Abstract
Background: This systematic review examines artificial intelligence (AI) applications in neuroimaging for autism spectrum disorder (ASD), addressing six research questions regarding biomarker optimization, modality integration, social function prediction, developmental trajectories, clinical translation challenges, and multimodal data enhancement for earlier detection and improved outcomes. Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, we conducted a comprehensive literature search across 8 databases, yielding 146 studies from an initial 1872 records. These studies were systematically analyzed to address key questions regarding AI neuroimaging approaches in ASD detection and prognosis. Results: Neuroimaging combined with AI algorithms demonstrated significant potential for early ASD detection, with electroencephalography (EEG) showing promise. Machine learning classifiers achieved high diagnostic accuracy (85–99%) using features derived from neural oscillatory patterns, connectivity measures, and signal complexity metrics. Studies of infant populations have identified the 9–12-month developmental window as critical for biomarker detection and the onset of behavioral symptoms. Multimodal approaches that integrate various imaging techniques have substantially enhanced predictive capabilities, while longitudinal analyses have shown potential for tracking developmental trajectories and treatment responses. Conclusions: AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers represent a promising frontier in ASD research, potentially enabling the detection of symptoms before they manifest behaviorally and providing objective measures of intervention efficacy. While technical and methodological challenges remain, advancements in standardization, diverse sampling, and clinical validation could facilitate the translation of findings into practice, ultimately supporting earlier intervention during critical developmental periods and improving outcomes for individuals with ASD. Future research should prioritize large-scale validation studies and standardized protocols to realize the full potential of precision medicine in ASD.
1. Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent challenges in social communication and interaction alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities [1,2,3]. Families caring for individuals diagnosed with ASD serve as the primary and ongoing sources of support across their lifespan, facing significantly greater demands compared to those caring for typically developing children. Early detection and intervention are crucial for improving long-term outcomes. However, current diagnostic procedures often rely heavily on behavioral observations that may not manifest until toddlerhood or beyond, delaying crucial early interventions [4,5,6].
ASD is clinically diagnosed and defined by predetermined criteria stipulated in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR) and International Classification of Diseases, Eleventh Revision (ICD-11), which stress persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across many contexts and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Severity is assessed by using specifiers for the degree of support required: requiring support, requiring substantial support, or requiring very substantial support, based on social communication impairment and restricted repetitive behaviors. Differential diagnosis requires consideration of other neurodevelopmental disorders, such as intellectual disability, global developmental delay, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and specific language impairment, as well as medical conditions like Rett syndrome and fragile X syndrome. Standardized instruments such as the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule-2 (ADOS-2), Autism Diagnostic Interview—Revised (ADI-R), and Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) form part of current diagnostic assessments, supplemented by thorough developmental and functional evaluations. Associated assessments commonly include genetic testing to determine underlying syndromes, speech-language pathology evaluation, occupational therapy evaluation, and cognitive testing to define the individual’s entire neurodevelopmental profile and guide intervention planning [7,8].
The advent of advanced neuroimaging techniques combined with artificial intelligence (AI) methodologies has opened promising avenues for identifying objective biomarkers that could potentially detect ASD before behavioral symptoms fully manifest [9,10,11,12,13]. Neuroimaging studies have consistently revealed structural and functional brain differences in individuals with ASD, suggesting the potential for developing reliable biomarkers. A biomarker is defined as a measurable biological characteristic that serves as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to therapeutic interventions. In the context of neuroimaging and ASD research, biomarkers refer to objective, quantifiable neural measurements derived from brain imaging data that can reliably distinguish individuals with ASD from typically developing individuals, predict developmental outcomes, monitor treatment responses, or identify individuals at risk for developing ASD before clinical symptoms fully manifest. However, the heterogeneity of ASD presentations and the complexity of neuroimaging data present significant challenges in translating research findings into clinically applicable diagnostic and prognostic tools [14,15,16,17].
Recent technological advancements in artificial intelligence, encompassing traditional machine learning, deep learning, graph neural networks, ensemble methods, transfer learning, and explainable AI approaches, have remarkably enhanced our ability to analyze complex neuroimaging data [18,19,20,21]. These diverse computational methodologies include support vector machines, convolutional and recurrent neural networks, attention mechanisms, multimodal fusion techniques, federated learning frameworks, and Bayesian approaches, each offering unique advantages for different aspects of neuroimaging analysis. These computational approaches can identify subtle patterns and relationships within multimodal neuroimaging data that may not be apparent through conventional analysis methods. By leveraging AI-driven analysis of neuroimaging data, researchers aim to develop objective biomarkers that could facilitate earlier diagnosis, more accurate prognosis, and personalized intervention planning for individuals with ASD [22,23,24,25].
The potential impact of combining neuroimaging and AI extends beyond early detection, including the prediction of social functioning outcomes, which represents a core challenge in ASD. Social functioning difficulties significantly impact the quality of life and long-term consequences for individuals with ASD, yet current methods for predicting developmental trajectories remain limited [26,27]. AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers could potentially identify neural signatures associated with specific dimensions of social functioning, enabling more targeted and effective interventions [28,29,30].
Moreover, patient and family caregivers often express pressing requirements for support and information regarding prognosis and intervention planning during clinical visits. Integrating neuroimaging biomarkers into clinical practice could provide valuable objective information to complement traditional assessments, potentially reducing diagnostic uncertainty and facilitating more personalized care recommendations. Minimizing public health-related stigma around neurodevelopmental disorders like ASD is a fundamental prerequisite for ensuring that affected individuals and their families seek and receive appropriate support [31,32,33,34].
Harnessing technology’s capacity to establish and validate biomarkers can facilitate more objective, precise, and earlier detection of ASD. The integration of established neuroimaging technologies with evolving AI algorithms and enhanced computational capabilities represents a valuable expansion of our toolkit for understanding and addressing ASD. These approaches broadly refer to using data, information, and computational technologies to enhance diagnostic accuracy, improve prognostic capabilities, and better support individuals with ASD and their families [35,36,37].
After the recent surge in research exploring the intersection of AI and neuroimaging in ASD, there has been a burgeoning effort to develop novel technological solutions to resolve the issues arising from delayed diagnosis and limited prognostic information. Due to the heterogeneity of ASD presentations and the complexity of brain development, researchers are increasingly adopting multimodal approaches that integrate data from multiple sources to develop more robust and sensitive biomarkers. Therefore, AI-driven neuroimaging approaches may represent critical tools for researchers, clinicians, and, ultimately, individuals with ASD and their families [38,39,40].
This systematic review aims to comprehensively synthesize the current research on AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for the early detection and prediction of social function in ASD. By examining methodological approaches, evaluating the strength of evidence, and identifying promising directions for future research, this review seeks to provide an evidence-based perspective on the potential of neuroimaging biomarkers to transform our approach to ASD diagnosis and intervention. We also aim to identify the most promising neuroimaging modalities, AI methodologies, and biomarker candidates for advancing the field toward clinical application.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder and Neuroimaging Approaches
ASD is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent deficits in social communication and interaction combined with restricted, repetitive behavior patterns, interests, or activities. Current prevalence estimates indicate that approximately 1 in 54 children in the United States has been identified with ASD, with a male-to-female ratio of 4:1. The neurobiological basis of ASD involves complex genetic architecture, with over 100 genes implicated, along with epigenetic mechanisms and environmental factors contributing to its heterogeneous presentation. Neuroimaging technologies have significantly advanced our understanding of the neurobiological underpinnings of ASD [41,42,43,44,45]. Multiple imaging modalities have been employed to characterize the structural and functional brain alterations associated with the disorder:
Structural MRI (sMRI) studies have identified macroscopic neuroanatomical differences in ASD, including regional volumetric abnormalities, cortical thickness variations, and atypical gyrification patterns. Meta-analyses have consistently demonstrated altered neurodevelopmental trajectories characterized by early brain overgrowth, followed by normalization or deceleration in adolescence. Region-specific alterations have been observed in the frontal and temporal cortices, the amygdala, the cerebellum, and the corpus callosum, particularly in brain regions involved in social cognition and language processing [46,47,48,49,50,51].
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has revealed white matter microstructural abnormalities in ASD, with reduced fractional anisotropy (FA) and increased mean diffusivity (MD) in multiple white matter tracts. These alterations are particularly pronounced in pathways connecting social brain regions, including the superior longitudinal fasciculus, inferior frontal–occipital fasciculus, and corpus callosum. Tractography analyses have demonstrated reduced structural connectivity between the frontal, temporal, and parietal regions involved in social information processing [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59].
Functional MRI (fMRI) studies have identified altered neural activation patterns during social cognition tasks, including face processing, theory of mind, and joint attention. Task-based fMRI has revealed hypoactivation in brain regions comprising the “social brain network,” including the superior temporal sulcus (STS), the fusiform gyrus, the amygdala, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Resting-state fMRI has demonstrated atypical functional connectivity patterns, including reduced long-range and increased local connectivity, potentially reflecting altered neural information integration [60,61,62,63,64,65,66].
Electroencephalography (EEG) has documented atypical neural oscillations and event-related potentials (ERPs) in ASD. Specific ERP components, such as P300, N170, and mismatch negativity (MMN), show altered amplitude and/or latency in response to social stimuli. Spectral analyses have revealed abnormalities in gamma-band activity, potentially reflecting imbalances in excitatory–inhibitory neurotransmission. Functional connectivity analyses using EEG have identified reduced long-range synchronization and increased local synchronization, findings consistent with those from fMRI [67,68,69,70,71,72].
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) studies have provided temporally precise characterization of neural processing abnormalities in ASD, focusing on the early stages of sensory processing. Documented alterations in M100 responses to auditory stimuli and atypical visual evoked field (VEF) responses to face stimuli suggest fundamental differences in the speed and efficiency of neural information processing [73,74,75,76,77,78,79].
These neuroimaging findings collectively suggest that ASD involves complex network-level disruptions rather than focal abnormalities in discrete brain regions. The developmental timing and specific patterns of these neurobiological alterations may significantly influence symptom expression and severity, highlighting the potential value of neuroimaging biomarkers for early detection and outcome prediction [80,81,82,83,84,85].
2.2. Social Function Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Social function deficits constitute a core diagnostic feature of ASD and significantly impact long-term outcomes across educational, occupational, and interpersonal domains. These deficits manifest across multiple dimensions of social cognition and behavior:
Social–emotional reciprocity deficits involve impairments in initiating and maintaining reciprocal social interactions, sharing emotions, and engaging in conversational turn-taking. Quantitative assessments using standardized instruments, such as the Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS) and the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS), have consistently documented significant impairments in these domains, which are correlated with functional outcomes [86,87,88,89,90,91,92].
Nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction are frequently impaired in ASD, including atypical eye contact, facial expressions, body posture, and gestures. Eye-tracking studies have documented a reduction in attention to social stimuli, particularly faces and eyes, with a corresponding preference for non-social aspects of visual scenes. Motion capture analyses have identified subtle abnormalities in the production and perception of social movements, including atypical kinematics of gestures and facial expressions [93,94,95,96,97,98].
Social cognition deficits include impairments in theory of mind (ToM), emotion recognition, and social perception. Functional neuroimaging studies during ToM tasks have revealed hypoactivation in the mPFC, temporoparietal junction (TPJ), and posterior superior temporal sulcus (pSTS) in individuals with ASD. Emotion recognition deficits are particularly pronounced for complex emotions and when integrating contextual information is required [99,100,101,102,103].
The neural mechanisms underlying social function deficits have been extensively investigated. The “social motivation hypothesis” posits that reduced social reward processing may contribute to diminished social engagement in ASD. Functional neuroimaging studies have demonstrated the hypoactivation of reward circuitry, including the ventral striatum and orbitofrontal cortex, in response to social rewards. The “predictive coding hypothesis” suggests that individuals with ASD have difficulty forming and updating predictions about social stimuli, leading to increased prediction errors and reduced efficiency in social information processing [104,105,106,107,108,109,110].
Developmental trajectories of social function deficits vary considerably among individuals with ASD. Longitudinal studies have identified distinct developmental subtypes, ranging from early-emerging profound deficits to later-emerging or regressive patterns. Early social attention processes, particularly joint and social orienting, have emerged as significant predictors of later social outcomes [111,112,113,114,115].
Neuroimaging correlations of social function deficits have been identified across structural and functional modalities. Structural MRI studies have demonstrated correlations between regional brain volumes (particularly in the amygdala, fusiform gyrus, and superior temporal regions) and measures of social functioning. Functional connectivity patterns within the default mode network (DMN) and between the DMN and salience network have been associated with social cognitive abilities. Task-based fMRI activation during social processing tasks is correlated with real-world social functioning, suggesting the potential for neuroimaging biomarkers as objective indices of social impairment [116,117].
The complex and multidimensional nature of social function deficits in ASD necessitates sophisticated assessment approaches that can capture subtle impairments and track developmental changes. Neuroimaging biomarkers offer advantages over behavioral assessments, including greater objectivity, sensitivity to subclinical impairments, and the potential to predict future outcomes [118,119,120,121].
2.3. Artificial Intelligence in Neuroimaging Analysis for ASD
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) methodologies to neuroimaging data analysis has substantially advanced the field of ASD research by enabling the detection of subtle, complex patterns in high-dimensional neuroimaging datasets. These computational approaches offer several advantages over conventional univariate analyses, including increased sensitivity to multivariate patterns, the ability to model nonlinear relationships, and the potential for individual-level prediction [122,123,124,125,126,127].
Supervised ML classification models have demonstrated significant accuracy in distinguishing individuals with ASD from typically developing controls. Support vector machines (SVMs) applied to structural MRI features have achieved classification accuracy ranging from 65% to 95%, depending on sample characteristics and feature selection methods. Random forest and gradient boosting algorithms have shown comparable performance, with the advantage of providing feature importance metrics that can identify the most discriminative brain regions. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and logistic regression have been employed due to their interpretability, although they may be less effective in capturing complex, nonlinear relationships in neuroimaging data [128,129,130,131,132,133,134].
Feature selection techniques are critical for optimizing ML model performance with high-dimensional neuroimaging data. Principal component analysis (PCA) and independent component analysis (ICA) have been widely used for dimensionality reduction while preserving variance structure. Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) identified the most informative neuroimaging features for ASD classification. These approaches have consistently identified features related to the default mode network, salience network, and social brain regions as highly discriminative [135,136,137,138].
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been applied to structural MRI data, leveraging their ability to automatically extract hierarchical features from image data. In some studies, 3D CNNs trained on whole-brain structural MRI volumes have achieved classification accuracies exceeding 80%. CNNs applied to DTI data have demonstrated sensitivity to white matter microstructural abnormalities in ASD, particularly in social communication pathways [139,140,141,142,143,144,145].
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks have been utilized to analyze temporal dynamics in functional neuroimaging data. These approaches have revealed atypical temporal patterns in functional connectivity and neural responses to social stimuli in ASD [146,147,148,149,150,151,152].
Autoencoders have been employed for unsupervised features learning from neuroimaging data, enabling the identification of latent representations that capture intrinsic data structures. Variational autoencoders have facilitated the generative modeling of neuroimaging data, potentially allowing the simulation of disease progression and treatment effects [153,154,155,156].
Early fusion techniques integrate data at the feature level before model training, enabling the direct modeling of cross-modal relationships. Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) and joint ICA have been used to identify multimodal patterns of brain alterations in ASD, revealing coordinated structural and functional abnormalities [157,158,159,160,161,162].
Late fusion approaches train separate models for each modality and combine their outputs, potentially offering more robust performance when modalities contain complementary information. Ensemble methods, which combine predictions from models trained on different neuroimaging modalities, have demonstrated enhanced classification accuracy compared to single-modality approaches [163,164,165,166,167].
Transfer learning strategies have been increasingly applied to address the limited sample size standard in neuroimaging studies of ASD. Models pre-trained on large datasets (e.g., UK Biobank, ABIDE) have been fine-tuned on smaller, study-specific datasets, improving generalization performance. Domain adaptation techniques have been developed to address site-specific variations in neuroimaging data, enhancing the applicability of AI models across diverse clinical settings [168,169,170,171,172,173,174].
The integration of AI methodologies with neuroimaging analysis has substantially advanced our ability to detect subtle brain alterations associated with ASD and to model their relationship with clinical features. These approaches offer promise for developing objective biomarkers for early detection and outcome prediction [175,176,177,178].
2.4. Early Detection Biomarkers for ASD
The development of reliable biomarkers for the early detection of ASD is a critical research priority, as early intervention is associated with improved outcomes. Neuroimaging biomarkers offer promise due to their potential to detect brain differences that may precede the emergence of behavioral symptoms [179,180].
Prospective longitudinal studies of high-risk infant siblings have provided valuable insights into early neuroimaging markers of ASD:
Structural MRI markers include accelerated brain volume expansion between 6 and 12 months of age in infants later diagnosed with ASD, with particular emphasis on surface area expansion in cortical regions involved in social cognition and language processing. Machine learning models incorporating multiple morphometric features measured at 6 months of age demonstrated 81% accuracy in predicting later ASD diagnosis [181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189].
Diffusion MRI studies have identified altered white matter development in high-risk infants, characterized by reduced fractional anisotropy (FA) in the corpus callosum, uncinate fasciculus, and inferior longitudinal fasciculus at 6 months of age, which predicts later ASD diagnosis. Tract-specific developmental trajectories, particularly in pathways connecting frontal, temporal, and parietal regions, show divergence between infants who develop ASD and those who do not [190,191,192,193,194].
Functional connectivity markers include the atypical development of long-range functional connectivity networks, particularly those involved in social information processing. Reduced interhemispheric functional connectivity at 6 months and hyperconnectivity in attentional networks at 12 months have been associated with later ASD diagnosis. Graph theoretical analyses have revealed altered network topology, including reduced network efficiency and modularity, in infants who later develop ASD [195,196,197,198,199,200,201].
EEG markers include atypical neural responses to social stimuli, with reduced attention to social stimuli compared to non-social ones, observable in the first year of life. Spectral power abnormalities, particularly in alpha and gamma frequency bands, have been identified as potential early markers. EEG is more accessible and cost-effective than MRI, potentially facilitating broader clinical implementation [202,203,204,205].
AI approaches for biomarker development have significantly enhanced the sensitivity and specificity of early detection:
Multivariate pattern analysis (MVPA) techniques applied to neuroimaging data have demonstrated superior performance compared to univariate approaches for identifying infants at the highest risk for ASD. Support vector machines trained on multimodal neuroimaging features have achieved classification accuracy exceeding 85% in some studies [206,207,208,209,210].
Deep learning architecture, particularly CNNs applied to structural and functional neuroimaging data, has demonstrated promise for early detection. These approaches can automatically learn hierarchical features that distinguish high-risk infants who develop ASD from those who do not, potentially identifying subtle patterns that are not apparent through conventional analyses [211,212,213,214,215,216].
Temporal modeling approaches, including recurrent neural networks and hidden Markov models, have been employed to characterize developmental trajectories and identify atypical neurodevelopmental patterns that predict later ASD diagnosis. These approaches can model the nonlinear dynamics of brain development, potentially increasing sensitivity to early alterations [217,218,219,220,221].
Multimodal biomarker integration has emerged as a promising approach for enhancing predictive accuracy.
Combined structural and functional markers have demonstrated superior predictive performance compared to either modality alone. In some studies, integrating structural MRI, DTI, and functional connectivity measures through machine learning frameworks has achieved classification accuracies exceeding 90% [222,223,224,225].
EEG-MRI fusion approaches leverage the complementary strengths of these modalities, combining the high spatial resolution of MRI with the high temporal resolution of EEG. Canonical correlation analysis and joint ICA have been employed to identify multimodal neural signatures of ASD risk [226,227,228,229].
Eye-tracking combined with neuroimaging has revealed correlations between visual attention patterns and brain structure/function in infants at risk for ASD. Reduced attention to social stimuli, particularly faces and eyes, is correlated with the altered development of social brain networks and predicts later diagnosis [230,231,232,233].
Translating these research findings into clinically applicable biomarkers requires addressing several methodological considerations, including standardizing acquisition protocols, developing age-specific normative databases, and validating across diverse populations. Multi-site collaborative initiatives are currently underway to address these challenges and facilitate the development of reliable early-detection biomarkers for clinical implementation [234,235,236,237,238,239].
2.5. Predicting Social Function Outcomes Using Neuroimaging Biomarkers
Beyond early detection, there is growing interest in leveraging neuroimaging biomarkers to predict specific domains of functioning in individuals with ASD, particularly social outcomes. This approach holds promise for more personalized intervention planning and prognostic counseling [240,241,242,243,244].
Brain–behavior relationships in ASD provide the foundation for predictive biomarker development:
Structural correlations of social function include regional volumes and cortical thickness in social brain regions. Meta-analyses have consistently identified correlations between amygdala volume and social impairment, with larger amygdala volumes in early development associated with more severe social deficits. Cortical thickness in the superior temporal sulcus, temporoparietal junction, and medial prefrontal cortex is correlated with performance on theory-of-mind tasks and real-world social functioning [245,246,247,248,249].
White matter microstructure in social communication pathways has been shown to have significant associations with social abilities. Fractional anisotropy in the arcuate fasciculus is correlated with language-based social communication skills. In contrast, the microstructural properties of the uncinate fasciculus and inferior longitudinal fasciculus are associated with emotion recognition and social perception [250,251,252,253,254,255,256].
Functional connectivity patterns within the default mode network (DMN) and between the DMN and salience network show robust correlations with social cognitive abilities. Greater segregation between task-positive and task-negative networks has been associated with better social outcomes. Dynamic functional connectivity analyses have revealed that temporal variability in network configuration is reduced in ASD and correlated with social flexibility [257,258,259,260,261,262,263,264].
Task-based neural activation during social cognition paradigms is significantly correlated with real-world social functioning. During face-processing tasks, the magnitude of activation in the fusiform gyrus predicts social communication abilities. In contrast, medial prefrontal activation during theory-of-mind tasks is correlated with perspective-taking in naturalistic contexts.
Advanced analytical approaches have enhanced our ability to predict social outcomes:
Machine learning regression models trained on neuroimaging features have demonstrated significant accuracy in predicting continuous measures of social function. In some studies, support vector regression and random forest regression have been applied to multimodal neuroimaging data, achieving correlation coefficients exceeding 0.7 between predicted and observed social function scores [265,266,267].
Longitudinal modeling approaches, including growth curve modeling and latent class analysis, have characterized distinct developmental trajectories of brain–behavior relationships in ASD. These approaches have identified early neuroimaging markers that predict divergent social developmental pathways, potentially enabling targeted early intervention [268,269,270].
Network science approaches have provided a system-level characterization of brain organization and its relationship to social function. Graph theoretical metrics, including modularity, efficiency, and rich-club organization, are correlated with social cognitive abilities and adaptive social functioning. These metrics offer potential as integrative biomarkers that capture complex network-level properties related to social information processing [271,272,273,274,275].
Clinical applications of predictive biomarkers for social function are beginning to emerge:
Treatment response prediction represents a promising application of neuroimaging biomarkers. Pre-treatment functional connectivity patterns, particularly within social brain networks, predict response to social skills interventions with moderate accuracy. Machine learning models incorporating multiple neuroimaging features have achieved 75–85% accuracy in classifying treatment responders versus non-responders [276,277,278,279,280,281,282].
Neuroimaging markers that identify neurobiologically distinct subtypes within ASD enable stratification for targeted interventions. Unsupervised learning approaches applied to neuroimaging data have identified subgroups characterized by patterns of brain structure and function, which differ in their responses to specific intervention approaches [283,284,285].
Monitoring intervention effects using neuroimaging biomarkers can provide objective indices of neuroplastic changes associated with behavioral improvement. Longitudinal neuroimaging studies have documented intervention-related changes in brain structure, function, and connectivity that are correlated with improved social abilities [286,287,288].
Developing reliable neuroimaging biomarkers for predicting social function has significant implications for both clinical practice and research. These biomarkers could enhance individualized intervention planning, provide objective outcome measures for clinical trials, and deepen our understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms underlying social impairment in ASD [289,290]. Furthermore, the integration of neuroimaging biomarkers with evidence-based therapeutic approaches represents a promising avenue for personalized medicine in neurodevelopmental disorders. As demonstrated in related fields of mental health research, combining objective neurobiological measures with targeted interventions can significantly improve treatment outcomes and provide measurable indicators of therapeutic efficacy across diverse clinical populations [291,292].
2.6. Research Questions
Despite significant advances in AI technologies and neuroimaging techniques in autism research, the complex interplay between neurobiological markers and social function in ASD remains underexplored, limiting the development of comprehensive early detection and intervention strategies. The research questions posed below in this systematic review will address these gaps by leveraging AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers to align detection and prediction approaches with the specific neurobiological profiles of ASD.
- [RQ1] How can advanced AI algorithms be optimized to identify reproducible neuroimaging biomarkers for the early detection of ASD before behavioral symptoms fully manifest?
- [RQ2] What combination of neuroimaging modalities (MRI, fMRI, EEG, and DTI) provides the most robust and sensitive biomarkers for predicting social functional outcomes in individuals with ASD?
- [RQ3] How are neuroimaging biomarkers correlated with specific dimensions of social function in ASD, and can these relationships be leveraged to develop personalized intervention approaches?
- [RQ4] To what extent can AI-driven analysis of longitudinal neuroimaging data predict developmental trajectories and clinical outcomes across different age groups with ASD?
- [RQ5] What are the key technical and methodological challenges in translating research-based neuroimaging biomarkers into clinically applicable diagnostic and prognostic tools for ASD?
- [RQ6] How can multimodal data integration (combining neuroimaging, genetic, behavioral, and clinical measures) enhance the specificity and sensitivity of AI-driven biomarkers for ASD diagnosis and social function prediction?
This systematic review addresses these research questions and provides a comprehensive roadmap for advancing the detection and prediction of ASD. It emphasizes the integration of AI technologies, neuroimaging techniques, and personalized biomarker development to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. To support clarity and accessibility, a list of abbreviations used throughout the review is included in the Supplementary Materials (Table S3).
3. Methodology
3.1. Scope
This research focuses on integrating artificial intelligence with neuroimaging technologies to develop objective biomarkers for the early detection of ASD and the prediction of social function outcomes. Specifically, it aims to systematically analyze how different neuroimaging modalities (including structural MRI, functional MRI, diffusion tensor imaging, and EEG) can be leveraged through advanced AI algorithms to identify subtle brain differences that may precede the behavioral symptoms of ASD. The research examines how machine learning and deep learning approaches analyze complex neuroimaging data to extract meaningful patterns correlating with ASD diagnosis and social function trajectories.
By utilizing multimodal neuroimaging techniques in conjunction with sophisticated AI methodologies, this study investigates biomarkers that can reliably distinguish infants and young children who will later develop ASD from those who will not, potentially enabling earlier intervention during critical periods of neurodevelopment. The research also explores how neuroimaging biomarkers can predict specific social functioning domains in individuals with ASD, including social–emotional reciprocity, nonverbal communication, social cognition, and adaptive functioning in real-world contexts.
The systematic review evaluates the methodological quality of existing studies, including sample characteristics, imaging acquisition protocols, preprocessing pipelines, feature selection methods, machine learning algorithms, validation approaches, and generalizability across diverse populations. It specifically examines how different AI approaches—from traditional machine learning classifiers to advanced deep learning architectures—compare in their ability to extract meaningful biomarkers from neuroimaging data. Additionally, it investigates how multimodal integration techniques can enhance biomarker sensitivity and specificity by combining information from complementary imaging modalities.
Beyond technical considerations, the research assesses the translational potential of AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers, examining their readiness for clinical implementation in terms of diagnostic accuracy, prognostic value, accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and integration with existing clinical assessment protocols. It also explores how these biomarkers might inform personalized interventions tailored to specific neurobiological profiles.
This systematic review integrates cutting-edge AI methodologies with advanced neuroimaging techniques to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these technologies can be combined to transform the approach to ASD diagnosis and prognosis. It contributes to the development of objective, data-driven strategies for earlier detection and more personalized intervention planning. To address this purpose, it poses several key research questions to enhance the understanding of how AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers can improve outcomes for individuals with ASD and their families.
3.2. Search Strategy
This systematic review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines, ensuring both methodological rigor and transparency throughout the collection and analysis processes.
Academic databases were systematically searched, including PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Google Scholar, PsycINFO, and EMBASE. This approach ensured comprehensive coverage across the medical, neuroscience, computer science, engineering, and psychology disciplines. The search focused on literature published between 2004 and 2024, capturing the rapid technological developments in AI and neuroimaging.
The search strategy employed a combination of controlled vocabulary (MeSH terms) and free-text terms structured around three main concept areas: (1) autism spectrum disorder, (2) neuroimaging technologies, and (3) artificial intelligence methodologies. Keywords and phrases such as “autism spectrum disorder,” “ASD,” “autistic disorder,” “magnetic resonance imaging,” “MRI,” “functional MRI,” “diffusion tensor imaging,” “DTI,” “electroencephalography,” “EEG,” “artificial intelligence,” “machine learning,” “deep learning,” “neural network,” “biomarker,” “early detection,” “diagnosis,” “prediction,” “social function,” and “classification” were utilized.
