Abstract
Background/Objectives: Umbilical cord blood (UCB) is a valuable source of hematopoietic stem cells used in treating blood and immune disorders. Despite its potential and the availability of public banking systems in Italy, donation rates remain low due to patient misinformation, emotional barriers, and organizational inefficiencies. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of integrating Narrative Medicine (NM) and Lean Management (LM) on UCB donation rates and operational effectiveness at the University Hospital of Alessandria. Methods: This prospective, single-center pre-post study ran from July 2022 to December 2024. Two interventions were introduced: NM training for healthcare staff to enhance empathetic communication, and LM-based reorganization of workflows to improve process efficiency. Outcomes included changes in UCB donation and adherence rates, transplant-eligible unit percentages, and patient satisfaction, assessed through institutional and project-specific surveys (PERLA–SIMeN). Results: Post-intervention, donation rates increased from 0% in early 2022 to 30.8% (2022), 25.8% (2023), and 30.6% (2024), with adherence rates near 40%, far exceeding the national average of ~3%. Patient satisfaction improved, resulting in PERLA certification in February 2025. Conclusions: The integration of NM and LM significantly improved both patient engagement and organizational efficiency. Empathetic communication fostered trust and reduced emotional barriers, while LM optimized workflows and resource use. These results suggest the model is applicable in other hospitals to enhance UCB donation outcomes and overall quality of maternal care.
1. Introduction
Umbilical cord blood (UCB) donation represents a critical resource in modern medicine due to its richness in hematopoietic stem cells, which serve as progenitors for all blood cell lineages [1,2]. These cells provide established, life-saving treatments for various severe congenital and acquired hematological disorders, such as leukemia, as well as immune deficiencies [1,2]. Beyond hematology recent research has expanded the therapeutic potential of UCB to include regenerative treatments for treating high-prevalence and high-mortality conditions including cardiovascular diseases [3], neurodegenerative disorders [4], and diabetes [5].
Umbilical cord blood (UCB) donation can be for allogenic solidaristic purposes, and in this case the Blood Units are stored in specific public Blood Banks, or for private purposes (autologous or family use) [6]. While the value of storing UCB in public banks for transplantation or research purposes is nowadays clear, the debate on private collection is still open and wide-ranging [7].
Despite the advancing knowledge beneath this practice, the advances in scientific research, and the regulations implemented in many countries, increasing donation rates through greater involvement of expectant mothers and healthcare professionals remains a complex challenge even today [8,9].
In Italy, the Italian Cord Blood Network (ITCBN), established in 2009, coordinates 18 public banks across 13 regions, connected to 269 collection centers. Although these centers account for 64% of national births, voluntary donation rates remain low, averaging below 3%, and only approximately 5% of collected units meet transplantation criteria and can be banked [10,11]. Barriers include informational gaps, concerns for newborn safety, social factors, and logistical difficulties, often exacerbated by the organizational model where external midwives recruit donors sporadically, limiting effective patient engagement.
In our country, UCB recruitment is frequently managed by external midwives funded through temporary research grants, who operate outside regular obstetric care workflows. This structural limitation reduces opportunities for trust-building and patient interaction, thus hindering effective donor recruitment. Within this context, two complementary approaches have gained attention for addressing the human and operational challenges in healthcare delivery: Narrative Medicine (NM) and Lean Management (LM). NM fosters empathetic listening and the co-construction of care pathways through patient storytelling, thereby improving communication and trust between patients and healthcare providers [12]. LM, originally developed for industrial efficiency, is increasingly applied in healthcare to identify and reduce inefficiencies, optimize organizational processes, may enhance donation rates by improving both patient engagement and operational efficiency [13]. For these reasons in 2022 in our center it was decided to apply these 2 techniques to improve recruitment results.
