Abstract
Health literacy (HL) is recognised as an important, modifiable factor in the self-management and health performance of elderly people. The aim of this preliminary study was to identify and analyse the level of health literacy among the elderly living in one of the eastern regions in Poland. The cross-sectional study was conducted among a convenience sample of 200 seniors aged 65+ after cognitive pre-screening with the use of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale. To collect data, the Polish version of the HLS-EU-Q47 was used. More than half of the elderly surveyed presented problematic levels of general HL (GEN-HL), and also problematic levels of other dimensions: health care health literacy (HC-HL), disease prevention health literacy (DP-HL), and health promotion health literacy (HP-HL). The level of seniors’ HL is dependent on the level of their education, place of living, participation in activities run by Daily Center for the Elderly, and their self-assessment of health condition (p < 0.05). These results imply the important message that there is a need to create initiatives and programs improving health literacy targeted at seniors living in rural areas, those with lower levels of education, and those with poor access to activities organised by institutions supporting seniors.
1. Introduction
Health literacy (HL) is an evolving concept that has been gaining in importance over the last decade [1]. According to the definition proposed by Sørensen in 2012: “Health literacy is linked to literacy and entails people’s knowledge, motivation, and competences to access, understand, appraise, and apply health information in order to make judgements and take decisions in everyday life concerning healthcare, disease prevention, and health promotion to maintain or improve quality of life during the life course” [2].
HL is recognised as an important determinant of society’s health and, thus, a key factor in efforts to improve it [3,4]. Many studies have shown that low levels of HL are of prognostic importance for various negative health effects [2,5,6,7]. It is also related to higher health care costs [8,9]. Research shows that a lower degree of health knowledge is associated with poorer mental and physical health [8] and adverse health behaviours such as: lower ability to take care of oneself [10], higher percentage of avoidable hospitalisations [6,11], and less frequent use of preventive health services [12,13]. People with low levels of HL are less likely to benefit from screening, and have considerable difficulty in understanding their disease, their treatment plan, and especially the treatment of chronic diseases [14,15,16,17]. Low HL is also associated with higher mortality and lower levels of care satisfaction [1,9].
HL is often referred to as an important indicator in population health monitoring [16]. Based on HL surveys in eight European countries, around 50% of European adults have low levels of health literacy [18]. These people have serious problems with health-related tasks and situations [19,20]. The elderly has been indicated as a group particularly vulnerable to health literacy deficits [20,21,22].
In an era of rapid medical and technological progress and changes in the way health care is provided, society requires high levels of health literacy [20,23]. Changes in the health systems of many countries pose increasingly greater requirements of society to take greater responsibility for its health [7,24]. Nevertheless, there is still a growing gap between the demand for health literacy and the actual health literacy of many patients [18,25]. Many studies have shown that HL levels are closely related to age [21,25,26]. Limited health literacy is more prevalent among older adults [22,27]. Knowledge and understanding of the factors related to the health literacy of the elderly can reduce the health problems of this group in all communities.
According to official forecasts, the population of people aged 65 and above in the European Union (EU) will increase to 148.3 million in 2060. As regards people aged 80 and over, according to the forecasts, their number will increase to 61.7 million in 2060. Consequently, the share of pensioners in the population will record a sharp increase to 50.1% in 2060 [28]. The low level of health knowledge is a particularly important problem among people over 65 years of age, most of whom achieve results below the basic levels of health literacy [26]. Health literacy is an important, modifiable factor in the self-management and health performance of elderly people [22,29]. Socio-economic status (lower income, poor education), age, level of education (lower education), and changes in cognitive and physical abilities associated with ageing are all factors contributing to lower health literacy among elderly people [30,31].