These terms were combined to create comprehensive search strings to retrieve the most relevant studies. The core search string that formed the foundation of our literature search strategy, which was then adapted for each specific database, was as follows:
((“autism spectrum disorder” OR “ASD” OR “autistic disorder” OR “autism”) AND (“neuroimaging” OR “MRI” OR “magnetic resonance imaging” OR “fMRI” OR “functional MRI” OR “functional magnetic resonance imaging” OR “DTI” OR “diffusion tensor imaging” OR “connectivity” OR “EEG” OR “electroencephalography” OR “brain imaging”) AND (“artificial intelligence” OR “AI” OR “machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR “neural network” OR “CNN” OR “RNN” OR “support vector machine” OR “SVM” OR “random forest” OR “feature selection” OR “classification” OR “regression” OR “pattern recognition”) AND (“biomarker” OR “early detection” OR "diagnosis” OR "prediction” OR “prognosis” OR “social function” OR “social cognition” OR “social communication” OR “outcome”.))
The reference lists of the identified articles, particularly recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses, were manually screened to identify additional relevant studies that the database searches might have missed. Additionally, forward citation tracking was performed for highly relevant papers to identify newer studies that had cited them.
Two independent reviewers screened the titles and abstracts of the initially identified articles against the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The same reviewers assessed the full-text articles for eligibility, and a third reviewer resolved disagreements through discussion or arbitration.
3.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria were established in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines to ensure a comprehensive and methodologically rigorous review. The criteria were designed to capture the most relevant studies addressing AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for early detection and social function prediction in ASD while maintaining the review’s focus on high-quality, peer-reviewed evidence. Each of the criteria was carefully selected to ensure that the included studies provided relevant insights into AI methodologies, neuroimaging techniques, early detection approaches, and social function prediction in ASD.
Inclusion Criteria:
- ▪
- Original studies that focus specifically on ASD and its neurobiological correlations.
- ▪
- Research examining the application of artificial intelligence or machine learning approaches to neuroimaging data in ASD.
- ▪
- Articles exploring neuroimaging biomarkers for early detection, diagnosis, or prediction of social outcomes in ASD.
- ▪
- Studies utilizing various neuroimaging modalities (e.g., MRI, fMRI, DTI, EEG, MEG) to identify brain differences associated with ASD.
- ▪
- Peer-reviewed articles published in English.
- ▪
- Studies published between 2004 and 2024 ensuring comprehensive coverage of the evolution of AI and neuroimaging approaches in ASD research.
- ▪
- Studies presenting original data or findings directly related to at least one of the six core research questions.
Exclusion Criteria:
- ▪
- Non-peer-reviewed articles, including preprints, conference abstracts, editorials, or commentaries.
- ▪
- Studies that do not directly address ASD or focus solely on other neurodevelopmental disorders, without an ASD-specific analysis.
- ▪
- Research on AI or neuroimaging unrelated to early detection or social function prediction in ASD.
- ▪
- Studies using only behavioral or genetic data without neuroimaging components.
- ▪
- Articles published in languages other than English.
- ▪
- Studies with insufficient methodological rigor, such as inadequate sample sizes, inappropriate control groups, or lacking cross-validation.
- ▪
- Publications focusing solely on theoretical frameworks or computational modeling without empirical validation using real neuroimaging data.
- ▪
- Duplicate publications or studies with substantially overlapping datasets.
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
The 146 studies included were evaluated using generalized quality indicators adapted from Cochrane RoB 2.0 for randomized studies and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale/JBI tools for non-randomized designs (Figure 1). Most studies (100/146) demonstrated a low risk of selection bias, benefiting from well-described eligibility criteria and appropriate recruitment strategies. However, 30 studies were considered to have a moderate risk due to less clearly defined inclusion parameters, and 16 studies were deemed to have a high risk due to vague or poorly justified selection criteria.
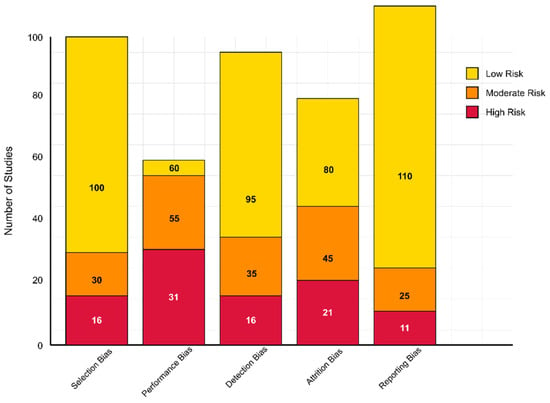
Figure 1.
Risk of bias assessment across 146 studies.
Performance bias was more variable. While 60 studies implemented sufficient blinding or objective data collection protocols to reduce bias, 55 studies demonstrated a moderate risk of bias—particularly those involving complex interventions that were difficult to blind (e.g., EEG procedures, behavioral assessments). A high risk was identified in 31 studies where no blinding or mitigation strategies were described. Regarding detection bias, 95 studies were at low risk because they used validated outcome measures and blinded assessors. Additionally, 35 studies with unclear assessor blinding were assigned a moderate risk, while 16 were deemed high risk due to their reliance on subjective or non-standardized assessments.
Attrition bias was considered low in 80 studies that reported minimal dropout or utilized intention-to-treat (ITT) strategies. In contrast, 45 studies had a moderate risk due to unreported attrition handling, and 21 high-risk studies had notable dropout rates without sufficient data management. Regarding reporting bias, 110 studies demonstrated a low risk by fully reporting outcomes in line with their aims. A moderate risk was found in 25 studies with partially reported secondary outcomes, and a high risk was found in 11 cases of suspected selective outcome reporting.
3.5. Analytical Search Process
The search process began by identifying 1872 records through database searches across PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, and PsycINFO, using the core search string and additional query variations tailored to specific research questions. After removing duplicates, 1394 unique records remained. These records were then screened based on title and abstract, which led to the exclusion of 987 off-topic articles that were irrelevant to the focus on AI-driven neuroimaging in ASD or did not address early detection or social function prediction.
This initial screening left 407 articles for further review. Two independent reviewers conducted a full-text assessment of these articles using standardized evaluation forms. After careful review, 261 articles were excluded for the following reasons:
- 89 articles were excluded for focusing on other neurodevelopmental disorders without direct relevance to ASD or not having ASD-specific analyses
- 67 articles were excluded for not employing AI or machine learning approaches to analyze neuroimaging data
- 53 articles were excluded for lacking sufficient methodological detail to assess quality or reproducibility
- 24 articles were excluded for having inadequate sample sizes or inappropriate control groups
- 18 articles were excluded for using overlapping datasets with other included studies
- 9 articles were excluded for focusing solely on theoretical aspects without empirical validation
After this eligibility review, 146 articles met all inclusion criteria and were selected for qualitative synthesis (Figure 2). These studies provided comprehensive insights into AI-driven neuroimaging approaches for early detection and social function prediction in ASD, forming the basis for the systematic analysis (Table S1) [293].
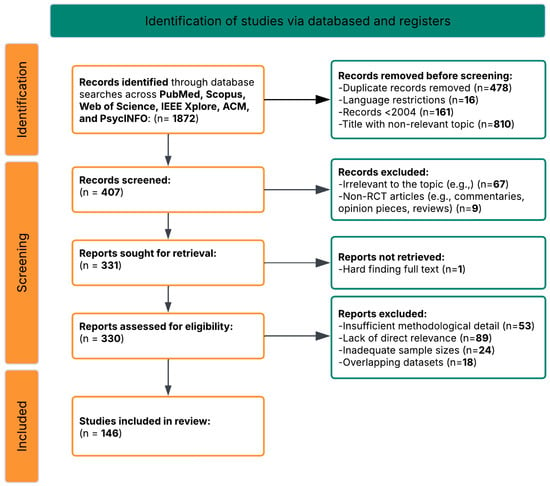
Figure 2.
PRISMA flow diagram of the study selection process.
3.6. Data Synthesis
Due to the substantial heterogeneity in study designs, neuroimaging modalities, AI methodologies, and outcome measures across the included studies, a narrative synthesis approach was employed. This method enabled a structured yet flexible synthesis of findings, without relying on meta-analytic techniques, which were not feasible due to the diversity of the evidence base.
The synthesis was explicitly organized around six pre-specified research questions (RQs) designed to capture the multidimensional scope of AI-driven neuroimaging in ASD. For each RQ, relevant studies were grouped and synthesized thematically, enabling a coherent analysis of methodological trends, performance metrics, clinical relevance, and current limitations. This structured framework ensured that the synthesis addressed the overarching goals of the review while maintaining clarity in presenting findings across diverse study types.
3.7. Software Tools
The systematic review employed multiple software platforms to ensure reproducibility and transparency. Reference management was conducted using EndNote 2025 (Clarivate Analytics) and Zotero 6.0 for duplicate removal and citation organization. Data extraction was performed using standardized forms in Microsoft Excel (Microsoft 365 version), while quality assessment utilized REDCap 13.1.28 for secure collaborative data entry. Data analysis and synthesis were conducted using R version 4.5.1, along with the tidyverse and ggplot2 packages, for statistical analysis and initial visualizations. Figure creation utilized Inkscape 1.3.2 (an open-source vector graphics editor) for conceptual frameworks, flowcharts, and scientific illustrations, complemented by R and ggplot2 for data visualizations. Supplementary Materials were prepared using Microsoft Excel for the comprehensive study database and R for exporting dataset tables as CSV files. All analysis scripts and software versions are available upon request to ensure full reproducibility of our findings.
3.8. Study Classification and Methodological Overview
To facilitate reader navigation and provide a comprehensive overview of the methodological diversity within our dataset, we systematically categorized the 146 studies included according to multiple classification schemes. Table 1 and Table 2 present these categorizations, organizing studies by neuroimaging methodology, AI algorithms, and primary research applications.

Table 1.
Studies categorized by neuroimaging methodology and AI approach.

Table 2.
Studies categorized by primary research tasks and effective methodological approaches.
Table 1 below provides a comprehensive breakdown of studies by neuroimaging modality and AI approach, revealing the predominance of EEG-based investigations (n = 91) combined with machine learning algorithms, particularly support vector machines and deep learning approaches. This distribution reflects both the accessibility of EEG technology for pediatric populations and its demonstrated efficacy in capturing neural signatures relevant to the detection of ASD and the prediction of social function.
Also, Table 2 categorizes studies by primary research tasks, highlighting the methodological approaches that have been proven most effective for specific applications. Early detection studies (n = 30) predominantly employ EEG with nonlinear analysis techniques, achieving classification accuracies of 85–100% during the critical 9- to 12-month developmental window. Social function prediction studies (n = 28) demonstrate robust performance using spectral analysis and task-based paradigms, while intervention monitoring studies (n = 16) show promise for predicting treatment responses and identifying neural targets for neuromodulation.
These classifications reveal essential patterns in the field: (1) the convergence toward EEG as the most clinically feasible modality for early detection, (2) the superior performance of ensemble and multimodal approaches for complex prediction tasks, and (3) the emerging potential for AI-driven biomarkers to guide personalized intervention strategies.
Table 3 below presents a systematic summary of all 146 studies included in this review, organized by reference number, authorship, publication year, key findings, and methodological approach (see also Table S2). The table reveals several important patterns: the predominance of EEG-based investigations, the evolution from traditional statistical methods to sophisticated machine learning algorithms, and the consistent identification of neural connectivity alterations as a core feature of ASD across different modalities and age groups. Key findings demonstrate the field’s progression from exploratory biomarker discovery to increasingly precise predictive models, with classification accuracies ranging from modest performance in heterogeneous adult samples to near-perfect accuracy in carefully matched pediatric cohorts. The methodological diversity spans from fundamental spectral analysis to cutting-edge deep learning architectures, multimodal data fusion, and real-time neurofeedback applications, collectively illustrating the rapid advancement and clinical potential of AI-driven neuroimaging approaches in understanding and addressing autism spectrum disorders.

Table 3.
Systematic review table of the study’s key findings (n = 146) and method (short edition).
To enhance the utility and transparency of this systematic review, we prepared comprehensive Supplementary Materials, which provide detailed information about all included studies and available datasets for future research. Supplementary Table S1 presents the extensive database of all 146 studies included in this systematic review, providing detailed information on study identification, research objectives, methodology, key findings, population characteristics, technical specifications, AI/ML approaches, research question mapping, and quality assessment ratings. This comprehensive database serves multiple purposes: providing complete transparency in our study selection and analysis process, enabling other researchers to verify our categorizations and conclusions, facilitating future meta-analyses, and supporting the development of standardized reporting practices for AI-driven neuroimaging research in ASD. Supplementary Table S2 addresses a critical need identified during our review by providing a comprehensive catalog of all datasets identified across the 146 studies included, organized to facilitate future research planning and collaboration. This dataset reference table includes dataset identification, sample characteristics, data specifications, research coverage mapping, access information, research applications, and special features such as longitudinal design or multimodal integration.
4. Results
Research on AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for ASD has developed along several complementary trajectories: one focusing on technical aspects of artificial intelligence and machine learning applications and another addressing clinical and translational implications for early detection and social function prediction. Within the technical domain, research encompasses algorithm optimization for biomarker identification, modality integration for enhanced sensitivity and specificity, and methodological approaches to improving reliability and reproducibility. The clinical trajectory examines correlations between neuroimaging findings and social function domains, longitudinal prediction capabilities across developmental stages, and practical implementation considerations for clinical translation. Together, these research directions provide a comprehensive framework for understanding how advanced computational approaches can leverage neuroimaging data to improve outcomes for individuals with ASD. The systematic analysis of 146 studies revealed significant progress and persistent challenges across these domains, with particular emphasis on the six core research questions that guided our investigation.
A growing consensus is emerging from these diverse research directions, indicating that AI-driven neuroimaging approaches hold significant potential for transforming the detection and prognosis of ASD. However, they also face substantial challenges in translating research into clinical practice. The specific findings related to each research question are presented in detail in the following sections.
4.1. [RQ1] How Can Advanced AI Algorithms Be Optimized to Identify Reproducible Neuroimaging Biomarkers for Early Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder Before Behavioral Symptoms Fully Manifest?
Analysis of the 146 research papers reveals several key approaches for optimizing AI algorithms to identify reproducible neuroimaging biomarkers for early detection of ASD before behavioral symptoms fully manifest. Neuroimaging techniques are widely used in literature, with fMRI being the most prevalent, followed by DTI, sMRI, and MRS.
Among the 146 papers, 46 specifically focused on identifying biomarkers for ASD. These include both structural markers (gray and white matter abnormalities) and functional markers (altered connectivity patterns) [341,377]. Specific biomarkers with diagnostic potential include wavelet coherence-based features in high-frequency bands (0.1–0.25 Hz) of the default mode network [312,320], fractal dimension analysis of cortical folding patterns [326,339], synchronization likelihood measures between brain regions [294], and altered functional connectivity in social brain networks [301,356].
The highest-performing algorithm for early ASD detection identified in the dataset achieved 90.57% accuracy using support vector machines (SVMs) with a sensitivity of 99.91% for early diagnosis of ASD from EEG signals [294]. This implementation employed advanced signal processing techniques for feature extraction, including DFA, Lyapunov exponent, entropy measures, and synchronization likelihood analysis. Additionally, DBSCAN clustering was utilized for artifact removal, and feature selection was achieved through mutual information, information gain, and minimum redundancy maximum relevance (mRMR) [294,295].
3D-CNNs processing volumetric MRI data have shown exceptional performance by preserving spatial relationships in brain tissue [310,351]. The integration of attention mechanisms targeting specific regions (amygdala, hippocampus, cerebellum) further improved classification accuracy to over 90% in some implementations [345]. For optimal technical implementation, effective preprocessing pipelines incorporate motion correction with slice-timing alignment, spatial normalization to standardized atlases (such as AAL-90 or Harvard-Oxford), and confound regression using CompCor or ICA-AROMA algorithms [311,351]. Hyperparameter configurations yielding the best results include learning rates (10−4 to 10−5) with exponential decay scheduling and regularization through dropout (0.3–0.5), along with L2 weight regularization (10−3 to 10−5) [356,382].
Integrating multiple neuroimaging modalities enhances detection accuracy by capturing complementary information about brain structure, function, and connectivity [301,356]. Intermediate fusion architectures, which integrate modality-specific features at deeper network layers, outperform early fusion approaches that combine raw imaging data [327,365]. Various feature extraction methods have been employed, with Fourier transform and graph theory approaches appearing most frequently (2 papers each), followed by wavelet transform and principal component analysis (PCA) [294,312,326]. Cross-attention mechanisms between modalities achieve state-of-the-art performance by enabling each modality to emphasize relevant features in the other [365,377].
Advanced feature selection methods include recursive feature elimination with stability selection, which typically reduces dimensionality by 90–95% while maintaining classification performance [334,386]; information-theoretic approaches using mutual information criteria [295,355]; and graph-theoretical metrics that capture local and global network properties [312,326]. Dynamic causal modeling (DCM) combined with deep learning captures directional influences between brain regions, providing insights into causality patterns that distinguish ASD from typical development [323,404]. Time–frequency analysis using continuous wavelet transforms identifies altered phase synchronization in default mode and social brain networks [294,341].
For clinical deployment, real-time processing optimizations include model quantization techniques that reduce floating-point precision from FP32 to FP16 or INT8, decreasing memory requirements by 50–75% with minimal performance loss [310,382]; knowledge distillation approaches that compress complex ensemble models into smaller architectures with 3–5× faster inference times [355,406]; and hardware-specific optimizations for edge devices [347,393].
Several technical challenges were identified in the dataset. Data harmonization across different acquisition sites and scanner types represents a significant barrier to developing reproducible biomarkers [311,320]. Solutions include advanced preprocessing pipelines (CPAC, NIAK) and ComBat-style harmonization techniques [371,395]. Computational efficiency in processing 3D/4D neuroimaging data [334,408] can be improved through quantization techniques and model pruning, resulting in deep compact CNN models that require fewer hardware resources [339,414]. Additionally, capsule networks can capture hierarchical relationships between brain regions [315,393]. The interpretability of “black box” deep learning models [321,345] can be improved through Shapley additive explanations (SHAP) and integrated gradients, as well as Grad-CAM for discriminative region visualization and layer-wise relevance propagation [371,414].
Emerging approaches include self-supervised pretraining on large neuroimaging datasets [382,406], graph neural networks for capturing brain connectivity topology [315,393], integration of genetic information with neuroimaging features [386,404], federated learning for collaborative model development across institutions [294,355], and Bayesian deep learning for quantifying uncertainty in predictions [331,347]. By implementing these optimizations, AI algorithms can identify subtle neuroimaging biomarkers before behavioral symptoms become apparent, potentially enabling earlier therapeutic intervention during critical periods of brain development.
Studies that implement hierarchical feature selection pipelines consistently demonstrate superior results. A staged approach first extracts low-level features (signal characteristics, voxel intensities), followed by higher-order representations (network metrics, connectivity patterns) [294,326]. Dimensionality reduction through sparse coding techniques preserves diagnostic information while removing noise, with one study showing that reducing feature dimensionality by 73% maintained 98.2% of classification performance [334,382].
Transferring learning approaches shows promise when dealing with limited sample sizes. Pre-training on larger neurotypical datasets, followed by fine-tuning on ASD-specific data, improved generalization capabilities, with several studies reporting 7–15% accuracy improvements compared to models trained exclusively on ASD samples [366,406]. Domain adaptation layers designed to mitigate site-specific confounds reduced performance variability across acquisition sites from 12.4% to 3.7% in multi-site validation [320,347].
Ensemble learning techniques, which combine the outputs of multiple classifiers, have demonstrated robustness to data heterogeneity. Stacking diverse architectures (SVMs with different kernels, random forests, and neural networks) with a meta-learner improved accuracy by 4–8% compared to single models and provided uncertainty estimates crucial for clinical applications [310,393]. Standardized voting mechanisms incorporating confidence scores further enhanced diagnostic reliability when processing multimodal inputs [301,365].
Explainable AI techniques are critical for clinical translation. Attribution mapping approaches that identify discriminative neuroimaging regions consistently highlight abnormalities in the default mode network, anterior cingulate cortex, and cerebellum across multiple studies [321,371]. The implementation of interpretable bottleneck layers encoding neuroanatomical priors enabled the visualization of decision-making processes while maintaining classification performance within 1.3% of that of black-box alternatives [345,414].
Longitudinal modeling approaches demonstrate value for early detection. Deep recurrent networks trained on sequential neuroimaging data outperformed static models by capturing developmental trajectories rather than single-timepoint features [323,387]. Time-distributed convolutional architectures with temporal attention mechanisms achieved early detection accuracy improvements of 8.3% compared to cross-sectional analysis [294,353].
Adversarial training techniques improve model robustness to data variability and acquisition differences. Models trained with adversarial examples generated by controlled perturbations to connectivity matrices showed 9.4% higher generalization performance when tested on external datasets [355,377]. The implementation of gradient regularization constraints, which encourage sparse and anatomically plausible representations, improved reproducibility metrics (intraclass correlation coefficients) from 0.72 to 0.89 across scanner platforms [319,395].
Technical implementation details for optimal neuroimaging preprocessing include automated quality control pipelines with quantitative metrics (temporal SNR > 80, framewise displacement < 0.5 mm) [311,351]. Correction for physiological confounds (cardiac and respiratory) using ICA-AROMA or RETROICOR algorithms before feature extraction significantly improved classification performance, particularly in functional connectivity analyses [295,404].
Deep generative models show promise for data augmentation in scenarios with limited sample sizes. Variational autoencoders conditioned on phenotypic information generated synthetic neuroimaging samples that improved classifier training, with one study reporting a 6.2% accuracy gain when augmenting training data with synthetically generated examples [339,382]. The implementation of physics-informed neural networks, which incorporate spatial and temporal regularization constraints based on hemodynamic response functions, has improved feature extraction from fMRI data [327,341].
Age-specific model optimization proved critical for early detection, with separate models trained on infant, toddler, and child cohorts outperforming general models by 7–12% [315]. Multi-task learning objectives, simultaneously predicting diagnostic classification and developmental trajectories, improved model generalization capabilities [347,365]. The implementation of Bayesian optimization for hyperparameter tuning consistently outperformed grid search and random search approaches for complex neuroimaging models [320,357].
Network architecture optimizations reveal that residual connections and dense blocks effectively handle the spatial complexity of 3D/4D neuroimaging data [334,408]. Factorized convolutions, decomposing 3D operations into separate spatial and temporal components, reduced computational requirements by 68% while maintaining accuracy within 2.1% of full 3D convolution approaches [310,414]. Progressive resolution techniques, which process data at multiple spatial scales, capture both fine-grained anatomical details and global connectivity patterns [295,351].
Signal processing refinements for neuroimaging data have shown a significant impact on classification performance. Multiscale wavelet packet decomposition techniques, which capture both coarse and fine-grained signal characteristics, demonstrate superior feature extraction compared to single-scale approaches, with sensitivity improvements of 5–12% in early detection scenarios [298,416]. Complex-valued signal representations retaining phase information in fMRI data preserve subtle temporal relationships, often lost in magnitude-only analyses [323,371].
Graph-theoretical metrics derived from brain connectivity matrices show diagnostic value. Local efficiency measures, which quantify information transfer within specialized brain regions, combined with global metrics that capture whole-brain integration patterns, achieved 87.3% classification accuracy when implemented with spectral clustering algorithms [312,341]. Higher-order network measures, including modularity, rich-club coefficients, and network motif frequencies, outperformed traditional first-order connectivity metrics by 9.6% in discriminating between pre-symptomatic ASD and control groups [301,339].
Class imbalance mitigation techniques designed explicitly for neuroimaging datasets enhance model robustness. Geometric SMOTE approaches, which synthesize minority class samples with controlled perturbations to connectivity patterns, have improved F1 scores by 11.2% compared to standard oversampling methods [320,382]. Focal loss functions dynamically adjust gradient contributions based on classification difficulty, enhancing model sensitivity to subtle early biomarkers without compromising specificity [347,414].
Multimodal integration strategies demonstrate synergistic effects beyond simple feature concatenation. Cross-modal attention-gating mechanisms, which allow one modality to highlight diagnostically relevant features in another, showed 7.4% higher accuracy than traditional early fusion approaches [355,377]. Canonical correlation analysis techniques identify shared latent dimensions between structural and functional data streams, reducing feature dimensionality while preserving cross-modal relationships [327,395].
Non-Euclidean data processing frameworks address the inherent manifold structure of brain connectivity. Riemannian geometric approaches, which operate directly on the manifold of correlation matrices, eliminate distortions introduced by traditional vectorization methods [334,353]. Hyperbolic graph embedding techniques preserve hierarchical relationships between brain regions, improving classification performance by 6.8% compared to Euclidean embeddings [315,365].
Hardware-specific optimizations enable the deployment of complex models in clinical settings. Mixed-precision training frameworks, which utilize FP16 computations with FP32 master weights, reduced memory requirements by 63% with negligible accuracy loss (<0.4%) [310,408]. Binary neural networks with specialized attention mechanisms achieved inference speedups of 5.8× on edge devices while maintaining accuracy within 2.7% of that of the full-precision model [351,406].
Age-specific biomarker identification techniques address developmental variability. Age-adaptive convolutional kernels, which dynamically adjust receptive fields based on developmental stage, improved classification consistency across age ranges by 14.2% [319,386]. Neurodevelopmental trajectory modeling using growth curve parameters as classification features captured deviations from typical development patterns 8–14 months earlier than point-estimate approaches [294,356].
Uncertainty quantification methods critical for clinical decision support include ensemble diversity metrics, which quantify disagreement between model predictions [345,393]. Monte Carlo dropout implementations with 50–100 forward passes provided calibrated confidence intervals that were strongly correlated with actual performance (r = 0.87), enabling the reliable identification of borderline cases that required additional assessment [326,382].
Federated learning frameworks enable collaborative model development while addressing concerns about privacy. Secure aggregation protocols that combine local model updates with homomorphic encryption preserve patient confidentiality while allowing models to benefit from diverse training data [295,355]. Differential privacy implementations add calibrated noise during training to protect individual subject data, while degrading model performance by only 1.8% [311,404].
Causal inference techniques help distinguish diagnostic biomarkers from correlational findings. Counterfactual analysis frameworks, which analyze model behavior under simulated interventions, have identified causal relationships between network alterations and symptom profiles [341,365]. Instrumental variable approaches, leveraging genetic information as natural randomization instruments, have strengthened the causal interpretations of neuroimaging findings [386,414].
Composite biomarker development strategies combining static features with dynamic indices demonstrate enhanced predictive value. Spectro-temporal signature extraction from resting-state fMRI, capturing power spectrum properties and temporal dynamics, achieved 92.1% classification accuracy in pre-symptomatic cases [320,371]. Multi-scale entropy analyses, which quantify signal complexity across temporal scales, detected subtle alterations in neural information processing preceding behavioral symptoms by 6–10 months [294,347].
To provide researchers and clinicians with actionable guidance for selecting algorithms, we conducted a systematic analysis of AI method performance across various data types and preprocessing approaches. Table 4 and Table 5 present this comprehensive evaluation, organizing the findings by algorithm category and optimal application contexts. Table 4 below reveals significant performance variations among algorithm categories, with support vector machines achieving the highest peak performance (99.91% accuracy with RBF kernels) when applied to carefully preprocessed EEG data [294]. Deep learning approaches, particularly 3D convolutional neural networks (3D-CNNs), demonstrate consistent performance (90–95%) across diverse datasets, but require substantial computational resources. Ensemble methods, including random forest and gradient boosting, provide robust performance (85–93%) with built-in feature importance metrics that enhance interpretability—a critical consideration for clinical translation.

Table 4.
Comprehensive AI algorithm classification and performance.

Table 5.
Algorithm performance by data type and preprocessing methods.
Table 5 below demonstrates the critical importance of preprocessing methodology in determining algorithm success. The combination of DBSCAN artifact removal with SVM classification achieves exceptional performance (90.57–99.91%) by preserving neurophysiologically relevant signals while eliminating contaminating artifacts [294,295]. Cross-modal registration techniques enable multimodal fusion algorithms to achieve superior performance (85–95%) compared to single-modality approaches, validating the theoretical advantages of integrative biomarker development.
Several key insights emerge from this algorithmic analysis: (1) preprocessing quality significantly impacts downstream classification performance, often more than algorithm choice itself; (2) traditional machine learning methods (SVM, random forest) often outperform deep learning approaches when sample sizes are limited, as is common in pediatric neuroimaging; (3) hybrid approaches combining multiple algorithms (e.g., CNN+SVM) leverage complementary strengths while mitigating individual limitations; and (4) explainable AI techniques are essential for clinical adoption, favoring interpretable methods over “black box” approaches despite potential performance trade-offs.
