Serum Vitamin D Level and Gut Microbiota in Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Population, and Sample Size
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Anthropometric Assessment
2.3.2. Biochemical Measurement
Vitamin D
Stool Sample
DNA Extraction
Library Preparation and Sequencing
Identification of the Microbial Composition
The CosmosID Bioinformatics Platform
Relative Abundance Stacked Bars
Alpha Diversity Boxplots (with Wilcoxon Rank-Sum)
Beta Diversity PCoA (with PERMANOVA)
2.3.3. Questionnaires
General Health History Questionnaire
Dietary Intake
Sun Exposure
Physical Activity
Sleeping Index: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
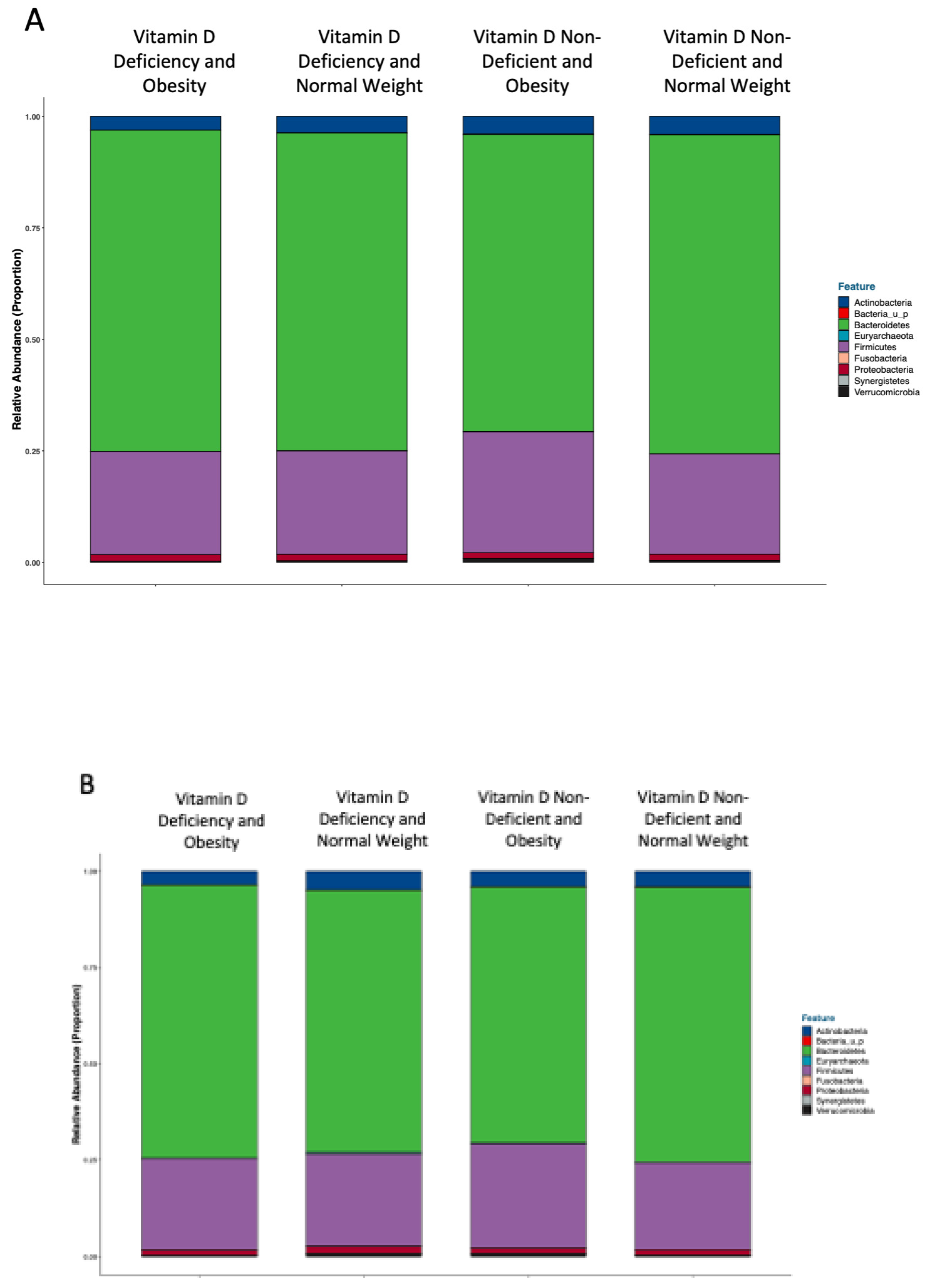
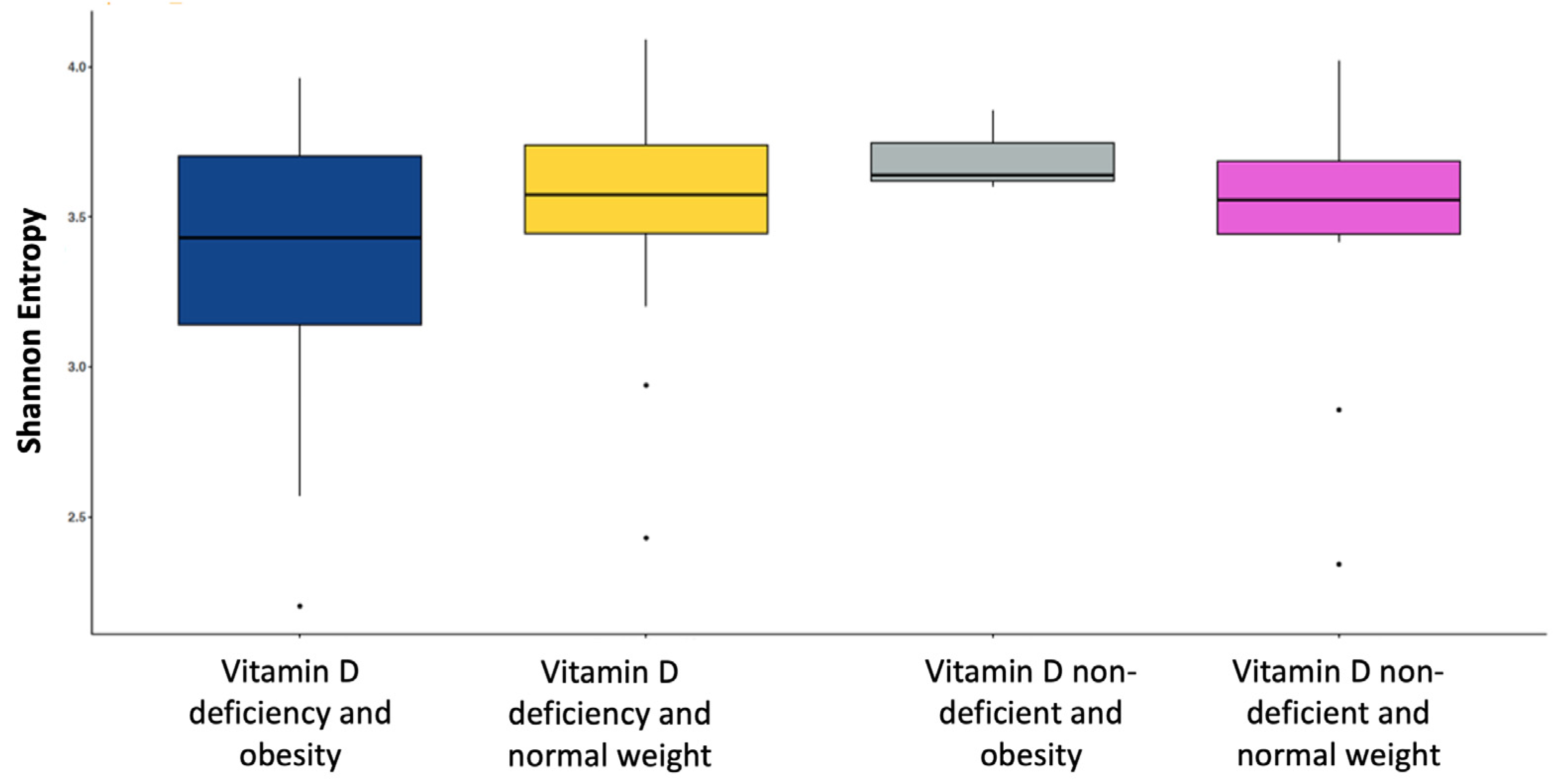
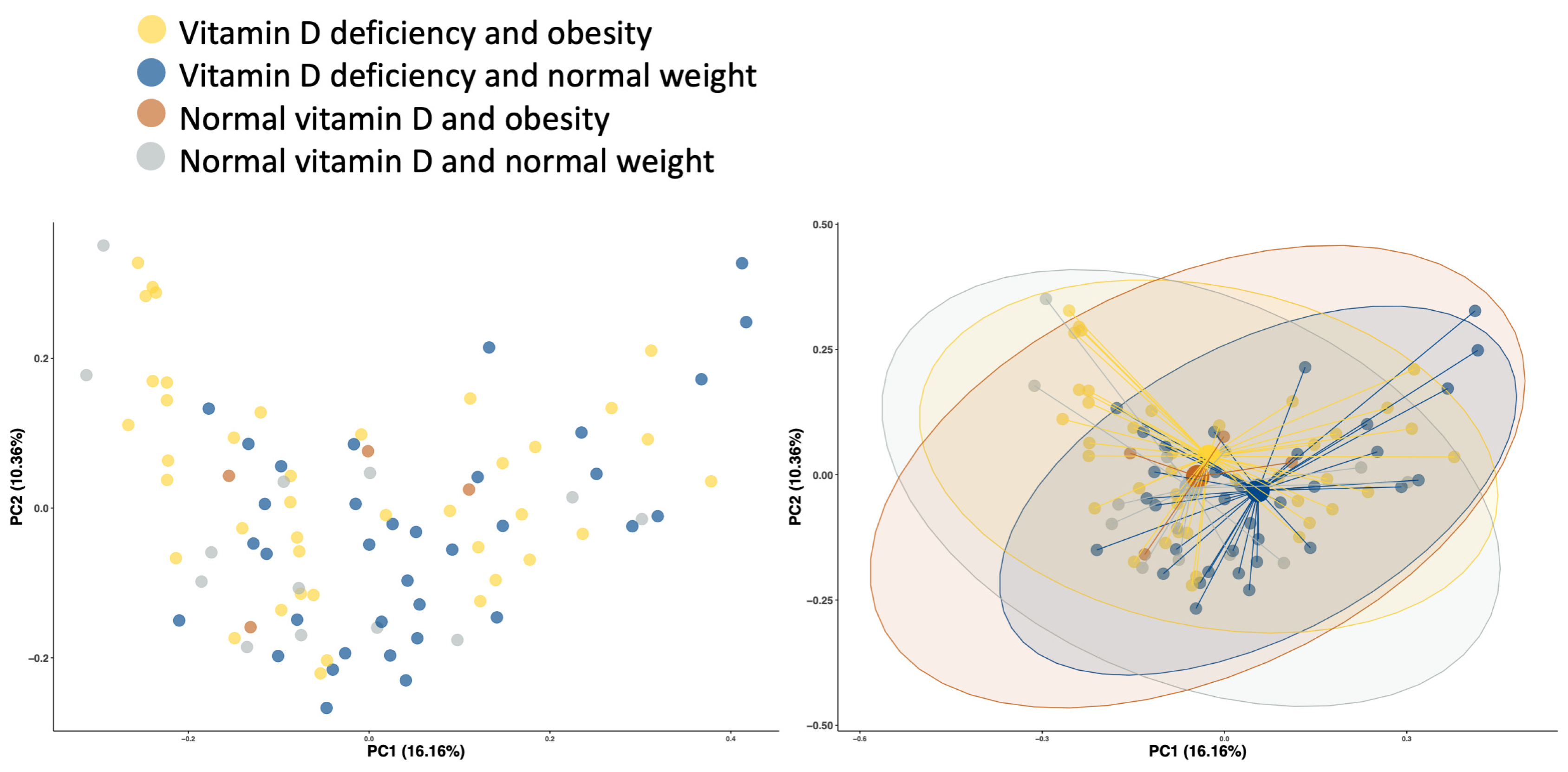
3.2. Analyses Performed According to Vitamin D Status and BMI Categories
Gut Microbiota Composition
3.3. The Correlation between BMI, Gut Microbiota, and Vitamin D Status
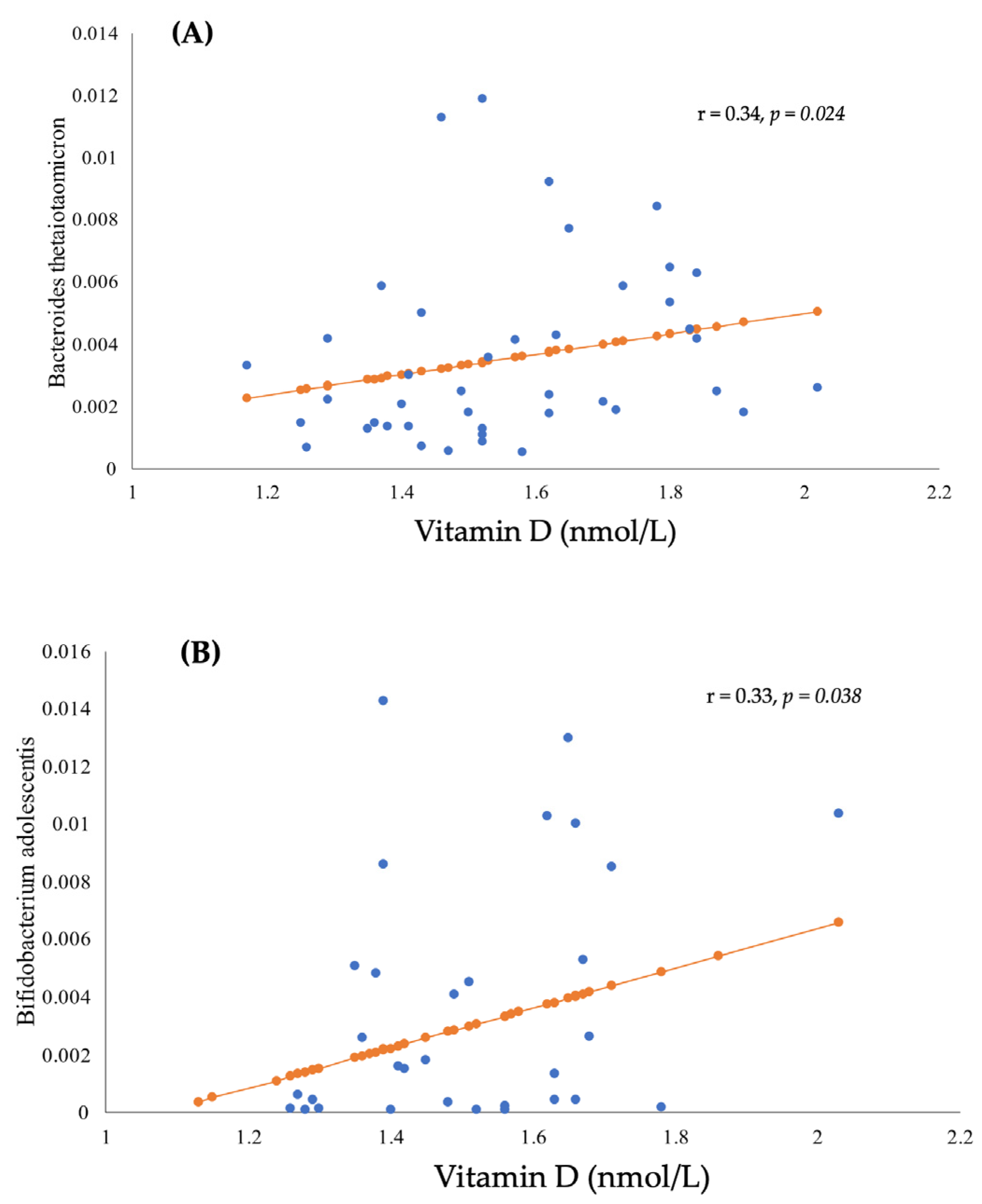
3.4. Gut Microbiota Analyses and Serum Vitamin D
3.4.1. Relative Abundance
3.4.2. Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The Epidemiology of Obesity. Metabolism. 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Survey—Saudi Arabia (KSAWHS). 2019. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/Statistics/Population-Health-Indicators/Documents/World-Health-Survey-Saudi-Arabia.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Yousef, M.; Sabico, S.L.; Chrousos, G.P. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Other Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases in the Central Region, Saudi Arabia (Riyadh Cohort 2): A Decade of an Epidemic. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Wormser, D.; Gao, P.; Kaptoge, S.; de Gonzalez, A.B.; Cairns, B.J.; Huxley, R.; Jackson, C.L.; Joshy, G.; et al. Body-Mass Index and All-Cause Mortality: Individual-Participant-Data Meta-Analysis of 239 Prospective Studies in Four Continents. Lancet 2016, 388, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, L.; Hale, L. Longitudinal Associations between Sleep Duration and Subsequent Weight Gain: A Systematic Review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, B.; Du, Y.; Rong, S.; Xu, G.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Bao, W. Inverse Association between Serum Vitamin B12 Concentration and Obesity among Adults in the United States. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, L.; Duan, Y.; Liang, W.; Nie, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, Y. A Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Vitamin D Deficiency and Obesity. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14977–14984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alou, M.T.; Lagier, J.C.; Raoult, D. Diet Influence on the Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis Related to Nutritional Disorders. Hum. Microbiome J. 2016, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altveş, S.; Yildiz, H.K.; Vural, H.C. Interaction of the Microbiota with the Human Body in Health and Diseases. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2020, 39, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, V.R.; Guarner, F. Linking the Gut Microbiota to Human Health. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, R.L.; Sternberg, M.R.; Looker, A.C.; Yetley, E.A.; Lacher, D.A.; Sempos, C.T.; Taylor, C.L.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Maw, K.L.; Chaudhary-Webb, M.; et al. National Estimates of Serum Total 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Metabolite Concentrations Measured by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in the US Population during 2007–2010. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, K.D.; Dowling, K.G.; Škrabáková, Z.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Valtueña, J.; De Henauw, S.; Moreno, L.; Damsgaard, C.T.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mølgaard, C.; et al. Vitamin D Deficiency in Europe: Pandemic? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Alyani, H.; Al-Turki, H.A.; Al-Essa, O.N.; Alani, F.M.; Sadat-Ali, M. Vitamin D Deficiency in Saudi Arabians: A Reality or Simply Hype: A Meta-Analysis (2008–2015). J. Family Community Med. 2018, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuffaha, M.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Daoud, F.; Al Hussaini, H.A.; Alamri, F.; Al Saeedi, M.; Basulaiman, M.; Memish, Z.A.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Al Rabeeah, A.A.; et al. Deficiencies under Plenty of Sun: Vitamin D Status among Adults in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2013. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 7, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, M.; Hope, B.; Krause, L.; Morrison, M.; Protani, M.M.; Zakrzewski, M.; Neale, R.E. Vitamin D and the Gut Microbiome: A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 2895–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xiang, S.; Ye, K.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) Induced a Shift in Microbial Composition and Metabolic Activity in an in Vitrocolon Simulation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, F.; Boccella, S.; Belardo, C.; Iannotta, M.; Piscitelli, F.; De Filippis, F.; Paino, S.; Ricciardi, F.; Siniscalco, D.; Marabese, I.; et al. Altered Gut Microbiota and Endocannabinoid System Tone in Vitamin D Deficiency-Mediated Chronic Pain. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNicola, E.; Aburizaiza, O.S.; Siddique, A.; Khwaja, H.; Carpenter, D.O. Obesity and Public Health in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Rev. Environ. Health 2015, 30, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljazairy, E.A.; Al-musharaf, S.; Abudawood, M.; Almaarik, B.; Hussain, S.D.; Alnaami, A.M.; Sabico, S.; Al-daghri, N.M.; Clerici, M.; Aljuraiban, G.S. Influence of Adiposity in the Gut Microbiota Composition of Arab Women: A Case-Control Study. Biology 2022, 11, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, M.A.; Turkestani, I.Z.; Almusharraf, S.; Al-Ajlan, A.; Angkaya-Bagayawa, F.F.; Sabico, S.; Mohammed, A.G.; Hassanato, R.; Al-Serehi, A.; Alshingetti, N.M.; et al. Extremely High Prevalence of Maternal and Neonatal Vitamin D Deficiency in the Arab Population. Neonatology 2017, 112, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalaf, M.M.; Edwards, C.A.; Combet, E. Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Specific for Salt Intake in Saudi Arabian Adults Using Urinary Biomarker and Repeated Multiple Pass 24-Hour Dietary Recall. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, E337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musharaf, S.; Fouda, M.A.; Turkestani, I.Z.; Al-Ajlan, A.; Sabico, S.; Alnaami, A.M.; Wani, K.; Hussain, S.D.; Alraqebah, B.; Al-Serehi, A.; et al. Vitamin D Deficiency Prevalence and Predictors in Early Pregnancy among Arab Women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkahtani, S.A. Convergent Validity: Agreement between Accelerometry and the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire in College-Age Saudi Men. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, K.H.; Yates, B.C.; Berger, A.M.; Pozehl, B.; Meza, J. Translating the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index into Arabic. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2010, 32, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Health Organization Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Nishida, C.; Ko, G.T.; Kumanyika, S. Body Fat Distribution and Noncommunicable Diseases in Populations: Overview of the 2008 WHO Expert Consultation on Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, W.Y.; Swearingin, B.; Crooms, B.; Lee, R.; Choi, Y.; Dail, T.K.; Melton, D.; Fuller, T.M.; Ha, C.H. Body Composition Measurements Determined by Air Displacement Plethysmography and Eight-Polar Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Are Equivalent in African American College Students. HealthMED 2012, 6, 1896–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.A.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 Report on Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What Clinicians Need to Know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood-Nichols, S.K.; Tinnemore, D.; Huang, R.R.; Napolitano, P.G.; Ippolito, D.L. Vitamin D Deficiency in Early Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. ‘Ggplot2′ Based Publication Ready Plots R Package Version 0.2.5. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Wickham, H. Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Entropy and Diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Available online: https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Constantin, A.-E.; Significance Brackets for ‘Ggplot2’. R Package Version 0.6.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=ggsignif (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A New Instrument for Psychiatric Practice and Research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.; Prietl, B.; Tauschmann, M.; Mautner, S.I.; Kump, P.K.; Treiber, G.; Wurm, P.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Högenauer, C.; Pieber, T.R. Effects of High Doses of Vitamin D3 on Mucosa-Associated Gut Microbiome Vary between Regions of the Human Gastrointestinal Tract. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Waubant, E.; Chehoud, C.; Kuczynski, J.; Desantis, T.Z.; Warrington, J.; Venkatesan, A.; Fraser, C.M.; Mowry, E.M. Gut Microbiota in Multiple Sclerosis: Possible Influence of Immunomodulators. J. Investig. Med. 2015, 63, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenngam, N.; Shirvani, A.; Kalajian, T.A.; Song, A.; Holick, M.F. The Effect of Various Doses of Oral Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Dose-Response Study. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciubotaru, I.; Green, S.J.; Kukreja, S.; Barengolts, E. Significant Differences in Fecal Microbiota Are Associated with Various Stages of Glucose Tolerance in African American Male Veterans. Transl. Res. 2015, 166, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Hendy, P.; Ding, J.N.; Shaw, S.; Hold, G.; Hart, A. The Effect of Vitamin D on Intestinal Inflammation and Faecal Microbiota in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 12, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhere, M.; He, J.; Chassaing, B.; Ziegler, T.R.; Alvarez, J.A.; Ivie, E.A.; Hao, L.; Hanfelt, J.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Tangpricha, V. Bolus Weekly Vitamin D3 Supplementation Impacts Gut and Airway Microbiota in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderpoor, N.; Mousa, A.; Arango, L.F.G.; Barrett, H.L.; Nitert, M.D.; de Courten, B. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Faecal Microbiota: A Randomised Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffler, H.; Herlemann, D.P.R.; Klinitzke, P.; Berlin, P.