Association Between Common Systemic Medications and the Presence and Severity of Furcation Involvement: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Data Source and Patient Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Variables
2.4. Independent Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, G.C. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann. Periodontol. 1999, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyle, J.; Chapple, I. Molecular aspects of the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Periodontology 2000 2015, 69, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C.; Dias-Pereira, A.C.; Branco-de-Almeida, L.S.; Martins, C.C.; Paiva, S.M. Impact of periodontal disease on quality of life: A systematic review. J. Periodontal Res. 2017, 52, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsos, H.; Schacher, B.; Ramich, T.; Nickles, K.; Dannewitz, B.; Arendt, S.; Seidel, K.; Eickholz, P. Retrospectively analysed tooth loss in periodontally compromised patients: Long-term results 10 years after active periodontal therapy—Patient-related outcomes. J. Periodontal Res. 2020, 55, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.X.; Zhong, Y.J.; Dong, Q.Q.; Wong, H.M.; Wen, Y.F. Global, regional, and national burden of severe periodontitis, 1990-2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Bernabé, E.; Dahiya, M.; Bhandari, B.; Murray, C.J.; Marcenes, W. Global burden of severe tooth loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93 (Suppl. S7), 20S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasperini, G.; Majzoub, J.; Tavelli, L.; Limiroli, E.; Katayama, A.; Barootchi, S.; Hill, R.; Wang, H.-L. Management of furcation-involved molars: Recommendation for treatment and regeneration. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, e137–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordland, P.; Garrett, S.; Kiger, R.; Vanooteghem, R.; Hutchens, L.H.; Egelberg, J. The effect of plaque control and root debridement in molar teeth. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1987, 14, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibali, L.; Zavattini, A.; Nagata, K.; Di Iorio, A.; Lin, G.; Needleman, I.; Donos, N. Tooth loss in molars with and without furcation involvement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, O.; Göstemeyer, G.; Krois, J.; El Sayed, K.F.; Graetz, C.; Schwendicke, F. Predictors for tooth loss in periodontitis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.C.; Offenbacher, S. Periodontal medicine: The emergence of a new branch of periodontology. Periodontology 2000 2000, 23, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsarrat, P.; Blaizot, A.; Kémoun, P.; Ravaud, P.; Nabet, C.; Sixou, M.; Vergnes, J. Clinical research activity in periodontal medicine: A systematic mapping of trial registers. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natto, Z.S.; Hameedaldain, A. Methodological Quality Assessment of Meta-analyses and Systematic Reviews of the Relationship Between Periodontal and Systemic Diseases. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2019, 19, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söder, B.; Jin, L.J.; Klinge, B.; Söder, P.O. Periodontitis and premature death: A 16-year longitudinal study in a Swedish urban population. J. Periodontal Res. 2007, 42, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y. Association of Antihypertensive Drugs With Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Drug-Target Mendelian Randomization Study. Quintessence Int. 2024, 55, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Wei, W.; Zhang, W.; Gao, M.; Fu, M.; Li, W. Inhibition of Angiotensin II Receptor I Prevents Inflammation and Bone Loss in Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.C.; Askar, H.; Ghassib, I.; Wang, C.W.; Wang, H.L. Association Between Periodontitis and Systemic Medication Intake: A Case-Control Study. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estanislau, I.M.; Terceiro, I.R.; Lisboa, M.R.; Barros, L.M.; Barros, F.C.; Pereira, A. Pleiotropic Effects of Statins on the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis—A Systematic Review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Batool, F.; Bugueno, I.M.; Cafferata, E.A.; Al-Samadi, A.; Al-Samadi, A.; Cárdenas, S.E. Contribution of Statins Towards Periodontal Treatment: A Review. Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 6367402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, M.G.; Papathanasiou, E.; Blix, I.J.; Van Dyke, T.E. Host Modulation and Treatment of Periodontal Disease. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzopoulos, G.S.; Jiang, Z.; Marka, N.; Wolff, L.F. Relationship of Medication Intake and Systemic Conditions with Periodontitis: A Retrospective Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzopoulos, G.S.; Koidou, V.P.; Tsalikis, L. Local drug delivery in the treatment of furcation defects in periodontitis: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavanelli, A.L.R.; de Menezes, B.S.; Pereira, E.B.B.; da Silva, P.P.N.J.; Tanganeli, E.; Soares, R.R.; Garcia, G.G.; Diniz, R.B.; Garlet, G.P.