Extended Stanford Type-A Aortic Dissection with Multivessel Coronary and Peripheral Artery Involvement: An Autopsy Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
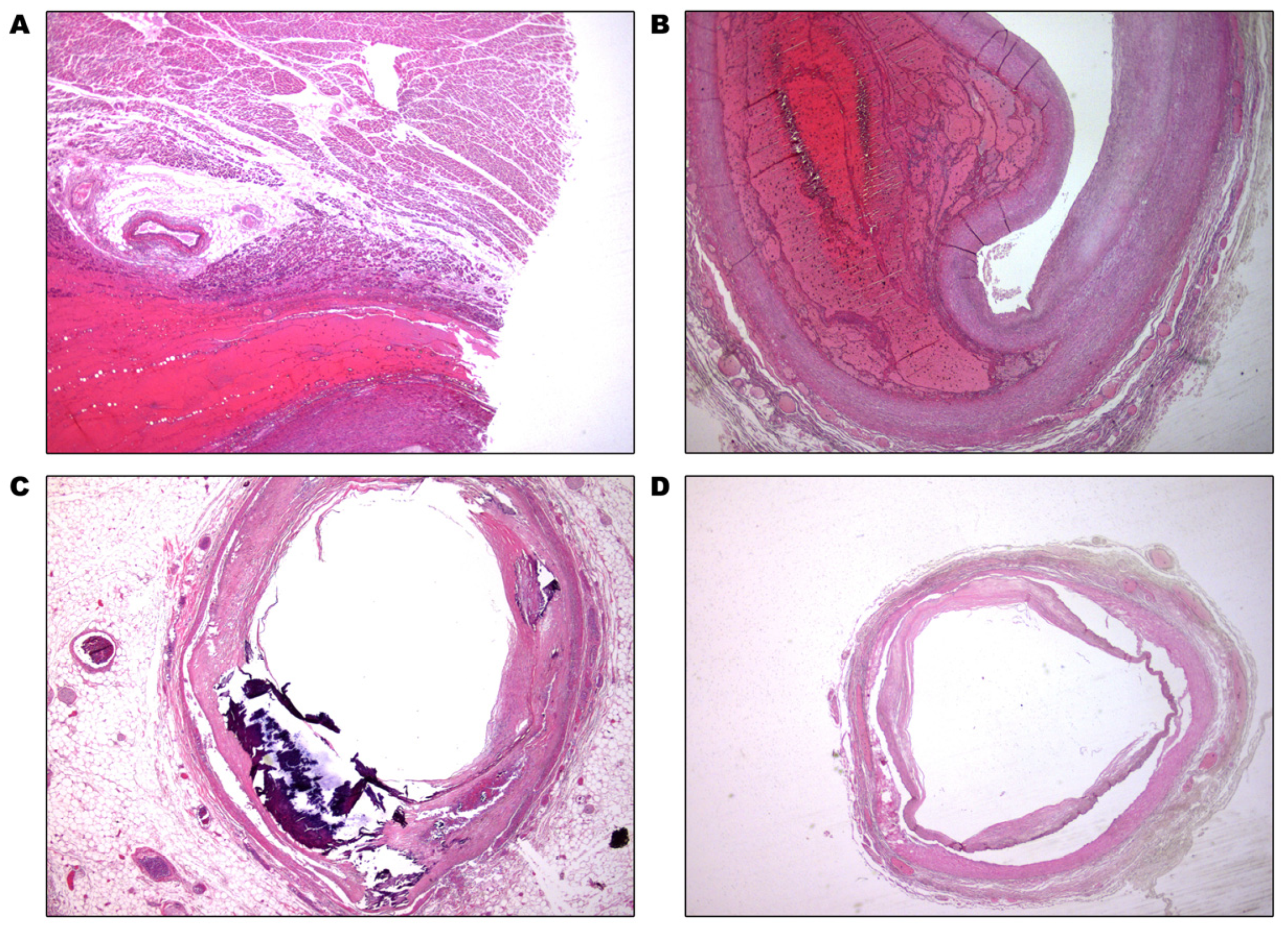
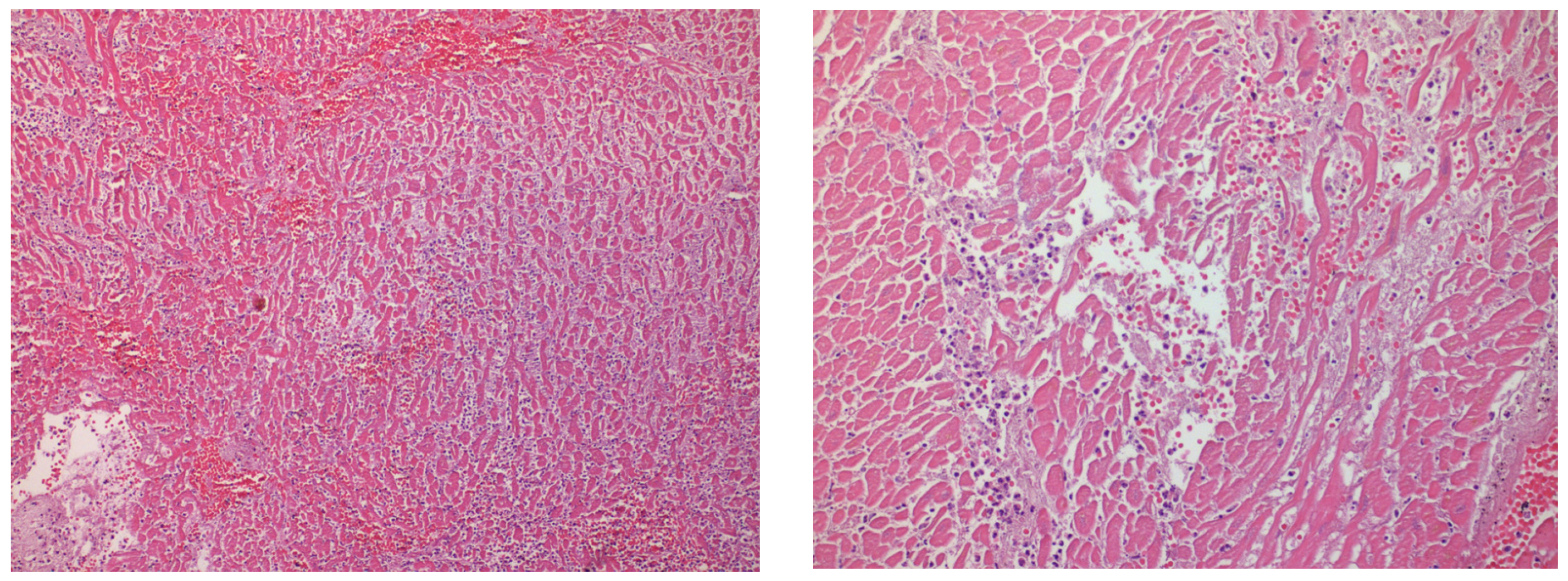
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, I.A.; Nair, C.K. Clinical, diagnostic, and management perspectives of aortic dissection. Chest 2002, 122, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazici, P.; Oz, K.; Celik, O.; Erek, E. Extensive anterior chest wall ecchymosis as a sign of subacute type A aortic dissection. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 15, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.D.; Arora, R.R. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of aortic dissection. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 2, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.E., Jr.; Johns, V.J., Jr.; Kime, S.W., Jr. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: A review of 505 cases. Medicine 1958, 37, 217–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Yin, K.; Zhou, N.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, D.; Bi, Q.; Quan, L.; Hu, B.; et al. The characteristics of thoracic aortic dissection in autopsy-diagnosed individuals: An autopsy study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 973530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nakai, M.; Yano, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Yoshino, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Sumita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Inoue, Y.; Okita, Y.; et al. Population-based incidence and outcomes of acute aortic dissection in Japan. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.; Thordsen, S.; Thomas, T.; Mackey-Bojack, S.M.; Duncanson, E.R.; Nwuado, D.; Garberich, R.F.; Harris, K.M. Clinical and pathologic findings of aortic dissection at autopsy: Review of 336 cases over nearly 6 decades. Am. Heart J. 2019, 209, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Mu, H.S.; Fan, S.L.; He, F.G.; Wang, Z.Y. Aortic Dissection and Sudden Unexpected Deaths: A Retrospective Study of 31 Forensic Autopsy Cases. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 60, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawinecka, J.; Schönrath, F.; von Eckardstein, A. Acute aortic dissection: Pathogenesis, risk factors and diagnosis. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2017, 147, w14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Lee, M.; Lewis, A. Splitting at the seams: Extensive Stanford Type A aortic dissection. SA Heart 2019, 16, 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gunduz, Y.; Ergüven, A.; Asil, K.; Tatli Ayhan, L.; Ozozen, Z. Extensive Type A Aortic Dissection; from Internal Carotid Artery to Iliac Artery: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cardiol. Angiol. Int. J. 2014, 3, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.W.; Jourabchi, N.; Sauk, S.C.; Lanum, D. An extensive stanford type a aortic dissection involving bilateral carotid and iliac arteries. Case Rep. Radiol. 2013, 2013, 607012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Koo, B.K. Coronary artery dissection associated with ascending aortic dissection. Can. J. Cardiol. 2008, 24, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, K.; Sheppard, M.N. Thoracic aortic dissection. Death may not always be due to rupture with haemorrhage. Unusual complications which can be missed at autopsy. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2018, 54, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Yamasaki, F.; Mitsuoka, H.; Miura, Y.; Terai, Y.; Goto, S.; Mizuno, Y.; Miyano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. Myocardial Ischemia in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection; Coronary Artery Dissection and Functional Ischemia. Kyobu Geka 2016, 69, 292–297. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishige, A.; Tanaka, H.; Ueda, T.; Ninomiya, M.; Ohtsuka, T. Type A aortic dissection with transient myocardial ischemia caused by intimal flap inverting into the left ventricle. J. Echocardiogr. 2011, 9, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Broder, J.; Mando-Vandrick, J.; Wendell, J.; Crowe, J. Acute aortic emergencies—Part 2: Aortic dissections. Adv. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2013, 35, 28–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilacosta, I.; Aragoncillo, P.; Cañadas, V.; San Román, J.A.; Ferreirós, J.; Rodríguez, E. Acute aortic syndrome: A new look at an old conundrum. Postgrad. Med. J. 2010, 86, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.D.; Bacha, E.A.; Dodson, T.F.; Martin, T.; Smith, R.B., 3rd; Chaikof, E.L. Peripheral vascular complications of aortic dissection. Am. J. Surg. 1995, 170, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, J.I.; Sarris, G.E.; Mitchell, R.S.; Shumway, N.E.; Stinson, E.B.; Oyer, P.E.; Miller, D.C. Treatment of patients with aortic dissection presenting with peripheral vascular complications. Ann