How Widely are Supportive and Flexible Food Service Systems and Mealtime Interventions Used for People in Residential Care Facilities? A Comparison of Dementia-Specific and Nonspecific Facilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Food Service Systems in Place
3.2. Use of Supportive Mealtime Interventions
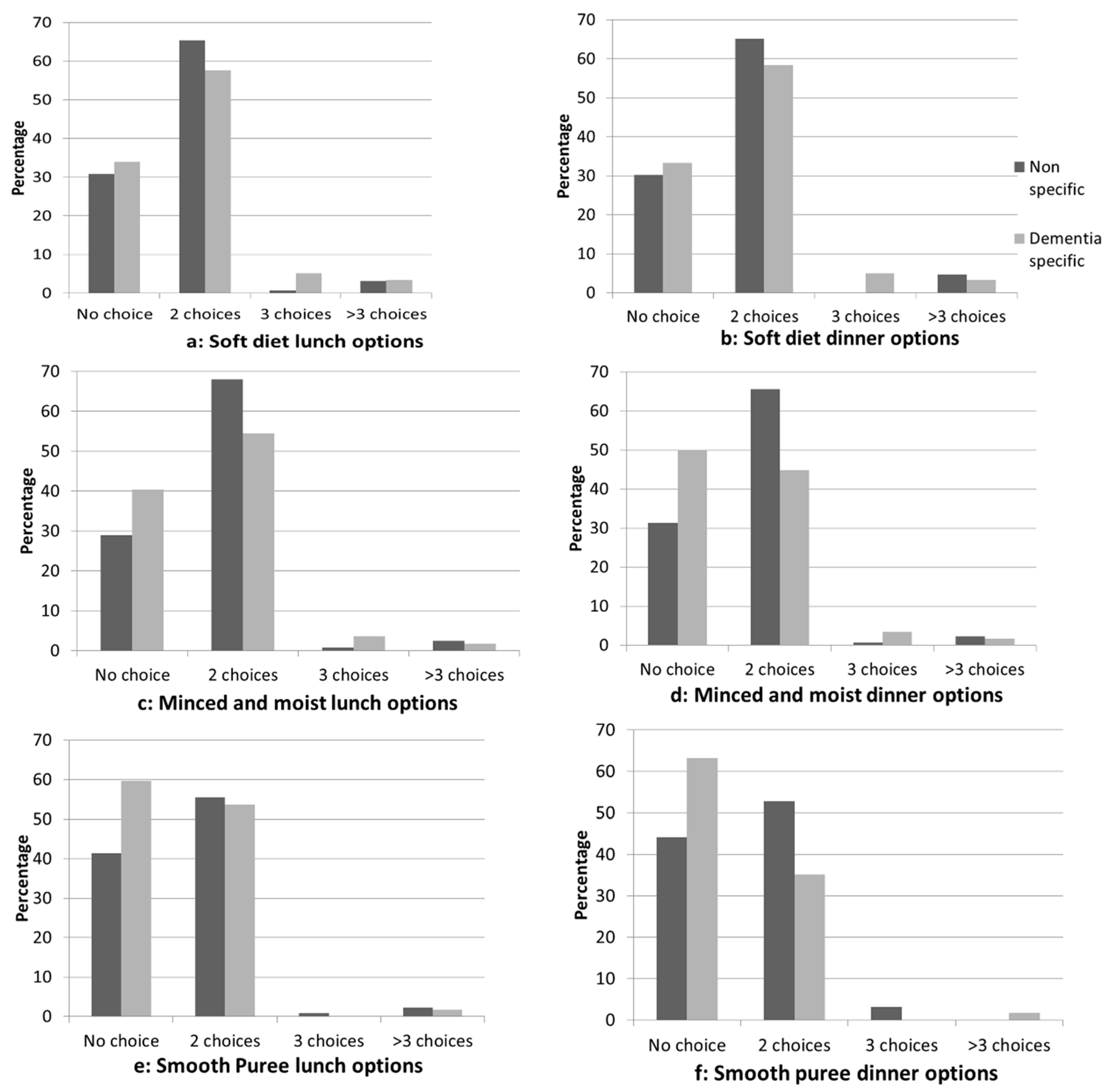
3.3. Support for Resident Choice and Flexibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, P.; Tilly, J. Dementia care practice recommendations for nursing homes and assisted living, phase 1: Dementia care fundamentals, food and fluid consumption, pain management, and social engagement. Alzheimer’s Care Today 2008, 9, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.W.; Lawrence, J.C. Environmental considerations for improving nutritional status in older adults with dementia: A narrative review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1815–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, H.; Beck, A.M.; Namasivayam, A. Improving food and fluid intake for older adults living in long-term care: A research agenda. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milte, R.; Shulver, W.; Killington, M.; Bradley, C.; Miller, M.; Crotty, M. Struggling to maintain individuality–Describing the experience of food in nursing homes for people with dementia. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 72, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurrle, S.; Brodaty, H.; Hogarth, R. Physical Comorbidities of Dementia; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Voluntary Organisations Involved in Caring in the Elderly Sector. Eating Well for Older People with Dementia; VOICES and Gardner Merchant: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, T.E.; Neargarder, S.A.; Cipolloni, P.B.; Cronin-Golomb, A. Visual contrast enhances food and liquid intake in advanced Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddaer, J.; Abraham, I.L. Effects of relaxing music on agitation during meals among nursing home residents with severe cognitive impairment. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 1994, 8, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragneskog, H.; Bråne, G.; Karlsson, I.; Kihlgren, M. Influence of dinner music on food intake and symptoms common in dementia. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 1996, 10, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altus, D.E.; Engelman, K.K.; Mathews, R.M. Using family-style meals to increase participation and communication in persons with dementia. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2002, 28, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, K.A.; de Graaf, C.; Kok, F.J.; van Staveren, W.A. Effect of family style mealtimes on quality of life, physical performance, and body weight of nursing home residents: Cluster randomized controlled trial. Br. Med. J. 2006, 332, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, N.; West, G.E.; Ouellet, D. Dining experience, foodservices and staffing are associated with quality of life in elderly nursing home residents. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.A.; Whear, R.; Thompson-Coon, J.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Rogers, M.; Bethel, A.; Hemsley, A.; Stein, K. Effectiveness of mealtime interventions on nutritional outcomes for the elderly living in residential care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, E.; Marshall, S.; Miller, M.; Isenring, E. Optimising nutrition in residential aged care: A narrative review. Maturitas 2016, 92, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbey, K.L.; Wright, O.R.; Capra, S. Menu planning in residential aged care-The level of choice and auality of planning of meals available to residents. