Hotspots and Trends in Research on Early Warning of Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis Using CiteSpace
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Who are the major contributors (disciplines, authors, institutions, and countries) to the field?
- (2)
- What are the hotspots and frontiers in the field?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Research Method
- (1)
- Timespan: 1999–2024 (timespan from first publication to search termination date);
- (2)
- Time slice: 1 year;
- (3)
- Node type = country/institution/author/journal/keyword/cited reference;
- (4)
- Threshold selection criteria = the top 25 results for each time slice (balancing computational feasibility with network representativeness, capturing the vast majority of important nodes while minimizing noise);
- (5)
- Other parameters were kept at default settings.
3. Results
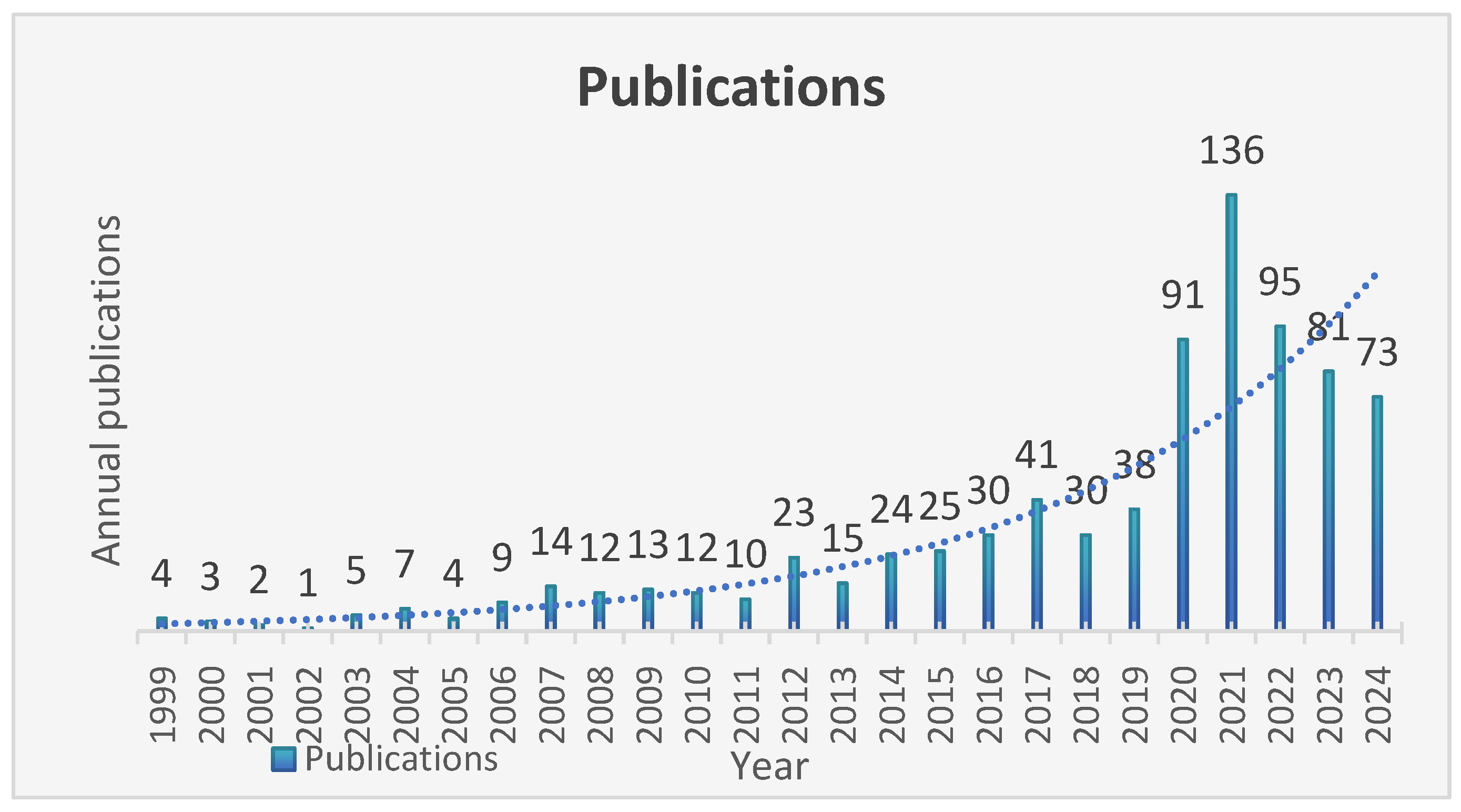
3.1. Basic Statistical Analysis
3.2. Co-Occurrence Analysis of Countries and Institutions
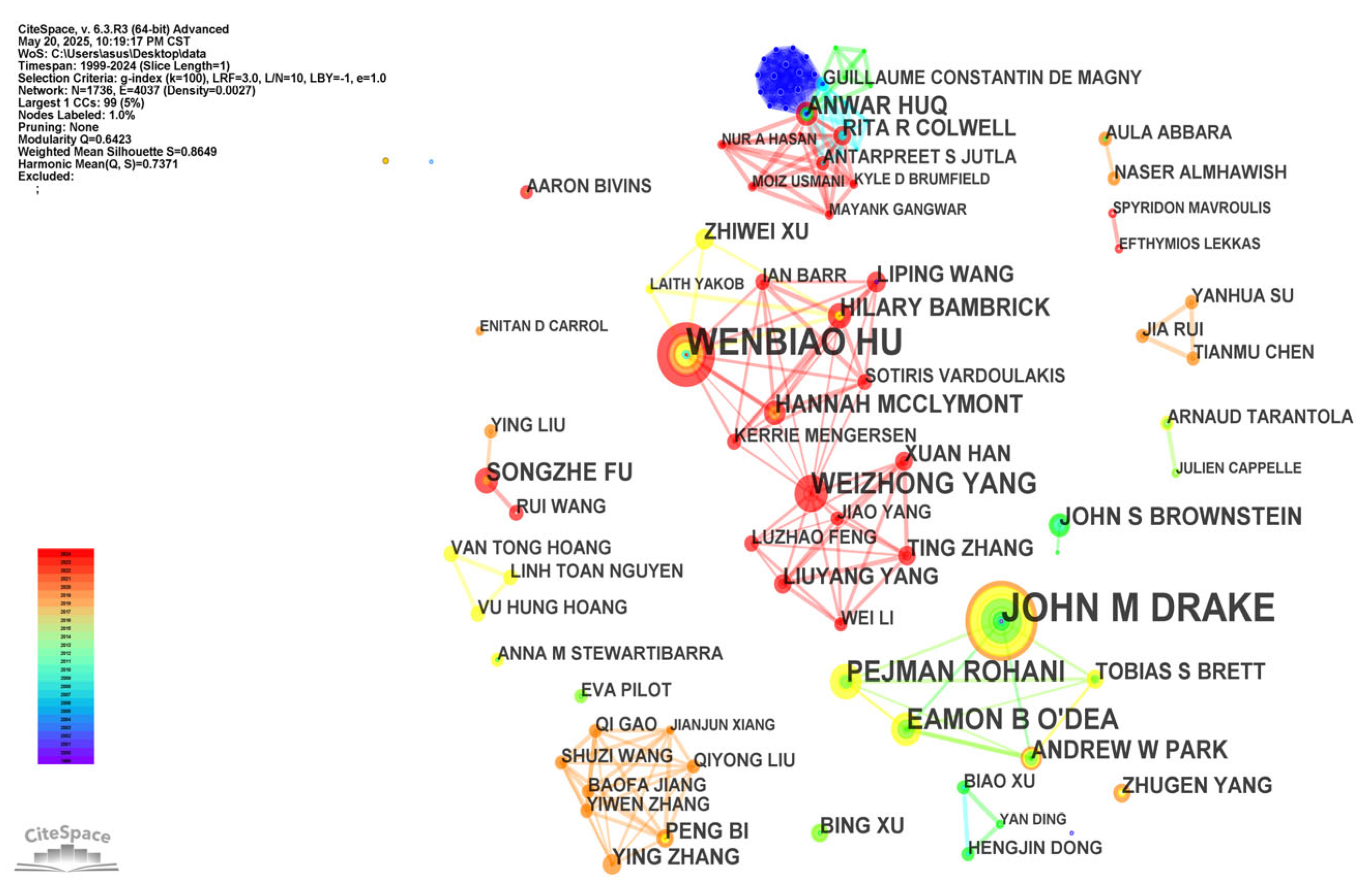
3.3. Analysis of Authors and Co-Cited Authors
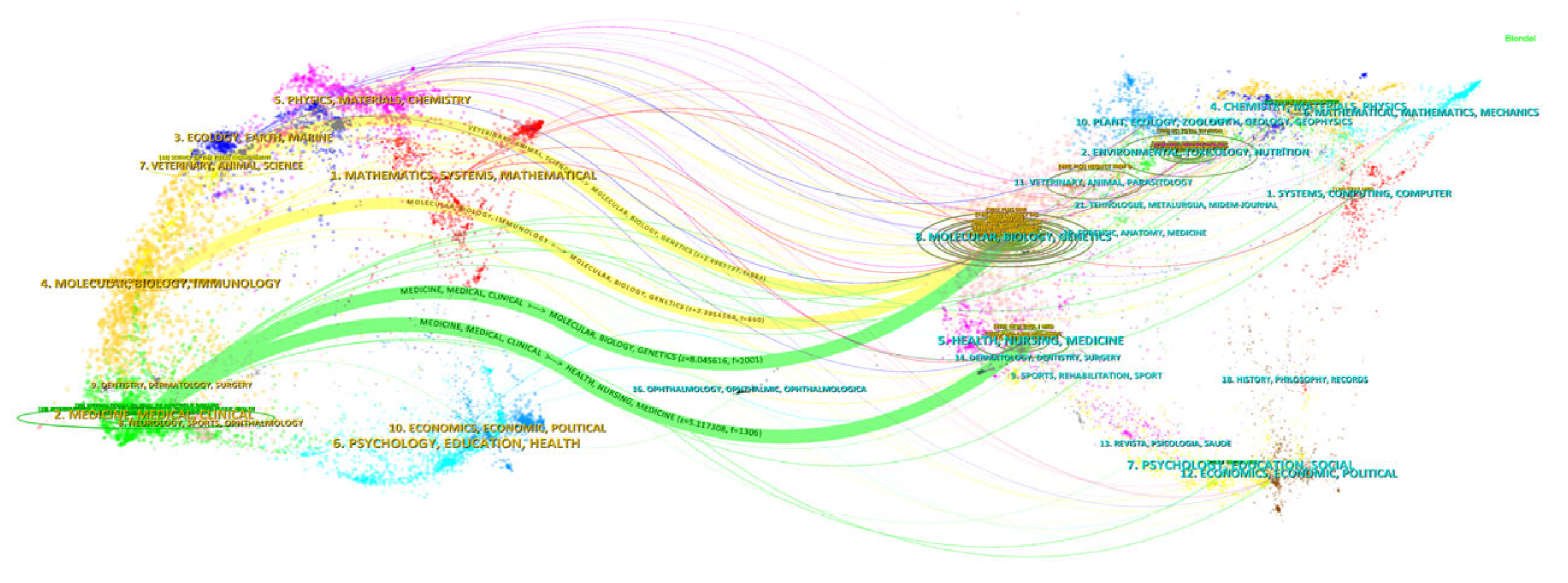
3.4. Dual-Map Overlay Analysis of Journals
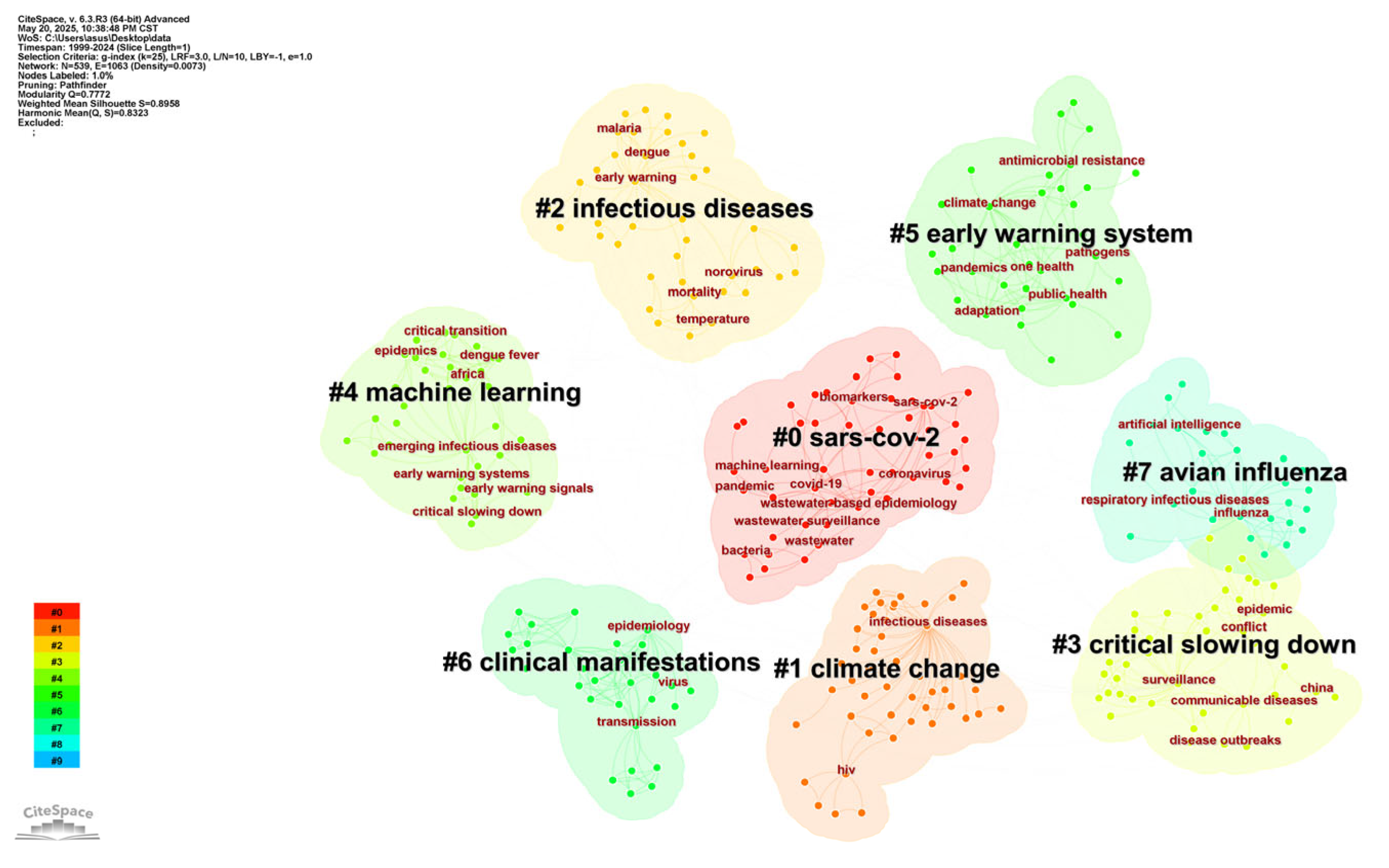
3.5. Analysis of Keywords
3.5.1. Analysis of Keyword Co-Occurrence
3.5.2. Analysis of Keyword Bursts
3.6. Analysis of Cited References
| Rank | Frequency | Year | Article Title | Journal Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 2020 | First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: A proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community [14] | Science of the Total Environment |
| 2 | 19 | 2020 | Future perspectives of wastewater-based epidemiology: Monitoring infectious disease spread and resistance to the community level [17] | Environment International |
| 3 | 17 | 2020 | Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China [18] | The Lancet |
| 4 | 17 | 2020 | Presence of SARS-Coronavirus-2 RNA in Sewage and Correlation with Reported COVID-19 Prevalence in the Early Stage of the Epidemic in The Netherlands [22] | Environmental Science & Technology Letters |
| 5 | 14 | 2020 | Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study [23] | The Lancet |
| 6 | 14 | 2020 | Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China [20] | The New England Journal of Medicine |
| 7 | 14 | 2020 | A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin [19] | Nature |
| 8 | 10 | 2020 | The effect of human mobility and control measures on the COVID-19 epidemic in China [24] | Science |
| 9 | 10 | 2017 | Anticipating the emergence of infectious diseases [21] | Journal of The Royal Society Interface |
| 10 | 10 | 2018 | Wastewater-based epidemiology biomarkers: Past, present and Future [25] | Trends in Analytical Chemistry |
4. Discussion
4.1. General Information
4.2. Research Hotspots and Frontiers
4.2.1. Climate, Machine Learning, and Avian Influenza
4.2.2. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology, One Health, and Artificial Intelligence
4.3. Advancing Infectious Disease Early Warning: Implementing the Human–Animal-Environment Monitoring System
4.4. Limitations and Future Research Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EIDs | emerging infectious diseases |
| Re-EIDs | re-emerging infectious diseases |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WoSCC | Web of Science Core Collection |