Surg. 1990, 212, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambria, R.P.; Brewster, D.C.; Gertler, J.; Moncure, A.C.; Gusberg, R.; Tilson, M.D.; Darling, R.C.; Hammond, G.; Mergerman, J.; Abbott, W.M. Vascular complications associated with spontaneous aortic dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 1988, 7, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.F.; Po, H.; Chien, C.Y. Ischaemic infarction masking aortic dissection: A pitfall to be avoided before thrombolysis. BMJ Case Rep. 2009, 2009, bcr10.2008.1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiryoguran, N.S.; Karcioglu, O.; Topacoglu, H.; Aksakalli, S. Painless aortic dissection with bilateral carotid involvement presenting with vertigo as the chief complaint. Emerg. Med. J. 2006, 23, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañer, E.; Andreu, M.; Gallardo, X.; Mata, J.M.; Cabezuelo, M.A.; Pallardó, Y. CT in nontraumatic acute thoracic aortic disease: Typical and atypical features and complications. Radiographics 2003, 23, S93–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, J.M.; Kochar, G.S.; Albornoz, M.A. Multivessel spontaneous coronary artery dissection in a patient with severe systolic hypertension: A possible association. A case report. Angiology 1999, 50, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexandri, M.; Tsellou, M.; Goutas, N.; Galani, K.; Papadodima, S. Extended Stanford Type-A Aortic Dissection with Multivessel Coronary and Peripheral Artery Involvement: An Autopsy Case Report. Healthcare 2023, 11, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030386
Alexandri M, Tsellou M, Goutas N, Galani K, Papadodima S. Extended Stanford Type-A Aortic Dissection with Multivessel Coronary and Peripheral Artery Involvement: An Autopsy Case Report. Healthcare. 2023; 11(3):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030386
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexandri, Maria, Maria Tsellou, Nikolaos Goutas, Konstantina Galani, and Stavroula Papadodima. 2023. "Extended Stanford Type-A Aortic Dissection with Multivessel Coronary and Peripheral Artery Involvement: An Autopsy Case Report" Healthcare 11, no. 3: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030386
APA StyleAlexandri, M., Tsellou, M., Goutas, N., Galani, K., & Papadodima, S. (2023). Extended Stanford Type-A Aortic Dissection with Multivessel Coronary and Peripheral Artery Involvement: An Autopsy Case Report. Healthcare, 11(3), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030386




