Efficacy of a Rehabilitation Program Using Mirror Therapy and Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise on Upper Limb Functionality in Patients with Acute Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Intervention
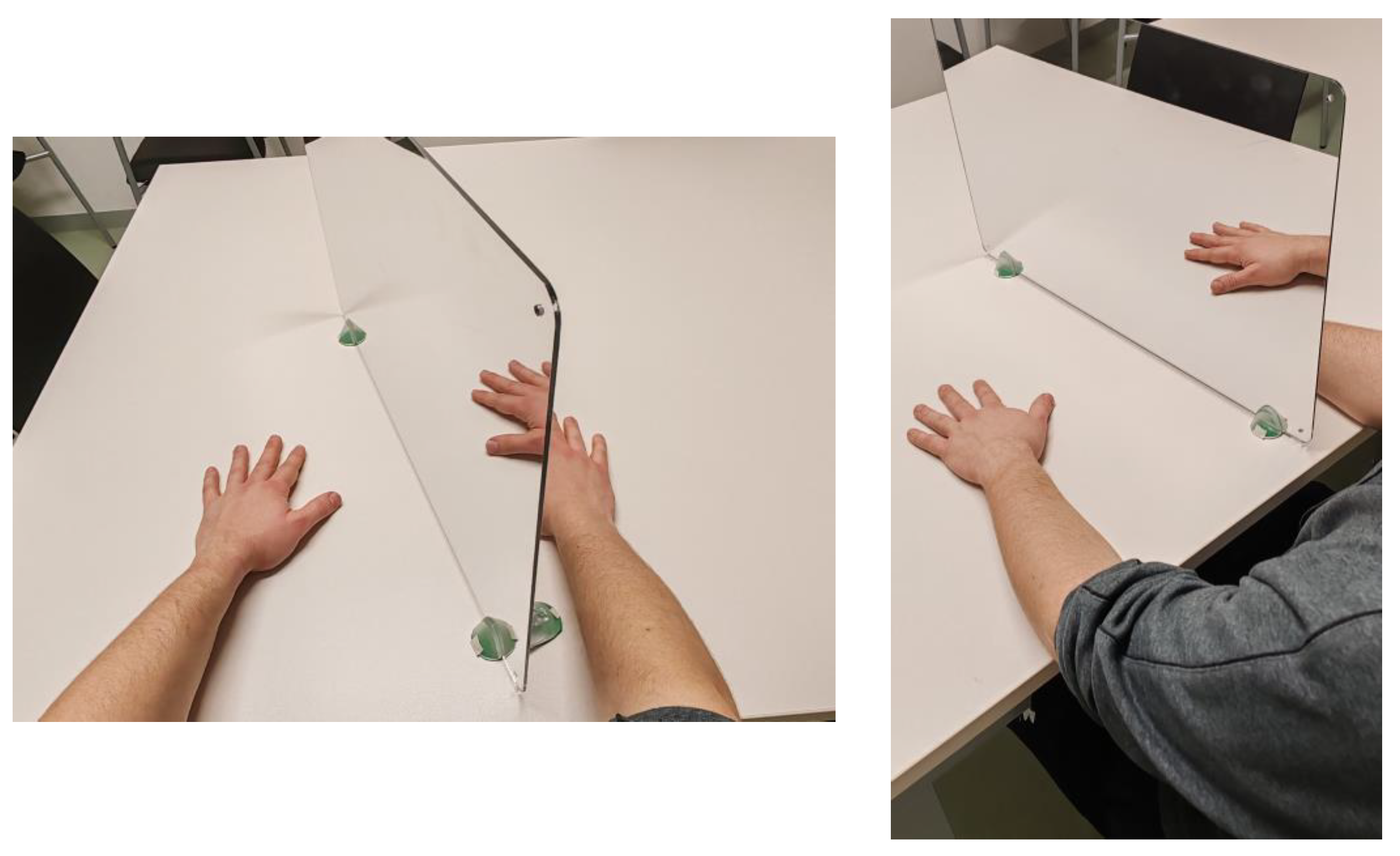
2.4.1. Mirror Therapy
2.4.2. Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise
2.4.3. Task-Oriented Training
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simats, A.; Liesz, A. Systemic inflammation after stroke: Implications for post-stroke comorbidities. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santos, J.; Rodríguez-Fernández, P.; Pardo-Hernández, R.; González-Bernal, J.J.; Fernández-Solana, J.; Santamaría-Peláez, M. A Cross-Sectional Study: Determining Factors of Functional Independence and Quality of Life of Patients One Month after Having Suffered a Stroke. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, T.B.H.; Tannous, J.; Vahidy, F.S. A Contemporary Review of Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Etiology, and Outcomes of Premature Stroke. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, H.P. Stroke Rehabilitation. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 35, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namaganda, P.; Nakibuuka, J.; Kaddumukasa, M.; Katabira, E. Stroke in young adults, stroke types and risk factors: A case control study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; An, C.S.; Lim, C.G. Effects of a Rehabilitation Program Using a Wearable Device on the Upper Limb Function, Performance of Activities of Daily Living, and Rehabilitation Participation in Patients with Acute Stroke. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondergem, R.; Pisters, M.F.; Wouters, E.J.; Olthof, N.; De Bie, R.A.; Visser-Meily, J.M.A.; Veenhof, C. The Course of Activities in Daily Living: Who Is at Risk for Decline after First Ever Stroke? Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A.; Llurda-Almuzara, L.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; De-la-Llave-Rincón, A.I.; Navarro-Santana, M.J. Is Dry Needling Effective for the Management of Spasticity, Pain, and Motor Function in Post-Stroke Patients? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tater, P.; Pandey, S. Post-stroke Movement Disorders: Clinical Spectrum, Pathogenesis, and Management. Neurol. India 2021, 69, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, H.; Morkisch, N.; Mehrholz, J.; Pohl, M.; Behrens, J.; Borgetto, B.; Dohle, C. Mirror therapy for improving motor function after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 7, CD008449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, P. Upper Limb Motor Impairment Post Stroke. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 26, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaría-Peláez, M.; Pardo-Hernández, R.; González-Bernal, J.J.; Soto-Cámara, R.; González-Santos, J.; Fernández-Solana, J. Reliability and Validity of the Motor Activity Log (MAL-30) Scale for Post-Stroke Patients in a Spanish Sample. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Solana, J.; Pardo-Hernández, R.; González-Bernal, J.J.; Sánchez-González, E.; González-Santos, J.; Soto-Cámara, R.; Santamaría-Pelaez, M. Psychometric Properties of the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Scale in Post-Stroke Patients-Spanish Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gor-García-Fogeda, M.D.; Molina-Rueda, F.; Cuesta-Gómez, A.; Carratalá-Tejada, M.; Alguacil-Diego, I.M.; Miangolarra-Page, J.C. Scales to assess gross motor function in stroke patients: A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharififar, S.; Shuster, J.J.; Bishop, M.D. Adding electrical stimulation during standard rehabilitation after stroke to improve motor function. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, H.C.; Danielsson, A.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. A cross sectional study of upper extremity strength ten days after a stroke; relationship between patient-reported and objective measures. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, E.R.; Moudgal, R.; Lang, K.; Hyacinth, H.I.; Awosika, O.O.; Kissela, B.M.; Feng, W. Early Rehabilitation after Stroke: A Narrative Review. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prange-Lasonder, G.B.; Alt Murphy, M.; Lamers, I.; Hughes, A.M.; Buurke, J.H.; Feys, P.; Keller, T.; Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Tarkka, I.M.; Timmermans, A.; et al. European evidence-based recommendations for clinical assessment of upper limb in neurorehabilitation (CAULIN): Data synthesis from systematic reviews, clinical practice guidelines and expert consensus. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, J.; Borschmann, K.N.; Kwakkel, G.; Burridge, J.H.; Eng, J.J.; Walker, M.F.; Bird, M.L.; Cramer, S.C.; Hayward, K.S.; O’Sullivan, M.J.; et al. Setting the scene for the Second Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable. Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Li, C.; Hua, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ya, R.; Meng, Q.; Bai, Y. Mirror therapy for unilateral neglect after stroke: A systematic review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaizumi, S.; Asai, T.; Koyama, S. Agency over Phantom Limb Enhanced by Short-Term Mirror Therapy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, X.; Fang, Q. Mirror therapy for motor function of the upper extremity in patients with stroke: A meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfetti, C.; Ghedina, R.; Hernández, D.J. El Ejercicio Terapéutico Cognoscitivo Para La Reeducación Motora Del Hemipléjico Adulto; Edika Med: Barcelona, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Bae, S.; Jeon, D.; Kim, K.Y. The effects of cognitive exercise therapy on chronic stroke patients’ upper limb functions, activities of daily living and quality of life. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almhdawi, K.A.; Mathiowetz, V.G.; White, M.; delMas, R.C. Efficacy of Occupational Therapy Task-oriented Approach in Upper Extremity Post-stroke Rehabilitation. Occup. Ther. Int. 2016, 23, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-de-la-Cuerda, R.; Molero-Sánchez, A.; Carratalá-Tejada, M.; Alguacil-Diego, I.M.; Molina-Rueda, F.; Miangolarra-Page, J.C.; Torricelli, D. Theories and control models and motor learning: Clinical applications in