Effect of a Tongue Training Device on Tongue Strength in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Varying Degrees of Tongue Base Collapse by DISE Undergoing Modified Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
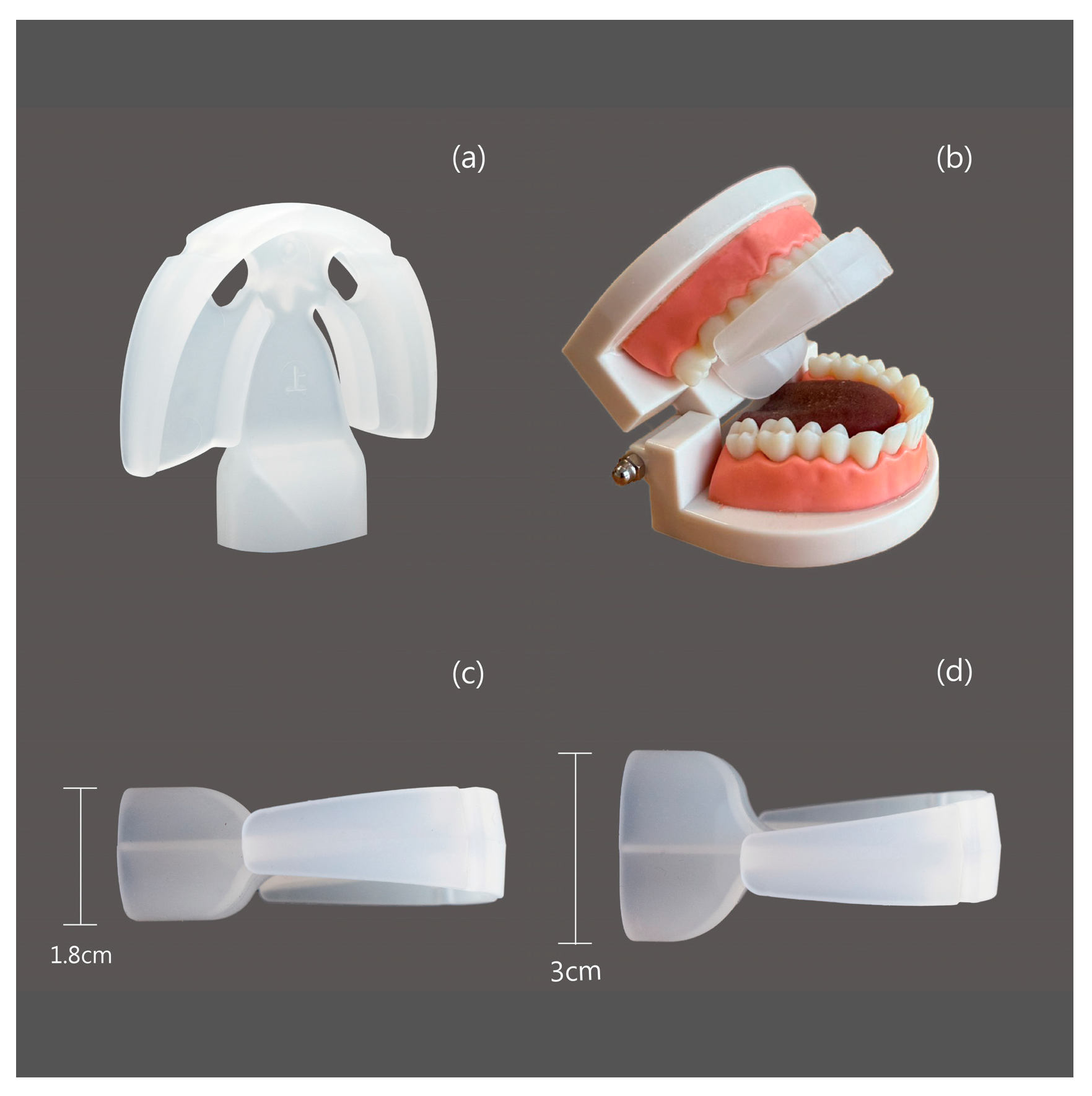
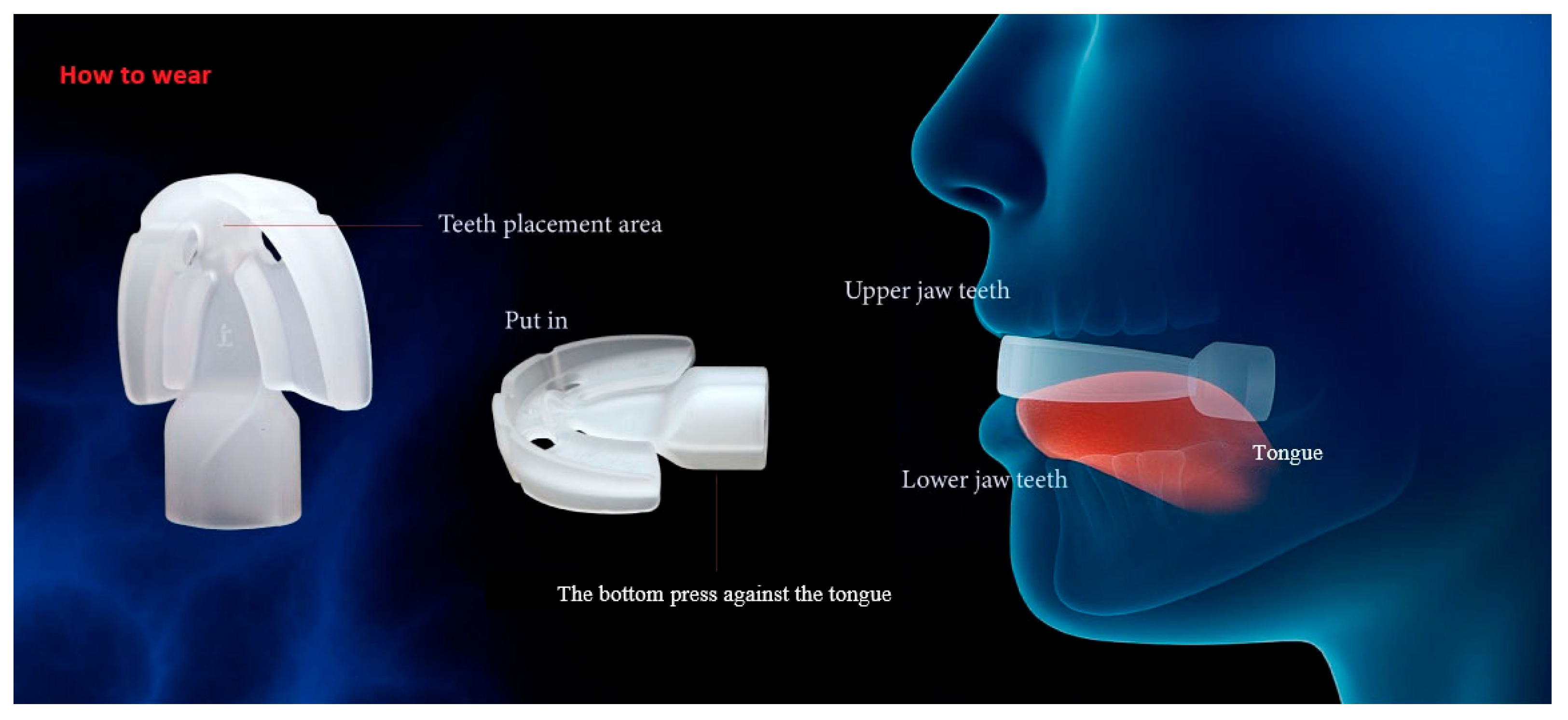
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
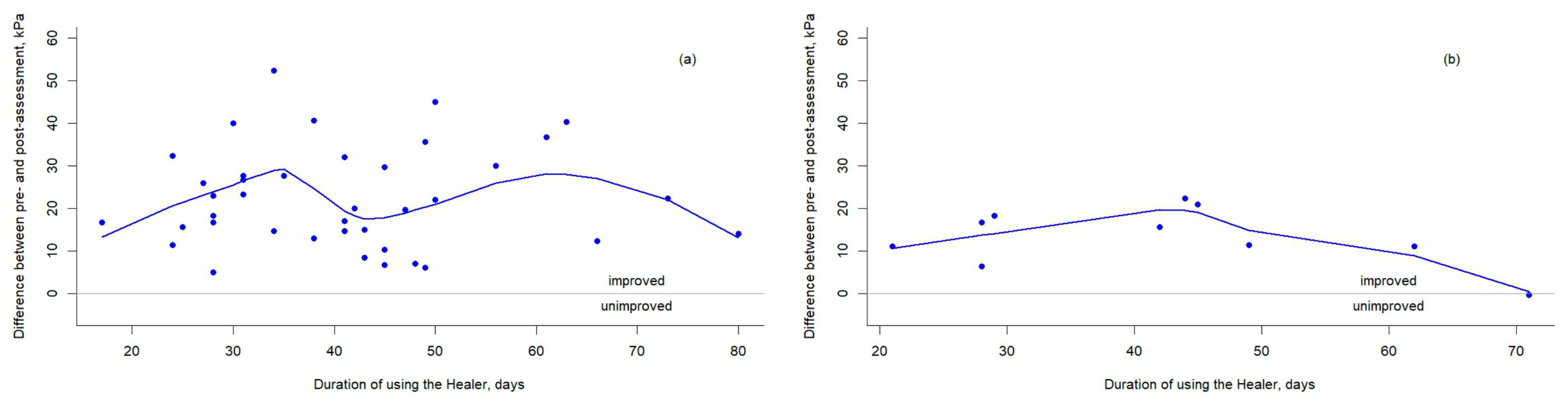
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | Apnea–hypopnea index |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CPAP | Continuous Positive Airway Pressure |
| DISE | Drug-induced sleep endoscopy |
| ENT | Ear, Nose, and Throat |
| IOPI | Iowa Oral Performance Instrument |
| ODI | Oxygen Desaturation Index |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| UPPP | Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty |
| VOTE | Velum (V), Oropharyngeal lateral walls (O), Tongue base (T), and Epiglottis (E) |
References
- Maimon, N.; Hanly, P.J. Does snoring intensity correlate with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea? J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2010, 6, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.A.; Lindberg, E. Obstructive sleep apnea is a common disorder in the population-a review on the epidemiology of sleep apnea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguet, J.P.; Barone-Rochette, G.; Pepin, J.L. Hypertension and obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome: Current perspectives. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2009, 23, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.L.; O’Driscoll, D.M. Hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2013, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, N.M.; Beamer, B.A. Alterations in Glucose Disposal in Sleep-disordered Breathing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Rodriguez, F.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; Reyes-Nunez, N.; Caballero-Martinez, I.; Catalan-Serra, P.; Almeida-Gonzalez, C.V. Role of sleep apnea and continuous positive airway pressure therapy in the incidence of stroke or coronary heart disease in women. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaggi, H.K.; Concato, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Lichtman, J.H.; Brass, L.M.; Mohsenin, V. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, T. Sleep-Disordered Breathing-a Real Therapeutic Target for Hypertension, Pulmonary Hypertension, Ischemic Heart Disease, and Chronic Heart Failure? J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2018, 85, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.M.; Agusti, A.; Villar, I.; Forner, M.; Nieto, D.; Carrizo, S.J.; Barbe, F.; Vicente, E.; Wei, Y.; Nieto, F.J.; et al. Association between treated and untreated obstructive sleep apnea and risk of hypertension. JAMA 2012, 307, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, B.; Won, C.; Yaggi, H.K. Cardiovascular consequences of sleep apnea. Clin. Chest Med. 2010, 31, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Yenokyan, G.; Newman, A.B.; O’Connor, G.T.; Punjabi, N.M.; Quan, S.F.; Redline, S.; Resnick, H.E.; Tong, E.K.; Diener-West, M.; et al. Prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: The sleep heart health study. Circulation 2010, 122, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzardi, E.; Sciatti, E.; Bonadei, I.; D’Aloia, A.; Curnis, A.; Metra, M. Obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea and arrhythmias: New updates. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 18, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Finn, L.; Peppard, P.E.; Szklo-Coxe, M.; Austin, D.; Nieto, F.J.; Stubbs, R.; Hla, K.M. Sleep disordered breathing and mortality: Eighteen-year follow-up of the Wisconsin sleep cohort. Sleep 2008, 31, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Rodriguez, F.; Pena-Grinan, N.; Reyes-Nunez, N.; De la Cruz-Moron, I.; Perez-Ronchel, J.; De la Vega-Gallardo, F.; Fernandez-Palacin, A. Mortality in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea patients treated with positive airway pressure. Chest 2005, 128, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askland, K.; Wright, L.; Wozniak, D.R.; Emmanuel, T.; Caston, J.; Smith, I. Educational, supportive and behavioural interventions to improve usage of continuous positive airway pressure machines in adults with obstructive sleep apnoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 4, CD007736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caples, S.M.; Rowley, J.A.; Prinsell, J.R.; Pallanch, J.F.; Elamin, M.B.; Katz, S.G.; Harwick, J.D. Surgical modifications of the upper airway for obstructive sleep apnea in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep 2010, 33, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, J.; Browaldh, N.; Fehrm, J.; Friberg, D. Eight-Year Follow-up of Modified Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E307–E313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijemeni, E.; D’Amone, G.; Gbati, I. Drug-induced sedation endoscopy (DISE) classification systems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 2017, 21, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, J.M.; Durr, M.L.; Nardone, H.C.; Baldassari, C.M.; Duggins, A.; Ishman, S.L. Systematic Review of Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy Scoring Systems. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 158, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezirian, E.J.; Hohenhorst, W.; de Vries, N. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy: The VOTE classification. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 268, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkins, T.; Tangutur, A.; Keenan, B.T.; Seay, E.G.; Thuler, E.; Dedhia, R.C.; Schwartz, A.R. Pharyngeal Manometry and Upper Airway Collapse During Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 150, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeltgen, S.H.; Kaur, H.; Daniels, S.K.; Mohammadi, L.; Murray, J. Behavioral Interventions Targeting Insufficient Upper Esophageal Sphincter Opening During Swallowing: A Scoping Review. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, G.H.; Kamarunas, E.; Mann, G.C.; Schmidley, J.W.; Robbins, J.A.; Crary, M.A. Effects of Mendelsohn maneuver on measures of swallowing duration post stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2012, 19, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Choi, J.B.; Yoo, S.J.; Chang, M.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Park, J.S. Tongue-to-palate resistance training improves tongue strength and oropharyngeal swallowing function in subacute stroke survivors with dysphagia. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2017, 44, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, J.Y.; Hyun, J.K.; Ko, K.R.; Lee, S.J. Chin tuck for prevention of aspiration: Effectiveness and appropriate posture. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.M.; Shelton, N. Training effects of the effortful swallow under three exercise conditions. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, C.; Wang, Y. Effect of respiratory training on swallowing function in swallowing disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Hsu, C.F.; Liu, S.J.; Li, J.Y.; Ho, Y.L.; Chen, H.H. Effects of tongue strengthening exercises on tongue muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.; Kays, S.A.; Gangnon, R.E.; Hind, J.A.; Hewitt, A.L.; Gentry, L.R.; Taylor, A.J. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, D.H. Effect of tongue strength training using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument in stroke patients with dysphagia. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 3631–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesti, J.J.; Cahali, M.B. Evolution of swallowing in lateral pharyngoplasty with stylopharyngeal muscle preservation. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 78, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HEAL. 2025. Available online: https://www.healwell.com.tw/about/1.htm (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- ISO 10993-5; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 10993-23; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 23: Tests for Irritation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 10993-10; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 10: Tests for Skin Sensitization. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 10993-12; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Burkhead, L.M.; Sapienza, C.M.; Rosenbek, J.C. Strength-training exercise in dysphagia rehabilitation: Principles, procedures, and directions for future research. Dysphagia 2007, 22, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stal, P.; Marklund, S.; Thornell, L.E.; De Paul, R.; Eriksson, P.O. Fibre composition of human intrinsic tongue muscles. Cells Tissues Organs 2003, 173, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, F.N.; Meadows, P.; Jacobowitz, O.; Davidson, T.M. Tongue anatomy and physiology, the scientific basis for a novel targeted neurostimulation system designed for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Neuromodulation 2013, 16, 376–386, discussion 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.B.; Lan, M.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, T.T.; Lan, M.C. The correlation between drug-induced sleep endoscopy findings and severity of obstructive sleep apnea. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgalas, C.; Garas, G.; Hadjihannas, E.; Oostra, A. Assessment of obstruction level and selection of patients for obstructive sleep apnoea surgery: An evidence-based approach. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, C.; Sommer, J.U.; Stuck, B.A.; Hormann, K.; Maurer, J.T. Does drug-induced sleep endoscopy change the treatment concept of patients with snoring and obstructive sleep apnea? Sleep Breath 2013, 17, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncin, W.; Willemsens, A.; Gely, L.; Contal, O. Assessment and rehabilitation of tongue motor skills with myofunctional therapy in obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2024, 20, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogisawa, S.; Nishikubo, S.; Nakajima, J.; Azaki, H.; Mayahara, K.; Shinozuka, K.; Tonogi, M. The changes in oral volume and hyoid bone position after maxillomandibular advancement and genioglossus advancement for patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 2023, 27, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, T.A.; Elhamshary, A.A.S.; Elkady, A.S.; Elhewity, A.M.M.; Abdelsamee, H.A. Modified genioglossus advancement with radiofrequency tongue base reduction for retroglossal collapse in Obstructive sleep apnea patients. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor-Reina, C.; Plaza, G.; Garcia-Iriarte, M.T.; Ignacio-Garcia, J.M.; Baptista, P.; Casado-Morente, J.C.; De Vicente, E. Tongue peak pressure: A tool to aid in the identification of obstruction sites in patients with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 2020, 24, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, H.M.; Henson, P.A.; Barber, W.D.; Stierwalt, J.A.; Sherrill, M. Relationships among subjective and objective measures of tongue strength and oral phase swallowing impairments. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2003, 12, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youmans, S.R.; Stierwalt, J.A. Measures of tongue function related to normal swallowing. Dysphagia 2006, 21, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, R.; Yu, M.; Gao, X. Efficacy of myofunctional therapy for obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2025, 25, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, S.A.; Cistulli, P.A.; Ng, A.T.; Zeng, B.; Petocz, P.; Darendeliler, M.A. Comparison of mandibular advancement splint and tongue stabilizing device in obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized controlled trial. Sleep 2009, 32, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.M.; Martinez Ruiz de Apodaca, P.; Carrasco, M.; Fernandez, S.; Wong, P.Y.; Zhang, H.; Hassaan, A.; Kotecha, B. Daytime Neuromuscular Electrical Therapy of Tongue Muscles in Improving Snoring in Individuals with Primary Snoring and Mild Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.R.; Jacobowitz, O.; Eisele, D.W.; Mickelson, S.A.; Miller, M.B.; Oliven, A.; Certal, V.; Hopp, M.L.; Winslow, D.H.; Huntley, T.C.; et al. Targeted Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2023, 149, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Total | M Group | S Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 49 | 39 | 10 | |
| Gender | 1.000 | |||
| Female | 10 (20.4%) | 8 (20.5%) | 2 (20%) | |