This study investigates the combined application of NM and LM within the Obstetrics and Gynecology Department of the University Hospital of Alessandria, assessing its impact on UCB donation rates, patient satisfaction, and organizational performance. Our findings suggest that integrating these approaches creates a potentially applicable model to enhance both patient-centered care and operational efficiency in maternal health services.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
This prospective, single-center pre-post study was conducted at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the University Hospital of Alessandria, Italy. This research was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University Hospital of Alessandria (n° 0021513). The study spanned from 1 July 2022 to 31 December 2024. The primary objective was to assess whether the integration of Narrative Medicine (NM) and Lean Management (LM) approaches would improve umbilical cord blood (UCB) donation rates, as well as increase patient satisfaction and the perceived quality of care.
The secondary objective was to evaluate the quality of collected UCB units, defined as the proportion of donated units eligible for hematopoietic transplantation, according to standards established by the national cord blood banking guidelines.
2.2. Participants (Study Population)
A total of 2636 women who gave birth during the study period were included. Eligibility criteria for UCB donation followed national protocols and excluded individuals with medical or obstetric contraindications (e.g., infections, autoimmune conditions, fever during labor, or preterm birth).
2.3. Intervention
The intervention involved two key components:
2.3.1. Narrative Medicine Integration
The NM integration initiatives built upon our earlier experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic, which had revealed the importance of narrative-based care in supporting isolated mothers [14].
Healthcare professionals—including physicians, midwives, and nurses, all employees of University Hospital of Alessandria—underwent NM training in collaboration with the Italian Society of Narrative Medicine (SIMeN). The training aimed to enhance empathetic listening, trust-building, and patient engagement through structured narrative workshops. These included close reading and reflection exercises using literature, visual arts, and cinema (Figure 1). All the healthcare professionals involved in the process, upon interview, declared that the NM implementation process was perceived as positive and useful. The major challenge was represented by the time required for the trainings: to this effect Staff Coordinators help was crucial.
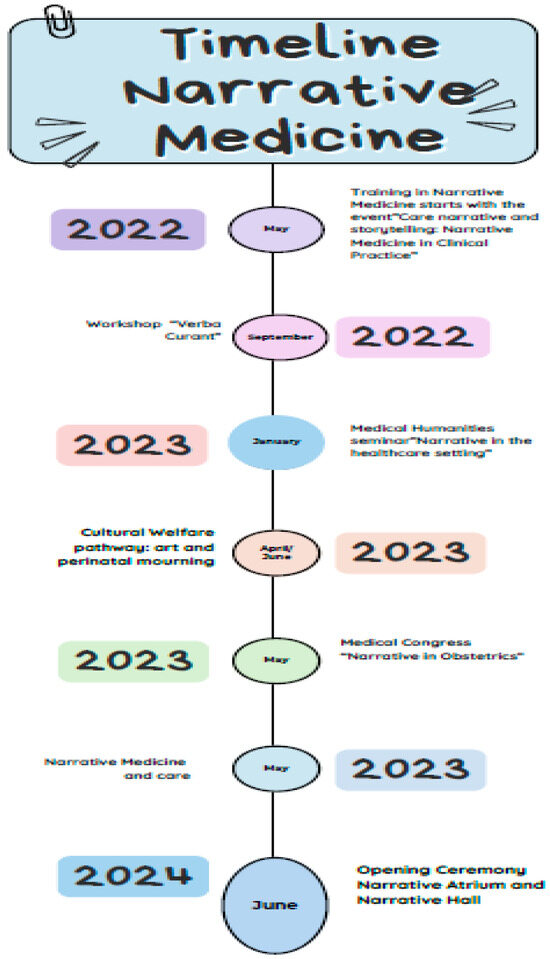
Figure 1.
Phases of Narrative Medicine Training and Educational Methodologies.
The hospital established two dedicated physical spaces to foster narrative practice:
- Narrative Atrium (Figure 2): A redesigned waiting area encouraging storytelling and relational engagement through an interactive journey.
