A Korean Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Characteristics of Sarcopenia in Men in Early Old Age
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
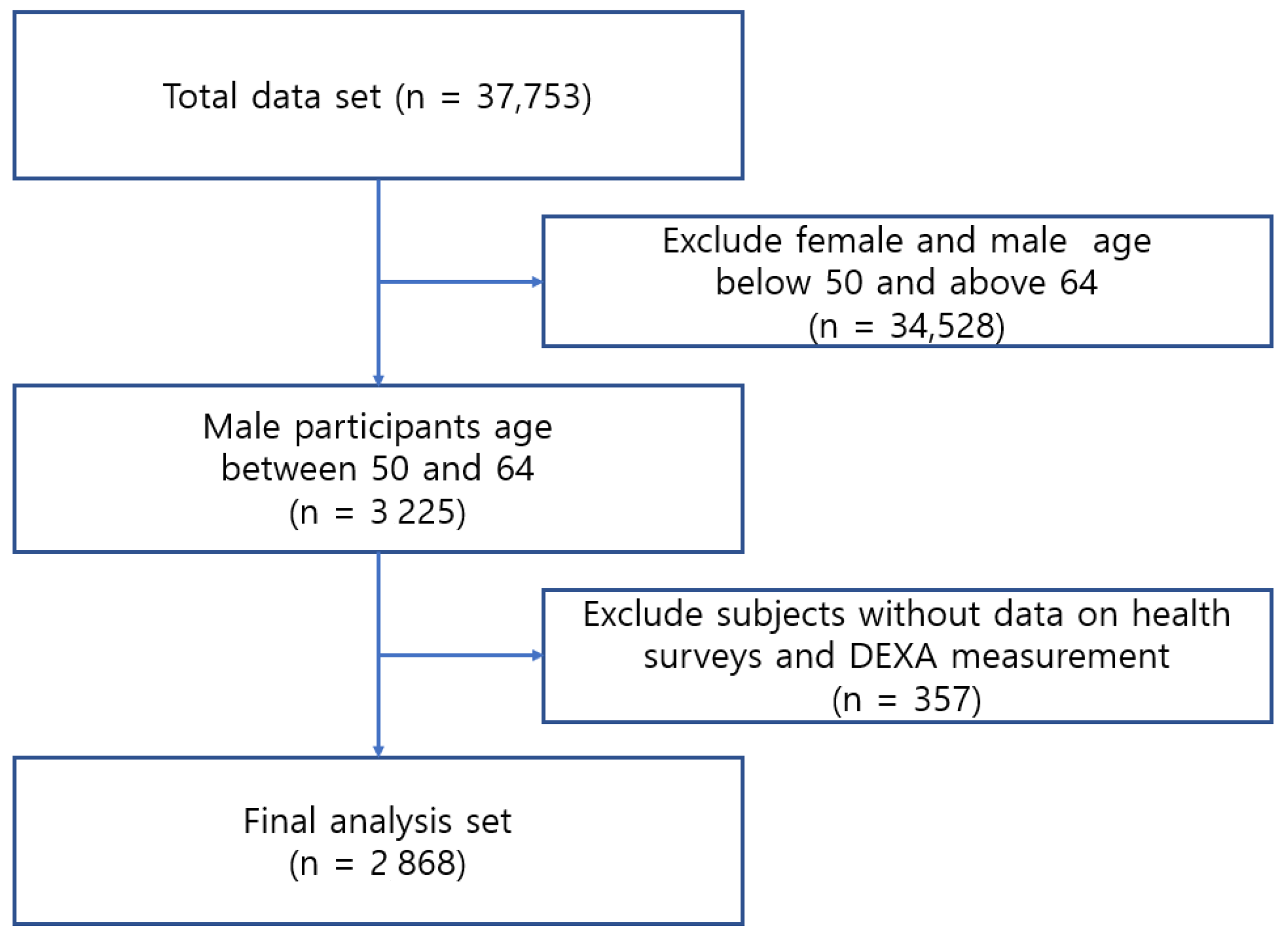
2.1. Study Sampling
2.2. Sarcopenia Criteria
2.3. Variables
2.3.1. Anthropometric Variables
2.3.2. Blood Pressure
2.3.3. Biochemical Variables
2.3.4. Tobacco Use and Alcohol Consumption
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence
3.2. Risk Factors
3.2.1. Anthropometric Variables, SMI, and Age
3.2.2. Blood Pressure
3.2.3. Biochemical Variables
3.2.4. Tobacco Use and Alcohol Consumption
3.3. Multiple Logistic Regression for Sarcopenia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabilpour, M.; Mayhew, J. Effect of peripheral heart action on body composition and blood pressure in women with high blood pressure. Int. J. Sport Stud. Health 2018, 1, e67514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, K.; Taheri, M. The effects of aquatic exercise on body composition and nonspecific low back pain in elderly males. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, L. Sarcopenia in the elderly: Basic and clinical issues. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, V.A.; Frontera, W.R.; Roubenoff, R.; Evans, W.J.; Singh, M.A. Longitudinal changes in body composition in older men and women: Role of body weight change and physical activity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, C.T.; Ryan, S.; Harper, S.; George, G. Aging populations and management. Acad. Manag. J. 2014, 57, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Harhay, M.N. Sarcopenia and mortality among a population-based sample of community-dwelling older adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, Q.; Yue, J.; Hou, L.; Xia, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Ge, N.; Dong, B. Sarcopenia, Obesity and Sarcopenia Obesity in Comparison: Prevalence, Metabolic Profile, and Key Differences: Results from WCHAT Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, S.; Wang, H.; Cao, L.; Liu, P.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Dong, B. Association between sarcopenia with lifestyle and family function among community-dwelling Chinese aged 60 years and older. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Leung, J.; Woo, J. A Prospective Cohort Study to Examine the Association Between Dietary Patterns and Sarcopenia in Chinese Community-Dwelling Older People in Hong Kong. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Lim, G.E.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, K.; Park, T.J.; Kim, J. Association between Sarcopenic Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Postmenopausal Women: A Cross-sectional Study Based on the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Surveys from 2008 to 2011. J. Bone Metab. 2017, 24, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, B. Convergence Factors Affecting Sarcopenia in Middle-Aged and Older Women in Korea: A Cross Sectional Study by Using 5th KNHANES. J. Korea Converg. Soc. 2020, 11, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiguchi, S.; Yamada, M.; Fukutani, N.; Adachi, D.; Tashiro, Y.; Hotta, T.; Morino, S.; Shirooka, H.; Nozaki, Y.; Hirata, H.; et al. Differential association of frailty with cognitive decline and sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Alva, M.C.; Irigoyen Camacho, M.E.; Lazarevich, I.; Delgadillo Velazquez, J.; Acosta Dominguez, P.; Zepeda Zepeda, M.A. Comparison of the prevalence of sarcopenia using skeletal muscle mass index and calf circumference applying the European consensus definition in elderly Mexican women. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.L.D.; Mulder, A.P. Sarcopenia and poor muscle quality associated with severe obesity in young adults and middle-aged adults. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. Gender-Specific Risk Factors and Prevalence for Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling Young-Old Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. Sex Differences of Sarcopenia in an Elderly Asian Population: The Prevalence and Risk Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, R.; Shafiee, G.; Motlagh, A.D.; Pasalar, P.; Esmailzadeh, A.; Siassi, F.