Raising Awareness of Intraoperative Diagnostic Challenges to Prevent Misdiagnosis and Overtreatment: Laparoscopic Management of Rare Cotyledonoid Dissecting Leiomyoma Mimicking Ovarian Tumour
Abstract
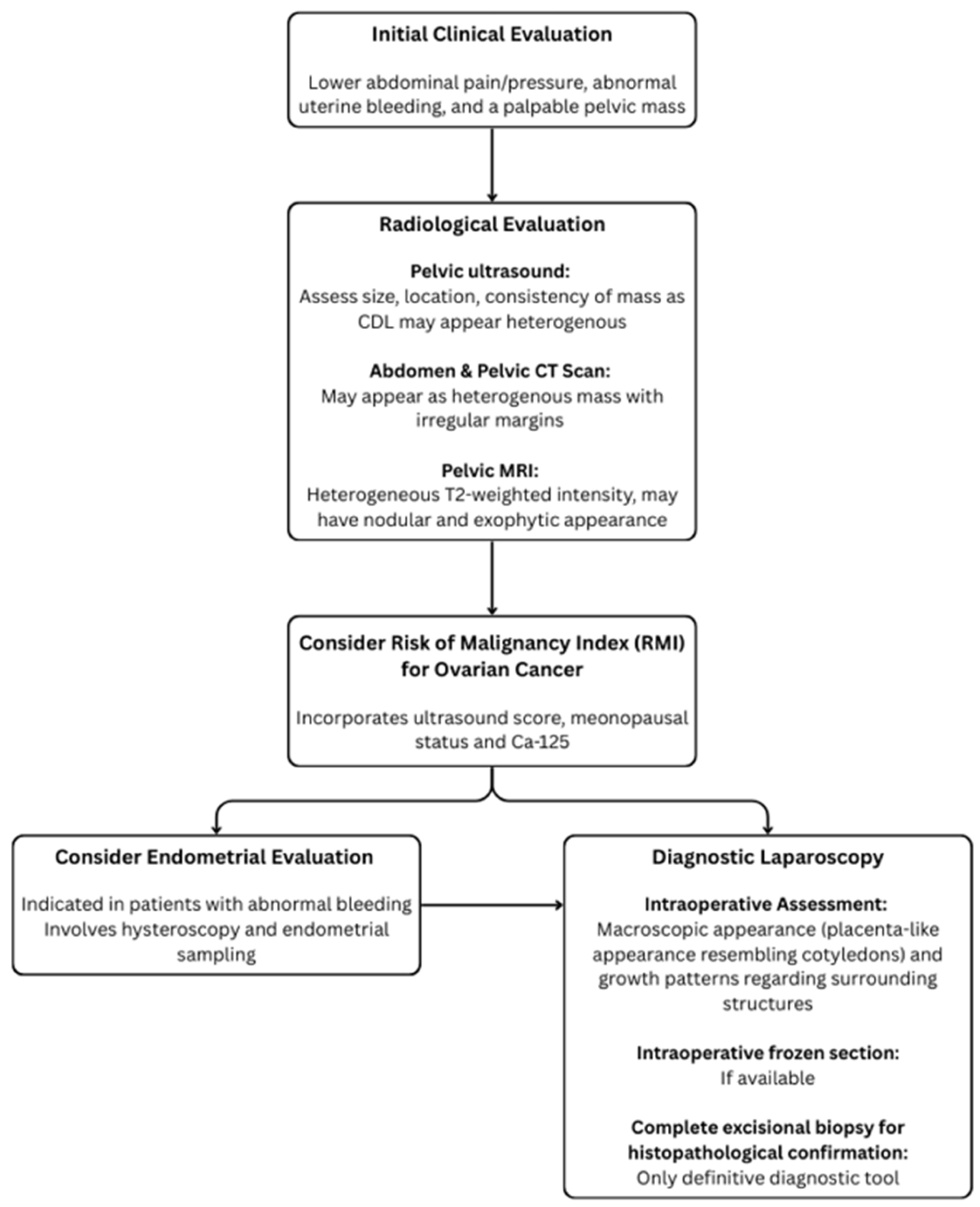
1. Introduction
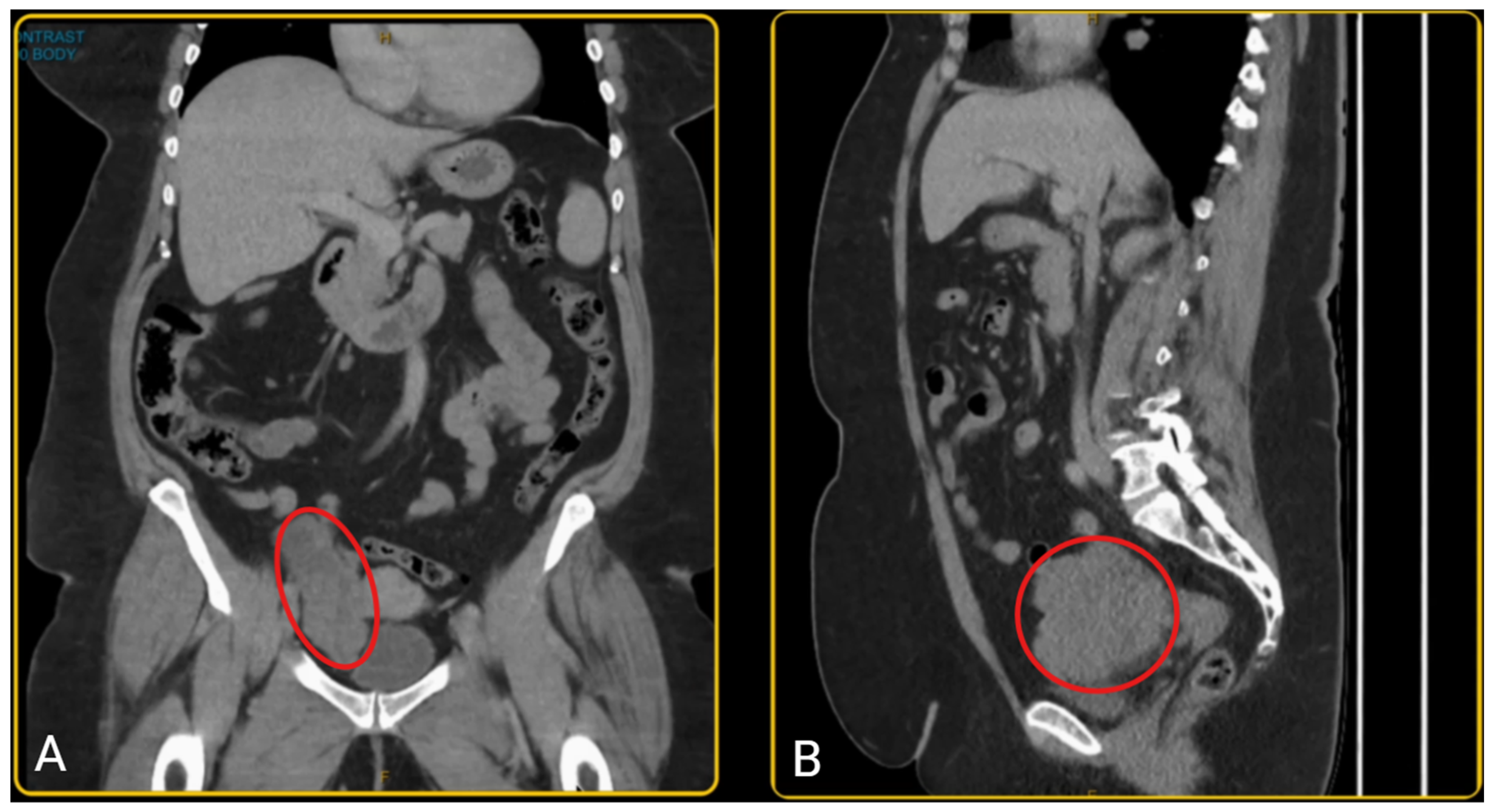
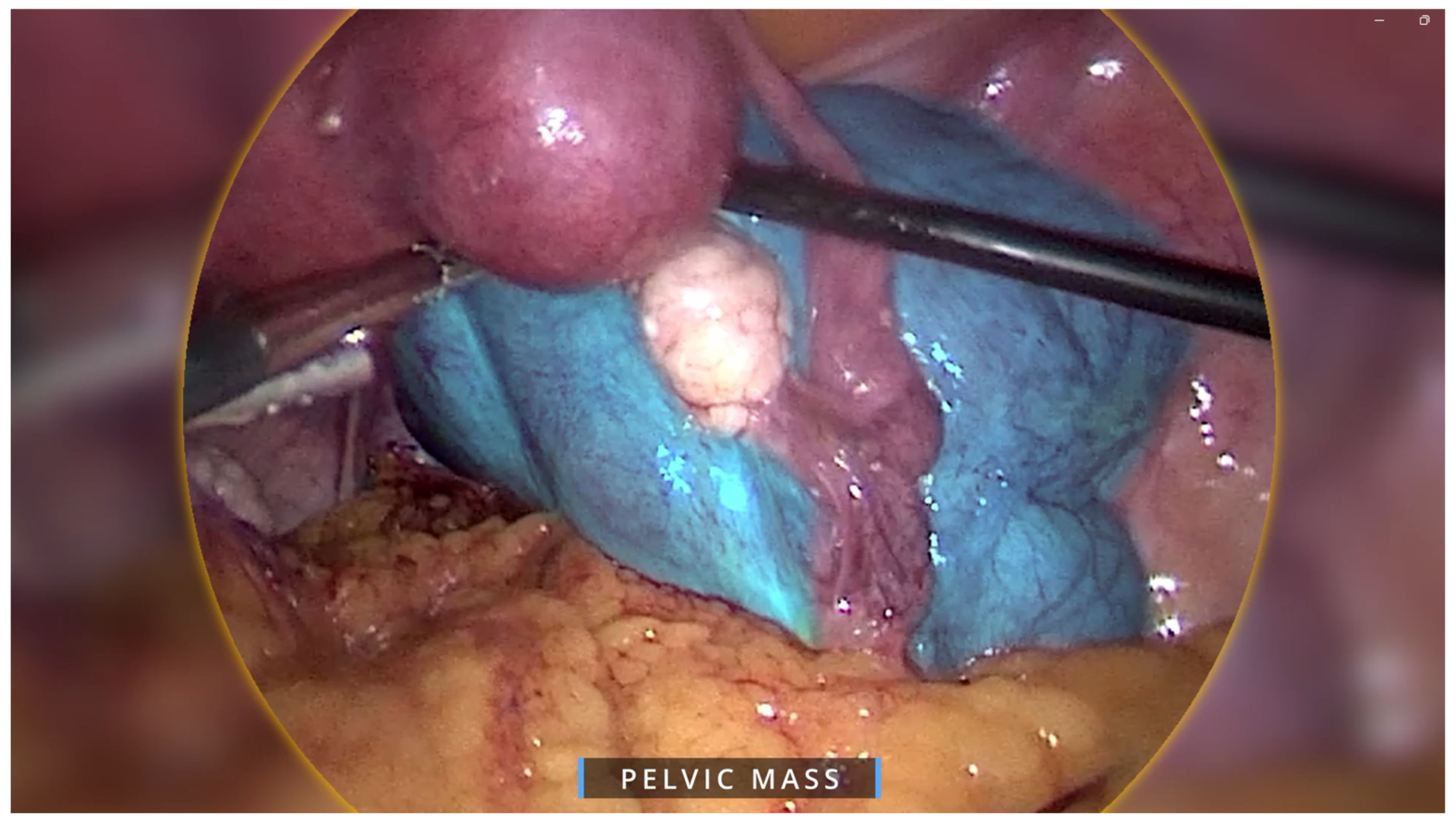
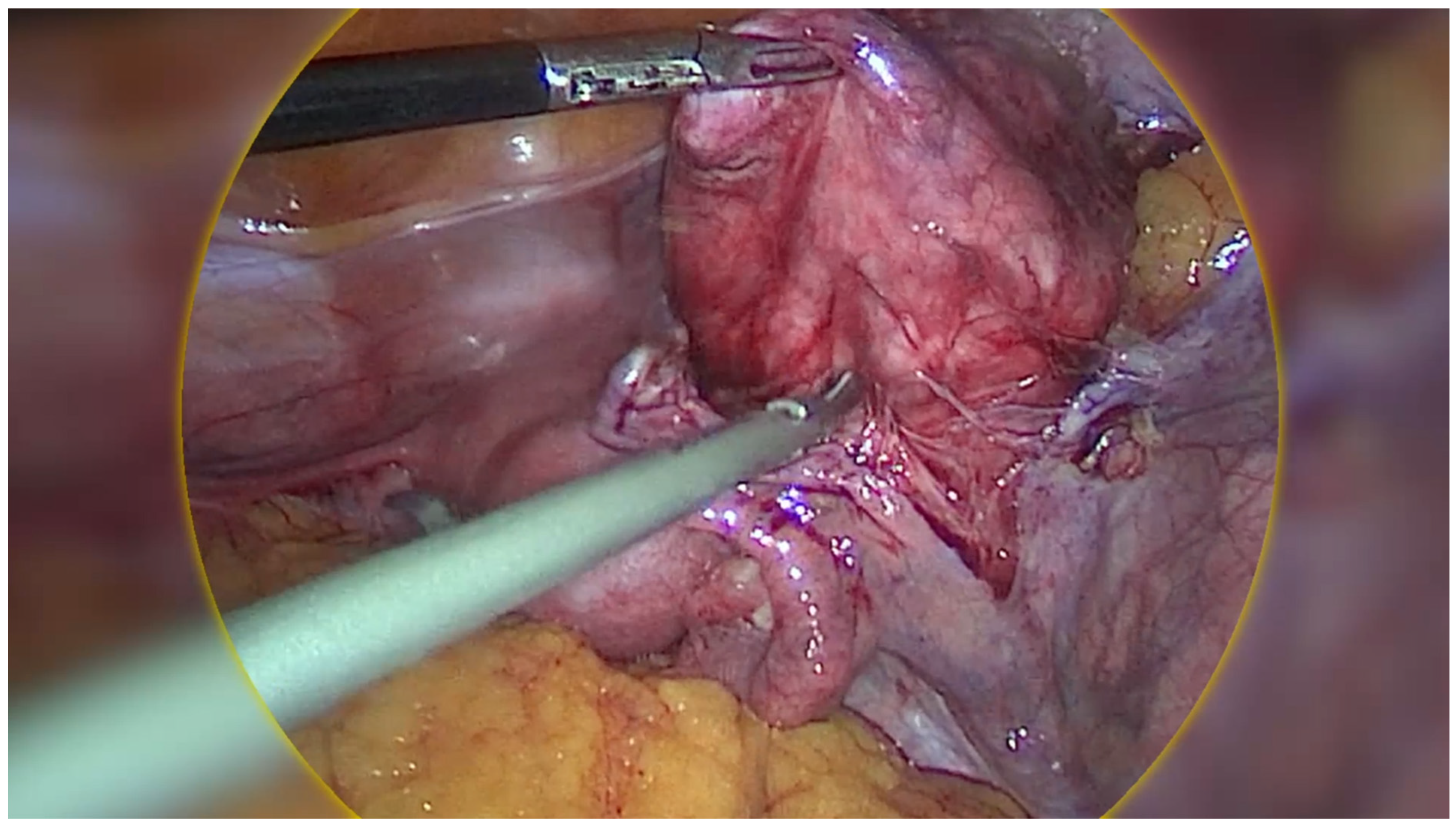
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, L.M.; Reed, R.J.; Sternberg, W.H. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus. The Sternberg tumor. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Wu, S.; Yang, R.; Zhao, L.; Sui, M.; Cui, M.; Chang, W. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A report of four cases and a review of the literature. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2865–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, I.; Gupta, R.K.; Sinha, R.K.; Bhadani, P.P. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma: An uncommon form of a common disease. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2019, 62, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, R.F.; Bovolim, G.; Baiocchi, G.; De Brot, L. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A gross and radiologic malignancy mimicker. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2023, 33, 1827–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.P.; Homonnai, T.Z.; Deligdish, L.; Loewenthal, M. Grape-like leiomyomas of the uterus. Int. Surg. 1975, 60, 238–239. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, A.H.; Scurry, J.P.; Planner, R.S.; Grant, P.T. Grape-like leiomyoma of the uterus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 173, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.M.; Reed, R.J. Dissecting leiomyomas of the uterus other than cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyomas: A report of eight cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Park, Y.K.; Cho, J.H. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A case report and review of the literature. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2002, 17, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuk, W.; Chan, J.K.; Liu, J.Y. Cotyledonoid leiomyoma: A benign uterine tumor with alarming gross appearance. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2002, 126, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.A.; Ireland-Jenkin, K.; Quinn, M.; Armes, J.E. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma. Pathology 2003, 35, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Gurbuz, A.; Karateke, A.; Kabaca, C.; Arik, H.; Bilgic, R. A case of cotyledonoid leiomyoma and review of the literature. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2005, 15, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, L.B.; Al-Nafussi, A.; Beattie, G. Cotyledonoid hydropic intravenous leiomyomatosis: A new variant leiomyoma. Histopathology 2002, 40, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.S.; Hanaa, B.; Faisal, A.S.; Najla, A.M. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A case report of a benign uterine tumor with sarcoma-like gross appearance and review of literature. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2006, 25, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimoon, S.; Wilkinson, A.; Mahore, S.; Bothale, K.; Patrikar, A. Cotyledonoid leiomyoma of the uterus. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2006, 49, 289–291. [Google Scholar]
- Shelekhova, K.V.; Kazakov, D.V.; Michal, M. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus with intravascular growth: Report of two cases. Virchows Arch. 2007, 450, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissferdt, A.; Maheshwari, M.B.; Downey, G.P.; Rollason, T.P.; Ganesan, R. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A case report. Diagn. Pathol. 2007, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedipe, T.O.; Vine, S.J. Dissecting Cotyledonoid Leiomyoma: A Rare Cause of Chronic Intractable Menorrhagia (Not Amenable to Medical Treatment). Case Report. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2010, 31, 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Raga, F.; Sanz-Cortés, M.; Casañ, E.M.; Burgues, O.; Bonilla-Musoles, F. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preda, L.; Rizzo, S.; Gorone, M.S.; Fasani, R.; Maggioni, A.; Bellomi, M. MRI features of cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus. Tumori 2009, 95, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, M.; Suzuki, K.; Hiruta, N. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A report of four cases. APMIS 2010, 118, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezginç, K.; Yazici, F.; Selimoğlu, R.; Tavli, L. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus with intravascular growth in postmenopausal woman: A case presentation. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 16, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Radhika, A.G.; Malik, R.; Radhakrishnan, G. Cotyledonoid leiomyoma and non-descent vaginal hysterectomy. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2010, 281, 971–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Toriyabe, K.; Senda, T.; Sakakura, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Asakura, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Nagao, K. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma treated by laparoscopic surgery: A case report. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2013, 6, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onu, D.O.; Fiorentino, L.M.; Bunting, M.W. Cotyledonoid Dissecting Leiomyoma as a Possible Cause of Chronic Lower Back Pain. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013201350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, E.A.; Cheng, G.; Post, M.D.; Guntupalli, S. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma with adipocytic differentiation: A case report. Gynecol. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 11, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Tanaka, H.; Iwasaki, S.; Wakui, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Suzuki, A. An unusual case of uterine cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma with adenomyosis. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, J.; Chvátal, R.; Konečná, P. Dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus with unusual clinical and pathological features. Ceska Gynekol. 2020, 85, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, A.C.; Oliveira, M.; Luís, P.; Nogueira, M. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: An unexpected diagnosis after delivery. Acta Med. Port. 2018, 31, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.H.; Turner, R.; Schwimer, S.; Foshag, L. Massive Cotyledenoid Leiomyoma Treated with Uterine-Conserving Surgery. FS Rep. 2020, 1, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashita, S.; Nonoshita, A.; Iwasaki, K.; Nakayama, D. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma: A rare benign uterine tumor mimicking malignancy. Clin Pathol. 2024, 17, 2632010X241281240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Kaur, L.; Bhardwaj, M. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma: A rare case report. Caspian J. Reprod. Med. 2024, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xue Dong, R. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma mimicking ovarian malignancy: A case report and literature review. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2024, 31, 817–818. [Google Scholar]
- Robichaud, S.; Wong, J.; Ouallouche, K.; Bleau, N.; Rahimi, K. Dissecting “Cotyledonoid” Leiomyoma Involved by Adenomyosis. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahkandi, M.; Ataei, M.; Bina, A.R.; Mozayani, F.; Fanoodi, A. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma of the uterus: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2023, 17, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Classification of Female Genital Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arleo, E.K.; Schwartz, P.E.; Hui, P.; McCarthy, S. Review of leiomyoma variants. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinelli, A.; D’Oria, O.; Civino, E.; Morciano, A.; Hashmi, A.A.; Baldini, G.M.; Stefanovic, R.; Malvasi, A.; Pecorella, G. Smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP): A comprehensive multidisciplinary update. Medicina 2023, 59, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). Leiomyosarcoma—Symptoms, Causes, Treatment. RareDiseases.org. 2023. Available online: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/leiomyosarcoma/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Asghari, K.M.; Tabrizi, A.D.; Madani, P.S. Unraveling the mystery of uterine cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma: A case report. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2024, 45, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Yarram, S.G.; Nghiem, H.V.; Higgins, E.; Fox, G.; Nan, B.; Francis, I.R. Evaluation of imaging-guided core biopsy of pelvic masses. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomo, F.; Bussolaro, S.; Fiorillo, C.d.A.; Giorda, G.; Romano, F.; Biffi, S.; Ricci, G. The management of the cotyledonoid leiomyoma of the uterus: A narrative review of the literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, K.; Cheung, L.; Taddesse-Heath, L. Cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma: A rare variant of leiomyoma of the uterus. Cureus 2022, 14, e30352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, D.; Shrestha, G.; Joshi, S.L. A case of cotyledonoid dissecting leiomyoma with associated disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis: The significance of frozen section in identification of this unusual entity. Cureus 2024, 16, e55781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Age | Clinical Presentation | Tumour Maximum Dimension (mm) | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roth et al. [1] | 39 | Pelvic mass | 103 | TH + BSO |
| 41 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 100 | ||
| 23 | Pelvic mass | 250 | ||
| David et al. [5] | 65 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 150 | TH |
| 48 | Uterine prolapse | 120 | ||
| Brand et al. [6] | 24 | Abdominal mass | NS | M |
| Roth & Reed [7] | 46 | Pelvic mass | 340 | TH + BSO |
| Kim et al. [8] | 26 | Incidental | 120 | M |
| Cheuk et al. [9] | 55 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 100 | TH + BSO |
| Stewart et al. [10] | 58 | Pelvic mass | 164 | TH + BSO + O |