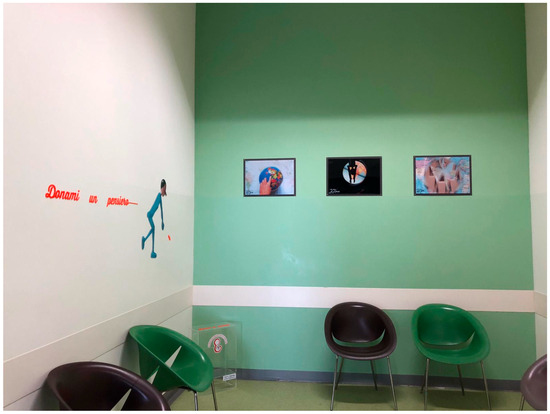 Figure 2. The Narrative Atrium: A storytelling-based waiting area for patients and families.
Figure 2. The Narrative Atrium: A storytelling-based waiting area for patients and families. - Narrative Hall (Figure 3): A therapeutic space for emotional expression through books, films, artwork, and narrative journals.
 Figure 3. Narrative Hall. Legend: The Narrative Hall: Resources and tools for therapeutic storytelling and reflection.
Figure 3. Narrative Hall. Legend: The Narrative Hall: Resources and tools for therapeutic storytelling and reflection.
2.3.2. Lean Management Implementation
In 2019, the department obtained “Advanced Level” certification in Lean Healthcare Management. Lean principles were applied to reorganize UCB donation workflows, emphasizing process mapping, waste reduction, and value creation for patients [15,16]. This included transitioning from reliance on an externally funded midwife via ADISCO (Italian Association of Female Cord Blood Donors) to a multidisciplinary, in-house care team.
Key Lean components included:
- Staff training and engagement
- Process flow mapping and optimization
- Standardization of procedures
- Continuous quality improvement
- Enhanced communication strategies
Informational and consent materials were incorporated into the hospital’s Birth Pathway and disseminated at multiple prenatal care points, including the first pregnancy visit, the ultrasound outpatient offices, the high-risk pregnancy outpatient clinic, the 34-week Health Check-Up Clinic, and during birth preparation classes hosted in our department. In order to guarantee LM implementation at all levels, a Small Working Group including Staff (Midwifes, Nurses) Coordinators, Physician’s Director and one representative for each category was created, and managed the transition perfectly. ADISCO was involved in the process, and the information’s sharing was considered positive from the Association point of view.
2.4. Data Collection
Data were collected from institutional clinical records, donation registries, and patient-reported feedback. The following indicators were monitored:
- Number of Donations: Number of successful donations.
- Donation Rate: Number of women who consented to donate UCB out of total births.
- Patient Satisfaction and Perceived Quality of Care: Measured via corporate satisfaction questionnaires and “PERLA–Person-Centered Care” surveys (https://www.certificazioneperla.it, accessed on 20 May 2025) in collaboration with SIMeN (Italian Society of Narrative Medicine).
- Transplant Eligibility: Proportion of collected UCB units banked for clinical use.
- Adherence Rate: Percentage of pregnant women who consented to the UCB donation during our Hospital’s Birth Pathway among the women who gave birth in our Hospital in the period July 2022–2024
2.5. Ethical Considerations
The study followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided informed consent for donation and participation in satisfaction assessments. Ethical approval was obtained from the institutional ethics committee of the University Hospital of Alessandria.
2.6. Data Analysis
Descriptive statistical analysis was performed to compare pre- and post-intervention outcomes. Donation rates, satisfaction scores, and transplant eligibility percentages were examined to evaluate the intervention’s effectiveness in enhancing patient-centered care and operational performance.
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
Between 1 July 2022 and 31 December 2024, a total of 2636 women gave birth at the University Hospital of Alessandria. All participants received information regarding umbilical cord blood (UCB) donation as part of their care pathway. No significant changes in the overall number of births or patient demographic profile were observed compared to previous years.
3.2. Improvement in Donation Rates
Following the implementation of the Narrative Medicine and Lean Management interventions, there was a notable increase in UCB donation rates.

Table 1.
Umbilical Cord Blood Donation Rates at the University Hospital of Alessandria from 2007 to June 2022.

Table 2.
Umbilical Cord Blood Donation Rates at the University Hospital of Alessandria from July 2022 to 2024.
