Living with Epilepsy in Adolescence in Italy: Psychological and Behavioral Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Questionnaire
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Clinical Variables
3.2. Psychological Variables
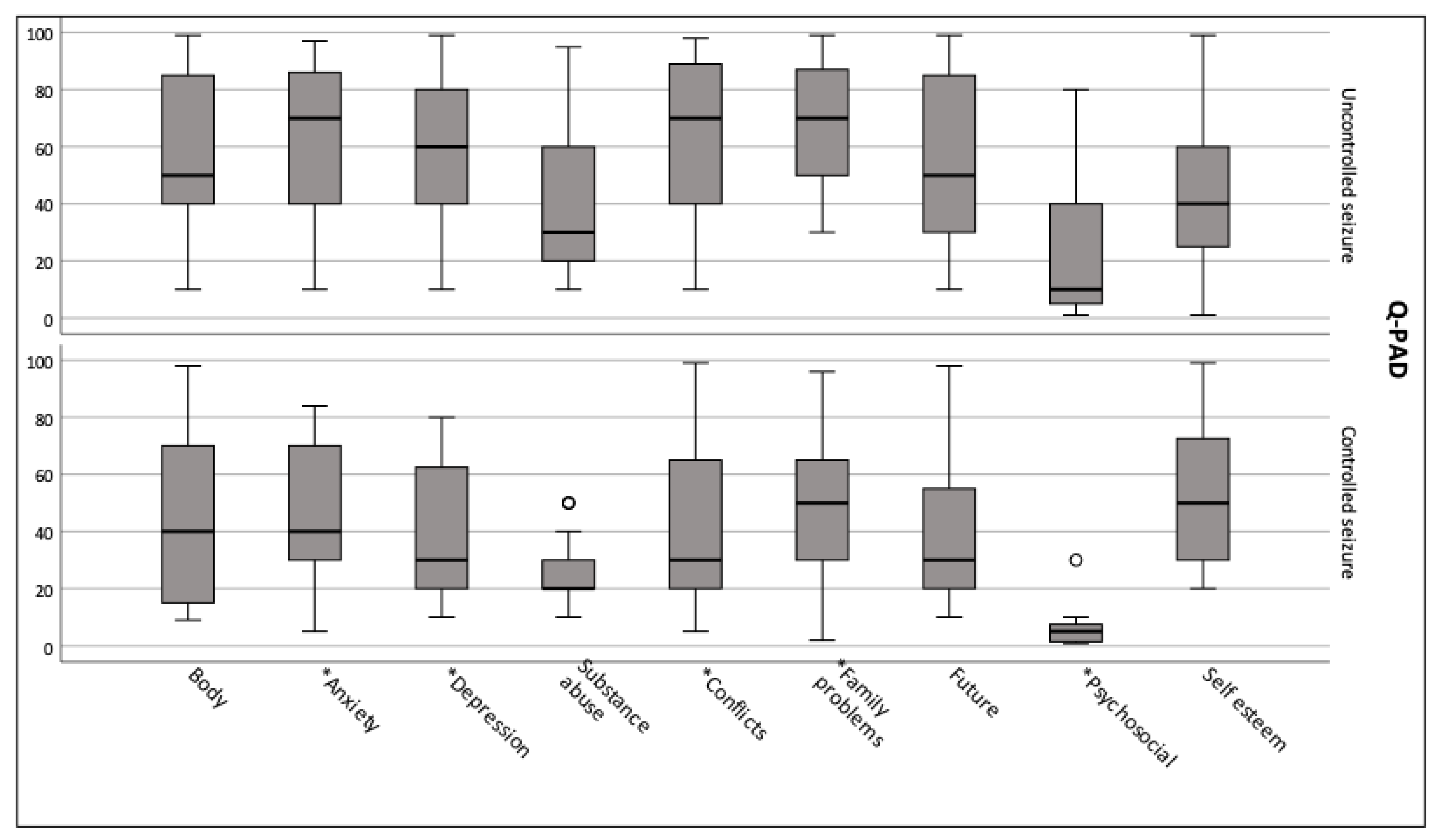
3.3. Clinical Variables x Psychological Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russ, S.A.; Larson, K.; Halfon, N. A National Profile of Childhood Epilepsy and Seizure Disorder. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, R.; Taylor, M.D. Young adults with epilepsy: Relationships between psychosocial variables and anxiety, depression, and suicidality. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 118, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, M.P.; Mensah, S.; Besag, F.; de Toffol, B.; Ettinger, A.; Kanemoto, K.; Kanner, A.; Kemp, S.; Krishnamoorthy, E.; Jr, W.C.L.; et al. International consensus clinical practice statements for the treatment of neuropsychiatric conditions associated with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, C.; Agnew, R.; Neville, B.G. Depression and anxiety in childhood epilepsy: A review. Seizure 2011, 20, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, L.; Jamieson, N.J.; Gill, D.; Singh-Grewal, D.; Craig, J.C.; Ju, A.; Hanson, C.S.; Tong, A. Children’s Experiences of Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Studies. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20160658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huemer, J.; Plattner, B.; Planer, N.; Steiner, H.; Feucht, M. Psychopathology in adolescents with TLE and FLE. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M. Is depression associated with an increased risk of treatment-resistant epilepsy? Research strategies to investigate this question. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 38, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFrance, W.C., Jr.; Kanner, A.M.; Hermann, B. Chapter 20 Psychiatric Comorbidities in Epilepsy. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 83, pp. 347–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula, M. Bidirectional link between epilepsy and psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M. Psychiatric comorbidities and epilepsy: Is it the old story of the chicken and the egg? Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M. Can neurobiological pathogenic mechanisms of depression facilitate the development of seizure disorders? Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, N.; McArthur, B.A.; Cooke, J.E.; Eirich, R.; Zhu, J.; Madigan, S. Global Prevalence of Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Children and Adolescents During COVID-19. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashakori-Miyanroudi, M.; Souresrafil, A.; Hashemi, P.; Ehsanzadeh, S.J.; Farrahizadeh, M.; Behroozi, Z. Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and psychological distress in patients with epilepsy during COVID-19: A systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 125, 108410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abokalawa, F.; Ahmad, S.F.; Al-Hashel, J.; Hassan, A.M.; Arabi, M. The effects of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on people with epilepsy (PwE): An online survey-based study. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 122, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Perez, E.R.; et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Berg, A.T.; Brodie, M.J.; Allen Hauser, W.; Mathern, G.; Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Wiebe, S.; French, J. Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: Consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders—Fifth Edition (DSM 5); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sica, C.; Chiri, L.R.; Favilli, R.; Marchetti, I. Questionario per la Valutazione Della Psicopatologia in Adolescenza; Erickson: Trento, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.J.; Mula, M.; Hermann, B.P. Uncovering the neurobehavioural comorbidities of epilepsy over the lifespan. Lancet 2012, 380, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrotti, A.; Carrozzino, D.; Milioni, M.; Minna, M.; Fulcheri, M. Epilepsy and its main psychiatric comorbidities in adults and children. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 343, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, R.; Tang, V.; Goldstein, L.H.; Reuber, M.; LaFrance, W.C., Jr.; Lundgren, T.; Modi, A.C.; Wagner, J.L. Psychological treatments for adults and children with epilepsy: Evidence-based recommendations by the International League Against Epilepsy Psychology Task Force. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1282–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, R.; Tang, V.; Wagner, J.L.; Modi, A.C.; Jr, W.C.L.; Goldstein, L.H.; Lundgren, T.; Reuber, M. Psychological treatments for people with epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 10, CD012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puka, K.; Widjaja, E.; Smith, M.L. The influence of patient, caregiver, and family factors on symptoms of anxiety and depression in children and adolescents with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 67, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.A.; Spector, S.; McGrath, Y.; Soteriou, H. Impact of epilepsy in adolescence: A UK controlled study. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 6, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, N.F.; Oliveira, F.L.B.B.; Siqueira, J.A.; De Souza, E.A.P. In adolescents with epilepsy, high scores of anxiety and depression are associated with occurrence of seizures in public places. Arq. de Neuro-Psiquiatria 2015, 73, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.; Heyman, I.; Goodman, R. A population survey of mental health problems in children with epilepsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 45, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragni, B.; Cappelletti, S.; De Stasio, S.; Tondo, I.; Specchio, N.; Vigevano, F.; Gentile, S. The impact of epilepsy on adolescence: A quali-quantitative investigation using focus group. Mediterr. J. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Caplan, R.; Siddarth, P.; Stahl, L.; Lanphier, E.; Vona, P.; Gurbani, S.; Koh, S.; Sankar, R.; Shields, W.D. Childhood absence epilepsy: Behavioral, cognitive, and linguistic comorbidities. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfstad, K.; Torgersen, H.; Van Roy, B.; Hessen, E.; Hansen, B.H.; Henning, O.; Clench-Aas, J.; Mowinckel, P.; Gjerstad, L.; Lossius, M.I. Psychiatric comorbidity in children and youth with epilepsy: An association with executive dysfunction? Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 56, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfstad, K.; Clench-Aas, J.; Van Roy, B.; Mowinckel, P.; Gjerstad, L.; Lossius, M.I. Psychiatric symptoms in Norwegian children with epilepsy aged 8-13 years: Effects of age and gender? Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Besag, F.; Aldenkamp, A.; Caplan, R.; Dunn, D.W.; Gobbi, G. Psychiatric and Behavioural Disorders in Children with Epilepsy (ILAE Task Force Report): Epidemiology of psychiatric/behavioural disorder in children with epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2016, 18, s2–s7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, N.; Kubota, T. Psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with epilepsy: A syste-matic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 124, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, C.; Viganò, I.; Ottaviano, E.; Massa, V.; Borghi, E.; Beretta, S.; Di Francesco, J.C.; Badioni, V.; Vignoli, A. Long-term analysis of the effects of COVID-19 in people with epilepsy: Results from a multicenter on-line survey across the pandemic waves. Epilepsy Behav. 2022, 135, 108900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | N = 58 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Mean | 17.24 |
| SD | 2.05 |
| Range | 14–19 |
| Younger Adolescents (14–15 years) | 18 (31.0%) |
| Older Adolescents (16–19 years) | 40 (69.0%) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 19 (32.8%) |
| Female | 39 (67.2%) |
| Education (years) | |
| Mean | 10.36 |
| SD | 2.13 |
| Range | 7–13 |
| Type of epilepsy | |
| Focal Epilepsy | |
| Unknown | 23 (39.7%) |
| Structural | 17 (29.3%) |
| Generalized Genetic Epilepsy | 18 (31.0%) |
| Epilepsy onset (years) | |
| Mean | 10.05 |
| SD | 5.1 |
| Range | 0–18 |
| Epilepsy duration (years) | |
| Mean | 8.07 |
| SD | 5.82 |
| Range | 0-28 |
| Anti-seizure Medications | |
| Monotherapy | 26 (44.8%) |
| Polytherapy | 23 (39.7%) |
| No anti-seizure Medications | 9 (15.5%) |
| Seizure frequency | |
| Daily | 3 (5.2%) |
| Weekly | 5 (8.6%) |
| Monthly | 4 (6.9%) |
| Sporadic | 15 (25.9%) |