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R. Sarcopenia and its associated factors in Iranian older individuals: Results of SARIR study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 66, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huschtscha, Z.; Parr, A.; Porter, J.; Costa, R.J.S. Sarcopenic Characteristics of Active Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Exploration. Sports Med.-Open 2021, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenholm, S.; Harris, T.B.; Rantanen, T.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Ferrucci, L. Sarcopenic obesity-definition, etiology and consequences. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. Gender-Specific Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sarcopenic Obesity in the Korean Elderly Population: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R. Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehayias, J.J.; Fiatarone, M.A.; Zhuang, H.; Roubenoff, R. Total body potassium and body fat: Relevance to aging. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, Z.M.; Ross, R. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18–88 yr. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexell, J.; Downham, D.; Sjostrom, M. Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscles. Fibre type arrangement in m. vastus lateralis from three groups of healthy men between 15 and 83 years. J. Neurol. Sci. 1986, 72, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharahdaghi, N.; Phillips, B.E.; Szewczyk, N.J.; Smith, K.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Atherton, P.J. Links between testosterone, oestrogen, and the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis and resistance exercise muscle adaptations. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 621226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hymer, W.C.; Nindl, B.C.; Fragala, M.S. Growth hormone (s), testosterone, insulin-like growth factors, and cortisol: Roles and integration for cellular development and growth with exercise. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, M.; Lauretani, F.; Ceda, G.P. Sex hormones and sarcopenia in older persons. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, F.; Barberi, L.; Dobrowolny, G.; Villa Nova Bacurau, A.; Nicoletti, C.; Rizzuto, E.; Rosenthal, N.; Scicchitano, B.M.; Musaro, A. Effects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festini, S.B.; Hertzog, C.; McDonough, I.M.; Park, D.C. What makes us busy? Predictors of perceived busyness across the adult lifespan. J. Gen. Psychol. 2019, 146, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wister, A.V.; Li, L.; Mitchell, B.A. A study of social isolation, multimorbidity and multiple role demands among middle-age adults based on the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 2022, 94, 312–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugge, A.B. Lovin’ It? Food Cult. Soc. 2015, 14, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. Nutrition and sarcopenia: A review of the evidence and implications for preventive strategies. In Clinical Nutrition and Aging, 1st ed.; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.; Kim, Y.; Kweon, S.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Park, O.; Jeong, E.K. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: Accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol. Health 2021, 43, e2021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Chun, C.; Khang, Y.H.; Oh, K. Data resource profile: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confortin, S.C.; Meneghini, V.; Ono, L.M.; Schneider, I.J.C.; Barbosa, A.R.; D’Orsi, E. Anthropometric indicators as a screening tool for sarcopenia in older adults from Florianopolis, Santa Catarina: EpiFloripa Ageing study. Rev. Nutr.-Braz. J. Nutr. 2017, 30, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, K.; Miyachi, M.; Tanimoto, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Murakami, H.; Okumura, S.; Gando, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tabata, I.; Higuchi, M. A cross-sectional study of sarcopenia in Japanese men and women: Reference values and association with cardiovascular risk factors. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, M.; Mazzali, G.; Fantin, F.; Rossi, A.; Di Francesco, V. Sarcopenic obesity: A new category of obesity in the elderly. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, K.S. Aging muscle. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Atkinson, H.H.; Penninx, B.W.; Lenchik, L.; Palla, S.L.