- Pre-intervention donation rate (2007–June 2022, mean): 3.93%
- Post-intervention donation rate (July 2022–December 2022): 30.8%
- Post-intervention donation rate (2023): 25.8%
- Post-intervention donation rate (2024): 30.6%
- Donation rate during study period (July 2022–2024, mean): 29.07%
This represents a noteworthy relative increase in the mean donation rate compared to the previous years, suggesting improved patient engagement and organizational efficiency. It is important to underline that the donation rate in 2021 and in the first six months of 2022 was 0, this due to the COVID-19 pandemics.
In addition, we also registered the percentage of pregnant women who consented to the UCB donation during our Hospital’s Birth Pathway among the 2636 women who gave birth in our Hospital: 40.4% between July and December 2022, 39.8% in 2023 and 41.6% in 2024. Of course, not all the women who agreed with donation could effectively do it, in most cases because of obstetrical contraindications occurred during the term of the pregnancy or the labour (e.g., infections, fever during labour, or preterm birth), and moreover we do not have data about the percentage of pregnant women who consented to the UCB donation between 2007 and June 2022. However, these numbers also suggest that the implementation of NM and LM in our clinical practice is effective in the enrolment process.
3.3. Collection and Transplant Eligibility
Of the 758 UCB donations collected post-intervention:
- Units eligible for transplant: 29 units (3.75% of donations, mean) met the national quality criteria for transplantation, as assessed by the Regional Cord Blood Bank in Turin (Table 3). This mean eligibility rate is just below the 2022 and 2023 national average (5–5.3% respectively) [10,11].
 Table 3. Percentage of Cord Blood Units Eligible for Transplantation (2022–2024).
Table 3. Percentage of Cord Blood Units Eligible for Transplantation (2022–2024).
The eligibility criteria for the Regional Cord Blood Bank in Turin are:
- -
- The medical history of the father and mother of the newborn must be known, as well as that of their respective families
- -
- No risk of transmission of genetic diseases
- -
- No positivity and/or risk of HIV and/or hepatitis
- -
- No previous travel to countries with risk of endemic diseases
- -
- No use of contraindicated medications, alcohol or drug abuse
- -
- Gestation that must have exceeded 37 weeks
- -
- Give birth in an accredited birthing center
- -
- Birth without fetal distress
3.4. Patient Satisfaction and Perceived Quality of Care
Post-intervention evaluation using both institutional satisfaction surveys and the “PERLA–Person-Centered Care” questionnaires indicated:
- 90.3% of patients reported feeling well-informed about UCB donation
- 88.7% indicated they felt “actively listened to” by the midwifery team
- 92.5% rated their overall care experience as “excellent” or “very good”
Qualitative feedback highlighted the importance of the Narrative Atrium and Hall in promoting emotional safety and enhancing trust during the birth experience. Corporate customer satisfaction surveys revealed progressive improvement in patient-reported outcomes over the two-year intervention period. In particular, ratings related to the quality of the operator-patient relationship, clarity of communication, and emotional support (these three items were the core domains of the PERLA questionnaire) showed statistically significant gains.
The department also participated in the national PERLA–SIMeN (Personalized and Person-Centered Care) initiative. Patient feedback collected through PERLA-specific tools led to the official PERLA Certification being awarded to the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology on 28 February 2025, recognizing its excellence in patient-centered care practices.
3.5. Operational and Organizational Improvements
The integration of Lean Management principles led to several improvements in workflow and care delivery:
- Reduction in missed donation opportunities due to more consistent patient engagement throughout the prenatal pathway
- Increased internal staff autonomy: trained in-house midwives replaced reliance on an external figure, ensuring continuity and sustainability of care and elimination of annual external grant costs (€5000) for a dedicated midwife (even if it is important to underline that we have not estimated the cost of the internal workforce)
- Shortened collection procedure times, due to smoother and standardized processes
- Increased process reliability and safety, as reported in internal observations. Staff reported greater motivation and ownership of the donation process, while delays caused by prior inefficiencies were notably reduced.
- Standardized communication protocols and training improved interdepartmental coordination and reduced delays in consent and collection logistics
These organizational changes contributed to a more robust and patient-centered UCB donation process.
