Autonomic Dysregulation Mediates the Association Between Childhood Trauma and Pain Severity: Evidence from a Mediation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Self-Report Measures
2.2.1. Sociodemographic and Clinical Data
2.2.2. Childhood Trauma
2.2.3. Cumulative Trauma Exposure
2.2.4. Autonomic Reactivity
2.2.5. Pain Severity
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Group Comparisons
3.2. Bivariate Correlations
3.3. Hierarchical Regression Results
3.3.1. Step 1: Predicting Autonomic Reactivity (BPQ)
3.3.2. Step 2: Predicting Pain Severity from CPEA
3.3.3. Step 3: Predicting Pain Severity from Autonomic Reactivity
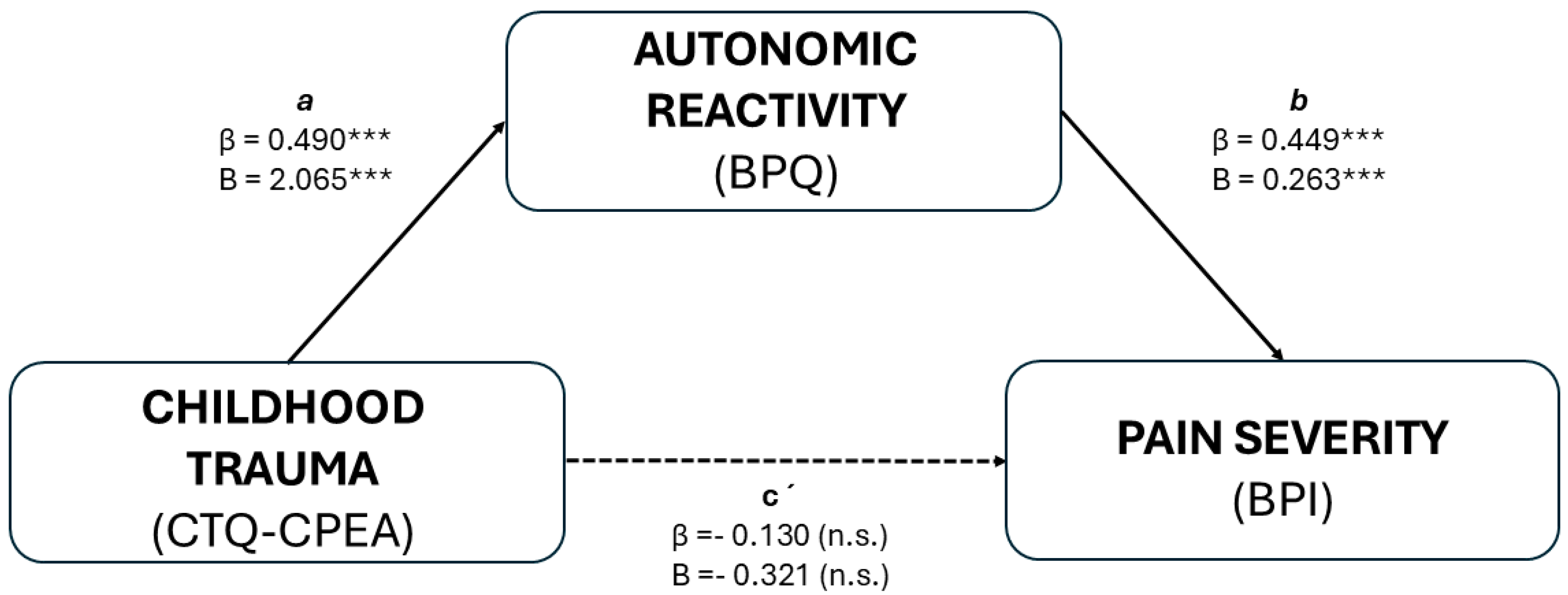
3.4. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Childhood Trauma and Autonomic Dysregulation
4.2. Autonomic Dysregulation and Pain Severity
Central Nervous System Connectivity and Pain Regulation
4.3. Mediation Pathway: Trauma, Autonomic Dysregulation, and Pain
4.4. Gender Effects and Structural Robustness
4.5. Theoretical and Clinical Implications
4.6. Limitations, Methodological Considerations, and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANS | Autonomic Nervous System |
| BPI | Brief Pain Inventory |
| BPQ | Body Perception Questionnaire |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CPEA | Childhood Physical and Emotional Abuse |
| CSA | Childhood Sexual Abuse |
| CTQ | Childhood Trauma Questionnaire |
| GNR | Guarda Nacional Republicana |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| LEC-17 | Life Events Checklist for DSM-IV (17 items) |
| PTSD | Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder |
| SEM | Structural Equation Modeling |
| VNS | Vagus Nerve Stimulation |
References
- Heim, C.; Nater, U.M.; Maloney, E.; Boneva, R.; Jones, J.F.; Reeves, W.C. Childhood Trauma and Risk for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Association with Neuroendocrine Dysfunction. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnar, M.; Quevedo, K. The Neurobiology of Stress and Development. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2007, 58, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S. Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation: Central Role of the Brain. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 873–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meaney, M.J. Maternal Care, Gene Expression, and the Transmission of Individual Differences in Stress Reactivity across Generations. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1161–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, E.; De Brito, S.A.; Viding, E. Research Review: The Neurobiology and Genetics of Maltreatment and Adversity. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.; Radua, J.; Rubia, K. Gray Matter Abnormalities in Childhood Maltreatment: A Voxel-Wise Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusslock, R.; Miller, G.E. Early-Life Adversity and Physical and Emotional Health Across the Lifespan: A Neuroimmune Network Hypothesis. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, B.D.; Pollard, R.A.; Blakley, T.L.; Baker, W.L.; Vigilante, D. Childhood Trauma, the Neurobiology of Adaptation, and “Use-Dependent” Development of the Brain: How “States” Become “Traits”. Infant Ment. Health J. 1995, 16, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.S.; McGee, S.J. Pain as a Global Public Health Priority. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.; Croft, P.; Langford, R.M.; Donaldson, L.J.; Jones, G.T. Prevalence of Chronic Pain in the UK: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Population Studies. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häuser, W.; Kosseva, M.; Üceyler, N.; Klose, P.; Sommer, C. Emotional, Physical, and Sexual Abuse in Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, K.G.; Widom, C.S. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Moderates the Relation between Documented Childhood Victimization and Pain 30 Years Later. Pain 2011, 152, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.A.; Luecken, L.J.; Zautra, A.J. Are Reports of Childhood Abuse Related to the Experience of Chronic Pain in Adulthood? A Meta-Analytic Review of the Literature. Clin. J. Pain 2005, 21, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchaine, T.P.; Thayer, J.F. Heart Rate Variability as a Transdiagnostic Biomarker of Psychopathology. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 98, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porges, S.W. The Polyvagal Perspective. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolacz, J.; Porges, S.W. Chronic Diffuse Pain and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders After Traumatic Stress: Pathophysiology Through a Polyvagal Perspective. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meints, S.M.; Edwards, R.R. Evaluating Psychosocial Contributions to Chronic Pain Outcomes. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 87, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarz, J.; Eich, W.; Treede, R.-D.; Gerhardt, A. Altered Pressure Pain Thresholds and Increased Wind-up in Adult Patients with Chronic Back Pain with a History of Childhood Maltreatment: A Quantitative Sensory Testing Study. Pain 2016, 157, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidmarsh, L.V.; Harrison, R.; Ravindran, D.; Matthews, S.L.; Finlay, K.A. The Influence of Adverse Childhood Experiences in Pain Management: Mechanisms, Processes, and Trauma-Informed Care. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 923866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzawa-Lee, G.A.; Knoerl, R.; Williams, D.A.; Clauw, D.J.; Bridges, C.M.; Harte, S.E.; Kolarik, E.; Houghtby, J.; Lavoie Smith, E.M. Childhood Trauma Predicts Cancer Treatment-Related Pain in Breast Cancer Survivors. Cancer Nurs. 2020, 43, E207–E216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paras, M.L.; Murad, M.H.; Chen, L.P.; Goranson, E.N.; Sattler, A.L.; Colbenson, K.M.; Elamin, M.B.; Seime, R.J.; Prokop, L.J.; Zirakzadeh, A. Sexual Abuse and Lifetime Diagnosis of Somatic Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2009, 302, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, K.P.; Mills, S.E.E.; Senaratne, D.N.S.; Colvin, L.A.; Smith, B.H. What Is the Association between Childhood Adversity and Subsequent Chronic Pain in Adulthood? A Systematic Review. BJA Open 2023, 6, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussières, A.; Hancock, M.J.; Elklit, A.; Ferreira, M.L.; Ferreira, P.H.; Stone, L.S.; Wideman, T.H.; Boruff, J.T.; Al Zoubi, F.; Chaudhry, F.; et al. Adverse Childhood Experience Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Reporting Chronic Pain in Adulthood: A Stystematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol. 2023, 14, 2284025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afari, N.; Ahumada, S.M.; Wright, L.J.; Mostoufi, S.; Golnari, G.; Reis, V.; Cuneo, J.G. Psychological Trauma and Functional Somatic Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biopsychosoc. Sci. Med. 2014, 76, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, D.; Kirchhoff, C.; Egle, U.T.; Nolte, T.; Tschuggnall, M.; Rumpold, G.; Kantner-Rumplmair, W.; Grote, V.; Fischer, M.J.; Lampe, A. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) in Specific Vulnerable Developmental Periods Can Increase the Likelihood of Chronic Pain in Adulthood-Results from a Cross-Sectional Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.K. Interoceptive Inference, Emotion, and the Embodied Self. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.F.; Simmons, W.K. Interoceptive Predictions in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Lane, R.D. A Model of Neurovisceral Integration in Emotion Regulation and Dysregulation. J. Affect. Disord. 2000, 61, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolacz, J.; Dale, L.P.; Nix, E.J.; Roath, O.K.; Lewis, G.F.; Porges, S.W. Adversity History Predicts Self-Reported Autonomic Reactivity and Mental Health in US Residents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 577728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, E.L.; Reese, S.E.; Bedford, C.E.; Baker, A.K. Adverse Childhood Experiences Predict Autonomic Indices of Emotion Dysregulation and Negative Emotional Cue-Elicited Craving among Female Opioid-Treated Chronic Pain Patients. Dev. Psychopathol. 