Prediction of Trained Panel Sensory Scores for Beef with Non-Invasive Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Preparation
2.2. Raman Spectral Measurements
2.3. Sensory Analysis
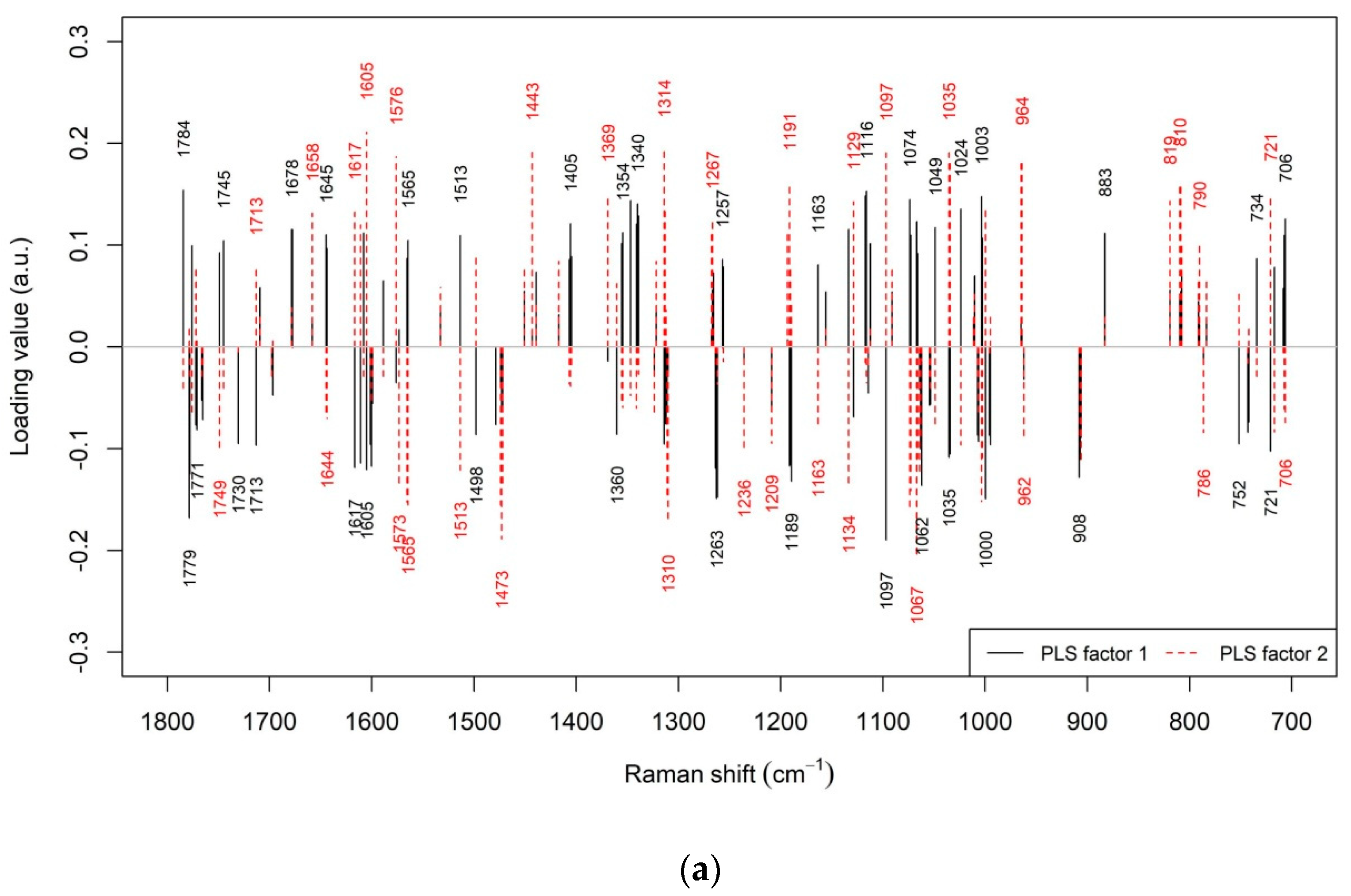
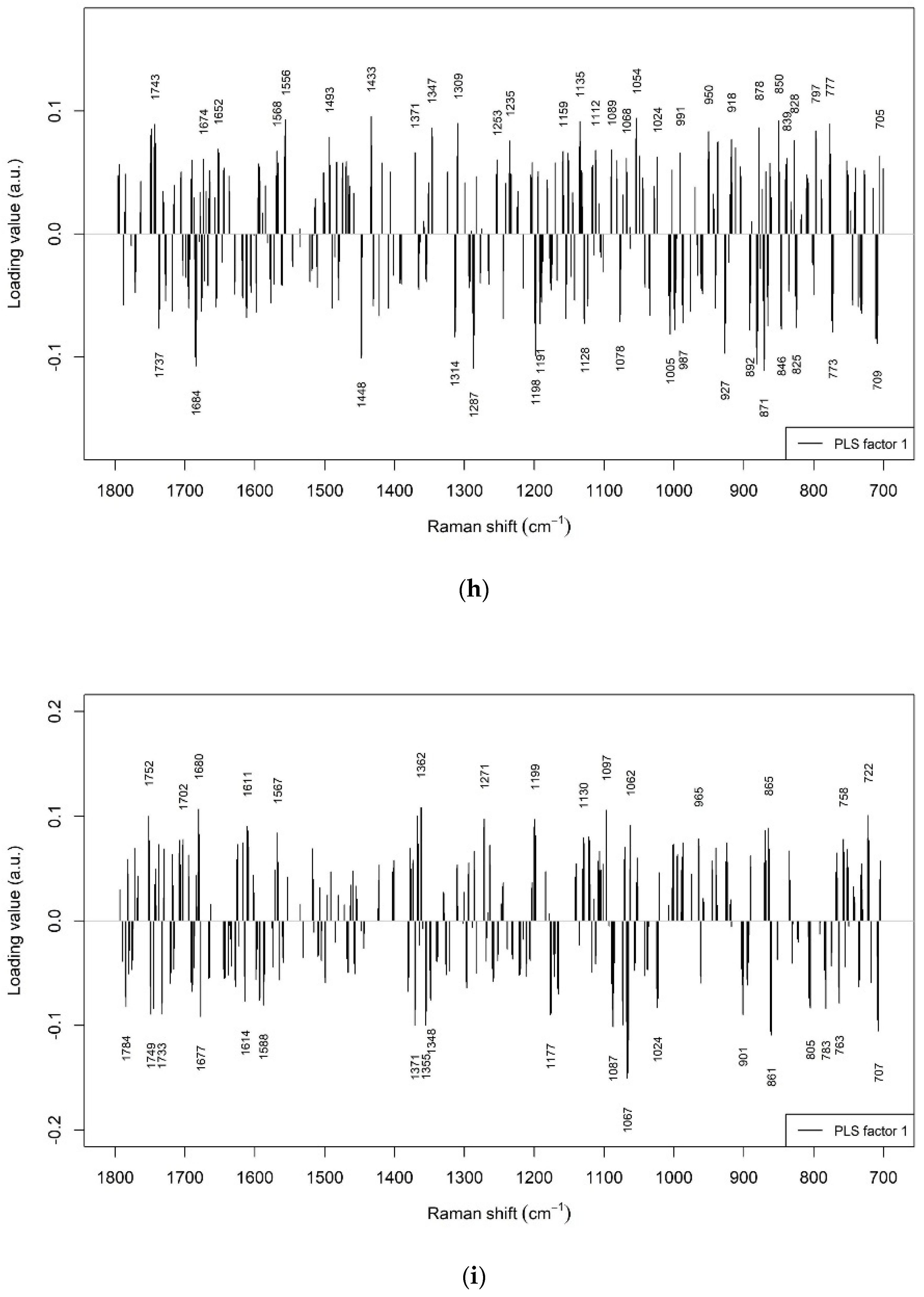
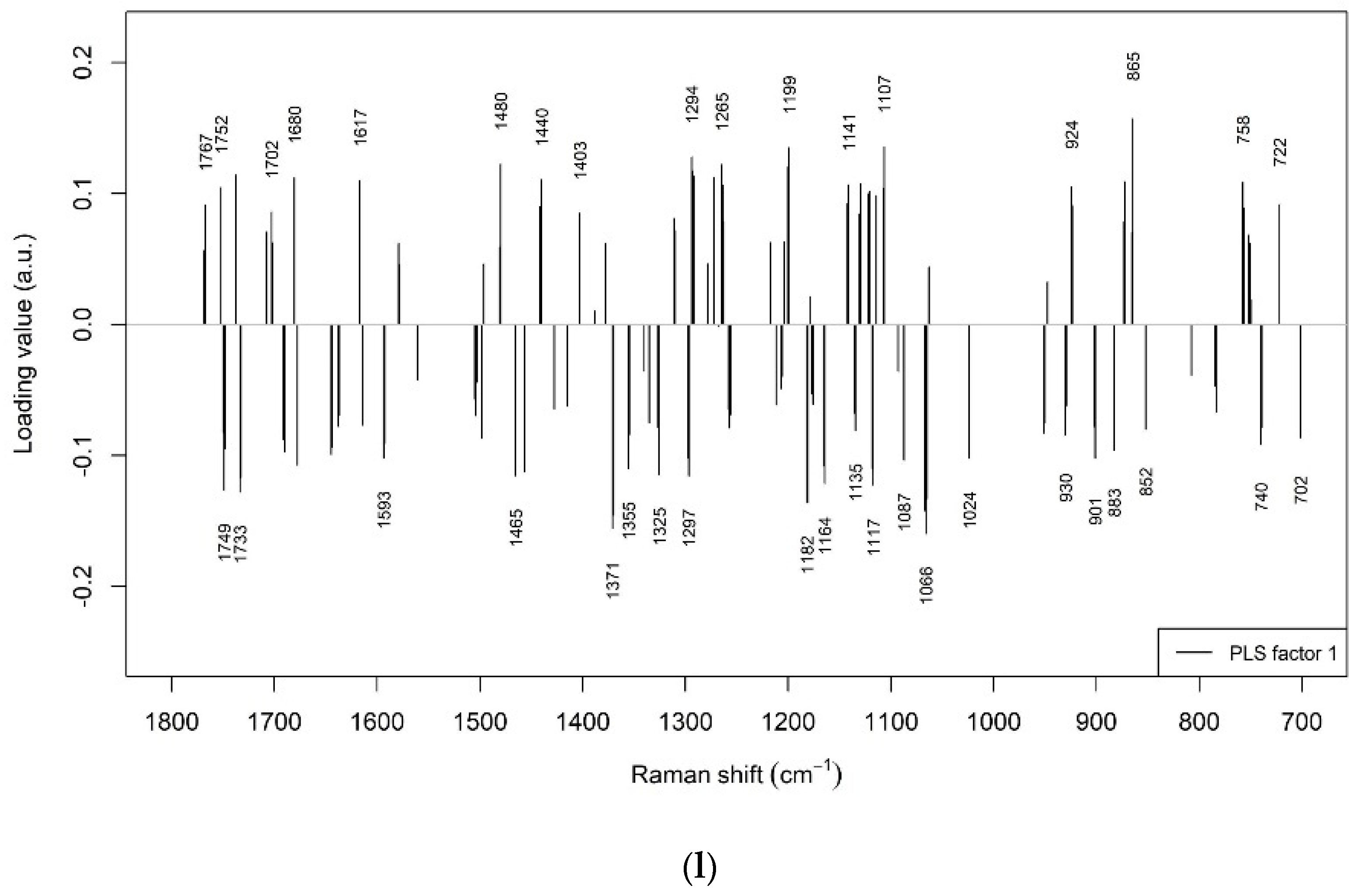
2.4. Chemometric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Sensory Traits
3.2. Prediction of Beef LTL Sensory Tenderness by Raman Spectroscopy
3.3. Prediction of Other Beef LTL Textural Traits by Raman Spectroscopy
3.4. Prediction of Beef LTL Sensory Flavour and Juiciness by Raman Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grunert, K.G.; Bredahl, L.; Brunsø, K. Consumer perception of meat quality and implications for product development in the meat sector—A review. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, D.; Kerry, J.P. Consumer perception and the role of science in the meat industry. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, R.J.; Bell, S.J.; Farmer, L.J.; Moss, B.W.; Patterson, D. Preliminary investigation of the application of Raman spectroscopy to the prediction of the sensory quality of beef silverside. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.C.; Zhao, J.; Dong, X.; Lonergan, S.; Lonergan, E.H.; Outhouse, A.; Carlson, K.; Prusa, K.; Fedler, C.; Yu, C.; et al. Predicting aged pork quality using a portable Raman device. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prevolnik, M.; Čandek-Potokar, M.; Škorjanc, D. Ability of NIR spectroscopy to predict meat chemical composition and quality—A review. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 49, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.M.; Schmidt, H.; van de Ven, R.; Hopkins, D.L. Preliminary investigation of the use of Raman spectroscopy to predict meat and eating quality traits of beef loins. Meat Sci. 2018, 138, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafferky, J.; Sweeney, T.; Allen, P.; Sahar, A.; Downey, G.; Cromie, A.R.; Hamill, R.M. Investigating the use of visible and near infrared spectroscopy to predict sensory and texture attributes of beef M. longissimus thoracis et lumborum. Meat Sci. 2019, 159, 107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nian, Y.; Zhao, M.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Downey, G.; Kerry, J.P.; Allen, P. Assessment of physico-chemical traits related to eating quality of young dairy bull beef at different ageing times using Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Nian, Y.; Allen, P.; Downey, G.; Kerry, J.P.; O’Donnell, C.P. Application of Raman spectroscopy and chemometric techniques to assess sensory characteristics of young dairy bull beef. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damez, J.-L.; Clerjon, S. Meat quality assessment using biophysical methods related to meat structure. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalhus, J.L.; López-Campos, Ó.; Prieto, N.; Rodas-González, A.; Dugan, M.E.R.; Uttaro, B.; Juárez, M. Review: Canadian beef grading—Opportunities to identify carcass and meat quality traits valued by consumers. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 94, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, S.; Stöckel, S.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Identification of meat-associated pathogens via Raman microspectroscopy. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheier, R.; Bauer, A.; Schmidt, H. Early Postmortem Prediction of Meat Quality Traits of Porcine Semimembranosus Muscles Using a Portable Raman System. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 2732–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.V.; Wold, J.P.; Gjerlaug-Enger, E.; Veiseth-Kent, E. Predicting post-mortem meat quality in porcine longissimus lumborum using Raman, near in-frared and fluorescence spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Scheier, R.; Eberle, T.; Schmidt, H. Assessment of tenderness of aged bovine gluteus medius muscles using Raman spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2016, 115, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama-Moncunill, R.; Cafferky, J.; Augier, C.; Sweeney, T.; Allen, P.; Ferragina, A.; Sullivan, C.; Cromie, A.; Hamill, R.M. Prediction of Warner-Bratzler shear force, intramuscular fat, drip-loss and cook-loss in beef via Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics. Meat Sci. 2020, 167, 108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafferky, J.; Hamill, R.M.; Allen, P.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Cromie, A.; Sweeney, T. Effect of Breed and Gender on Meat Quality of M. longissimus thoracis et lumborum Muscle from Crossbred Beef Bulls and Steers. Foods 2019, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AMSA. Research Guidelines for Cookery, Sensory Evaluation and Instrumental Tenderness Measurements of Meat; American Meat Science Association: Champaign, IL, USA, 2015; Available online: https://www.meatscience.org/docs/default-source/publications-resources/amsa-sensory-and-tenderness-evaluation-guidelines/research-guide/2015-amsa-sensory-guidelines-1-0.pdf?sfvrsn=6 (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Chong, I.-G.; Jun, C.-H. Performance of some variable selection methods when multicollinearity is present. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2005, 78, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, W. Detection Techniques of Meat Tenderness: State of the Art. Meat Quality Analysis: Advanced Evaluation Methods, Techniques, and