neuro-rehabilitation. Neurologia 2015, 30, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayón-Calatayud, M.; Gil-Agudo, A.; Benavente-Valdepeñas, A.M.; Drozdowskyj-Palacios, O.; Sanchez-Martín, G.; Del Alamo-Rodriguez, M.J. Eficacia de nuevas terapias en la neurorrehabilitación del miembro superior en pacientes con ictus. Rehabilitación 2014, 48, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, S.M.; Dannenbaum, R.; Levin, M.F. Task-specific training with trunk restraint on arm recovery in stroke: Randomized control trial. Stroke 2006, 37, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shu, T.; Niu, W. Comparison Between Movement-Based and Task-Based Mirror Therapies on Improving upper Limb Functions in Patients with Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; He, H.; Lin, S.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Zou, J.; et al. Synergistic Effect of Combined Mirror Therapy on Upper Extremity in Patients with Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-García, A.; Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Lucena-Anton, D. Mirror therapy simultaneously combined with electrical stimulation for upper limb motor function recovery after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cruzado, D.; Merchán-Baeza, J.A.; González-Sánchez, M.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Systematic review of mirror therapy compared with conventional rehabilitation in upper extremity function in stroke survivors. Aust. Occup. Ther. J. 2017, 64, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiragami, S.; Inoue, Y.; Harada, K. Minimal clinically important difference for the Fugl-Meyer assessment of the upper extremity in convalescent stroke patients with moderate to severe hemiparesis. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2019, 31, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.E.; Crowner, B.E.; Kluding, P.M.; Nichols, D.; Rose, D.K.; Yoshida, R.; Pinto Zipp, G. Outcome measures for individuals with stroke: Process and recommendations from the American Physical Therapy Association neurology section task force. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer González, B. Adaptación y Validación al Español de la Escala Fugl-Meyer en el Manejo de la Rehabilitación de Pacientes Con Ictus; Universidad de Sevilla: Sevilla, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Page, S.J.; Fulk, G.D.; Boyne, P. Clinically important differences for the upper-extremity Fugl-Meyer Scale in people with minimal to moderate impairment due to chronic stroke. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística (INE). Problemas o Enfermedades Crónicas o de Larga Evolución en Los Últimos 12 Meses Según Sexo, País de Nacimiento y Grupo de Edad; Población de 15 y Más Años; Instituto Nacional de Estadística: Madrid, Spain, 2014; Available online: https://www.ine.es/jaxi/Datos.htm?path=/t15/p420/a2014/p01/l0/&file=02009.px (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Madhoun, H.Y.; Tan, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yu, L. Task-based mirror therapy enhances the upper limb motor function in subacute stroke patients: A randomized control trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zha, H.