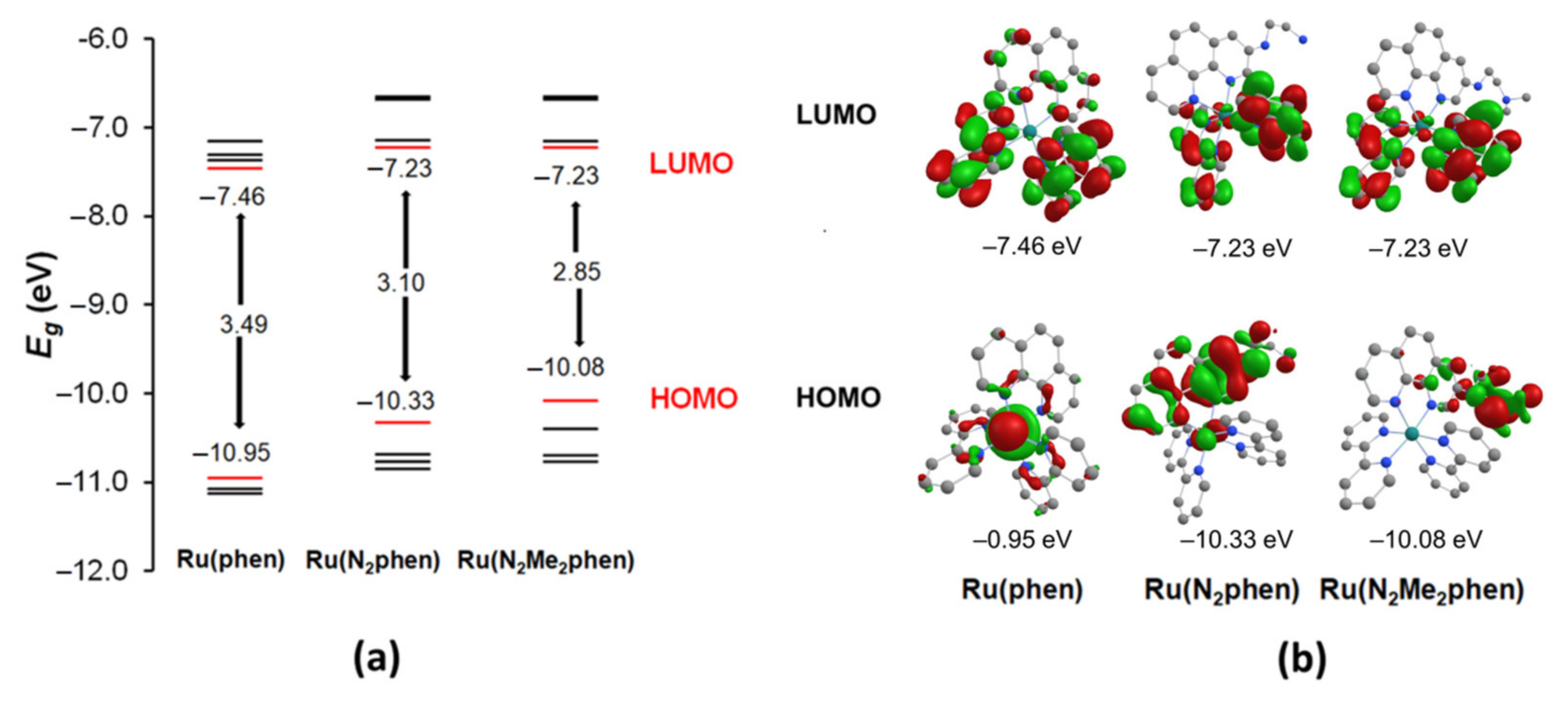
Figure 2.
The schematic representation of the calculated energy levels in Ru(phen), Ru(N2phen), and Ru(N2Me2phen) (a) and isodensity plots of the HOMO and LUMO orbitals for these complexes (b).
The DFT calculations with the Firefly quantum chemistry package [64], which is partially based on the GAMESS (US) [65] source code, were used to model the structure of the complexes. The B3LYP functional with the STO 6–31G(d,p) basis set was used in the calculations for all elements except ruthenium, for which the Stuttgart valence basis set and pseudopotential were employed [66]. The amidophosphonate fragment of Ru(N2P2phen) was replaced by a smaller methyl group and the corresponding complex was labeled Ru(N2Me2phen). The optimized geometries of complexes Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2Me2phen) are depicted in Figures S20 and S21 (see Supplementary Materials). The metal atom had a distorted octahedral geometry and bonded to three chelate groups. The key structural parameters (i.e., Ru–Nphen, Ru–Nbpy bond length, and dihedral angles between ligand planes) of the chromogenic unit changed only slightly when alkyl substituents were introduced at the nitrogen atom of 1,10-phenanthroline ligand.
The isodensity plot of their HOMO and LUMO orbitals and the diagram showing their energy levels are shown in Figure 2 and compared to those of the parent complex [Ru(bpy)2(phen)]2+. Comparing the frontier orbitals of amino-substituted complexes to those of parent Ru(phen), one can notice that only in the last complex are both HOMO and HOMO−1 localized mainly on the Ru atom, while in other complexes the contribution of π orbitals of phen ligand is much more significant and dependent on the substitution pattern of the phenanthroline ring. The LUMO0 and LUMO+1 orbitals of all complexes were constructed mainly of π orbitals of bipyridine ligands, and only LUMO+3 and LUMO+4 (not shown in Figure 2, see Tables S2 and S3) consisted of π orbitals of the aminophenanthroline ligand. Thus, the ligand to ligand charge transfer transition is supposed to give rise to intensive bands and can be red-shifted compared to the parent Ru(phen) complex. The absorption bands in the 340–360 nm region of the electronic absorption spectra of these complexes could correspond to MLCT transitions or an LL’ transition with participation of the phenanthroline π orbitals. To obtain deeper insight into the studied question, correct modeling of the exited states of Ru2+ complexes is required, which can only be performed by sophisticated methods beyond the popular TD-DFT approach and, therefore, is beyond the scope of our work focusing on practical aspects of their use in analytic chemistry.