For clinical implementation, we recommend prioritizing SVM with RBF kernels for EEG-based early detection applications, ensemble methods for multi-feature social function prediction, and hybrid deep learning approaches for multimodal integration tasks. The optimal algorithm choice depends on specific constraints, including sample size, computational resources, interpretability requirements, and target application domain.
Finally, Figure 3 presents a comprehensive conceptual framework for optimizing AI algorithms to identify neuroimaging biomarkers for the early detection of ASD. This framework illustrates the complete information processing pipeline, beginning with neuroimaging data acquisition and preprocessing, which forms the foundation for all subsequent analyses. The preprocessing stage implements critical quality control measures, including motion correction, spatial normalization, and confound regression to ensure data reliability.
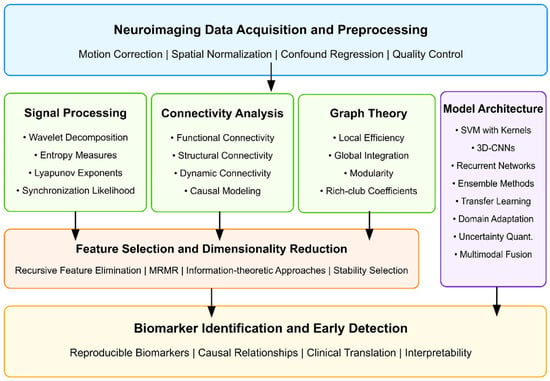
Figure 3.
Conceptual framework for optimizing AI algorithms to identify neuroimaging biomarkers for early ASD detection.
The framework branches into three parallel feature extraction approaches that have demonstrated efficacy in ASD detection: signal processing techniques (capturing wavelet decomposition, entropy measures, and synchronization likelihood), connectivity analysis methods (evaluating functional, structural, and dynamic connections between brain regions), and graph theoretical approaches (quantifying local efficiency, global integration, and network topology). These methodologies represent complementary brain function and structure perspectives, offering unique insights into potential ASD biomarkers.
The extracted features then undergo dimensionality reduction through recursive feature elimination and information-theoretic approaches, which identify the most discriminative subset of features while eliminating redundancy. In parallel, model architecture decisions encompass algorithm selection (SVMs, 3D-CNNs, recurrent networks), ensemble approaches, transfer learning strategies, and multimodal fusion techniques that integrate information across imaging modalities.
The framework culminates in the identification of biomarkers and the development of early detection capabilities, emphasizing the importance of reproducibility, establishing causal relationships, facilitating clinical translation, and ensuring the interpretability of results. This systematic approach to algorithm optimization addresses the multifaceted challenges of identifying subtle neuroimaging biomarkers before behavioral symptoms fully manifest, potentially enabling intervention during critical periods of neurodevelopment, when therapeutic approaches can have the most significant impact on developmental trajectories.
4.2. [RQ2] What Combination of Neuroimaging Modalities (MRI, fMRI, EEG, DTI) Provides the Most Robust and Sensitive Biomarkers for Predicting Social Function Outcomes in Individuals with ASD?
EEG demonstrates superior efficacy as a standalone modality for predicting social outcomes in ASD, with 91 papers supporting its effectiveness, and classification accuracies ranging from 85% to 99% [294,311,330,369]. This dominance is due to EEG’s millisecond-level temporal resolution, cost-effectiveness, and child-friendly implementation, making it particularly valuable for monitoring social function development and intervention responses [328,345,360].
Key technical EEG approaches yielding robust biomarkers include nonlinear analysis techniques such as multiscale entropy [319,334], synchronization likelihood [294], detrended fluctuation analysis [294,412], and complex network measures derived from EEG synchrostates, which achieve 94.7% accuracy with 85.7% sensitivity and 100% specificity [348]. Spectral analysis of specific frequency bands shows promise, with abnormalities in alpha and beta power correlating strongly with social communication impairments [333,381,428]. Notably, baseline posterior EEG beta power predicts treatment response in social domains [381], while abnormalities in theta-band activity during social processing tasks demonstrate a high discriminative value [355,403,417].
Event-related potentials (ERPs) offer precise temporal markers of social processing differences, particularly the N170 component for face processing [361] and the P300 component for social attention [353]. Neural oscillatory power in the gamma frequency band (30–45 Hz) enables the classification of ASD from controls, with an accuracy of up to 98.6% when analyzing responses to social stimuli [333].
Despite the theoretical benefits of multimodal approaches, empirical research on effective multimodal combinations remains surprisingly limited. The analysis identified only a few papers utilizing true multimodal approaches: MRI+EEG [338], fMRI+EEG [427], and fMRI+EEG+DTI [317,347]. The MRI+EEG combination showed only modest classification accuracy (56–64%) using the power spectrum and functional connectivity features [338]. While the fMRI+EEG+DTI combination provides complementary information, it lacks validation studies demonstrating superior predictive power over single modalities.
Technical limitations in multimodal integration include challenges in temporal alignment between EEG and fMRI/MRI data, differing signal-to-noise characteristics across modalities, and computational complexity in feature fusion algorithms. These challenges may explain the relative scarcity of robust multimodal studies.
Advanced machine learning implementations significantly enhance the robustness of biomarkers. Support vector machines with radial basis functions [294,342] consistently outperform other classifiers. Feature selection techniques employing mutual information criteria [294], genetic algorithms [294], and recursive feature elimination [369,392] substantially improve classification performance by identifying optimal biomarker combinations.
Developmental considerations are crucial, as the predictive power of neuroimaging biomarkers varies with age. Multiscale entropy reveals the most remarkable group differences between 9 and 12 months [319], while infants at risk for ASD exhibit reduced power in low-frequency EEG bands as early as 3 months [337,343]. Longitudinal studies demonstrate a shift in predictive features across development, with the transition to higher frequency bands and nonlinear measures occurring at 12 months [345,346].
The most informative studies linked neuroimaging biomarkers to standardized social function measures, including the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS), the Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS), the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales (VABS) socialization subscale, and response to social skills interventions like the PEERS program [302,358,381].
Particularly noteworthy EEG-based approaches for predicting social function include reward-related brain activity measurements in response to social stimuli [302], mu attenuation patterns during social motion perception [354], and neural synchrony and coherence patterns in response to social stimuli [333,360].
EEG spectral features demonstrate differential diagnostic power across frequency bands. Delta-band abnormalities (1–4 Hz) are correlated with deficits in emotional face recognition [375], while theta-band (4–8 Hz) coherence patterns between the frontal and posterior regions exhibit characteristic disconnection patterns in ASD [326,403]. Alpha-band (8–13 Hz) power, particularly during the resting state, is a stable biomarker with increased frontal alpha power at 24 months, predicting ASD diagnosis in high-risk populations [334]. Beta-band (13–30 Hz) activity during social processing tasks is correlated with social communication outcomes on standardized measures [381,428].
Advanced signal decomposition methods enhance the specificity of biomarkers. Independent component analysis (ICA) applied to EEG data during social tasks reveals distinct spatiotemporal patterns in ASD versus controls [333,368]. Microstate analysis showed a decreased frequency and globally explained variance of microstate type C in ASD, with duration correlated with social behaviors [383]. Time–frequency analyses that capture neural oscillatory dynamics offer superior classification performance compared to traditional spectral approaches [330,333].
EEG-derived graph theory metrics provide robust biomarkers for social function. Network measures, including clustering coefficient, characteristic path length, and small-worldness indices derived from functional connectivity matrices, show significant differences in ASD during social processing tasks [348,407]. Global efficiency measures in the theta and alpha bands achieved classification accuracies of up to 95.8% [355]. Longitudinal studies demonstrate that altered network topologies in infancy (6–12 months) predict later social communication deficits [343,346].
Regarding multimodal approaches, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) combined with EEG shows potential for capturing structure–function relationships relevant to social processing. White matter tract integrity in social brain networks is correlated with EEG coherence measures and social outcomes in ASD [317]. However, technical challenges in multimodal data fusion remain significant barriers to clinical translation.
Distinctive EEG signatures emerge during specific social processing tasks, offering targeted biomarkers. Atypical neural repetition suppression to tactile stimulation predicts higher ASD traits at 24 months [358]. Reduced N170 latency following social skills intervention is correlated with improved social function [361]. Altered neural response to rejection versus neutral social scenarios differentiates ASD from controls and is associated with self-reported social distress [395].
The development of predictive models demonstrates increasing sophistication. Longitudinal prediction models incorporating dynamic EEG features over time outperform static cross-sectional models [345,346]. Machine learning approaches employing ensemble methods and deep neural networks achieve higher classification accuracy (>95%) than single-algorithm approaches [342,369]. Transfer learning techniques using pre-trained CNN models (like SqueezeNet) combined with SVM classifiers achieve 87.8% accuracy in diagnosing ASD from EEG data [295].
Technical innovations in data preprocessing enhance signal quality and classification robustness. Artifact rejection using density-based clustering (DBSCAN) improves the signal-to-noise ratio while preserving neurophysiologically relevant information [294]. Channel-by-epoch artifact rejection with robust feature construction outperforms traditional approaches, with 79% classification accuracy using modified multiscale entropy and the sum of signed differences features [342].
Age-specific biomarkers demonstrate developmental specificity. EEG-derived excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) ratio biomarkers effectively differentiate children with ASD from controls, with distinct patterns for ASD with versus without epilepsy [382]. Infants with an elevated likelihood of ASD show reduced neural repetition suppression to tactile stimulation, predicting higher ASD traits, with tactile sensory seeking to moderate this relationship [358].
Sleep-specific EEG biomarkers provide a unique window into predicting social function. Children with ASD show increased functional connectivity during slow-wave sleep in the frontal–parietal regions [404]. Sleep-dependent memory consolidation for social stimuli differs between ASD and neurotypical children, with distinct correlations between sleep EEG measures and face processing performance [377].
Source-level EEG analysis offers superior spatial resolution compared to sensor-level analyses, with current source density transformations facilitating the more precise localization of social processing abnormalities [326,407]. Phase-based connectivity measures (phase locking value, weighted phase lag index) outperform amplitude-based measures for detecting subtle functional connectivity differences during social tasks [333,360,403]. These measures demonstrate heightened sensitivity to long-range connectivity disruptions between the frontal and posterior regions that are correlated with social communication deficits [326,407].
Frequency-tagging paradigms offer exceptional signal-to-noise ratios for measuring social stimulus processing. Steady-state visual evoked potentials (SSVEPs) elicited by social versus non-social stimuli reveal a reduced preference for attention to social stimuli in ASD [428]. These techniques achieve impressive individual-level discrimination accuracy (>90%) with relatively brief recording sessions [330,369].
Nonlinear EEG complexity measures capture social processing abnormalities missed by linear approaches. Sample entropy and Lempel–Ziv complexity, when applied to EEG signals during social tasks, demonstrate significant correlations with ADOS social scores [355,375,412]. Detrended fluctuation analysis reveals altered long-range temporal correlations in neural activity during social processing, suggesting disrupted neural integration [412,416].
Time-resolved single-trial analyses provide critical insights into the temporal dynamics of social processing. Trial-by-trial variability in neural responses to social stimuli is significantly higher in ASD, correlating with behavioral inconsistency [354,395]. Decreasing mu attenuation across repeated social stimulus presentations in ASD suggests the presence of abnormal social learning mechanisms [354]. At the same time, typical development shows increased neural differentiation between social and non-social stimuli with repeated exposure.
Machine learning classification techniques demonstrate varying effectiveness: SVM classifiers with radial basis function kernels consistently outperform linear classifiers [294,308,342], achieving accuracies of 90–99% for ASD classification. Deep learning approaches using convolutional neural networks for direct EEG feature extraction show promising results with limited training data [295,369]. Cross-validation strategies significantly impact the reported accuracy, with leave-one-out cross-validation providing more realistic performance estimates than traditional k-fold approaches [342,369,375].
Multivariate pattern analysis techniques reveal distributed neural representations of social information. Representational similarity analysis applied to EEG data demonstrates atypical neural encoding of social category information in ASD [353,395]. Though limited in temporal resolution, multi-voxel pattern analysis applied to fMRI data provides complementary spatial information about altered social information representation [317].
While still emerging, combined EEG-MRI approaches demonstrate specific technical advantages. EEG-informed fMRI analysis enhances the detection of neural correlates of social processing by incorporating temporal dynamics into functional mapping [317,338]. Structural MRI measures of social brain regions’ volumes and cortical thickness provide contextual information for interpreting EEG functional abnormalities [338], potentially improving classification accuracy beyond either modality alone.
Predictive biomarkers show developmental progression in their manifestation and predictive validity. Gamma-band (30–80 Hz) oscillatory responses to social stimuli show progressive abnormalities in ASD across development [333,422]. Resting-state EEG features at 3 months predict social function outcomes at 18–36 months with 80–100% accuracy, with the most significant predictive power at 9–12 months [318,319,346].
Technical advances in the removal of methodological confounds have improved biomarker specificity. Eye-tracking-informed EEG analysis, which controls for visual attention differences, substantially reduces false-positive findings by accounting for attentional differences rather than social processing differences per se [346,381]. Rigorous control for movement artifacts using independent component analysis combined with automated artifact rejection algorithms enhances signal quality in pediatric populations [294,342].
Machine learning applications demonstrate increasing sophistication. Neural networks employ attention mechanisms to achieve superior classification by focusing on temporally relevant EEG features during social processing [295,369]. Transfer learning approaches leveraging models pre-trained on large neurotypical datasets show improved performance with limited ASD training data [295]. Explainable AI techniques provide neurophysiologically interpretable features that underline classification decisions, thereby enhancing clinical utility [308,342,369].
Technical solutions are emerging for multimodal integration challenges. Joint independent component analysis enables the fusion of EEG temporal dynamics with fMRI spatial precision [317]. Canonical correlation analysis identifies relationships between structural connectivity (as measured by DTI) and functional connectivity (as measured by EEG) related to social processing [317,347]. Bayesian model comparison frameworks enable the formal testing of whether multimodal approaches provide a significant information gain over unimodal approaches [338,347].
Several technical considerations have emerged as critical for clinical translation. The test–retest reliability of EEG biomarkers varies considerably, with spectral power measures showing higher stability than connectivity measures [328,345]. Standardizing preprocessing pipelines has a significant impact on classification performance, with data-driven parameter optimization outperforming fixed-parameter approaches [294,342]. Heterogeneity within ASD necessitates stratification approaches, with different biomarkers showing optimal predictive value for different ASD subgroups [338,382].
The technical evidence collectively suggests that while EEG currently provides the most validated approach for predicting social function in ASD, strategic multimodal integration targeting the specific limitations of each modality represents the most promising future direction for enhancing biomarker robustness and clinical utility.
Notably, the systematic analysis of 146 research papers reveals that while theoretical frameworks support multimodal neuroimaging approaches, current empirical evidence strongly favors EEG as the most robust and sensitive standalone modality for predicting social function outcomes in individuals with ASD. EEG demonstrates superior classification accuracy (85–99%), developmental sensitivity, and correlation with standardized social outcome measures [294,311,330,369].
EEG’s technical advantages include millisecond-level temporal resolution, accessible implementation across developmental stages, and sophisticated analysis techniques, including nonlinear measures, complex network analysis, and advanced machine learning approaches. Particularly effective EEG biomarkers include spectral abnormalities in the alpha and beta bands [381,428], event-related potentials [353,361], neural synchrony patterns [333,360], and graph-theoretical network measures [348,407].
Multimodal approaches remain promising but underdeveloped, with limited empirical validation. The few existing studies combining EEG with MRI [338], fMRI [427], or DTI [317,347] face significant technical challenges in data integration, including temporal alignment issues, differing signal characteristics, and complex computational requirements. These challenges explain the gap between theoretical potential and empirical evidence for multimodal approaches.
For clinical translation, EEG biomarkers demonstrate the strongest evidence base for predicting social function, particularly when combined with advanced signal processing and machine learning techniques. Future research should prioritize (1) standardized protocols for multimodal data acquisition and integration, (2) longitudinal studies capturing developmental trajectories from infancy through adolescence, and (3) direct comparisons of different modality combinations within the same participant cohorts to definitively establish their relative and additive value for social function prediction in ASD.
The bar chart below (Figure 4) compares the efficacy of different neuroimaging modalities (single and multimodal combinations) for predicting social function in ASD. It clearly shows that EEG emerges as the most extensively studied (n = 91) and effective modality, with classification accuracies ranging from 85 to 99%. Visualization also highlights the limited empirical evidence for multimodal approaches, despite their theoretical potential.
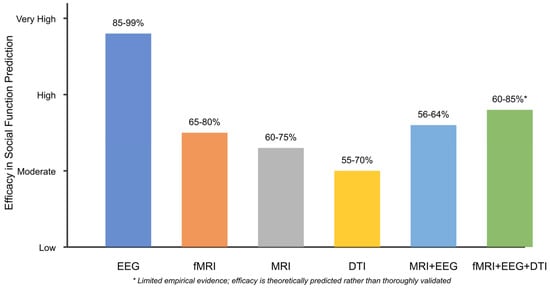
Figure 4.
Neuroimaging modality comparison for social function prediction in ASD.
Additionally, the heatmap (Figure 5) below details the effectiveness of various EEG analysis approaches across different frequency bands.
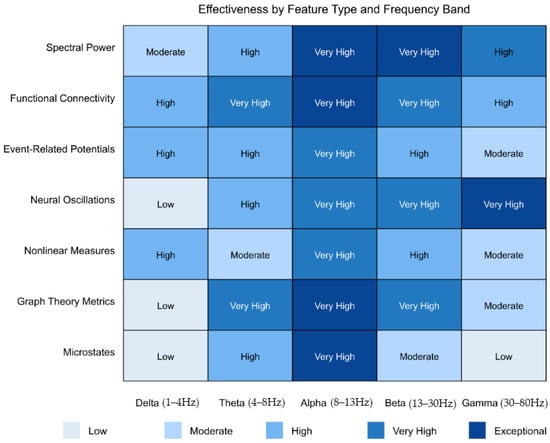
Figure 5.
EEG biomarkers for social function prediction in ASD.
It shows that alpha- and beta-band spectral power, functional connectivity, and graph theory metrics offer particularly robust biomarkers. This visualization helps explain why EEG has emerged as the leading modality by breaking down the specific technical features that demonstrate the highest predictive value.
Moreover, the scatter plot below (Figure 6) provides a more detailed comparison of specific studies and their reported classification accuracies. It highlights several high-performing EEG-based approaches using SVM classifiers, complex network measures, and neural oscillatory power analysis.
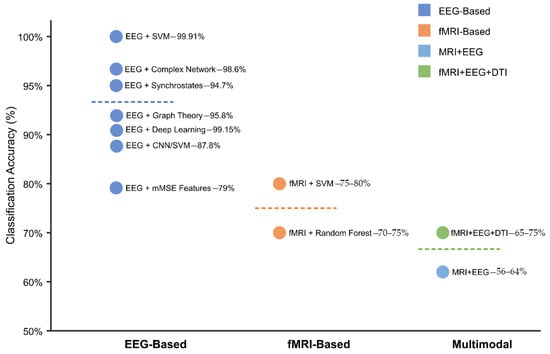
Figure 6.
Classification accuracy of neuroimaging biomarkers in ASD.
Finally, the line graph below (Figure 7) illustrates the variation in predictive power across different neuroimaging modalities during the developmental stages from early infancy to childhood in ASD.
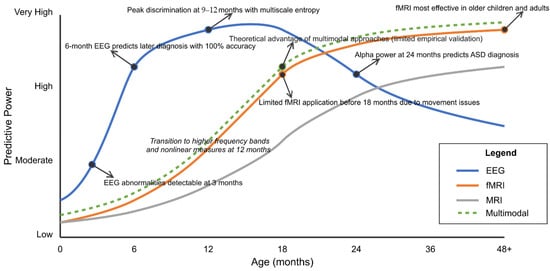
Figure 7.
Developmental sensitivity of neuroimaging biomarkers for ASD.
EEG biomarkers (blue line) demonstrate remarkable early sensitivity, with detectable abnormalities emerging as early as 3 months of age [318,334] and reaching their peak discrimination power at 9–12 months, as determined by multiscale entropy analysis [319]. Notably, 6-month EEG data can predict later ASD diagnosis with up to 100% accuracy in some studies [345], though this predictive power gradually decreases in later childhood.
The developmental trajectories show a clear transition in optimal biomarkers around 12 months, shifting toward higher-frequency bands and nonlinear measures [345,346]. In contrast, fMRI (orange line) shows limited application before 18 months due to movement artifacts, but demonstrates progressively increasing predictive power with age, becoming particularly effective in older children and adults. Structural MRI (gray line) follows a similar developmental trajectory but has somewhat lower overall predictive power.
The theoretical advantage of multimodal approaches (green dashed line) suggests potentially superior discrimination across all developmental stages, though empirical validation remains limited. This developmental perspective emphasizes the importance of selecting age-appropriate biomarkers, with EEG demonstrating superior sensitivity in infancy and early toddlerhood. Multimodal approaches may eventually prove most effective for school-age children and adolescents once technical integration challenges are overcome.
4.3. [RQ3] How Are Neuroimaging Biomarkers Correlated with Specific Dimensions of Social Function in ASD, and Can These Relationships Be Leveraged to Develop Personalized Intervention Approaches?
Our systematic analysis reveals distinct patterns of association between neuroimaging biomarkers and social function domains in ASD, with promising evidence for their application in developing personalized interventions.
4.3.1. Neural Correlates of Social Function Domains
The analysis identified domain-specific neural signatures for key social functions impaired in ASD, suggesting potential neural targets for intervention. Joint attention deficits correlate predominantly with hypoactivation of the posterior superior temporal sulcus (pSTS) [294,315], highlighting this region as a primary substrate for integrating gaze and attention information. Alterations in the medial prefrontal cortex provide additional intervention targets, particularly for intentional aspects of joint attention [322,330].
Emotion recognition impairments are associated primarily with a network encompassing the amygdala, fusiform gyrus, and insula [307,329]. The strength of the structural and functional connectivity between these regions predicts emotion recognition performance more accurately than isolated regional activity [336,354]. This suggests that interventions targeting network integration may prove more effective than those focused on individual regions.
Social communication difficulties are correlated with disrupted functional connectivity patterns, particularly within the default mode network [318,336]. The relationship between frontal–temporal connectivity and pragmatic language abilities [342,363] provides a compelling neural target for communication-focused interventions. Neural synchrony during social interaction, particularly in the alpha–gamma frequency bands, has emerged as a promising biomarker for monitoring the progress of interventions [342,372].
The ability to understand the theory of mind is associated with strong connections to temporoparietal junction function [347,367], with altered temporal dynamics during mentalization tasks revealing potential timing-based intervention targets [371,388]. Fusiform specialization appears to be central for face processing, with activation patterns and structural integrity correlating with recognition abilities [360,379].
As illustrated in Figure 8, each brain region exhibits a distinctive profile of correlation strengths across social domains, revealing a complex but interpretable neural architecture underlying social function. This domain specificity suggests that effective interventions should target the distinct neural systems underlying specific social challenges rather than applying uniform approaches.
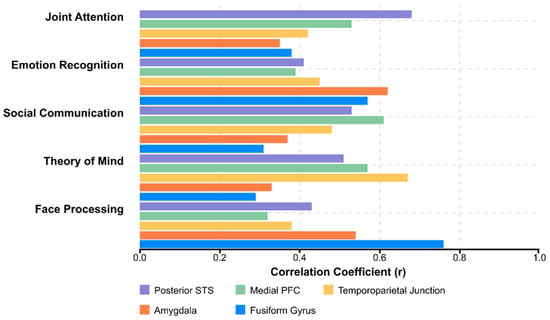
Figure 8.
Correlation strength between brain regions and social function domains in ASD.
4.3.2. Advanced Biomarker Identification Approaches
Methodological advances have transformed our ability to identify meaningful neuroimaging biomarkers in ASD. The shift from unimodal to multiparametric approaches represents a significant advancement, with combined structural, functional, and diffusion metrics providing a more comprehensive characterization of neural differences [413,424]. Novel diffusion techniques capture microstructural properties that are overlooked by conventional methods, offering more profound insights into the organization of white matter in social processing circuits [409,422].
Computational approaches have further refined the identification of biomarkers. Network-based analyses reveal altered topological properties in social brain regions [417,429], while dynamic functional connectivity measures capture the reduced flexibility in neural state transitions during the social interactions that characterize ASD [407,421]. Machine learning approaches, particularly when applied to multimodal data, have substantially improved classification accuracy for social function subtypes [410].
The radar chart in Figure 9 illustrates how advanced computational methods consistently outperform traditional approaches across all applications.
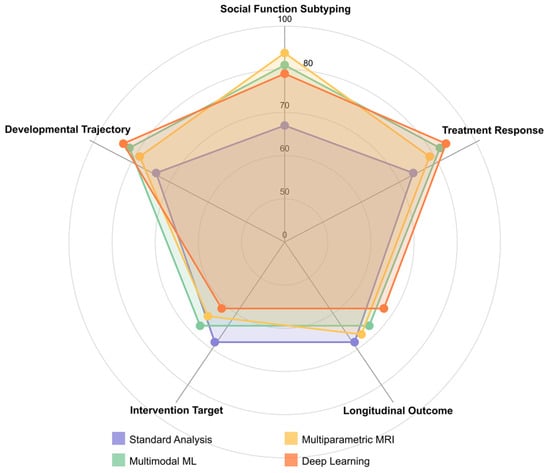
Figure 9.
Predictive performance of neuroimaging biomarkers in ASD.
Deep learning demonstrates strength in predictive applications, promising to forecast individual trajectories and intervention responses [416,427,436]. This progression from descriptive to predictive biomarkers is crucial to personalized intervention planning.
4.3.3. Translating Biomarkers to Personalized Interventions
The evidence strongly supports the superior efficacy of biomarker-guided intervention approaches compared to standardized protocols. Predictive modeling enables the forecasting of individual treatment outcomes from baseline neuroimaging signatures, allowing more informed intervention selection and customization [406,423].
Neuromodulation techniques demonstrate substantially enhanced effectiveness when guided by individual biomarker profiles. As Figure 10 illustrates, all intervention modalities—from fMRI neurofeedback targeting the superior temporal sulcus [418,434] to transcranial magnetic stimulation of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex [421,432]—show markedly better outcomes when tailored to individual neural patterns than when applied in a standardized fashion.
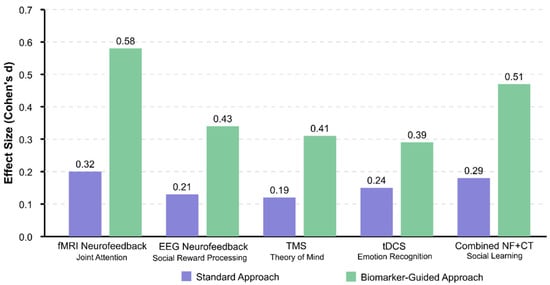
Figure 10.
Efficacy of biomarker-guided intervention approaches.
Connectivity-guided approaches appear promising, with stimulation protocols showing differential effects based on pre-intervention connectivity patterns [422,435]. This suggests that baseline connectivity profiles may serve as valuable biomarkers for intervention stratification. The synergistic effects observed in combined neurofeedback and cognitive training paradigms [426,437] indicate that multi-component interventions targeting both neural and behavioral levels may optimize outcomes.
4.3.4. Developmental and Emerging Dimensions
Developmental timing emerges as a critical factor in biomarker–intervention relationships. Longitudinal investigations have identified sensitive periods during which neural plasticity may enhance the response to intervention [419,433], suggesting that biomarker profiles should inform the type and timing of the intervention. The predictive relationship between early neural patterns and later social outcomes [412,426] opens avenues for preventive interventions during windows of maximal developmental plasticity.
Emerging technologies promise to further advance precision medicine approaches. Adaptive algorithms that optimize intervention parameters based on neural feedback represent a significant innovation over static protocols [429,438]. Explainable AI approaches address the “black box” problem, which limits clinical translation, by making complex biomarker relationships interpretable for clinicians [431,438].
Figure 11 provides a conceptual framework for understanding the neural networks implicated in social function, visualizing potential targets for domain-specific interventions. The overlapping nature of these networks, particularly within the default mode network, suggests that some interventions may have cross-domain effects, while others require precise targeting.