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Therapeutic Role of Additional Mirror Therapy on the Recovery of Upper Extremity Motor Function after Stroke: A Single-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Neural. Plast. 2022, 2022, 8966920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirela Cristina, L.; Matei, D.; Ignat, B.; Popescu, C.D. Mirror therapy enhances upper extremity motor recovery in stroke patients. Acta. Neurol. Belg. 2015, 115, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Chang, M.; Kim, K.M.; An, D.H. The effects of mirror therapy with tasks on upper extremity function andself-care in stroke patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lim, K.B.; Lee, H.J.; Yoo, J.; Yun, H.J.; Hwang, H.J. Efficacy of Mirror Therapy Containing Functional Tasks in Poststroke Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Shim, J. Investigation of the effects of mirror therapy on the upper extremityfunctions of stroke patients using the manual function test. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, S.T. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of neural repair after stroke: Making waves. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W. Effects of Cognitive Exercise Therapy on Upper Extremity Sensorimotor Function and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare 2022, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, S.; Yamada, M.; Komori, T. Frontal Lobe Activity during the Performance of Spatial Tasks: fNIRS Study. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2008, 20, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanes, J.N. Skill learning: Motor cortex rules for learning and memory. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, R495–R497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Deblock-Bellamy, A.; Lamontagne, A.; Blanchette, A.K. Cognitive-Locomotor Dual-Task Interference in Stroke Survivors and the Influence of the Tasks: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunketorp-Käll, L.; Lundgren-Nilsson, Å.; Samuelsson, H.; Pekny, T.; Blomvé, K.; Pekna, M.; Pekny, M.; Blomstrand, C.; Nilsson, M. Long-Term Improvements after Multimodal Rehabilitation in Late Phase after Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Stroke 2017, 48, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, V.; Del Valle-Gratacós, M.; Fernández-Matías, R.; Carratalá-Tejada, M.; Cuesta-Gómez, A.; Molina-Rueda, F. The Long-Term Maintenance of upper Limb Motor Improvements Following Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with Rehabilitation in People with Stroke: A Systematic Review of Randomized Sham-Controlled Trials. Sensors 2021, 21, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, A.; Farmer, S.E.; Brady, M.C.; Langhorne, P.; Mead, G.E.; Mehrholz, J.; van Wijck, F. Interventions for improving upper limb function after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD010820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Inclusion Criteria | |
| 1 | Being over 18 years old |
| 2 | Having been diagnosed with residual hemiparesis due to an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke |
| 3 | Presenting a level of movement in the affected upper limbs within stages II to IV according to the Brunnstrom scale [31] |
| 4 | Obtaining a score in the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) equal to or higher than 26 [32,33] |
| 5 | Obtaining informed consent from all participants |
| Exclusion criteria (based on diagnostic information provided by the neurologist’s clinical evaluation) | |
| 1 | Participants exhibiting hemineglect |
| 2 | Wernicke’s aphasia or mixed aphasia |
| 3 | Visual impairment (homonymous hemianopsia) |
| Variables | Group | First Evaluation Mean (SD) | Second Evaluation Mean (SD) | Treatment Group | Mean Difference | SD | p | 95% CI | Observed Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LI | LS | |||||||||
| Functionality | CG | 90.25 (29.978) | 92.78 (29.873) | CTE | −7.90 | 2.264 | 0.001 ** | −12.392 | −3.425 | 0.994 |
| MT | −10.56 | 2.260 | <0.001 ** | −15.041 | −6.088 | |||||
| CTE | 86.33 (26.774) | 97.23 (24.433) | CG | 7.90 | 2.264 | 0.001 ** | 3.425 | 12.392 | ||
| MT | −2.65 | 2.263 | 0.243 | −7.139 | 1.827 | |||||
| MT | 89.95 (27.964) | 103.08 (25.998) | CG | 10.56 | 2.260 | <0.001 ** | 6.088 | 15.041 | ||
| CTE | 2.65 | 2.263 | 0.243 | −1.827 | 7.139 | |||||
| Motor domain | CG | 40.48 (21.903) | 42.03 (22.208) | CTE | −6.28 | 1.919 | 0.001 ** | −10.086 | −2.485 | 0.977 |
| MT | −7.88 | 1.915 | <0.001 ** | −11.677 | −4.092 | |||||
| CTE | 36.85 (20.314) | 45.05 (18.474) | CG | 6.28 | 1.919 | 0.001 ** | 2.485 | 10.086 | ||
| MT | −1.59 | 1.915 | 0.406 | −5.392 | 2.195 | |||||
| MT | 38.83 (19.945) | 48.43 (20.671) | CG | 7.88 | 1.915 | <0.001 ** | 4.092 | 11.677 | ||
| CTE | 1.59 | 1.915 | 0.406 | −2.195 | 5.392 | |||||
| Sensory domain | CG | 9.15 (3.585) | 9.10 (3.720) | CTE | −1.67 | 0.425 | <0.001 ** | −2.512 | −0.827 | 0.955 |
| MT | −1.17 | 0.425 | 0.007 * | −2.018 | −0.335 | |||||
| CTE | 9.57 (3.720) | 11.05 (2.062) | CG | 1.67 | 0.425 | <0.001 ** | 0.827 | 2.512 | ||
| MT | 0.49 | 0.425 | 0.248 | −0.348 | 1.335 | |||||
| MT | 9.38 (3.600) | 10.43 (3.145) | CG | 1.17 | 0.425 | 0.007 * | 0.335 | 2.018 | ||
| CTE | −0.49 | 0.425 | 0.248 | −1.335 | 0.348 | |||||
| Range of motion and pain domain | CG | 40.63 (10.883) | 41.65 (9.919) | CTE | 0.46 | 0.903 | 0.612 | −1.328 | 2.247 | 0.595 |
| MT | −1.69 | 0.903 | 0.063 | −3.486 | 0.092 | |||||
| CTE | 39.90 (8.924) | 40.63 (9.903) | CG | −0.46 | 0.903 | 0.612 | −2.247 | 1.328 | ||
| MT | −2.16 | 0.905 | 0.019 * | −3.949 | −0.364 | |||||
| MT | 41.75 (9.009) | 44.23 (6.379) | CG | 1.69 | 0.903 | 0.063 | −0.092 | 3.486 | ||
| CTE | 2.16 | 0.905 | 0.019 * | 0.364 | 3.949 | |||||
| Variables | Group | First Evaluation Mean (SD) | Third Evaluation Mean (SD) | Treatment Group | Mean Difference | SD | p | 95% CI | Observed Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LI | LS | |||||||||
| Functionality | CG | 90.25 (29.978) | 94.95 (27.556) | CTE | −7.78 | 2.815 | 0.007 * | −13.356 | −2.203 | 0.983 |
| MT | −12.41 | 2.811 | <0.001 ** | −17.978 | −6.843 | |||||
| CTE | 86.33 (26.774) | 99.65 (25.172) | CG | 7.78 | 2.815 | 0.007 * | 2.203 | 13.356 | ||
| MT | −4.63 | 2.815 | 0.103 | −10.206 | 0.944 | |||||
| MT | 89.95 (27.964) | 107.13 (23.516) | CG | 12.41 | 2.811 | <0.001 ** | 6.843 | 17.978 | ||