Health literacy is well explored in many different populations around the world, including the elderly population. However, in many studies, the elderly constituted only part of the studied group, e.g., in the Polish national research by Słońska et al. [32] and Duplaga [33]. Therefore, our intention in this current study was to focus only on seniors’ health literacy level, collecting data in face-to-face interviews after cognitive pre-screening of every respondent. The astern part of Poland—Lubelskie Voivodship—was chosen, as it is a region that may serve as a specific lens on which the main problems of an aging population can be focused. Considering the prognosis of the Statistical Office, the Lubelskie Voivodeship will be among the fastest ageing Polish voivodships with a so-called double ageing, in which the highest increase is observed in the number of people aged 80+ [34,35]. Research regarding health literacy in this population may support discussions and initiatives regarding micro, mezzo, and macro strategies to maintain healthy ageing with longer independence of seniors in this age group.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aim
The aim of the study was to identify and analyse the level of health literacy among the elderly living in one of the eastern regions in Poland.
2.2. Study Participants and Setting
The study was carried out as part of the Erasmus+ project ‘Healthy lifestyle for aging well (HLAW)’ among convenience sample of 200 seniors aged 65+, living in one of the eastern regions in Poland. The study was carried out in day-care centres for the elderly, senior citizens’ clubs, the University of the Third Age, and the respondents’ living environment. Prepared interviewers met with seniors, explained the purpose and process data collection, asked for the consent to participate in the study, and when consent was given, assisted seniors during filling in the questionnaire in case of any difficulties. The return rate of the surveys was at 69%. A total of 150 questionnaires were obtained, 138 of which were correctly filled in and accepted for analysis.
2.3. Research Instruments
The basis for the qualification of seniors for the study was the use of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale, which is a screening tool to detect mild cognitive disorders. Behaviour is assessed, including: abstraction, short-term memory, visual-spatial functions, executive functions, language, verbal fluency, allopsychic orientation, and attention [36]. Persons who received at least 26 points on a maximum scale of 30 points were eligible for the further stage of research.
To collect the material, the Polish version of the HLS-EU-Q47 research tool was used, which is a part of the European Health Literacy Survey HLS-EU. The HLS-EU survey was conducted in eight European countries in 2011 [18,37]. Consent for the use of the Polish version of the questionnaire was given by the Polish coordinator of HLS-EU, Zofia Słońska [32].
The HLS-EU-Q47 questionnaire contains 47 questions, which cover the different stages of information processing (finding health information, understanding health information, judging health information, and applying health information) in three main dimensions: health care health literacy (HC-HL), disease prevention health literacy (DP-HL), and health promotion health literacy (HP-HL). Respondents participating in the survey evaluate individual questions according to four categories of answers (very easy, rather easy, rather difficult, very difficult). The HLS-EU-Q47 tool enables us to calculate a general-HL index, comprising all items and providing a general picture and overview of respondents’ health literacy (GEN-HL), and it provides an index for all three dimensions of health literacy: HC-HL, DP-HL, and HP-HL.
The Cronbach alpha coefficient for the Polish version of the scale measured in this current study was as follows: GEN-HL: 0.90, HC-HL: 0.95, DP-HL: 0.94, and HP-HL: 0.94.
2.4. Analysis
Quantitative variables were described by mean and standard deviation. To compare the two groups, the Mann–Whitney test was used. Differences among three and more groups were verified by the Kruskal–Wallis test. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 23. Statistically significant results accepted were p ≤ 0.05.
According to authors of the HLS-EU-Q47 [18,37], the scores for general HL, health care HL, disease prevention HL, and health promotion HL were categorised into ‘inadequate HL’: score 0–25, ‘problematic HL’: score 25.01–33, ‘sufficient HL’: score 33.01–42, and ‘excellent HL’: score 42.01–50.
2.5. Ethical Aspects
The research was conducted in accordance with the research protocol approved by the Ethical Committee at the Medical University of Lublin—no KE-0254/31/2016—and the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. Each of the respondents gave their voluntary consent in writing before the start of the study and were informed about the purpose of the study. Consent was also obtained from the directors of the institutions where research was carried out.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Studied Group
Participants were predominantly female (65.2%). The age of respondents ranged from 65 to 94 years (M = 72.41, SD = 6.90). Most of them had secondary (42.8%) and primary (40.6%) education. More than half of the elders (56.5%) were living in urban areas and with family (39.9%). More than half (55.8%) of the elders rated their personal health as ‘bad’ or ‘fair’. More detailed data are included in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographic and socio-economic variables.