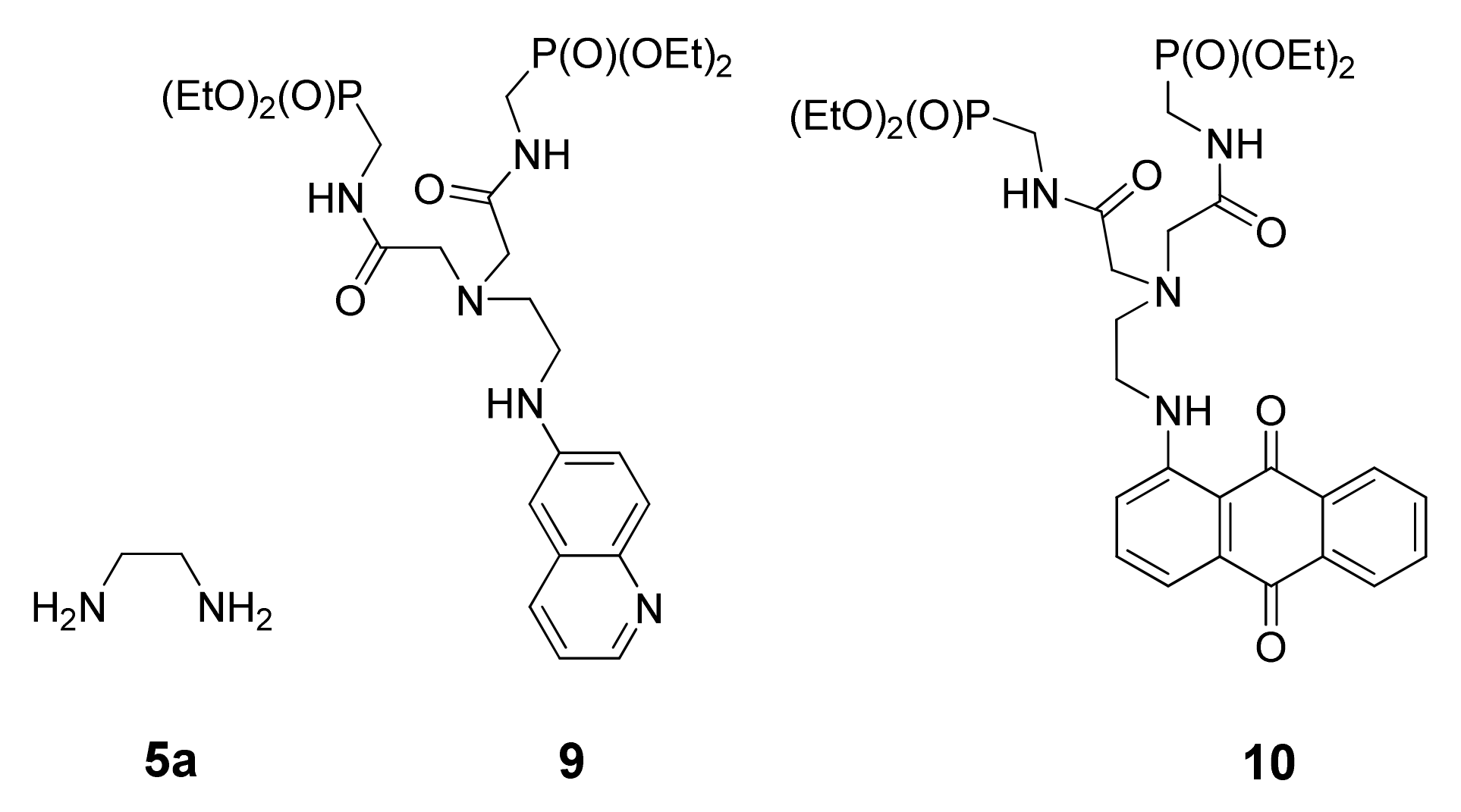
To determine the apparent protonation constants, numerical data fitting of spectrophotometric titration curves was performed using the HypSpec program (Figures S1–S3 and S5–S7) [30]. The best fits for both complexes were obtained when the UV–Vis titration data were processed with a single equilibrium model (L + H+ ⮀ LH+) that confirmed that the nitrogen atom directly linked to the phenanthroline ring cannot be protonated in aqueous medium. The refined values are collected in Table 3, together with the literature data for 1,2-diaminoethane (5a) [67] and the previously reported chemosensors 9 and 10 both bearing the same ionophore unit as the studied Ru(N2P2phen) (Figure 3) [68,69]. The distribution diagrams and electronic absorption spectra of the complexes, Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen), and their monoprotonated forms calculated using the HypSpec program are shown in Figures S3 and S7, respectively.

Table 3.
Apparent protonation constants or pKa of Ru(N2phen), Ru(N2P2phen), 5a, 9, and 10 1.
Figure 3.
Structure of relevant compounds (i.e., 5a, 9, and 10) for which protonation constants have been reported in the literature. The corresponding values are summarized in Table 3.
As it can be seen from Table 3, the protonation of Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) occurs in separate pH ranges, in full agreement with the expected lower basicity of nitrogen atoms of Ru(N2P2phen) due to the presence of two electron-withdrawing substituents. It is noteworthy that under physiological conditions, Ru(N2phen) predominantly exists in the monoprotonated form while the polyamine chain of Ru(N2P2phen) is not protonated.
Comparing Ru(N2phen) with 1,2-ethanediamine and Ru(N2P2phen) with dyes 9 and 10 bearing the same receptor unit (Figure 3), it can be concluded that the presence of a signaling group and its nature (organic vs. [Ru(bpy)2(phen)]2+ chromophore) has only a weak influence on the acidity of the studied compounds, despite the positive charge of Ru(II)-based signaling group, which can be explained by separation of the protonated nitrogen atoms from this signaling group by aminoethylene linkers.
The emission of the complexes Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) remained virtually constant over a wide pH range (pH = 0.5–10) (Figures S4 and S8). However, it diminished quickly and in a similar manner for both complexes in more basic solutions probably due to the fact of their partial decomposition under irradiation in the presence of strong bases, as it was already reported for the [Ru(bpy)2(5-aminophenanthroline)](PF6)2 complex [61]. We assumed that the protonation of the polyamine chain had a negligible effect on the emission properties of the complexes due to the lack of efficient photoinduced electron transfer (PET) process from the side-chain amine groups to the [Ru(bpy)2(phen)]2+ moiety as already reported for aliphatic amines and ruthenium–polypyridyl complexes [70]. It is noteworthy that this is in contrast to the behavior of the analogous compound 9 bearing the same polyamine chain attached to the 6-quinolinyl signaling group in which the protonation of the nitrogen atom leads to the increase in fluorescence intensity [68].
Thus, Ru(N2phen) and Ru(N2P2phen) can be considered suitable dyes for spectroscopic monitoring of various analytes in aqueous media due to the fact of their high solubility and brightness. The low basicity of Ru(N2P2phen) is favorable for sensing metal ions at physiological pH (pH = 7.4), avoiding the competitive protonation of the ionophore under nearly neutral conditions.