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Jaster, R.; Lamprecht, G. Vitamin D Administration Leads to a Shift of the Intestinal Bacterial Composition in Crohn’s Disease Patients, but Not in Healthy Controls. J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 19, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Rawat, A.; Alwakeel, M.; Sharif, E.; Al Khodor, S. The Potential Role of Vitamin D Supplementation as a Gut Microbiota Modifier in Healthy Individuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthold, R.V.; Fernandes, G.R.; Franco-de-Moraes, A.C.; Folchetti, L.G.D.; Ferreira, S.R.G. Gut Microbiota Interactions with the Immunomodulatory Role of Vitamin D in Normal Individuals. Metabolism 2017, 69, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Cagan, A.; Gainer, V.S.; Cheng, S.C.; Cai, T.; Szolovits, P.; Shaw, S.Y.; Churchill, S.; Karlson, E.W.; Murphy, S.N.; et al. Higher Plasma Vitamin D Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Clostridium Difficile Infection in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.L.; Jiang, L.; Adams, J.S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Shen, J.; Janssen, S.; Ackermann, G.; Vanderschueren, D.; Pauwels, S.; Knight, R.; et al. Vitamin D Metabolites and the Gut Microbiome in Older Men. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantorna, M.T.; McDaniel, K.; Bora, S.; Chen, J.; James, J. Vitamin D, Immune Regulation, the Microbiota, and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R.; Carmeliet, G.; Verlinden, L.; Van Etten, E.; Verstuyf, A.; Luderer, H.F.; Lieben, L.; Mathieu, C.; Demay, M. Vitamin D and Human Health: Lessons from Vitamin D Receptor Null Mice. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 726–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, D.; Kállay, E.; Cross, H.S. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Downregulates CYP27B1 and Induces CYP24A1 in Colon Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 263, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pinto, R.; Ferri, C.; Cominelli, F. Vitamin D Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Role, Current Uses and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Annunziata, G.; Laudisio, D.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. A New Light on Vitamin d in Obesity: A Novel Association with Trimethylamine-n-Oxide (Tmao). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comstock, L.E.; Coyne, M.J. Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron: A Dynamic, Niche-Adapted Human Symbiont. BioEssays 2003, 25, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, E.; Anderson, R.C.; Roy, N.C. Understanding How Commensal Obligate Anaerobic Bacteria Regulate Immune Functions in the Large Intestine. Nutrients 2015, 7, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; Hong, C.V.; Gordon, J.I. Angiogenins: A New Class of Microbicidal Proteins Involved in Innate Immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokhale, S.; Bhaduri, A. Provitamin D3 Modulation through Prebiotics Supplementation: Simulation Based Assessment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pludowski, P.; Holick, M.F.; Pilz, S.; Wagner, C.L.; Hollis, B.W.; Grant, W.B.