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7580–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, A.; Jensen, J.; Field, P. Eating environment in the aged-care residential setting in New Zealand: Promoters and barriers to achieving optimum nutrition. Observations of the foodservice, menu and meals. Nutr. Diet. 2011, 68, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondahl, V.A.; Aagaard, H. Older people’s involvement in activities related to meals in nursing homes. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2016, 11, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.; Currie, K.; Graham, C.; Robb, Y. The effectiveness of interventions to reduce undernutrition and promote eating in older adults with dementia: A systematic review. JBI Libr. Syst. Rev. 2011, 9, 1509–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, S.F.; Lam, H.Y.; Rao, G.; Schnelle, J.F. Family members’ preferences for nutrition interventions to improve nursing home residents’ oral food and fluid intake. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofod, J.; Birkemose, A. Meals in nursing homes. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 2004, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Kiesswetter, E.; Gietl, A.; Pfannes, U.; Arens-Azevedo, U.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D. Size matters! Differences in nutritional care between small, medium and large nursing homes in Germany. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietitians Association of Australia. Submission From the Dietitians Association of Australia to the Productivity Commission: Caring for Older Australians. Available online: https://www.pc.gov.au/inquiries/completed/aged-care/submissions/sub371.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- van Nie, N.C.; Meijers, J.M.M.; Schols, J.M.G.A.; Lohrmann, C.; Spreeuwenberg, M.; Halfens, R.J.G. Do structural quality indicators of nutritional care influence malnutrition prevalence in Dutch, German and Austrian nursing homes? Nutrition 2014, 30, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, G.; Collini, F.; Castagnoli, M.; Di Bari, M.; Cavallini, M.C.; Zaffarana, N.; Pepe, P.; Mugelli, A.; Lucenteforte, E.; Vannacci, A.; et al. A cross-sectional survey to investigate the quality of care in Tuscan (Italy) nursing homes: The structural, process and outcome indicators of nutritional care. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2015, 15, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrer, O.; Sasanelli, L.; Matwiejczyk, L.; Yaxley, A.; Miller, M. The role of dietitians in residential aged care: How do cooks and chefs perceive their contribution? Australas. J. Ageing 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, W.J.; Whiting, S.J.; Tyler, R.T. Protein content of puréed diets: Implications for planning. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2007, 68, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.; Cotter, D.; Hickson, M.; Frost, G. Comparison of energy and protein intakes of older people consuming a texture modified diet with a normal hospital diet. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2005, 18, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Residential aged care and home care 2014-15 supporting data. Canberra, Australia, 2016. Available online: https://www.gen-agedcaredata.gov.au/Resources/Access-data/2015/December/Residential-aged-care-and-Home-Care-2014%E2%80%9315-suppo (accessed on 5 March 2018).