3.3. Detection of Metal Cations in Solution
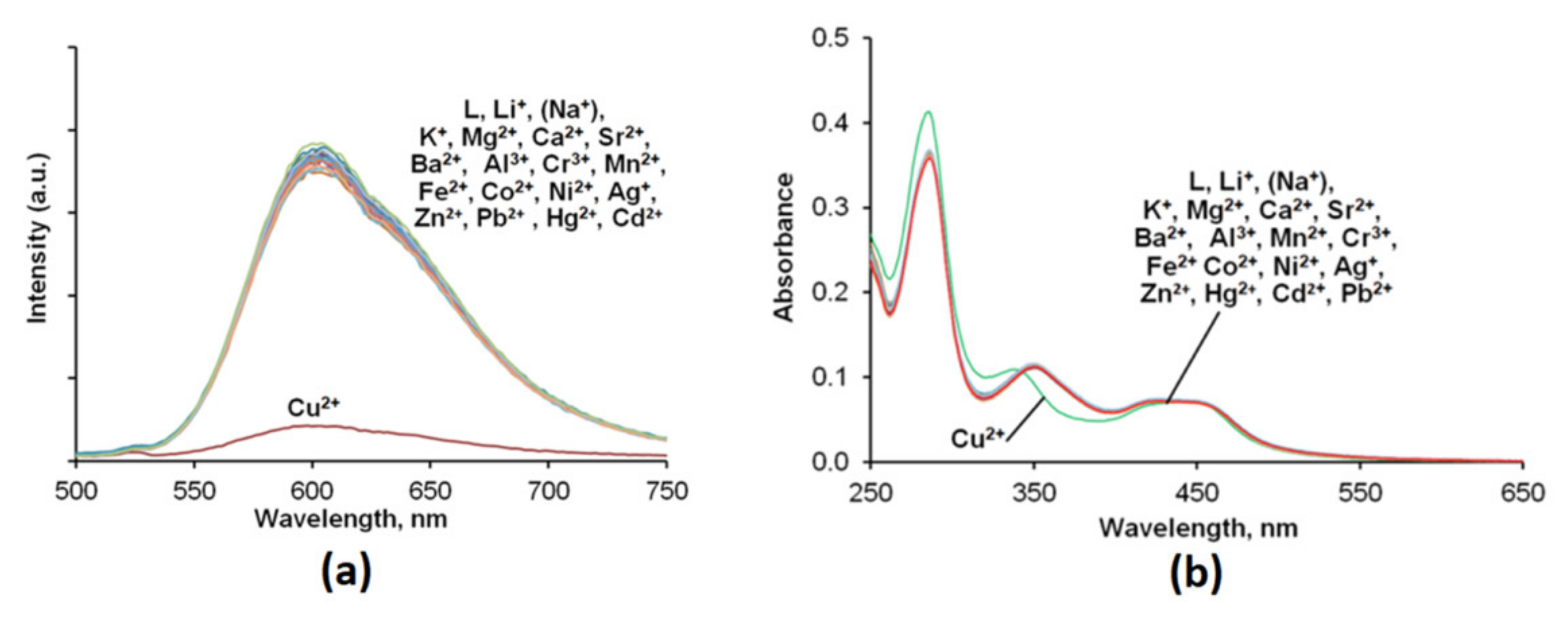
The sensing properties Ru(N2P2phen) were evaluated at a constant pH of 7.4 in HEPES buffered (c = 0.03 M) aqueous solutions. Firstly, UV–Vis absorption and emission spectra were recorded before and after the addition of 15 equivalents of 18 different metal perchlorate salts to the same Ru(N2P2phen) solution (Figure 4 and Figure S10). Among all tested cations (i.e., Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Ag+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Al3+, and Cr3+), only Cu2+ induced an immediate change in the electronic absorption spectrum in the UV region (Figure S12), together with a partial but significant quenching of the luminescence (Figure 4) that could be detected instrumentally but also visually. The detection of Cu2+ ions, which are abundant in tap water and many food products, attracts considerable attention [71,72,73,74] due to the harmful effects of this metal on human health [75,76]. Sensing of Cu2+ by related [Ru(bpy–ionophore)(bpy)2] complexes in which the signaling and receptor moieties are separated by an alkyl group was also investigated and led to the conclusion that emission quenching proceeds via the energy transfer rather than the electron transfer mechanism [77,78].
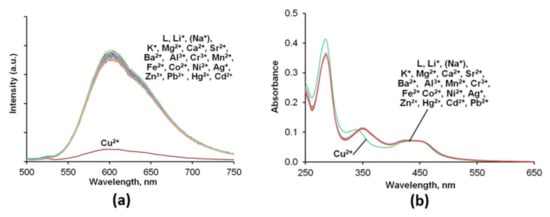
Figure 4.
Fluorescence (a) and absorption spectra (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution before and after addition of 15 equivalents of metal perchlorate salts. [Ru(N2P2phen)]tot = 5.4 μM, pH = 7.4, [HEPES] = 0.03 M, and [Mn+]tot = 81.0 μM for each metal ion. λex = 450 nm.
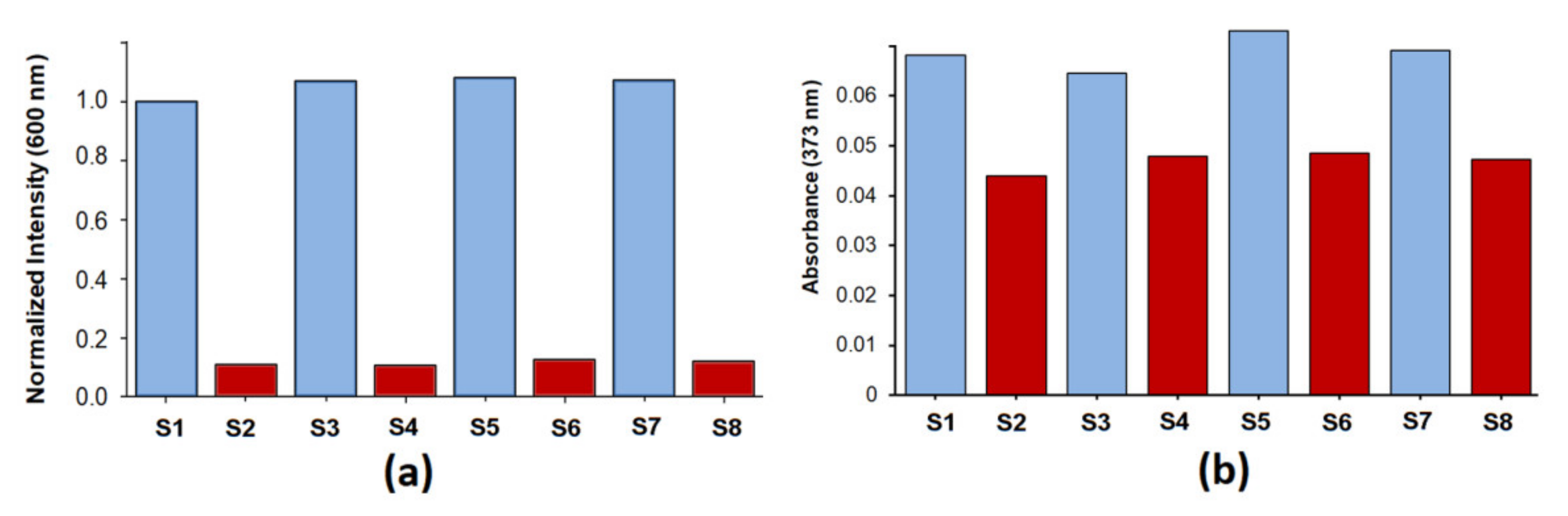
As shown in Figure 5a,b and Figures S11 and S13, the competitive binding study revealed that Cu2+ could effectively be monitored in the presence of other metal ions including Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Ag+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, and Al3+.
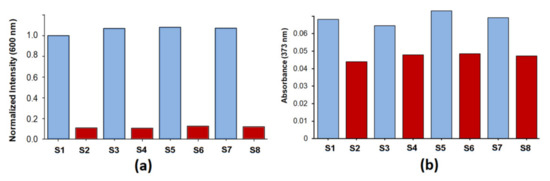
Figure 5.
Cross-selectivity studies of metal ion binding by the ligand Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 5.4 μM, pH = 7.4, [HEPES] = 0.03 M, and λex = 450 nm) using fluorescence spectroscopy (a) and electronic absorption spectroscopy (b): (S1) intensity at 600 nm (a) and absorption at 326 nm (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution; (S2) intensity at 600 nm (a) and absorption at 326 nm (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents); (S3) intensity at 600 nm (a) and absorption at 326 nm (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Li+, (Na+), K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, and Al3+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S4) spectrum of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Li+, (Na+), K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Al3+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion), and Cu2+ (15 equivalents); (S5) intensity at 600 nm (a) and absorption at 326 nm (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S6) spectrum of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion), and Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents); (S7) intensity at 600 nm (a) and absorption at 326 nm (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S8) intensity at 600 nm (a) and absorption at 326 nm (b) of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution after addition of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion), and Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents).