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Tracy, R.P.; Pahor, M. Sarcopenia, obesity, and inflammation—Results from the Trial of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factors study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Oh, C.; No, J. Associations between Sarcopenia and Metabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidin Ozturk, Z.A.; Turkbeyler, I.H.; Demir, Z.; Bilici, M.; Kepekci, Y. The effect of blood glucose regulation on sarcopenia parameters in obese and diabetic patients. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 64, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sofiani, M.E.; Ganji, S.S.; Kalyani, R.R. Body composition changes in diabetes and aging. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, M.; Edelman, S.V.; Brechtel, G.; Baron, A.D. Decreased effect of insulin to stimulate skeletal muscle blood flow in obese man. A novel mechanism for insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulett, N.A.; Scalzo, R.L.; Reusch, J.E.B. Glucose Uptake by Skeletal Muscle within the Contexts of Type 2 Diabetes and Exercise: An Integrated Approach. Nutrients 2022, 14, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscemi, C.; Ferro, Y.; Pujia, R.; Mazza, E.; Boragina, G.; Sciacqua, A.; Piro, S.; Pujia, A.; Sesti, G.; Buscemi, S.; et al. Sarcopenia and Appendicular Muscle Mass as Predictors of Impaired Fasting Glucose/Type 2 Diabetes in Elderly Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.; Chen, P.J.; Xiao, W.H. Mechanism of increased risk of insulin resistance in aging skeletal muscle. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, N.; Nikolov, J.; Spira, D.; Demuth, I.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Eckardt, R.; Norman, K. Identifying Sarcopenia in Metabolic Syndrome: Data from the Berlin Aging Study II. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S.; Wu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Li, H.; Hong, W.; et al. Sex differences in the prevalence and adverse outcomes of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in community dwelling elderly in East China using the AWGS criteria. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.W.; Yang, K.C.; Chang, H.H.; Lee, L.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, K.C. Sarcopenic obesity is closely associated with metabolic syndrome. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 7, e301–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleasby, M.E.; Jamieson, P.M.; Atherton, P.J. Insulin resistance and sarcopenia: Mechanistic links between common co-morbidities. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 229, R67–R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrager, M.A.; Metter, E.J.; Simonsick, E.; Ble, A.; Bandinelli, S.; Lauretani, F.; Ferrucci, L. Sarcopenic obesity and inflammation in the InCHIANTI study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androga, L.; Sharma, D.; Amodu, A.; Abramowitz, M.K. Sarcopenia, obesity, and mortality in US adults with and without chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, J.L.; Whincup, P.H.; Morris, R.W.; Lennon, L.T.; Papacosta, O.; Wannamethee, S.G. Sarcopenic obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: A population-based cohort study of older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.M.; Magkos, F.; Atherton, P.; Selby, A.; Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J.; Pedersen, B.K.; Mittendorfer, B. Smoking impairs muscle protein synthesis and increases the expression of myostatin and MAFbx in muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E843–E848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oca, M.M.; Loeb, E.; Torres, S.H.; De Sanctis, J.; Hernández, N.; Tálamo, C. Peripheral muscle alterations in non-COPD smokers. Chest 2008, 133, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.; El Salam, M.A.; Zaki, S.; Motawi, A. Effect of cigarette smoking on serum testosterone level among male smokers: A cross-sectional study. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2021, 70, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmleeh, M.M.; Abdrabo, A. Influence of chronic cigarettes smoking on serum testosterone and prolactin levels among Sudanese smokers. Int. J. Ther. Appl. 2013, 10, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Duca, Y.; Aversa, A.; Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E.; La Vignera, S. Substance Abuse and Male Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Dhindsa, S.; Ghanim, H.; Saad, F. Mechanisms underlying the metabolic actions of testosterone in humans: A narrative review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, F.X.