| CTE | 4.63 | 2.815 | 0.103 | −0.944 | 10.206 | |||||
| Motor domain | CG | 40.48 (21.903) | 43.05 (20.539) | CTE | −6.63 | 2.165 | 0.003 * | −10.920 | −2.343 | 0.993 |
| MT | −10.28 | 2.161 | <0.001 ** | −14.564 | −6.004 | |||||
| CTE | 36.85 (20.314) | 46.75 (18.648) | CG | 6.63 | 2.165 | 0.003 * | 2.343 | 10.920 | ||
| MT | −3.65 | 2.161 | 0.094 | −7.934 | 0.628 | |||||
| MT | 38.83 (19.945) | 52.00 (18.753) | CG | 10.28 | 2.161 | <0.001 ** | 6.004 | 14.564 | ||
| CTE | 3.65 | 2.161 | 0.094 | −0.628 | 7.934 | |||||
| Sensory domain | CG | 9.15 (3.585) | 9.65 (3.585) | CTE | −1.26 | 0.468 | 0.008 * | −2.192 | −0.339 | 0.721 |
| MT | −1.02 | 0.467 | 0.030 * | −1.952 | −0.100 | |||||
| CTE | 9.57 (3.720) | 11.15 (2.155) | CG | 1.26 | 0.468 | 0.008 * | 0.339 | 2.192 | ||
| MT | 0.24 | 0.467 | 0.609 | −0.686 | 1.165 | |||||
| MT | 9.38 (3.600) | 10.80 (2.747) | CG | 1.02 | 0.467 | 0.030 * | 0.100 | 1.952 | ||
| CTE | −0.24 | 0.467 | 0.609 | −1.165 | 0.686 | |||||
| Range of motion and pain domain | CG | 40.63 (10.883) | 42.25 (9.647) | CTE | −0.711 | 1.230 | 0.564 | −3.147 | 1.724 | 0.150 |
| MT | −1.359 | 1.231 | 0.272 | −3.797 | 1.079 | |||||
| CTE | 39.90 (8.924) | 42.50 (7.643) | CG | 0.711 | 1.230 | 0.564 | −1.724 | 3.147 | ||
| MT | −0.647 | 1.233 | 0.601 | −3.090 | 1.795 | |||||
| MT | 41.75 (9.009) | 44.33 (7.180) | CG | 1.359 | 1.231 | 0.272 | −1.079 | 3.797 | ||
| CTE | 0.647 | 1.233 | 0.601 | −1.795 | 3.090 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Solana, J.; Álvarez-Pardo, S.; Moreno-Villanueva, A.; Santamaría-Peláez, M.; González-Bernal, J.J.; Vélez-Santamaría, R.; González-Santos, J. Efficacy of a Rehabilitation Program Using Mirror Therapy and Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise on Upper Limb Functionality in Patients with Acute Stroke. Healthcare 2024, 12, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12050569
Fernández-Solana J, Álvarez-Pardo S, Moreno-Villanueva A, Santamaría-Peláez M, González-Bernal JJ, Vélez-Santamaría R, González-Santos J. Efficacy of a Rehabilitation Program Using Mirror Therapy and Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise on Upper Limb Functionality in Patients with Acute Stroke. Healthcare. 2024; 12(5):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12050569
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Solana, Jessica, Sergio Álvarez-Pardo, Adrián Moreno-Villanueva, Mirian Santamaría-Peláez, Jerónimo J. González-Bernal, Rodrigo Vélez-Santamaría, and Josefa González-Santos. 2024. "Efficacy of a Rehabilitation Program Using Mirror Therapy and Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise on Upper Limb Functionality in Patients with Acute Stroke" Healthcare 12, no. 5: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12050569
APA StyleFernández-Solana, J., Álvarez-Pardo, S., Moreno-Villanueva, A., Santamaría-Peláez, M., González-Bernal, J. J., Vélez-Santamaría, R., & González-Santos, J. (2024). Efficacy of a Rehabilitation Program Using Mirror Therapy and Cognitive Therapeutic Exercise on Upper Limb Functionality in Patients with Acute Stroke. Healthcare, 12(5), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12050569