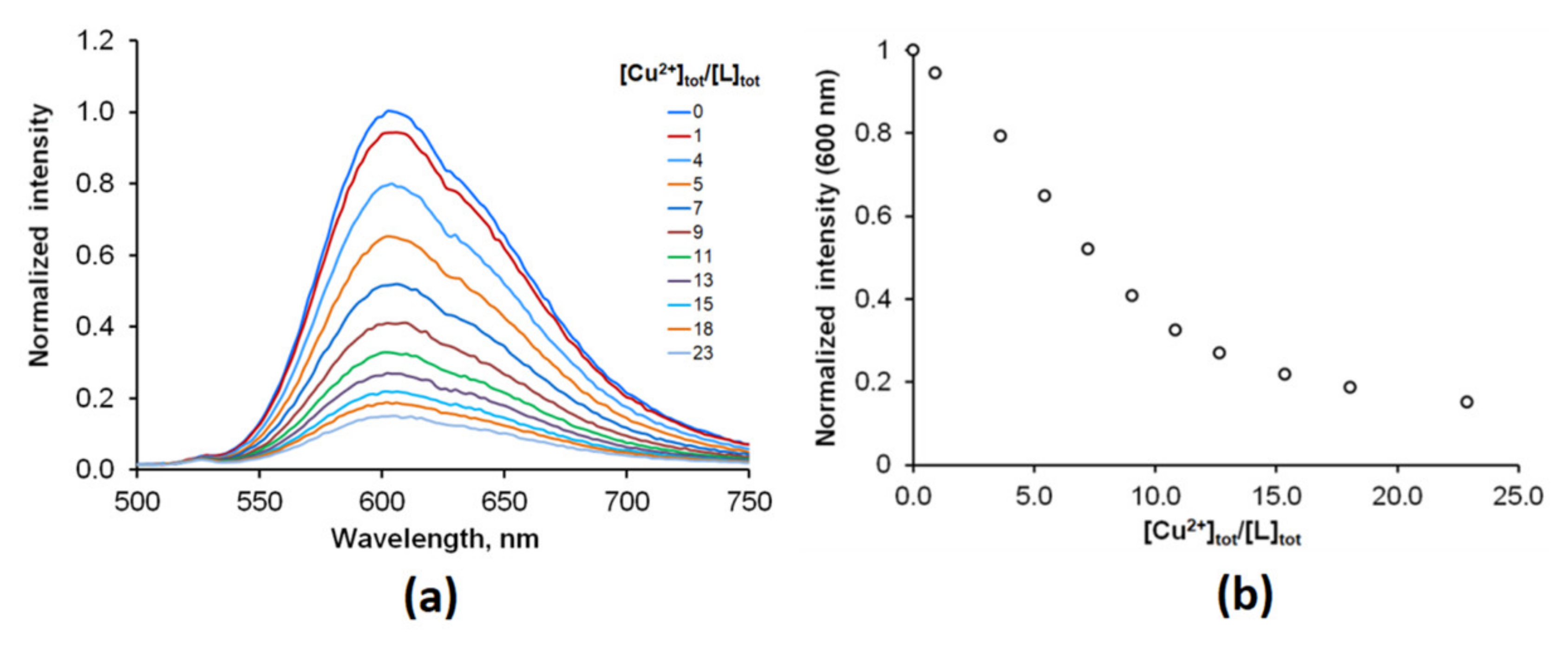
The selectivity did not change with time and can be explained by a higher affinity of Ru(N2P2phen) for Cu2+ compared to other metal ions. The titration experiments showed that the stability constant of the bimetallic {Cu[Ru(N2P2phen)]}4+ complex was as low as log β = 4.2 (1), and more than 20 equivalents of copper are required to saturate the receptor (Figure 6 and Figure S14).
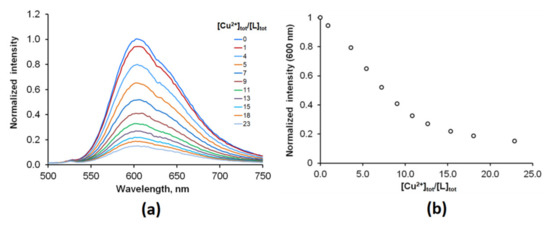
Figure 6.
(a) Evolution of the fluorescence spectrum of the Ru(N2P2phen) solution upon addition of Cu(ClO4)2 (0–23 equivalents) ([Ru(N2P2phen)]tot = 5.4 μM, pH = 7.4, [HEPES] = 0.03 M, ([Cu2+]tot = 0–128 μM and λex = 450 nm). (b) Changes in the fluorescence intensity with [Cu2+]tot/[Ru(N2P2phen)]tot ratio at λem = 600 nm. [Cu2+]tot concentrations for each point: 1–0; 2–5.2; 3–20.7; 4–31.0; 5–41.3; 6–51.5; 7–61.7; 8–71.8; 9–86.9; 10–102.0; 11–128.0 μM.
However, with a detection limit (LOD) of 9 and 6 µM, as estimated by absorption and emission spectrophotometry, respectively, Ru(N2P2phen) can be used for the analysis of tap water, because the copper action level in drinking water is fixed at 20 µM by the US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) [79]. Interestingly, despite its rather low affinity to Cu2+ ion, the sensibility of Ru(N2P2phen) is comparable to other organic molecular probes, including chemosensors 9 [68] and 10 [69], as a consequence of its high brightness in aqueous media. It is also worth noting that chemosensors based on luminescent ruthenium tris(diimine) complexes have previously been reported, and some of them displayed lower detection limits [19,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87].
Unfortunately, all our attempts to grow single crystals of the copper(II) complex of Ru(N2P2phen) failed. Hence, structural information on the complex was gained by combining UV–Vis, FTIR, and ESI-HRMS analyses of the sample prepared by the treatment of the Ru(N2P2phen) chemosensor with one equivalent of Cu(ClO4)2 in methanol and the evaporation of the solvent to dryness.
The ESI-HRMS signal corresponding to the [Cu+Ru(N2P2phen)–2H]2+ species confirmed the formation of 1:1 copper adduct (Figure S17). A hypsochromic shift of the absorption maximum observed for Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Cu2+ ions in electronic absorption spectrum, presumably indicates that the coordination of the aromatic nitrogen atom to Cu2+ was observed under studied conditions.