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; et al. Pharmacological Therapies for the Management of Inflammatory Bone Resorption in Periodontal Disease: A Review of Preclinical Studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5832009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Wang, C.Y. Osteoporosis and Periodontal Diseases—An Update on Their Association and Mechanistic Links. Periodontology 2000 2022, 89, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G. Interconnection of Periodontal Disease and Comorbidities: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Implications. Periodontology 2000 2022, 89, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Medication Class | Specific Medication | Patients with Furcation Involvement (N) | With Furcation (%) | Patients without Furcation Involvement (N) | Without Furcation (%) | Total Patients (N) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors | Lisinopril | 661 | 72.8% | 247 | 27.2% | 908 | <0.0001 |
| Benazepril | 83 | 77.6% | 24 | 22.4% | 107 | 0.0006 | |
| Ramipril | 56 | 77.8% | 16 | 22.2% | 72 | 0.0008 | |
| Enalapril | 52 | 78.8% | 14 | 21.2% | 66 | 0.0004 | |
| Quinapril | 32 | 84.2% | 6 | 15.8% | 38 | 0.0001 | |
| Antidepressants | Trazodone | 145 | 67.4% | 70 | 32.6% | 215 | 0.8143 |
| Sertraline | 102 | 68.0% | 48 | 32.0% | 150 | 0.6953 | |
| Citalopram | 96 | 68.1% | 45 | 31.9% | 141 | 0.7029 | |
| Fluoxetine | 92 | 64.3% | 51 | 35.7% | 143 | 0.4497 | |
| Bupropion | 86 | 65.6% | 45 | 34.4% | 131 | 0.5471 | |
| Venlafaxine | 69 | 66.3% | 35 | 33.7% | 104 | 0.8576 | |
| Duloxetine | 57 | 69.5% | 25 | 30.5% | 82 | 0.5592 | |
| Mirtazapine | 53 | 69.7% | 23 | 30.3% | 76 | 0.5891 | |
| Amitriptyline | 49 | 71.0% | 20 | 29.0% | 69 | 0.4192 | |
| Paroxetine | 47 | 66.2% | 24 | 33.8% | 71 | 0.9413 | |
| Quetiapine | 28 | 65.1% | 15 | 34.9% | 43 | 0.8804 | |
| Nortriptyline | 18 | 72.0% | 7 | 28.0% | 25 | 0.4900 | |
| Desvenlafaxine | 10 | 71.4% | 4 | 28.6% | 14 | 0.6482 | |
| Aripiprazole | 7 | 63.6% | 4 | 36.4% | 11 | 1.0000 | |
| Doxepin | 3 | 75.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 4 | 0.5960 | |
| Lithium | 2 | 66.7% | 1 | 33.3% | 3 | 1.0000 | |
| Anti-coagulants | Aspirin | 549 | 71.0% | 224 | 29.0% | 773 | 0.0000 |
| Clopidogrel | 163 | 73.1% | 60 | 26.9% | 223 | 0.0000 | |
| Warfarin | 90 | 71.4% | 36 | 28.6% | 126 | 0.0270 | |
| Plavix | 62 | 72.9% | 23 | 27.1% | 85 | 0.0132 | |
| Xarelto | 47 | 72.3% | 18 | 27.7% | 65 | 0.0382 | |
| Apixaban | 30 | 73.2% | 11 | 26.8% | 41 | 0.0469 | |
| Brilinta | 3 | 75.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 4 | 0.5960 | |
| Cilostazol | 2 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.5484 | |
| Statins | Atorvastatin | 425 | 70.0% | 182 | 30.0% | 607 | 0.0001 |
| Simvastatin | 258 | 69.9% | 111 | 30.1% | 369 | 0.0011 | |
| Pravastatin | 119 | 70.8% | 49 | 29.2% | 168 | 0.0076 | |
| Lovastatin | 91 | 70.0% | 39 | 30.0% | 130 | 0.0264 | |
| Rosuvastatin | 82 | 70.7% | 34 | 29.3% | 116 | 0.0280 | |
| Bisphosphonates | Alendronate | 79 | 72.5% | 30 | 27.5% | 109 | 0.0478 |