| Characteristic | n (%) | Chi-Square | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Not Dementia-Specific (n = 141) | Dementia-Specific (n = 63) | ||
| State | ||||
| ACT NSW NT Queensland SA Tasmania Victoria WA | 4 (2.0) 71 (34.8) 1 (0.5) 43 (21.1) 11 (5.4) 11 (5.4) 46 (22.5) 17 (8.3) | 2 (1.4) 50 (35.5) 0 (0) 24 (17.0) 9 (6.4) 7 (5.0) 35 (24.8) 14 (9.9) | 2 (3.4) 21 (33.3) 1 (1.6) 19 (30.2) 2 (3.2) 4 (6.3) 11 (17.5) 3 (4.8) | 10.1, df = 7, p = 0.183 |
| Location | ||||
| Metropolitan Outer metropolitan Rural or Remote | 68 (33.3) 49 (24.0) 87 (42.6) | 46 (32.6) 32 (22.7) 63 (44.7) | 22 (34.9) 17 (27.0) 24 (38.1) | 0.9, df = 2, p = 0.655 |
| How many beds in this does this kitchen cater for? | ||||
| 1 to 99 100 to 199 200 and above | 144 (70.6) 50 (24.5) 10 (4.9) | 111 (78.7) 26 (18.4) 4 (2.8) | 33 (52.4) 24 (38.1) 6 (9.5) | 16.8, df = 4, p ≤ 0.001 |
| What type of facility is this 1 | ||||
| Aging in place Dementia-specific Low care High and Low care High care Other | 112 (55) 63 (31) 19 (9.3) 116 (57) 36 (18) 16 (8) | 69 (48.9) 0 (0.0) 9 (6.4) 65 (46.1) 23 (16.3) 9 (6.4) | 43 (68.3) 63 (100) 10 (15.9) 51 (81.0) 13 (20.6) 7 (11.1) | 5.8, df = 1, p = 0.016 199.3, df = 1, p ≤ 0.001 3.6, df = 1, p = 0.058 20.2, df = 1, p ≤ 0.001 0.3, df = 1, p = 0.583 0.8, df = 1, p = 0.266 |
| Characteristic | n (%) | Chi-Square | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Not Dementia-Specific | Dementia-Specific | ||
| What is the main food service system used? | ||||
| Cook-Chill/Freeze Cook-Fresh Meals are brought in from an external company/kitchen Mixture of Cook-Fresh and Cook-Chill/Freeze | 16 (7.8) 158 (77.5) 9 (4.4) 21 (10.3) | 10 (7.1) 110 (78.0) 8 (5.7) 13 (9.2) | 6 (9.5) 48 (76.2) 1 (1.6) 8 (12.7) | 2.9, df = 3, p = 0.422 |
| How are meals distributed to the residents? | ||||
| Bulk food plated in dining room Centrally plated Meals cooked in small kitchens accessible to residents Other | 41 (20.1) 120 (58.8) 12 (5.9) 31 (15.2) | 26 (18.4) 83 (58.9) 9 (6.4) 23 (16.3) | 15 (23.8) 37 (58.7) 3 (4.8) 8 (12.7) | 1.2, df = 3, p = 0.755 |
| What is your current menu cycle length | ||||
| 1 to 3 weeks 4 weeks 5 or more weeks | 10 (5) 163 (81.1) 27 (13.5) | 7 (5.0) 110 (79.1) 21 (15.2) | 3 (4.8) 53 (85.5) 6 (9.7) | 1.2, df = 2, p = 0.562 |
| Is a seasonal menu offered at your facility? | ||||
| Yes No | 169 (82.8) 32 (15.7) | 115 (82.7) 24 (17.3) | 54 (87.1) 8 (12.9) | 0.3, df = 1, p = 0.567 |
| When is the main meal? | ||||
| Both have the same number of hot and cold options Evening meal Lunchtime | 60 (29.4) 3 (1.5) 138 (67.6) | 33 (23.7) 2 (1.4) 104 (74.8) | 27 (43.5) 1 (1.6) 34 (54.8) | 7.9, df = 2, p = 0.019 |
| How many hot choices are available at the main mealtime? | ||||
| 1 2 3 or more No choice available | 44 (21.6) 127 (62.3) 25 (12.4) 5 (2.5) | 34 (24.5) 84 (60.4) 17 (12.2) 4 (2.9) | 10 (16.1) 43 (69.4) 8 (12.9) 1 (1.6) | 2.3, df = 3, p = 0.515 |
| How many cold options are available at the main mealtime? | ||||