| Gurbuz et al. [11] | 67 | Incidental | 100 | TH + BSO |
| Jordan et al. [12] | 46 | Adnexal mass | 220 | H +/− BSO |
| 46 | Pelvic mass | 200 | ||
| 46 | Pelvic mass | 100 | ||
| 46 | Pelvic mass | 180 | ||
| 36 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 130 | ||
| 34 | Uterine mass | 180 | M | |
| Saeed et al. [13] | 27 | Pelvic mass | 410 | TH + BSO |
| Maimoon et al. [14] | 40 | Urinary retention | 100 | TH + SO |
| Shelekhova et al. [15] | 73 | Uterine mass | 80 | TH + BSO |
| Weissferdt et al. [16] | 52 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 62 | TH + S |
| Adedipe et al. [17] | 52 | Menorrhagia | NS | TH + O |
| Raga et al. [18] | 33 | Abdominal pain | 60 | UPA + M |
| Preda et al. [19] | 41 | Uterine mass | 90 | TH + ovariectomy |
| Fukunaga et al. [20] | 56 | Constipation | 300 | TH + BSO |
| 47 | Abdominal pain | 260 | ||
| 36 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 40 | ||
| 35 | Abdominal pain | 180 | ||
| Gezginç K et al. [21] | 57 | Pelvic pain | 45 | TH + BSO |
| Agarwal et al. [22] | 52 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 85 | TH |
| Tanaka et al. [23] | 36 | Incidental | 100 | M |
| Onu et al. [24] | 50 | Incidental | 100 | RH + BSO + O + A |
| Blake et al. [25] | 56 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 300 | RH + BSO + O |
| Shimizu et al. [26] | 40 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 100 | TH + BS |
| Xu et al. [2] | 55 | Pelvic mass | 60 | TH + BSO |
| 43 | Pelvic mass | 30 | ||
| 37 | Plevic mass | 300 | ||
| 48 | Abdominal pain | 67 | ||
| Lenz et al. [27] | 64 | Pelvic pain, loss of R kidney function | NS | TH + R |
| Rocha et al. [28] | 38 | Abdominal pain and menorrhagia | 250 | TH + BSO |
| Parker et al. [29] | 39 | Abdominal mass | NS | M |
| Kawashita et al. [30] | 45 | Pelvic mass | 220 | TH + SO |
| Yadav et al. [31] | 65 | Pelvic pain, urinary retention, abnormal uterine bleeding | NS | TH |
| Dong et al. [32] | 39 | Pelvic mass | 73 | TH + BSO |
| Robichaud et al. [33] | 29 | Abdominal pain and menorrhagia | 110 | M |
| Chahkandi et al. [34] | 55 | Abnormal uterine bleeding | 140 | TH + BSO |