Technologies; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama-Moncunill, R.; Gavaldà, M.P.C.; Cama-Moncunill, X.; Markiewicz-Kęszycka, M.; Dixit, Y.; Cullen, P.; Sullivan, C. Quantification of trace metals in infant formula premixes using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 135, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.M. Raman spectroscopy a promising technique for quality assessment of meat and fish: A review. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies. Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max | CV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenderness | 51.85 | 11.98 | 54.91 | 23.25 | 70.75 | 23.1% |
| Chewiness | 26.98 | 12.55 | 23.35 | 6.83 | 56.33 | 46.5% |
| Stringiness | 12.31 | 9.95 | 8.81 | 0.43 | 40.94 | 80.8% |
| Difficulty to swallow | 12.25 | 8.09 | 10.14 | 0.83 | 33.13 | 66.0% |
| Crumbliness | 20 | 11.21 | 17.63 | 2.33 | 45.3 | 56.1% |
| Beef flavour | 41.16 | 7.22 | 41.27 | 20.6 | 60.88 | 17.5% |
| Beef AE | 31.2 | 5.76 | 31.23 | 16.5 | 45 | 18.5% |
| Juiciness | 33.51 | 7.06 | 33.2 | 17.5 | 54.35 | 21.1% |
| Fatty mouthfeel | 5.96 | 4.56 | 4.63 | 0.21 | 19.63 | 76.5% |
| Fatty AE | 6.38 | 4.91 | 5 | 0.5 | 24.25 | 77.0% |
| Metallic flavour | 13.91 | 5.9 | 12.77 | 1.42 | 29.5 | 42.4% |
| Metallic AE | 18.49 | 7.54 | 18.65 | 3.67 | 37.63 | 40.8% |
| Variable | Math Treatment | Var | P | R2Cal | RMSEC | R2CV | RMSECV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenderness | EMSC | 131 | 2 | 0.66 | 6.92 | 0.46 | 8.74 |
| SG2 | 265 | 2 | 0.61 | 7.41 | 0.33 | 9.74 | |
| Chewiness | EMSC | 119 | 2 | 0.64 | 7.54 | 0.43 | 9.46 |
| SG2 | 255 | 2 | 0.59 | 8.05 | 0.34 | 10.15 | |
| Stringiness | EMSC | 120 | 1 | 0.46 | 7.31 | 0.35 | 7.96 |
| SG1 | 69 | 3 | 0.46 | 7.27 | 0.35 | 7.97 | |
| Diff. swallow | SG2 | 270 | 2 | 0.61 | 5.03 | 0.33 | 6.59 |
| EMSC | 358 | 1 | 0.51 | 5.67 | 0.33 | 6.62 | |
| Crumbliness | EMSC | 126 | 1 | 0.45 | 8.27 | 0.36 | 8.92 |