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Lerchbaum, E.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Kienreich, K.; et al. Vitamin D Effects on Musculoskeletal Health, Immunity, Autoimmunity, Cardiovascular Disease, Cancer, Fertility, Pregnancy, Dementia and Mortality-A Review of Recent Evidence. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Peano, C.; Pass, D.A.; Foroni, E.; Severgnini, M.; Claesson, M.J.; Kerr, C.; Hourihane, J.; Murray, D.; Fuligni, F.; et al. Diversity of Bifidobacteria within the Infant Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.L.; Liu, G.; Darby, T.M.; Fernandes, L.M.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.E.; Jones, R.M.; Drissi, H. Bifidobacterium Adolescentis Supplementation Attenuates Fracture-Induced Systemic Sequelae. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, L.; Mackie, J.; Lenardon, M.D.; Jukes, C.; Hegazy, A.N.; Brown, A.J.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Walker, A.W. Bifidobacterium Adolescentis Shows Potential to Strengthen Host Defence against Gastrointestinal Infection via Inhibition of the Opportunistic Pathogen Candida Albicans and Stimulation of Human-Isolated Macrophages Killing Capacity In Vitro. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autier, P.; Boniol, M.; Pizot, C.; Mullie, P. Vitamin D Status and Ill Health: A Systematic Review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, J.P.; Deng, K.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Xuan, Q.; Xie, J.; He, X.M.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.J.; et al. Prophylactic Effects of Bifidobacterium Adolescentis on Anxiety and Depression-like Phenotypes after Chronic Stress: A Role of the Gut Microbiota-Inflammation Axis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Li, X.F.; Wang, R.L. Bifidobacterium Adolescentis Supplementation Ameliorates Visceral Fat Accumulation and Insulin Sensitivity in an Experimental Model of the Metabolic Syndrome. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangestani, H.; Boroujeni, H.K.; Djafarian, K.; Emamat, H.; Shab-Bidar, S. Vitamin D and The Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Literature Review. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2021, 10, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Páez, A.; del Pugar, E.M.G.; López-Almela, I.; Moya-Pérez, Á.; Codoñer-Franch, P.; Sanz, Y. Depletion of Blautia Species in the Microbiota of Obese Children Relates to Intestinal Inflammation and Metabolic Phenotype Worsening. mSystems 2020, 5, e00857-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S.; Tuomas, B.; Felix, E.G.M. Microbiome Diversity; Orchestrating Microbiome Analysis; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut Microbiota: Role in Pathogen Colonization, Immune Responses, and Inflammatory Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and Disease Markers Correlate with Gut Microbiome Composition across Thousands of People. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmas, V.; Pisanu, S.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Loviselli, A.; Manzin, A.; et al. Gut Microbiota Markers Associated with Obesity and Overweight in Italian Adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanislawski, M.A.; Dabelea, D.; Lange, L.A.; Wagner, B.D.; Lozupone, C.A. Gut Microbiota Phenotypes of Obesity. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Mai, M.; Yang, W.; Du, G. Vitamin B and Vitamin D as Modulators of Gut Microbiota in Overweight Individuals. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A Core Gut Microbiome in Obese and Lean Twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, A.; Leclerc, M.; Hugot, J.P. Gut Microbiota Diversity and Human Diseases: Should We Reintroduce Key Predators in Our Ecosystem? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmann, B.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Zhu, Q.; Gohl, D.M.; Beckman, K.B.; Knight, R.; Knights, D. Evaluating the Information Content of Shallow Shotgun Metagenomics. mSystems 2018, 3, e00069-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschasaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Attaye, I.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J.; et al. Depicting the Composition of Gut Microbiota in a Population with Varied Ethnic Origins but Shared Geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellerba, F.; Muzio, V.; Gnagnarella, P.; Facciotti, F.; Chiocca, S.; Bossi, P.; Cortinovis, D.; Chiaradonna, F.; Serrano, D.; Raimondi, S.; et al. The Association between Vitamin D and Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Human Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Non-Obese | Obese | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D > 25 nmol/L | Vitamin D < 25 nmol/L | p-Value | Vitamin D > 25 nmol/L | Vitamin D < 25 nmol/L | p-Value | |
| N | n = 34 | n = 9 | n = 24 | n = 16 | ||
| Age (y) | 20.6 ± 1.1 | 20.3 ± 1.1 | 0.550 | 21.5 ± 1.8 | 21.5 ± 1.7 | 1.000 |
| Anthropometric measurements | ||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 54.1 ± 6.6 | 53.9 ± 5.2 | 0.917 | 89.5 ± 12.3 | 89.2 ± 12.5 | 0.947 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 21.7 ± 1.9 | 22.0 ± 2.0 | 0.661 | 35.8 ± 4.8 | 36.6 ± 5.1 | 0.609 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 68.1 ± 4.0 | 66.2 ± 3.7 | 0.220 | 95.4 ± 10.2 | 96.3 ± 18.1 | 0.840 |