2019, 31, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddell, B.J.; Kemp, A.H.; Steel, Z.; Nickerson, A.; Bryant, R.A.; Tam, N.; Tay, A.K.; Silove, D. Heart Rate Variability and the Relationship between Trauma Exposure Age, and Psychopathology in a Post-Conflict Setting. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, G.; Troisi, G.; Pazzaglia, M.; Pascalis, V.D.; Casagrande, M. Heart Rate Variability and Pain: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D.P.; Fink, L.; Handelsman, L.; Foote, J.; Lovejoy, M.; Wenzel, K.; Sapareto, E.; Ruggiero, J. Initial Reliability and Validity of a New Retrospective Measure of Child Abuse and Neglect. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Litz, B.T.; Hsu, J.L.; Lombardo, T.W. Psychometric Properties of the Life Events Checklist. Assessment 2004, 11, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, C.; Maia, Â. Dados de Exposição Potencialmente Traumática na População Portuguesa Utilizando as Versões Portuguesas do Life Events Checklist e o Life Stressor Checklist—Revised; Psiquilibrios Edições: Braga, Portugal, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Porges, S.W. Body Perception Questionnaire; Traumatic Stress Research Consortium: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, C.; Rocha, N.; Barbosa, F. Untangling Self-Reported Interoceptive Attention and Accuracy: Evidence from the European Portuguese Validation of the Body Perception Questionnaire and the Interoceptive Accuracy Scale. PsyArxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A.; Kolacz, J.; Pailhez, G.; Bulbena-Cabre, A.; Bulbena, A.; Porges, S.W. Assessing Body Awareness and Autonomic Reactivity: Factor Structure and Psychometric Properties of the Body Perception Questionnaire-Short Form (BPQ-SF). Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 27, e1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Chiorri, C.; Mazzoni, G.-P.; Orrù, G.; Kolacz, J.; Porges, S.W.; Conversano, C.; Gemignani, A.; Miccoli, M. Item Reduction, Psychometric and Biometric Properties of the Italian Version of the Body Perception Questionnaire-Short Form (BPQ-SF): The BPQ-22. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolacz, J.; Chen, X.; Nix, E.J.; Roath, O.K.; Holmes, L.G.; Tokash, C.; Porges, S.W.; Lewis, G.F. Measuring Autonomic Symptoms with the Body Perception Questionnaire Short Form (BPQ-SF): Factor Analysis, Derivation of U.S. Adult Normative Values, and Association with Sensor-Based Physiological Measures. MedRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolacz, J.; Chen, X.; Nix, E.J.; Roath, O.K.; Holmes, L.G.; Tokash, C.; Porges, S.W.; Lewis, G.F. Association of Self-Reported Autonomic Symptoms With Sensor-Based Physiological Measures. Psychosom. Med. 2023, 85, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; da-Silva, M.; Carvalho, L.; Ribeiro-Carreira, A.; Pereira, A.R.; Sampaio, A.; Coutinho, J.; González-Villar, A.J. Interplay Between Cortical and Neurocardiac Interoceptive Processes and Its Association with Self-Reported Interoceptive Sensibility. Brain Topogr. 2025, 38, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleeland, C.S.; Ryan, K.M. Pain Assessment: Global Use of the Brief Pain Inventory. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 1994, 23, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, L.F.; Costa-Pereira, A.; Mendonça, L.; Dias, C.C.; Castro-Lopes, J.M. Epidemiology of Chronic Pain: A Population-Based Nationwide Study on Its Prevalence, Characteristics and Associated Disability in Portugal. J. Pain 2012, 13, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloitre, M.; Stolbach, B.C.; Herman, J.L.; van der Kolk, B.; Pynoos, R.; Wang, J.; Petkova, E. A Developmental Approach to Complex PTSD: Childhood and Adult Cumulative Trauma as Predictors of Symptom Complexity. J. Trauma. Stress 2009, 22, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.; Widom, C.S.; Browne, K.; Fergusson, D.; Webb, E.; Janson, S. Burden and Consequences of Child Maltreatment in High-Income Countries. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2009, 373, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechtel, P.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Effects of Early Life Stress on Cognitive and Affective Function: An Integrated Review of Human Literature. Psychopharmacology 2011, 214, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutner, M.; Nachtsheim, C.; Neter, J.; Li, W. Applied Linear Statistical Models; McGraw-Hill/Irwin: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-07-310874-2. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S.; Wingfield, J.C. The Concept of Allostasis in Biology and Biomedicine. Horm. Behav. 2003, 43, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teicher, M.H.; Samson, J.A. Annual Research Review: Enduring Neurobiological Effects of Childhood Abuse and Neglect. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2016, 57, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis, Second Edition: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4625-3466-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, M.S.; MacKinnon, D.P. Required Sample Size to Detect the Mediated Effect. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 18, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-203-77444-1. [Google Scholar]
- Preacher, K.J.; Hayes, A.F. Asymptotic and Resampling Strategies for Assessing and Comparing Indirect Effects in Multiple Mediator Models. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, L.P.; Cuffe, S.P.; Kolacz, J.; Leon, K.G.; Bossemeyer Biernacki, N.; Bhullar, A.; Nix, E.J.; Porges, S.W. Increased Autonomic Reactivity and Mental Health Difficulties in COVID-19 Survivors: Implications for Medical Providers. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 830926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, L.M.; Ioannou, L.; Baker, K.S.; Gibson, S.J.; Georgiou-Karistianis, N.; Giummarra, M.J. Meta-Analytic Evidence for Decreased Heart Rate Variability in Chronic Pain Implicating Parasympathetic Nervous System Dysregulation. Pain 2016, 157, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizes, V.; Rakel, D.; Niemiec, C. Integrative Medicine and Patient-Centered Care. Explore 2009, 5, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.J.; Shore, K.K.; Tice, J.A. Effectiveness and Value of Integrating Behavioral Health Into Primary Care. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 691–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigrist, C.; Mürner-Lavanchy, I.; Peschel, S.K.V.; Schmidt, S.J.; Kaess, M.; Koenig, J. Early Life Maltreatment and Resting-State Heart Rate Variability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kang, H.-J.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.-C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Shin, I.-S.; Kim, J.-M. Impacts of Heart Rate Variability on Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Risks after Physical Injuries: Amplification with Childhood Abuse Histories. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1474650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesarg, C.; Van den Akker, A.L.; Oei, N.Y.L.; Wiers, R.W.; Staaks, J.; Thayer, J.F.; Williams, D.P.; Hoeve, M. Childhood Adversity and Vagal Regulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 143, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.; Thayer, J.F. Sex Differences in Healthy Human Heart Rate Variability: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalsa, S.S.; Adolphs, R.; Cameron, O.G.; Critchley, H.D.; Davenport, P.W.; Feinstein, J.S.; Feusner, J.D.; Garfinkel, S.N.; Lane, R.D.; Mehling, W.E.; et al. Interoception and Mental Health: A Roadmap. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.-A.; Mora, T.; Vargas, A.; Fuentes-Iniestra, M.; Martínez-Lavín, M. Sympathetic Nervous System Dysfunction in Fibromyalgia, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and Interstitial Cystitis: A Review of Case-Control Studies. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 20, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, B.Y. Heart Rate Variability for Quantification of Autonomic Dysfunction in Fibromyalgia. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Pérez, S.E.; Losada-Delgado, P.; Padrón-Rubio, K.; Pérez-Acosta, C.; Alonso-Pérez, J.L.; Sánchez-Romero, E.A.; Sosa-Reina, M.D.; Martín-Pérez, I.M. Association of pain intensity and psychological factors among patients with complex regional pain syndrome.a correlational, cross-sectional study mar. Cuest. Fisioter. 2023, 52, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, P.R.; Austin, T.; DeBarros, A.; Brown, T. The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure, and Mood. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehling, W.E.; Wrubel, J.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Price, C.J.; Kerr, C.E.; Silow, T.; Gopisetty, V.; Stewart, A.L. Body Awareness: A Phenomenological Inquiry into the Common Ground of Mind-Body Therapies. Philos. Ethics Humanit. Med. PEHM 2011, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutch, J.J.; Ichesco, E.; Hampson, J.P.; Labus, J.S.; Farmer, M.A.; Martucci, K.T.; Ness, T.J.; Deutsch, G.; Apkarian, A.V.; Mackey, S.C.; et al. Brain Signature and Functional Impact of Centralized Pain: A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain (MAPP) Network Study. Pain 2017, 158, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, P.; Deak, B.; Mayr, A.; Stankewitz, A.; Keeser, D.; Griffanti, L.; Witkovsky, V.; Irving, S.; Schulz, E. Intrinsic Network Activity Reflects the Ongoing Experience of Chronic Pain. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napadow, V.; Sclocco, R.; Henderson, L.A. Brainstem Neuroimaging of Nociception and Pain Circuitries. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, J.G., Jr.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: Myths and Truths about Mediation Analysis. J. Consum. Res. 2010, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, E.J.; Gerin, M.I.; Viding, E. Annual Research Review: Childhood Maltreatment, Latent Vulnerability and the Shift to Preventative Psychiatry—The Contribution of Functional Brain Imaging. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2017, 58, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Johnson, A.C. Stress-Induced Chronic Visceral Pain of Gastrointestinal Origin. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloner, A.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. Early Life Adversity as a Risk Factor for Visceral Pain in Later Life: Importance of Sex Differences. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, M.P.; Feinstein, J.S.; Khalsa, S.S. An Active Inference Approach to Interoceptive Psychopathology. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2019, 15, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lozano, P.; Sousa-Pitti, M.; Toro-Pérez, N.; Cuenca-Zaldívar, J.N.; Cid-Verdejo, R.; Martínez-Pozas, O.; Jiménez-Ortega, L.; Sánchez-Romero, E.A. Altered Pain Perception in a Young Adult with Childhood Trauma and Suspected Riley-Day Syndrome: A Case Report. Reports 2025, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felitti, V.J.; Anda, R.F.; Nordenberg, D.; Williamson, D.F.; Spitz, A.M.; Edwards, V.; Koss, M.P.; Marks, J.S. Relationship of Childhood Abuse and Household Dysfunction to Many of the Leading Causes of Death in Adults: The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1998, 14, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.A.; Mary, D.A.; Witte, K.K.; Greenwood, J.P.; Deuchars, S.A.; Deuchars, J. Non-Invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Healthy Humans Reduces Sympathetic Nerve Activity. Brain Stimulat. 2014, 7, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machetanz, K.; Berelidze, L.; Guggenberger, R.; Gharabaghi, A. Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Heart Rate Variability: Analysis of Parameters and Targets. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2021, 236, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.Y.Y.; Keatch, C.; Lambert, E.; Woods, W.; Stoddart, P.R.; Kameneva, T. Critical Review of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Challenges for Translation to Clinical Practice. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, A.; Clement, S.; Filson, B.; Kennedy, A. Trauma-Informed Mental Healthcare in the UK: What Is It and How Can We Further Its Development? Ment. Health Rev. J. 2016, 21, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillingim, R.B.; King, C.D.; Ribeiro-Dasilva, M.C.; Rahim-Williams, B.; Riley, J.L. Sex, Gender, and Pain: A Review of Recent Clinical and Experimental Findings. J. Pain 2009, 10, 447–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenspan, J.D.; Craft, R.M.; LeResche, L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Berkley, K.J.; Fillingim, R.B.; Gold, M.S.; Holdcroft, A.; Lautenbacher, S.; Mayer, E.A.; et al. Studying Sex and Gender Differences in Pain and Analgesia: A Consensus Report. Pain 2007, 132, S26–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, H.; Takeuch, S.; Nishida, Y. Sex Differences in Conditioned Pain Modulation Effects and Its Associations with Autonomic Nervous System Activities in Healthy, Younger Individuals: A Pilot Study. Pain Rep. 2024, 9, e1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easton, S.D.; Renner, L.M.; O’Leary, P. Suicide Attempts among Men with Histories of Child Sexual Abuse: Examining Abuse Severity, Mental Health, and Masculine Norms. Child Abuse Negl. 2013, 37, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatchel, R.J.; Peng, Y.B.; Peters, M.L.; Fuchs, P.N.; Turk, D.C. The Biopsychosocial Approach to Chronic Pain: Scientific Advances and Future Directions. Psychol. Bull. 2007, 133, 581–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley, M.A.; Cohen, J.L.; Borszcz, G.S.; Cano, A.; Radcliffe, A.M.; Porter, L.S.; Schubiner, H.; Keefe, F.J. Pain and Emotion: A Biopsychosocial Review of Recent Research. J. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 67, 942–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, I.; Bushnell, M.C. How Neuroimaging Studies Have Challenged Us to Rethink: Is Chronic Pain a Disease? J. Pain 2009, 10, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafañe, J.H.; Valdes, K.; Pedersini, P.; Berjano, P. Osteoarthritis: A Call for Research on Central Pain Mechanism and Personalized Prevention Strategies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehuda, R.; Daskalakis, N.P.; Desarnaud, F.; Makotkine, I.; Lehrner, A.L.; Koch, E.; Flory, J.D.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Meaney, M.J.; Bierer, L.M. Epigenetic Biomarkers as Predictors and Correlates of Symptom Improvement Following Psychotherapy in Combat Veterans with PTSD. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kolk, B. The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma; Penguin Books: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-14-312774-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lanius, R.A.; Vermetten, E.; Pain, C. (Eds.) The Impact of Early Life Trauma on Health and Disease: The Hidden Epidemic; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-521-88026-8. [Google Scholar]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Thayer, J.F. Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Vagal Tone in Psychophysiological Research—Recommendations for Experiment Planning, Data Analysis, and Data Reporting. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, D.J.; Hochman, S. Hypothesis: Pulmonary Afferent Activity Patterns During Slow, Deep Breathing Contribute to the Neural Induction of Physiological Relaxation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman-Olivier, Z.; Trombka, M.; Lovas, D.A.; Brewer, J.A.; Vago, D.R.; Gawande, R.; Dunne, J.P.; Lazar, S.W.; Loucks, E.B.; Fulwiler, C. Mindfulness and Behavior Change. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2020, 28, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneau, M. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback to Treat Fibromyalgia: An Integrative Literature Review. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2020, 21, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.; Gianlorenço, A.C.; Andrade, M.F.; Camargo, L.; Menacho, M.; Arias Avila, M.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Choi, H.; Song, J.-J.; Fregni, F. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Effects on Chronic Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Rep. 2024, 9, e1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidan, F.; Baumgartner, J.N.; Coghill, R.C. The Neural Mechanisms of Mindfulness-Based Pain Relief: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Review and Primer. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzoli, S.F.M.; Marzorati, C.; Gatti, D.; Monzani, D.; Mazzocco, K.; Pravettoni, G. A Meta-Analysis on Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback and Depressive Symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.J.; Hooven, C. Interoceptive Awareness Skills for Emotion Regulation: Theory and Approach of Mindful Awareness in Body-Oriented Therapy (MABT). Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehling, W.E.; Hamel, K.A.; Acree, M.; Byl, N.; Hecht, F.M. Randomized, Controlled Trial of Breath Therapy for Patients with Chronic Low-Back Pain. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2005, 11, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.E.; Sanchez-Romero, E.A.; Turroni, S.; Fernandez-Carnero, J.; Villafañe, J.H. Correlation between the Altered Gut Microbiome and Lifestyle Interventions in Chronic Widespread Pain Patients: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, M.P.; Stein, M.B. Interoception in Anxiety and Depression. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Sheridan, M.A.; Lambert, H.K. Childhood Adversity and Neural Development: Deprivation and Threat as Distinct Dimensions of Early Experience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, S.N.; Seth, A.K.; Barrett, A.B.; Suzuki, K.; Critchley, H.D. Knowing Your Own Heart: Distinguishing Interoceptive Accuracy from Interoceptive Awareness. Biol. Psychol. 2015, 104, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, H.D.; Garfinkel, S.N. Interoception and Emotion. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2017, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Gevirtz, R. Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback: How and Why Does It Work? Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, S.; Bann, C.M.; Dodd, S.L.; Schein, J.; Mendoza, T.R.; Cleeland, C.S. Validity of the Brief Pain Inventory for Use in Documenting the Outcomes of Patients with Noncancer Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2004, 20, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca-Zaldívar, J.N.; Del Corral-Villar, C.; García-Torres, S.; Araujo-Zamora, R.; Gragera-Peña, P.; Martínez-Lozano, P.; Sánchez-Romero, E.A. Fourteen-Year Retrospective Cohort Study on the Impact of Climatic Factors on Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: A Spanish Primary Care Analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2025, 28, e70125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, C.; Gerlach, A.L.; Pohl, A. Interoceptive Accuracy and Bias in Somatic Symptom Disorder, Illness Anxiety Disorder, and Functional Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartana, P.J.; Campbell, C.M.; Edwards, R.R. Pain Catastrophizing: A Critical Review. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.D. Social Communication Model of Pain. Pain 2015, 156, 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolacz, J.; Kovacic, K.K.; Porges, S.W. Traumatic Stress and the Autonomic Brain-Gut Connection in Development: Polyvagal Theory as an Integrative Framework for Psychosocial and Gastrointestinal Pathology. Dev. Psychobiol. 2019, 61, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J. The Inflammatory Reflex. Nature 2002, 420, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, B.M.; Luecken, L. Heart Rate Variability as an Index of Regulated Emotional Responding. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2006, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, O.G. Visceral Sensory Neuroscience: Interoception; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-19-513601-2. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Overall (n = 124) | Trauma-Exposed Group (n = 64) | Comparison Group (n = 60) | Statistical Test (t/χ2) | p-Value | Cohen’s d [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (M ± SD) | 37.45 (13.48) | 42.78 (14.05) | 31.77 (10.21) | t(122) = −4.97 | <0.001 *** | 0.89 [0.52, 1.26] |
