Factors Related to Diabetes Mellitus in the Middle-Aged and Over in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
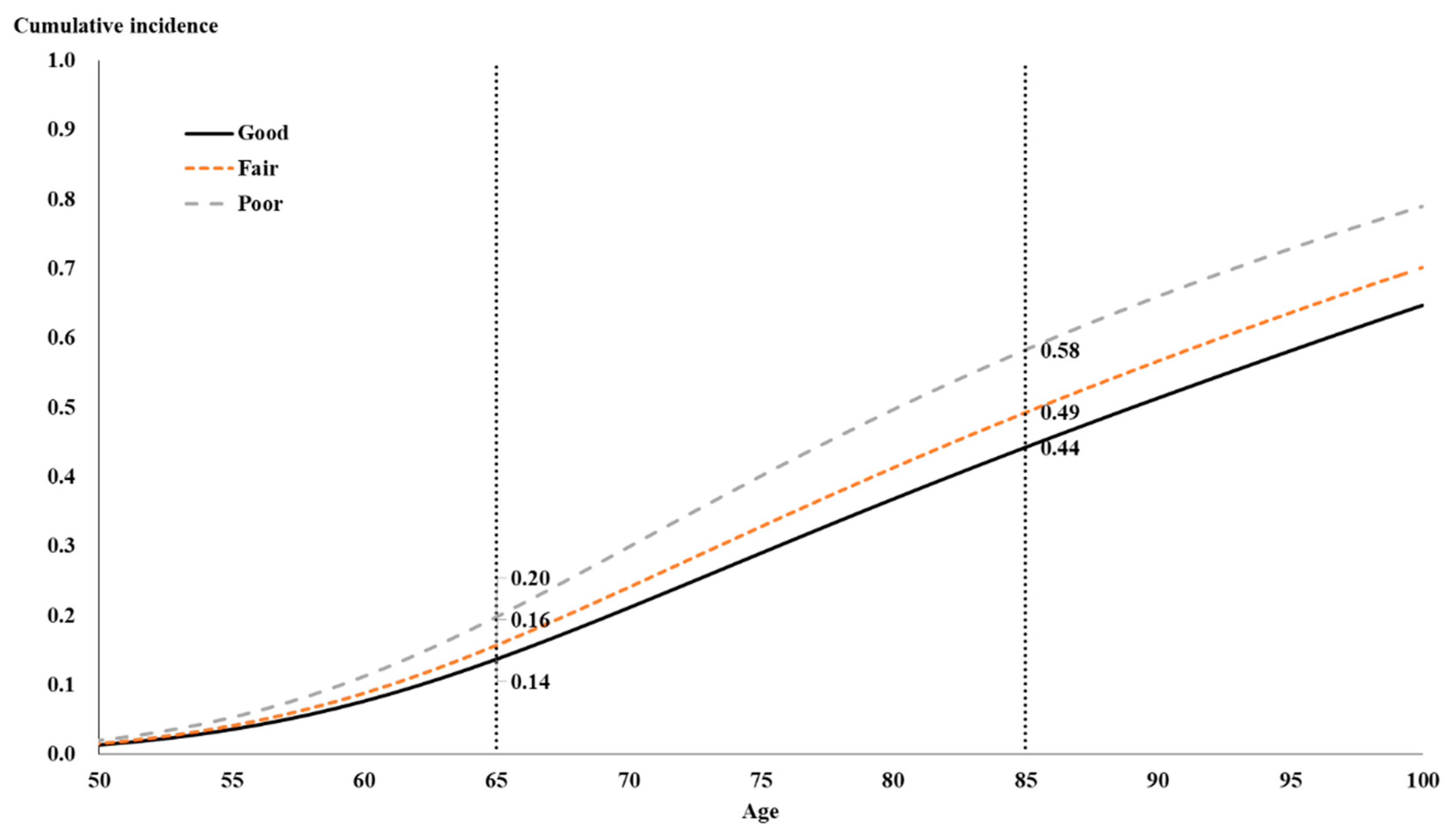
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistics Division, Ministry of Health and Welfare, ROC (Taiwan). 2018 Cause of Death Statistics; Ministry of Health and Welfare, ROC (Taiwan): Taipei, Taiwan, 2020. Available online: https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/DOS/lp-4927–113.html (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Assmann, G.; Schulte, H. Diabetes mellitus and hypertension in the elderly: Concomitant hyperlipidemia and coronary heart disease risk. Am. J. Cardiol. 1989, 63, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.; Pan, W.H. Coagulation activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: The higher coronary risk of female diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 1995, 12, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, S.J.; Petrie, J.R.; Ueda, S.; Elliott, H.L.; Connell, J.M. Insulin as a vascular hormone: Implications for the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1998, 25, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, N.M. The deadly quartet. Upper-body obesity, glucose intolerance, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension. Arch. Intern. Med. 1989, 149, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.T.; Chen, C.J.; Fuh, M.M.; Narayan, K.M. Cause of death and associated factors among patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Taipei, Taiwan. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1999, 43, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, ROC (Taiwan). National Health Insurance Annual Statistical Report 2018; National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, ROC (Taiwan): Taipei, Taiwan, 2020. Available online: https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-4574-49817-2.html (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Lin, C.H.; Liu, S.C.; Liu, G.W. The effects of trends in mortality due to the leading causes of death on potential lost life and economic loss in Taiwan. Taiwan J. Public Health 2015, 34, 168–179. [Google Scholar]
- Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, ROC (Taiwan). Statistics of Health Promotion 2018; Ministry of Health and Welfare, ROC (Taiwan): Taipei, Taiwan, 2020. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=268&pid=12886 (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Tseng, C.H.; Chong, C.K.; Heng, L.T.; Tseng, C.P.; Tai, T.Y. The incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Taiwan. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2000, 50, S61–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development Council, ROC (Taiwan). Population Projections for ROC (Taiwan): 2018-2065; National Development Council, ROC (Taiwan): Taipei, Taiwan, 2018. Available online: https://pop-proj.ndc.gov.tw/main_en/dataSearch.aspx?uid=78&pid=78&upn=8D038F3F06D3982D (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Molarius, A.; Janson, S. Self-rated, Chronic disease, and symptoms among middle-aged and elderly men and women. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2002, 55, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, G.; Gariépy, G.; Pagé, V.; Schmitz, N. Indicators of self-rated health in the Canadian population with diabetes. Diabetic Med. 2012, 29, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.T.; James, M.K.; Miller, M.E.; Worley, A.S.; Longino, C.F., Jr. The timing of change: Patterns in transitions in functional status among elderly persons. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 1998, 53, S17–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Huang, Z.S.; Ng, S.K.; Chan, K.W.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, H.W.; Lee, J.J. Impact of alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking on stroke among the elderly in Taiwan. Stroke 1995, 26, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.C.; Chi, S.H.; Wang, J.Y. Association of perceived stress with depressive symptoms in older Taiwanese: Results of a population-based study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Wang, J.Y. The decline in physical and mental health among older chronic stroke patients in Taiwan. Taiwan J. Public Health 2013, 32, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, H.P.; Tsai, A.C.; Wang, J.Y. Combined effect of body mass index and physical activity on the decline in walking ability amongst older Taiwanese. Taiwan J. Public Health 2014, 33, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.J.; Wang, J.Y. Association between reading and cognitive decline in older Taiwanese people. Taiwan J. Public Health 2016, 35, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, S.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Tsai, A.C. Combined association of leisure-time physical activity and fruit and vegetable consumption with depressive symptoms in older Taiwanese: Results of a national cohort study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.C.; Chen, L.C.; Wang, J.Y. Predicting emerging care-need with simple functional indicators-findings from a national cohort study in Taiwan. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.C.; Liou, J.C.; Chang, M.C. Interview to study the determinants of hypertension in older adults in Taiwan: A population based cross-sectional survey. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Tsai, A.C. The short-form mini-nutritional assessment is as effective as the full-mini nutritional assessment in predicting follow-up 4-year mortality in elderly Taiwanese. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pimienta, E.; González-Castro, T.B.; Fresan, A.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; Martínez-López, M.C.; Barjau-Madrigal, H.A.; Ramírez-González, I.R.; Martínez-Villaseñor, E.