| WBE | wastewater-based epidemiology |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
References
- Li, Z.; Meng, F.; Wu, B.; Kong, D.; Geng, M.; Qiu, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, T.; Su, Y.; Liu, S. Reviewing the progress of infectious disease early warning systems and planning for the future. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Moeti, M.; Gao, G.F.; Herrman, H. Global pandemic perspectives: Public health, mental health, and lessons for the future. Lancet 2022, 400, e3–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Hussain-Alkhateeb, L.; Rivera Ramírez, T.; Kroeger, A.; Gozzer, E.; Runge-Ranzinger, S. Early warning systems (EWSs) for chikungunya, dengue, malaria, yellow fever, and Zika outbreaks: What is the evidence? A scoping review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.P.; Cao, W.C. Surveillance as an effective approach to infectious diseases control and prevention. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2017, 38, 417–418. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.O.; Bao, C.J.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, L.P.; Li, Y.; Leng, H.B.; Peng, Z.H. Progress of research regarding the influenza early warning system, based on “Big Data”. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2020, 41, 975–980. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraisl, D.; See, L.; Estevez, D.; Tomaska, N.; MacFeely, S. Citizen science for monitoring the health and well-being related Sustainable Development Goals and the World Health Organization’s Triple Billion Targets. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1202188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Baskaran, S.; Panner Selvam, M.K.; Barbăroșie, C.; Master, K. Unraveling the Footsteps of Proteomics in Male Reproductive Research: A Scientometric Approach. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shen, H.; Ke, L.; Chen, J.; Dang, X.; Liu, B.; Hua, Y. Knowledge Mapping of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bibliometric Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 815575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Thelwall, M.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Delgado López-Cózar, E. Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, Scopus, Dimensions, Web of Science, and OpenCitations’ COCI: A multidisciplinary comparison of coverage via citations. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 871–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. CiteSpaceII: Detecting and Visualizing Emerging Trends and Transient Patterns in Scientific Literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 3, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H. Co-Citation in the Scientific Literature: A New Measure of the Relationship Between Two Documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1973, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Angel, N.; Edson, J.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; O’Brien, J.W.; Choi, P.M.; Kitajima, M.; Simpson, S.L.; Li, J.; et al. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: A proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Bueno, R.; Claro, I.C.M.; Augusto, M.R.; Duran, A.F.A.; Camillo, L.M.B.; Cabral, A.D.; Sodré, F.F.; Brandão, C.C.S.; Vizzotto, C.S.; Silveira, R.; et al. Wastewater-based epidemiology: A Brazilian SARS-CoV-2 surveillance experience. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakariya, M.; Ahmed, F.; Islam, M.A.; Al Marzan, A.; Hasan, M.N.; Hossain, M.; Ahmed, T.; Hossain, A.; Reza, H.M.; Hossen, F.; et al. Wastewater-based epidemiological surveillance to monitor the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in developing countries with onsite sanitation facilities. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Future perspectives of wastewater-based epidemiology: Monitoring infectious disease spread and resistance to the community level. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. China Medical Treatment Expert Group for COVID-19. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, T.S.; Drake, J.M.; Rohani, P. Anticipating the emergence of infectious diseases. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medema, G.; Heijnen, L.; Elsinga, G.; Italiaander, R.; Brouwer, A. Presence of SARS-Coronavirus-2 RNA in Sewage and Correlation with Reported COVID-19 Prevalence in the Early Stage of the Epidemic in The Netherlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Yang, C.H.; Gutierrez, B.; Wu, C.H.; Klein, B.; Pigott, D.M.; Open COVID-19 Data Working Group; du Plessis, L.; Faria, N.R.; Li, R.; et al. The effect of human mobility and control measures on the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Science 2020, 368, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.M.; Tscharke, B.J.; Donner, E.; O’Brien, J.W.; Grant, S.C.; Kaserzon, S.L.; Mackie, R.; O’Malley, E.; Crosbie, N.D.; Thomas, K.V.; et al. Wastewater-based epidemiology biomarkers: Past, present and future. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Ma, Q.; Yang, X.; Song, Y. Study on Pain Catastrophizing From 2010 to 2020: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 759347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Liang, C.; Jiang, B.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y. Major Natural Disasters in China, 1985-2014: Occurrence and Damages. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2016, 13, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, R. Global climate change and the emergence/re-emergence of infectious diseases. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 293 (Suppl. 37), 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaratunga, D.; Fernando, N.; Haigh, R.; Jayasinghe, N. Jayasinghe. The COVID-19 outbreak in Sri Lanka: A synoptic analysis focusing on trends, impacts, risks and science-policy interaction processes. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 8, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.C.; Attanayake, J.; King, A.; Prideaux, F. A multi-hazards earth science perspective on the COVID-19 pandemic: The potential for concurrent and cascading crises. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2020, 40, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Martinez, G.S.; Kendrovski, V.; Diaz, J. A new integrative perspective on early warning systems for health in the context of climate change. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, C.J.E.; Lessler, J. Opportunities and challenges in modeling emerging infectious diseases. Science 2017, 357, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Qi, X.; Ji, H.; Struchiner, C.J.; Villela, D.A.; Karamov, E.V.; Turgiev, A.S. Big data technology in infectious diseases modeling, simulation, and prediction after the COVID-19 outbreak. Intell. Med. 2023, 3, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, M.d.M.; Aktar, S.; Rashed-Al-Mahfuz Md Uddin, S.; Liò, P.; Xu, H.; Summers, M.A.