Prolonged Running Using Bionic Footwear Influences Lower Limb Biomechanics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
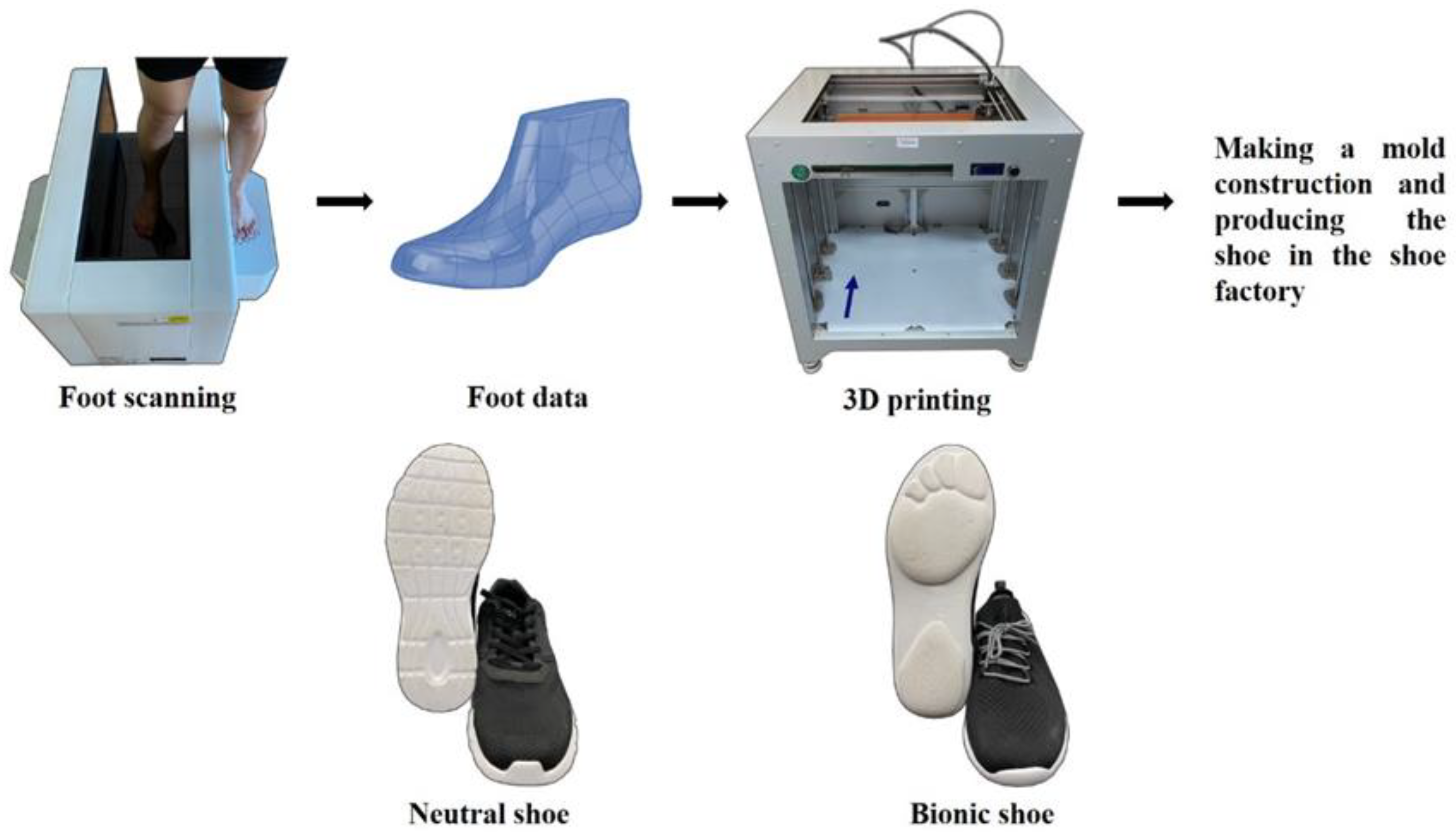
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
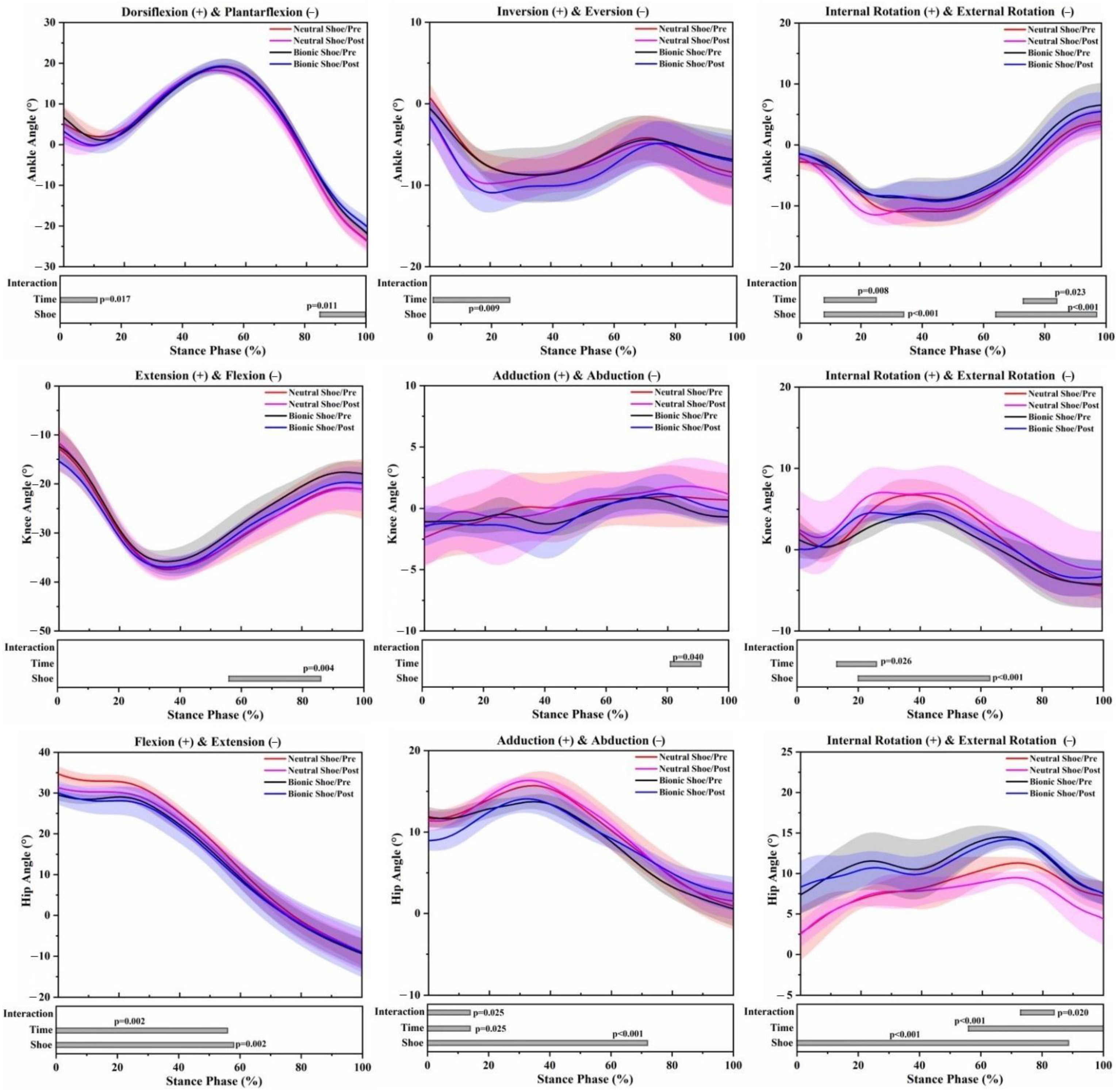
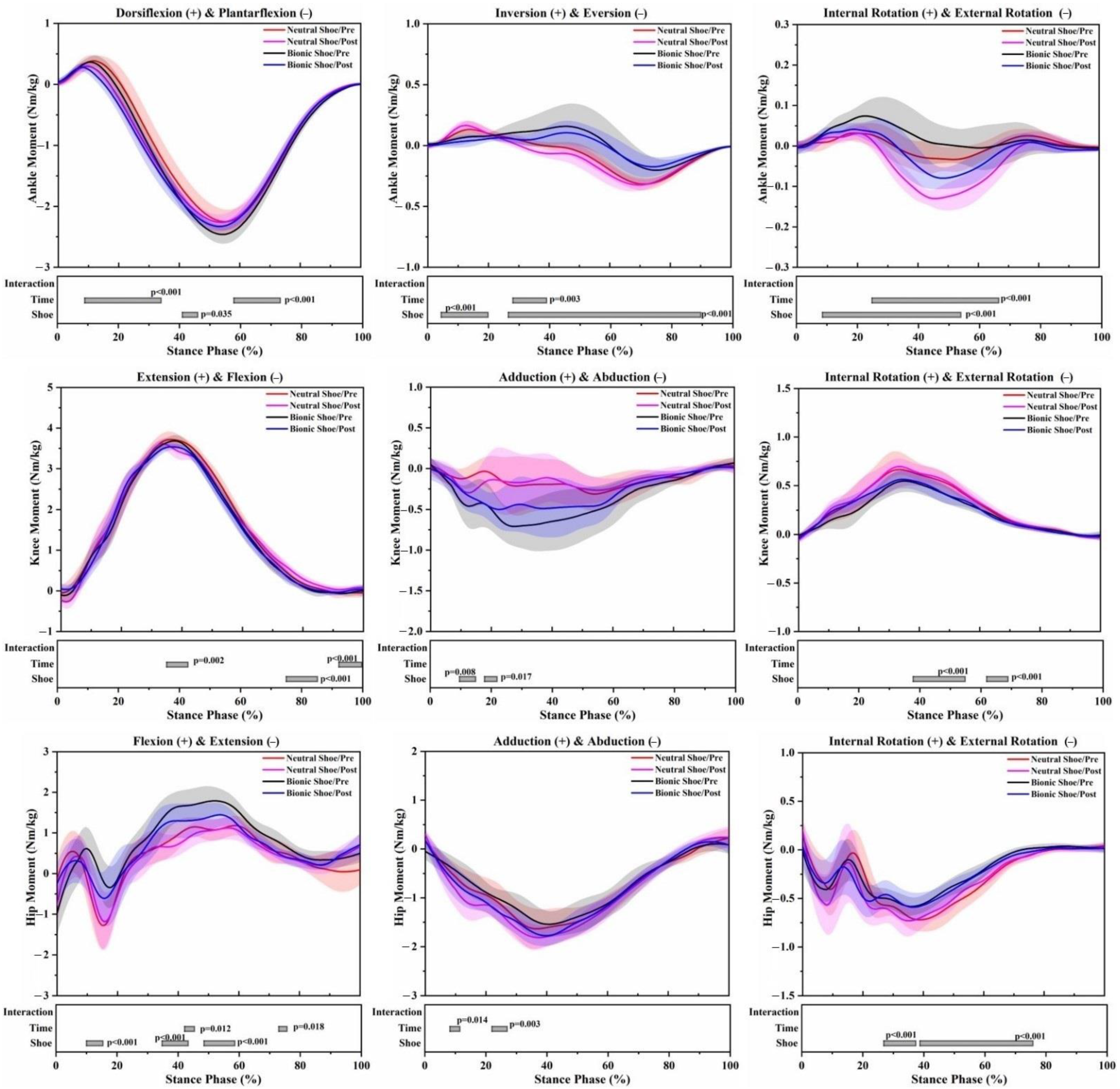
3.1. Effects of the Shoe Condition
3.2. Effects of the 5 km Run (Time)
3.3. Interaction Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Messier, S.P.; Martin, D.F.; Mihalko, S.L.; Ip, E.; DeVita, P.; Cannon, D.W.; Love, M.; Beringer, D.; Saldana, S.; Fellin, R.E. A 2-year prospective cohort study of overuse running injuries: The runners and injury longitudinal study (TRAILS). Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, V.; Meeuwisse, W.; Stergiou, P.; Stefanyshyn, D. Relation between running injury and static lower limb alignment in recreational runners. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, R.; Hreljac, A.; Kendall, K.D. Suspected mechanisms in the cause of overuse running injuries: A clinical review. Sports Health 2009, 1, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noehren, B.; Schmitz, A.; Hempel, R.; Westlake, C.; Black, W. Assessment of strength, flexibility, and running mechanics in men with iliotibial band syndrome. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 44, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.S. Is there an economical running technique? A review of modifiable biomechanical factors affecting running economy. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, B.M.; Baltich, J.; Hoerzer, S.; Enders, H. Running shoes and running injuries: Mythbusting and a proposal for two new paradigms:‘preferred movement path’and ‘comfort filter’. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gent, R.; Siem, D.; van Middelkoop, M.; Van Os, A.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Koes, B. Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, G.; Wyatt, H.; Van Emmerik, R.; Trudeau, M.B.; Willwacher, S.; Brüggemann, G.-P.; Hamill, J. Influence of neutral and stability athletic footwear on lower extremity coordination variability during a prolonged treadmill run in male rearfoot runners. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 20, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacoff, A.; Reinschmidt, C.; Nigg, B.M.; Van Den Bogert, A.J.; Lundberg, A.; Denoth, J.; Stüssi, E. Effects of shoe sole construction on skeletal motion during running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, L. The differential effects of foot sole sensory on plantar pressure distribution between balance and gait. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, B.M.; Emery, C.; Hiemstra, L.A. Unstable shoe construction and reduction of pain in osteoarthritis patients. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sacco, I.C.; Sartor, C.D.; Cacciari, L.P.; Onodera, A.N.; Dinato, R.C.; Pantaleão, E., Jr.; Matias, A.B.; Cezário, F.G.; Tonicelli, L.M.; Martins, M.C.S. Effect of a rocker non-heeled shoe on EMG and ground reaction forces during gait without previous training. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöggl, T.; Haudum, A.; Birklbauer, J.; Murrer, M.; Müller, E. Short and long term adaptation of variability during walking using unstable (Mbt) shoes. Clin. Biomech. 2010, 25, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Fekete, G.; Fernandez, J.; Gu, Y.D. Analysis of Foot Kinematics with Unstable Sole Structure Using Oxford Foot Model. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Mei, Q.; Li, J.; Ren, J. Effects of different unstable sole construction on kinematics and muscle activity of lower limb. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 36, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsak, B.; Heller, M.; Baca, A. Muscle co-contraction around the knee when walking with unstable shoes. J. Electromyogr. kinesiol. 2015, 25, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Tateuchi, H.; Takeoka, T.; Ichihashi, N. Kinematic and kinetic characteristics of Masai Barefoot Technology footwear. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, S.; Hijmans, J.; van den Heuvel, E.; Zwerver, J.; Dekker, R.; Postema, K. Biomechanics of slow running and walking with a rocker shoe. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, K.A.; Andriacchi, T.P. Changes in running kinematics and kinetics in response to a rockered shoe intervention. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, B.M.; Davis, E.; Lindsay, D.; Emery, C. The effectiveness of an unstable sandal on low back pain and golf performance. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009, 19, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesar, N.G.Z.; Van Ginckel, A.; Cools, A.; Peersman, W.; Roosen, P.; De Clercq, D.; Witvrouw, E. A prospective study on gait-related intrinsic risk factors for lower leg overuse injuries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elfattah, H.M.; Abdelazeim, F.H.; Elshennawy, S. Physical and cognitive consequences of fatigue: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.; Gu, Y.; Xiang, L.; Baker, J.S.; Fernandez, J. Foot pronation contributes to altered lower extremity loading after long distance running. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierks, T.A.; Davis, I.S.; Hamill, J. The effects of running in an exerted state on lower extremity kinematics and joint timing. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2993–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Shen, S.Q.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y.D. Effects of different hardness in bionic soles on lower limb biomechanics. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.; Jewell, C.; Wyatt, H.; Trudeau, M.B.; Rohr, E.; Brüggemann, G.-P.; Hamill, J. The influence of prolonged running and footwear on lower extremity biomechanics. Footwear Sci. 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, X.; Cen, X.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Single-Leg Landings Following a Volleyball Spike May Increase the Risk of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury More Than Landing on Both-Legs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Cen, X.; Wang, M.; Rong, M.; István, B.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Temporal Kinematic Differences between Forward and Backward Jump-Landing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santuz, A.; Ekizos, A.; Janshen, L.; Baltzopoulos, V.; Arampatzis, A. The influence of footwear on the modular organization of running. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsak, B.; Baca, A. Effects of toning shoes on lower extremity gait biomechanics. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romkes, J.; Rudmann, C.; Brunner, R. Changes in gait and EMG when walking with the Masai Barefoot Technique. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Fekete, G. Unstable Structure to Adjust Lower Limb Motion Based on Oxford Foot Model in Order to Control Foot Arthritis. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, A.S.; Silva, A.; Tavares, J.M.R. Biomechanical and neurophysiological mechanisms related to postural control and efficiency of movement: A review. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2012, 29, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, N.; Rao, G.; Berton, E.; Delattre, N. The stiff plate location into the shoe influences the running biomechanics. Sports Biomech. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, W. Changes in Ground Reaction Forces, Joint Mechanics, and Stiffness during Treadmill Running to Fatigue. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.; Gordon, S.; Watt, K. Effects of fatigue on kinematics and kinetics during overground running: A systematic review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2016, 57, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christina, K.A.; White, S.C.; Gilchrist, L.A. Effect of localized muscle fatigue on vertical ground reaction forces and ankle joint motion during running. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2001, 20, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, T.M.; Feuerbach, J.W.; Grabiner, M.D. Effect of plantar flexor and dorsiflexor fatigue on unilateral postural control. J. Appl. Biomech. 1993, 9, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierks, T.A.; Manal, K.T.; Hamill, J.; Davis, I. Lower extremity kinematics in runners with patellofemoral pain during a prolonged run. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, J.; Miller, R.; Noehren, B.; Davis, I. A prospective study of iliotibial band strain in runners. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, M.B.; Willwacher, S.; Weir, G.; Rohr, E.; Ertel, C.; Bruggemann, G.-P.; Hamill, J. A novel method for estimating an individual’s deviation from their habitual motion path when running. Footwear Sci. 2019, 11, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willwacher, S.; Sanno, M.; Brüggemann, G.-P. Fatigue matters: An intense 10 km run alters frontal and transverse plane joint kinematics in competitive and recreational adult runners. Gait Posture 2019, 76, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollock, R.O.; Andrews, C.; Johnston, A.; Elliott, T.; Wilson, A.E.; Games, K.E.; Sefton, J.M. A meta-analysis to determine if lower extremity muscle strengthening should be included in military knee overuse injury-prevention programs. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, R.; Davis, J.I.; Williams, E.S.C.P. Gender differences in lower extremity mechanics during running. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, S.; Pierce, B. How Aging Impacts Runners’ Goals of Lifelong Running. Phys. Act. Health 2019, 3, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Joint | Variables | Neutral Shoe/Pre | Neutral Shoe/Post | Bionic Shoe/Pre | Bionic Shoe/Post | Main Effect Shoe | Main Effect Time | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle | Sagittal ROM (°) | 42.90 (2.20) | 42.30 (2.46) | 41.10 (3.82) | 39.58 (3.63) | F = 6.813; p = 0.020 | F = 1.813; p = 0.198 | F = 0.602; p = 0.450 |
| Frontal ROM (°) | 10.55 (3.53) | 10.04 (2.80) | 9.00 (3.04) | 9.87 (1.23) | F = 4.490; p = 0.051 | F = 0.049; p = 0.827 | F = 0.696; p = 0.417 | |
| Horizontal ROM (°) | 15.30 (2.78) | 15.22 (2.16) | 16.58 (4.34) | 15.87 (4.16) | F = 0.843; p = 0.373 | F = 0.654; p = 0.431 | F = 0.282; p = 0.603 | |
| Knee | Sagittal ROM (°) | 26.86 (3.42) | 25.78 (3.53) | 23.90 (4.53) | 21.77 (3.39) | F = 8.823; p = 0.010 | F = 6.136; p = 0.026 | F = 0.570; p = 0.462 |
| Frontal ROM (°) | 4.66 (1.34) | 4.36 (1.59) | 3.30 (0.97) | 4.68 (2.40) | F = 0.684; p = 0.421 | F = 3.322; p = 0.088 | F = 3.120; p = 0.030 | |
| Horizontal ROM (°) | 11.74 (1.09) | 10.59 (2.34) | 9.70 (2.03) | 9.18 (1.50) | F = 13.675; p = 0.002 | F = 4.675; p = 0.057 | F = 0.333; p = 0.572 | |
| Hip | Sagittal ROM (°) | 43.64 (3.99) | 40.44 (4.35) | 39.17 (3.32) | 39.16 (5.55) | F = 14.138; p = 0.002 | F = 4.944; p = 0.042 | F = 13.252; p = 0.002 |
| Frontal ROM (°) | 14.93 (1.84) | 14.95 (2.20) | 13.50 (2.39) | 11.69 (0.87) | F = 50.948; p < 0.001 | F = 4.180; p = 0.059 | F = 5.986; p = 0.027 | |
| Horizontal ROM (°) | 9.41 (2.99) | 8.87 (2.45) | 9.25 (1.55) | 7.84 (1.69) | F = 0.911; p = 0.355 | F = 3.237; p = 0.092 | F = 0.426; p = 0.524 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Prolonged Running Using Bionic Footwear Influences Lower Limb Biomechanics. Healthcare 2021, 9, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020236
Jiang X, Yang X, Zhou H, Baker JS, Gu Y. Prolonged Running Using Bionic Footwear Influences Lower Limb Biomechanics. Healthcare. 2021; 9(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xinyan, Xiaoyi Yang, Huiyu Zhou, Julien S. Baker, and Yaodong Gu. 2021. "Prolonged Running Using Bionic Footwear Influences Lower Limb Biomechanics" Healthcare 9, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020236
APA StyleJiang, X., Yang, X., Zhou, H., Baker, J. S., & Gu, Y. (2021). Prolonged Running Using Bionic Footwear Influences Lower Limb Biomechanics. Healthcare, 9(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020236