| WHR (ratio) | 96.5 ± 8.3 | 94.4 ± 6.1 | 0.476 | 123.9 ± 9.9 | 123.7 ± 13.2 | 0.949 |
| Body fat (%) | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.0 | 0.787 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.549 |
| Blood parameters | ||||||
| Vitamin D (nmol/L) | 39.6 (31.9–59.7) | 19.7 (18.0–22.8) | <0.001 | 40.0 (32.7–46.4) | 19.8 (18.6–23.8) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.0 ± 1.7 | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 0.057 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | 0.899 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 0.760 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.814 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 0.048 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 3.4 ± 1.0 | 0.877 |
| Total cholesterol/HDL ratio | 4.2 ± 1.8 | 3.0 ± 0.6 | 0.065 | 4.7 ± 1.8 | 4.6 ± 1.5 | 0.845 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) # | 0.6 (0.4–0.8) | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.034 | 1.0 (0.9–1.2) | 0.9 (0.7–1.1) | 0.266 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 4.6 ± 1.0 | 0.702 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.6 | 0.168 |
| Insulin (µIU/mL) # | 5.8 (4.6–9.2) | 10.9 (6.9–15.3) | 0.009 | 14.9 (12.7–18.3) | 16.0 (10.7–20.4) | 0.619 |
| HOMA-IR # | 1.1 (0.9–1.5) | 1.6 (1.2–3.0) | 0.042 | 3.5 (2.5–4.0) | 3.6 (2.2–4.8) | 0.885 |
| HOMA-β # | 106.6 (65.4–142.9) | 131.3 (92.5–246.9) | 0.161 | 215.2 (165.7–319.2) | 274.8 (192.5–395.4) | 0.364 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Khaldy, N.S.; Al-Musharaf, S.; Aljazairy, E.A.; Hussain, S.D.; Alnaami, A.M.; Al-Daghri, N.; Aljuraiban, G. Serum Vitamin D Level and Gut Microbiota in Women. Healthcare 2023, 11, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030351
Al-Khaldy NS, Al-Musharaf S, Aljazairy EA, Hussain SD, Alnaami AM, Al-Daghri N, Aljuraiban G. Serum Vitamin D Level and Gut Microbiota in Women. Healthcare. 2023; 11(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030351
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Khaldy, Noorah S., Sara Al-Musharaf, Esra’a A. Aljazairy, Syed Danish Hussain, Abdullah M. Alnaami, Nasser Al-Daghri, and Ghadeer Aljuraiban. 2023. "Serum Vitamin D Level and Gut Microbiota in Women" Healthcare 11, no. 3: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030351
APA StyleAl-Khaldy, N. S., Al-Musharaf, S., Aljazairy, E. A., Hussain, S. D., Alnaami, A. M., Al-Daghri, N., & Aljuraiban, G. (2023). Serum Vitamin D Level and Gut Microbiota in Women. Healthcare, 11(3), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11030351









