Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Intervention Is the Key for Prevention
Abstract
1. Introduction
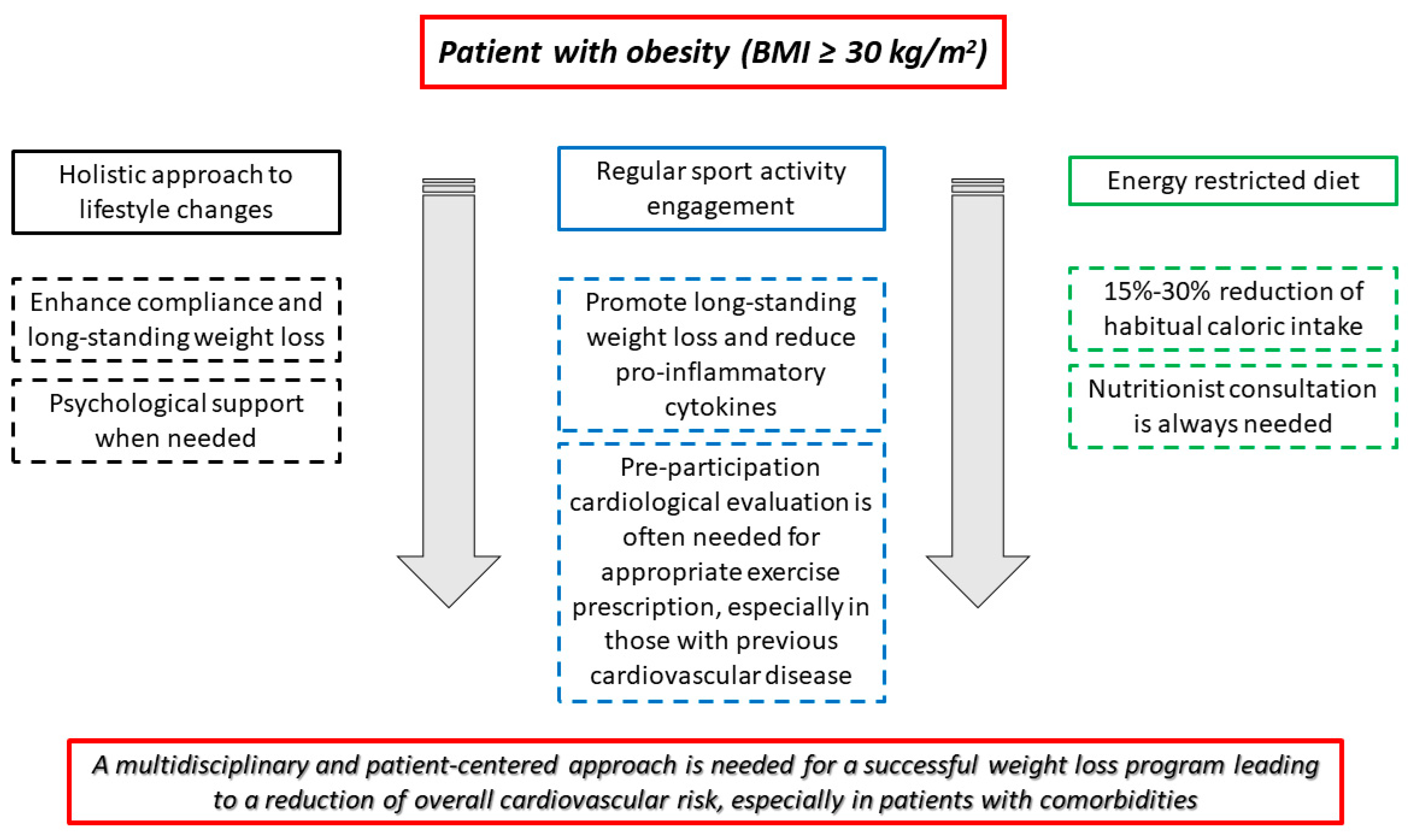
2. Physical Activity and Diet
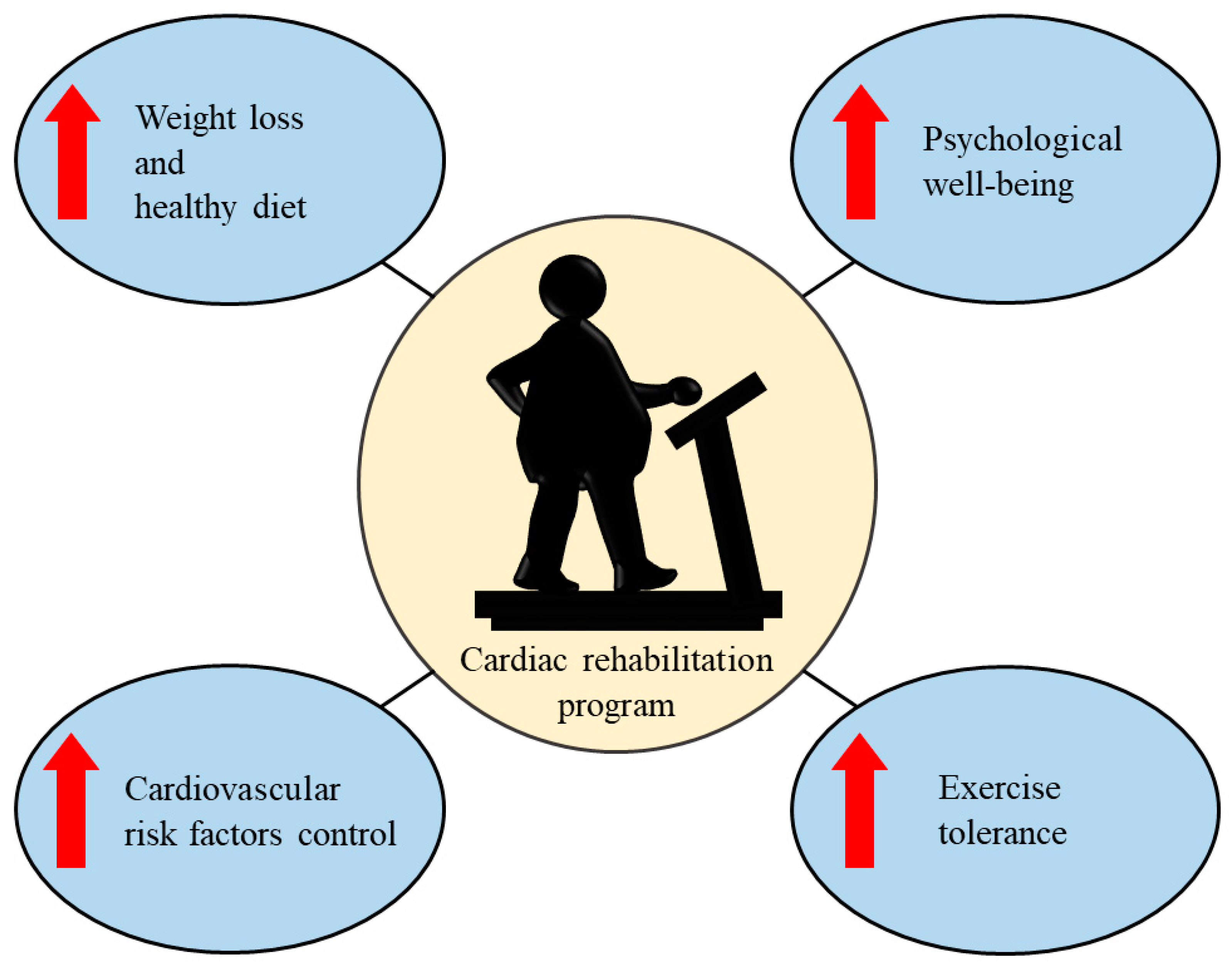
3. Cardiac Rehabilitation
4. Medical Treatment
| Active Principle | Mechanism of Action | Effect | Indication | Dosage | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orlistat (Xenical; H-2 Pharma; OTC: Alli; GlaxoSmithKline) [55] | Selective inhibitor of pancreatic lipase | Reduces the absorption of dietary fat from the digestive tract | Treatment of obese patients with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, or overweight patients (BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2) with associated risk factors in combination with a moderately hypocaloric diet | Xenical: 120 mg; OTC: 60 mg; Max dose: 1 × 3 | Approved by EMA and FDA |
| Naltrexone/Bupropione (Contrave; Currax Pharmaceuticals) [55] | Naltrexone: μ-opiate receptor antagonist Bupropion: weak inhibitor of neuronal dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake | Reduces appetite and increases energy expenditure | Weight management in adults with baseline BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 or ≥27 to 30 kg/m2 in the presence of one or more weight-related comorbidities (type 2 DM, dyslipidemia, or controlled hypertension) in addition to a low-calorie diet and increased physical activity | 32/360 mg/die | Approved by EMA and FDA |
| Liraglutide (Saxenda®; Novo Nordisk) [61] | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Increase in the sense of fullness and satiety | Chronic weight management in adults with an initial BMI ≥30 kg/m2 or ≥27 kg/m2 in the presence of ≥1 weight related comorbid condition (e.g., hypertension, type 2 DM, dyslipidemia), in addition to a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity | 3 mg/die | Approved by EMA and FDA |
| Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy, Rybelsus) [63] | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Reduces hunger, food cravings, and body fat | Long-term weight management in adults with obesity (initial BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) or overweight (initial BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2) with at least one weight-related comorbidity in adjunct to diet and physical exercise | 2.4 mg subcutaneously once weekly | Approved by EMA |
| Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) [66] | GIP/GLP1 dual receptor agonist with increased affinity for GIP receptors | Reduces glycated hemoglobin and body weight | Weight management in obese or overweight, nondiabetic adults, with at least one comorbidity | 5–10–15 mg/die | Approved by FDA, waiting for approval by EMA |
| Cagrilintide [75] | Long-acting acylated amylin analogue of action with high homology with natural amylin | Reduces intake food and body weight in a dose-dependent manner | Weight management in obese or overweight adults | 0.3, 0.6, 1.2, 2.4 o 4.5 mg subcutaneously once weekly | Waiting for approval |
| Cagrilintide/Semaglutide [75] | acylated amylin + GLP-1 receptor agonist | Reduces hunger and food craving | Weight management in obese or overweight adults | Cagrilintide: 1.2 mg, 2.4 mg and 4.5 mg Semaglutide: 2.4 mg subcutaneously once weekly | Waiting for approval |
5. Surgical Management
| Procedure Type | Sleeve Gastrectomy | Roux-en-Y Gastric By-Pass | Intragastric Ballon | Adjustable Gastric Banding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Laparoscopic | Laparoscopic | Endoscopic | Laparoscopic |
| Mechanism of Action | Restrictive + hormonal | Mixed (restrictive + malabsorbitive) | Restrictive | Restrictive |
| Benefits |
|
|
|
|
| Early Complications (<90 days) |
|
|
|
|
| Late Complications (>90 days) |
|
|
|
|