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. A machine learning model to identify early stage symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2020, 160, 113661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Mengersen, K.; Barr, I.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Vardoulakis, S.; Bambrick, H.; Hu, W. Towards development of functional climate-driven early warning systems for climate-sensitive infectious diseases: Statistical models and recommendations. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina MacIntyre, C.; Lim, S.; Gurdasani, D.; Miranda, M.; Metcalf, D.; Quigley, A.; Hutchinson, D.; Burr, A.; Heslop, D.J. Early detection of emerging infectious diseases—Implications for vaccine development. Vaccine 2024, 42, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.R.; Hwang, C.K.; Chen, S.Y.; Shih, F.Y.; Han, H.C.; King, C.C.; Gilbert, J.R.; Fang, C.C.; Oyang, Y.J. Machine learning for emerging infectious disease field responses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Kam, Y.W. Insights from Avian Influenza: A Review of Its Multifaceted Nature and Future Pandemic Preparedness. Viruses 2024, 16, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S. Pandemic influenza threat and preparedness. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Hermann, E.; Rasmussen, A.L. Highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: History, current situation, and outlook. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0220924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Tseng, H. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: A scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Zumla, A.; Gautret, P.; Gray, G.C.; Hui, D.S.; Al-Rabeeah, A.A.; Memish, Z.A. Surveillance for emerging respiratory viruses. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G. Emerging pollutants, and communicating the science of environmental chemistry and mass spectrometry: Pharmaceuticals in the environment. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2001, 12, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Chiabrando, C.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Fanelli, R. Estimating community drug abuse by wastewater analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nuijs, A.L.; Castiglioni, S.; Tarcomnicu, I.; Postigo, C.; Lopez de Alda, M.; Neels, H.; Zuccato, E.; Barcelo, D.; Covaci, A. Illicit drug consumption estimations derived from wastewater analysis: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3564–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Eaglesham, G.; Covaci, A.; Mueller, J.F.; Thai, P.K. Stability of alcohol and tobacco consumption biomarkers in a real rising main sewer. Water Res. 2018, 138, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Venkatesan, A.K.; Halden, R.U. Alcohol and nicotine consumption trends in three U.S. communities determined by wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.Y.; Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Garneau, P.