| Risedronate | 5 | 71.4% | 2 | 28.6% | 7 | 0.6558 | |
| Ibandronate | 4 | 66.7% | 2 | 33.3% | 6 | 1.0000 | |
| Zoledronic acid | 1 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 1.0000 | |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | Omeprazole | 214 | 67.5% | 103 | 32.5% | 317 | 0.8354 |
| Pantoprazole | 133 | 66.8% | 66 | 33.2% | 199 | 0.9423 | |
| Lansoprazole | 57 | 69.5% | 25 | 30.5% | 82 | 0.5592 | |
| Esomeprazole | 42 | 67.7% | 20 | 32.3% | 62 | 0.8374 | |
| Dexilant | 2 | 66.7% | 1 | 33.3% | 3 | 1.0000 |
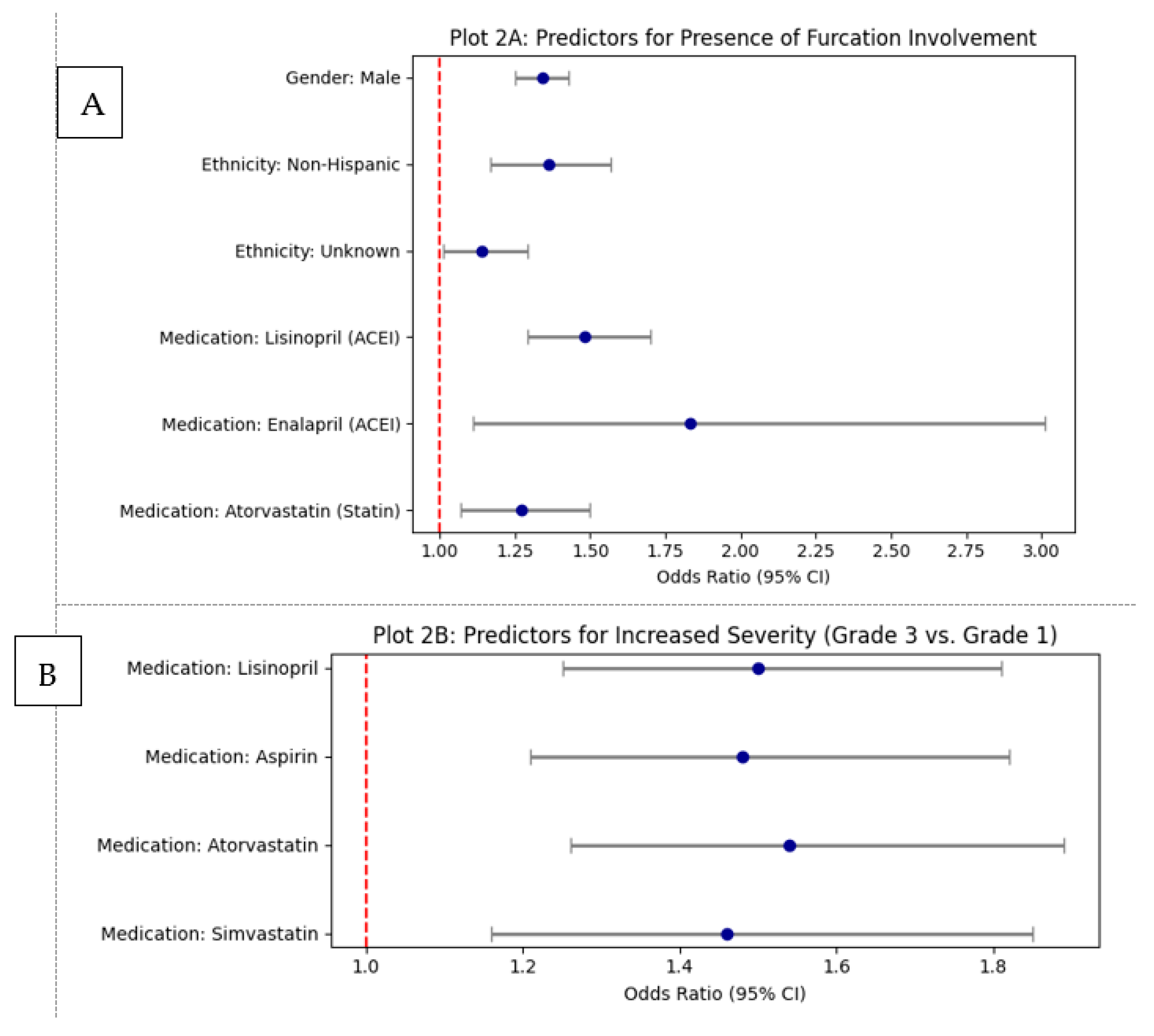
| Parameter | Category | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medication | Takes_Lisinopril | 1.48 | 1.29 | 1.70 | 0.0000 |
| Takes_Benazepril | 0.72 | 0.45 | 1.14 | 0.1601 | |
| Takes_Ramipril | 2.21 | 0.97 | 5.04 | 0.0588 | |
| Takes_Enalapril | 1.83 | 1.11 | 3.01 | 0.0179 | |
| Takes_Quinapril | 1.46 | 0.53 | 4.07 | 0.4687 | |
| Takes_Aspirin | 1.14 | 0.97 | 1.33 | 0.1064 | |
| Takes_Clopidogrel | 0.79 | 0.55 | 1.13 | 0.1993 | |
| Takes_Warfarin | 1.63 | 0.88 | 3.04 | 0.1221 | |
| Takes_Plavix | 1.41 | 0.88 | 2.25 | 0.1508 | |
| Takes_Xarelto | 1.28 | 0.71 | 2.33 | 0.4124 | |
| Takes_Apixaban | 2.65 | 0.58 | 12.21 | 0.2104 | |
| Takes_Atorvastatin | 1.27 | 1.07 | 1.50 | 0.0051 | |
| Takes_Simvastatin | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.22 | 0.9634 | |
| Takes_Pravastatin | 1.16 | 0.86 | 1.58 | 0.3308 | |
| Takes_Lovastatin | 1.06 | 0.66 | 1.71 | 0.8034 | |
| Takes_Rosuvastatin | 0.86 | 0.58 | 1.28 | 0.4532 | |
| Takes_Alendronate | 1.35 | 0.89 | 2.05 | 0.1528 | |
| Demographics | Gender: Male | 1.34 | 1.25 | 1.43 | 0.0000 |
| Ethnicity: Non-Hispanic | 1.36 | 1.17 | 1.57 | 0.0001 | |
| Ethnicity: Unknown | 1.14 | 1.01 | 1.29 | 0.0406 | |
| Race: Black or African American | 1.12 | 0.57 | 2.19 | 0.7455 |
| Medication Class | Specific Medication | Grade 1 (N) | Grade 1 (%) | Grade 2 (N) | Grade 2 (%) | Grade 3 (N) | Grade 3 (%) | Grade 4 (N) | Grade 4 (%) | Total Patients (N) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors | Lisinopril | 661 | 41.9% | 722 | 45.8% | 194 | 12.3% | 1 | 0.1% | 1578 | 0.0000 |
| Benazepril | 83 | 43.7% | 89 | 46.8% | 18 | 9.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 190 | 0.6548 | |
| Ramipril | 56 | 44.1% | 58 | 45.7% | 13 | 10.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 127 | 0.8227 | |
| Enalapril | 52 | 43.3% | 55 | 45.8% | 13 | 10.8% | 0 | 0.0% | 120 | 0.8441 | |
| Quinapril | 32 | 43.2% | 35 | 47.3% | 7 | 9.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 74 | 0.8651 | |
| Antidepressants | Trazodone | 145 | 42.5% | 158 | 46.3% | 38 | 11.1% | 0 | 0.0% | 341 | 0.6865 |
| Sertraline | 102 | 42.3% | 109 | 45.2% | 30 | 12.4% | 0 | 0.0% | 241 | 0.9103 | |