| 1 2 3 or more No choice available | 50 (24.9) 115 (57.2) 14 (7) 22 (10.9) | 37 (26.6) 78 (56.1) 8 (5.8) 16 (5.8) | 13 (21.0) 37 (59.7) 6 (9.7) 6 (9.7) | 1.7, df = 3, p = 0.632 |
| Are residents offered any of the following? | ||||
| Morning tea Afternoon tea Before bed snack Light refreshments available all day | 196 (96.1) 196 (96.1) 184 (90.2) 138 (67.6) | 136 (96.5) 136 (96.5) 126 (89.4) 95 (67.4) | 60 (95.2) 60 (95.2) 58 (92.1) 43 (68.3) | 0.0, df = 1, p = 0.704 0.0, df = 1, p = 0.704 0.1, df = 1, p = 0.730 0.0, df = 1, p = 1.000 |
| Do you cater for the following special diets? | ||||
| Nourishing or High Energy High Protein Low fat Allergy meals (e.g. lactose free and gluten free) Low potassium/sodium Other | 183 (89.7) 174 (85.3) 192 (94.1) 148 (72.5) 36 (17.6) | 126 (89.4) 121 (85.8) 130 (92.2) 106 (75.2) 23 (16.3) | 57 (90.5) 53 (84.1) 62 (98.4) 42 (66.7) 13 (20.6) | 0.0, df = 1, p = 1.000 0.0, df = 1, p = 0.920 2.0, df = 1, p = 0.110 1.2, df = 1, p = 0.276 0.3, df = 1, p = 0.583 |
| Technique | Facilities Indicating Use of Intervention n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Dementia Specific (n = 63) | Non-Dementia Specific (n = 141) | Chi-Square | |
| Adaptive equipment (e.g. large handled cutlery or plate guards) | 184 (90.2) | 57 (90.5) | 127 (90.1) | 0.000, df = 1, p = 1.000 |
| Commercial oral nutritional supplements | 178 (87.3) | 54 (85.7) | 124 (87.9) | 0.046, df = 1, p = 0.831 |
| Redesigning menu to include resident favorite meals | 138 (67.6) | 46 (73) | 92 (65.2) | 0.872, df = 1, p = 0.350 |
| Table cloths in dining room | 136 (66.7) | 41 (65.1) | 95 (67.4) | 0.026, df = 1, p = 0.872 |
| Snacks available on demand | 131 (64.2) | 44 (69.8) | 87 (61.7) | 0.926, df = 1, p = 0.336 |
| Involving family in feeding residents | 123 (60.3) | 36 (57.1) | 87 (61.7) | 0.212, df = 1, p = 0.645 |
| Finger foods available on menu | 121 (59.3) | 40 (63.5) | 81 (57.4) | 0.433, df = 1, p = 0.511 |
| Music during mealtimes | 105 (51.5) | 30 (47.6) | 75 (53.2) | 0.341, df = 1, p = 0.559 |
| Use of volunteers during mealtimes | 87 (42.6) | 32 (50.8) | 55 (39.0) | 2.015, df = 1, p = 0.156 |
| Staff joining residents for meals | 53 (26.0) | 17 (27.0) | 36 (25.5) | 0.002, df = 1, p = 0.964 |
| High contrast plates | 51 (25) | 25 (39.7) | 26 (18.4) | 9.377, df = 1, p = 0.002 |
| Using molds to re-form texture modified foods | 41 (201) | 16 (25.4) | 25 (17.7) | 1.152, df = 1, p = 0.283 |
| Other | 15 (7.4) | 3 (4.8) | 12 (8.5) | 0.432, df = 1, p = 0.402 |
| Resident helping with preparation for meals | 33 (16.3) | 12 (19.4) | 21 (15.0) | 0.320, df = 1, p = 0.572 |
| Characteristic | Facilities Indicating Use of Intervention n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Dementia-Specific (n = 63) | Non-Dementia-Specific (n = 141) | Chi-Square | |
| When do residents choose the content of their meal? | ||||