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2985–3023, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Almahmeed, W.; Bays, H.; Cuevas, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Sun, M.C.; Wittert, G.; Pinto, F.J.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Mechanistic insights and management strategies. A joint position paper by the World Heart Federation and World Obesity Federation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 2218–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Mechanick, J.I.; Brett, E.M.; Garber, A.J.; Hurley, D.L.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Nadolsky, K.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Plodkowski, R.; Reviewers of the AACE/ACE Obesity Clinical Practice Guidelines. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines for Medical Care of Patients with Obesity. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22 (Suppl. S3), 1–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharton, S.; Lau, D.C.; Vallis, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Biertho, L.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Adamo, K.; Alberga, A.; Bell, R.; Boulé, N.; et al. Obesity in adults: A clinical practice guideline. CMAJ 2020, 192, E875–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Soldati, L.; Sarlo, F.; Calvani, M.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Di Renzo, L. New obesity classification criteria as a tool for bariatric surgery indication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 681–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Kim, K.K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; World Obesity Federation. Obesity: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; Taub, P.R.; Epstein, E.; Michos, E.D.; Ferraro, R.A.; Bailey, A.L.; Kelli, H.M.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Echols, M.R.; Weintraub, H.; et al. Ten things to know about ten cardiovascular disease risk factors. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 5, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ades, P.A.; Savage, P.D.M. The Treatment of Obesity in Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Review and Practical Recommendations. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2021, 41, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosetti, M.; Abreu, A.; Corrà, U.; Davos, C.H.; Hansen, D.; Frederix, I.; Iliou, M.C.; Pedretti, R.F.E.; Schmid, J.-P.; Vigorito, C.; et al. Secondary prevention through comprehensive cardiovascular rehabilitation: From knowledge to implementation. 2020 update. A position paper from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 7, 2047487320913379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumuk, V.; Tsigos, C.; Fried, M.; Schindler, K.; Busetto, L.; Micic, D.; Toplak, H. European Guidelines for obesity management in adults. Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shai, I.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Henkin, Y.; Shahar, D.R.; Witkow, S.; Greenberg, I.; Golan, R.; Fraser, D.; Bolotin, A.; Vardi, H.; et al. weight loss with a low-carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or low-fat diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Bray, G.A.; Carey, V.J.; Smith, S.R.; Ryan, D.H.; Anton, S.D.; McManus, K.; Champagne, C.M.; Bishop, L.M.; Laranjo, N.; et al. Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.M.; Dalskov, S.-M.; van Baak, M.; Jebb, S.A.; Papadaki, A.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Martinez, J.A.; Handjieva-Darlenska, T.; Kunešová, M.; Pihlsgård, M.; et al. Diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index for weight-loss maintenance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2102–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Johnson, N.; Mielke, G.; Coombes, J.S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of interval training versus moderate-intensity continuous training on body adiposity. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 943–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, D.L.; Johannsen, N.M.; Lavie, C.J.; Earnest, C.P.; Church, T.S. The role of exercise and physical activity in weight loss and maintenance. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, T.; Arsenis, N.C.; Disanzo, B.L.; Lamonte, M.J. Effects of exercise training on chronic inflammation in obesity: Current evi-dence and potential mechanisms. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R.; Adeniran, S.B.; Etheridge, G.L. Effects of different running programs on VO2 max, percent fat, and plasma lipids. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1984, 9, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Devin, J.L.; Sax, A.T.; Hughes, G.I.; Jenkins, D.; Aitken, J.; Chambers, S.K.; Dunn, J.; Bolam, K.A.; Skinner, T. The influence of high-intensity compared with moderate-intensity exercise training on cardiorespiratory fitness and body composition in colorectal cancer survivors: A randomised controlled trial. J. Cancer Surviv. 2016, 10, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelliccia, A.; Sharma, S.; Gati, S.; Bäck, M.; Börjesson, M.; Caselli, S.; Collet, J.-P.; Corrado, D.; Drezner, J.A.; Halle, M.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines on sports cardiology and exercise in patients with cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 17–96, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, L.H.; Slentz, C.A.; Bateman, L.A.; Shields, A.T.; Piner, L.W.; Bales, C.W.; Houmard, J.A.; Kraus, W.E. Effects of aerobic and/or resistance training on body mass and fat mass in overweight or obese adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebe, D.; Franklin, B.A.; Thompson, P.D.; Garber, C.E.; Whitfield, G.P.; Magal, M.; Pescatello, L.S. Updating ACSM’s Recommendations for Exercise Preparticipation Health Screening. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcell, T.J.; McAuley, K.A.; Traustadóttir, T.; Reaven, P.D. Exercise training is not associated with improved levels of C-reactive protein or adiponectin. Metabolism 2005, 54, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N.; Layne, J.E.; Gordon, P.L.; Roubenoff, R.; Nelson, M.E.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Strength training improves muscle quality and insulin sensitivity in Hispanic older adults with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 4, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.; Stamp, N.; Ngui, A.; Litton, E. Cardiac Prehabilitation. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.A.; Harrison, A.S.; Doherty, P. Obese patients’ characteristics and weight loss outcomes in cardiac rehabilitation: An observational study of registry data. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 337, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V.; Morshedi-Meibodi, A. Impact of cardiac rehabilitation on coronary risk factors, inflammation, and the metabolic syndrome in obese coronary patients. J. Cardiometab. Syndr. 2008, 3, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Missiri, A.; Halim, W.A.A.; Almaweri, A.S.; Mohamed, T.R. Effect of a phase 2 cardiac rehabilitation program on obese and non-obese patients with stable coronary artery disease. Egypt. Heart J. 2021, 73, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, G.; Kerins, M.; Fitzgerald, G.; Spain, M.; Morrison, K. Factors that influence obesity, functional capacity, anxiety and depression outcomes following a Phase III cardiac rehabilitation programme. J. Clin. Nurs. 2013, 22, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Rodríguez, M.M.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Ruiz-Nava, J.; Alcaide-Torres, J.; Saracho-Domínguez, H.; Rioja-Vázquez, R.; García-Fernández, C.; Gómez-González, A.; Montiel-Trujillo, A.; Tinahones-Madueño, F.J. Impact of an outpatient cardiac rehabilitation program on clinical and analytical variables in cardiovascular disease. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2014, 34, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degli Esposti, L.; Perrone, V.; Veronesi, C.; Gambera, M.; Nati, G.; Perone, F.; Tagliabue, P.F.; Buda, S.; Borghi, C. Modifications in drug adherence after switch to fixed-dose combination of perindopril/amlodipine in clinical practice. Results of a large-scale Italian experience. The amlodipine-perindopril in real settings (AMPERES) study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, V.; Veronesi, C.; Gambera, M.; Nati, G.; Perone, F.; Tagliabue, P.F.; Degli Esposti, L.; Volpe, M. Treatment with Free Triple Combination Therapy of Atorvastatin, Perindopril, Amlodipine in Hypertensive Patients: A Real-World Population Study in Italy. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2019, 26, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, G.M.; Cribbie, R.; Villa, V.; Arpin-Cribbie, C.; Gondoni, L.; Castelnuovo, G. Psychological well-being in obese inpatients with ischemic heart disease at entry and at discharge from a four-week cardiac rehabilitation program. Front. Psychol. 2010, 1, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, G.M.; Villa, V.; Compare, A.; Castelnuovo, G.; Nibbio, F.; Titon, A.M.; Molinari, E.; Gondoni, L.A. Short-term effects of a multi-disciplinary cardiac rehabilitation programme on psychological well-being, exercise capacity and weight in a sample of obese in-patients with coronary heart disease: A practice-level study. Psychol. Health Med. 2011, 16, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Chirico, D.; Tulloch, H.E.; Scott, K.; Doucet, É.; Pipe, A.L.; Reed, J.L. Psychosocial and Cardiometabolic Health of Patients with Differing Body Mass Index Completing Cardiac Rehabilitation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrabissa, G.; Castelnuovo, G.; Manzoni, G.M.; Cattivelli, R.; Molinari, E.; Gondoni, L.A. Psychological Well-Being as an Independent Predictor of Exercise Capacity in Cardiac Rehabilitation Patients with Obesity. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondoni, L.A.; Nibbio, F.; Titon, A. Beneficial Effect on Exercise Tolerance of a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program in Elderly Obese Patients Affected with Heart Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 652921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atti, V.; Devarakonda, P.K.; Raina, S. Differential Effects of Cardiac Rehabilitation in Obese and Non-Obese Population. Cureus 2021, 13, e18227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.; Nascimento, H.; Pinto, R.; Araújo, P.; Nunes, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Araújo, V.; Parada-Pereira, F.; Maciel, M.J.; Rocha, J.A. Benefits of Cardiac Rehabilitation in Coronary Artery Disease: Does weight Matter? J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2019, 39, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashghaei, F.E.; Sadeghi, M.; Mostafavi, S.; Heidari, H.; Sarrafzadegan, N. The effect of the cardiac rehabilitation program on obese and non-obese females with coronary heart disease. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2012, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Esteki Ghashghaei, F.; Rouhafza, H. Comparing the effects of a cardiac rehabilitation program on functional capacity of obese and non-obese women with coronary artery disease. ARYA Atheroscler. 2012, 8, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Shubair, M.M.; Kodis, J.; McKelvie, R.S.; Arthur, H.M.; Sharma, A.M. Metabolic profile and exercise capacity outcomes: Their relationship to overweight and obesity in a Canadian cardiac rehabilitation setting. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. 2004, 24, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-M.; Li, L.S.-W.; Ho, H.; Lau, C.