| Citalopram | 96 | 42.3% | 104 | 45.8% | 27 | 11.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 227 | 0.8624 | |
| Fluoxetine | 92 | 41.8% | 101 | 45.9% | 27 | 12.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 220 | 0.8906 | |
| Bupropion | 86 | 42.4% | 91 | 44.8% | 26 | 12.8% | 0 | 0.0% | 203 | 0.9702 | |
| Venlafaxine | 69 | 42.1% | 75 | 45.7% | 20 | 12.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 164 | 0.9419 | |
| Duloxetine | 57 | 42.5% | 61 | 45.5% | 16 | 11.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 134 | 0.9254 | |
| Mirtazapine | 53 | 42.4% | 57 | 45.6% | 15 | 12.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 125 | 0.9427 | |
| Amitriptyline | 49 | 43.0% | 52 | 45.6% | 13 | 11.4% | 0 | 0.0% | 114 | 0.8967 | |
| Paroxetine | 47 | 42.3% | 51 | 45.9% | 13 | 11.7% | 0 | 0.0% | 111 | 0.8953 | |
| Quetiapine | 28 | 43.1% | 30 | 46.2% | 7 | 10.8% | 0 | 0.0% | 65 | 0.9056 | |
| Nortriptyline | 18 | 42.9% | 20 | 47.6% | 4 | 9.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 42 | 0.9213 | |
| Desvenlafaxine | 10 | 41.7% | 11 | 45.8% | 3 | 12.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 24 | 0.9754 | |
| Aripiprazole | 7 | 41.2% | 8 | 47.1% | 2 | 11.8% | 0 | 0.0% | 17 | 0.9760 | |
| Doxepin | 3 | 42.9% | 3 | 42.9% | 1 | 14.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 7 | 0.9892 | |
| Lithium | 2 | 40.0% | 2 | 40.0% | 1 | 20.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 5 | 0.9818 | |
| Anti-coagulants | Aspirin | 549 | 41.9% | 591 | 45.1% | 169 | 12.9% | 2 | 0.2% | 1311 | 0.0000 |
| Clopidogrel | 163 | 42.0% | 178 | 45.9% | 47 | 12.1% | 0 | 0.0% | 388 | 0.2520 | |
| Warfarin | 90 | 42.7% | 96 | 45.5% | 25 | 11.8% | 0 | 0.0% | 211 | 0.7788 | |
| Plavix | 62 | 42.5% | 68 | 46.6% | 16 | 11.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 146 | 0.6865 | |
| Xarelto | 47 | 41.6% | 52 | 46.0% | 14 | 12.4% | 0 | 0.0% | 113 | 0.8711 | |
| Apixaban | 30 | 42.3% | 33 | 46.5% | 8 | 11.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 71 | 0.8651 | |
| Brilinta | 3 | 42.9% | 3 | 42.9% | 1 | 14.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 7 | 0.9892 | |
| Cilostazol | 2 | 50.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 4 | 0.8944 | |
| Statins | Atorvastatin | 425 | 41.8% | 463 | 45.5% | 129 | 12.7% | 0 | 0.0% | 1017 | 0.0001 |
| Simvastatin | 258 | 42.1% | 277 | 45.2% | 78 | 12.7% | 0 | 0.0% | 613 | 0.0435 | |
| Pravastatin | 119 | 42.2% | 129 | 45.7% | 34 | 12.1% | 0 | 0.0% | 282 | 0.5306 | |
| Lovastatin | 91 | 42.1% | 98 | 45.4% | 27 | 12.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 216 | 0.8524 | |
| Rosuvastatin | 82 | 41.8% | 89 | 45.4% | 25 | 12.8% | 0 | 0.0% | 196 | 0.9023 | |
| Bisphosphonates | Alendronate | 79 | 44.1% | 82 | 45.8% | 18 | 10.1% | 0 | 0.0% | 179 | 0.5794 |