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, Y. The Association Between Sarcopenic Obesity and Hypertension, Diabetes, and Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Chinese Adults. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M. The cardiometabolic syndrome and sarcopenic obesity in older persons. J. Cardiometab. Syndr. 2007, 2, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.; Snijder, M.B.; Twisk, J.W.; van Mechelen, W.; Kemper, H.C.; Seidell, J.C.; Stehouwer, C.D. Central fat mass versus peripheral fat and lean mass: Opposite (adverse versus favorable) associations with arterial stiffness? The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2632–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, M.B.; Henry, R.M.; Visser, M.; Dekker, J.M.; Seidell, J.C.; Ferreira, I.; Bouter, L.M.; Yudkin, J.S.; Westerhof, N.; Stehouwer, C.D. Regional body composition as a determinant of arterial stiffness in the elderly: The Hoorn Study. J. Hypertens. 2004, 22, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Reang, T.; Sarkar, S.; Sengupta, S.; Bhattacharjee, B. Role of body visceral fat in hypertension and dyslipidemia among the diabetic and nondiabetic ethnic population of Tripura-A comparative study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 2885–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sarcopenia | Normal | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 328) | (n = 2540) | (n = 2868) | |
| Un-weighted (%) | 11.44 | 88.56 | 100 |
| Weighted (%) | 10.25 (8.98–11.69) | 89.75 (88.31–91.02) | 100 |
| Sarcopenia | Normal | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 328) | (n = 2540) | ||
| Age (years) | 56.6 ± 5.4 | 53.9 ± 5.7 | <0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 161.4 ± 5.1 | 169.2 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 67.4 ± 9.6 | 68.8 ± 9.5 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.7 ± 3.0 | 23.9 ± 2.8 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 89.0 ± 8.3 | 85.1 ± 8.2 | <0.001 |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 742.4 ± 41.1 | 926.3 ± 84.8 | <0.001 |
| Sarcopenia | Normal | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 328) | (n = 2540) | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | 126.9 ± 15.7 | 123.9 ± 16.4 | 0.002 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81.6 ± 10.5 | 81.8 ± 10.6 | 0.734 |
| FG (mg/dL) | 111.3 ± 37.0 | 103.9 ± 26.7 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 201.2 ± 151.1 | 172.0 ± 156.9 | 0.002 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 191.5 ± 40.8 | 191.5 ± 36.4 | 0.974 |
| Sarcopenia | Normal | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 328) | (n = 2540) | ||
| Tobacco use (%) (current/ex-/non-user) | 64.4/19.3/16.2 | 56.9/30.2/12.8 | 0.001 |
| Alcohol consumption (%) (current/ex-/non-user) | 80.5/12.3/7.0 | 84.7/10.5/4.7 | 0.175 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio (95% of CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Height | 47.0 (2.8–764.6) | 0.007 |
| Weight | 0.0 (0.0–0.2) | 0.007 |
| WC | 1.4 (1.2–1.7) | <0.001 |
| SMI | 38.0 (18.0–80.3) | <0.001 |
| SBP | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 0.043 |
| FG | 1.5 (1.4–1.5) | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.; Park, S. A Korean Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Characteristics of Sarcopenia in Men in Early Old Age. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212860
Hwang J, Park S. A Korean Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Characteristics of Sarcopenia in Men in Early Old Age. Healthcare. 2023; 11(21):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212860
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jongseok, and Soonjee Park. 2023. "A Korean Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Characteristics of Sarcopenia in Men in Early Old Age" Healthcare 11, no. 21: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212860
APA StyleHwang, J., & Park, S. (2023). A Korean Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Characteristics of Sarcopenia in Men in Early Old Age. Healthcare, 11(21), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11212860