| Male | 39 (79.6%) | 31 (79.5%) | 8 (80%) | |
| Age, years old | 38.3 ± 7.4 | 37.2 ± 7.2 | 42.6 ± 7.5 | 0.066 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.8 ± 3.9 | 28.4 ± 3.7 | 25.6 ± 4.3 | 0.050 |
| Smoking history | 12 (24.5%) | 10 (25.6%) | 2 (20%) | 1 |
| Variables | Total | M Group | S Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 49 | 39 | 10 | |
| AHI, events/h | 36.0 ± 29.4 | 35.7 ± 28.1 | 37.0 ± 35.4 | 0.825 |
| IOPI 1 month after surgery before training, kPa | 27.6 ± 13.5 | 28.1 ± 13.7 | 25.6 ± 13.1 | 0.607 |
| Training days | 41.4 ± 14.3 | 41.3 ± 14.1 | 41.9 ± 16.0 | 0.901 |
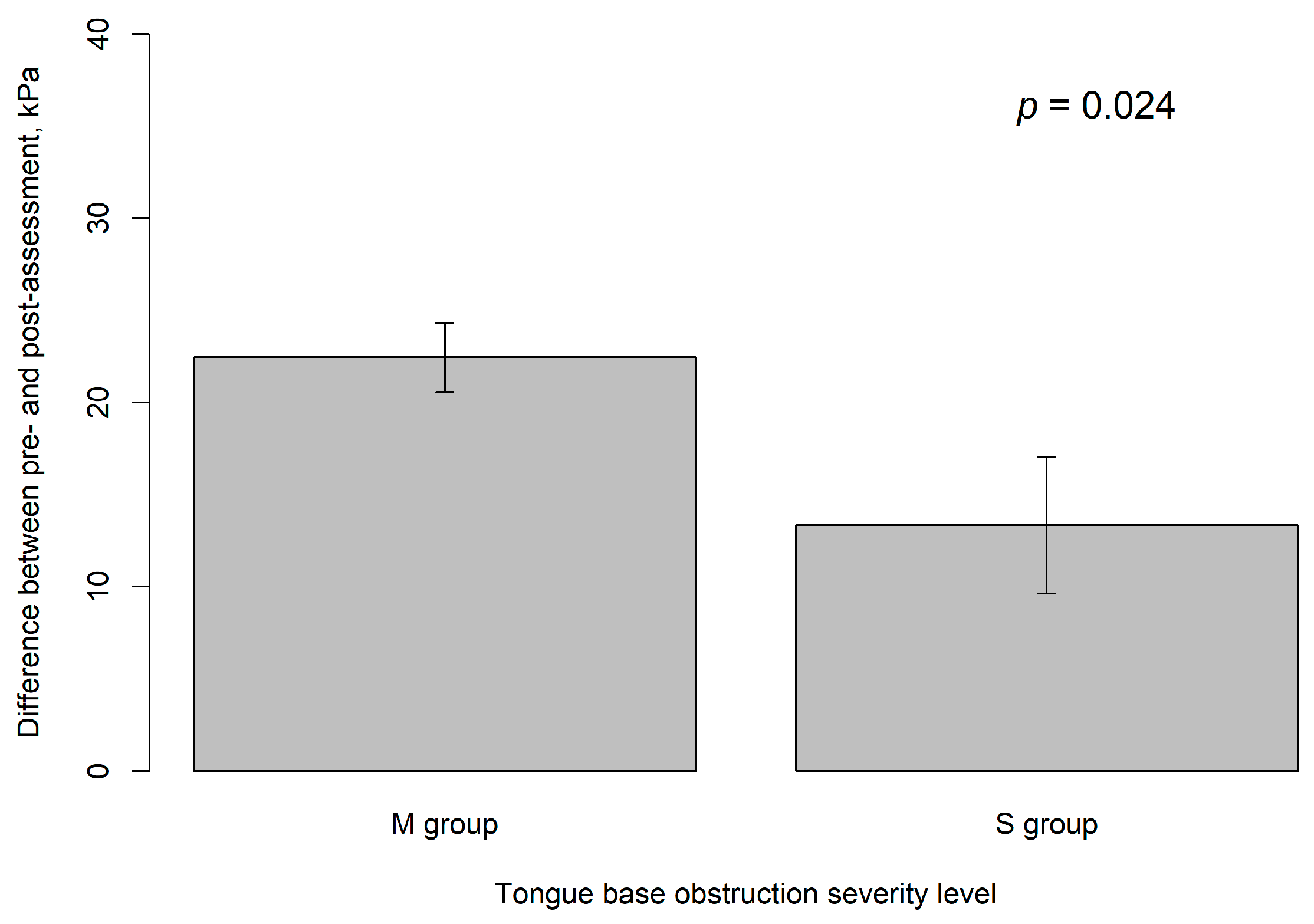
| IOPI after training, kPa | 48.1 ± 13.0 | 50.5 ± 11.9 | 38.9 ± 13.7 | 0.010 |
| Difference, kPa | 20.6 ± 11.5 | 22.5 ± 11.8 | 13.3 ± 6.9 | 0.024 |
| Variables | Estimate | S.E. | t Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male vs. female | 0.49 | 4.12 | 0.12 | 0.905 |
| Age, years | −0.06 | 0.22 | −0.27 | 0.786 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.84 | 0.403 |
| Smoking history | 5.29 | 3.79 | 1.40 | 0.169 |
| Alcohol history | 1.12 | 5.49 | 0.21 | 0.839 |
| Hypertension | −2.77 | 4.27 | −0.65 | 0.52 |
| Diabetes | −4.01 | 11.74 | −0.34 | 0.734 |
| AHI, events/h | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.67 | 0.507 |
| M group vs. S group | 9.12 | 3.90 | 2.34 | 0.024 |
| Training days | −0.02 | 0.12 | −0.21 | 0.833 |
| Model | Covariate | Estimate (95%C.I.) | S.E. | t Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | M group vs. S group | 9.10 (−0.17, 18.37) | 4.57 | 1.99 | 0.054 |
| Male vs. female | 0.25 (−7.99, 8.49) | 4.06 | 0.06 | 0.952 | |
| Age, years | 0.07 (−0.42, 0.57) | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.764 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −0.17 (−1.01, 0.67) | 0.42 | −0.41 | 0.682 | |
| Smoking | 0.13 (−8.27, 8.52) | 4.13 | 0.03 | 0.976 | |
| Training day | −0.003 (−0.25, 0.24) | 0.12 | −0.02 | 0.983 | |
| intercept | 13.76 (−19.65, 47.16) | 16.45 | 0.84 | 0.409 | |
| Model 2 | M group vs. S group | 9.12 (0.14, 18.09) | 4.43 | 2.06 | 0.047 |
| Male vs. female | 0.24 (−7.83, 8.31) | 3.98 | 0.06 | 0.953 | |
| Age, years | 0.08 (−0.39, 0.54) | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.746 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −0.17 (−1.00, 0.65) | 0.41 | −0.43 | 0.673 | |
| Smoking | 0.10 (−7.90, 8.10) | 3.94 | 0.03 | 0.979 | |
| intercept | 13.62 (−16.91, 44.16) | 15.05 | 0.91 | 0.372 | |
| Model 3 | M group vs. S group | 9.11 (0.27, 17.95) | 4.36 | 2.01 | 0.044 |