| Risedronate | 5 | 41.7% | 6 | 50.0% | 1 | 8.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 12 | 0.9416 | |
| Ibandronate | 4 | 40.0% | 5 | 50.0% | 1 | 10.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 10 | 0.9634 | |
| Zoledronic acid | 1 | 50.0% | 1 | 50.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 1.0000 | |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | Omeprazole | 214 | 41.8% | 231 | 45.1% | 67 | 13.1% | 0 | 0.0% | 512 | 0.2982 |
| Pantoprazole | 133 | 41.6% | 144 | 45.0% | 43 | 13.4% | 0 | 0.0% | 320 | 0.4907 | |
| Lansoprazole | 57 | 42.5% | 61 | 45.5% | 16 | 11.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 134 | 0.9254 | |
| Esomeprazole | 42 | 41.6% | 46 | 45.5% | 13 | 12.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 101 | 0.9238 | |
| Dexilant | 2 | 40.0% | 2 | 40.0% | 1 | 20.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 5 | 0.9818 |
| Comparison | Medication | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 2 vs. Grade 1 | Takes Lisinopril | 1.15 | 1.01 | 1.31 | 0.038 |
| Takes Aspirin | 1.10 | 0.95 | 1.28 | 0.208 | |
| Takes Atorvastatin | 1.13 | 0.98 | 1.32 | 0.101 | |
| Takes Simvastatin | 1.10 | 0.92 | 1.32 | 0.288 | |
| Grade 3 vs. Grade 1 | Takes Lisinopril | 1.50 | 1.25 | 1.81 | 0.000 |
| Takes Aspirin | 1.48 | 1.21 | 1.82 | 0.000 | |
| Takes Atorvastatin | 1.54 | 1.26 | 1.89 | 0.000 | |
| Takes Simvastatin | 1.46 | 1.16 | 1.85 | 0.001 | |
| Grade 4 vs. Grade 1 | Takes Lisinopril | 0.58 | 0.08 | 4.38 | 0.598 |
| Takes Aspirin | 0.73 | 0.17 | 3.16 | 0.669 | |
| Takes Atorvastatin | - | - | - | - | |
| Takes Simvastatin | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatzopoulos, G.S.; Wolff, L.F. Association Between Common Systemic Medications and the Presence and Severity of Furcation Involvement: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222930
Chatzopoulos GS, Wolff LF. Association Between Common Systemic Medications and the Presence and Severity of Furcation Involvement: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare. 2025; 13(22):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222930
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatzopoulos, Georgios S., and Larry F. Wolff. 2025. "Association Between Common Systemic Medications and the Presence and Severity of Furcation Involvement: A Cross-Sectional Study" Healthcare 13, no. 22: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222930
APA StyleChatzopoulos, G. S., & Wolff, L. F. (2025). Association Between Common Systemic Medications and the Presence and Severity of Furcation Involvement: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare, 13(22), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222930