-P. Long-term changes in exercise capacity, quality of life, body anthropometry, and lipid profiles after a cardiac rehabilitation program in obese patients with coronary heart disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V. Effects of cardiac rehabilitation and exercise training on peak aerobic capacity and work efficiency in obese patients with coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fusco, S.A.; Arca, M.; Scicchitano, P.; Alonzo, A.; Perone, F.; Gulizia, M.M.; Gabrielli, D.; Oliva, F.; Imperoli, G.; Colivicchi, F. Lipoprotein(a): A risk factor for atherosclerosis and an emerging therapeutic target. Heart 2022, 109, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Khonsari, S.; Gallagher, R.; Gallagher, P.; Clark, A.M.; Freedman, B.; Briffa, T.; Bauman, A.; Redfern, J.; Neubeck, L. Telehealth interventions for the secondary prevention of coronary heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2019, 18, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, S.J.; Mills, B.; Birch, E.M.; Thompson, S.C. Smartphones in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A sys-tematic review. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Ning, H.; Wilkins, J.T.; Allen, N.; Carnethon, M.; Berry, J.D.; Sweis, R.N.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M. Association of body mass index with lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease and compression of morbidity. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Montani, J.-P. Pathways from dieting to weight regain, to obesity and to the metabolic syndrome: An overview. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Kahlhöfer, J.; Lagerpusch, M.; Skurk, T.; Müller, M.J. Deep body composition phenotyping during weight cycling: Relevance to metabolic efficiency and metabolic risk. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Choi, S.; Chang, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.M.; Hwang, S.Y.; Son, J.S.; Lee, G.; Park, S.M. Association of weight fluctuation with cardiovascular disease risk among initially obese adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montani, J.-P.; Schutz, Y.; Dulloo, A.G. Dieting and weight cycling as risk factors for cardiometabolic diseases: Who is really at risk? Obes. Rev. 2015, 16 (Suppl. S1), 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmalski, M.; Deska, K.; Bąk, B.; Różycka-Kosmalska, M.; Pietras, T. Pharmacological Support for the Treatment of Obesity-Present and Future. Healthcare 2023, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.H.; Hauptman, J.; DiGirolamo, M.; Foreyt, J.P.; Halsted, C.H.; Heber, D.; Heimburger, D.C.; Lucas, C.P.; Robbins, D.C.; Chung, J.; et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999, 281, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hill, J.; Hauptman, J.; Anderson, J.W.; Fujioka, K.; O’Neil, P.M.; Smith, D.K.; Zavoral, J.H.; Aronne, L.J. Orlistat, a lipase inhibitor, for weight maintenance after conventional dieting: A 1-y study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhunen, L.; Franssila-Kallunki, A.; Rissanen, P.; Valve, R.; Kolehmainen, M.; Uusitupa, M. Effect of orlistat treatment on body composition and resting energy expenditure during a two-year weight-reduction programme in obese Finns. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelsen, B.; Tonstad, S.; Rossner, S.; Toubro, S.; Niskanen, L.; Madsbad, S.; Mustajoki, P.; Rissanen, A. Effect of orlistat on weight regain and cardiovascular risk factors following a very-low-energy diet in abdominally obese patients: A 3-year randomized, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, F.L.; Fujioka, K.; Plodkowski, R.A.; Mudaliar, S.; Guttadauria, M.; Erickson, J.; Kim, D.D.; Dunayevich, E. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuffer, W.A.; Trujillo, J.M. Liraglutide: A New Option for the Treatment of Obesity. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2015, 35, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyer, X.P.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.; Le Roux, C.W.; Violante Ortiz, R.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3·0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Færch, L.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Pakseresht, A.; Pedersen, S.D.; Perreault, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Shimomura, I.; Viljoen, A.