3.2. The General Level of Health Literacy Among Seniors
Health literacy of seniors is on average somewhat higher for health care (M = 32.82) or disease prevention (M = 31.83) than for health promotion (M = 31.02) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Means results in HL Indices and the level of HL.
More than half of the elderly surveyed presented a problematic level of general HL (50.4%), and also a problematic level of other dimensions of HL (Figure 1).
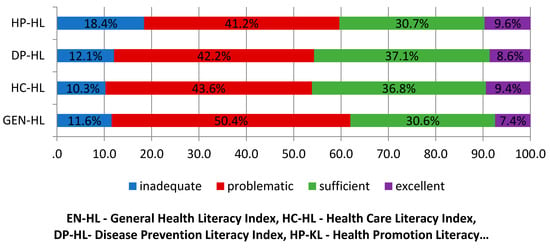
Figure 1.
Percentages of HL indices levels thresholds.
3.3. HLS-EU Health Literacy Indices of Seniors vs Their Sociodemographic Characteristics
No statistical differences between men and women were found regarding GEN-HL and all three dimensions of HL. Seniors with higher education tend to have higher health literacy level in general and in all three dimensions, as compared to seniors with primary and secondary education. Differences for GEN-HL and HC-HL are statistically significant (p < 0.05). Seniors from urban area obtained higher mean results for GEN-HL and all three dimensions of HL than seniors from rural areas, and these differences are statistically significant (p < 0.05). The age of the seniors did not differentiate their mean results for GEN-HL and all its dimensions. Seniors who participated in activities run by the Daily Center for the Elderly or other organisations/institutions and those who self-assessed their health condition as very good and good obtained higher mean results for GEN-HL and two out of the three dimensions of HL. Differences are statistically significant (p < 0.05). (Table 3).

Table 3.
Mean Scores for GEN-HL, HC-HL, DP-HL, and HP-HL by gender, education, place of residence, age, participation in activities run by Daily Center for the Elderly or other organisations/institutions, and self-assessment of health condition.
Seniors aged over 75 years (58.0%), those with higher education (55%), and those who self-assessed their health condition as fair or bad (61.1%) more often presented a problematic level of GEN-HL. Seniors from rural areas (16.3%) and those who did not participate in activities run by the Daily Center for the Elderly or other organisations/institutions (15.9%) more often showed inadequate levels of GEN-HL than seniors from urban areas (8.3%) and seniors who admitted their participation in such activities (2.6%). None of the seniors with higher education presented an inadequate level of GEN-HL (Figures S1–S6 in supplementary materials).
4. Discussion
Improving people’s health literacy is one of the most basic, effective, and economic measures to improve the health of the whole population [9,22]. Improved HL levels contribute to increased health outcomes, well-being, and reduced health inequalities [39].
The aim of this study was to determine the level of health literacy in the group of people above 65 years old. The study showed that 62% of the surveyed people had insufficient General HL, (11.6% inadequate, 50.4% problematic), and only 7.4% had excellent General HL. This is a significantly lower HL than in people under 65 years of age. Research conducted by Słońska et al. [32] indicated that in the group of people over 65 years of age, the percentage of people with insufficient HL was the highest when comparing with younger respondents, and it exceeded 60%. Similarly, in another study that evaluated health literacy according to demographic characteristics of Americans aged 16 and over, the oldest group of adults (65 and over) had the lowest HL levels [26]. In our study, there were no statistical differences between respondents representing early and late elderly groups; however, those over 75 years of age more often presented problematic levels of GEN-HL.
As it is shown by other studies, as people get older, they have limited resources such as cognitive skills and social capital, resulting in limited access to information about health services [40,41,42,43]. Therefore, following the results of this current study, interventions that enhance health literacy should be particularly planned for the ageing population. The main aim is to make older adults more independent when searching for information about health and protection, and in understanding and applying this information in their daily lives for the successful self-management of long-term conditions [44].