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; Villar-Soto, M.; et al. Decreased quality of life in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with emotional distress. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzol, D.; Smith, L.; Koyanagi, A.; Stubbs, B.; Grabovac, I.; Jackson, S.E.; Veronese, N. Do older people with diabetes meet the recommended weekly physical activity targets? An analysis of objective physical activity data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.J.; Li, S.L.; Wu, C.H.; Du, Y.F. BMI trajectories as a harbinger of pre-diabetes or underdiagnosed diabetes: An 18-year retrospective cohort study in Taiwan. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2015, 31, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.C.; Lee, S.H. Determinants of new-onset diabetes in older adults—Results of a national cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.C.; Hsu, W.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Weng, S.J.; Yang, H.P.; Liu, S.C. Healthy life expectancies by the effects of hypertension and diabetes for the middle aged and over in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.C.; Ku, C.C.; Chiou, S.T.; Chan, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Lai, M.S.; Lin, H.H. Adult mortality of diseases and injuries attributable to selected metabolic, lifestyle, environmental, and infectious risk factors in Taiwan: A comparative risk assessment. Popul. Health Metr. 2017, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics and Status | Cohort B (n = 4049) | Cohort A (n = 2462) | Cohort C (n = 1599) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Gender | Female | 1738 | 42.92 | 1194 | 48.50 | 786 | 49.16 |
| Male | 2311 | 57.08 | 1268 | 51.50 | 813 | 50.84 | |
| Ethnicity | Fukien | 2451 | 60.92 | 1808 | 73.47 | 1200 | 75.04 |
| Hakka | 603 | 14.99 | 425 | 17.27 | 278 | 17.39 | |
| Mainlander | 900 | 22.37 | 189 | 7.68 | 85 | 5.32 | |
| Aboriginal | 69 | 1.72 | 39 | 1.58 | 36 | 2.25 | |
| Education | Illiteracy | 1676 | 41.58 | 625 | 25.38 | 47 | 2.94 |
| Elementary school | 1595 | 39.57 | 1237 | 50.24 | 777 | 48.59 | |
| Junior high school | 327 | 8.11 | 251 | 10.19 | 231 | 14.45 | |
| Senior high school | 433 | 10.74 | 349 | 14.18 | 544 | 34.02 | |
| Spouse | Yes | 2618 | 64.69 | 2061 | 83.71 | 1327 | 82.99 |
| No | 1429 | 35.31 | 401 | 16.29 | 272 | 17.01 | |
| Residential location | City | 1917 | 47.35 | 935 | 38.33 | 777 | 48.81 |
| Town | 726 | 17.93 | 575 | 23.58 | 367 | 23.05 | |
| Countryside | 1406 | 34.72 | 929 | 38.09 | 448 | 28.14 | |
| Economic status | Good | 1683 | 43.20 | 822 | 35.16 | 577 | 36.76 |
| Fair | 1524 | 39.12 | 1068 | 45.68 | 499 | 31.78 | |
| Poor | 689 | 17.68 | 448 | 19.16 | 494 | 31.46 | |
| Social activity | Yes | 1564 | 38.63 | 978 | 39.79 | 649 | 40.59 |
| No | 2485 | 61.37 | 1480 | 60.21 | 950 | 59.41 | |
| Characteristics and Status | Cohort B (n = 4049) | Cohort A (n = 2462) | Cohort C (n = 1599) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Hypertension | No | 2960 | 73.43 | 1906 | 78.73 | 1283 | 80.79 |