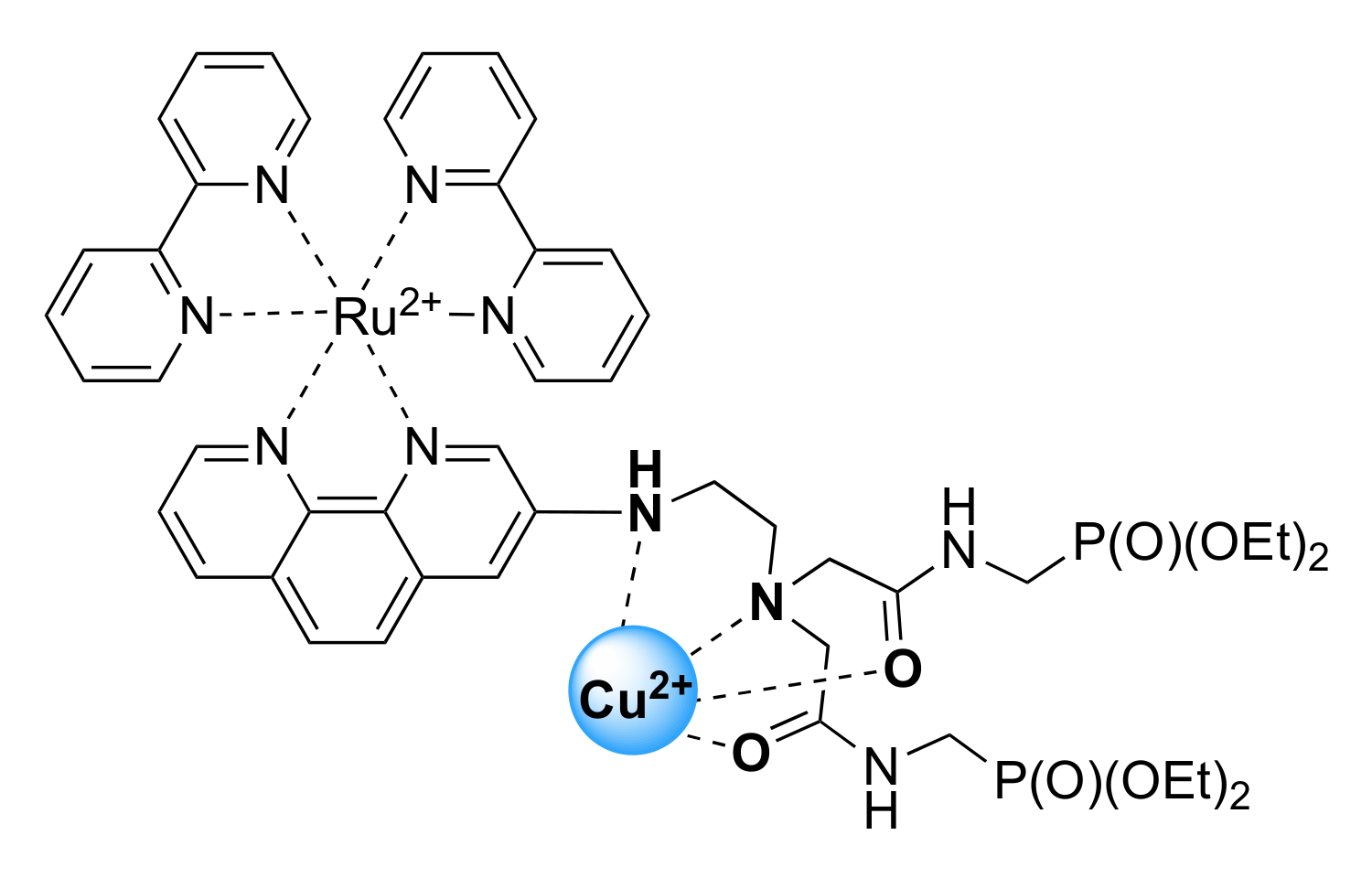
Coordination of the amide groups was inferred from FTIR spectra collected in the 1500–1700 cm−1 region for {Cu[Ru(N2P2phen)]}4+ and Ru(N2P2phen) (Figures S18 and S19). The amide I (νC=O = 1669–1671 cm−1) and amide II (δCNH = 1524–1531 cm−1) bands of the ligands were present in the spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) (Figure S18). The νC=O vibration energy is diagnostic for the extent of π-electron delocalization. The amide I band appears in the 1615–1625 cm−1 region when the carbonyl oxygen atom is bound to a metal [88], whereas coordination of the deprotonated nitrogen atom (the amidate binding mode) produces a red shift of the ν=O vibration mode down to ~1580 cm−1. In our case, the spectral interpretation is intricate owing to the overlap of several other bands in this region. Nevertheless, we can safely conclude that the νC=O stretching modes appear in the 1635–1590 cm−1 region, indicating that most probably the oxygen atom of the amide group is coordinated to the metal center (Figure 7).
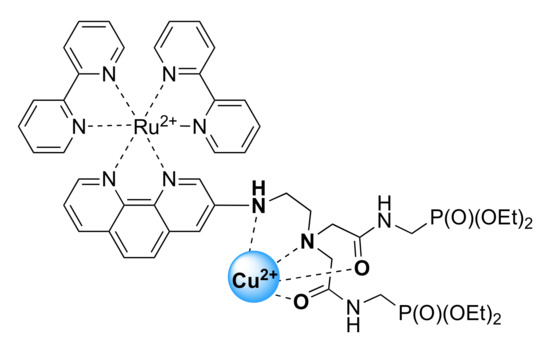
Figure 7.
Schematic presentation of binding mode of Ru(N2P2phen) ligand in coordination shell of copper(II) ion.
The importance of the functionalization of the primary amine group for Cu2+ complex formation was demonstrated in comparative studies of Cu2+ binding by Ru(N2P2phen) and Ru(N2phen) chelators. Both the UV–Vis and emission spectra of Ru(N2phen) were insensitive to the presence of Cu2+ ions, even when these ions were present in the studied solution in large excess (30 equivalents), which indicates that the diaminoethylene residue of Ru(N2phen) does not ligate any metal ions in aqueous media (Figure S9). The lower affinity of Ru(N2phen) to Cu2+ ions compared to that of Ru(N2P2phen) can likely be explained by the protonation of its probably primary amine group at physiological pH (Table 2) and a decrease in the number of donor groups in the receptor unit. Thus, the electron-withdrawing amide groups may be expected to play a decisive role in the complexation of Cu2+ ions while the selectivity of this ligand probably resulted from a rather low metal affinity of diaminoethane fragment bearing heteroaromatic substituent (1,10-phenanthroline) at the nitrogen atom.
Ru(N2P2phen) would be suitable for the real-time dual-channel (UV–Vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopies) analysis of tap water. It is noteworthy that most of the so far reported luminescent [Ru(diimine–ionophore)(diimine)2] conjugates exhibited negligible changes in their electronic absorption properties upon addition of Cu2+ ions [19,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,89]. The markedly enhanced spectral response of Ru(N2P2phen) can be directly ascribed to the conjugation of the ionophore with the 1,10-phenanthroline core. Another important advantage of the newly synthesized chemosensor is the presence of the phosphonate anchoring groups that do not participate in the coordination of the copper atom (Figure 7) and can be used in developing photochemical sensing devices.
4. Conclusions
3-Polyamine-substituted 1,10-phenanthtrolines are now available from commercial starting compounds in one step. These compounds were prepared by the selective Pd-catalyzed amination of 3-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline by PAs. These ditopic ligands are of interest for developing bimetallic supramolecular polymers and molecular probes. In this work, synthetic approaches to their Ru2+ complexes were investigated to prepare emissive complexes for sensing applications. We also demonstrated using Ru(N2phen) as a representative example that parent Ru2+ complexes bearing PA receptors can be modified by diethyl ((bromoacetylamino)methyl)phosphonate to obtain water-soluble molecular probes. The target complex Ru(N2P2phen) was also prepared using a stepwise modification of [Ru(bpy)2(Brphen)](PF6)2 to compare “chemistry-on-the-complex” and “chemistry-on-the-ligand” synthetic approaches. These studies demonstrated that the functionalization of ligands is more convenient in the synthesis of Ru2+ complexes with hydrophilic functional groups.
