Oral Appliances in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
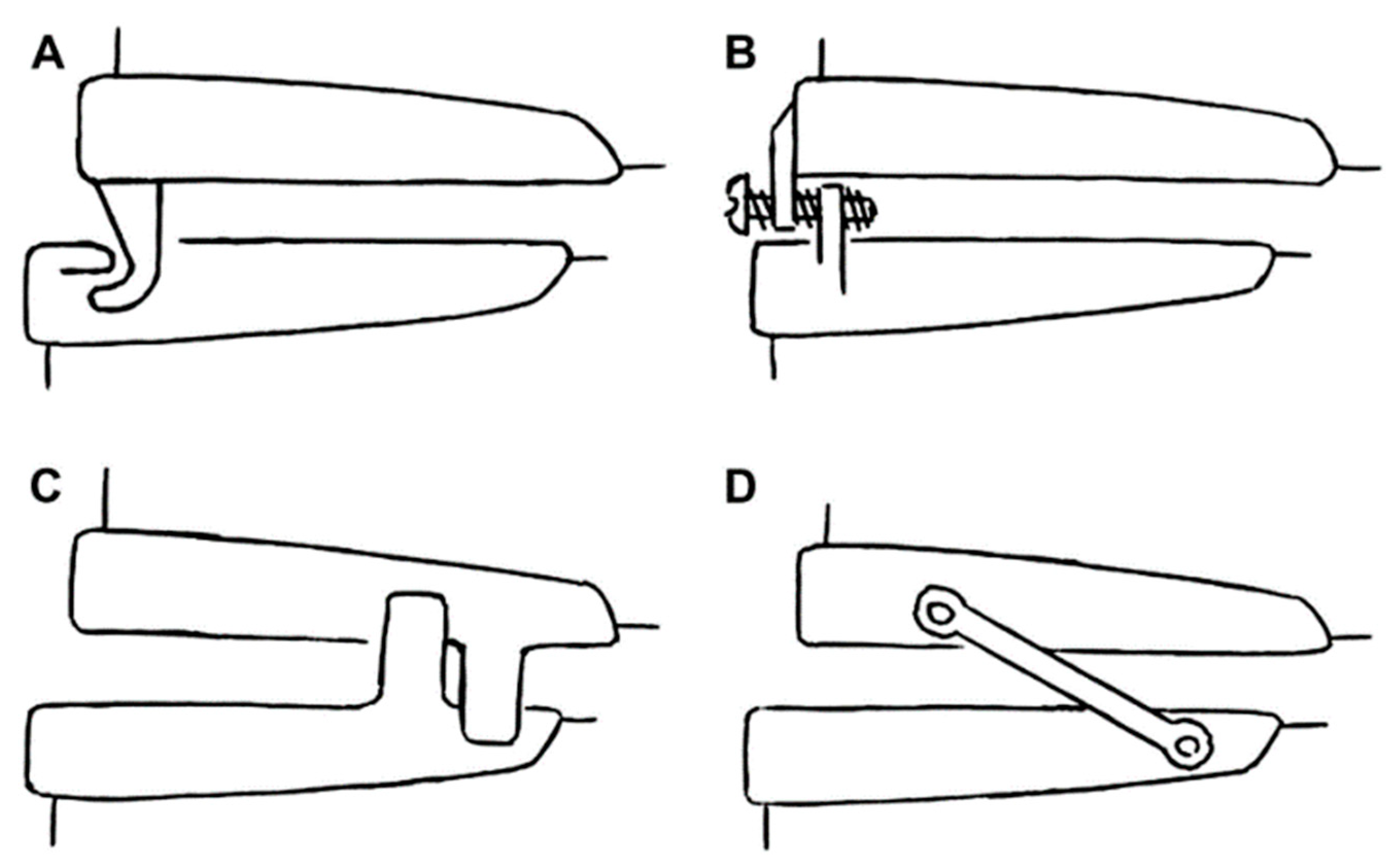
2. Types of Oral Appliances
3. Side Effects
4. Effectiveness and Health Outcomes
4.1. Efficacy
4.2. Adherence
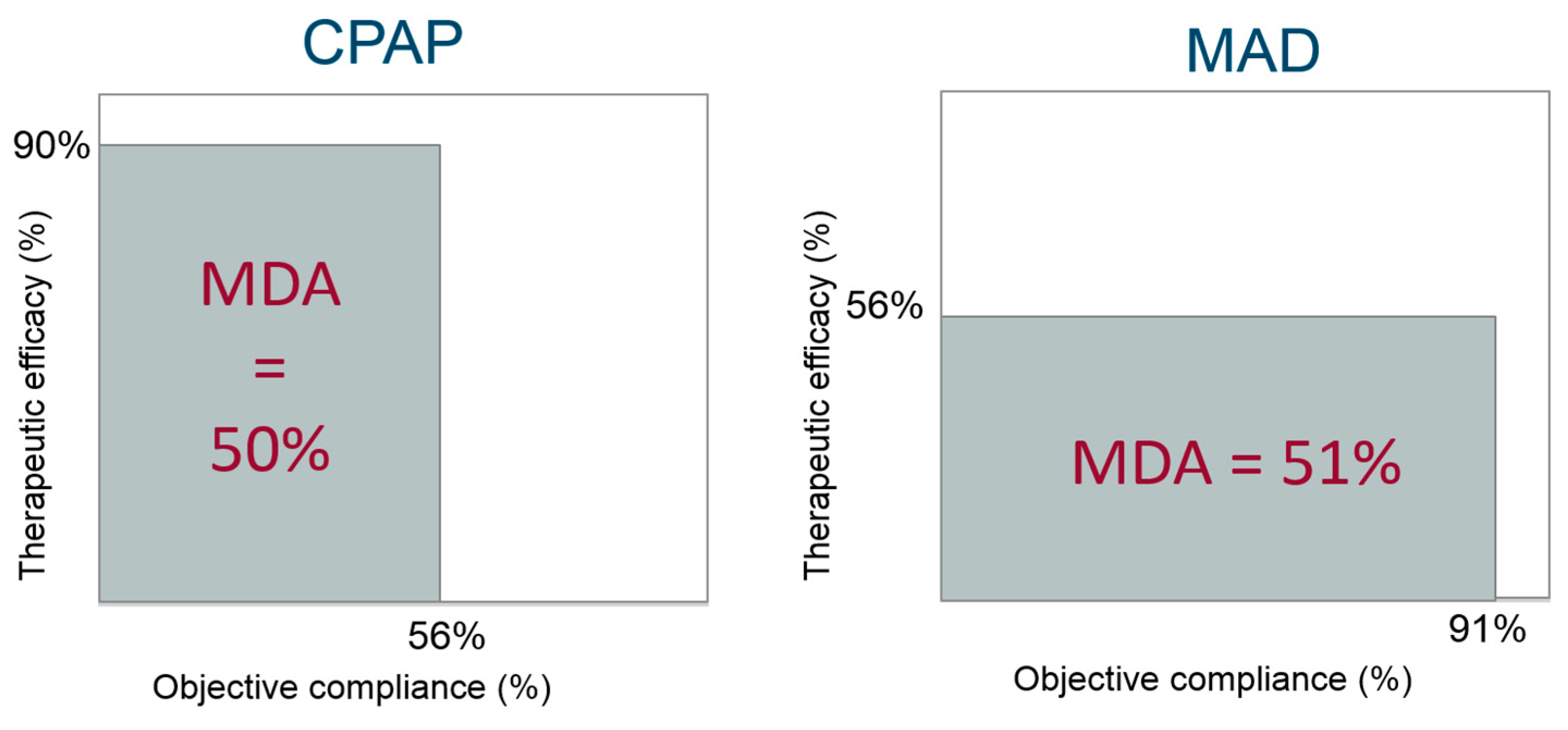
4.3. Overall Clinical Effectiveness
4.4. Health Outcomes
5. Patient Selection
6. Combination Therapy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased Prevalence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilleminault, C.; Tilkian, A.; Dement, W.C. The sleep apnea syndromes. Annu. Rev. Med. 1976, 27, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tregear, S.; Reston, J.; Schoelles, K.; Phillips, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Risk of Motor Vehicle Crash: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seetho, I.W.; Wilding, J.P. Sleep-disordered breathing, type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2014, 11, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, F.J.; Young, T.B.; Lind, B.K.; Shahar, E.; Samet, J.M.; Redline, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Newman, A.B.; Lebowitz, M.D.; Pickering, T.G.; et al. Association of Sleep-Disordered Breathing, Sleep Apnea, and Hypertension in a Large Community-Based Study. JAMA 2000, 283, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Carrizo, S.; Vicente, E.; Agustí, A. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: An observational study. Lancet 2005, 365, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.E.; Issa, F.G.; Berthon-Jones, M.; Eves, L. Reversal of obstructive sleep apnoea by continuous positive airway pressure applied through the nares. Lancet 1981, 1, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotenberg, B.W.; Murariu, D.; Pang, K.P. Trends in CPAP adherence over twenty years of data collection: A flattened curve. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 45, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, C.A.; Littner, M.R.; Hirshkowitz, M.; Morgenthaler, T.I.; Alessi, C.A.; Bailey, D.; Boehlecke, B.; Brown, T.M.; Coleman, J.; Friedman, L.; et al. Practice parameters for the use of continuous and bilevel positive airway pressure devices to treat adult patients with sleep-related breathing disorders. Sleep 2006, 29, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, M.; Franklin, K.A. Dental appliances in the treatment of snoring. A comparison between an activator, a soft-palate lifter, and a mouth-shield. Swed. Dent. J. 1996, 20, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ramar, K.; Dort, L.C.; Katz, S.G.; Lettieri, C.J.; Harrod, C.G.; Thomas, S.M.; Chervin, R.D. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring with Oral Appliance Therapy: An Update for 2015. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 773–827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleetham, J.A.; de Almeida, F.R. Oral Appliances, in European Respiratory Monograph; European Respiratory Society: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 267–285. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.S.; Cistulli, P.A. Oral appliance treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: An update. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2009, 15, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklund, M.; Verbraecken, J.; Randerath, W. Non-CPAP therapies in obstructive sleep apnoea: Mandibular advancement device therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuiki, S.; Lowe, A.; Almeida, F.; Kawahata, N.; Fleetham, J. Effects of mandibular advancement on airway curvature and obstructive sleep apnoea severity. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Gotsopoulos, H.; Darendeliler, A.M.; Cistulli, P.A.; Darendeliler, M.A. Oral Appliance Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Treat. Respir. Med. 2005, 4, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.T.; Arand, D.; Chung, E.; Tong, D. Effect of Anterior Mandibular Positioning on Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, A.; McGrath, C.P.J.; Hägg, U. A systematic review of the efficacy of oral appliance design in the management of obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderveken, O.M.; Devolder, A.; Marklund, M.; Boudewyns, A.N.; Braem, M.J.; Okkerse, W.; Verbraecken, J.A.; Franklin, K.A.; De Backer, W.A.; Van De Heyning, P.H. Comparison of a Custom-made and a Thermoplastic Oral Appliance for the Treatment of Mild Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.A.C.; Juliano, L.; Taga, M.; De Carvalho, L.B.C.; Prado, L.B.F.D.; Prado, G.F.D.; Carvalho, L.B.C.; Prado, L.B.F.; Prado, G.F. Titratable mandibular repositioner appliances for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: Are they an option? Sleep Breath. 2007, 11, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cistulli, P.A.; Gotsopoulos, H.; Marklund, M.; Lowe, A.A. Treatment of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea with mandibular repositioning appliances. Sleep Med. Rev. 2004, 8, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pépin, J.L.; Raymond, N.; Lacaze, O.; Aisenberg, N.; Forcioli, J.; Bonte, E.; Bourdin, A.; Launois, S.; Tamisier, R.; Molinari, N. Heat-moulded versus custom-made mandibular advancement devices for obstructive sleep apnoea: A randomised non-inferiority trial. Thorax 2019, 74, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Isono, S.; Tanaka, A.; Watanabe, T.; Araki, D.; Tanzawa, H.; Nishino, T. Dose-dependent effects of mandibular advancement on pharyngeal mechanics and nocturnal oxygenation in patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Chest 2000, 117, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmers, J.; Charkhandeh, S.; Grosse, J.; Topor, Z.; Brant, R.; Santosham, P.; Bruehlmann, S. Remotely Controlled Mandibular Protrusion during Sleep Predicts Therapeutic Success with Oral Appliances in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep 2013, 36, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, K.A.; Ono, T.; Lowe, A.A.; Al-Majed, S.; Love, L.L.; Fleetham, J.A. A short-term controlled trial of an adjustable oral appliance for the treatment of mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax 1997, 52, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Qian, J.; Petocz, P.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Cistulli, P.A. A Randomized, Controlled Study of a Mandibular Advancement Splint for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johal, A.; Gill, G.; Ferman, A.; McLaughlin, K. The effect of mandibular advancement appliances on awake upper airway and masticatory muscle activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2007, 27, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancer, J.; Al-Faifi, S.; Al-Faifi, M.; Hoffstein, V. Evaluation of variable mandibular advancement appliance for treatment of snoring and sleep apnea. Chest 1999, 116, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.R.; Parker, J.A.; Hodges, J.S.; Lowe, A.A.; Ferguson, K.A. Effect of a Titration Polysomnogram on Treatment Success with a Mandibular Repositioning Appliance. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Fleury, B.; Rakotonanahary, D.; Petelle, B.; Vincent, G.; Fleury, N.P.; Meyer, B.; Lebeau, B. Mandibular advancement titration for obstructive sleep apnea: Optimization of the procedure by combining clinical and oximetric parameters. Chest 2004, 125, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieltjens, M.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Braem, M.J. Current opinions and clinical practice in the titration of oral appliances in the treatment of sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastoer, C.; Dieltjens, M.; Oorts, E.; Braem, M.J.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Hamans, E. The Use of Remotely Controlled Mandibular Positioner as a Predictive Screening Tool for Mandibular Advancement Device Therapy in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea through Single-Night Progressive Titration of the Mandible: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dort, L.C.; Hadjuk, E.; Remmers, J.E. Mandibular advancement and obstructive sleep apnoea: A method for determining effective mandibular protrusion. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.H.; Vázquez, J.-C.; Oshima, T.; Dort, L.; Roycroft, B.; Lowe, A.A.; Hajduk, E.; Remmers, J.E. Remotely Controlled Mandibular Positioner Predicts Efficacy of Oral Appliances in Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, K.A.; Cartwright, R.; Rogers, R.; Schmidt-Nowara, W. Oral Appliances for Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review. Sleep 2006, 29, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsis, A.J.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Gotsopoulos, H.; Petocz, P.; Cistulli, P.A. Effect of Vertical Dimension on Efficacy of Oral Appliance Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolopoulou, M.; Naeije, M.; Aarab, G.; Hamburger, H.L.; Visscher, C.M.; Lobbezoo, F. The effect of raising the bite without mandibular protrusion on obstructive sleep apnoea. J. Oral Rehabil. 2011, 38, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vroegop, A.V.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Braem, M.J. Effects of vertical opening on pharyngeal dimensions in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meurice, J.C.; Marc, I.; Carrier, G.; Series, F. Effects of mouth opening on upper airway collapsibility in normal sleeping subjects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, F.R.; Lowe, A.A.; Tsuiki, S.; Otsuka, R.; Wong, M.; Fastlicht, S.; Ryan, F. Long-term compliance and side effects of oral appliances used for the treatment of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2005, 1, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Marklund, M.; Franklin, K.A. Long-term effects of mandibular repositioning appliances on symptoms of sleep apnoea. J. Sleep Res. 2007, 16, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, M. Predictors of long-term orthodontic side effects from mandibular advancement devices in patients with snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, F.R.; Lowe, A.A.; Otsuka, R.; Fastlicht, S.; Farbood, M.; Tsuiki, S. Long-term sequellae of oral appliance therapy in obstructive sleep apnea patients: Part 2. Study-model analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, E.C.; Staats, R.; Virchow, C.; Jonas, I.E. Occlusal and skeletal effects of an oral appliance in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 2002, 122, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantin, C.C.; Hillman, D.R.; Tennant, M. Dental side effects of an oral device to treat snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 1999, 22, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoda, M.M.; Almeida, F.R.; Pliska, B.T. Long-term