| At the mealtime Morning of meal service Evening prior to meal service More than 24 h prior No choice provided Other | 35 (17.2) 59 (28.9) 33 (16.2) 63 (30.9) 5 (2.5) 35 (17.2) | 16 (25.4) 17 (27.0) 10 (15.9) 20 (31.7) 2 (3.2) 11 (17.5) | 19 (13.5) 42 (29.8) 23 (16.3) 43 (30.5) 3 (2.1) 24 (17.0) | 3.6, df = 1, p = 0.059 0.1, df = 1, p = 0.810 0.0, df = 1, p = 1.000 0.0, df = 1, p = 0.988 0.0, df = 1, p = 1.000 0.0, df = 1, p = 1.000 |
| Which meal serve sizes are offered? | ||||
| Small Regular Large Choice of meal size provided at mealtime | 128 (62.7) 160 (78.4) 123 (60.3) 103 (50.5) | 45 (71.4) 52 (82.5) 45 (71.4) 32 (50.8) | 83 (58.9) 108 (76.6) 78 (55.3) 71 (50.4) | 2.4, df = 1, p = 0.119 0.6, df = 1, p = 0.442 4.1, df = 1, p = 0.044 0.0, df = 1, p = 1.0 |
| Are residents able to access and use a kitchen area? | ||||
| Yes, also utilized for service meals Yes, separate to the kitchen used for serving meals No | 32 (15.8) 120 (59.4) 50 (24.8) | 12 (19.4) 31 (50.0) 19 (30.6) | 20 (14.3) 89 (63.6) 31 (22.1) | 3.3, df = 2, p = 0.194 |
| Does the facility have a set time for meals? | ||||
| Yes, for all meals Yes, for lunch and dinner only No, all meals are offered at a range of times | 143 (70.8) 50 (24.8) 9 (4.5) | 39 (62.9) 18 (29.0) 5 (8.1) | 104 (74.3) 32 (22.9) 4 (2.9) | 4.1, df = 2, p = 0.131 |
| Does you facility cater for any of the following texture modified diets? | ||||
| Soft diet Minced and moist diet Smooth puree diet | 195 (95.6) 191 (93.6) 196 (96.1) | 62 (98.4) 60 (95.2) 62 (98.4) | 133 (94.3) 131 (92.9) 134 (95.0) | 0.9, df = 1, p = 0.280 0.1, df = 1, p = 0.758 0.6, df = 1, p = 0.439 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milte, R.; Bradley, C.; Miller, M.; Farrer, O.; Crotty, M. How Widely are Supportive and Flexible Food Service Systems and Mealtime Interventions Used for People in Residential Care Facilities? A Comparison of Dementia-Specific and Nonspecific Facilities. Healthcare 2018, 6, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040140
Milte R, Bradley C, Miller M, Farrer O, Crotty M. How Widely are Supportive and Flexible Food Service Systems and Mealtime Interventions Used for People in Residential Care Facilities? A Comparison of Dementia-Specific and Nonspecific Facilities. Healthcare. 2018; 6(4):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040140
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilte, Rachel, Clare Bradley, Michelle Miller, Olivia Farrer, and Maria Crotty. 2018. "How Widely are Supportive and Flexible Food Service Systems and Mealtime Interventions Used for People in Residential Care Facilities? A Comparison of Dementia-Specific and Nonspecific Facilities" Healthcare 6, no. 4: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040140
APA StyleMilte, R., Bradley, C., Miller, M., Farrer, O., & Crotty, M. (2018). How Widely are Supportive and Flexible Food Service Systems and Mealtime Interventions Used for People in Residential Care Facilities? A Comparison of Dementia-Specific and Nonspecific Facilities. Healthcare, 6(4), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040140