3.6. Perception of Emotional and Informational Support
The empathetic communication approach introduced through Narrative Medicine training was positively received by patients. Survey data and narrative feedback qualitatively indicated:
- Increased trust in healthcare professionals
- Greater participation in decision-making
- Enhanced perception of being welcomed and understood
4. Discussion
This study demonstrates the effectiveness of an integrated approach combining Narrative Medicine (NM) and Lean Management (LM) in improving outcomes related to umbilical cord blood (UCB) donation within a hospital-based obstetric setting. Following the implementation at the University Hospital of Alessandria, we observed a significant increase in donation rates, improved patient satisfaction, enhanced quality of collected units, and greater organizational efficiency.
4.1. Integration of Humanistic and Operational Models
The use of Narrative Medicine contributed to a more empathetic and trust-based clinician–patient relationship, which literature suggests is a key factor in increasing voluntary health behaviors [12,17]. Training programs and the establishment of narrative spaces (e.g., the Narrative Atrium and Hall) created environments where patients felt heard, supported, and better informed, thus reducing emotional barriers to participation [18].
Simultaneously, the application of Lean Management principles helped optimize workflow efficiency and staff engagement, aligning with previous research showing that LM can reduce waste and enhance care quality in obstetric and gynecological services [15,16,19]. By eliminating the dependency on externally funded personnel and integrating recruitment into routine care, the model became more sustainable and applicable.
4.2. Comparison with National and International Data
The post-intervention mean donation rate of 29.7% compare favorably with national Italian averages (2.98%) [10,11]. This outcome support the hypothesis that informational and organizational barriers, rather than clinical limitations, are the primary factors inhibiting public UCB donation—an argument also supported by earlier findings in Italy and other countries [6,7,8]. The post-intervention mean UCB eligibility rate of 3.75% is just below the 2022 and 2023 Italian averages (5–5.3% respectively). This outcome needs further analysis (that is ongoing) and suggests to improve the collection practical method in our Hospital.
4.3. Implications for Healthcare Delivery
This model highlights the potential of interdisciplinary strategies to improve both clinical outcomes and patient experience. The convergence of NM and LM addresses two traditionally separate domains—empathy and efficiency—proving that they can be mutually reinforcing when implemented cohesively. Moreover, the approach aligns with the person-centered care framework endorsed by PERLA–SIMeN, suggesting broader applicability across maternal health services.
4.4. Limitations
This study was conducted in a single center and may reflect context-specific strengths such as strong leadership, existing NM culture, and prior Lean certification. Additionally, the absence of a randomized control group limits causal inference. Nonetheless, the pre-post design allowed for real-time and real-life implementation and adjustment.
4.5. Future Directions
Further multi-center studies are warranted to validate the generalizability of these findings and assess long-term sustainability. Future research should also investigate the cost-effectiveness of this integrated model and its applicability in other areas of maternal–child healthcare, such as breastfeeding support or perinatal mental health.
5. Conclusions
The integration of Narrative Medicine and Lean Management within the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University Hospital of Alessandria led to measurable improvements in umbilical cord blood donation rates, patient satisfaction, and organizational efficiency. By combining empathetic patient engagement with streamlined operational workflows, the project successfully addressed both human and systemic barriers to UCB collection.