The optical and sensing properties of the water-soluble Ru(N2P2phen) complex were investigated and compare to those of the parent Ru(N2phen). The Ru(N2P2phen) complex allows for selective double-channel detection of the Cu2+ ion at physiological pH by monitoring simultaneously the absorption changes and the phosphorescence turn-off (ON–OFF probe) of the test solution. Among all tested cations (i.e., Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Ag+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Al3+, and Cr3+), only Cu2+ induced an immediate change in the electronic absorption spectrum in the UV region, together with a partial but significant quenching of the luminescence that could be detected instrumentally but also visually. The LOD of Cu2+, determined by spectrophotometry and fluorescence spectroscopy, was equal to 9 and 6 μM, respectively. The importance of functionalization of the primary amine group for sensing was demonstrated in comparative studies of Cu2+ binding by Ru(N2P2phen) and Ru(N2phen) chelators. Ru(N2P2phen) can be used for the analysis of tap water and hold promise in the development of photochemical sensing devices due to the presence at the periphery of the phenanthroline ligand of two phosphonate anchoring groups.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors10020079/s1, Synthetic prosedures, Figure S1: Spectrophotometric titration of Ru(N2phen) ([Ru(N2phen)] = 33 μM, I = 0.1 M KCl, pH = 5.7–11.6), Figure S2: Absorbance changes with pH at λ = 367 nm for Ru(N2phen), Figure S3: (a) UV–vis spectra of Ru(N2phen) and [Ru(N2phen)H]+ in water calculated using Hyperquad program [31]. (b) Species distribution diagram for the Ru(N2phen)/H+ system in water calculated using Hyperquad program [31], Figure S4: Fluorimetric titration of Ru(N2phen) ([Ru(N2phen)] = 11 μM, I = 0.1 M KCl, λex = 450 nm, pH = 5.7–10.5), Figure S5: Spectrophotometric titration of Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 21 μM, I = 0.1 M KCl, pH = 1.0–9.2), Figure S6: Absorbance changes with pH at λ = 330 nm for Ru(N2P2phen), Figure S7: (a) UV–vis spectra of Ru(N2P2phen) and [Ru(N2P2phen)H]+ in water calculated using Hyperquad program [31]. (b) Species distribution diagram for the Ru(N2P2phen)/H+ system in water calculated using Hyperquad program [31], Figure S8: Fluorimetric titration of Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 6.6 μM, I = 0.1 M KCl, λex = 450 nm, pH = 1.1–9.3), Figure S9: Evolution of fluorescence spectrum of Ru(N2phen) upon addition of Cu(ClO4)2 (0–30 equivivalents) ([Ru(N2phen)] = 11 μM, 0.03M HEPES buffer, pH = 7.4, λex = 450 nm), Figure S10: Fluorescence spectra of Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 5.4 μM, 0.03M HEPES buffer, pH = 7.4, λex = 450 nm) before and after addition of 15 equivalents of metal perchlorates ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM for each metal ion); (b) Normalized fluorescence intensity of the studied solutions at λem = 600 nm, Figure S11: Cross-selectivity studies of metal ion binding by ligand Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 5.4 μM, 0.03M HEPES buffer, pH = 7.4, λex = 450 nm) using fluorescence spectroscopy: (S1) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen); (S2) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Cu2+ (15 equivalents, [Cu2+]tot = 81 μM); (S3) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Li+, (Na+), K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Al3+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S4) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Li+, (Na+), K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Al3+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion) and Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents); (S5) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S6) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion) and Cu2+ (15 equivalents, [Cu2+]tot = 81 μM); (S7) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S8) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion) and Cu2+ (15 equivalents, [Cu2+]tot = 81 μM), Figure S12: (a) Absorption spectra of Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 5.4 μM, 0.03M HEPES buffer, pH = 7.4) before and after addition of 15 equivalents of metal perchlorates ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM); (b) Absorbance of the studied solutions at λ = 380 nm, Figure S13: Cross-selectivity studies of metal ion binding by ligand Ru(N2P2phen) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 5.4 μM, 0.03M HEPES buffer, pH = 7.4) using UV-vis spectroscopy: (S1) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen); (S2) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents); (S3) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Li+, (Na+), K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Al3+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S4) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Li+, (Na+), K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Al3+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion) and Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents); (S5) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S6) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion) and Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents); (S7) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion); (S8) emission spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) after addition of Ag+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ ([Mn+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents of each metal ion) and Cu2+ ([Cu2+]tot = 81 μM, 15 equivalents), Figure S14: (a) Evolution of UV–vis spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) upon addition of Cu(ClO4)2 (0–18) equivalents) ([Ru(N2P2phen)] = 5.6 μM, 0.03M HEPES buffer, pH = 7.4). (b) Changes of absorbance with [Cu2+]tot/[Ru(N2P2phen)]tot ratio at λ = 326 nm upon addition of Cu(ClO4)2 (0–18), Figure S15: (a) UV–vis spectra of Ru(N2P2phen)2+ and [Ru(N2P2phen)Cu]4+ in water calculated using Hyperquad program [31], Figure S16: Species distribution diagram for the Ru(N2P2phen)/Cu2+ system in water calculated using Hyperquad program [31] (Model for calculation: L⮀LH+; Cu2++L⮀[CuL]2+; Cu2+⮀Cu(OH)+⮀Cu2(OH)22+⮀Cu(OH)2), Figure S17: HRMS (ESI) spectrum of the {Cu[Ru(N2P2phen)]}(ClO4)2 complex, Figure S18: FTIR spectrum of Ru(N2P2phen) (neat), Figure S19: FTIR spectrum of complex {Cu[Ru(N2P2phen)]}(ClO4)2 (neat), Figure S20: The structure of Ru(N2phen) complex obtained by full geometry optimization at B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level, Figure S21: The structure of Ru(N2Me2phen) complex obtained by full geometry optimization at B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level, Figures S22–S45: NMR spectra of new compounds, Figure S46: FTIR spectrum of Ru(Bnphen) (neat), Figure S47: FTIR spectrum of Ru(N2phen) (neat); Table S1: Optimization of the amination reaction conditions, Table S2: Calculated isodensity plot of the HOMO and LUMO orbitals for complex Ru(N2phen), Table S3: Calculated isodensity plot of the HOMO and LUMO orbitals for complex Ru(N2Me2phen).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.-L. and I.P.B.; Methodology, A.S.A.; Investigation, A.S.A., A.V.C. and A.D.A.; Writing—Original draft preparation, A.S.A.; Writing—Review and editing, A.B.-L., M.M. and A.S.A.; Visualization, A.S.A.; Project administration, A.B.-L. and A.D.A.; Funding acquisition, A.B.-L., A.S.A. and I.P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grant no. 18-33-00279). Financial support from the CNRS, the Conseil Régional de Bourgogne (PARI IME SMT8 and PARI II CDEA programs), and the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) is also acknowledged. A.S.A. is grateful to the French government and French embassy in Russia for the SSTE-2016 grant. This work was carried out in the frame of the International Associated French–Russian Laboratory of Macrocycle Systems and Related Materials (LIA LAMREM) of CNRS and RAS (2011–2019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Quentin Bonnin, Penouilh Marie-José, Diana Del Bianco, and Marcel Soustelle are warmly acknowledged for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Santos, J.L.; Farahi, F. (Eds.) Handbook of Optical Sensors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; 718p. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnlaugsson, T.; Leonard, J.P.; Murray, N.S. Highly selective colorimetric naked-eye Cu(II) detection using an Azobenzene Chemosensor. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Kumar, S. A diamide–diamine based Cu2+ chromogenic sensor for highly selective visual and spectrophotometric detection. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 4109–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranyuk, E.; Douaihy, C.M.; Bessmertnykh, A.; Denat, F.; Averin, A.; Beletskaya, I.; Guilard, R. Diaminoanthraquinone-linked polyazamacrocycles: Efficient and simple colorimetric sensor for lead ion in aqueous solution. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-D.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical methods for sensing and imaging oxygen: Materials, spectroscopies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3666–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ye, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, J. Development of a ruthenium(II) complex based luminescent probe for imaging nitric oxide production in living cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 6884–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Chung, Y.K. Ru(II)–M(I) (M = Rh and Ir) bimetallic complexes based on a bridging ligand composed of 1,10-phenanthroline and N-heterocyclic carbene: Coordination chemistry and detection property of carbon monoxide. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 391, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, X.; Ye, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, J. Turn-on luminescent probe for cysteine/homocysteine based on a ruthenium(II) complex. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 7898–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.R.; Thomas, J.A. Ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes and DNA—From structural probes to cellular imaging and therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3179–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.-L.; Song, B.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, J. Red-emitting ruthenium(II) and iridium(III) complexes as phosphorescent probes for methylglyoxal in vitro and in vivo. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Huang, C. Phosphorescent chemosensors based on heavy-metal complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3007–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Bar, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Baitalik, S. Design of Ru(II) complexes based on anthraimidazoledione-functionalized terpyridine ligand for improvement of room-temperature luminescence characteristics and recognition of selective anions: Experimental and DFT/TD-DFT study. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 9707–9724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Tosta, M.E.; Lloris, J.M.; Martinez-Máñez, R.; Benito, A.; Soto, J.; Pardo, T.; Miranda, M.A.; Marcos, M.D. Bis(terpyridyl)-ruthenium(II) units attached to polyazacycloalkanes as sensing fluorescent receptors for transition metal ions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 2000, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Ikishima, S.; Matsuo, T.; Yoshida, K. A Luminescent metalloreceptor exhibiting remarkably high selectivity for Mg2+ over Ca2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8402–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Huo, F.; Cheng, F.; Zhu, X.; Mafireyi, T.; Strongin, R.M.; Yin, C. Functional synthetic probes for selective targeting and multi-analyte detection and imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4155–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-N.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.-H. Turn-on luminescent sensing of metal cations via quencher displacement: Rational design of a highly selective chemosensor for chromium(III). Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 13103–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Mi, X.; Guan, L.; Tang, X.; Ju, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Liu, W. Design and application of a water-soluble phosphorescent Ru(II) complex as turn-on sensing material for Hg2+. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6205–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, W.; Lin, C.; Wu, Y. Highly stable and NIR luminescent Ru–LPMSN hybrid materials for sensitive Detection of Cu2+ in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26964–26971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Arora, A.; Kaushal, J.; Oswal, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Developing a simple and water soluble thiophene-functionalized Ru(II)-polypyridyl complex for ferric ion detection. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 107, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-L.; Bünzli, J.-C.G.; Tanner, P.A. Quantum yield and brightness. J. Lumin. 2020, 224, 117256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-J.; Chu, B.W.-K.; Zhu, N.; Yam, V.W.-W. Synthesis, structure, photophysics, electrochemistry, and ion-binding studies of ruthenium(II) 1,10-phenanthroline complexes containing thia-, selena-, and aza-crown pendants. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittel, M.; Lin, H.-W. Quadruple-channel sensing: A molecular sensor with a single type of receptor site for selective and quantitative multi-ion analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtright, A.E.; McCusker, J.K. Static and time-resolved spectroscopic studies of low-symmetry Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 7032–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abel, A.S.; Zenkov, I.S.; Averin, A.D.; Cheprakov, A.V.; Bessmertnykh-Lemeune, A.G.; Orlinson, B.S.; Beletskaya, I.P. Tuning the luminescent properties of ruthenium(II) amino-1,10-phenanthroline complexes by varying the position of the amino group on the heterocycle. ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kálmán, F.K.; Woods, M.; Caravan, P.; Jurek, P.; Spiller, M.; Tircsó, G.; Király, R.; Brücher, E.; Sherry, A.D. Potentiometric and relaxometric properties of a gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent for sensing tissue pH. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 5260–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukai, T.; Kawazura, H.; Ishii, Y.; Bonnet, J.J.; Ibers, J.A. Chemistry of dibenzylideneacetone-palladium(0) complexes: I. Novel tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(solvent) complexes and their reactions with quinones. J. Organomet. Chem. 1974, 65, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzalis, D.; Tor, Y.; Salvatorre, F.; Jay Siegel, S. Simple one-step synthesis of 3-bromo- and 3,8-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline: Fundamental building blocks in the design of metal chelates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3489–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, P.A.; Sargeson, A.M.; Taube, H.; Chou, M.H.; Creutz, C. Cis-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-N,N′) complexes of ruthenium(III)/(II) and osmium(III)/(II). Inorg. Synth. 1986, 24, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.B. Standards for photoluminescence quantum yield measurements in solution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 2213–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.J. Determination of the lower limit of detection. Clin. Chem. 1989, 35, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.T.; Nagypál, I. Chemistry of Complex Equilibria; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1990; 402p. [Google Scholar]
- Schmittel, M.; Ammon, H. Synthesis and spectroscopy of new iron(II) complexes of 4,7-bis(aza-crown ether)-phenanthrolines with unusual complexation properties. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittel, M.; Lin, H.-W.; Thiel, E.; Meixner, A.J.; Ammon, H. Effects of multiple ion loading on redox and luminescence properties of ruthenium trisphenanthroline crown ether hybrids. Dalton Trans. 2006, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kanbara, T.; Yamamoto, T. Ru(II) complexes with new redox-active 1,10-phenanthroline derivatives: Structural, spectral, and electrochemical investigations. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2004, 357, 4335–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.-G.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Li, H.-B.; Wang, S.; Zhu, D.-X.; Li, P.; Wang, C.-G.; Su, Z.-M.; Liao, Y. A cationic iridium(III) complex showing aggregation-induced phosphorescent emission (AIPE) in the solid state: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, T.; Zhan, L.; Zhong, C.; Gong, S.; Lu, Z.-H.; Yang, C. Tailoring optoelectronic properties of phenanthroline-based thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters through isomer engineering. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2016, 4, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, M.; Thomas, H.; Gmelch, M.; Haft, A.; Fries, F.; Reineke, S. Blue-light-absorbing thin films showing ultralong room-temperature phosphorescence. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-P.; Acharjya, A.; Anito, D.A.; Vogl, S.; Wang, T.-X.; Thomas, A.; Han, B.-H. Rhenium-metalated polypyridine-based porous polycarbazoles for visible-light CO2 photoreduction. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, J.P.; Wagaw, S.; Marcoux, J.-F.; Buchwald, S.L. Rational development of practical catalysts for aromatic carbon−nitrogen bond formation. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, J.F. Carbon−heteroatom bond-forming reductive eliminations of amines, ethers, and sulfides. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Castillo, P.; Buchwald, S.L. Applications of palladium-catalyzed C–N cross-coupling reactions. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beletskaya, I.P.; Cheprakov, A.V. Copper in cross-coupling reactions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2337–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletskaya, I.P.; Cheprakov, A.V. The complementary competitors: Palladium and copper in C–N cross-coupling reactions. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7753–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagaw, S.; Buchwald, S.L. The synthesis of aminopyridines: A method employing palladium-catalyzed carbon−nitrogen bond formation. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7240–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Shekhar, S.; Stambuli, J.P.; Hartwig, J.F. Highly Reactive, general, and long-lived catalysts for coupling heteroaryl and aryl chlorides with primary nitrogen nucleophiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, J.P.W.; Lüning, U.; Näther, C. Synthesis and functionalisation of 5-substituted neocuproine derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletskaya, I.P.; Bessmertnykh, A.G.; Guilard, R. Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of aryl-substituted polyamine compounds from aryl halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 2287–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.R.; Stang, P.J. Recent developments in the preparation and chemistry of metallacycles and metallacages via coordination. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7001–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mede, T.; Jäger, M.; Schubert, U.S. “Chemistry-on-the-complex”: Functional RuII polypyridyl-type sensitizers as divergent building blocks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7577–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzani, V.; Juris, A.; Venturi, M.; Campagna, S.; Serroni, S. Luminescent and redox-active polynuclear transition metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 759–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Véry, T.; Ambrosek, D.; Otsuka, M.; Gourlaouen, C.; Assfeld, X.; Monari, A.; Daniel, C. Photophysical properties of ruthenium(II) polypyridyl DNA Intercalators: Effects of the molecular surroundings investigated by theory. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 12901–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Ganguly, B.; Das, A. Urea-based ruthenium(II)−polypyridyl complex as an optical sensor for anions: Synthesis, characterization, and binding studies. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 9912–9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juris, A.; Balzani, V.; Barigelletti, F.; Campagna, S.; Belser, P.; von Zelewsky, A. Ru(II) polypyridine complexes: Photophysics, photochemistry, eletrochemistry, and chemiluminescence. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1988, 84, 85–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.J.; Lewis, A.P.; McAuliffe, G.S.G.; Skarda, V.; Thomson, A.J.; Glasper, J.L.; Robbins, D.J. Luminescent metal complexes. Part 1. Tris-chelates of substituted 2,2′-bipyridyls with ruthenium (II) as dyes for luminescent solar collectors. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1984, 2, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J.G. Excited-state acid-base properties of inorganic compounds. Polyhedron 1992, 11, 2285–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, A.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Borisov, S.M. Optical sensing and imaging of pH values: Spectroscopies, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12357–12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-M.; Wong, K.-Y. Evaluation of a luminescent ruthenium complex immobilized inside Nafion as optical pH sensor. Analyst 1998, 123, 1843–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, Y.; Xu, W.; Demas, J.N.; DeGraff, B.A. Lifetime-based pH sensor system based on a polymer-supported ruthenium(II) complex. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3468–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malins, C.; Glever, H.G.; Keyes, T.E.; Vos, J.G.; Dressick, W.J.; MacCraith, B.D. Sol–gel immobilised ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes as chemical transducers for optical pH sensing. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 67, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Niu, C.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Huang, D. Determination of dissolved oxygen in water based on its quenching effect on the fluorescent intensity of bis(2,2’-bipyridine)-5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline ruthenium complex. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giordano, P.J.; Bock, C.R.; Wrighton, M.S. Excited state proton transfer of ruthenium(II) complexes of 4,7-dihydroxy-1,10-phenanthroline. Increased acidity in the excited state. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 6960–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.M.W.C.; Smailes, M.C.C.; Jeffery, J.C.; Ward, M.D. Ruthenium tris-(bipyridyl) complexes with pendant protonatable and deprotonatable moieties: pH sensitivity of electronic spectral and luminescence properties. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1997, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovsky, A.A. Firefly Version 8. Available online: http://classic.chem.msu.su/gran/firefly/index.html (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Comput. Chem. 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H.; Pitzer, R.M. Relativistic and correlation effects for element 105 (hahnium, Ha): A comparative study of M and MO (M = Nb, Ta, Ha) using energy-adjusted ab initio pseudopotentials. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 5852–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryantsev, V.S.; Diallo, M.S.; Goddard, W.A. pKa calculations of aliphatic amines, diamines, and aminoamides via density functional theory with a Poisson−Boltzmann continuum solvent model. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 4422–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.S.; Averin, A.D.; Cheprakov, A.V.; Roznyatovsky, V.A.; Denat, F.; Bessmertnykh-Lemeune, A.; Beletskaya, I.P. 6-Polyamino-substituted quinolines: Synthesis and multiple metal (CuII, HgII and ZnII) monitoring in aqueous media. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 4243–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranyuk, E.; Uglov, A.; Meyer, M.; Bessmertnykh Lemeune, A.; Denat, F.; Averin, A.; Beletskaya, I.; Guilard, R. Rational design of aminoanthraquinones for colorimetric detection of heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 10491–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballardini, R.; Varani, G.; Indelli, M.T.; Scandola, F.; Balzani, V. Free energy correlation of rate constants for electron transfer quenching of excited transition metal complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 7219–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdass, A.; Sathish, V.; Babu, E.; Velayudham, M.; Thanasekaran, P.; Rajagopal, S. Recent developments on optical and electrochemical sensing of copper(II) ion based on transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 343, 278–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, G.; Iniya, M.; Anand, T.; Kotla, N.G.; Sunnapu, O.; Singaravadivel, S.; Gulyani, A.; Chellappa, D. Chemically diverse small molecule fluorescent chemosensors for copper ion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 357, 50–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okda, H.E.; El Sayed, S.; Ferreira, R.C.M.; Gonçalves, R.R.; Costa, S.P.G.; Raposo, M.M.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. N,N-Diphenylanilino-heterocyclic aldehyde-based chemosensors for UV-vis/NIR and fluorescence Cu(II) detection. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 7393–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okda, H.E.; El Sayed, S.; Otri, I.; Ferreira, R.C.M.; Costa, S.P.G.; Raposo, M.M.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. 2,4,5-Triaryl imidazole probes for the selective chromo-fluorogenic detection of Cu(II). Prospective use of the Cu(II) complexes for the optical recognition of biothiols. Polyhedron 2019, 170, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiero, H.; Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Copper. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaglia, M.; Bubacco, L. Copper ions and Parkinson′s disease: Why is homeostasis so relevant? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawle, S.C.; Moore, P.; Alcock, N.W. Synthesis and coordination chemistry of 1-(2′,2″-bipyridyl-5′-yl-methyl)-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane L1. Quenching of fluorescence from [Ru(bipy)2(L1)]2+ by coordination of NiII or CuII in the cyclam cavity (bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine; cyclam = 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolletta, F.; Costa, I.; Fabbrizzi, L.; Licchelli, M.; Montalti, M.; Pallavicini, P.; Prodi, L.; Zaccheroni, N. A [RuII(bipy)3]-[1,9-diamino-3,7-diazanonane-4,6-dione] two-component system, as an efficient ON–OFF luminescent chemosensor for Ni2+ and Cu2+ in water, based on an ET (energy transfer) mechanism. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1999, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Website of ERA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/battery-manufacturing-effluent-guidelines-documents (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Comba, P.; Krämer, R.; Mokhir, A.; Naing, K.; Schatz, E. Synthesis of new phenanthroline-based heteroditopic ligands—Highly efficient and selective fluorescence sensors for copper(II) ions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 4442–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.-T.; Pei, L.-M.; Xu, W.-C.; Chao, H.; Ji, L.-N. [Ru(bpy)2(pipdpa)]2+ as a highly sensitive and selective luminescent chemosensor for Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2012, 16, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Pei, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, Y.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. A Dinuclear ruthenium(II) complex as a one- and two-photon luminescent probe for biological Cu2+ detection. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15494–15503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Tang, N.; Miao, K.; Wang, F. A dinuclear ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complex containing a terpy-like fragment for Cu2+ probing. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Kang, S.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yi, X.; Wang, K.-Z. pH and copper ion luminescence on/off sensing by a dipyrazinylpyridine-appended ruthenium complex. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 221, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.-B.; Lu, J.-L. A selective luminescent sensor for the detection of copper(II) ions based on a ruthenium complex containing DPA moiety. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 84, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Han, Y.-F.; Zuo, J.; Ma, Y.-N. Ruthenium(II) complex-based chemosensors for highly sensitive and selective sequential recognition of copper ion and cyanide. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 253, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S. Copper ion luminescence on/off sensing by a quinoline-appended ruthenium(II)-polypyridyl complex in aqueous media. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1202, 127242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Frémond, L.; Espinosa, E.; Guilard, R.; Ou, Z.; Kadish, K.M. Synthesis, characterization, and X-ray crystal structures of cyclam derivatives. 5. Copper(II) binding studies of a pyridine-strapped 5,12-dioxocyclam-based macrobicycle. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 5572–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, A.; Sun, S. A reversible and selective luminescent probe for Cu2+ detection based on a ruthenium(II) complex in aqueous solution. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 211, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).