| Gender (% Female) | 66.9% | 70.3% | 63.3% | χ2(1) = 0.682 | 0.409 | — |
| CTQ—Childhood Physical and Emotional Abuse (CPEA) | 7.96(3.49) | 8.88 (4.13) | 6.99 (2.30) | t(122) = −3.12 | 0.002 ** | 0.56 [0.20, 0.92] |
| LEC-17—Cumulative Trauma Exposure | 10.41 (8.10) | 13.20 (8.43) | 7.43 (6.60) | t(122) = −4.23 | <0.001 *** | 0.76 [0.39, 1.12] |
| BPQ—Autonomic Reactivity | 33.88 (14.67) | 38.19 (18.26) | 29.28 (7.13) | t(122)= −3.53 | <0.001 *** | 0.64 [0.27, 1.00] |
| Pain Severity (Brief Pain Inventory) | 7.69(8.58) | 7.03 (9.36) | 8.40 (7.68) | t(122) = 0,89 | 0.377 | −0.16 [−0.51, 0.19] |
| CTQ–CPEA | BPQ—Reactivity | Pain Severity | Age | Gender | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTQ–CPEA | — | 0.524 *** | 0.120 | 0.136 | −0.105 |
| BPQ—Reactivity | — | 0.408 *** | 0.206 * | −0.194 * | |
| Pain Severity | — | 0.081 | −0.208 * | ||
| Age | — | 0.000 | |||
| Gender | — |
| Regression Step | Predictor | Outcome | B (unstd.) [95% CI] | β (std.) | p-value | R2 | F(df) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression 1: Predicting Autonomic Reactivity (BPQ) | 0.41 | F(4,119) = 20.65, p < 0.001 | |||||
| Age | BPQ | 0.123 [−0.031, 0.277] | 0.113 | 0.116 | |||
| Gender | BPQ | −3.854 [−8.215, 0.508] | −0.124 | 0.083 | |||
| LEC-17 | BPQ | 0.609 [0.335, 0.882] | 0.336 | <0.001 *** | |||
| CPEA | BPQ | 1.558 [0.921, 2.194] | 0.370 | <0.001 *** | |||
| Regression 2: Predicting Pain Severity (CPEA only) | 0.05 | F(2,121) = 3.37, p = 0.038 | |||||
| Gender | Pain Severity | −3.58 [−6.778, −0.380] | −0.20 | 0.029 * | |||
| CPEA | Pain Severity | 0.24 [−0.189, 0.677] | 0.10 | 0.267 | |||
| Regression 3: Predicting Pain Severity (with BPQ) | 0.18 | F(2,121) = 13.59, p < 0.001 | |||||
| Gender | Pain Severity | −2.43 [−5.437, 0.585] | −0.13 | 0.0113 | |||
| BPQ | Pain Severity | 0.22 [0.126, 0.320] | 0.38 | <0.001 *** | |||
| Pathway | Total Effect β [95% CI] | Direct Effect β [95% CI] | Indirect Effect β [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTQ_CPEA → BPQ → Pain Severity | 0.090 [−0.198, 0.397] | −0.130 [−0.379, 0.131] | 0.220 * [0.087, 0.422] |
| Constraint | Path Compared | χ2 | df | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 = p10 | a: CTQ_CPEA → BPQ | 3.880 | 1 | 0.049 |
| p2 = p11 | b: BPQ → Pain | 0.005 | 1 | 0.941 |
| p3 = p12 | c: CTQ_CPEA → Pain | 0.361 | 1 | 0.548 |
| Group | Path | Estimate (Std.all) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | a: CTQ_CPEA → BPQ | 0.427 | [0.243, 0.611] | <0.001 *** |
| Men | b: BPQ → Pain | 0.391 | [0.266, 0.516] | <0.001 *** |
| Men | c: CTQ_CPEA → Pain | −0.098 | [−0.717, 0.521] | 0.315 |
| Women | a: CTQ_CPEA → BPQ | 0.523 | [0.298, 0.748] | <0.001 *** |
| Women | b: BPQ → Pain | 0.470 | [0.345, 0.595] | <0.001 *** |
| Women | c: CTQ_CPEA → Pain | −0.144 | [−0.763, 0.475] | 0.315 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, E.C.V.; Gonçalves, P.; Martins, F.; Monteiro, S.; Pais-Vieira, C. Autonomic Dysregulation Mediates the Association Between Childhood Trauma and Pain Severity: Evidence from a Mediation Model. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182310
Costa ECV, Gonçalves P, Martins F, Monteiro S, Pais-Vieira C. Autonomic Dysregulation Mediates the Association Between Childhood Trauma and Pain Severity: Evidence from a Mediation Model. Healthcare. 2025; 13(18):2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182310
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Eleonora C. V., Patrícia Gonçalves, Fernando Martins, Sílvia Monteiro, and Carla Pais-Vieira. 2025. "Autonomic Dysregulation Mediates the Association Between Childhood Trauma and Pain Severity: Evidence from a Mediation Model" Healthcare 13, no. 18: 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182310
APA StyleCosta, E. C. V., Gonçalves, P., Martins, F., Monteiro, S., & Pais-Vieira, C. (2025). Autonomic Dysregulation Mediates the Association Between Childhood Trauma and Pain Severity: Evidence from a Mediation Model. Healthcare, 13(18), 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182310