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. Waterborne pathogens: Detection methods and challenges. Pathogens 2015, 4, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, M.; Picó, Y. Wastewater-based epidemiology: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 9, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Flamholz, A.; Phillips, R.; Milo, R. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by the numbers. eLife 2020, 9, e57309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, V.; Maday, Y.; Wallet, C.; Cluzel, N.; Borde, C. SIGOBEPINE Wastewater-based epidemiology: Retrospective, current status, and future prospects. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain. Med. 2023, 42, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verani, M.; Pagani, A.; Federigi, I.; Lauretani, G.; Atomsa, N.T.; Rossi, V.; Viviani, L.; Carducci, A. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology for Viral Surveillance from an Endemic Perspective: Evidence and Challenges. Viruses 2024, 16, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantilli, A.; Cola, G.D.; Castro, G.; Sicilia, P.; Cachi, A.M.; de Los Ángeles Marinzalda, M.; Ibarra, G.; López, L.; Valduvino, C.; Barbás, G.; et al. Hepatitis A virus monitoring in wastewater: A complementary tool to clinical surveillance. Water Res. 2023, 241, 120102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares-Jimenez, M.; Garcia-Garcia, T.; Suárez-Cárdenas, J.M.; Perez-Jimenez, A.B.; Martín, M.A.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Michán, C.; Corona-Mata, D.; Risalde, M.A.; Perez-Valero, I.; et al. Correlation of hepatitis E and rat hepatitis E viruses urban wastewater monitoring and clinical cases. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Lee, W.L.; Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Chandra, F.; Armas, F.; Xiao, A.; Leifels, M.; Rhode, S.F.; Wuertz, S.; et al. Making waves: Wastewater surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in an endemic future. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. One Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/one-health (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Karesh, W.B.; Dobson, A.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Lubroth, J.; Dixon, M.A.; Bennett, M.; Aldrich, S.; Harrington, T.; Formenty, P.; Loh, E.H.; et al. Ecology of zoonoses: Natural and unnatural histories. Lancet 2012, 380, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Jeggo, M. One Health Approach-Why Is It So Important? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.; Pal, N.; Sarma, D.K.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, M. Holistic One Health Surveillance Framework: Synergizing Environmental, Animal, and Human Determinants for Enhanced Infectious Disease Management. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordier, M.; Uea-Anuwong, T.; Binot, A.; Hendrikx, P.; Goutard, F.L. Characteristics of One Health surveillance systems: A systematic literature review. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castañeda, R.R.; Villers, J.; Guzmán, C.A.F.; Eslanloo, T.; de Paula, N.; Machalaba, C.; Zinsstag, J.; Utzinger, J.; Flahault, A.; Bolon, I. One Health and planetary health research: Leveraging differences to grow together. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e109–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, P.; Relimpio, D.; Zearra, J.A.; Cerón, J.J.; Palencia, P.; Cardoso, B.; Ferreras, E.; Escobar, M.; Cáceres, G.; López-Olvera, J.R.; et al. Using integrated wildlife monitoring to prevent future pandemics through one health approach. One Health 2022, 16, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.S.