| SG2 | 244 | 2 | 0.49 | 7.96 | 0.31 | 9.28 | |
| Beef flavour | EMSC | 149 | 1 | 0.36 | 5.77 | 0.22 | 6.36 |
| SG2 | 286 | 2 | 0.54 | 4.87 | 0.16 | 6.60 | |
| Beef AE | EMSC | 391 | 1 | 0.42 | 4.35 | 0.27 | 4.91 |
| SG2 | 233 | 2 | 0.53 | 3.92 | 0.14 | 5.32 | |
| Juiciness | SG2 | 275 | 2 | 0.60 | 4.43 | 0.36 | 5.63 |
| EMSC | 132 | 2 | 0.60 | 4.46 | 0.30 | 5.88 | |
| Fatty mouthfeel | EMSC | 353 | 1 | 0.51 | 3.19 | 0.34 | 3.70 |
| SG2 | 286 | 2 | 0.58 | 2.94 | 0.31 | 3.76 | |
| Fatty AE | EMSC | 338 | 1 | 0.41 | 2.90 | 0.23 | 3.31 |
| SG2 | 265 | 2 | 0.70 | 2.08 | 0.44 | 2.82 | |
| Metallic flavour | SG2 | 258 | 2 | 0.70 | 3.25 | 0.52 | 4.08 |
| EMSC | 128 | 1 | 0.45 | 4.35 | 0.35 | 4.74 | |
| Metallic AE | EMSC | 128 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.33 | 0.37 | 5.94 |
| SG2 | 212 | 2 | 0.54 | 5.08 | 0.28 | 6.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cafferky, J.; Cama-Moncunill, R.; Sweeney, T.; Allen, P.; Cromie, A.; Hamill, R.M. Prediction of Trained Panel Sensory Scores for Beef with Non-Invasive Raman Spectroscopy. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10010006
Cafferky J, Cama-Moncunill R, Sweeney T, Allen P, Cromie A, Hamill RM. Prediction of Trained Panel Sensory Scores for Beef with Non-Invasive Raman Spectroscopy. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleCafferky, Jamie, Raquel Cama-Moncunill, Torres Sweeney, Paul Allen, Andrew Cromie, and Ruth M. Hamill. 2022. "Prediction of Trained Panel Sensory Scores for Beef with Non-Invasive Raman Spectroscopy" Chemosensors 10, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10010006
APA StyleCafferky, J., Cama-Moncunill, R., Sweeney, T., Allen, P., Cromie, A., & Hamill, R. M. (2022). Prediction of Trained Panel Sensory Scores for Beef with Non-Invasive Raman Spectroscopy. Chemosensors, 10(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10010006