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Semaglutide 2·4 Mg Once a Week in Adults with Overweight or Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes (STEP 2): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves New Drug Treatment for Chronic Weight Management, First Since 2014. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014 (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. SURMOUNT-1 Investigators. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W. Emerging Role of SGLT-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Obesity. Drugs 2019, 79, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidus, L.; Bengtsson, C.; Larsson, B.; Pennert, K.; Rybo, E.; Sjostrom, L. Distribution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: A 12 year follow up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden. Br. Med. J. 1984, 289, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, E.O.; Palmer, A.J.; Berryman, D.E.; Bower, B.; Kelder, B.; Kopchick, J.J. Growth hormone improves body composition, fasting blood glucose, glucose tolerance and liver triacylglycerol in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.R.; Nam, S.Y.; Song, Y.D.; Kil Lim, S.; Lee, H.C.; Huh, K.B. Low-dose growth hormone treatment with diet restriction accelerates body fat loss, exerts anabolic effect and improves growth hormone secretory dysfunction in obese adults. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 1999, 51, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.K.; Clemmons, D.R.; Underwood, L.E. Treatment of obese, diet-restricted subjects with growth hormone for 11 weeks: Effects on anabolism, lipolysis, and body composition. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 67, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drent, M.L.; Wever, L.D.; Adèr, H.J.; van der Veen, E.A. Growth hormone administration in addition to a very low calorie diet and an exercise program in obese subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1995, 132, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.H. Obesity, growth hormone and weight loss. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.K.Y. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adults with GH deficiency II: A statement of the GH Research Society in association with the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology, Lawson Wilkins Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Japan Endocrine Society, and Endocrine Society of Australia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Conlon, J.M. An update on peptide-based therapies for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Peptides 2023, 161, 170939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornier, M.A. A review of current guidelines for the treatment of obesity. Am. J. Manag. Care 2022, 28, S288–S296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brito, J.P.; Montori, V.M.; Davis, A.M. Metabolic Surgery in the Treatment Algorithm for Type 2 Diabetes: A Joint Statement by International Diabetes Organizations. JAMA 2017, 317, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, D.E.; Olsen, M.K.; Smith, V.A.; Livingston, E.H.; Van Scoyoc, L.; Yancy, W.S.; Eid, G.; Weidenbacher, H.; Maciejewski, M.L. Association Between Bariatric Surgery and Long-term Survival. JAMA 2015, 313, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.D.; Meeks, H.; Fraser, A.; Davidson, L.E.; Holmen, J.; Newman, M.; Ibele, A.R.; Richards, N.; Hunt, S.C.; Kim, J. Long-term all-cause and cause-specific mortality for four bariatric surgery procedures. Obesity 2023, 31, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, D.E.; Telem, D.A.; Kushner, R.F.; Courcoulas, A.P. Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luesma, M.J.; Fernando, J.; Cantarero, I.; Lucea, P.; Santander, S. Surgical Treatment of Obesity. Special Mention to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Vertical Gastrectomy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 867838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Metablolic and Bariatric Surgery. Estimate of Bariatric Surgery Numbers, 2011–2020. Available online: https://asmbs.org/resources/estimate-of-bariatric-surgery-numbers (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Risi, R.; Rossini, G.; Tozzi, R.; Pieralice, S.; Monte, L.; Masi, D.; Castagneto-Gissey, L.; Gallo, I.F.; Strigari, L.; Casella, G.; et al. Sex difference in the safety and efficacy of bariatric procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022, 18, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kirwan, J.P.; Wolski, K.; Aminian, A.; Brethauer, S.A.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Singh, R.P.; Pothier, C.E.; Nissen, S.E.; et al. Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical Therapy for Diabetes—5-Year Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrone, G.; Panunzi, S.; De Gaetano, A.; Guidone, C.; Iaconelli, A.; Nanni, G.; Castagneto, M.; Bornstein, S.; Rubino, F. Bariatric–metabolic surgery versus conventional medical treatment in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 5 year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeter, A.T.; Scheurlen, K.M.; Probst, P.; Eichel, S.; Nickel, F.; Kopf, S.; Fischer, L.; Diener, M.K.; Nawroth, P.P.; Müller-Stich, B.P. Meta-analysis of metabolic surgery versus medical treatment for microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Truong, K.; Spitler, H.; Zhang, L.; Tong, X.; Chen, L. The Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Remission, Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2724–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesconetto, L.D.A.; da Silva, R.B.R.; Galletti, R.P.; Agareno, G.A.; Colonno, B.B.; de Sousa, J.H.B.; Tustumi, F. Scores for Predicting Diabetes Remission in Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Doumouras, A.G.; Yu, J.; Aditya, I.; Gmora, S.; Anvari, M.; Hong, D. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Versus Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Weight Loss, Comorbidities, and Biochemical Outcomes from Randomized Controlled Trials. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Ding, H.; Zhu, T.; Wang, G. A Comprehensive Comparison of LRYGB and LSG in Obese Patients Including the Effects on QoL, Comorbidities, Weight Loss, and Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, E.; Goday, A.; Pedro-Botet, J.; Solà, I.; Oliveras, A.; Ramón, J.M.; Roux, J.A.F.-L.; Checa, M.; Benaiges, D. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for 5-year hypertension remission in obese patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, L.; Lindroos, A.-K.; Peltonen, M.; Torgerson, J.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; Larsson, B.; Narbro, K.; Sjöström, C.D.; et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenburg, D.L.; Lettieri, C.J.; Eliasson, A.H. Effects of surgical weight loss on measures of obstructive sleep apnea: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamish, A.; Olbers, T.; Kelly, A.S.; Inge, T.H. Cardiovascular effects of bariatric surgery. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavarretta, E.; Casella, G.; Calì, B.; Dammaro, C.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Iossa, A.; Leonetti, F.; Frati, G.; Basso, N. Cardiac remodeling in obese patients after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotrionte, M.; Cavarretta, E.; Abbate, A.; Mezzaroma, E.; De Marco, E.; Di Persio, S.; Loperfido, F.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Frati, G.; Palazzoni, G. Temporal changes in standard and tissue Doppler imaging echocardiographic parameters after anthracycline chemotherapy in women with breast cancer. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagneto-Gissey, L.; Angelini, G.; Mingrone, G.; Cavarretta, E.; Tenori, L.; Licari, C.; Luchinat, C.; Tiepner, A.L.; Basso, N.; Bornstein, S.R.; et al. The early reduction of left ventricular mass after sleeve gastrectomy depends on the fall of branched-chain amino acid circulating levels. eBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Veldhuisen, S.L.; Gorter, T.M.; van Woerden, G.; de Boer, R.A.; Rienstra, M.; Hazebroek, E.J.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Bariatric surgery and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakran, N.; Soifer, K.; Hod, K.; Sherf-Dagan, S.; Soued, S.; Kessler, Y.; Adelson, D.; Biton, R.; Buchwald, J.N.; Goitein, D.; et al. Long-term Reported Outcomes Following Primary Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.S.; Manuel, K.M.; Wu, Y.; Livingston, J.; Papasavas, P.K.; Baillot, A.; Pescatello, L.S. Exercise for counteracting weight recurrence after bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppre, G.; Diniz-Sousa, F.; Veras, L.; Oliveira, J.; Fonseca, H. Can exercise promote additional benefits on body composition in patients with obesity after bariatric surgery? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2021, 8, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, C.M.; Cohen, R.V.; Sumithran, P.; Clément, K.; Frühbeck, G. Contemporary medical, device, and surgical therapies for obesity in adults. Lancet 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanick, J.I.; Apovian, C.; Brethauer, S.; Garvey, W.T.; Joffe, A.M.; Kim, J.; Kushner, R.F.; Lindquist, R.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Seger, J.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the perioperative nutrition, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of patients undergoing bariatric procedures—2019 update: Cosponsored by American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, The Obesity Society, American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery, Obesity Medicine Association, and American Society of Anesthesiologists. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2020, 16, 175–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, I.; Birch, D.W.; Sharma, A.M.; Sherman, V.; Karmali, S. Complications associated with adjustable gastric banding for morbid obesity: A surgeon’s guides. Can. J. Surg. 2011, 54, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
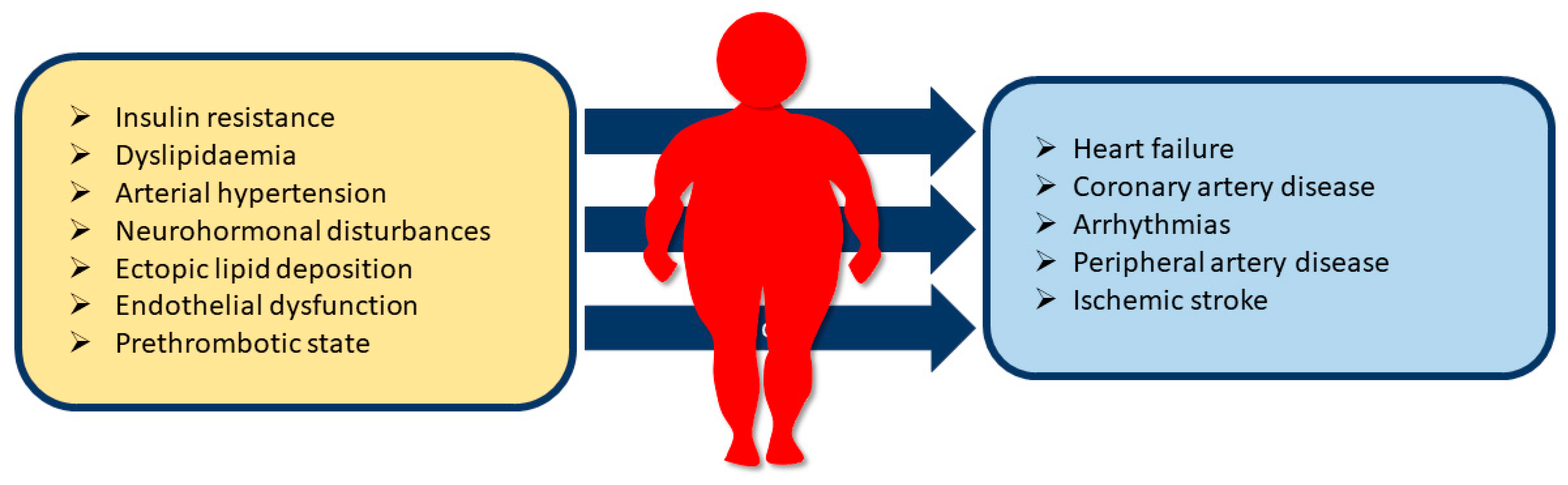
| Diseases | Complications |
|---|---|
| Aortic valve stenosis Heart failure Coronary heart disease Atrial fibrillation Subarachnoid hemorrhage Intracerebral hemorrhage Ischemic stroke Transient ischemic attack Deep vein thrombosis Peripheral artery disease Thoracic aortic aneurysm Abdominal aortic aneurysm | Type 2 diabetes Dyslipidaemia Arterial hypertension Obstructive sleep apnoea Kidney disease Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases Polycystic ovary syndrome Hypogonadism Psychological disorders |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perone, F.; Pingitore, A.; Conte, E.; Halasz, G.; Ambrosetti, M.; Peruzzi, M.; Cavarretta, E. Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Intervention Is the Key for Prevention. Healthcare 2023, 11, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060902
Perone F, Pingitore A, Conte E, Halasz G, Ambrosetti M, Peruzzi M, Cavarretta E. Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Intervention Is the Key for Prevention. Healthcare. 2023; 11(6):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060902
Chicago/Turabian StylePerone, Francesco, Annachiara Pingitore, Edoardo Conte, Geza Halasz, Marco Ambrosetti, Mariangela Peruzzi, and Elena Cavarretta. 2023. "Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Intervention Is the Key for Prevention" Healthcare 11, no. 6: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060902
APA StylePerone, F., Pingitore, A., Conte, E., Halasz, G., Ambrosetti, M., Peruzzi, M., & Cavarretta, E. (2023). Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Intervention Is the Key for Prevention. Healthcare, 11(6), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060902