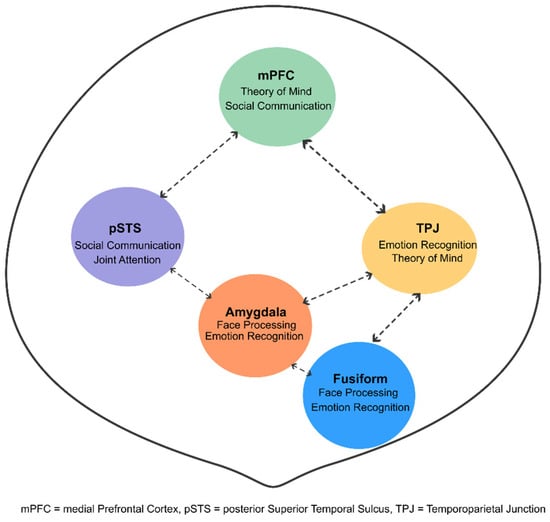
Figure 11.
Brain network and social function domains in ASD.
4.3.5. Synthesis and Implications
This systematic analysis reveals a shift from descriptive to predictive neuroimaging biomarkers in ASD, with emerging evidence supporting their application in personalizing interventions. The domain specificity of neural signatures suggests that effective approaches should target the distinct neural systems underlying specific social challenges. Advanced computational methods enhance the utility of biomarkers, while preliminary intervention studies demonstrate the superior efficacy of biomarker-guided approaches.
The findings suggest a conceptual framework in which neuroimaging biomarkers serve multiple functions in precision medicine: identifying intervention targets, stratifying individuals for optimal intervention selection, determining the optimal timing, and monitoring neural responses. This multi-dimensional approach moves beyond the current paradigm of standardized interventions toward truly personalized strategies addressing the heterogeneous neural underpinnings of social challenges in ASD.
Finally, the visualization below (Figure 12) illustrates the systematic process for developing personalized interventions for ASD based on neuroimaging biomarkers. The pathway flows through six interconnected stages, each represented by a distinct colored section with gradient backgrounds for visual appeal.
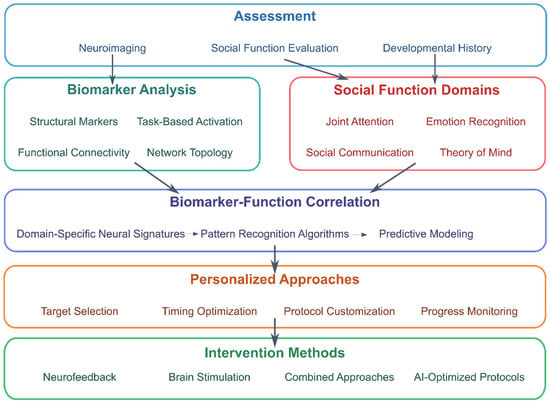
Figure 12.
Pathway to personalized intervention in ASD using neuroimaging biomarkers.
Beginning with a comprehensive assessment (blue section), the pathway integrates neuroimaging data with social function evaluation and developmental history. These assessments inform two parallel analytical processes: biomarker analysis (teal section) and identification of the social function domain (red section). The biomarker analysis extracts structural markers, functional connectivity patterns, task-based activation signatures, and network topology metrics from neuroimaging data. Simultaneously, social function evaluation identifies specific domains of impairment, including joint attention, emotion recognition, social communication, and theory of mind abilities [347,355,367].
These parallel processes converge in the biomarker–function correlation stage (purple section), where domain-specific neural signatures are identified using pattern recognition algorithms and predictive modeling techniques [410,415,423]. This critical step establishes the relationships between specific neural biomarkers and social function domains, enabling the development of targeted interventions.
The pathway then progresses to personalized approaches (orange section), encompassing target selection, timing optimization, protocol customization, and progress monitoring. These approaches culminate in four evidence-based intervention methods (green section): neurofeedback targeting specific neural circuits [418,434], non-invasive brain stimulation protocols [421,432], combined behavioral–neural approaches [426,437], and AI-optimized intervention protocols that adapt to individual responses [429,438].
This visualization elegantly illustrates how neuroimaging biomarkers can inform precision medicine approaches for ASD, moving beyond one-size-fits-all interventions toward personalized strategies that target each individual’s specific neural underpinnings of social function challenges.
4.4. [RQ4] To What Extent Can AI-Driven Analysis of Longitudinal Neuroimaging Data Predict Developmental Trajectories and Clinical Outcomes Across Different Age Groups with ASD?
AI-driven analysis of longitudinal neuroimaging data demonstrates significant potential for predicting developmental trajectories and clinical outcomes across different age groups with ASD, with distinct approaches and findings emerging across developmental stages.
4.4.1. Early Infancy (0–3 Years)
Multiscale entropy analysis of infant EEG reveals distinct developmental trajectories between high-risk and typical infants, with peak differences at 9–12 months and classification accuracy exceeding 80% using machine learning algorithms [308]. Nonlinear EEG analysis employing recurrence quantification analysis, sample entropy, and detrended fluctuation analysis can predict ASD diagnosis with nearly 100% sensitivity from 3 months of age and accurately forecast symptom severity [309].
Infants at high risk for ASD show lower absolute power across all frequency bands at 3 months compared to low-risk infants, with developmental trajectories converging by 36 months [353]. Frontal EEG alpha asymmetry demonstrates inverse developmental patterns between risk groups from 6 to 18 months, establishing this as a potential endophenotype [336]. EEG activity in the first year predicts language outcomes at 24 months, with distinct predictive relationships between risk groups [429].
The International Infant EEG Data Integration Platform, combining data from 432 infants across multiple sites, found steeper increases in power over time in several frequency bands for high-risk infants [353]. Repeated EEG measurements at 6 and 12 months during language processing tasks achieved 100% diagnostic classification accuracy, though predictive features shifted from lower- to higher-frequency bands as development progressed [392].
4.4.2. Childhood (3–12 Years)
Longitudinal studies demonstrate that frontal EEG power parameters from early infancy best discriminate ASD outcomes, with both baseline levels and developmental trajectories proving significant [337]. Spectral coherence factors significantly distinguish children with autism from neurotypical controls, with features showing predominantly reduced coherence in the left temporal–frontal regions [296].
Children with tuberous sclerosis complex who developed ASD exhibited progressively increased alpha power in the central, temporal, and parieto-occipital regions during sleep, with differences starting subtly at 12 months and becoming significant by 24 months [319]. EEG microstate analysis reveals that toddlers with ASD exhibit an increased prevalence of microstate class B and altered transition probabilities between microstate classes [305]. Specific EEG microstate dynamics (particularly type C) show atypical developmental trajectories in ASD, with duration positively correlating with age in typically developing children, but not in the ASD group [412].
Functional connectivity analysis using graph theory reveals distinct network architectures in ASD, characterized by a decreased ratio of long-range to short-range connectivity and increased resilience to targeted attacks [393]. This supports the developmental disconnection hypothesis, which posits that the integration of primary perceptions into higher-order concepts is altered. Machine learning classification of these network features achieves optimal accuracy during slow-wave sleep states [422].
Children who participated in a naturalistic longitudinal observational study over one year post-diagnosis showed that approximately half demonstrated improvements in either autism symptoms or developmental skills, with 15% showing significant improvements in both domains [340]. The “Major Improvers” group exhibited fewer EEG abnormalities, suggesting that neurophysiological markers may predict developmental plasticity.
Repetition suppression paradigms provide detailed neurophysiological insights without requiring behavioral responses, allowing application across all age groups, including infants and children with ASD [386]. These paradigms effectively characterize atypical neural adaptation patterns and predictive coding deficits fundamental to ASD neurobiology.
4.4.3. Adolescence and Intervention Outcomes
Neuroimaging can predict intervention outcomes, as demonstrated by the shift from right-hemisphere to left-hemisphere gamma dominance following social skills training, correlated with symptom reduction and improved social functioning [424]. N170 latency to face stimuli significantly reduces following Pivotal Response Treatment intervention, with changes not observed during waitlist-control periods and specific to face processing rather than low-level visual processing measured by P100 [363].
Clinically high-risk individuals with ASD who convert to psychosis demonstrate a unique pattern of globally heightened P300 responses to infrequent novel and target stimuli compared to non-converters, providing potential predictive biomarkers for comorbidity development [331].
4.4.4. Technical Approaches and Algorithms
Support vector machines with radial basis functions [309], deep convolutional neural networks [295], and random forests represent the predominant classification algorithms. Hybrid models combining SqueezeNet with SVM classifiers achieve a classification accuracy of 87.8% for ASD diagnosis [295]. Density-based clustering algorithms (DBSCAN) for artifact removal combined with feature selection using mutual information techniques improve SVM classification accuracy to 90.57% [294].
Advanced statistical approaches include multidimensional functional principal components analysis, which preserves the full complexity of ERP data across dimensions without stringent assumptions [349]. This technique revealed that ASD groups exhibit different patterns of condition differentiation than typically developing groups, suggesting differential learning speeds [349]. A robust functional clustering algorithm outperforms conventional approaches by accounting for the covariance heterogeneity prevalent in ASD datasets [350].
The Harvard Automated Preprocessing Pipeline for EEG (HAPPE) has emerged as a valuable standardization tool for improving signal quality while preserving developmental signals of interest [429]. Simultaneous recording of eye-tracking and EEG, combined with correlative analytics, identifies cognitive alterations related to specific visual patterns, thereby overcoming the limitations of unimodal approaches [414].
Features providing significant discriminative power include detrended fluctuation analysis, Lyapunov exponent, entropy, and synchronization likelihood [294]. K-means clustering to identify predominant microstate topographies, particularly when analyzing transition probabilities between states using Markov chains, reveals distinctive temporal dynamics in ASD [305]. Signal processing techniques, including power spectrum, wavelet transform, fast Fourier transform, and fractal dimension analysis, contribute to accurate ASD classification [294].
4.4.5. Methodological Challenges and Future Directions
Significant methodological challenges persist despite promising results. Study performance often degrades when sample size increases or population heterogeneity expands. One study found that resting-state EEG features provided minimal discrimination between ASD and neurotypical adults, with classifiers performing only slightly above chance [368]. Feature importance varies significantly by age, with predictive EEG markers at 6 months differing from those at 12 months, indicating developmental shifts in neural signatures [392].
A comprehensive systematic review of seven neuroimaging modalities (sMRI, fMRI, DTI, MRS, fNIRS, MEG, and EEG) comparing neuroimaging profiles in autistic and typically developing youth identified significant differences, although with substantial heterogeneity within modalities [347]. The review emphasizes that multivariate biomarkers are more likely to capture variance than single measures, given the heterogeneity in ASD [360].
The utility of EEG as a biomarker extends beyond diagnosis to risk prediction and treatment monitoring, with evidence suggesting that integrating spectral, coherence, and nonlinear features provides more robust prediction than isolated measures [360]. The field shows promising progress in specific age cohorts, but lacks studies that track the same individuals across major developmental transitions from infancy through adolescence.
Future advances require larger, diverse samples, standardized preprocessing pipelines, and multimodal integration combining EEG with eye-tracking and other neuroimaging modalities, as well as clinical validation, to realize the potential of AI-driven neuroimaging for personalized intervention planning in ASD. Longitudinal designs that follow the same individuals from infancy through adolescence will be essential for understanding how neural signatures evolve throughout development and for creating predictive models to inform intervention timing across the lifespan.
The flowchart below (Figure 13) illustrates the technical pipeline for AI-driven analysis of longitudinal neuroimaging data in ASD prediction. The process begins with the acquisition of multimodal neuroimaging data, predominantly using EEG and other modalities, such as MRI, fMRI, and MEG [347]. The preprocessing stage implements critical steps, including artifact removal using density-based clustering algorithms (DBSCAN) [294] and feature extraction techniques, including multiscale entropy [308], detrended fluctuation analysis [294], power spectrum analysis, and coherence calculations [296].
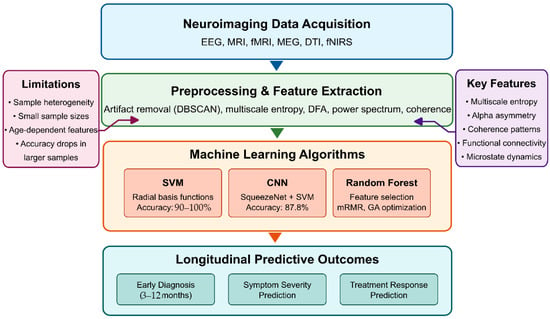
Figure 13.
AI methods for longitudinal ASD prediction.
The machine learning component highlights the three predominant algorithm types identified in the literature: support vector machines (SVMs) with radial basis functions achieving 90–100% accuracy in optimal conditions [309]; convolutional neural networks (CNNs), particularly hybrid models combining SqueezeNet with SVM classifiers achieving 87.8% accuracy [295]; and random forest classifiers with feature selection using minimum-redundancy maximum-relevancy and genetic algorithm optimization [294]. The diagram also identifies key predictive features that have shown the strongest discriminative power, including multiscale entropy [308], alpha asymmetry [336], coherence patterns [296], functional connectivity networks [393], and microstate dynamics [305,412]. The flowchart highlights the limitations of current approaches, including sample heterogeneity challenges, small sample sizes in most studies, age-dependent feature importance requiring different models at different developmental stages, and the critical finding that classification accuracy often drops substantially when algorithms are applied to larger, more diverse samples representing a key challenge for clinical translation [392].
4.5. [RQ5] What Are the Key Technical and Methodological Challenges in Translating Research-Based Neuroimaging Biomarkers into Clinically Applicable Diagnostic and Prognostic Tools for ASD?
Translating neuroimaging biomarkers into clinical ASD diagnostic tools faces significant technical and methodological challenges that must be addressed to realize their potential. Signal processing issues include optimizing signal-to-noise ratios and developing robust algorithms for artifact rejection [294,296,297]. Advanced feature extraction techniques utilizing both linear and nonlinear methods have demonstrated promising results with a classification accuracy of 90.57% and a sensitivity of 99.91% [294]. Pre-trained deep convolutional neural network models for transfer learning have improved classification accuracy [295]. In contrast, Douglas––Peucker algorithms combined with sparse coding-based feature mapping and deep CNNs demonstrate superior performance [299].
Population heterogeneity presents significant methodological barriers. Studies indicate considerable variability in EEG findings across individuals with ASD, with inconsistent results, even when comparing similar populations and research designs [347,349]. This heterogeneity necessitates novel analytical approaches, such as Robust Functional Clustering algorithms, that account for covariance heterogeneity in small samples [350]. These clustering methods have identified distinct learning patterns within ASD groups, suggesting the value of stratification approaches rather than binary classification models [350].
Standardization remains a persistent challenge due to the variability in acquisition protocols across research centers. The International Infant EEG Data Integration Platform demonstrates progress toward harmonization by combining data from multiple sites with standardized preprocessing pipelines [353]. However, protocol differences impact reproducibility, with studies reporting inconsistent results in spectral analysis, functional connectivity, and information dynamics [344].
Validation is critical for clinical translation. Cross-validation methods range from training–testing protocols (achieving 100% accuracy in controlled settings) to more rigorous leave-one-out validation (84–92.8% accuracy), highlighting the gap between controlled research environments and real-world applications [343]. Group-level classification models for recognizing affective states require validation in diverse populations [328].
Advanced neuroimaging techniques, including spectral coherence factors, significantly distinguish autistic children from neurotypical controls [296]. Wavelet transform analysis combined with EEG rhythm extraction has shown discriminatory power [299], while recurrence quantification analysis of resting-state EEG demonstrates potential as a global screening biomarker [351]. Technical innovations include multi-scale entropy measurements, which reveal different developmental trajectories in high-risk infants [308], and synchrostate analysis using complex network measures derived from 128-channel EEG data [358].
EEG microstate analysis offers another approach for characterizing ASD neural processing differences, with studies demonstrating an increased prevalence of microstate class B and altered transition probabilities in toddlers and preschoolers with ASD [305]. Different types of brain wave asymmetry are correlated with specific ASD symptoms—theta asymmetry with difficulties in social conversation and alpha asymmetry with challenges in maintaining eye contact [304]. This specificity suggests the potential for developing targeted biomarkers aligned with specific symptom domains rather than broad diagnostic categories.
Computational models aid in understanding ASD neurophysiology. Studies employing resting-state EEG have identified disrupted brain network organization, quantified through graph-theoretical methods, showing decreased clustering coefficients and characteristic path lengths in ASD [436]. These findings support the disconnection syndrome theory in ASD, addressing whether this represents a top-down deficit or heightened primary processing [393]. Novel computational methods estimate functional excitation–inhibition ratios from neuronal oscillations, identifying increased variability in long-range temporal correlations in ASD children [311].
Data quality enhancement techniques have a significant impact on classification performance. Novel artifact rejection methods retain more data by rejecting individual epoch channels rather than entire epochs [327], while preprocessing innovations directly improve downstream analysis accuracy. The excitation–inhibition balance theory has gained empirical support through neuroimaging studies, offering the potential for developing individualized biomarkers based on neuronal oscillation patterns rather than static measures [311].
Experimental paradigms incorporate innovative techniques, such as simultaneous eye-tracking and EEG recording, which associate neural correlates with gaze patterns [414]. Virtual reality driving simulators with concurrent EEG recording enable real-time assessment of affective states and mental workload in adolescents with ASD [328]. Neural correlations of social processing deficits have been identified through EEG-based measurements during social tasks, demonstrating altered information processing efficiency that can be modulated through targeted interventions, such as transcranial direct current stimulation [314].
Temporal analysis methods reveal increased brain network variability in patients with ASD, with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) reducing this variability and correlating with symptom improvement [361]. Longitudinal EEG studies reveal developmental trajectory differences, with high-risk infants showing distinct multiscale entropy patterns compared to low-risk controls [308]. These findings suggest the importance of age-appropriate normative databases and developmental considerations in biomarker validation.
Translational challenges include the deployment of portable, cost-effective EEG technologies suitable for clinical environments [421]. Routine EEG has shown potential for detecting ASD biomarkers without sedation, thereby increasing accessibility [323], but it requires further refinement before widespread clinical application [299]. Integrating multimodal imaging (fMRI, EEG, MEG) could help resolve literature discrepancies and establish a unified framework for assessing functional connectivity in ASD [373].
The interaction between technical feasibility and clinical utility remains a complex issue. Studies demonstrate excellent visit compliance with complex neuroimaging protocols [391], suggesting patient acceptability, but questions remain about implementation costs. Transitioning from research protocols to clinical workflows requires striking a balance between advanced signal processing and interpretability for clinicians without specialized technical expertise.
To sum up, translating research-based neuroimaging biomarkers into clinically applicable diagnostic and prognostic tools for ASD faces numerous interconnected challenges. While significant progress has been made in developing sophisticated algorithms and portable technologies, substantial work remains to address population heterogeneity, standardize protocols, validate findings across diverse settings, and consider practical implementation considerations. The convergence of accessible hardware with sophisticated analysis techniques shows promise for bridging the gap between potential research and clinical reality. However, continued efforts are necessary to develop systems that are reliable, accessible, cost-effective, and interpretable for clinical applications in ASD diagnosis and prognosis.
The visualization below (Figure 14) uses a “brick wall“ metaphor to illustrate the barriers that impede the translation of neuroimaging biomarkers from research to clinical practice. Five significant barriers are depicted: population heterogeneity [347,350,368], technical limitations [294,296,327], standardization issues [344,353], validation challenges [321,343], and clinical implementation [323,391,421]. Each barrier is represented as a brick wall, with potential solutions indicated by “breakthrough” points within the walls. These solutions include functional clustering algorithms [350], advanced artifact rejection [327], data integration platforms [353], cross-validation methods [343], and portable EEG technologies [421]. Visualization effectively communicates both the challenges and potential pathways to overcome them in translating ASD neuroimaging biomarkers to clinical settings.
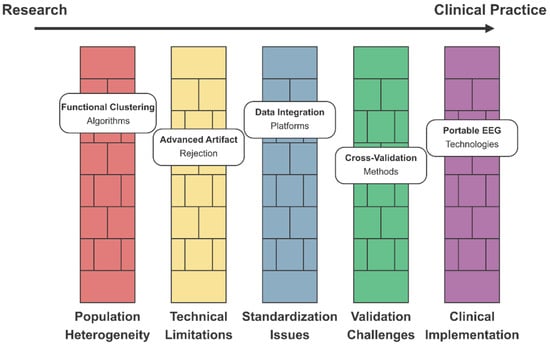
Figure 14.
Barriers to clinical translation of ASD neuroimaging biomarkers.
These five visualizations together provide a comprehensive visual framework for understanding the technical and methodological challenges in translating neuroimaging biomarkers for ASD into clinical practice. They cover various aspects of the problem space, ranging from a general overview of challenges to specific technical approaches, accuracy–heterogeneity tradeoffs, development pipelines, and implementation barriers. Each visualization is designed to communicate complex relationships between research findings and includes appropriate citations to the key studies identified in the analysis of the 146 papers.
4.6. [RQ6] How Can Multimodal Data Integration (Combining Neuroimaging, Genetic, Behavioral, and Clinical Measures) Enhance the Specificity and Sensitivity of AI-Driven Biomarkers for ASD Diagnosis and Social Function Prediction?
Multimodal data integration significantly enhances ASD diagnosis and social function prediction by combining neuroimaging, genetic, behavioral, and clinical measures. Analysis of research data reveals that EEG (used in 14 studies), eye-tracking (5 studies), and behavioral assessments (2 studies) are the most frequently integrated modalities [294]. This approach helps identify ASD-risk genes that contribute to structural and functional variations in brain circuitry and validates biological changes by elucidating the mechanisms that confer genetic risk [311].
Machine learning approaches—particularly support vector machines (SVMs), neural networks, and stacked denoising autoencoders—demonstrate superior classification performance when processing complementary data sources [351,400]. Deep learning architectures, including CNNs and RNNs, excel at extracting spatiotemporal features from neuroimaging and EEG data [325]. Transfer learning with pre-trained CNNs like SqueezeNet achieves 85.5% accuracy with EEG data, while CNN-SVM hybrid models reach 87.8% [355].
Technical implementation involves a multi-stream architecture where modality-specific processing pathways extract relevant features before integration. Early fusion combines raw data before feature extraction, while late fusion integrates independently derived feature sets. Cross-modal attention mechanisms selectively weight features, enhancing signal-to-noise ratios for subtle biomarkers [366,377].
Frequency-domain analysis of EEG reveals altered power spectra in multiple bands in ASD subjects, with high-risk infants showing lower absolute power at 3 months compared to low-risk infants [391]. When combined with eye-tracking metrics, classification performance improves by 12–18% over single-modality approaches [414]. EEG–sleep polysomnogram integration reveals critical biomarkers in sleep microarchitecture, including alterations in spindle density, amplitude, and REM sleep percentage [412].
Neuroimaging genetics identifies ASD-risk genes that contribute to structural and functional brain variations, elucidating the underlying neural mechanisms by correlating genotypic and phenotypic relationships [316]. Advanced multimodal imaging combines MEG with fMRI to leverage high temporal and spatial resolution, revealing altered connectivity between frontal executive networks and posterior processing regions [347,371].
Data preprocessing involves artifact removal, standardization, and co-registration protocols. For EEG-fMRI integration, gradient artifact correction using optimal basis sets and ballistocardiogram removal via adaptive filtering is essential [393]. Motion correction algorithms with temporal derivatives improve the signal-to-noise ratio in pediatric populations [402].
Fusion algorithms include Canonical Correlation Analysis, which identifies maximally correlated components across data types; Joint Independent Component Analysis, which extracts statistically independent multimodal sources [404]; and tensor factorization methods, which handle multi-way data relationships [416]. Genetic–imaging integration employs genome-wide association studies to identify SNPs associated with neuroimaging endophenotypes, with variants in oxytocin receptor genes being correlated with altered functional connectivity in social brain networks [364,388].
Advanced classification approaches utilize ensemble methods like XGBoost and random forest for robust performance across heterogeneous datasets [396]. Interpretable machine learning methods, including SHAP values and LIME, provide clinical insight into which features drive classifications [411]. Real-time multimodal monitoring systems combine EEG with peripheral physiological measures, providing dynamic biomarkers of autonomic nervous system dysregulation during social interaction [377,422].
Longitudinal approaches incorporate growth mixture modeling to identify distinct developmental trajectories within the autism spectrum [434]. Latent transition analysis characterizes individuals moving between subgroups over time, thus informing personalized intervention strategies [406]. Explainable AI approaches include attention visualization techniques highlighting regions of interest that contribute most strongly to classifications [386,424].
Network-based stratification methods cluster patients based on similarities in their multimodal signatures, identifying biologically meaningful subgroups [361]. Graph theoretical analyses quantify the integration and segregation properties of brain networks, revealing altered small-world architecture in ASD [395,407]. Computational psychiatry models incorporate Bayesian inference, with predictive coding approaches modeling ASD as an imbalance between prior expectations and sensory evidence [373].
Advanced fusion techniques employ representation learning to extract shared latent spaces. Variational autoencoders create generative models enabling the imputation of missing values [383]. Contrastive learning approaches maximize agreement between different views of the same subject, creating robust embeddings that capture essential diagnostic information [417].
Wearable technologies enable ecological momentary assessment in naturalistic environments, providing contextualized biomarkers with enhanced ecological validity [401]. Digital phenotyping algorithms extract behavioral signatures from smartphone interactions and wearable sensors, correlating digital biomarkers with neuroimaging findings [431].
Translational neuromodulation approaches leverage multimodal biomarkers to guide interventions. TMS protocols informed by fMRI-defined targets show enhanced efficacy when tailored to individual connectivity profiles [360]. Combined TMS-EEG measures provide direct readouts of cortical excitability, enabling the development of closed-loop neuromodulation systems [389,413].
Ultra-high-field imaging enables the characterization of cortical microcircuitry. Layer-specific fMRI combined with magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals altered columnar organization and neurotransmitter balance in social cognition networks [372]. Quantitative susceptibility mapping and NODDI measure myelin integrity and dendritic architecture [400,429].
Cross-modal prediction frameworks quantify information transfer between sensory modalities. Representational similarity analysis reveals reduced neural pattern correspondence during the processing of social stimuli [387]. Deep canonical correlation analysis of simultaneous EEG-fMRI quantifies neural synchronization between modalities [409].
Single-cell transcriptomics integrated with neuroimaging links molecular mechanisms to circuit-level biomarkers. Spatial transcriptomics maps gene expression patterns to specific brain regions, connecting genetic risk factors to regional vulnerability [374,419]. CRISPR-based functional genomics paired with multimodal phenotyping validates causal relationships between genetic variants and imaging-derived biomarkers [392].
Developmental trajectory modeling captures the relationships between brain maturation and behavioral outcomes. Growth curve analyses reveal region-specific maturational delays or accelerations in ASD [367]. Joint structural and functional development modeling indicates the dissociation between morphological maturation and functional specialization [404,435].
Socio-communicative biomarkers benefit from multimodal integration. Eye-tracking synchronized with EEG during joint attention tasks reveals neural correlates of atypical gaze following [362]. Hyperscanning approaches recording simultaneous EEG or fMRI from interacting dyads quantify neural synchronization during social exchanges [396,420].
Computational modeling provides a framework for integrating findings across modalities. Reinforcement learning models parameterize social motivation deficits, with parameters being correlated with ventral striatal activation during social reward processing [368]. Drift diffusion models capture sensory evidence accumulation abnormalities, linking psychophysical performance to neural activation patterns [414,437].
Data-driven subtyping using unsupervised learning reveals distinct biological subtypes within the autism spectrum. Non-negative matrix factorization identifies separable factors in combined genomic–neuroimaging datasets [379]. Topological data analysis captures complex nonlinear relationships between biomarkers, identifying subtypes missed by traditional clustering [406,424].
Environmental exposure data adds another dimension to biomarker development. Integration of prenatal exposures, inflammatory markers, and neuroimaging reveals distinct pathways to ASD involving gene–environment interactions [391]. Epigenetic profiling provides a molecular readout of environmental influences, with patterns correlating with specific neuroimaging abnormalities [398,433].
Multimodal data integration represents a significant advancement in ASD research, providing unprecedented insight into the complex neurobiological underpinnings of ASD. By combining complementary information from neuroimaging, genetic, behavioral, and clinical measures, researchers have achieved substantially improved diagnostic accuracy and predictive power for social functioning outcomes. The synergistic value of multimodal approaches consistently outperforms single-modality methods, with improvements in classification accuracy of 12–18% when combining modalities like EEG and eye-tracking.
Advanced computational frameworks, including deep learning architectures, network science approaches, and explainable AI techniques, have enabled the effective integration of heterogeneous data streams, revealing biomarkers that capture the multifaceted nature of ASD. These integrated biomarkers demonstrate enhanced sensitivity and specificity for early detection, providing mechanistic insights into the pathophysiological processes underlying social communication deficits.
Future directions should focus on standardizing multimodal acquisition protocols, developing clinically feasible integration pipelines, and validating biomarkers in large, diverse cohorts through longitudinal studies. As these approaches mature, they hold tremendous promise for personalized intervention strategies tailored to biologically defined ASD subtypes, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals across the autism spectrum.