| Yes | 1071 | 26.57 | 515 | 21.27 | 305 | 19.21 | |
| Heart disease | No | 3159 | 78.29 | 2197 | 90.90 | 1494 | 93.84 |
| Yes | 876 | 21.71 | 220 | 9.10 | 98 | 6.16 | |
| Cataract | No | 3460 | 85.56 | 2247 | 91.34 | 1554 | 97.43 |
| Yes | 584 | 14.44 | 213 | 8.66 | 41 | 2.57 | |
| Stroke | No | 3856 | 95.66 | 2392 | 97.35 | 1570 | 98.25 |
| Yes | 175 | 4.34 | 65 | 2.65 | 28 | 1.75 | |
| Kidney disease | No | 3786 | 93.71 | 1313 | 94.22 | 1485 | 93.28 |
| Yes | 254 | 6.29 | 142 | 5.78 | 107 | 6.72 | |
| ADL a | Good | 3801 | 94.04 | 2425 | 98.50 | 1590 | 99.44 |
| Fair | 93 | 2.30 | 20 | 0.81 | 3 | 0.19 | |
| Poor | 148 | 3.66 | 17 | 0.69 | 6 | 0.38 | |
| Physical function b | Good | 3307 | 81.73 | 2319 | 94.19 | 1532 | 95.81 |
| Fair | 510 | 12.61 | 102 | 4.14 | 48 | 3.00 | |
| Poor | 229 | 5.66 | 41 | 1.67 | 19 | 1.19 | |
| Depression c | No | 3036 | 77.91 | 1943 | 82.86 | 1397 | 88.98 |
| Yes | 861 | 22.09 | 402 | 17.14 | 173 | 11.02 | |
| Self-rated health | Good | 1526 | 37.99 | 988 | 42.08 | 902 | 56.41 |
| Fair | 1491 | 37.12 | 783 | 33.35 | 443 | 27.70 | |
| Poor | 1000 | 24.89 | 577 | 24.57 | 254 | 15.88 | |
| Smoking | No | 2649 | 65.44 | 1752 | 71.16 | 1168 | 73.05 |
| Yes | 1399 | 34.56 | 710 | 28.84 | 431 | 26.95 | |
| Alcohol | No | 3191 | 78.81 | 1846 | 74.98 | 941 | 58.85 |
| Yes | 858 | 21.19 | 616 | 25.02 | 658 | 41.15 | |
| Betel nut chewing | No | 3825 | 94.58 | 2227 | 90.45 | 1444 | 90.31 |
| Yes | 219 | 5.42 | 235 | 9.55 | 155 | 9.69 | |
| Outdoor activity | Yes | 3906 | 96.47 | 2442 | 99.19 | 1593 | 99.62 |
| No | 143 | 3.53 | 20 | 0.81 | 6 | 0.38 | |
| Variables | Overall | Cohort B | Cohort A | Cohort C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | ||
| Hypertension | No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 2.53 *** | 2.35–2.73 | 3.56 *** | 3.18–3.98 | 1.79 *** | 1.49–2.14 | 2.45 *** | 1.86–3.23 | |
| Heart disease | No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1.10 | 0.99–1.21 | 1.06 | 0.94–1.21 | 1.20 | 0.94–1.54 | 0.98 | 0.62–1.54 | |
| Cataract | No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1.04 | 0.93–1.16 | 1.04 | 0.90–1.20 | 1.15 | 0.89–1.47 | 1.52 | 0.82–2.81 | |
| Stroke | No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1.18 | 0.97–1.44 | 1.07 | 0.80–1.43 | 1.26 | 0.78–2.03 | 1.12 | 0.52–2.41 | |
| Kidney disease | No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1.26 *** | 1.11–1.44 | 1.50 *** | 1.24–1.81 | 1.07 | 0.78–1.48 | 0.88 | 0.54–1.43 | |
| ADL | Good | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Fair | 0.68 * | 0.48–0.98 | 0.65 | 0.42–1.02 | 0.54 | 0.17–1.76 | 1.40 | 0.24–8.23 | |
| Poor | 0.53 ** | 0.34–0.83 | 0.63 | 0.38–1.05 | 0.56 | 0.10–3.21 | 1.38 | 0.14–13.35 | |
| Physical function | Good | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Fair | 1.02 | 0.89–1.16 | 0.86 | 0.73–1.02 | 1.37 | 0.98–1.91 | 1.10 | 0.57–2.15 | |