This study assesses HL in three health-related areas: health care (HC-HL), disease prevention (DP-HL), and health promotion (HP-HL). In all areas studied, the level of HL was insufficient in more than half of the elderly people. The biggest deficits in HL were found in the area of health promotion (18.4% inadequate and 41.2% problematic). Few studies have been conducted that have mainly focused on the impact of health literacy in relation to health promotion alone [45]. One such study on the relationship between health literacy and health-related behaviour was conducted in the context of health promotion in China. It was concluded that in order to reduce risky habits, educational interventions to improve health awareness should be carried out simultaneously within the framework of health promotion activities [46].
Our current research has shown that factors such as education level, place of residence, and participation in activities run by the Daily Center for the Elderly or other organisations/institutions significantly differentiate the HL level of elderly people. People with higher education, who live in the city, and who participate in activities run by the Daily Center for the Elderly or other organisations/institutions were more likely to have sufficient and/or excellent HL. The results of Cordasco et al. [47] and Patel et al. [48] confirm that education is the strongest predictor of health knowledge and clearly shows the importance of education in shaping health literacy.
Our study has also shown that people who perceive their health as very good or good have a significantly higher level of HL than those who assess their health condition badly. Statistically significant differences have been shown in both the general level of HL and in the area of HC-HL and HP-HL. This result is consistent with studies by other authors. The National Assessment of Adult Literacy Report [26] in the USA indicates that 16% of adults (50 million people) who do not have basic health knowledge report their health as poor (42%) more often than adults with good health knowledge. These people are also less likely to benefit from preventive health measures. They make greater use of services designed to treat complications of the disease. The same people tend to use the health care system only when they are very ill, which consequently increases the length of treatment and reduces positive health outcomes [49].
Other studies have shown that having limited literacy and numeracy also acts as an independent risk factor for ill health, leading to medication errors and insufficient understanding of the disease and treatment [50]. In addition, there is a link between literacy and health outcomes that directly corresponds to several health-related disadvantages, such as health and health care knowledge, hospitalisation, and some chronic diseases. Poor knowledge of health issues and limited access to education can lead to a deficiency in managing one’s own health potential [51].
In the context of the unsatisfactory level of health literacy among the elderly and the growing ageing population of European society, there is a great need to increase the level of knowledge about health among people over 65 years of age. The results of the presented study allow us to consider the elderly as a particularly vulnerable group also in the context of health literacy. Taking into account the increase in the dynamics of the demographic process and the reduction of the caring potential of families, it is recommended that we develop an effective, easily accessible system of care for the elderly, in which health education would play a crucial role. In order to be effective, health education requires tailored communication based on trust developed between health care professionals and seniors as a facilitating factor for meeting their health literacy needs [44]. This, in turn, requires specific skills of health professionals, knowledge of the learning styles of seniors, their cognitive and technical resources, and the time to conduct individualised education.
It is worth stressing that the approach towards health literacy in the field of public health is based on the premise that health literacy is ‘not only a personal resource with leads to personal benefits, e.g., healthier life choices and effective use of available health services’ [3], but also a community source that enables community action on health and allows for better control of social and environmental health determinants.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. The main limitation is the relatively small number of seniors who took part in the study and the convenience sampling methodology, which is a non-probabilistic method and, as such, prevents the generalizability of the result. Even though seniors were willing to cooperate and most of them agreed to take part in the study, not all of them fulfilled the criteria of a minimum of 26 points on the MoCa scale to be eligible for the study group. Another limitation is in regards the questionnaire used in the study, which consisted of 47 items. It could had made respondents confused in providing reliable answers to all the questions included in the questionnaire. Additionally, the eligible seniors represented only one of regions from Poland, which can be seen as a selection bias.