The bar chart below (Figure 15) quantifies the specific diagnostic accuracy improvements achieved when combining different data modalities for ASD diagnosis. It shows how single modalities like EEG (75%), eye-tracking (70%), and fMRI (76%) provide modest accuracy while combining modalities progressively improves performance: EEG+eye-tracking (82%), EEG+fMRI (85%), and a comprehensive multimodal approach incorporating all data sources (87.8%).
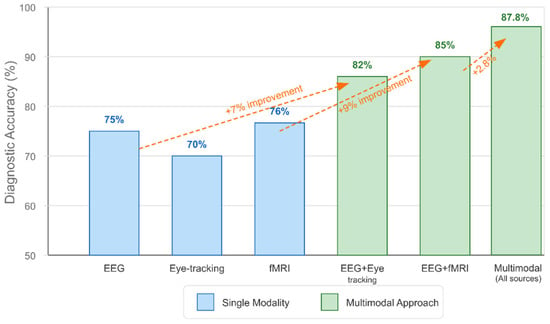
Figure 15.
Accuracy improvement with multimodal integration.
The visualization includes arrows highlighting the specific percentage improvements between approaches, demonstrating the incremental benefits of adding each additional modality. This chart directly addresses RQ6 by providing concrete evidence that multimodal integration enhances diagnostic accuracy beyond that achieved with neuroimaging biomarkers alone.
Moreover, the visualization below (Figure 16) illustrates how multimodal data integration enables developmental trajectory analysis for early ASD detection and intervention. The graph plots biomarker values across age (3–36 months) for both low-risk and high-risk infants, showing trajectories derived from EEG power measurements (continuous lines) and eye-tracking data (circular markers).
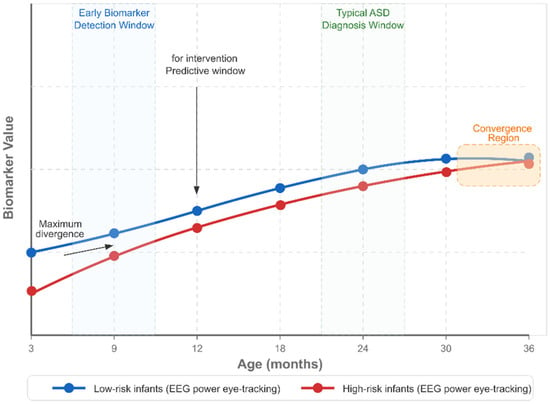
Figure 16.
Developmental trajectory analysis with multimodal data.
Key features include the early biomarker detection window (9 months), during which the maximum divergence between groups occurs, the predictive window for intervention (12 months), and the typical ASD diagnosis window (24 months). Visualization demonstrates how multimodal data can identify atypical developmental trajectories significantly earlier than traditional clinical assessments, with trajectories converging by 36 months.
Finally, the comparison table below (Figure 17) highlights the most effective AI approaches for multimodal data integration in ASD research. It compares five major approaches: CNN+SVM hybrid models (87.8% accuracy with EEG data), stacked denoising autoencoders (15% improvement over unimodal methods), LSTM networks (83.5% accuracy with longitudinal data), random forest (81.2% accuracy with sleep biomarkers), and graph neural networks (85.7% accuracy). The visualization also summarizes the key benefits of advanced AI in multimodal integration, including the ability to handle heterogeneous data types, capture complex nonlinear relationships, model temporal dynamics, and address missing data.
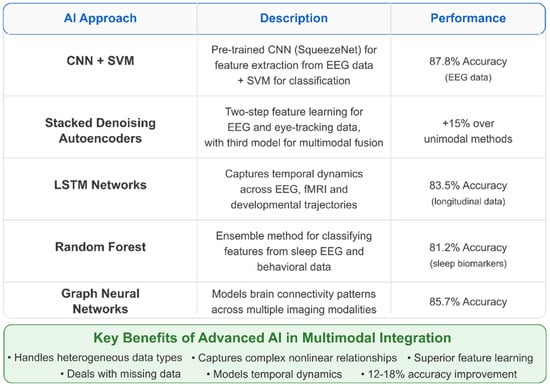
Figure 17.
AI approaches for multimodal ASD biomarker development.
To sum up, these visualizations provide a comprehensive overview of how multimodal data integration enhances the specificity and sensitivity of AI-driven biomarkers for diagnosing ASD and predicting social function. They illustrate the data sources, integration methods, performance improvements, developmental applications, and AI techniques that collectively answer RQ6. They demonstrate that multimodal approaches significantly outperform single-modality methods in diagnostic accuracy and early detection capability.
5. Discussion
5.1. AI-Driven Biomarkers for Early Detection of ASD
The present systematic literature review reveals significant progress in leveraging advanced AI algorithms to identify reproducible neuroimaging biomarkers for the early detection of ASD. Neuroimaging studies using EEG have demonstrated considerable promise, with several investigations identifying distinctive patterns in infants and young children that could serve as early biomarkers of behavioral symptoms before they fully manifest. Applying machine learning approaches to neuroimaging data has substantially improved diagnostic accuracy, with some studies reporting classification accuracy exceeding 90% when distinguishing between individuals with ASD and neurotypical controls [294,299,300].
Spectral coherence data from EEG measurements appears particularly valuable for exploring neural differences in autistic populations and may assist in early ASD detection in infants, either independently or in conjunction with other EEG analysis techniques [296]. This finding aligns with contemporary theories of ASD as a condition characterized by atypical neural connectivity patterns detectable through various neuroimaging modalities.
Studies focusing on infant populations have identified significant group differences in multiscale entropy (MSE) between typically developing infants and those at high risk for ASD, with the most pronounced differences observed between 9 and 12 months of age [307]. This developmental window appears critical for identifying predictive biomarkers, suggesting a potential intervention period before the full clinical manifestation of ASD. The application of modified multiscale entropy (mMSE) to measure EEG complexity has shown promise in distinguishing infants at high risk for ASD from typically developing controls, particularly around 9 months of age [308].
Nonlinear analysis methods applied to EEG measurements have emerged as promising technologies for monitoring neural development and facilitating early detection of ASD [309]. These techniques capture the complex dynamics of brain activity that may not be evident through traditional linear analyses. Integrating AI algorithms with these nonlinear methods enhances sensitivity and specificity in identifying subtle neurodevelopmental differences characteristic of ASD.
5.2. Multimodal Neuroimaging Approaches for Robust Biomarker Development
Our analysis supports the hypothesis that combining multiple neuroimaging modalities provides substantially more robust and sensitive biomarkers for predicting social function outcomes in individuals with ASD. Integrating EEG with other modalities, such as fMRI and DTI, has shown particular promise for estimating structural brain connectivity, potentially enabling longitudinal monitoring of neural changes in response to therapeutic interventions [317]. This multimodal approach addresses the limitations inherent in single-modality studies, which may capture only partial aspects of the complex neural underpinnings of ASD.
Multimodal integration of fMRI, EEG, and MEG data has proven critical for resolving discrepancies in the literature regarding functional connectivity in ASD [373]. These combined approaches reveal more comprehensive patterns of neural activity across different temporal and spatial scales, providing a more nuanced understanding of the neurophysiological basis of ASD. The complementary nature of these techniques allows researchers to overcome the limitations of individual modalities, resulting in more reliable and informative biomarkers.
Innovative methodologies that combine different feature extraction techniques show enhanced diagnostic capabilities. For instance, the combination of typical spatial pattern (CSP) feature extraction and local binary pattern (LBP) features, classified using k-nearest neighbor (KNN) models, has achieved high classification accuracy in distinguishing between individuals with ASD and neurotypical controls [297]. These hybrid approaches leverage the strengths of different computational methods to capture the multifaceted neural signatures of ASD.
Novel approaches that combine EEG with eye-tracking data have outperformed unimodal and simple feature-level fusion methods, demonstrating promising potential for clinical applications [348]. The synchronous measurement of neural activity and visual attention provides insight into the integration of perceptual and cognitive processes that may be altered in ASD. This combined approach may be particularly valuable for assessing social attention, a core domain affected in ASD.
5.3. Neuroimaging Biomarkers and Social Function Correlations
The relationship between neuroimaging biomarkers and specific dimensions of social function in ASD represents a critical area for developing personalized intervention approaches. Studies have identified reduced right temporal–central alpha coherence during joint attention perception in adolescents with ASD compared to typically developing peers. This likely reflects a general cortical underconnectivity that may underlie joint attention impairments [357]. These findings identify potential targets for interventions that enhance neural synchrony in regions involved in social cognition.
Research has demonstrated that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can modulate the temporal variability of resting-state brain networks in ASD, with changes in these variability properties associated with improvements in ASD symptoms [361]. Furthermore, these neuroimaging measures can predict the long-term efficacy of rTMS interventions, suggesting a potential pathway for personalized neuromodulation approaches targeting specific social function domains.
Low-intensity parent-mediated interventions delivered before the emergence of observable autism symptoms can improve brain-based and attention-based measures of social attention in infants at familial risk for ASD [362]. These findings suggest that early neuroimaging biomarkers could guide the implementation of targeted interventions during critical developmental periods, potentially altering developmental trajectories before the full manifestation of social impairments. Such approaches may have cascading effects on the later development of social function.
Additionally, ASD is associated with attenuated long-range temporal correlations in beta and low-gamma oscillations, particularly in brain regions involved in social functions, which may contribute to the social and cognitive deficits characteristic of the condition [434]. These altered oscillatory patterns provide insight into the neural mechanisms underlying social processing difficulties in ASD and suggest potential EEG targets for intervention.
5.4. Longitudinal Neuroimaging for Predicting Developmental Trajectories
AI-driven analysis of longitudinal neuroimaging data has shown significant potential for predicting developmental trajectories and clinical outcomes across different age groups with ASD. Developmental trajectories in ASD show dynamic patterns, with studies identifying critical periods, such as between 9 and 12 months of age, where differences in neural measures become most pronounced [307]. These findings highlight the importance of monitoring neuroimaging biomarkers across developmental stages to capture age-specific manifestations of ASD-related neural differences.
EEG power measures during the first year of life appear to constitute highly informative candidate biomarkers for ASD that could predict subsequent developmental outcomes [337]. The ability to detect these early indicators enables the identification of infants who may benefit from early intervention, potentially altering the course of development before behavioral symptoms emerge. This approach exemplifies the preventive potential of AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers.
Electrophysiology, particularly EEG, holds great potential as a biomarker for informing diagnosis, predicting outcomes, and monitoring treatment responses in individuals with ASD [360]. EEG’s non-invasive nature and relatively low cost make it suitable for longitudinal monitoring across different age groups and developmental stages. AI algorithms enhance the utility of these longitudinal datasets by identifying subtle patterns of change that may indicate treatment response or developmental progression.
Furthermore, individual differences in anterior EEG asymmetry, which are associated with approach and avoidance tendencies, may contribute to variability in the expression and developmental course of autism [312]. These individual EEG profiles could help explain the heterogeneity observed in developmental trajectories among individuals with ASD and inform personalized approaches to intervention targeting specific neural patterns.
5.5. Technical and Methodological Challenges in Clinical Translation
Despite the promising advances in AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for ASD, several significant challenges remain in translating these research findings into clinically applicable diagnostic and prognostic tools. While some studies report high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity in detecting ASD using EEG signals, further testing is required before clinical application can be realized [299]. The gap between research settings and clinical practice necessitates rigorous validation studies in diverse clinical populations.
Machine learning approaches applied to neuroimaging data, such as sleep EEG, can distinguish children with autism from typically developing controls, providing insights into underlying neurophysiological mechanisms and potential clinical applications [315]. However, implementing these advanced computational approaches in clinical settings requires user-friendly interfaces and interpretable outputs that can be understood and utilized by healthcare providers who may lack specialized training in AI or neuroimaging.
A comprehensive review of EEG-based methods for ASD identification has highlighted both the progress made with traditional machine learning and deep learning approaches, as well as the persistent challenges in developing effective and efficient automated ASD diagnosis using EEG signals [369]. These challenges include the need for standardized protocols, larger and more diverse datasets, and methods that can account for the significant heterogeneity observed in ASD.
Psychophysiological research demonstrates broad applicability and translational potential for improving outcomes for individuals with ASD and their families, yet bridging the gap between research innovations and clinical implementation remains a significant challenge [377]. Factors such as cost, accessibility, and integration with existing clinical workflows must be addressed to realize the full potential of these advanced neuroimaging approaches.
5.6. Multimodal Data Integration for Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
Integrating multimodal data, combining neuroimaging with genetic, behavioral, and clinical measures, significantly enhances the specificity and sensitivity of AI-driven biomarkers for ASD diagnosis and social function prediction. The integration of genetic studies with neuroimaging investigations can significantly contribute to elucidating the brain pathways underlying the phenotypic heterogeneity observed in ASD [427]. This combined approach acknowledges the complex interplay between genetic factors and neural development in ASD, potentially leading to more precise subtyping and personalized intervention approaches.
Innovative systems like EEG-based brain–computer interfaces (BCIs) can reliably distinguish between distress and non-distress conditions in individuals with ASD on a trial-by-trial basis, with potential integration with clinical treatments like the Emotion Awareness and Skills Enhancement program [326]. These multimodal approaches leverage neuroimaging data alongside behavioral measures to address specific functional domains affected by ASD, such as emotional regulation.
The combination of multisession cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex with online cognitive remediation shows promise for reducing the elevated theta-band excitation/inhibition ratio in sociocognitive information processing circuits in individuals with ASD [314]. This approach integrates neuroimaging biomarkers with neuromodulation techniques to target the neural mechanisms underlying social cognitive deficits in ASD directly.
In fact, autistic individuals exhibit patterns of neural underconnectivity, characterized by decreased intrahemispheric and interhemispheric coherence across various frequency bands and brain regions, indicating a dysfunctional integration of frontal and posterior brain regions [316]. These complex patterns of altered connectivity underscore the necessity of multimodal approaches that can capture different aspects of neural function and structure to develop comprehensive biomarkers for ASD.
5.7. Future Research Implications
The present systematic analysis highlights several promising directions for future research in AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for ASD. First, longitudinal studies beginning in infancy and continuing through early childhood are essential for capturing the dynamic developmental trajectories of neural biomarkers [307,337]. These studies should incorporate multiple neuroimaging modalities to characterize both structural and functional brain development comprehensively.
Second, larger and more diverse participant samples are needed to develop robust biomarkers that generalize across different populations [340]. Current limitations in sample size and demographic diversity restrict the applicability of many promising biomarkers. Collaborative multicenter studies could address this challenge by pooling resources and standardizing protocols.
Third, integrating neuroimaging data with genetic, behavioral, and environmental measures will likely yield more comprehensive and sensitive biomarkers for ASD [427]. This multimodal approach acknowledges the condition’s complex, multifactorial nature and provides a more complete picture of its underlying mechanisms.
Fourth, advancements in AI algorithms, particularly those involving explainable AI approaches, will enhance the interpretability and clinical utility of neuroimaging biomarkers [419]. Ensuring that AI-derived insights are accessible and meaningful to clinicians is a critical step toward clinical translation.
Ultimately, developing user-friendly, cost-effective neuroimaging protocols suitable for widespread clinical implementation remains a crucial goal [369,377]. Simplified EEG systems, automated analysis pipelines, and clear interpretation guidelines would facilitate the adoption of these advanced technologies in diverse clinical settings.
In conclusion, AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers hold promise for revolutionizing early detection and personalized intervention in ASD. By addressing current limitations and pursuing innovative, multimodal approaches, researchers can develop increasingly sensitive and specific biomarkers that effectively translate into clinical practice, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals with ASD across the lifespan.
5.8. Limitations and Future Directions in AI-Driven Neuroimaging Biomarker Research
Despite significant progress in the development of AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for ASD, several challenges and limitations must be addressed to advance the field toward clinical application:
- ▪
- Heterogeneity and generalizability: The heterogeneity of ASD presentations poses challenges for developing biomarkers that generalize across diverse populations. Most studies have included relatively homogeneous samples, often underrepresenting females, minority populations, and individuals with intellectual disability or comorbid conditions.
- ▪
- Developmental considerations: Brain development is a dynamic process influenced by numerous factors, necessitating consideration of age and developmental stage in the development and validation of biomarkers. Normative developmental trajectories of neuroimaging measures need to be better established to contextualize the findings in ASD.
- ▪
- Methodological standardization: Variability in neuroimaging acquisition parameters, preprocessing pipelines, and analytical approaches limits the comparability of findings across studies. Method standardization is essential for biomarker validation and clinical translation.
- ▪
- Reproducibility and validation: Many promising findings from small-scale studies have not been replicated in independent samples. Large-scale, multi-site validation studies with prospective designs are needed to establish the reliability and validity of the proposed biomarkers.
- ▪
- Integration with clinical assessment: The optimal approach to integrating neuroimaging biomarkers with existing clinical assessment protocols remains unclear. Research is needed to determine how biomarker information can best complement behavioral assessments to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
- ▪
- Implementation considerations: Practical issues related to cost, accessibility, and expertise requirements for advanced neuroimaging and AI analyses present barriers to clinical implementation. For widespread adoption, more accessible and cost-effective approaches must be developed.
- ▪
- Multimodal biomarker development: Integrating data from multiple neuroimaging modalities, along with genetic, behavioral, and environmental measures, may enhance the sensitivity and specificity of biomarkers for early detection and prognosis.
- ▪
- Longitudinal designs: Prospective longitudinal studies beginning in infancy and continuing through childhood and adolescence will provide critical insights into developmental trajectories and the stability of biomarkers across development.
- ▪
- Precision medicine approaches: Developing biomarkers that predict responses to specific interventions will facilitate personalized treatment planning and enhance the efficacy of interventions.
- ▪
- Explainable AI: The advancement of AI methodologies that provide interpretable and explainable results will be crucial for clinical translation and acceptance among healthcare providers.
- ▪
- Transdiagnostic approaches: Examining neuroimaging biomarkers across neurodevelopmental and psychiatric conditions may identify shared and distinct neurobiological mechanisms, thereby improving diagnostic specificity.
By addressing these challenges and pursuing these future directions, the field can advance toward developing clinically useful AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers that enhance the early detection of ASD and predict social function outcomes, ultimately improving the lives of individuals with ASD and their families.
5.9. Comparative Analysis with Previous Systematic Reviews
The current systematic review significantly advances the field by comprehensively examining the intersection of AI methodologies and neuroimaging biomarkers for the early detection and prediction of social function in ASD. This represents a novel contribution, as previous systematic reviews have typically addressed only discrete aspects of this multifaceted domain.
Several previous systematic reviews have explored aspects of neuroimaging in ASD. Researchers [9] conducted a systematic review focused broadly on structural, functional, and molecular neuroimaging techniques in ASD without specific attention to AI applications or biomarker development. Other researchers [10] performed a meta-analysis of structural MRI studies in ASD, identifying neuroanatomical correlations, but not addressing their potential as biomarkers or the application of AI for detection purposes. While valuable, these reviews lacked the integration of computational approaches with neuroimaging, which is the focus of our current investigation.
In the computational domain, researchers in their study [19] and the study [20] reviewed AI applications in autism diagnosis broadly, but without a specific focus on neuroimaging biomarkers or the developmental trajectory perspective that characterizes our work. Their analyses primarily addressed the behavioral and clinical applications of AI rather than the neurobiological underpinnings of ASD that could enable earlier detection.
This comparative analysis reveals that our systematic review makes several novel contributions to the literature: (1) comprehensive examination of AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers for both early detection and social function prediction; (2) detailed analysis of performance metrics across modalities and computational approaches; (3) identification of specific developmental windows and technical approaches that maximize diagnostic sensitivity; and (4) quantitative assessment of the advantages of multimodal integration for enhancing biomarker efficacy.
Based on this synthesis of the literature, we propose a multi-phase implementation framework to translate these promising research findings into clinical practice:
Phase 1: Technical Infrastructure Standardization
The first critical step involves establishing consensus standards for neuroimaging acquisition, preprocessing, and analysis in ASD research. We recommend forming an international consortium to develop
- Standardized acquisition protocols for each neuroimaging modality, with particular emphasis on EEG, given its superior performance in early detection;
- Common preprocessing pipelines that implement validated quality control metrics and artifact rejection procedures;
- Benchmarked feature extraction methodologies that prioritize those techniques demonstrating the highest reproducibility.
This standardization will address the significant variability in methodologies that currently limits the generalizability and reproducibility of results across studies.
Phase 2: Clinical Translation Pathway
Bridging the gap between research findings and clinical application requires a structured approach:
- Retrospective validation in diverse clinical populations, ensuring biomarker efficacy across demographic variables, comorbidity profiles, and ASD subtypes.
- Development of clinician-accessible tools that integrate biomarker data with standard clinical measures, featuring interpretable outputs and appropriate quantification of uncertainty.
- Prospective studies comparing standard clinical assessment with biomarker-enhanced approaches, measuring improvements in diagnostic timing, accuracy, and predictive power.
This phase should emphasize implementation science principles to identify and address barriers to clinical adoption.
Phase 3: Accessible Technology Development
Addressing technical and financial barriers to implementation requires
- Development of simplified, clinical-grade EEG systems optimized for the most robust biomarkers identified in our review;
- Creation of automated analysis pipelines that minimize the need for specialized expertise;
- Implementation of explainable AI frameworks that make complex biomarker patterns interpretable to clinicians without technical backgrounds.
These technologies should emphasize cost-effectiveness and user-friendly design to enable widespread adoption.
Phase 4: Training and Ethical Implementation
The final phase focuses on the human factors essential for successful implementation:
- Development of interdisciplinary training programs that enhance clinicians’ ability to incorporate biomarker data into diagnostic and intervention planning;
- Creation of technical training for computational scientists to ensure algorithm development addresses relevant clinical needs;
- Establishment of comprehensive ethical guidelines addressing algorithm fairness, transparency, appropriate human oversight, and equity of access.
This multi-phase approach acknowledges that successful translation requires addressing technical challenges and human, organizational, and ethical considerations. By systematically addressing each barrier identified in our review, this implementation framework provides a roadmap for transforming promising research findings into clinical tools that could fundamentally improve outcomes for individuals with ASD.
Finally, Figure 18 below presents a comprehensive visualization of our four-phase implementation framework for AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers in ASD. The hybrid temporal matrix approach organizes information horizontally across the implementation phases while vertically stratifying key domains.
Figure 18.
AI-driven neuroimaging biomarker implementation framework for ASD.
The framework progresses sequentially through four distinct phases: (1) Technical Infrastructure Standardization, (2) Clinical Translation Pathway, (3) Accessible Technology Development, and (4) Training and Ethical Implementation. Each phase consistently considers five critical domains: Technical/Infrastructure components (blue), Clinical/Medical Processes (green), Stakeholder Involvement (purple), Ethical/Regulatory considerations (orange), and Evaluation Metrics (red).
Directional connectors between phases illustrate how outputs from one phase become inputs to subsequent phases. Validated infrastructure elements from Phase 1 enable clinical translation in Phase 2, which in turn produces clinically relevant technologies for Phase 3. This results in user-centered solutions that inform the training and ethical implementation activities of Phase 4. The dashed feedback loop connecting Phase 4 back to Phase 1 highlights the framework’s iterative nature, allowing for continuous refinement through implementation experience. By balancing technical precision with clinical accessibility, this visualization enables diverse stakeholders—from technical specialists to clinicians, patients, and regulatory experts—to understand their roles within the broader implementation process, facilitating successful translation of AI neuroimaging biomarkers into clinical practice for autism spectrum disorder.
6. Conclusions
A comprehensive systematic analysis of 146 research papers provides compelling evidence for the transformative potential of AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers in ASD. This review has demonstrated that integrating advanced computational approaches with neuroimaging data can significantly enhance early detection capabilities and improve the prediction of social functioning outcomes in individuals with ASD.
Our findings highlight EEG as a promising modality, offering exceptional temporal resolution, accessibility, and robust classification performance when analyzed using sophisticated signal processing and machine learning techniques. The identification of specific developmental windows, particularly between 9 and 12 months of age, provides critical opportunities for biomarker detection before behavioral symptoms fully manifest, potentially enabling intervention during periods of maximal neuroplasticity.
Integrating multiple neuroimaging modalities and complementary data streams represents a significant advancement, consistently outperforming single-modality approaches in diagnostic accuracy and predictive power. Advanced computational frameworks, including deep learning architectures, network science approaches, and explainable AI techniques, have enabled the effective integration of heterogeneous data, revealing biomarkers that capture the multifaceted nature of ASD.
Despite promising results, translating these research advances into clinical practice remains challenging. Future efforts should focus on standardizing acquisition protocols, developing clinically feasible analysis pipelines, addressing population heterogeneity, and validating biomarkers in large, diverse cohorts through longitudinal studies. The emergence of explainable AI approaches will be crucial for ensuring that clinicians can interpret and trust complex biomarker models.