| None | 31 (53.4%) |
| Intelligence assessment | |
| Total IQ | |
| Mean | 86.50 |
| SD | 23.69 |
| Verbal IQ | |
| Mean | 80.66 |
| SD | 25.67 |
| Performance IQ | |
| Mean | 82.90 |
| SD | 20.80 |
| Verbal Comprehension | |
| Mean | 100.33 |
| SD | 14.54 |
| Perceptual Reasoning | |
| Mean | 113.56 |
| SD | 12.32 |
| Working Memory | |
| Mean | 96.89 |
| SD | 15.10 |
| Processing Speed | |
| Mean | 87.78 |
| SD | 14.63 |
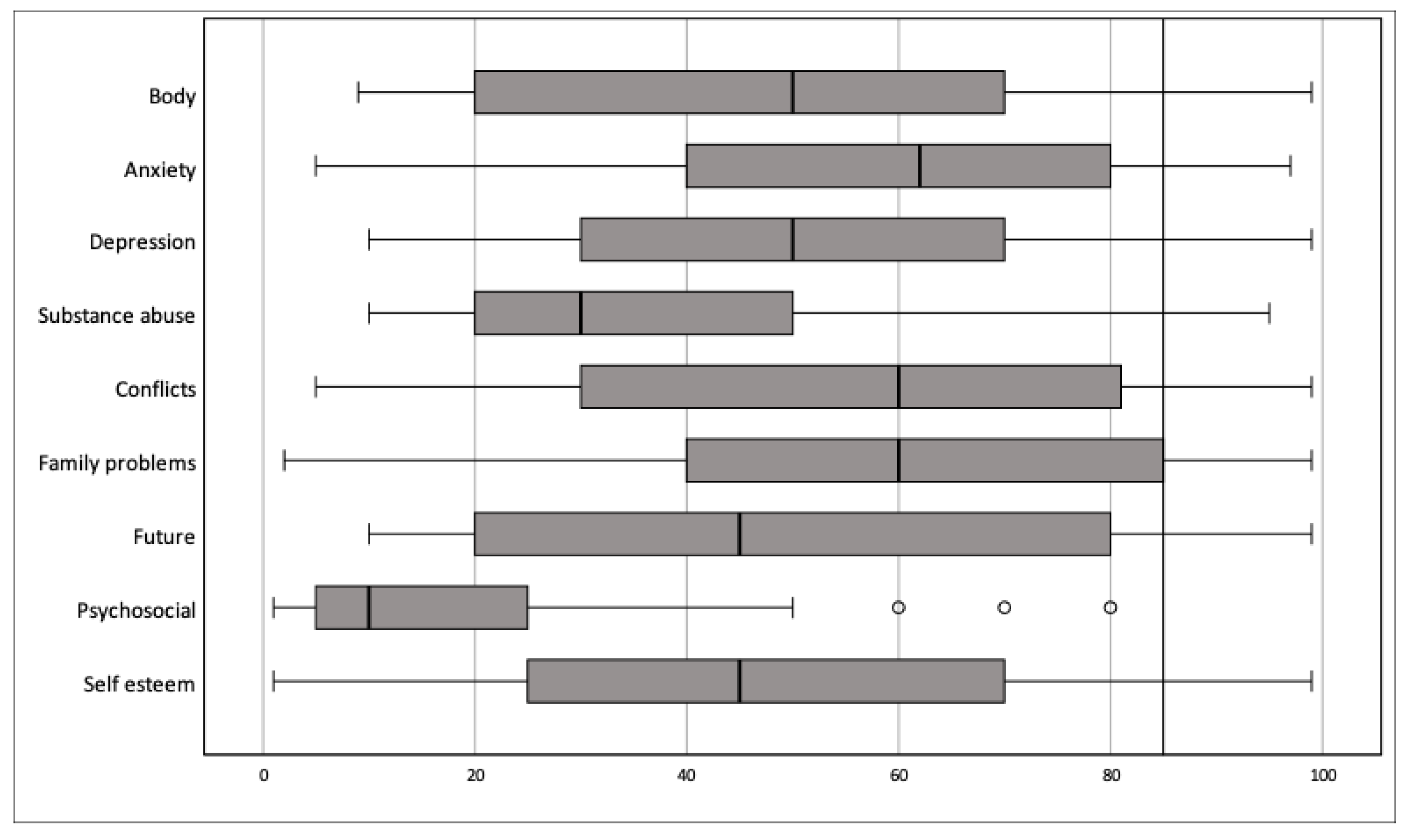
| Q-PAD Scores | |
|---|---|
| Variable | N = 58 |
| Body dissatisfaction | |
| Mean | 51.59 |
| SD | 28.87 |
| Range | 9–99 |
| Normal range | 47 (81.03%) |
| Clinical range | 11 (18.97%) |
| Anxiety | |
| Mean | 57.16 |
| SD | 26.84 |
| Range | 5–97 |
| Normal range | 47 (81.03%) |
| Clinical range | 11 (18.97%) |
| Depression | |
| Mean | 49.22 |
| SD | 27.67 |
| Range | 10–99 |
| Normal range | 54 (93.10%) |
| Clinical range | 4 (6.90%) |
| Substance abuse | |
| Mean | 34.47 |
| SD | 21.85 |
| Range | 10–95 |
| Normal range | 57 (98.28%) |
| Clinical range | 1 (1.72%) |
| Interpersonal conflicts | |
| Mean | 57.10 |
| SD | 29.23 |
| Range | 5–99 |
| Normal range | 45 (77.6%) |
| Clinical range | 13 (22.4%) |
| Family problems | |
| Mean | 59.71 |
| SD | 25.67 |
| Range | 2–99 |
| Normal range | 43 (74.1%) |
| Clinical range | 15 (25.9%) |
| Uncertainty about the future | |
| Mean | 50.07 |
| SD | 29.66 |
| Range | 10–99 |
| Normal range | 45 (77.6%) |
| Clinical range | 13 (22.4%) |
| Psychosocial risk | |
| Mean | 16.44 |
| SD | 19.49 |
| Min-Max | 1–80 |
| Normal range | 58 (100%) |
| Self-esteem/well-being | |
| Mean | 48.58 |
| SD | 27.88 |
| Range | 1–99 |
| Normal range | 18 (31.6%) |
| Borderline | 12 (21.0%) |
| Clinical range | 27 (47.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turner, K.; La Briola, F.; Vignoli, A.; Zambrelli, E.; Chiesa, V.; Fongoni, L.; Baldi, O.; Canevini, M.P. Living with Epilepsy in Adolescence in Italy: Psychological and Behavioral Impact. Healthcare 2023, 11, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11050687
Turner K, La Briola F, Vignoli A, Zambrelli E, Chiesa V, Fongoni L, Baldi O, Canevini MP. Living with Epilepsy in Adolescence in Italy: Psychological and Behavioral Impact. Healthcare. 2023; 11(5):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11050687
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurner, Katherine, Francesca La Briola, Aglaia Vignoli, Elena Zambrelli, Valentina Chiesa, Laura Fongoni, Olivia Baldi, and Maria Paola Canevini. 2023. "Living with Epilepsy in Adolescence in Italy: Psychological and Behavioral Impact" Healthcare 11, no. 5: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11050687
APA StyleTurner, K., La Briola, F., Vignoli, A., Zambrelli, E., Chiesa, V., Fongoni, L., Baldi, O., & Canevini, M. P. (2023). Living with Epilepsy in Adolescence in Italy: Psychological and Behavioral Impact. Healthcare, 11(5), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11050687