5. Conclusions
Our study revealed that the level of health literacy of seniors aged 65+ is insufficient. Among variables that differentiate the level of seniors’ health literacy are the level of education, place of living, self-assessment of health condition, and participation in activities run by different institutions that support healthy ageing. These results imply an important message that there is a need to create initiatives and programs improving health literacy targeted at seniors living in rural areas, those with lower levels of education, and those with poor access to activities organised by institutions supporting seniors. The improvement of health literacy may help to improve the control of elders over their health and its determinants, and to maintain their independence in this regard. More research of a qualitative nature would make it possible to deepen knowledge regarding the reasons of poor health literacy among seniors and their expectations in its improvement.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/8/3/277/s1, Figure S1: Percentages of HL Indices Levels Thresholds by gender; Figure S2: Percentages of HL Indices Levels Thresholds by age; Figure S3: Percentages of HL Indices Levels Thresholds by education; Figure S4: Percentages of HL Indices Levels Thresholds by place of living; Figure S5: Percentages of HL Indices Levels Thresholds by participation in activities run by Daily Center for the Elderly or other organizations/institutions; Figure S6: Percentages of HL Indices Levels Thresholds by Self-assessment of health condition
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.K., A.D. and B.D.; Data curation, A.D., J.B., J.C.-M., M.B., M.M., A.C.-R. and B.D.; Formal analysis, B.K., J.B., J.C.-M., M.B., M.M., A.C.-R., K.J. and B.D.; Investigation, A.D., J.B., J.C.-M., M.B., M.M., A.C.-R. and B.D.; Methodology, B.K., J.B. J.C.-M., M.B., M.M., A.C.-R., K.J. and B.D.; Project administration, B.D.; Supervision, B.D.; Writing—original draft, B.K. and A.D.; Writing—review & editing, B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Erasmus+ program KA2-HE-19/14, Strategic partnership in HE, grant number nr 14-203-000685.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge all seniors who agreed to participate in the study and also directors of daily centers for elderly. Additionally, we would like to thank coordinator of the project Healthy lifestyle for ageing well (HLAW)—Nursing College in Celje (Slovenia) and project partners (representatives from University of Oulu (Finland) and CESPU (Portugal) for cooperation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Couture, E.M.; Chouinard, M.-C.; Fortin, M.; Hudo, C. The relationship between health literacy and quality of life among frequent users of health care services: A cross-sectional study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Pelikan, J.; Slonska, Z.; Brand, H. Health literacy and public health: A systematic review and integration of definitions and models. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutbeam, D. Health literacy as a public health goal: A challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promot. Int. 2000, 15, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.J.; Terry, A.; McHorney, C.A. Impact of health literacy on medication adherence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, S.; Jungeblut, K.; Jenkins, L.; Kolstad, A. Adult Literacy in America a First Look at the Findings of the National Adult Literacy Survey, 3rd ed.; Department of Education Office of Educational Research and Improvement: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorsi, G.; Lorini, C.; Baldasseroni, A.; Porchia, B.R.; Capecchi, L. Health services and health literacy: From the rationale to the many facets of a fundamental concept. A literature review. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanità 2016, 52, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, R. Designing health-literate health care organization: A literature review. Health Serv. Manag. Res. 2016, 29, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkman, N.; Sheridan, S.; Donahue, K.; Halpern, D.; Crotty, K. Low health literacy and health outcomes: An updated systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Nutbeam, D.; Kato, M.; Okuhara, T.; Okada, M.; Kiuchi, T. Improving health literacy in a Japanese community population-A pilot study to develop an educational programme. Health Expect. 2018, 21, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çaylan, A.; Yayla, K.; Öztora, S.; Dağdeviren, H.N. Assessing health literacy, the factors affecting it and their relation to some health behaviors among adults. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, 6803–6807. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.W.; Gazmararian, J.A.; Williams, M.V.; Scott, T.; Parker, R.M.; Green, D.; Ren, J.; Peel, J. Functional health literacy and the risk of hospital admission among Medicare managed care enrollees. Am. J. Public Health 2002, 92, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.W.; Hawkins, M.; Collins, P.A.; Buchbinder, R.; Osborne, R.H. Health literacy: Applying current concepts to improve health services and reduce health inequalities. Public Health 2016, 132, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, N.S.; Field, T.S.; Wagner, J.L.; Cutrona, S.L.; Roblin, D.W.; Gaglio, B. The association between health literacy and cancer-related attitudes, behaviors, and knowledge. J. Health Commun. 2013, 18, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, K.W.; Santiago-Turla, C.; Stinnett, S.S.; Herndon, L.W.; Allingham, R.R.; Challa, P.; Lee, P.P. Health literacy and adherence to glaucoma therapy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 142, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, J.; Williams, A.; Dennis, S.; Newall, A.; Shortus, T.; Zwar, N.; Denney-Wilson, E.; Harris, M.F. A systematic review of interventions in primary care to improve health literacy for chronic disease behavioral risk factors. BMC Fam. Pract. 2012, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, I.; Tighe, E.L.; Greenberg, D.; Mavreles, M. Health Literacy and Adults with Low Basic Skills. Adult Educ. Q. 2018, 68, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhaldi, T.M.; Al-Jumaili, A.A.; Alnemer, K.A.; Alharbi, K.; Al-Akeel, E.S.; Alharbi, M.H.; Alshabanah, O.; Juwair, A.B.; Khoja, A. Measuring the health literacy level of Arabic speaking population in Saudi Arabia using translated health literacy instruments. J. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 16, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, K.; Pelikan, J.M.; Rothlin, F.; Ganahl, K.; Slonska, Z.; Doyle, G.; Fullam, J.; Kondilis, B.; Agrafiotis, D.; Uiters, E.; et al. HLS-EU Consortium. Health literacy in Europe: Comparative results of the European health literacy survey (HLS-EU). Eur. J. Public Health 2015, 25, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Osaka, W.; Togari, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Yonekura, Y.; Sekido, A.; Matsumoto, M. Comprehensive health literacy in Japan is lower than in Europe: A validated Japanese- language assessment of health literacy. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heide, I.; Uiters, E.; Sørensen, K.; Rothlin, F.; Pelikan, J.; Rademakers, J.; Boshuizen, H. Health literacy in Europe: The development and validation of health literacy prediction models. Eur. J. Public Health 2016, 26, 906–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafo, E.; Wong, S. Health literacy programs for older adults: A systematic literature review. Health Educ. Res. 2012, 27, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geboers, B.; de Winter, A.F.; Spoorenberg, S.L.W.; Wynia, K.; Reijneveld, S.A. The association between health literacy and self-management abilities in adults aged 75 and older, and its moderators. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 25, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Jin, H.; Shi, N.; Duan, C.; Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Li, X. The relationship between health literacy and quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2018, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storms, H.; Claes, N.; Aertgeerts, B.; Van den Broucke, S. Measuring health literacy among low literate people: An exploratory feasibility study with the HLS-EU questionnaire. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safeer, R.S.; Keenan, J. Health literacy: The gap between physicians and patients. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kutner, M.; Greenberg, E.; Jin, Y.; Paulsen, C. The Health Literacy of America’s Adults: Results from the 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy; United States Department of Education; National Center for Education Statistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/pubs2006/2006483.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2020).
- Javadzade, S.; Sharifirad, G.; Radjati, F.; Mostafavi, F.; Reisi, M.; Hasanzade, A. Relationship between health literacy, health status, and healthy behaviors among older adults in Isfahan, Iran. Educ. Health Promot. 2012, 1, 31. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Directorate-General for Economic and Financial Affairs. The 2015 Ageing Report Underlying Assumptions and Projection Methodologies. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/economy_finance/publications/european_economy/2014/pdf/ee8_en.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2020).