| Abreu et al. [4] | 44 | Abdominal pain | 100 | TH + SO + S |
| Leiomyoma Variants | Histological Features |
|---|---|
| Cellular leiomyoma | Increased cellularity compared to surrounding myometrium Lacks nuclear atypia, elevated mitotic activity or necrosis |
| Mitotically active leiomyoma | 6–14 mitoses per 10 high-power fields Lacks nuclear atypia or necrosis |
| Leiomyoma with bizarre nuclei | Marked nuclear atypia (including multinucleation and hyperchromasia) Lacks elevated mitotic activity or necrosis |
| Epithelioid leiomyoma | Rounded or polygonal cells with eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm arranged in nests or cords Lacks nuclear atypia, mitosis, or necrosis |
| Myxoid leiomyoma | Hypocellular tumour with abundant myxoid stroma Lacks nuclear atypia, mitosis, or necrosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, K.; Rao, T. Raising Awareness of Intraoperative Diagnostic Challenges to Prevent Misdiagnosis and Overtreatment: Laparoscopic Management of Rare Cotyledonoid Dissecting Leiomyoma Mimicking Ovarian Tumour. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13121367
Nguyen K, Rao T. Raising Awareness of Intraoperative Diagnostic Challenges to Prevent Misdiagnosis and Overtreatment: Laparoscopic Management of Rare Cotyledonoid Dissecting Leiomyoma Mimicking Ovarian Tumour. Healthcare. 2025; 13(12):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13121367
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Kathy, and Tanushree Rao. 2025. "Raising Awareness of Intraoperative Diagnostic Challenges to Prevent Misdiagnosis and Overtreatment: Laparoscopic Management of Rare Cotyledonoid Dissecting Leiomyoma Mimicking Ovarian Tumour" Healthcare 13, no. 12: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13121367
APA StyleNguyen, K., & Rao, T. (2025). Raising Awareness of Intraoperative Diagnostic Challenges to Prevent Misdiagnosis and Overtreatment: Laparoscopic Management of Rare Cotyledonoid Dissecting Leiomyoma Mimicking Ovarian Tumour. Healthcare, 13(12), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13121367