side effects of sleep apnea treatment with oral appliances: Nature, magnitude and predictors of long-term changes. Sleep Med. 2019, 56, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araie, T.; Okuno, K.; Minagi, H.O.; Sakai, T. Dental and skeletal changes associated with long-term oral appliance use for obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 41, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagi, H.O.; Okuno, K.; Nohara, K.; Sakai, T. Predictors of Side Effects With Long-Term Oral Appliance Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, L.; Hedner, J.; Grunstein, R.; Kraiczi, H. Therapy with nCPAP: Incomplete elimination of Sleep Related Breathing Disorder. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 16, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderveken, O.M.; Dieltjens, M.; Wouters, K.; De Backer, W.A.; Van de Heyning, P.H.; Braem, M.J. Objective measurement of compliance during oral appliance therapy for sleep-disordered breathing. Thorax 2013, 68, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, K.E.; Iseli, A.; Zhang, J.N.; Xie, X.; Kaplan, V.; Stoeckli, P.W.; Russi, E.W. A Randomized, Controlled Crossover Trial of Two Oral Appliances for Sleep Apnea Treatment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Pazos, M.T.A.; Lamela, C.; Quintanilla, D.S. Prospective evaluation of an oral appliance in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2005, 9, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.D.; Gleadhill, I.C.; Cinnamond, M.J.; Gabbey, J.; Burden, D.J. Mandibular advancement appliances and obstructive sleep apnoea: A randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2002, 24, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, R.A.; Hillman, D.R.; Mateljan, R.; Pantin, C.; Finucane, K.E. Mandibular advancement splint: An appliance to treat snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, C.J.; Paolino, N.; Eliasson, A.H.; Shah, A.A.; Holley, A.B. Comparison of Adjustable and Fixed Oral Appliances for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, L.; Laberge, L.; Beaudry, M.; Laforte, M.; Rompré, P.H.; Lavigne, G.J. Efficacy of two mandibular advancement appliances in the management of snoring and mild-moderate sleep apnea: A cross-over randomized study. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, K.; Takaya, H.; Qian, J.; Petocz, P.; Ng, A.T.; Cistulli, P.A. Oral Appliance Treatment Response and Polysomnographic Phenotypes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.L.; Grunstein, R.R.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Mihailidou, A.S.; Srinivasan, V.K.; Yee, B.J.; Marks, G.B.; Cistulli, P.A. Health Outcomes of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Versus Oral Appliance Treatment for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnadoux, F.; Fleury, B.; Vielle, B.; Pételle, B.; Meslier, N.; N’Guyen, X.L.; Trzepizur, W.; Racineux, J.L. Titrated mandibular advancement versus positive airway pressure for sleep apnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engleman, H.M.; McDonald, J.P.; Graham, D.; Lello, G.E.; Kingshott, R.N.; Coleman, E.L.; Mackay, T.W.; Douglas, N.J. Randomized crossover trial of two treatments for sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome: Continuous positive airway pressure and mandibular repositioning splint. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; McEvoy, R.D.; Banks, S.; Tarquinio, N.; Murray, C.G.; Vowles, N.; Pierce, R.J. Efficacy of Positive Airway Pressure and Oral Appliance in Mild to Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.A.; Ono, T.; Lowe, A.A.; Keenan, S.P.; Fleetham, J.A. A Randomized Crossover Study of an Oral Appliance vs. Nasal-Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in the Treatment of Mild-Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Chest 1996, 109, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.K.; L’Estrange, P.R.; Luo, Y.; Smith, C.; Grant, H.R.; Simonds, A.K.; Spiro, S.G.; Battagel, J.M. Mandibular advancement splints and continuous positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: A randomized cross-over trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2002, 24, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dort, L.; Remmers, J. A Combination Appliance for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: The Effectiveness of Mandibular Advancement and Tongue Retention. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklund, M.; Stenlund, H.; Franklin, K.A. Mandibular advancement devices in 630 men and women with obstructive sleep apnea and snoring: Tolerability and predictors of treatment success. Chest 2004, 125, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kribbs, N.B.; Pack, A.I.; Kline, L.R.; Smith, P.L.; Schwartz, A.R.; Schubert, N.M.; Redline, S.; Henry, J.N.; Getsy, J.E.; Dinges, D.F. Objective Measurement of Patterns of Nasal CPAP Use by Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, M.B.; McRae, M.S.; Longley, W.H. Microsensor technology to help monitor removable appliance wear. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, T.C.; Goz, G. Applicative characteristics of new microelectronic sensors Smart Retainer(R) and TheraMon(R) for measuring wear time. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2010, 71, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.A.; Sjöholm, T.T.; Ryan, C.F.; Fleetham, J.A.; Ferguson, K.A.; Remmers, J.E. Treatment, airway and compliance effects of a titratable oral appliance. Sleep 2000, 23, S172–S178. [Google Scholar]
- Inoko, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Kato, C.; Morita, O.; Kohno, M. Efficacy and safety of temperature data loggers in measuring compliance with the use of oral appliances. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2009, 7, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieltjens, M.; Braem, M.J.; Vroegop, A.V.M.T.; Wouters, K.; Verbraecken, J.A.; De Backer, W.A.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Vanderveken, O.M. Objectively Measured vs. Self-Reported Compliance during Oral Appliance Therapy for Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Chest 2013, 144, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieltjens, M.; Verbruggen, A.E.; Braem, M.J.; Wouters, K.; Verbraecken, J.A.; De Backer, W.A.; Hamans, E.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Vanderveken, O.M. Determinants of Objective Compliance During Oral Appliance Therapy in Patients With Sleep-Disordered Breathing: A Prospective Clinical Trial. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirshenblatt, S.J.; Chen, H.; Dieltjens, M.; Pliska, B.; Almeida, F.R. Accuracy of Thermosensitive Microsensors Intended to Monitor Patient Use of Removable Oral Appliances. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2018, 84, i2. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, K.; Cistulli, P. Mandibular advancement splints for the treatment of sleep apnea syndrome. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2011, 141, 13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, F.R. Complexity and efficacy of mandibular advancement splints: Understanding their mode of action. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ravesloot, M.; De Vries, N. Reliable Calculation of the Efficacy of Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Revisited. Sleep 2011, 34, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, K.; Phillips, C.L.; Cistulli, P.A. Efficacy versus Effectiveness in the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: CPAP and Oral Appliances. J. Dent. Sleep Med. 2015, 2, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haesendonck, G.; Dieltjens, M.; Kastoer, C.; Shivalkar, B.; Vrints, C.; Van De Heyning, C.M.; Braem, M.J.; Vanderveken, O.M. Cardiovascular Benefits of Oral Appliance Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review. J. Dent. Sleep Med. 2015, 2, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, G.E.; Wijkstra, P.J.; Houwerzijl, E.J.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Hoekema, A. Cardiovascular effects of oral appliance therapy in obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Acosta, L.; Hung, Y.L.; Padilla, M.; Enciso, R. Effects of CPAP and mandibular advancement device treatment in obstructive sleep apnea patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2018, 22, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.; Sam, K.; Mok, W.Y.; Cheung, M.T.; Fong, D.Y.; Lam, J.C.; Lam, D.C.; Yam, L.Y.; Ip, M.S. Randomised study of three non-surgical treatments in mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax 2007, 62, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandam, A.; Patil, M.; Akinnusi, M.; Jaoude, P.; El-Solh, A.A. Cardiovascular mortality in obstructive sleep apnoea treated with continuous positive airway pressure or oral appliance: An observational study. Respirology 2013, 18, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, R.; De Almeida, F.R.; Lowe, A.A.; Ryan, F. A comparison of responders and nonresponders to oral appliance therapy for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lowe, A.A.; Orthodont, D.; Fleetham, J.A.; Park, Y.-C. Cephalometric and physiologic predictors of the efficacy of an adjustable oral appliance for treating obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 120, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, K.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Tsuda, H.; Marklund, M.; Gagnadoux, F.; Kushida, C.A.; Cistulli, P.A. Oral Appliance Treatment for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An Update. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.A.; Andara, C.; Landry, S.; Sands, S.A.; Joosten, S.A.; Owens, R.L.; White, D.P.; Hamilton, G.S.; Wellman, A. Upper-Airway Collapsibility and Loop Gain Predict the Response to Oral Appliance Therapy in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denolf, P.L.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Marklund, M.E.; Braem, M.J.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. The status of cephalometry in the prediction of non-CPAP treatment outcome in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Med. Rev. 2016, 27, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, C.B.; Pringle, M. Sleep nasendoscopy: A technique of assessment in snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin. Otolaryngol. 1991, 16, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, N.S.; de Vries, N. Results of uvulopalatopharyngoplasty after diagnostic workup with polysomnography and sleep endoscopy: A report of 136 snoring patients. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 260, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Battagel, J.M.; Johal, A.; Kotecha, B.T. Sleep nasendoscopy as a predictor of treatment success in snorers using mandibular advancement splints. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2005, 119, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johal, A.; Battagel, J.M.; Kotecha, B.T. Sleep nasendoscopy: A diagnostic tool for predicting treatment success with mandibular advancement splints in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. J. Orthod. 2005, 27, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op de Beeck, S.; Dieltjens, M.; Verbruggen, A.E.; Vroegop, A.V.; Wouters, K.; Hamans, E.; Willemen, M.; Verbraecken, J.; De Backer, W.A.; Van de Heyning, P.H.; et al. Phenotypic Labelling Using Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy Improves Patient Selection for Mandibular Advancement Device Outcome: A Prospective Study. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderveken, O.M.; Vroegop, A.V.; van de Heyning, P.H.; Braem, M.J. The procedure of drug-induced sleep endoscopy with simulation bite. Oper. Tech. Otolaryngol. 2011, 22, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroegop, A.V.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Dieltjens, M.; Wouters, K.; Saldien, V.; Braem, M.J.; Van de Heyning, P.H. Sleep endoscopy with simulation bite for prediction of oral appliance treatment outcome. J. Sleep Res. 2013, 22, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastoer, C.; Dieltjens, M.; De Beeck, S.O.; Braem, M.J.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Vanderveken, O.M. Remotely Controlled Mandibular Positioning during Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy Toward Mandibular Advancement Device Therapy: Feasibility and Protocol. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmers, J.E.; Topor, Z.; Grosse, J.; Vranjes, N.; Mosca, E.V.; Brant, R.; Bruehlmann, S.; Charkhandeh, S.; Jahromi, S.A.Z. A Feedback-Controlled Mandibular Positioner Identifies Individuals with Sleep Apnea Who Will Respond to Oral Appliance Therapy. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieltjens, M.; Braem, M.J.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Wouters, K.; Vanderveken, O.M. Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Supine-Dependent Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients Using Oral Appliance Therapy. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristanovic, R.; Diaz, F.; Caldarelli, D.; Alder, G.; Cartwright, R. A Comparative Study of Treatments for Positional Sleep Apnea. Sleep 1991, 14, 546–552. [Google Scholar]
- Dieltjens, M.; Vroegop, A.V.; Verbruggen, A.E.; Wouters, K.; Willemen, M.; De Backer, W.A.; Verbraecken, J.A.; Van De Heyning, P.H.; Braem, M.J.; De Vries, N.; et al. A promising concept of combination therapy for positional obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2014, 19, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dieltjens, M.; Vanderveken, O.M. Oral Appliances in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Healthcare 2019, 7, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040141
Dieltjens M, Vanderveken OM. Oral Appliances in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Healthcare. 2019; 7(4):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040141
Chicago/Turabian StyleDieltjens, Marijke, and Olivier M. Vanderveken. 2019. "Oral Appliances in Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Healthcare 7, no. 4: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040141
APA StyleDieltjens, M., & Vanderveken, O. M. (2019). Oral Appliances in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Healthcare, 7(4), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040141