| Poor | 1.14 | 0.87–1.48 | 0.78 | 0.55–1.11 | 2.07 | 0.78–5.51 | 2.46 | 0.91–6.64 | |
| Depression | No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1.03 | 0.93–1.14 | 0.97 | 0.84–1.12 | 0.94 | 0.75–1.19 | 1.27 | 0.86–1.87 | |
| Self-rated health | Good | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Fair | 1.16 *** | 1.07–1.27 | 1.20 ** | 1.06–1.37 | 1.04 | 0.85–1.27 | 1.59 ** | 1.18–2.16 | |
| Poor | 1.50 *** | 1.35–1.67 | 1.51 *** | 1.27–1.79 | 1.42 ** | 1.13–1.79 | 1.88 ** | 1.26–2.81 | |
| Age | Overall | Cohort B | Cohort A | Cohort C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 0.0028 | 0.0029 | 0.0047 | |
| 51 | 0.0033 | 0.0034 | 0.0056 | |
| 52 | 0.0039 | 0.0040 | 0.0066 | |
| 53 | 0.0046 | 0.0046 | 0.0076 | |
| 54 | 0.0052 | 0.0053 | 0.0087 | |
| 55 | 0.0060 | 0.0060 | 0.0099 | |
| 56 | 0.0068 | 0.0068 | 0.0112 | |
| 57 | 0.0076 | 0.0077 | 0.0124 | |
| 58 | 0.0084 | 0.0085 | 0.0137 | |
| 59 | 0.0093 | 0.0094 | 0.0150 | |
| 60 | 0.0101 | 0.0084 | 0.0102 | 0.0163 |
| 61 | 0.0110 | 0.0092 | 0.0111 | 0.0175 |
| 62 | 0.0118 | 0.0099 | 0.0119 | 0.0186 |
| 63 | 0.0126 | 0.0105 | 0.0127 | 0.0197 |
| 64 | 0.0133 | 0.0112 | 0.0134 | 0.0206 |
| 65 | 0.0139 | 0.0117 | 0.0141 | |
| 66 | 0.0145 | 0.0123 | 0.0146 | |
| 67 | 0.0150 | 0.0127 | 0.0151 | |
| 68 | 0.0154 | 0.0131 | 0.0155 | |
| 69 | 0.0157 | 0.0134 | 0.0158 | |
| 70 | 0.0159 | 0.0136 | 0.0160 | |
| 71 | 0.0161 | 0.0138 | 0.0162 | |
| 72 | 0.0162 | 0.0140 | 0.0163 | |
| 73 | 0.0162 | 0.0141 | 0.0164 | |
| 74 | 0.0163 | 0.0141 | 0.0164 | |
| 75 | 0.0162 | 0.0142 | 0.0163 | |
| 76 | 0.0162 | 0.0142 | 0.0163 | |
| 77 | 0.0161 | 0.0142 | 0.0162 | |
| 78 | 0.0160 | 0.0141 | 0.0161 | |
| 79 | 0.0158 | 0.0141 | 0.0159 | |
| 80 | 0.0157 | 0.0140 | 0.0158 | |
| 81 | 0.0155 | 0.0139 | 0.0156 | |
| 82 | 0.0153 | 0.0138 | ||
| 83 | 0.0152 | 0.0137 | ||
| 84 | 0.0150 | 0.0136 | ||
| 85 | 0.0148 | 0.0135 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, C.-C.; Hsu, W.-C.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Weng, S.-J.; Liu, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Factors Related to Diabetes Mellitus in the Middle-Aged and Over in Taiwan. Healthcare 2020, 8, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8030242
Liang C-C, Hsu W-C, Tsai Y-T, Weng S-J, Liu S-C, Lin C-H. Factors Related to Diabetes Mellitus in the Middle-Aged and Over in Taiwan. Healthcare. 2020; 8(3):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8030242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Chia-Chun, Wei-Chung Hsu, Yao-Te Tsai, Shao-Jen Weng, Shih-Chia Liu, and Cheng-Hsiang Lin. 2020. "Factors Related to Diabetes Mellitus in the Middle-Aged and Over in Taiwan" Healthcare 8, no. 3: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8030242
APA StyleLiang, C.-C., Hsu, W.-C., Tsai, Y.-T., Weng, S.-J., Liu, S.-C., & Lin, C.-H. (2020). Factors Related to Diabetes Mellitus in the Middle-Aged and Over in Taiwan. Healthcare, 8(3), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8030242