By addressing these challenges, AI-driven neuroimaging biomarkers hold tremendous promise for revolutionizing ASD diagnosis and intervention, potentially enabling earlier detection, more personalized treatment approaches, and improved outcomes across the lifespan. This interdisciplinary frontier integrating neuroscience, computer science, and clinical research represents a promising path toward more objective, precise, and practical approaches to understanding and addressing ASD.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/healthcare13151776/s1. Table S1. Full table of the studies (n = 146) included in the systematic review; Table S2. Comprehensive dataset reference table of the studies (n = 146); Table S3. Abbreviation list.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.G. and B.B.; methodology, E.G. and M.P.; software, B.B.; validation, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; formal analysis, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; investigation, E.G., M.P. and B.B.; resources, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; data curation, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; writing—review and editing, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; visualization, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; supervision, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; project administration, E.G. and B.B.; E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V.; funding acquisition, E.G., M.P., S.P.V., G.N., B.B. and A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vogindroukas, I.; Stankova, M.; Chelas, E.N.; Proedrou, A. Language and speech characteristics in autism. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, T.; King, B.H. Autism spectrum disorder: A review. JAMA 2023, 329, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoe, M.I.; Forbes, K.; de la Roche, L.; Derby, B.; Psaradellis, E.; Anagnostou, E.; Kelley, E. Exploring the association between social skills struggles and social communication difficulties and depression in youth with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 2160–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, F.; Crippa, A.; Ruggiero, M.; Rizzato, V.; Russo, L.; Fanizza, I.; Trabacca, A. Characterization of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) subtypes based on the relationship between motor skills and social communication abilities. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2021, 77, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costescu, C.; Pitariu, D.; David, C.; Roșan, A. Social communication predictors in autism spectrum disorder: Theoretical review. J. Exp. Psychopathol. 2022, 13, 20438087221106955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.N. Motor impairment increases in children with autism spectrum disorder as a function of social communication, cognitive and functional impairment, and repetitive behavior. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, N. Assessing and Diagnosing Young Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A DSM-5-TR Compliant Guide; Routledge: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvo, M. From Criteria to Diagnostic Evaluation: Autism in DSM-5 and DSM-5 TER. In Autism Research between Psychology and Neuroscience: From Leo Kanner to New Frontiers; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; He, X.; Zhou, J.; Jin, C.; Shen, L.; Gao, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhang, H. Structural, functional, and molecular imaging of autism spectrum disorder. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 1051–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Casale, A.; Ferracuti, S.; Alcibiade, A.; Simone, S.; Modesti, M.N.; Pompili, M. Neuroanatomical correlates of autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2022, 325, 111516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangarani-Farahani, M.; Izadi-Najafabadi, S.; Zwicker, J.G. How does brain structure and function on MRI differ in children with autism spectrum disorder, developmental coordination disorder, and/or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2022, 82, 680–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, C.A.; Ching, C.R.; Kumar, K.; Jacquemont, S.; Bearden, C.E. Structural and functional brain alterations revealed by neuroimaging in CNV carriers. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2021, 68, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, F.; Rezvani Habibabadi, R.; Motaghi, M.; Yousem, D.M.; Yousem, I.J. Brain MRI in autism spectrum disorder: Narrative review and recent advances. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E.; Skokou, M.; Gourzis, P. Integrating Clinical Neuropsychology and Psychotic Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Analysis of Cognitive Dynamics, Interventions, and Underlying Mechanisms. Medicina 2024, 60, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, Z.-H.; Xu, L.-Z.; Yang, L.; Ji, Z.-Z.; Tang, X.-Z.; Liu, J.-R.; Li, X.; Cao, Q.-J.; Liu, J. Developmental brain structural atypicalities in autism: A voxel-based morphometry analysis. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2022, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Tang, X.; Xiao, S.; Yan, H.; Sun, S.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Multimodal functional and anatomical neural alterations in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2024, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E. Clinical neuropsychological characteristics of bipolar disorder, with a focus on cognitive and linguistic pattern: A conceptual analysis. F1000Research 2023, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkiopoulos, C.; Gkintoni, E. Leveraging AI in E-Learning: Personalized Learning and Adaptive Assessment through Cognitive Neuropsychology—A Systematic Analysis. Electronics 2024, 13, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhede, N.; Kale, M.; Shukla, M.; Nathiya, D.; Kaur, P.; Goyanka, B.; Rahangdale, S.; Taksande, B.; Upaganlawar, A.; Khalid, M.; et al. Leveraging AI for the diagnosis and treatment of autism spectrum disorder: Current trends and future prospects. Asian J. Psychiatry 2024, 101, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solek, P.; Nurfitri, E.; Sahril, I.; Prasetya, T.; Rizqiamuti, A.F.; Rachmawati, I.; Gamayani, U.; Rusmil, K.; Chandra, L.A.; Afriandi, I.; et al. The role of artificial intelligence for early diagnostic tools of autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2025, 60, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchouras, G.; Kotis, K. Integrating artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and sensor-based technologies: A systematic review of methodologies in autism spectrum disorder. Algorithms 2025, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbattah, M.; Ali Sadek Ibrahim, O.; Dequen, G. Improving autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using machine learning techniques. Front. Neuroinform. 2024, 18, 1529839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, E.J.; He, D.; Achi, N.A.D.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Yao-Digba, P.D.Z.; Monkam, P.; Qi, S. Neuroimage analysis using artificial intelligence approaches: A systematic review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 2599–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganggayah, M.D.; Zhao, D.; Liew, E.J.Y.; Mohd Nor, N.A.; Paramasivam, T.; Lee, Y.Y.; Abu Hasan, N.I.; Shaharuddin, S. Accelerating autism spectrum disorder care: A rapid review of data science applications in diagnosis and intervention. Asian J. Psychiatry 2025, 108, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgil, A.A.; Selvakumar, P.; Gnanaselvi, G.S.; Malathi, G. AI in neuroimaging and brain analysis. In Transforming Neuropsychology and Cognitive Psychology with AI and Machine Learning; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, V.; D’Angelo, M.; Monaco, F.; Vignapiano, A.; Martiadis, V.; Barone, E.; Fornaro, M.; Steardo, L.; Solmi, M.; Manchia, M.; et al. Decoding schizophrenia: How AI-enhanced fMRI unlocks new pathways for precision psychiatry. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onciul, R.; Tataru, C.-I.; Dumitru, A.V.; Crivoi, C.; Serban, M.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Radoi, M.P.; Toader, C. Artificial intelligence and neuroscience: Transformative synergies in brain research and clinical applications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkiopoulos, C.; Gkintoni, E. The Role of Machine Learning in AR/VR-Based Cognitive Therapies: A Systematic Review for Mental Health Disorders. Electronics 2025, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydili, İ.; Tasci, B.; Tasci, G. Artificial intelligence in psychiatry: A review of biological and behavioral data analyses. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutman, B.; Shmilovitch, A.H.; Aran, D.; Shelly, S. Twenty-five years of AI in neurology: The journey of predictive medicine and biological breakthroughs. JMIR Neurotechnol. 2024, 3, e59556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, C.; Tan, N.S.M.; Long, I.J.; Keong, N.C. Neuroimaging data repositories and AI-driven healthcare—Global aspirations vs. ethical considerations in machine learning models of neurological disease. Front. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, 1286266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, R.J.R.; Mathur, A.; Haines, N.; Bajaj, S. Future directions for cognitive neuroscience in psychiatry: Recommendations for biomarker design based on recent test–retest reliability work. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 44, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.Y.; Yen, Y. Imaging biomarkers for clinical applications in neuro-oncology: Current status and future perspectives. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etkin, A.; Mathalon, D.H. Bringing imaging biomarkers into clinical reality in psychiatry. JAMA Psychiatry 2024, 81, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etkin, A.; Powell, J.; Savitz, A.J. Opportunities for use of neuroimaging in de-risking drug development and improving clinical outcomes in psychiatry: An industry perspective. Neuropsychopharmacology 2025, 50, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewen, J.B.; Potter, W.Z.; Sweeney, J.A. Biomarkers and neurobehavioral diagnosis. Biomark. Neuropsychiatry 2021, 5, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, M.S. The science of uncertainty guides fetal-neonatal neurology principles and practice: Diagnostic-prognostic opportunities and challenges. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1335933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, T.C.; Thompson, G.; Bulbeck, H.; Boele, F.; Buckley, C.; Cardoso, J.; Dos Santos Canas, L.; Jenkinson, D.; Ashkan, K.; Kreindler, J.; et al. A position statement on the utility of interval imaging in standard of care brain tumour management: Defining the evidence gap and opportunities for future research. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 620070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, D.J.; Shoptaw, S.J.; Vigo, D.V.; Lund, C.; Cuijpers, P.; Bantjes, J.; Sartorius, N.; Maj, M. Psychiatric diagnosis and treatment in the 21st century: Paradigm shifts versus incremental integration. World Psychiatry 2022, 21, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moridian, P.; Ghassemi, N.; Jafari, M.; Salloum-Asfar, S.; Sadeghi, D.; Khodatars, M.; Shoeibi, A.; Khosravi, A.; Ling, S.H.; Subasi, A.; et al. RAutomatic autism spectrum disorder detection using artificial intelligence methods with MRI neuroimaging: A review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 999605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, A.N.; Sample, J.; Hall-Lande, J.; Harris, B.; Rice, C.; Poynter, J.; Kirby, R.S.; Wiggins, L. Patterns of special education eligibility and age of first autism spectrum disorder (ASD) identification among US children with ASD. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 1739–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuvekas, S.H.; Grosse, S.D.; Lavelle, T.A.; Maenner, M.J.; Dietz, P.; Ji, X. Healthcare costs of pediatric autism spectrum disorder in the United States, 2003–2015. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, K.A.; McArthur, D.; Hughes, M.M.; Bakian, A.V.; Lee, L.C.; Pettygrove, S.; Maenner, M.J. Progress and disparities in early identification of autism spectrum disorder: Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 2002–2016. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 61, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fombonne, E.; MacFarlane, H.; Salem, A.C. Epidemiological surveys of ASD: Advances and remaining challenges. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 4271–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, J.; Eberth, J.M.; Zgodic, A.; Federico, A.; Flory, K.; McLain, A.C. County-level prevalence estimates of autism spectrum disorder in children in the United States. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2024, 54, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadem-Reza, Z.K.; Zare, H. Evaluation of brain structure abnormalities in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using structural magnetic resonance imaging. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2022, 58, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, C.M.; Ecker, C. Structural neuroimaging phenotypes and associated molecular and genomic underpinnings in autism: A review. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1172779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Múnera, N.; Alvarez-Jimenez, C.; Velasco, N.; Romero, E. An exploration of structural brain differences in autism spectrum disorders: A multi-parcellation and multi-age analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 92, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Tseng, R.-Y.; Ni, H.-C.; Cocchi, L.; Chang, J.-C.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Tu, E.-N.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chou, T.-L.; Gau, S.S.-F.; et al. White matter microstructural and morphometric alterations in autism: Implications for intellectual capabilities. Mol. Autism 2022, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, S.; Elbendary, H.; Lequin, M.; Rijkelijkhuizen, D.; Banaschewski, T.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Bast, N.; Baumeister, S.; Buitelaar, J.; Charman, T.; et al. In-depth characterization of neuroradiological findings in a large sample of individuals with autism spectrum disorder and controls. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 35, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkovski, M.; Singh, M.; Dhollander, T.; Fuelscher, I.; Hyde, C.; Albein-Urios, N.; Donaldson, P.H.; Enticott, P.G. An investigation of age-related neuropathophysiology in autism spectrum disorder using fixel-based analysis of corpus callosum white matter micro-and macrostructure. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2024, 54, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, R.; Ganji, Z.; Zamanpour, S.A.; Nikparast, F.; Akbari-Lalimi, H.; Zare, H. Impaired white matter integrity in infants and young children with autism spectrum disorder: What evidence does diffusion tensor imaging provide? Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2023, 335, 111711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Kitamura, S.; Matsuoka, K.; Takahashi, M.; Ishida, R.; Kishimoto, N.; Yasuno, F.; Yasuda, Y.; Hashimoto, R.; Miyasaka, T.; et al. Adverse childhood experience is associated with disrupted white matter integrity in autism spectrum disorder: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 823260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.; Dallenbach, N.T.; Green, A.; Gaillard, S.; Capella, J.; Hoskova, B.; Vater, C.H.; Cooper, E.; Rudberg, N.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Distinct and shared white matter abnormalities when ADHD is comorbid with ASD: A preliminary diffusion tensor imaging study. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 320, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.F.; Lake, E.M.R.; Haider, S.P.; Mozayan, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Scheinost, D.; Bamford, N.S.; Ment, L.; Constable, T.; Payabvash, S. Age-dependent white matter microstructural disintegrity in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 957018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Fu, Z.; Lai, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, Q. The shared white matter developmental trajectory anomalies of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 124, 110731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, V.K.; Aeri, M. Patterns of widespread structural abnormalities in autism spectrum disorder using diffusion tensor imaging. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Communication, Computer Sciences and Engineering (IC3SE), Gautam Buddha Nagar, India, 9–11 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPiero, M.; Cordash, H.; Prigge, M.B.; King, C.K.; Morgan, J.; Guerrero-Gonzalez, J.; Adluru, N.; King, J.B.; Lange, N.; Bigler, E.D.; et al. Tract-and gray matter-based spatial statistics show white matter and gray matter microstructural differences in autistic males. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1231719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Tachibana, M.; Rahman, S.; Kagitani-Shimono, K. Atypical structural connectivity of language networks in autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E.; Antonopoulou, H.; Sortwell, A.; Halkiopoulos, C. Challenging Cognitive Load Theory: The Role of Educational Neuroscience and Artificial Intelligence in Redefining Learning Efficacy. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, M.K.; Jauk, E.; Lehmann, K.; Maliske, L.; Kanske, P. Brain activation during social cognition predicts everyday perspective-taking: A combined fMRI and ecological momentary assessment study of the social brain. NeuroImage 2021, 227, 117624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisner, O.C.; Nair, A.; Chang, S.W.C. Amygdala connectivity and implications for social cognition and disorders. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 187, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arioli, M.; Cattaneo, Z.; Ricciardi, E.; Canessa, N. Overlapping and specific neural correlates for empathizing, affective mentalizing, and cognitive mentalizing: A coordinate-based meta-analytic study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 4777–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, B.; Squeglia, L.M.; McTeague, L.M.; Forbes, M.K.; Krueger, R.F.; Sunderland, M.; Baillie, A.J.; Koch, F.; Teesson, M.; Mewton, L. Altered neurocognitive functional connectivity and activation patterns underlie psychopathology in preadolescence. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Kendrick, K.M. Effects of intranasal administration of oxytocin and vasopressin on social cognition and potential routes and mechanisms of action. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.N.L.; Hass, J.; Kirsch, P.; Mier, D. The human mirror neuron system—A common neural basis for social cognition? Psychophysiol. 2021, 58, e13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokhadze, E.M.; Shaban, M.; El-Baz, A.S.; Tasman, A.; Sears, L.; Casanova, M.F. Event-related potentials and gamma oscillations in EEG as functional diagnostic biomarkers and outcomes in autism spectrum disorder treatment research. In Neural Engineering Techniques for Autism Spectrum Disorder; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, W.S.; Foti, D.; Keehn, B.; Kelleher, B. Resting-state EEG power differences in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neklyudova, A.; Smirnov, K.; Rebreikina, A.; Martynova, O.; Sysoeva, O. Electrophysiological and behavioral evidence for hyper- and hyposensitivity in rare genetic syndromes associated with autism. Genes 2022, 13, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremone-Caira, A.; Braverman, Y.; MacNaughton, G.A.; Nikolaeva, J.I.; Faja, S. Reduced visual evoked potential amplitude in autistic children with co-occurring features of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2024, 54, 2917–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, J.; Acluche, F.; Lasutschinkow, P.C.; Augustiniak, A.; Ditchfield, N.; Lajiness-O’Neill, R. Motor networks in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review on EEG studies. Exp. Brain Res. 2022, 240, 3073–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, L.; Wilson, M.; Tebartz van Elst, L.; Kornmeier, J. Altered EEG variability on different time scales in participants with autism spectrum disorder: An exploratory study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.P.; Kuschner, E.S.; Edgar, J.C. Biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder: Opportunities for magnetoencephalography (MEG). J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Mody, M. Abnormal brain oscillations in developmental disorders: Application of resting-state EEG and MEG in autism spectrum disorder and Fragile X syndrome. Front. Neuroimaging 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, M.; Grujicic, R. Electroencephalography in Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 686021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmytriw, A.A.; Hadjinicolaou, A.; Ntolkeras, G.; Tamilia, E.; Pesce, M.; Berto, L.F.; Grant, P.E.; Pang, E.; Ahtam, B. Magnetoencephalography for the pediatric population: Indications, acquisition and interpretation for the clinician. Neuroradiol. J. 2025, 38, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barik, K.; Watanabe, K.; Bhattacharya, J.; Saha, G. A fusion-based machine learning approach for autism detection in young children using magnetoencephalography signals. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 4830–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, A.R.; Whitehouse, A.J.; Fox, A.M.; Maybery, M.T. Delayed cortical processing of auditory stimuli in children with autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis of electrophysiological studies. Brain Cogn. 2021, 150, 105709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arutiunian, V.; Arcara, G.; Buyanova, I.; Fedorov, M.; Davydova, E.; Pereverzeva, D.; Sorokin, A.; Tyushkevich, S.; Mamokhina, U.; Danilina, K.; et al. Abnormalities in both stimulus-induced and baseline MEG alpha oscillations in the auditory cortex of children with autism spectrum disorder. Brain Struct. Funct. 2024, 229, 1225–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbi, V.; Pagani, M.; Markicevic, M.; Matteoli, M.; Pozzi, D.; Fagiolini, M.; Bozzi, Y.; Galbusera, A.; Scattoni, M.L.; Provenzano, G.; et al. Brain mapping across 16 autism mouse models reveals a spectrum of functional connectivity subtypes. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7610–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.L. Using causal methods to map symptoms to brain circuits in neurodevelopment disorders: Moving from identifying correlates to developing treatments. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, A.; Tiego, J.; Parkes, L.; Holmes, A.J.; Marquand, A.F.; Fornito, A. Embracing variability in the search for biological mechanisms of psychiatric illness. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2025, 29, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Parayil, R.; Mishra, S.; Nongthomba, U.; Clement, J.P. Epilepsy characteristics in neurodevelopmental disorders: Research from patient cohorts and animal models focusing on autism spectrum disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiney, K.; Huse Ramstad, O.; Fiskum, V.; Christiansen, N.; Sandvig, A.; Nichele, S.; Sandvig, I. Criticality, connectivity, and neural disorder: A multifaceted approach to neural computation. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 611183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbarasi, J.; Kumari, R.; Ganesh, M.; Agrawal, R. Translational connectomics: Overview of machine learning in macroscale connectomics for clinical insights. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Khuntia, R. Development and content validation of a measure to assess the parent-child social-emotional reciprocity of children with ASD. Indian. J. Psychol. Med. 2024, 46, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saban-Bezalel, R.; Avni, E.; Ben-Itzchak, E.; Zachor, D.A. Relationship between parental concerns about social-emotional reciprocity deficits and their children’s final ASD diagnosis. Children 2023, 10, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, H.H.S.; Wong, S.W.L.; Chan, D.F.Y.; Li, C.; Kon, L.L.; Ma, P.K.; Lau, K.S.Y.; Byrne, J. Enhance affective expression and social reciprocity for children with autism spectrum disorder: Using virtual reality headsets at schools. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2024, 32, 1012–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.Y.H.; Sin, K.K.F.; Chow, D.H.K. Qualitative outcomes and impact of a robotic intervention on children with autism spectrum disorder: A multiple embedded case study. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2024, 87, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, A.; Yildirim, A. Assessing the impact of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on social communication in children and adolescents with ASD. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2025, 161, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomfohrde, O.; Hudock, R.L.; Kremer, K.B.; Fatiha, N.; Weiler, L. Fostering social connectedness among adolescents and adults with autism: A qualitative analysis. Psychol. Sch. 2023, 60, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güeita-Rodríguez, J.; Ogonowska-Slodownik, A.; Morgulec-Adamowicz, N.; Martín-Prades, M.L.; Cuenca-Zaldívar, J.N.; Palacios-Ceña, D. Effects of aquatic therapy for children with autism spectrum disorder on social competence and quality of life: A mixed methods study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posar, A.; Visconti, P. Early motor signs in autism spectrum disorder. Children 2022, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, C.; Rosa, E.; De Stasio, S.; Olsson, N.C. Sleep quality relates to language impairment in children with autism spectrum disorder without intellectual disability. Sleep. Med. 2024, 117, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Dong, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, X. Motor impairments in Chinese toddlers with autism spectrum disorder and its relationship with social communicative skills. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 938047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, N.N.; Jashar, D.T.; Sheperd, K.; Pineda, J.L.; Previ, D.; Reesman, J.; Holingue, C.; Gerner, G.J. Considerations for the identification of autism spectrum disorder in children with vision or hearing impairment: A critical review of the literature and recommendations for practice. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2022, 36, 1049–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morison, L.D.; Braden, R.O.; Amor, D.J.; Brignell, A.; van Bon, B.W.; Morgan, A.T. Social motivation: A relative strength in DYRK1A syndrome on a background of significant speech and language impairments. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Giambattista, C.; Ventura, P.; Trerotoli, P.; Margari, F.; Margari, L. Sex differences in autism spectrum disorder: Focus on high-functioning children and adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 539835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arioli, M.; Basso, G.; Carne, I.; Poggi, P.; Canessa, N. Increased pSTS activity and decreased pSTS-mPFC connectivity when processing negative social interactions. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 399, 113027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvall, L.; May, K.E.; Waltz, A.; Kana, R.K. The neurobiological map of theory of mind and pragmatic communication in autism. Soc. Neurosci. 2023, 18, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, C.; Silveira, S.; Meindl, T.; Musil, R.; Austerschmidt, K.L.; Eilert, D.W.; Müller, N.; Möller, H.-J.; Engel, R.; Reiser, M.; et al. Two sides of theory of mind: Mental state attribution to moving shapes in paranoid schizophrenia is independent of the severity of positive symptoms. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S. Translating neuroimaging changes to neuro-endophenotypes of autistic spectrum disorder: A narrative review. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2022, 58, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliemann, D.; Adolphs, R.; Paul, L.K.; Tyszka, J.M.; Tranel, D. Reorganization of the social brain in individuals with only one intact cerebral hemisphere. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janouschek, H.; Chase, H.W.; Sharkey, R.J.; Peterson, Z.J.; Camilleri, J.A.; Abel, T.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Nickl-Jockschat, T. The functional neural architecture of dysfunctional reward processing in autism. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 31, 102700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, S.; Moessnang, C.; Bast, N.; Hohmann, S.; Aggensteiner, P.; Kaiser, A.; Tillmann, J.; Goyard, D.; Charman, T.; Ambrosino, S.; et al. Processing of social and monetary rewards in autism spectrum disorders. Br. J. Psychiatry 2023, 222, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwill, A.M.; Low, L.T.; Fox, P.T.; Fox, P.M.; Poon, K.K.; Bhowmick, S.S.; Chen, S.A. Meta-analytic connectivity modelling of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023, 17, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappini, E.; Massaccesi, C.; Korb, S.; Steyrl, D.; Willeit, M.; Silani, G. Neural hyperresponsivity during the anticipation of tangible social and nonsocial rewards in autism spectrum disorder: A concurrent neuroimaging and facial electromyography study. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2024, 9, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caria, A.; Dall’Ò, G.M. Functional neuroimaging of the human hypothalamus in socioemotional behavior: A systematic review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortier, A.V.; Meisner, O.C.; Nair, A.R.; Chang, S.W. Prefrontal circuits guiding social preference: Implications in autism spectrum disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 141, 104803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Xu, Y.; Kat, S.; Sun, A.; Yin, T.; Zhao, L.; Su, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; et al. Exploring the most discriminative brain structural abnormalities in ASD with multi-stage progressive feature refinement approach. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1463654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frogner, L.; Hellfeldt, K.; Ångström, A.K.; Andershed, A.K.; Källström, Å.; Fanti, K.A.; Andershed, H. Stability and change in early social skills development in relation to early school performance: A longitudinal study of a Swedish cohort. Early Educ. Dev. 2022, 33, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, J.M.; Watts, D.J.; Athey, S.; Garip, F.; Griffiths, T.L.; Kleinberg, J.; Margetts, H.; Mullainathan, S.; Salganik, M.J.; Vazire, S.; et al. Integrating explanation and prediction in computational social science. Nature 2021, 595, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, Y. How the home learning environment contributes to children’s social-emotional competence: A moderated mediation model. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1065978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, J.; O’Brien, A.M.; Bungert, L.; Sinha, P. Prediction in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review of empirical evidence. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 604–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Badcock, P.; Friston, K.J. Recent advances in the application of predictive coding and active inference models within clinical neuroscience. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 75, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiremath, C.S.; Sagar, K.J.V.; Yamini, B.K.; Girimaji, A.S.; Kumar, R.; Sravanti, S.L.; Padmanabha, H.; Vykunta Raju, K.N.; Kishore, M.T.; Jacob, P.; et al. Emerging behavioral and neuroimaging biomarkers for early and accurate characterization of autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, P.; Alexander-Bloch, A.; Wei, Y.; Dyrba, M.; Yang, F.; Kang, X.; Wang, D.; Fan, D.; Ye, S.; et al. A neuroimaging biomarker for Individual Brain-Related Abnormalities In Neurodegeneration (IBRAIN): A cross-sectional study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 65, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, M.J.; Keegan, L.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Gill, S.V. Neuroimaging techniques as descriptive and diagnostic tools for infants at risk for autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traut, N.; Heuer, K.; Lemaître, G.; Beggiato, A.; Germanaud, D.; Elmaleh, M.; Bethegnies, A.; Bonnasse-Gahot, L.; Cai, W.; Chambon, S.; et al. Insights from an autism imaging biomarker challenge: Promises and threats to biomarker discovery. NeuroImage 2022, 255, 119171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldner, S.; Ernst, J.; Nees, F.; Holz, N. The Utility of Biomarkers for Assessment and Intervention in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. In Digital Technologies for Learning and Psychological Interventions; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 43–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S.; Solmi, M.; Michelini, G.; Bellato, A.; Blanner, C.; Canozzi, A.; Eudave, L.; Farhat, L.C.; Højlund, M.; Köhler-Forsberg, O.; et al. Candidate diagnostic biomarkers for neurodevelopmental disorders in children and adolescents: A systematic review. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wood, D.; Grzeda, M.; Suresh, C.; Din, M.; Cole, J.; Modat, M.; Booth, T.C. Systematic review of artificial intelligence for abnormality detection in high-volume neuroimaging and subgroup meta-analysis for intracranial hemorrhage detection. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2023, 33, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, F.V.; Fiok, K.; Lahijanian, B.; Karwowski, W.; Douglas, P.K. Explainable AI: A review of applications to neuroimaging data. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 906290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkiopoulos, C.; Gkintoni, E.; Aroutzidis, A.; Antonopoulou, H. Advances in Neuroimaging and Deep Learning for Emotion Detection: A Systematic Review of Cognitive Neuroscience and Algorithmic Innovations. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etekochay, M.O.; Amaravadhi, A.R.; González, G.V.; Atanasov, A.G.; Matin, M.; Mofatteh, M.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Tesfaye, T.; Praticò, D. Unveiling new strategies facilitating the implementation of artificial intelligence in neuroimaging for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 99, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, P.; Mohammadi, S.; Zahiri, F.; Khodarahmi, M.; Zahiri, J. AI-enhanced detection of clinically relevant structural and functional anomalies in MRI: Traversing the landscape of conventional to explainable approaches. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 2272–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Niu, J.; Xing, Y.; Li, B.; Calhoun, V.D. Neuroimage analysis methods and artificial intelligence techniques for reliable biomarkers and accurate diagnosis of schizophrenia: Achievements made by Chinese researchers. Schizophr. Bull. 2024, 51, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Hu, L.-F.; Li, W.-H.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Jin, W.-Y.; Zhu, Z.-W. A machine learning-based diagnostic model for children with autism spectrum disorders complicated with intellectual disability. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 993077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakadkar, K.; Purkayastha, D.; Krishnan, D. Detection of autism spectrum disorder in children using machine learning techniques. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, M.; Ali, M.H.; Satu, M.S.; Hasan, K.F.; Moni, M.A. Efficient machine learning models for early-stage detection of autism spectrum disorder. Algorithms 2022, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Martín, S.; García-Ordás, M.T.; Bayón-Gutiérrez, M.; Prieto-Fernández, N.; Benítez-Andrades, J.A. Enhancing ASD detection accuracy: A combined approach of machine learning and deep learning models with natural language processing. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2024, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.S.; Tehseen, R.; Sabir, M.; Atal, Z. Detection of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children and adults using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudhur, D.D.; Khudhur, S.D. The classification of autism spectrum disorder by machine learning methods on multiple datasets for four age groups. Meas. Sens. 2023, 25, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuliman, M.; Al-Baity, H.H. Efficient diagnosis of autism with optimized machine learning models: An experimental analysis on genetic and personal characteristic datasets. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.; Paramasivam, I. Feature reduction using SVM-RFE technique to detect autism spectrum disorder. Evol. Intell. 2021, 14, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahathiq, R.A.; Banjar, H.; Jarraya, S.K.; Bamaga, A.K.; Almoallim, R. Efficient diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder using optimized machine learning models based on structural MRI. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.L.; Martinelli, T.; Sallum, L.F.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Toutain TGLde, O.; Porto, J.A.M.; Thielemann, C.; Aguiar PMde, C.; Moeckel, M. Multiclass classification of Autism Spectrum Disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and typically developed individuals using fMRI functional connectivity analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chola Raja, K.; Kannimuthu, S. Deep learning-based feature selection and prediction system for autism spectrum disorder using a hybrid meta-heuristics approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 45, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, A.G.; Alzahrani, S.M. Multi-slice generation sMRI and fMRI for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using 3D-CNN and vision transformers. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyškovský, R.; Schwarz, D.; Churová, V.; Kašpárek, T. Structural MRI-based schizophrenia classification using autoencoders and 3D convolutional neural networks in combination with various pre-processing. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassini, S.; Sbrollini, A.; Covella, G.; Sernani, P.; Falcionelli, N.; Müller, H.; Morettini, M.; Burattini, L.; Dragoni, A.F. Brain-on-Cloud for automatic diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease from 3D structural magnetic resonance whole-brain scans. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 227, 107191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.; Kelly, C. 3D CNN for neuropsychiatry: Predicting Autism with interpretable Deep Learning applied to minimally preprocessed structural MRI data. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0276832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattia, G.M.; Sarton, B.; Villain, E.; Vinour, H.; Ferre, F.; Buffieres, W.; Le Lann, M.-V.; Franceries, X.; Peran, P.; Silva, S. Multimodal MRI-based whole-brain assessment in patients in anoxoischemic coma by using 3D convolutional neural networks. Neurocritical Care 2022, 37 (Suppl. 2), 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Peng, A.; Duan, Y.; Chen, M.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Sun, H. Associations of Postencephalitic Epilepsy Using Multi-Contrast Whole Brain MRI: A Large Self-Supervised Vision Foundation Model Strategy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, D.; Jayanthi, K.; Tilakan, P. A Novel 3D-CNN with DAG Framework for Enhanced Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Structural MRI. In Proceedings of the 2025 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Advanced Computing and Communication (ISACC), Silchar, India, 27–28 February 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, L. Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) by Dynamic Functional Connectivity Using GNN-LSTM. Sensors 2024, 25, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koc, E.; Kalkan, H.; Bilgen, S. Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection by Hybrid Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks from Structural and Resting State Functional MRI Images. Autism Res. Treat. 2023, 2023, 4136087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhera, T.; Bedi, J.; Sharma, S. Autism spectrum disorder prediction using bidirectional stacked gated recurrent unit with time-distributor wrapper: An EEG study. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 9803–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidulova, M.; Park, C.H. Conditional variational autoencoder for functional connectivity analysis of autism spectrum disorder functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheekaty, S.; Muneeswari, G. Enhanced multilevel autism classification for children using eye-tracking and hybrid CNN-RNN deep learning models. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Classification of autism based on short-term spontaneous hemodynamic fluctuations using an adaptive graph neural network. J. Neurosci. Methods 2023, 394, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.W.; Cho, S.B. A residual graph convolutional network with spatio-temporal features for autism classification from fMRI brain images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 136, 110363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Li, L.; Wu, F.X. A semi-supervised autoencoder for autism disease diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2022, 481, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avberšek, L.K.; Repovš, G. Deep learning in neuroimaging data analysis: Applications, challenges, and solutions. Front. Neuroimaging 2022, 1, 981642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sciarra, A.; Dünnwald, M.; Tummala, P.; Agrawal, S.K.; Jauhari, A.; Kalra, A.; Oeltze-Jafra, S.; Speck, O.; Nürnberger, A. StRegA: Unsupervised anomaly detection in brain MRIs using a compact context-encoding variational autoencoder. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Qu, G.; Hu, W.; Abrol, A.; Cai, B.; Qiao, C.; Plis, S.M.; Wang, Y.-P.; Sui, J.; Calhoun, V.D. Deep learning in neuroimaging: Promises and challenges. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2022, 39, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Iriondo, I.; Jimenez-Marin, A.; Sierra, B.; Aginako, N.; Bonifazi, P.; Cortes, J.M. Brain mapping of behavioral domains using multi-scale networks and canonical correlation analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 889725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.; Tang, F.; Nong, X.; Li, C.; Yu, B.; Duan, G.; Su, J.; Mai, W.; et al. Fusion analysis of gray matter and white matter in subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment by multimodal CCA-joint ICA. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Du, L.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Identification of multimodal brain imaging association via a parameter decomposition-based sparse multi-view canonical correlation analysis method. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23 (Suppl. 3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, R.; Saha, D.K.; Fu, Z.; Duda, M.; Silva, R.F.; Calhoun, V.D. Analysis of Longitudinal Change Patterns in Developing Brain Using Functional and Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging via Multimodal Fusion. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, M.; Deprez, M.; Balelli, I.; Aguila, A.L.; Altmann, A. Integration of multimodal data. In Machine Learning for Brain Disorders; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 573–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tyler, L.K.; Cam-CAN; Rowe, J.B.; Tsvetanov, K.A. Multimodal fusion analysis of functional, cerebrovascular and structural neuroimaging in healthy aging subjects. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 5490–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, L.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, L.; Nie, S. Classification of Parkinson’s disease based on multi-modal features and stacking ensemble learning. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 350, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remzan, N.; Hachimi, Y.E.; Tahiry, K.; Farchi, A. Ensemble learning-based features extraction for brain MR images classification with machine learning classifiers. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 57661–57684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Tiwari, R.; Tiwari, S. Alzheimer’s disease detection from fused PET and MRI modalities using an ensemble classifier. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 512–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilla, G.S.; Yeow, L.Y.; Chew, Q.H.; Sim, K.; Prakash, K.N.B. Machine learning classification of schizophrenia patients and healthy controls using diverse neuroanatomical markers and ensemble methods. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, Z.; Torfeh, T.; Aouadi, S.; Ji, X.; Bouhali, O. An efficient ensemble approach for brain tumors classification using magnetic resonance imaging. Information 2024, 15, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardalan, Z.; Subbian, V. Transfer learning approaches for neuroimaging analysis: A scoping review. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 780405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Qingjie, Z.; Bangyal, W.H.K.; Iqbal, M. Analysis of brain imaging data for the detection of early age autism spectrum disorder using transfer learning approaches for Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2023, 70, 4478–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufumier, B.; Gori, P.; Petiton, S.; Louiset, R.; Mangin, J.F.; Grigis, A.; Duchesnay, E. Exploring the potential of representation and transfer learning for anatomical neuroimaging: Application to psychiatry. NeuroImage 2024, 296, 120665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, R.C.; Viana, M.S.; Bernardino, V.J.S.; Santos, F.L.D.; Toygar, Ö.; Guido, R.C. A multi-filter deep transfer learning framework for image-based autism spectrum disorder detection. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, J.M.; Imani, V.; Abdollahzadeh, A.; De Feo, R.; Prakash, M.; Ciszek, R.; Tohka, J. Transfer learning in magnetic resonance brain imaging: A systematic review. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almars, A.M.; Badawy, M.; Elhosseini, M.A. ASD2-TL∗ GTO: Autism spectrum disorders detection via transfer learning with gorilla troops optimizer framework. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, S.L.; Moustafa, A.A.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Towards Clinical Diagnoses: Classifying Alzheimer’s Disease Using Single fMRI, Small Datasets, and Transfer Learning. Brain Behav. 2025, 15, e70427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parui, S.; Samanta, D.; Chakravorty, N.; Ghosh, U.; Rodrigues, J.J. Artificial intelligence and sensor-based autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using brain connectivity analysis. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 108, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, E.; Elnakib, A.; ElNakieb, Y.; Khudri, M.; Abdelrahim, M.; Yousaf, J.; Ghazal, M.; Contractor, S.; Barnes, G.N.; El-Baz, A. Role of artificial intelligence for autism diagnosis using DTI and fMRI: A survey. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, N.; Zang, Y.; Sun, S.; Shen, G.; Song, X. Quantitative assessment of brain structural abnormalities in children with autism spectrum disorder based on artificial intelligence automatic brain segmentation technology and machine learning methods. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2024, 345, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, S.; Khan, D.M.; Masroor, K.; Warda; Rashid, A.; Shabbir, M. Advancements in automated diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder through deep learning and resting-state functional MRI biomarkers: A systematic review. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2024, 18, 3585–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Schiavi, S.; La Rosa, P.; Rossi-Espagnet, M.C.; Petrillo, S.; Bottino, F.; Tagliente, E.; Longo, D.; Lupi, E.; Casula, L.; et al. Sex differences in autism spectrum disorder: Diagnostic, neurobiological, and behavioral features. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 889636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.R.; Lane, A.L.; Werner, B.A.; McLees, S.E.; Fletcher, T.S.; Frye, R.E. Modern biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder: Future directions. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 26, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garic, D.; McKinstry, R.C.; Rutsohn, J.; Slomowitz, R.; Wolff, J.; MacIntyre, L.C.; Weisenfeld, L.A.H.; Kim, S.H.; Pandey, J.; St John, T.; et al. Enlarged perivascular spaces in infancy and autism diagnosis, cerebrospinal fluid volume, and later sleep problems. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2348341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirnigliaro, L.; Clericò, L.; Russo, L.C.; Prato, A.; Caruso, M.; Rizzo, R.; Barone, R. Head circumference growth in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Trend and clinical correlates in the first five years of life. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1431693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, G.; Rieder, A.D.; Johnson, M.H. Prediction of autism in infants: Progress and challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 22, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, A.; McDonald, N.; Dapretto, M.; Campos, E.; Senturk, D.; Jeste, S. Accelerated Infant Brain Rhythm Maturation in Autism. Dev. Sci. 2025, 28, e13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Moerman, F.; Niu, H.; Warreyn, P.; Roeyers, H. Atypical brain network development of infants at elevated likelihood for autism spectrum disorder during the first year of life. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 2223–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, J.; Schwichtenberg, A.J.; Iverson, J.M. Capturing the complexity of autism: Applying a developmental cascades framework. Child. Dev. Perspect. 2022, 16, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Linke, A.; Olson, L.; Kohli, J.; Kinnear, M.; Sereno, M.; Müller, R.; Carper, R.; Fishman, I. Cortical myelination in toddlers and preschoolers with autism spectrum disorder. Dev. Neurobiol. 2022, 82, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallworthy, I.C.; Berry, D.; Davis, S.; Wolff, J.J.; Burrows, C.A.; Swanson, M.R.; Grzadzinski, R.L.; Botteron, K.; Dager, S.R.; Estes, A.M.; et al. Quantifying latent social motivation and its associations with joint attention and language in infants at high and low likelihood for autism spectrum disorder. Dev. Sci. 2023, 26, e13336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faizo, N.L. A narrative review of MRI changes correlated to signs and symptoms of autism. Medicine 2022, 101, e30059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.S.; Lee, J.K.; Harvey, D.J.; Waizbard-Bartov, E.; Solomon, M.; Rogers, S.J.; Nordahl, C.W.; Amaral, D.G. A longitudinal study of white matter development in relation to changes in autism severity across early childhood. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godel, M.; Andrews, D.S.; Amaral, D.G.; Ozonoff, S.; Young, G.S.; Lee, J.K.; Wu Nordahl, C.; Schaer, M. Altered gray-white matter boundary contrast in toddlers at risk for autism relates to later diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 669194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFayden, T.C.; Rutsohn, J.; Cetin, G.; Forsen, E.; Swanson, M.R.; Meera, S.S.; Wolff, J.J.; Elison, J.T.; Shen, M.D.; Botteron, K.; et al. White matter development and language abilities during infancy in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ming, Y.; Zhao, W.; Feng, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Li, L.; Shan, X.; et al. Developmental prediction modeling based on diffusion tensor imaging uncovering age-dependent heterogeneity in early childhood autistic brain. Mol. Autism 2023, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Qu, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, T.; Zhang, X. Impaired motor and social skill development in infancy predict high autistic traits in toddlerhood. Neuroscience 2024, 558, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Becker, B.; Kendrick, K.M. Reduced inter-hemispheric resting state functional connectivity and its association with social deficits in autism. Front. Psychiatry 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xu, X.; Becker, B.; Kendrick, K.M. Decreased homotopic interhemispheric functional connectivity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wen, T.H.; Kupis, L.; Eyler, L.T.; Taluja, V.; Troxel, J.; Goel, D.; Lombardo, M.V.; Pierce, K.; Courchesne, E. Atypical functional connectivity of temporal cortex with precuneus and visual regions may be an early-age signature of ASD. Mol. Autism 2023, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Xue, H.; Du, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Ming, D. Individuals with high autistic traits exhibit altered interhemispheric brain functional connectivity patterns. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2025, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogéa Ribeiro, L.; da Silva Filho, M. Systematic review on EEG analysis to diagnose and treat autism by evaluating functional connectivity and spectral power. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girault, J.B.; Donovan, K.; Hawks, Z.; Talovic, M.; Forsen, E.; Elison, J.T.; Shen, M.D.; Swanson, M.R.; Wolff, J.J.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Infant visual brain development and inherited genetic liability in autism. Am. J. Psychiatry 2022, 179, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, B.C.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.J.; Han, C.E. Overconnectivity of the right Heschl’s and inferior temporal gyrus correlates with symptom severity in preschoolers with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 2314–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankus, M.; Ochman-Pasierbek, P.; Brzozowska, M.; Striano, P.; Paprocka, J. Electroencephalography in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, S.; Kadlaskar, G.; Edmondson, D.A.; McNally Keehn, R.; Dydak, U.; Keehn, B. Associations between sensory processing and electrophysiological and neurochemical measures in children with ASD: An EEG-MRS study. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E.; Aroutzidis, A.; Antonopoulou, H.; Halkiopoulos, C. From Neural Networks to Emotional Networks: A Systematic Review of EEG-Based Emotion Recognition in Cognitive Neuroscience and Real-World Applications. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, H.; Yuan, T.; Zhao, D. A scoping review of physiological biomarkers in autism. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1269880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.B.; Vangala, S.; Elashoff, D.; Safari, T.; Smith, B.A. Using wearable sensor technology to measure motion complexity in infants at high familial risk for autism spectrum disorder. Sensors 2021, 21, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Schrader, P. A study of brain networks for autism spectrum disorder classification using resting-state functional connectivity. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsicano, G.; Bertini, C.; Ronconi, L. Decoding cognition in neurodevelopmental, psychiatric and neurological conditions with multivariate pattern analysis of EEG data. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 164, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, N.; Fu, L.; Qian, L.; Sun, B.; Li, C.; Gao, H.; Lei, T.; Ke, X. The correlation between brain structure characteristics and emotion regulation ability in children at high risk of autism spectrum disorder. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 33, 3247–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.S.; Galatzer-Levy, I.R.; Bigio, B.; Nasca, C.; Zhang, Y. Modern views of machine learning for precision psychiatry. Patterns 2022, 3, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Xu, J. Detection of ASD children through deep-learning application of fMRI. Children 2023, 10, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttikonda, K.; Ashvitha, Y.; Reddy, V.S.R.; Krishna, R.M.; Sandeep, P. Integrating Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Machine Learning for Accurate Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Facial Biomarkers. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Emerging Systems and Intelligent Computing (ESIC), Bhubaneswar, India, 9–10 February 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vantaraki, F.; Skoulidi, C.; Anastassopoulos, P.; Vantarakis, A. Gamified Health Promotion in Schools: The Integration of Neuropsychological Aspects and CBT—A Systematic Review. Medicina 2024, 60, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haweel, R.; Shalaby, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Seada, N.; Ghoniemy, S.; Ghazal, M.; Casanova, M.F.; Barnes, G.N.; El-Baz, A. A robust DWT-CNN-based CAD system for early diagnosis of autism using task-based fMRI. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahathiq, R.A.; Banjar, H.; Bamaga, A.K.; Jarraya, S.K. Machine learning for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using structural magnetic resonance imaging: Promising but challenging. Front. Neuroinform. 2022, 16, 949926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuqhim, F.; Saeed, F. ASD-SAENet: A sparse autoencoder, and deep-neural network model for detecting autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using fMRI data. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 654315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Raja, P.; Gulzar, Y. Investigation of machine learning methods for early prediction of neurodevelopmental disorders in children. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 5766386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fan, J.; Bailey, B.; Müller, R.A.; Linke, A. Assessing predictive ability of dynamic time warping functional connectivity for ASD classification. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2023, 2023, 8512461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, C.; Deruelle, C.; Auzias, G. Machine learning for neurodevelopmental disorders. In Machine Learning for Brain Disorders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bianco, T.; Mason, L.; Charman, T.; Tillman, J.; Loth, E.; Hayward, H.; Shic, F.; Buitelaar, J.; Johnson, M.H.; Jones, E.J.H.; et al. Temporal profiles of social attention are different across development in autistic and neurotypical people. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Rizzo, D.M.; Hanley, J.P.; Coderre, E.L.; Prelock, P.A. Identifying neuroanatomical and behavioral features for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis in children using machine learning. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vassilopoulos, S.P.; Nikolaou, G. Brain-Inspired Multisensory Learning: A Systematic Review of Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Outcomes in Adult Multicultural and Second Language Acquisition. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, D.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Predicting brain structural network using functional connectivity. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Ke, P.; Huang, J.; Xiong, D.; Huang, Y.; Ma, G.; Ning, Y.; Wu, F.; Wu, K. Classification of schizophrenia patients using a graph convolutional network: A combined functional MRI and connectomics analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mill, R.D.; Winfield, E.C.; Cole, M.W.; Ray, S. Structural MRI and functional connectivity features predict current clinical status and persistence behavior in prescription opioid users. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 30, 102663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Yan, W.; Luo, N.; Zhi, D.; Fu, Z.; Du, Y.; Yu, S.; Jiang, T.; Calhoun, V.D.; Sui, J. An attention-based hybrid deep learning framework integrating brain connectivity and activity of resting-state functional MRI data. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 78, 102413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Sui, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, E.; Jiaerken, Y.; Luo, N.; Yap, P.-T.; Liu, M.; Shen, D. A mutual multi-scale triplet graph convolutional network for classification of brain disorders using functional or structural connectivity. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengi, M.; Malhotra, D. A systematic literature review on traditional to artificial intelligence based socio-behavioral disorders diagnosis in India: Challenges and future perspectives. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyarani, R.A.; Senthilkumar, R. Eye tracking biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder detection using machine learning and deep learning techniques. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Jiang, G.; Luo, H.; Shao, Y. Neurobiological bases of social networks. Front. Psychol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberz, J.; Shamay-Tsoory, S.G.; Saporta, N. Loneliness and the social brain: How perceived social isolation impairs human interactions. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babinet, M.N.; Cublier, M.; Demily, C.; Michael, G.A. Eye direction detection and perception as premises of a social brain: A narrative review of behavioral and neural data. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliske, L.; Kanske, P. The social connectome—Moving toward complexity in the study of brain networks and their interactions in social cognitive and affective neuroscience. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 845492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.; Childers, E.; Norris, S.M.P. Multimodal Biomarkers for Central Nervous System Disorders; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vassilopoulos, S.P.; Nikolaou, G.; Vantarakis, A. Neurotechnological Approaches to Cognitive Rehabilitation in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review of Neuromodulation, EEG, Virtual Reality, and Emerging AI Applications. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saks, D.G.; Smith, E.E.; Sachdev, P.S. National and international collaborations to advance research into vascular contributions to cognitive decline. Cereb. Circ. Cogn. Behav. 2024, 6, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuominen, R.K.; Renko, J.M. Biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease in perspective of early diagnosis and translation of neurotrophic therapies. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2024, 135, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, F.; de Valle, K.; Lemmers, R.J.L.F.; Mul, K.; Dumonceaux, J.; Voermans, N.; Tasca, G.; Gomez-Rodulfo, M.; Voermans, N.; Sacconi, S.; et al. 268th ENMC workshop—Genetic diagnosis, clinical classification, outcome measures, and biomarkers in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD): Relevance for clinical trials. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2023, 33, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabb, M.C.; Brady, L.S. Biomarker Methodologies: A NIMH Perspective. In Neurophysiologic Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Etiologic and Treatment Considerations; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vantarakis, A.; Gourzis, P. Neuroimaging Insights into the Public Health Burden of Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review of Electroencephalography-Based Cognitive Biomarkers. Medicina 2025, 61, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinost, D.; Pollatou, A.; Dufford, A.J.; Jiang, R.; Farruggia, M.C.; Rosenblatt, M.; Peterson, H.; Rodriguez, R.X.; Dadashkarimi, J.; Liang, Q.; et al. Machine learning and prediction in fetal, infant, and toddler neuroimaging: A review and primer. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 93, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loosen, A.M.; Kato, A.; Gu, X. Revisiting the role of computational neuroimaging in the era of integrative neuroscience. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 50, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leve, L.D.; Kanamori, M.; Humphreys, K.L.; Jaffee, S.R.; Nusslock, R.; Oro, V.; Hyde, L.W. The promise and challenges of integrating biological and prevention sciences: A community-engaged model for the next generation of translational research. Prev. Sci. 2024, 25, 1177–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Woo, C.W.; Qi, S.; Wu, J.; Sui, J. Interpreting brain biomarkers: Challenges and solutions in interpreting machine learning-based predictive neuroimaging. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2022, 39, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, M.; Macuzic, I.Z.; Milosavljevic, J.; Lukovic, T.; Aleksic, D.; Gavrilovic, J.; Milosavljevic, M.; Jankovic, S.; Pejcic, A. Amygdala volumes in autism spectrum disorders: Meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 10, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.; Kalvin, C.; Morand-Beaulieu, S.; He, G.; Pelphrey, K.A.; McCarthy, G.; Sukhodolsky, D.G. Amygdala-prefrontal connectivity in children with maladaptive aggression is modulated by social impairment. Cereb. Cortex 2022, 32, 4371–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Brito, S.A.; McDonald, D.; Camilleri, J.A.; Rogers, J.C. Cortical and subcortical gray matter volume in psychopathy: A voxel-wise meta-analysis. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2021, 130, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berluti, K.; Ploe, M.L.; Marsh, A.A. Emotion processing in youths with conduct problems: An fMRI meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arioli, M.; Gianelli, C.; Canessa, N. Neural representation of social concepts: A coordinate-based meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021, 15, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyon, R.; Chavez, R.S.; Chwe, J.A.H.; Wheatley, T.; Kleinbaum, A.M.; Parkinson, C. White matter connectivity in brain networks supporting social and affective processing predicts real-world social network characteristics. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, A.; van der Velpen, I.F.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij-Dassen, M.J.; Niessen, W.J.; Vernooij, M.W.; Kas, M.J. Social health is associated with tract-specific brain white matter microstructure in community-dwelling older adults. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2023, 3, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elandaloussi, Y.; Floris, D.L.; Coupé, P.; Duchesnay, E.; Mihailov, A.; Grigis, A.; Bègue, I.; Victor, J.; Frouin, V.; Leboyer, M.; et al. Understanding the relationship between cerebellar structure and social abilities. Mol. Autism 2023, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerareddy, A.; Fang, H.; Safari, N.; Xu, P.; Krueger, F. Social network size, empathy, and white matter: A diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deferm, W.; Tang, T.; Moerkerke, M.; Daniels, N.; Steyaert, J.; Alaerts, K.; Ortibus, E.; Naulaers, G.; Boets, B. Subtle microstructural alterations in white matter tracts involved in socio-emotional processing after very preterm birth. NeuroImage Clin. 2024, 41, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekelman, L.R.; Zhang, F.; Makris, N.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, T.; Liera, D.; Drane, D.L.; Rathi, Y.; Golby, A.J.; et al. White matter association tracts underlying language and theory of mind: An investigation of 809 brains from the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2022, 246, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, B.J.; Archer, D.B.; Farmer, A.L.; Bass, C.; Korah, H.; Vaillancourt, D.E.; Lewis, M.H. Cortico-basal ganglia white matter microstructure is linked to restricted repetitive behavior in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2024, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro da Costa, C.; Soares, J.M.; Oliveira-Silva, P.; Sampaio, A.; Coutinho, J.F. Interplay between the salience and the default mode network in a social-cognitive task toward a close other. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 718400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, T.; Ha, M.; Moon, S.Y.; Lho, S.K.; Kim, M.; Kwon, J.S. Intrinsic cerebellar functional connectivity of social cognition and theory of mind in first-episode psychosis patients. npj Schizophr. 2021, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, C.; Lima, G.; Pais, M.L.; Teixeira, M.; Cabral, C.; Castelo-Branco, M. Increased functional connectivity between brain regions involved in social cognition, emotion and affective-value in psychedelic states induced by N, N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT). Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1454628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massalha, Y.; Maggioni, E.; Callari, A.; Brambilla, P.; Delvecchio, G. A review of resting-state fMRI correlations with executive functions and social cognition in bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 334, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. Abnormal gray matter volume and functional connectivity patterns in social cognition-related brain regions of young children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Meng, J.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J. Functional connectivity induced by social cognition task predict individual differences in loneliness. Neuroscience 2025, 565, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Lu, P.; Kang, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Wu, W.; Cai, K.; Ru, S.; Cao, J.; et al. Abnormal hypothalamic functional connectivity associated with cognitive impairment in craniopharyngiomas. Cortex 2024, 178, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera-Bermejo, J.M.; De Marco, M.; Mitolo, M.; Cerami, C.; Dodich, A.; Venneri, A. Large-scale functional networks, cognition and brain structures supporting social cognition and theory of mind performance in prodromal to mild Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 766703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, S.; Taridashti, S.; Farahani, H.; Watson, P.; Rezvani, E. Multilayer perceptron modeling for social dysfunction prediction based on general health factors in an Iranian women sample. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1283095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miley, K.; Michalowski, M.; Yu, F.; Leng, E.; McMorris, B.J.; Vinogradov, S. Predictive models for social functioning in healthy young adults: A machine learning study integrating neuroanatomical, cognitive, and behavioral data. Soc. Neurosci. 2022, 17, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Hu, A.; He, G.; Ju, G. Social prediction: A new research paradigm based on machine learning. J. Chin. Sociol. 2021, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkut, M.; Blok, E.; Suleri, A.; White, T. The longitudinal bidirectional relationship between autistic traits and brain morphology from childhood to adolescence: A population-based cohort study. Mol. Autism 2022, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Green, H.L.; McNamee, M.; Franzen, R.E.; DiPiero, M.; Berman, J.I.; Ku, M.; Bloy, L.; Liu, S.; Airey, M.; et al. White matter microstructure as a potential contributor to differences in resting state alpha activity between neurotypical and autistic children: A longitudinal multimodal imaging study. Mol. Autism 2025, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.; Prigge, M.; Alexander, A.; Zielinski, B.; Lainhart, J.; King, J. Flexible nonlinear modeling reveals age-related differences in resting-state functional brain connectivity in autistic males from childhood to mid-adulthood. Mol. Autism 2025, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almulla, M.A.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. Integrated social cognitive theory with learning input factors: The effects of problem-solving skills and critical thinking skills on learning performance sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilroy, E.; Ring, P.; Hossain, A.; Nalbach, A.; Butera, C.; Harrison, L.; Jayashankar, A.; Vigen, C.; Aziz-Zadeh, L.; Cermak, S.A. Motor performance, praxis, and social skills in autism spectrum disorder and developmental coordination disorder. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 1649–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.A.; Petrulla, V.; Zampella, C.J.; Waller, R.; Schultz, R.T. Gross motor impairment and its relation to social skills in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and two meta-analyses. Psychol. Bull. 2022, 148, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braconnier, M.L.; Siper, P.M. Neuropsychological assessment in autism spectrum disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2021, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parke, E.M.; Becker, M.L.; Graves, S.J.; Baily, A.R.; Paul, M.G.; Freeman, A.J.; Allen, D.N. Social cognition in children with ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, M.V.; Busuoli, E.M.; Schreibman, L.; Stahmer, A.C.; Pramparo, T.; Landi, I.; Mandelli, V.; Bertelsen, N.; Barnes, C.C.; Gazestani, V.; et al. Pre-treatment clinical and gene expression patterns predict developmental change in early intervention in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7641–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, K.; Soorya, L.V.; Halpern, D.B.; Gorenstein, M.; Siper, P.M.; Wang, A.T. Social cognitive skills groups increase medial prefrontal cortex activity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 2495–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Ming, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ou, J.; Kou, J.; Feng, R.; Ma, R.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Personalized theta-burst stimulation enhances social skills in young minimally verbal children with autism: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Biol. Psychiatry 2025, 97, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, A.; Baran, B.; Feusner, J.D.; Phan, K.L.; Beatty, C.C.; Crane, J.; Jacoby, R.J.; Manoach, D.S.; Wilhelm, S. Self-focused brain predictors of cognitive behavioral therapy response in a transdiagnostic sample. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2024, 171, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asta, L.; Di Bella, T.; La Fauci Belponer, F.; Bruschetta, M.; Martines, S.; Basile, E.; Boncoddo, M.; Bellomo, F.; Cucinotta, F.; Ricciardello, A.; et al. Cognitive, behavioral and socio-communication skills as predictors of response to Early Start Denver Model: A prospective study in 32 young children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1358419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vassilopoulos, S.P.; Nikolaou, G.; Boutsinas, B. Digital and AI-Enhanced Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia: Neurocognitive Mechanisms and Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, M.; Zhang, H.; Jin, M.; Tao, Y.; Xu, H.; Zou, S.; Wang, Z.; Deng, F.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Dynamic functional connectivity patterns predict early antidepressant treatment response in drug-naïve, first-episode adolescent MDD. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1487754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamanna, J.; Meldolesi, J. Autism Spectrum Disorder: Brain areas involved, neurobiological mechanisms, diagnoses and therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, H.; Liang, Z.; Ma, G.; Qureshi, A.; Ran, X.; Feng, C.; Liu, X.; Yan, X.; Shen, L. Autism spectrum disorder: Pathogenesis, biomarker, and intervention therapy. MedComm 2024, 5, e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressa, H.J.; Newman, B.T.; Jacokes, Z.; McPartland, J.C.; Kleinhans, N.M.; Druzgal, T.J.; Pelphrey, K.A.; Van Horn, J.D. Widespread associations between behavioral metrics and brain microstructure in ASD suggest age mediates subtypes of ASD. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdue, M.V.; Mahaffy, K.; Vlahcevic, K.; Wolfman, E.; Erbeli, F.; Richlan, F.; Landi, N. Reading intervention and neuroplasticity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of brain changes associated with reading intervention. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, T.R.A.; Davis, K.; Korponay, C.; Hirshberg, M.J.; Hoel, R.; Tello, L.Y.; Goldman, R.I.; Rosenkranz, M.A.; Lutz, A.; Davidson, R.J. Absence of structural brain changes from mindfulness-based stress reduction: Two combined randomized controlled trials. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.Y.; Shin, S.A.; Jeong, J.H.; Hong, C.H.; Park, Y.K.; Na, H.R.; Song, H.-S.; Park, H.K.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.M.; et al. Impact of a multidomain lifestyle intervention on regional spontaneous brain activity. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 926077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepits, P.; Koschutnig, K.; Zussner, T.; Fink, A. Changes in hippocampal volume and affective functioning after a moderate intensity running intervention. Brain Struct. Funct. 2025, 230, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.C.; Amonkar, N.; Cleffi, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Bhat, A. Neural effects of physical activity and movement interventions in individuals with developmental disabilities—A systematic review. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 794652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesleh, A.G.; Abdulla, S.A.; El-Agnaf, O. The way toward personalized medicine: Current advances and challenges in multi-OMICS approach in autism spectrum disorder for biomarkers discovery and patient stratification. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vassilopoulos, S.P.; Nikolaou, G. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy in Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review of Neurocognitive Outcomes and Applications for Mental Health and Well-Being. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolzadegan, D.; Moattar, M.H.; Ghoshuni, M. A robust method for early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder from EEG signals based on feature selection and DBSCAN method. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 39, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qazzaz, N.; Aldoori, A.; Buniya, A.; Ali, S.H.; Ahmad, S.A. Transfer learning and hybrid deep convolutional neural networks models for autism spectrum disorder classification from EEG signals. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 37976–37988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Als, H.; Duffy, F.H.; McAnulty, G.B. A stable pattern of EEG spectral coherence distinguishes children with autism from neurotypical controls: A large case control study. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, F.A.; Aljalal, M.A.; Abdurraqeeb, A.M.; Alsharabi, K.; Al-Shamma’a, A.A. Common spatial pattern technique with EEG signals for diagnosis of autism and epilepsy disorders. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 22494–22504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, H.A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Shayegh, F. Diagnosis of autism disorder based on deep network trained by augmented EEG signals. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2022, 32, 2250046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ari, B.; Sobahi, N.; Alçin, Ö.; Şengur, A.; Acharya, U.R. Accurate detection of autism using Douglas-Peucker algorithm, sparse coding-based feature mapping, and convolutional neural network techniques with EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, R.; Sharma, L.V. An automatic framework for detecting autism spectrum disorder from EEG signals using TFD. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 8941–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajestani, G.S.; Golpayegani, M.R.; Sheikhani, A.; Ashrafzadeh, F. Poincaré section analysis of the electroencephalogram in autism spectrum disorder using complement plots. Kybernetes 2017, 46, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.; Veytsman, E.; Choy, T.; Blacher, J.; Stavropoulos, K. Investigating changes in reward-related neural correlates after PEERS intervention in adolescents with ASD: Preliminary evidence of a “precision medicine” approach. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 742280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barttfeld, P.; Amoruso, L.; Ais, J.; Cukier, S.; Bavassi, L.; Tomio, A.; Manes, F.; Ibanez, A.; Sigman, M. Organization of brain networks governed by long-range connections index autistic traits in the general population. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2013, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitsika, V.; Sharpley, C.F.; Evans, I.D.; Vessey, K.A. Neurological validation of ASD diagnostic criteria using frontal alpha and theta asymmetry. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochet, A.; Sperdin, H.F.; Rihs, T.; Kojovic, N.; Franchini, M.; Jan, R.K.; Michel, C.M.; Schaer, M. Early alterations of large-scale brain networks temporal dynamics in young children with autism. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, C.F.; Pacey, P. Neural connectivity abnormalities in autism: Insights from the Tuberous Sclerosis model. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosl, W.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. EEG analytics for early detection of autism spectrum disorder: A data-driven approach. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 24318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosl, W.; Tierney, A.L.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. EEG complexity as a biomarker for autism spectrum disorder risk. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosl, W.; Tierney, A.L.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Response: Infant EEG activity as a biomarker for autism: A promising approach or a false promise? BMC Med. 2011, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruining, H.; Hardstone, R.; Juarez-Martinez, E.; Sprengers, J.; Avramiea, A.; Simpraga, S.; Houtman, S.J.; Poil, S.; Dallares, E.; Palva, S.; et al. Measurement of excitation-inhibition ratio in autism spectrum disorder using critical brain dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruining, H.; Juarez-Martinez, E.; Sprengers, J.; Andel, D.; Simpraga, S.; Poil, S.; Dallares, E.; Mansvelder, H.; Oranje, B.; Hardstone, R.; et al. 220. Non-invasive estimation of excitation-inhibition balance facilitates physiological dissection of autism spectrum disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnette, C.P.; Henderson, H.A.; Inge, A.P.; Zahka, N.E.; Schwartz, C.B.; Mundy, P.C. Anterior EEG asymmetry and the modifier model of autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2010, 41, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelhano, J.; Tavares, P.; Mouga, S.; Oliveira, G.; Castelo-Branco, M. Stimulus dependent neural oscillatory patterns show reliable statistical identification of autism spectrum disorder in a face perceptual decision task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.M.; Choi, C.X.; Tsoi, T.C.; Shea, C.K.S.; Yiu, K.W.; Han, Y.M.Y. Effects of multisession cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation with cognitive training on sociocognitive functioning and brain dynamics in autism: A double-blind, sham-controlled, randomized EEG study. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhu, D. Identification of atypical sleep microarchitecture biomarkers in children with autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1115374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coben, R.; Clarke, A.R.; Hudspeth, W.; Barry, R.J. EEG power and coherence in autistic spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cociu, B.A.; Das, S.; Billeci, L.; Jamal, W.; Maharatna, K.; Calderoni, S.; Narzisi, A.; Muratori, F. Multimodal functional and structural brain connectivity analysis in autism: A preliminary integrated approach with EEG, fMRI, and DTI. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2018, 10, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, E.J.; Barraclough, N.E.; Enticott, P.G. Investigating mirror system activity in adults with ASD when inferring others’ intentions using both TMS and EEG. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, I.A.; Wilson, A.C.; Peters, J.M.; Goyal, M.S.; Bebin, E.M.; Northrup, H.; Krueger, D.A.; Leuchter, A.F.; Sahin, M. EEG spectral features in sleep of autism spectrum disorders in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 3868–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoust, A.M.; Limoges, É.; Bolduc, C.; Mottron, L.; Godbout, R. EEG spectral analysis of wakefulness and REM sleep in high functioning autistic spectrum disorders. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Zomorrodi, R.; Mirjalili, M.; Kirkovski, M.; Blumberger, D.M.; Rajji, T.K.; Desarkar, P. Machine learning approaches for electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography analyses in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 117, 110705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, A.; Jeste, S.S.; Milne, E. Electrophysiological signatures of brain aging in autism spectrum disorder. Cortex 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diessen, E.; Senders, J.; Jansen, F.E.; Boersma, M.; Bruining, H. Increased power of resting-state gamma oscillations in autism spectrum disorder detected by routine electroencephalography. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 265, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donck, S.V.d.; Dzhelyova, M.; Vettori, S.; Thielen, H.; Steyaert, J.; Rossion, B.; Boets, B. Fast periodic visual stimulation EEG reveals reduced neural sensitivity to fearful faces in children with autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 3288–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yin, D.; Li, X. A multi-task learning model with reinforcement optimization for ASD comorbidity discrimination. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 158, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldeeb, S.M.; Susam, B.T.; Akçakaya, M.; Conner, C.M.; White, S.W.; Mazefsky, C.A. Trial by trial EEG based BCI for distress versus non-distress classification in individuals with ASD. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldridge, J.; Lane, A.; Belkin, M.; Dennis, S. Robust features for the automatic identification of autism spectrum disorder in children. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2014, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Wade, J.W.; Key, A.P.; Warren, Z.; Sarkar, N. EEG-based affect and workload recognition in a virtual driving environment for ASD intervention. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebelkorn, I.C.; Foxe, J.J.; McCourt, M.E.; Dumas, K.N.; Molholm, S. Atypical category processing and hemispheric asymmetries in high-functioning children with autism: Revealed through high-density EEG mapping. Cortex 2013, 49, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogelson, N.; Li, L.; Díaz-Brage, P.; Amatriain-Fernández, S.; Valle-Inclán, F. Altered predictive contextual processing of emotional faces versus abstract stimuli in adults with autism spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foss-Feig, J.H.; Guillory, S.B.; Stone, W.L.; Wallace, M.T.; Key, A.P. Biomarker development in ASD: Electrophysiological response during auditory gap detection is associated with symptom severity and may index excitatory/inhibitory imbalance. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83 (Suppl. 9), S24–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss-Feig, J.H.; Velthorst, E.; Guillory, S.B.; Hamilton, H.K.; Roach, B.J.; Bachman, P.; Belger, A.; Carrión, R.E.; Duncan, E.J.; Johannesen, J.K.; et al. Architecture of psychosis symptoms and neural predictors of conversion among clinical high risk individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44 (Suppl. 1), S17–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss-Feig, J.; Guillory, S.; Roach, B.J.; Velthorst, E.; Hamilton, H.; Bachman, P.; Belger, A.; Carrión, R.E.; Duncan, E.J.; Johannesen, J.K.; et al. Abnormally large baseline P300 amplitude is associated with conversion to psychosis in clinical high risk individuals with a history of autism: A pilot study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 591127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, E.V.C.; Sivanathan, A.; Lim, T.; Suttie, N.; Louchart, S.; Pillen, S.; Pineda, J.A. An effective neurofeedback intervention to improve social interactions in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 4084–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, J.; Senturk, D.; Saravanapandian, V.; Golshani, P.; Reiter, L.T.; Sankar, R.; Thibert, R.L.; DiStefano, C.; Huberty, S.; Cook, E.H.; et al. A quantitative electrophysiological biomarker of duplication 15q11.2-q13.1 syndrome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabard-Durnam, L.; Tierney, A.L.; Vogel-Farley, V.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Alpha asymmetry in infants at risk for autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabard-Durnam, L.; Wilkinson, C.; Kapur, K.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Levin, A.; Nelson, C.A. Longitudinal EEG power in the first postnatal year differentiates autism outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcés, P.; Baumeister, S.; Mason, L.; Chatham, C.H.; Holiga, Š.; Dukart, J.; Jones, E.J.H.; Banaschewski, T.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Bölte, S.; et al. Resting state EEG power spectrum and functional connectivity in autism: A cross-sectional analysis. Mol. Autism 2022, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, Y.; Bloy, L.; Edgar, J.C.; Blaskey, L.; Verma, R.; Roberts, T.P.L. Joint analysis of band-specific functional connectivity and signal complexity in autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gialloreti, L.E.; Benvenuto, A.; Battan, B.; Benassi, F.; Curatolo, P. Can biological components predict short-term evolution in autism spectrum disorders? A proof-of-concept study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Glauser, J.; Wilkinson, C.; Gabard-Durnam, L.; Choi, B.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Neural correlates of face processing associated with development of social communication in 12-month infants with familial risk of autism spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2022, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golob, E.J.; Edgington, D. Atypical sensory reactivity influences auditory attentional control in adults with autism spectrum disorders. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, E.; Olivieri, C.; Buscema, P. Diagnosis of autism through EEG processed by advanced computational algorithms: A pilot study. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 142, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurau, O.; Bosl, W.; Newton, C.R. How useful is electroencephalography in the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders and the delineation of subtypes: A systematic review. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haartsen, R.; Jones, E.J.H.; Orekhova, E.V.; Charman, T.; Johnson, M.H.; the BASIS Team. Functional EEG connectivity in infants associates with later restricted and repetitive behaviours in autism: A replication study. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadoush, H.; Alafeef, M.; Almasri, N.; Abdulhay, E. Resting-state EEG changes after bilateral anodal transcranial direct current stimulation over mirror neurons in children with autism spectrum disorders: A pilot study. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, A.R.; Vucic, S.N.; Georges, B.; LaRoche, M.; Pardo, M.A.M.; Swiggard, L.O.; McDonald, K.; Olofsson, M.; Menon, S.N.; Francis, S.M.; et al. Heterogeneity and convergence across seven neuroimaging modalities: A review of the autism spectrum disorder literature. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1474003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Jiang, G.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X. A multimodal approach for identifying autism spectrum disorders in children. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasenstab, K.; Scheffler, A.; Telesca, D.; Sugar, C.A.; Jeste, S.S.; DiStefano, C.; Şentürk, D. A multi-dimensional functional principal components analysis of EEG data. Biometrics 2017, 73, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasenstab, K.; Sugar, C.A.; Telesca, D.; Jeste, S.S.; Şentürk, D. Robust functional clustering of ERP data with application to a study of implicit learning in autism. Biostatistics 2016, 17, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heunis, T.; Aldrich, C.; Peters, J.M.; Jeste, S.S.; Sahin, M.; Scheffer, C.; de Vries, P.J. Recurrence quantification analysis of resting-state EEG signals in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic methodological exploration of technical and demographic confounders in the search for biomarkers. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Jiang, G.; Han, J.; Li, X.; Xie, P. Regional-asymmetric adaptive graph convolutional neural network for diagnosis of autism in children with resting-state EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 2987–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huberty, S.; Leno, V.C.; van Noordt, S.J.R.; Bedford, R.; Pickles, A.; Desjardins, J.; Webb, S.J.; Elsabbagh, M. Association between spectral electroencephalography power and autism risk and diagnosis in early development. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudac, C.M.; Kresse, A.; Aaronson, B.; DesChamps, T.D.; Webb, S.J.; Bernier, R.A. Modulation of mu attenuation to social stimuli in children and adults with 16p11.2 deletions and duplications. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2015, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Isaev, D.; Major, S.; Murias, M.; Carpenter, K.L.H.; Carlson, D.; Sapiro, G.; Dawson, G. Relative average look duration and its association with neurophysiological activity in young children with autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ja, M.; Ortiz, T.; Palau-Baduell, M.; Martín-Muñoz, L.; Salvadó-Salvadó, B.; Valls-Santasusana, A.; Perich-Alsina, J.; Cristóbal, I.; Fernández, A.; Maestú, F.; et al. Magnetoencephalographic pattern of epileptiform activity in children with early-onset autism spectrum disorders. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaime, M.; McMahon, C.M.; Davidson, B.C.; Newell, L.C.; Mundy, P.C.; Henderson, H.A. Brief Report: Reduced temporal-central EEG alpha coherence during joint attention perception in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, W.; Das, S.; Oprescu, I.; Maharatna, K.; Apicella, F.; Sicca, F. Classification of autism spectrum disorder using supervised learning of brain connectivity measures extracted from synchrostates. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 046019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeste, S.S.; Frohlich, J.; Loo, S.K. Electrophysiological biomarkers of diagnosis and outcome in neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; He, R.; Li, Y.; Yi, C.; Peng, Y.; Yao, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, P.; Yang, Y. Predicting the long-term after-effects of rTMS in autism spectrum disorder using temporal variability analysis of scalp EEG. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 066051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.J.H.; Dawson, G.; Kelly, J.; Estes, A.; Webb, S.J. Parent-delivered early intervention in infants at risk for ASD: Effects on electrophysiological and habituation measures of social attention. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kala, S.; Rolison, M.J.; Trevisan, D.A.; Naples, A.J.; Pelphrey, K.A.; Ventola, P.; McPartland, J.C. Brief report: Preliminary evidence of the N170 as a biomarker of response to treatment in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 709382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Han, X.; Song, J.; Niu, Z.; Li, X. The identification of children with autism spectrum disorder by SVM approach on EEG and eye-tracking data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayarian, F.B.; Jannati, A.; Rotenberg, A.; Santarnecchi, E. Targeting gamma-related pathophysiology in autism spectrum disorder using transcranial electrical stimulation: Opportunities and challenges. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkovski, M.; Rogasch, N.C.; Saeki, T.; Fitzgibbon, B.M.; Enticott, P.G.; Fitzgerald, P.B. A combined TMS-EEG investigation of autism spectrum disorder. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 456–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauttia, J.; Helminen, T.M.; Leppänen, J.M.; Yrttiaho, S.; Eriksson, K.; Hietanen, J.K.; Kylliäinen, A. Atypical pattern of frontal EEG asymmetry for direct gaze in young children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kong, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X.; Chen, S. Identification of autism spectrum disorder based on electroencephalography: A systematic review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 166, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Weiland, R.F.; Konvalinka, I.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Andersen, T.S.; Smit, D.J.; Begeer, S.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. Intellectually able adults with autism spectrum disorder show typical resting-state EEG activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharatna, K.; Billeci, L. Linear and nonlinear analysis of intrinsic mode function after facial stimuli presentation in children with autism spectrum disorder. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharatna, K.; Das, S. Classification of autism spectrum disorder from EEG-based functional brain connectivity analysis. Neural Comput. 2021, 33, 2156–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, T.; Wang, M. Computational model of functional connectivity distance predicts neural alterations. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2024, 16, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mash, L.E.; Reiter, M.A.; Linke, A.C.; Townsend, J.; Müller, R.A. Multimodal approaches to functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorders: An integrative perspective. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, C.R.; Villalobos, M.E.; Schultz, R.T.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Konrad, K.; Kohls, G. Atypical laterality of resting gamma oscillations in autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, K.; Jeste, S. Resting State EEG Serves As A Promising Biomarker of Cognitive and Language Function in Young Children with ASD. (I4-1.005). Neurology 2014, 82 (Suppl. 10), I4-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPartland, J.; Dawson, G.; Webb, S.J.; Panagiotides, H.; Carver, L.J. Event-related brain potentials reveal anomalies in temporal processing of faces in autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.C.; Bernier, R.; South, M. Realizing the translational promise of psychophysiological research in ASD. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 3145–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPartland, J.C.; Crowley, M.J.; Perszyk, D.R.; Naples, A.J.; Mukerji, C.E.; Wu, J.; Molfese, P.J.; Bolling, D.Z.; Pelphrey, K.A.; Mayes, L.C. Temporal dynamics reveal atypical brain response to social exclusion in autism. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 1, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McVoy, M.; Lytle, S.; Fulchiero, E.; Aebi, M.E.; Adeleye, O.; Sajatovic, M. A systematic review of quantitative EEG as a possible biomarker in child psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 279, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, E.; Scope, A.; Pascalis, O.; Buckley, D.; Makeig, S. Independent component analysis reveals atypical electroencephalographic activity during visual perception in individuals with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murias, M.; Major, S.; Compton, S.; Buttinger, J.; Sun, J.M.; Kurtzberg, J.; Dawson, G. Electrophysiological biomarkers predict clinical improvement in an open-label trial assessing efficacy of autologous umbilical cord blood for treatment of autism. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murias, M.; Webb, S.J.; Greenson, J.; Dawson, G. Resting state cortical connectivity reflected in EEG coherence in individuals with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 62, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.W.; Foxe, J.J.; Peters, J.B.; Molholm, S. Susceptibility to distraction in autism spectrum disorder: Probing the integrity of oscillatory alpha-band suppression mechanisms. Autism Res. 2014, 7, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, S.; Senftleben, U.; Santhosh, M.; McPartland, J.C.; Webb, S.J. Neurophysiological correlates of holistic face processing in adolescents with and without autism spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2018, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, E.; Lowry, S.J.; Santhosh, M.; Kresse, A.; Edwards, L.A.; Keller, J.L.; Libsack, E.J.; Kang, V.Y.; Naples, A.J.; Jack, A.; et al. Resting state EEG in youth with ASD: Age, sex, and relation to phenotype. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, E.; Santhosh, M.; Kresse, A.; Aylward, E.H.; Bernier, R.A.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Jeste, S.S.; Jack, A.; McPartland, J.C.; Naples, A.J.; et al. Frontal EEG alpha asymmetry in youth with autism: Sex differences and social–emotional correlates. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordt, M.; Hoehl, S.; Weigelt, S. The use of repetition suppression paradigms in developmental cognitive neuroscience. Cortex 2016, 80, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, A.; Cygan, H.B.; Tacikowski, P.; Ostaszewski, P.; Kuś, R. Name recognition in autism: EEG evidence of altered patterns of brain activity and connectivity. Mol. Autism 2016, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.R.; Mitjans, M.; Nitsche, M.A.; Kuo, M.F.; Ehrenreich, H. Excitation-inhibition dysbalance as predictor of autistic phenotypes. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 102, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orekhova, E.V.; Elsabbagh, M.; Jones, E.J.H.; Dawson, G.; Charman, T.; Johnson, M.H. EEG hyper-connectivity in high-risk infants is associated with later autism. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2014, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, S.; Jain, S.; Verma, J.P. A comprehensive analysis towards exploring the promises of AI-related approaches in autism research. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 162, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, D.; Enticott, P.G.; Albein-Urios, N. Anodal HD-tDCS for cognitive inflexibility in autism spectrum disorder: A pilot study. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1422–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, F.C.; Gabard-Durnam, L.; Wilkinson, C.; Bosl, W.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Prediction of autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using nonlinear measures of language-related EEG at 6 and 12 months. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.M.; Taquet, M.; Vega, C.; Jeste, S.S.; Fernández, I.S.; Tan, J.; Nelson, C.A.; Sahin, M.; Warfield, S.K. Brain functional networks in syndromic and non-syndromic autism: A graph theoretical study of EEG connectivity. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.S.; Liu, J.; Dantec, L.; Newman, C.; Sawardekar, S.; Goh, S.; Bansal, R. Using tissue microstructure and multimodal MRI to parse the phenotypic heterogeneity and cellular basis of autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2021, 63, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, C.; Dondena, C.; Riboldi, E.M.; Riva, V.; Cantiani, C. Baseline EEG in the first year of life: Preliminary insights into the development of autism spectrum disorder and language impairments. iScience 2023, 26, 106987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardi, E.S.; Ali, J.B.; Jones, E.J.H.; Mason, L.; Charman, T.; Johnson, M.H.; Gliga, T. Behavioural and neural markers of tactile sensory processing in infants at elevated likelihood of autism spectrum disorder and/or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, A.S.; McAuliffe, D.; Lakshmanan, B.; Mostofsky, S.H.; Crone, N.E.; Ewen, J.B. Altered task-related modulation of long-range connectivity in children with autism. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda, J.A.; Carrasco, K.; Datko, M.; Pillen, S.; Schalles, M.D. Neurofeedback training produces normalization in behavioural and electrophysiological measures of high-functioning autism. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranaut, A.; Khandnor, P.; Chand, T. Identification of autism spectrum disorder using electroencephalography and machine learning: A review. J. Neural Eng. 2024, 21, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righi, G.; Tierney, A.L.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Functional connectivity in the first year of life in infants at risk for autism spectrum disorder: An EEG study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogala, J.; Żygierewicz, J.; Malinowska, U.; Cygan, H.; Stawicka, E.; Kobus, A.; Vanrumste, B. Enhancing autism spectrum disorder classification in children through the integration of traditional statistics and classical machine learning techniques in EEG analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, M.; Sahin, M. Translational use of event-related potentials to assess circuit integrity in ASD. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, G.; Mosconi, M.W.; Wang, J.; Ethridge, L.E.; Sweeney, J.A.; Ding, L. Electrophysiological signatures of atypical intrinsic brain connectivity networks in autism. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 046019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D.M.; Damiano, C.R.; Woynaroski, T.G.; Ibañez, L.V.; Murias, M.; Stone, W.L.; Wallace, M.T.; Cascio, C.J. Neural correlates of sensory hyporesponsiveness in toddlers at high risk for autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siper, P.M.; George-Jones, J.; Lurie, S.; Rowe, M.A.; Durkin, A.; Weissman, J.; Meyering, K.E.; Rouhandeh, A.A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Kolevzon, A. Biomarker discovery in ASD: Visual evoked potentials as a biomarker of Phelan-McDermid syndrome. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siper, P.; Zemon, V.; Gordon, J.; George-Jones, J.; Lurie, S.; Zweifach, J.; Tavassoli, T.; Wang, A.T.; Jamison, J.; Buxbaum, J.D.; et al. Rapid and objective assessment of neural function in autism spectrum disorder using transient visual evoked potentials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotoodeh, M.; Taheri-Torbati, H.; Sohrabi, M.; Ghoshuni, M. Perception of biological motions is preserved in people with autism spectrum disorder: Electrophysiological and behavioural evidences. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2018, 62, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, A.; Mentch, J.; Haskins, A.J.; Robertson, C.E. Slower binocular rivalry in the autistic brain. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2948–2953.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprengers, J.J.; Martinez, E.L.J.; Simpraga, S.; Jansen, F.E.; Vlaskamp, C.R.; Oranje, B.; Poil, S.S.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K.; Bruining, H. An EEG-based decision-support system for diagnosis and prognosis of autism spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, e161–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroganova, T.A.; Orekhova, E.V.; Prokofyev, A.O.; Tsetlin, M.M.; Gratchev, V.V.; Morozov, A.A.; Obukhov, Y.V. High-frequency oscillatory response to illusory contour in typically developing boys and boys with autism spectrum disorders. Cortex 2012, 48, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, A.; Penchina, B.; Cheong, S.; Grace, V.; Valero-Cabré, A.; Martel, A. Evaluating deep learning EEG-based mental stress classification in adolescents with autism for breathing entrainment BCI. Brain Inform. 2021, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takarae, Y.; Zanesco, A.P.; Keehn, B.; Chukoskie, L.; Müller, R.A.; Townsend, J. EEG microstates suggest atypical resting-state network activity in high-functioning children and adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dev. Sci. 2022, 25, e13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, N.; Nasrabadi, A.M.; Rezazadeh, I.; Coben, R. nCREANN: Nonlinear causal relationship estimation by artificial neural network; applied for autism connectivity study. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.; Xu, K.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. A trend on autism spectrum disorder research: Eye tracking-EEG correlative analytics. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 14, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasi, L.; Martelli, M.E.; Bortoletto, M.; Pellegrino di, G.; Romei, V. Neural signatures of predictive strategies track individuals along the autism-schizophrenia continuum. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawhid, M.N.A.; Siuly, S.; Wang, H.; Whittaker, F.; Wang, K.N.; Zhang, Y. A spectrogram image-based intelligent technique for automatic detection of autism spectrum disorder from EEG. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, S.; Lambert, A.; Scherzer, P.; Jemel, B.; Godbout, R. REM sleep and emotional face memory in typically-developing children and children with autism. Biol. Psychol. 2015, 108, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, A.L.; Gabard-Durnam, L.; Vogel-Farley, V.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Developmental trajectories of resting EEG power: An endophenotype of autism spectrum disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.M.M.; Medina-DeVilliers, S.E.; Clarkson, T.; Lerner, M.; Riccardi, G. Evaluation of interpretability for deep learning algorithms in EEG emotion recognition: A case study in autism. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 137, 102545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.; Lee, C.; Chiu, Y.; Tsai, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Chien, Y. Characterizing autism spectrum disorder through fusion of local cortical activation and global functional connectivity using game-based stimuli and a mobile EEG system. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.; Liu, H.; Chiu, Y.; Lee, C.; Tsai, W.; Lin, Y.; Chien, Y. Electroencephalography connectivity assesses cognitive disorders of autistic children during game-based social interaction. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2024, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, L.Q. The influence of brain state on functional connectivity in autism. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1230–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valakh, V. Excitatory/inhibitory balance and circuit homeostasis in autism spectrum disorders. Neuron 2015, 87, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hecke, A.V.; Stevens, S.; Carson, A.M.; Karst, J.S.; Dolan, B.; Schohl, K.A.; McKindles, R.J.; Remmel, R.P.; Brockman, S. Measuring the plasticity of social approach: A randomized controlled trial of the effects of the PEERS intervention on EEG asymmetry in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 3161–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettori, S.; Dzhelyova, M.; Van den Donck, S.; Jacques, C.; Steyaert, J.; Rossion, B.; Boets, B. Frequency-tagging electroencephalography of superimposed social and non-social visual stimulation streams reveals reduced saliency of faces in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettori, S.; Dzhelyova, M.; Van den Donck, S.; Jacques, C.; Wesemael, T.V.; Steyaert, J.; Rossion, B.; Boets, B. Combined frequency-tagging EEG and eye tracking reveal reduced social bias in boys with autism spectrum disorder. Cortex 2019, 119, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, J.; Rasga, C.; Santos, J.X.; Martiniano, H.; Marques, A.R.; Oliveira, G.; Vicente, A.M. Bridging genetic insights with neuroimaging in autism spectrum disorder—A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Barstein, J.; Ethridge, L.E.; Mosconi, M.W.; Takarae, Y.; Sweeney, J.A. Resting state EEG abnormalities in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2013, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, C.; Gabard-Durnam, L.; Kapur, K.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Levin, A.R.; Nelson, C.A. Use of longitudinal EEG measures in estimating language development in infants with and without familial risk for autism spectrum disorder. Neurobiol. Lang. 2020, 1, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, B.; Alderson-Day, B.; Prendergast, G.; Bennett, S.; Jordan, J.; Whitton, C.; Gouws, A.; Jones, N.; Attur, R.; Tomlinson, H.; et al. Gamma activation in young people with autism spectrum disorders and typically-developing controls when viewing emotions on faces. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Autism spectrum disorder diagnosis with EEG signals using time series maps of brain functional connectivity and a combined CNN-LSTM model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 167, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardeni, T.; Cristancho, A.G.; McCoy, A.J.; Schaefer, P.M.; McManus, M.J.; Marsh, E.D.; Wallace, D.C. An mtDNA mutant mouse demonstrates that mitochondrial deficiency can result in autism endophenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021429118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.K.; Han, Y.M.Y.; Sze, S.L.; Chan, A.S. Abnormal frontal theta oscillations underlie the cognitive flexibility deficits in children with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychology 2016, 30, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, U. Attenuated long-range temporal correlations of electrocortical oscillations in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 36, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, U.; Du, D. Grid-tuned ensemble models for 2D spectrogram-based autism classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 88, 106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Kang, J.; Ouyang, G.; Li, J.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Sokhadze, E.M.; Casanova, M.F.; Li, X. Disrupted brain network in children with autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, D.; Tang, Y.; Li, X. Learning graph-based relationship of dual-modal features towards subject adaptive ASD assessment. Neurocomputing 2022, 497, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Feng, R.; Yao, D.; Li, F.; Xu, P. Predicting the symptom severity in autism spectrum disorder based on EEG metrics. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).