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Han, L.F.; Xia, S.; Kassegne, K.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Yin, K.; Hu, Q.Q.; Xiu, L.S.; et al. China’s application of the One Health approach in addressing public health threats at the human-animal-environment interface: Advances and challenges. One Health 2023, 17, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Zhu, S.; An, Z.; You, B.; Li, Z.; Yao, Y.; Nair, V.; Liao, M. Dissection of key factors correlating with H5N1 avian influenza virus driven inflammatory lung injury of chicken identified by single-cell analysis. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangsiriwut, K.; Uiprasertkul, M.; Payungporn, S.; Auewarakul, P.; Ungchusak, K.; Chantratita, W.; Puthavathana, P. Complete Genomic Sequences of Highly Pathogenic H5N1 Avian Influenza Viruses Obtained Directly from Human Autopsy Specimens. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01498-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D.; Christison, K.W.; Stentiford, G.D.; Cook, L.S.J.; Hartikainen, H. Environmental DNA/RNA for pathogen and parasite detection, surveillance, and ecology. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-García, G.; Pérez-Sancho, M.; Barroso, P.; Herranz-Benito, C.; Relimpio, D.; García-Seco, T.; Perelló, A.; Díez-Guerrier, A.; Pozo, P.; Balseiro, A.; et al. One Health Farming: Noninvasive monitoring reveals links between farm vertebrate richness and pathogen markers in outdoor hoofstock. One Health 2024, 19, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, G.K.; Lambrou, A.S.; Thumrin, P.; Thukngamdee, Y.; Tangwangvivat, R.; Doungngern, P.; Noradechanon, K.; Netrabukkana, P.; Meidenbauer, K.; Mehoke, T.; et al. Enhancing global health security in Thailand: Strengths and challenges of initiating a One Health approach to avian influenza surveillance. One Health 2022, 14, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.; Hopper, J.L. Co-evolution of epidemiology and artificial intelligence: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, D.; Adib, K.; Buttigieg, S.; Goiana-da-Silva, F.; Ladewig, K.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Figueras, J.; Novillo-Ortiz, D.; McKee, M. Artificial intelligence in public health: Promises, challenges, and an agenda for policy makers and public health institutions. Lancet Public Health 2025, 10, e428–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, D.; Presanis, A.M.; Birrell, P.J.; Tomba, G.S.; House, T. Four key challenges in infectious disease modelling using data from multiple sources. Epidemics 2015, 10, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Kamarthi, H.; Agarwal, P.; Ho, J.; Patel, M.; Sapre, S.; Prakash, B.A. Machine learning for data-centric epidemic forecasting. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Du, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Li, W.; Ma, L.; et al. Deep-Learning Model for Influenza Prediction from Multisource Heterogeneous Data in a Megacity: Model Development and Evaluation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e44238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S. Generative AI in healthcare: An implementation science informed translational path on application, integration and governance. Implement. Sci. 2024, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Lee, H.C.; Diao, K.Y.; Huang, M.; Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Ma, Y.; Robson, P.M.; Chung, M.; et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled rapid diagnosis of patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Collins, J.J. Leveraging artificial intelligence in the fight against infectious diseases. Science 2023, 381, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ye, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yang, M. Artificial Intelligence in battling infectious diseases: A transformative role. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, J.A.; Zehe, E.; Redick, C.; Bah, A.; Cowger, K.; Camara, M.; Diallo, A.; Gigo, A.N.; Dhillon, R.S.; Liu, A. Introduction of Mobile Health Tools to Support Ebola Surveillance and Contact Tracing in Guinea. Glob. Health Sci. Pract. 2015, 3, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.A.; Bukhari, S.H.R.; Daud, A.; Awan, S.E.; Raja, M.A.Z. COVICT: An IoT based architecture for COVID-19 detection and contact tracing. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 7381–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar, A.W.; Ullah, F.; Bacha, J.; Khan, J.; Ali, F.; Lee, S. Mobile sensors based platform of Human Physical Activities Recognition for COVID-19 spread minimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.S.; Zade, N.; Kumar, P.; Gundewar, S.; Weerarathna, I.N.; Verma, P. The role of artificial intelligence in pandemic responses: From epidemiological modeling to vaccine development. Mol. Biomed. 2025, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degeling, C.; Chen, G.; Gilbert, G.L.; Brookes, V.; Thai, T.; Wilson, A.; Johnson, J. Changes in public preferences for technologically enhanced surveillance following the COVID-19 pandemic: A discrete choice experiment. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, I.Y.; Ma, Y.X.; Yu, M.W.C.; Liu, J.; Dong, W.N.; Pang, Q.; Lu, X.Q.; Molassiotis, A.; Holroyd, E.; Wong, C.W.W. Ethics, Integrity, and Retributions of Digital Detection Surveillance Systems for Infectious Diseases: Systematic Literature Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e32328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo Dos Santos, M.; Cerqueira Silva, A.C.; Dos Reis Teixeira, C.; Pinheiro Macedo Prazeres, F.; Fernandes Dos Santos, R.; de Araújo Rolo, C.; de Souza Santos, E.; Santos da Fonseca, M.; Oliveira Valente, C.; Saraiva Hodel, K.V.; et al. Wastewater surveillance for viral pathogens: A tool for public health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Aguiar-Oliveira, M.L.; Campos, A.; Matos, A.R.; Rigotto, C.; Sotero-Martins, A.; Teixeira, P.F.P.; Siqueira, M.M. Wastewater-based epidemiology (Wbe) and viral detection in polluted surface water: A valuable tool for COVID-19 surveillance—A brief review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Fan, Z.