- Serper, M.; Patzer, R.E.; Curtis, L.M.; Smith, S.G.; O’Conor, R.; Baker, D.W.; Wolf, M.S. Health literacy, cognitive ability, and functional health status among older adults. Health Serv. Res. 2014, 49, 1249–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutilli, C.C. Health literacy in geriatric patients: An integrative review of the literature. Orthop. Nurs. 2007, 26, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, L.C.; Wardle, J.; Wolf, M.S.; von Wagner, C. Cognitive function and health literacy decline in a cohort of aging English adults. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słońska, Z.A.; Borowiec, A.A.; Aranowska, A.E. Health literacy and health among the elderly: Status and challenges in the context of the Polish population aging process. Anthropol. Rev. 2015, 78, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplaga, M. Determinants and consequences of limited health literacy in Polish society. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Poland. Sytuacja Demograficzna Osób Starszych i Konsekwencje Starzenia się Ludności Polski w Świetle proGnozy na Lata 2014–2050. In Demographic Situation of the Elderly and the Consequences of the Aging of the Polish Population in the Light of the Forecast for 2014–2050; Główny Urząd Statystyczny: Warsaw, Poland, 2014. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/files/gfx/portalinformacyjny/pl/defaultaktualnosci/5468/18/1/1/ludnosc_w_starszym_wieku.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Adamczyk, M. The Specificity of Ageing Processes of Population of the Lubelskie Voivodship. In Demographic Situation of Lubelskie Voivodship as a Challenge for Social and Economic Policy; Hrynkiewicz, J., Potrykowska, A., Eds.; The Government Population Council: Warsaw, Poland, 2017; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Montreal Cognitive Assessment Test (MoCA). Available online: https://www.mocatest.org/ (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Pelikan, J.M.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Slonska, Z.; Kondilis, B.; Stoffels, V.; Osborne, R.H.; Brand, H. Measuring health literacy in populations: Illuminating the design and development process of the European Health Literacy Survey Questionnaire (HLS-EU-Q). BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimo, H.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, T.; Araki, A.; Hosoi, T.; Sawabe, M. Reviewing the definition of “elderly”. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2006, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okan, O.; Lopes, E.; Bollweg, T.M.; Bröder, J.; Messer, M.; Bruland, D.; Bond, E.; Carvalho, G.S.; Sørensen, K.; Saboga-Nunes, L.; et al. Generic health literacy measurement instruments for children and adolescents: A systematic review of the literature. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, G.J.; Mackert, M.; Becker, H. Memory performance, health literacy, and instrumen- tal activities of daily living of community residing older adults. Nurs. Res. 2012, 61, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.S.; Feinglass, J.; Thompson, J.; Baker, D.W. In search of “low health literacy”: Threshold vs. gradient effect of literacy on health status and mortality. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 70, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Lee, H.J.; Chung, S. Age Differencesin Health Literacy: Korean Adults Havea Higher Level of Health Literacy than Older Korean Adults? Health Soc. Work 2017, 42, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzer, C.A.; Insel, K.C.; Ritter, L.S. Associations between working memory, health literacy, and recall of the signs of stroke among older adults. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2012, 44, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.; Ballinger, C.; Nutbeam, D.; Adams, J. The importance of building trust and tailoring interactions when meeting older adults’ health literacy needs. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wagner, C.; Knight, K.; Steptoe, A.; Wardle, J. Functional health literacy and health-promoting behavior in a national sample of British adults. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2007, 61, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.L. Relationship between Health Literacy, Health-Related Behaviors and Health Status: A Survey of Elderly Chinese. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9714–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordasco, K.M.; Homeier, D.C.; Franco, I.; Wang, P.C.; Sarkisian, C.A. Health literacy screening of geriatric monolingual Spanish-speaking patients using single-item literacy screening questions and education. Health Educ. J. 2012, 71, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.J.; Joel, S.; Rovena, G.; Pedireddy, S.; Saad, S.; Rachmale, R.; Shukla, M.; Deol, B.B.; Cardozo, L. Testing the utility of the newest vital sign (NVS) health literacy assessment tool in older African-American patients. Patient Educ. Couns. 2011, 85, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesser, A.K.; Keene Woods, N.; Smothers, K.; Rogers, N. Health literacy and older adults: A systematic review. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2016, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.A.M.; Franklin, G.V. Health Literacy: An Intervention to Improve Health. In Strategies to Reduce Hospital Mortality in Lower and Middle Income Countries (LMICs) and Resource-Limited Settings; Mullings, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/strategies-to-reduce-hospital-mortality-in-lower-and-middle-income-countries-lmics-and-resource-limited-settings (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- De Walt, D.A.; Broucksou, K.A.; Hawk, V.; Brach, C.; Hink, A.; Rudd, R.; Callahan, L. Developing and testing the health literacy universal precautions toolkit. Nurs. Outlook 2011, 59, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).