These findings offer a promising model for enhancing patient-centered care and clinical outcomes in maternal health settings. The success of this intervention suggests that multidimensional approaches—rooted in both communication and process management—can significantly improve participation in public health initiatives like UCB donation. Broader adoption of similar models, supported by institutional commitment and interprofessional collaboration, could help bridge the gap between scientific opportunity and real-world implementation in obstetrics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D. and C.P.; methodology, V.G.; software, J.O.S.P.S.; validation, D.D., G.S. and V.G.; formal analysis, B.F.; investigation, E.R.; resources D.D.; data curation, M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, D.B.; writing—review and editing, D.D.; visualization, C.P.; supervision, M.T.D.; project administration, G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved on 26 June 2022 by the Institutional Review Board of the University Hospital of Alessandria (ASO. Gine.22.01).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Paola Barbero, Nadia Biancato, Laura Mazzucco, Antonella Dragonetti and Federico Genzano Besso for their technical support. We also thank Stefania Polvani for her kind contribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UCB | Umbilical cord blood |
| NM | Narrative Medicine |
| LM | Lean Management |
| SIMeN | Italian Society of Narrative Medicine |
| ADISCO | Italian Association of Female Cord Blood Donors |
References
- Zhu, X.; Tang, B.; Sun, Z. Umbilical cord blood transplantation: Still growing and improving. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10 (Suppl. 2), S62–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Zheng, C.; Yao, W.; Zhu, X.; Tang, B.; Wan, X.; Song, K.; et al. Umbilical cord blood transplantation can overcome the poor prognosis of KMT2A-MLLT3 acute myeloid leukemia and can lead to good GVHD-free/relapse-free survival. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, N.; Harris, D.; Gaballa, M.A. Human umbilical cord blood stem cells, myocardial infarction and stroke. Clin. Med. 2009, 9, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanberg, P.R.; Eve, D.J.; Willing, A.E.; Garbuzova-Davis, S.; Tan, J.; Sanberg, C.D.; Allickson, J.G.; Cruz, L.E.; Borlongan, C.V. The treatment of neurodegenerative disorders using umbilical cord blood and menstrual blood-derived stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Kong, R.; Peng, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Z. Umbilical cord blood and peripheral blood-derived regulatory T cells therapy: Progress in type 1 diabetes. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 255, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballen, K.K.; Verter, F.; Kurtzberg, J. Umbilical cord blood donation: Public or private? Bone Marrow Transpl. 2015, 50, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on Obstetric Practice; Committee on Genetics. ACOG committee opinion number 399, February 2008, Umbilical cord blood banking. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 111 Pt 1, 475–477. [Google Scholar]
- Benvenuti, M.; Cavallini, E.; Battello, G.; Zullo, F.; Driul, L.; Cromi, A.; Mannella, P.; Nappi, R.E.; Scambia, G.; De Franciscis, P.; et al. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Pregnant Women and Hospital Staff Regarding Umbilical Cord Blood Banking: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlihy, M.M.; Delpapa, E.H. Obstetricians and their role in cord blood banking: Promoting a public model. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 121, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banche del Sangue di Cordone Ombelicale Report 2023. Centro Nazionale Sangue, Ministero della Salute. Centro Nazionale Sangue Report Database. Available online: https://www.centronazionalesangue.it/rapporti-di-attivita-delle-banche-sco/#flipbook-df_18255/1/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Banche del Sangue di Cordone Ombelicale Report 2022. Centro Nazionale Sangue, Ministero della Salute. Centro Nazionale Sangue Report Database. Available online: https://www.centronazionalesangue.it/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Banche-sco-Report-2022.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Charon, R. Narrative Medicine: Honoring the Stories of Illness, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Black, N.; Mays, N. Public inquiries into health care in the UK: A sound basis for policy-making? J. Health Serv. Res. Policy. 2013, 18, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgeo, T.; Gambalunga, F.; Di Matteo, R.; Gatti, D.; Roberti, E.; Dealberti, D.; Fadda, B.; Grassi, E.; Gambarini, L.; Iacorossi, L.; et al. Becoming a mother during the COVID-19 pandemic: The lived experience as told by birthing mothers: A qualitative study. J. Nurs. Manag. 2022, 30, 4138–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, A. Lean Healthcare Management: Meno Sprechi, più Competitività; Wolters Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands; IPSOA Editore: Milan, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Boggetti, M. Pattern Comportamentali: Percorsi di Eccellenza per Guidare L’innovazione Organizzativa; Edra: Milan, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Trenta, P. La postura Narrativa: I Modi di Essere Della Cura; Castelvecchi Editore: Roma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Charon, R. Narrative medicine: Caring for the sick is a work of art. JAAPA 2013, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Womack, J.P.; Jones, D.T. Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation; Simon & Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).