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Luo, Y.; Huo, D.; Yu, X.; Xin, L.; Han, X.; et al. Comparison Between Threshold Method and Artificial Intelligence Approaches for Early Warning of Respiratory Infectious Diseases—Weifang City, Shandong Province, China, 2020–2023. China CDC Wkly. 2024, 6, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Li, G.; et al. Ecological Barrier Deterioration Driven by Human Activities Poses Fatal Threats to Public Health due to Emerging Infectious Diseases. Engineering 2022, 10, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeldayem, O.M.; Dabbish, A.M.; Habashy, M.M.; Mostafa, M.K.; Elhefnawy, M.; Amin, L.; Al-Sakkari, E.G.; Ragab, A.; Rene, E.R. Viral outbreaks detection and surveillance using wastewater-based epidemiology, viral air sampling, and machine learning techniques: A comprehensive review and outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Carson, S.; Reyne, M.I.; Marshall, A.; Moody, D.; Allen, D.M.; Allingham, P.; Levickas, A.; Fitzgerald, A.; Bell, S.H.; et al. Wastewater monitoring of human and avian influenza A viruses in Northern Ireland: A genomic surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

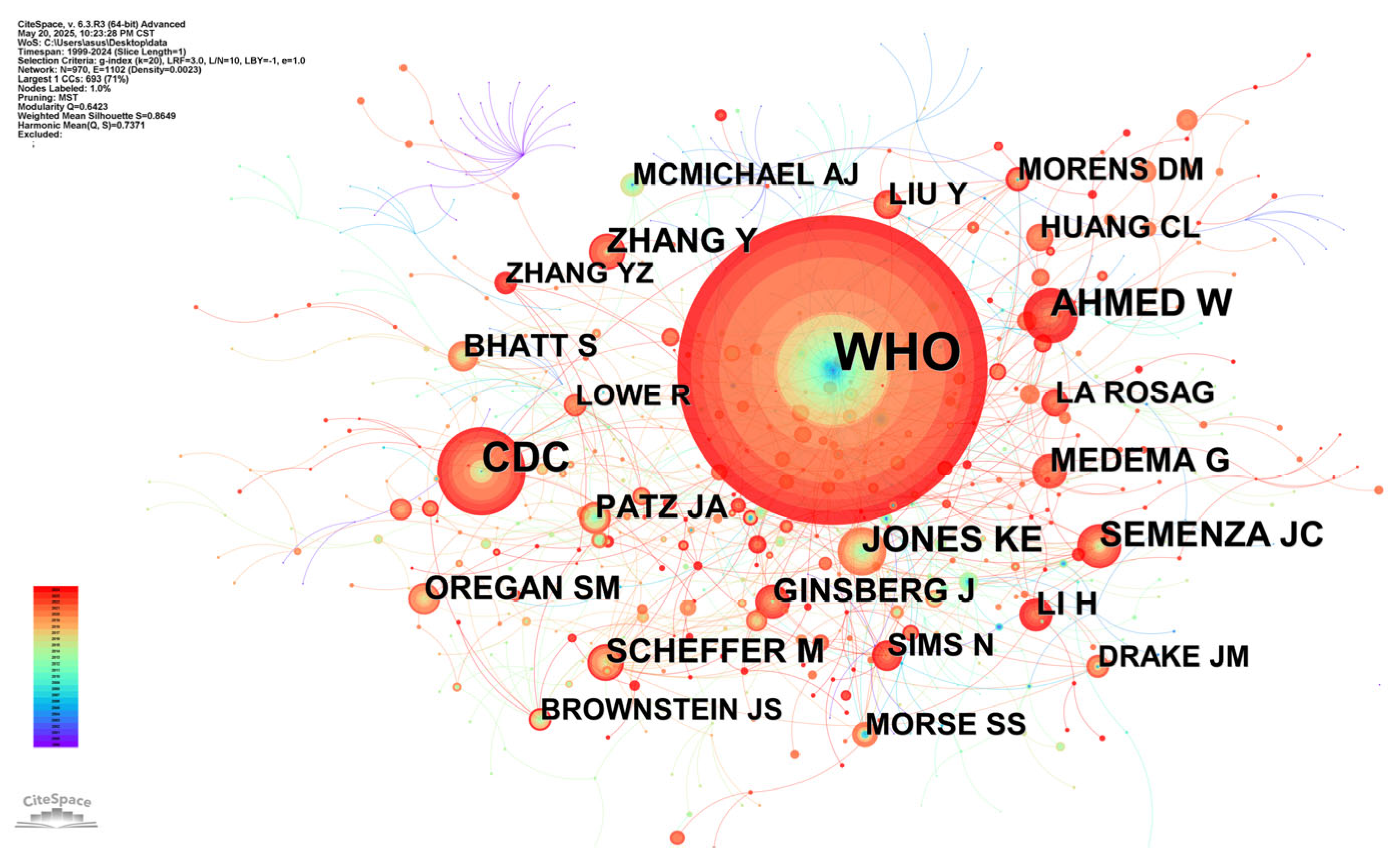


| Rank | Centrality | Publications | Institution | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.22 | 17 | World Health Organization | International organization |
| 2 | 0.20 | 18 | Harvard University | United States |
| 3 | 0.14 | 36 | Chinese Center for Disease Control & Prevention | China |
| 4 | 0.12 | 21 | University of California System | United States |
| 5 | 0.09 | 22 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | China |
| 6 | 0.06 | 9 | University System of Maryland | United States |
| 7 | 0.06 | 9 | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique | France |
| 8 | 0.05 | 21 | University of London | United Kingdom |
| 9 | 0.05 | 6 | Universite Paris Cite | France |
| 10 | 0.04 | 16 | London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine | United Kingdom |
| Rank | Frequency | Centrality | Keyword | Centrality | Frequency | Keyword |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 181 | 0.31 | infectious diseases | 0.31 | 181 | infectious diseases |
| 2 | 64 | 0.06 | transmission | 0.16 | 50 | disease |
| 3 | 57 | 0.06 | virus | 0.15 | 53 | climate change |
| 4 | 53 | 0.10 | outbreak | 0.11 | 34 | early warning system |
| 5 | 53 | 0.15 | climate change | 0.1 | 53 | outbreak |
| 6 | 50 | 0.16 | disease | 0.1 | 21 | children |
| 7 | 48 | 0.07 | public health | 0.07 | 48 | public health |
| 8 | 48 | 0.04 | surveillance | 0.07 | 36 | early warning |
| 9 | 39 | 0.04 | infection | 0.07 | 31 | risk |
| 10 | 38 | 0.05 | epidemiology | 0.07 | 25 | emerging infectious diseases |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, H. Hotspots and Trends in Research on Early Warning of Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis Using CiteSpace. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111293
Yang X, Wang H, Lu H. Hotspots and Trends in Research on Early Warning of Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis Using CiteSpace. Healthcare. 2025; 13(11):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111293
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xue, Hao Wang, and Hui Lu. 2025. "Hotspots and Trends in Research on Early Warning of Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis Using CiteSpace" Healthcare 13, no. 11: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111293
APA StyleYang, X., Wang, H., & Lu, H. (2025). Hotspots and Trends in Research on Early Warning of Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis Using CiteSpace. Healthcare, 13(11), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111293