| Male vs. female | 0.24 (−7.72, 8.19) | 3.92 | 0.06 | 0.952 | |
| Age, years | 0.08 (−0.38, 0.53) | 0.23 | 0.34 | 0.738 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −0.17 (−0.98, 0.63) | 0.40 | −0.43 | 0.668 | |
| intercept | 13.58 (−16.32, 43.48) | 14.76 | 0.92 | 0.363 | |
| Model 4 | M group vs. S group | 9.07 (0.27, 17.95) | 4.24 | 2.14 | 0.039 |
| Age | 0.07 (−0.37, 0.52) | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.738 | |
| BMI | −0.17 (−0.96, 0.62) | 0.39 | −0.43 | 0.667 | |
| intercept | 13.83 (−16.32, 43.48) | 13.99 | 0.99 | 0.329 | |
| Model 5 | M group vs. S group | 8.85 (0.58, 17.12) | 4.11 | 2.15 | 0.037 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.10 (−0.76, 0.95) | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.817 | |
| intercept | 10.80 (−12.25, 33.85) | 11.45 | 0.94 | 0.351 | |
| Model 6 | M group vs. S group | 9.12 (1.27, 16.97) | 3.90 | 2.34 | 0.024 |
| intercept | 13.33 (6.33, 20.34) | 3.48 | 3.83 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsou, Y.-A.; Kao, H.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chou, Y.-J.; Kao, Y.-H.; Chiang, J.-K. Effect of a Tongue Training Device on Tongue Strength in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Varying Degrees of Tongue Base Collapse by DISE Undergoing Modified Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192509
Tsou Y-A, Kao H-H, Lin Y-H, Chou Y-J, Kao Y-H, Chiang J-K. Effect of a Tongue Training Device on Tongue Strength in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Varying Degrees of Tongue Base Collapse by DISE Undergoing Modified Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Healthcare. 2025; 13(19):2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192509
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsou, Yung-An, Hsueh-Hsin Kao, Ya-Han Lin, Yu-Jen Chou, Yee-Hsin Kao, and Jui-Kun Chiang. 2025. "Effect of a Tongue Training Device on Tongue Strength in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Varying Degrees of Tongue Base Collapse by DISE Undergoing Modified Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty" Healthcare 13, no. 19: 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192509
APA StyleTsou, Y.-A., Kao, H.-H., Lin, Y.-H., Chou, Y.-J., Kao, Y.-H., & Chiang, J.-K. (2025). Effect of a Tongue Training Device on Tongue Strength in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Varying Degrees of Tongue Base Collapse by DISE Undergoing Modified Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Healthcare, 13(19), 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192509






