The Impact of Social Distancing Due to COVID-19 on Activities of Daily Living in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Variables and Data Measurements
2.5. Data Analysis
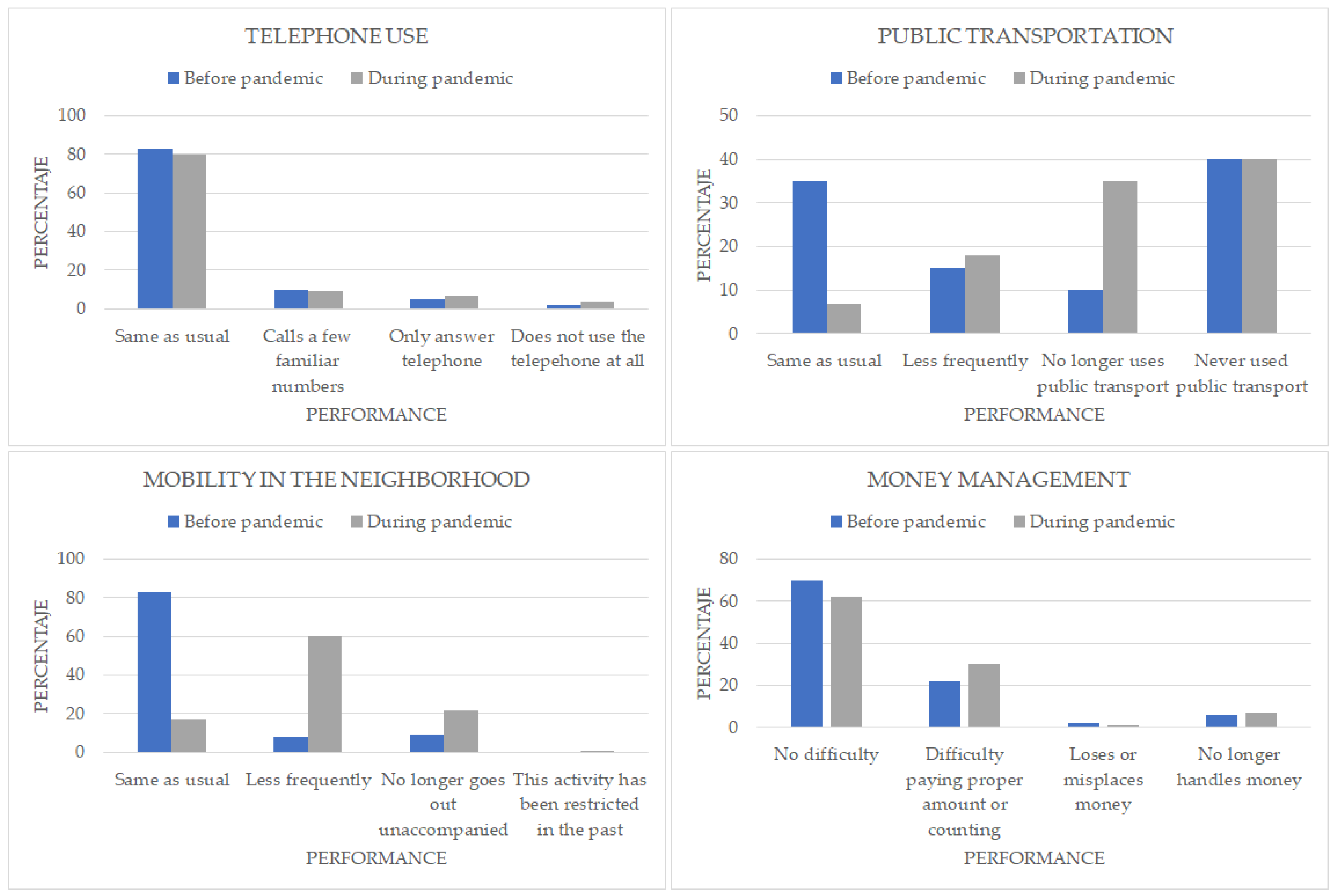
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Cheon, S.M.; Seo, J.W.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, J.W. Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire from Patients’ Perspectives in Parkinson’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperens, M.; Georgiev, D.; Eriksson Domellöf, M.; Forsgren, L.; Hamberg, K.; Hariz, G.M. Activities of Daily Living in Parkinson’s Disease: Time/Gender Perspective. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 141, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Schirinzi, T.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Salimei, C.; Cerroni, R.; Liguori, C.; Scalise, S.; Alwardat, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Pierantozzi, M.; Stefani, A.; et al. Physical Activity Changes and Correlate Effects in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease during COVID-19 Lockdown. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-García, D.; Oreiro, M.; Pérez, P.; Fanjul, G.; Paz González, J.M.; Feal Painceiras, M.J.; Cores Bartolomé, C.; Valdés Aymerich, L.; García Sancho, C.; Castellanos Rodrigo, M. del M. Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic on Parkinson’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Survey of 568 Spanish Patients. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanff, A.M.; Pauly, C.; Pauly, L.; Schröder, V.E.; Hansen, M.; Meyers, G.R.; Kaysen, A.; Hansen, L.; Wauters, F.; Krüger, R. Unmet Needs of People with Parkinson’s Disease and Their Caregivers During COVID-19-Related Confinement: An Explorative Secondary Data Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 615172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heide, A.; Meinders, M.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Helmich, R.C. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Psychological Distress, Physical Activity, and Symptom Severity in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Han, B.; Lu, Y.; Lv, C.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Quality of Life of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2020, 2020, 1216568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.K.; Webster, R.K.; Smith, L.E.; Woodland, L.; Wessely, S.; Greenberg, N.; Rubin, G.J. The Psychological Impact of Quarantine and How to Reduce It: Rapid Review of the Evidence. Lancet 2020, 395, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, I.; Mun, J.K.; Cho, J.W.; Youn, J. The Changes of Exercise Pattern and Clinical Symptoms in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease in the Era of COVID-19 Pandemic. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 80, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.; Tommasini, L.; Baldacci, F.; Del Prete, E.; Siciliano, G.; Ceravolo, R. Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic on Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1717–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmich, R.C.; Bloem, B.R. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Parkinson’s Disease: Hidden Sorrows and Emerging Opportunities. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, I.; Farahnik, J.; Mischley, L.K. Synergy of Pandemics-Social Isolation Is Associated with Worsened Parkinson Severity and Quality of Life. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.G.; Chahine, L.M.; Goldman, S.M.; Korell, M.; Mann, E.; Kinel, D.R.; Arnedo, V.; Marek, K.L.; Tanner, C.M. The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on People with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, W.M. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.; Barion, A.; Rademaker, A.; Rehkemper, G.; Weintraub, S. The Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire A Validation Study in Patients with Dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2004, 18, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbellingen, T.; Nyffeler, T.; Nef, T.; Kwakkel, G.; Bohlhalter, S.; van Wegen, E.E.H. Reliability and Validity of a New Dexterity Questionnaire (DextQ-24) in Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleichgerrcht, E.; Camino, J.; Roca, M.; Torralva, T.; Manes, F. Assessment of Functional Impairment in Dementia with the Spanish Version of the Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2009, 28, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicklund, A.H.; Johnson, N.; Rademaker, A.; Weitner, B.B.; Weintraub, S. Profiles of Decline in Activities of Daily Living in Non-Alzheimer Dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2007, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.; Leger, G.C.; Banks, S.J.; Miller, J.B. Relationship between the Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancey, C.P.; Reidy, J. Statistics without Maths for Psychology, 4th ed.; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Harlow, UK, 2007; ISBN 0132051605, 9780132051606. [Google Scholar]
- Frutos, M.L.; Cruzado, D.P.; Lunsford, D.; Orza, S.G.; Cantero-Téllez, R. Impact of Social Isolation Due to COVID-19 on Daily Life Activities and Independence of People over 65: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogev-Seligmann, G.; Kafri, M. COVID-19 Social Distancing: Negative Effects on People with Parkinson Disease and Their Associations with Confidence for Self-Management. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis-Martínez, R.; Di Marco, R.; Weis, L.; Cianci, V.; Pistonesi, F.; Baba, A.; Carecchio, M.; Biundo, R.; Tedesco, C.; Masiero, S.; et al. Impact of Social and Mobility Restrictions in Parkinson’s Disease during COVID-19 Lockdown. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pišot, S.; Milovanović, I.; Šimunič, B.; Gentile, A.; Bosnar, K.; Prot, F.; Bianco, A.; Lo Coco, G.; Bartoluci, S.; Katović, D.; et al. Maintaining Everyday Life Praxis in the Time of COVID-19 Pandemic Measures (ELP-COVID-19 Survey). Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 30, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeney, M.P.; Xu, Y.; Surface, M.; Shah, H.; Vanegas-Arroyave, N.; Chan, A.K.; Delaney, E.; Przedborski, S.; Beck, J.C.; Alcalay, R.N. The Impact of COVID-19 and Social Distancing on People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Survey Study. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Holla, V.V.; Neeraja, K.; Surisetti, B.K.; Kamble, N.; Yadav, R.; Pal, P.K. Parkinson’s Disease and COVID-19: Perceptions and Implications in Patients and Caregivers. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, C.; Bove, F.; Tufo, T.; Imbimbo, I.; Genovese, D.; Stefani, A.; Marano, M.; Peppe, A.; Brusa, L.; Cerroni, R.; et al. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Movement Disorders Patients With Deep Brain Stimulation: A Multicenter Survey. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaza, S.; Wright-De Agüero, L.K.; Briss, P.A.; Truman, B.I.; Hopkins, D.P.; Hennessy, M.H.; Sosin, D.M.; Anderson, L.; Carande-Kulis, V.G.; Teutsch, S.M.; et al. Data Collection Instrument and Procedure for Systematic Reviews in the Guide to Community Preventive Services. Task Force on Community Preventive Services. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2000, 18, 44–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Size N = 126 | |
|---|---|
| Age M (SD) | 68.03 (10.05) |
| Range of age (years) | 36–89 |
| Sex [N (%)] | |
| Male/Female | 73 (58%)/53 (42%) |
| Disease duration (years) M (SD) | 8.89 (7.77) |
| Place of residence [N (%)] | |
| Madrid | 27 (21%) |
| Andalucía | 23 (18%) |
| Valencia | 23 (18%) |
| Extremadura | 20 (16%) |
| Galicia | 17 (13%) |
| Castilla y León | 9 (7%) |
| Canary Islands | 8 (6%) |
| Caregiver [N (%)] | |
| None | 79 (63%) |
| Relatives | 28 (23%) |
| External caregiver | 15 (12%) |
| Other | 4 (3%) |
| Family living environment [N (%)] | |
| Lives with husband or wife | 65 (52%) |
| Lives with partner and children / no children | 30 (24%)/7 (6%) |
| Alone | 15 (12%) |
| Other | 9 (7%) |
| Rehabilitation treatment prior to pandemic [N (%)] | |
| Daycare center | 4 (3.2%) |
| Patients’ association | 103 (81.7%) |
| Home therapy | 3 (2.4%) |
| Others | 7 (5.6%) |
| No | 9 (7.1%) |
| Interruption of rehabilitation treatment during pandemic [N (%)] | |
| Yes/No | 125 (99.2%)/1 (0.2%) |
| DextQ-24 | Buttoning | Eating | Drinking | Brushing Teeth | Shaving/Making Up | Combing | Dialing a Phone Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADLQ (IADL’s) | ||||||||
| Bathing | 0.532 ** | 0.454 ** | 0.541 ** | 0.332 ** | 0.393 ** | 0.579 ** | 0.460 ** | |
| Elimination | 0.385 ** | 0.263 ** | 0.392 ** | 0.326 ** | 0.254 ** | 0.455 ** | 0.354 ** | |
| Dressing | 0.626 ** | 0.456 ** | 0.410 ** | 0.225 ** | 0.287 * | 0.368 * | 0.398 ** | |
| Eating | 0.524 ** | 0.686 ** | 0.549 ** | 0.394 ** | 0.269 ** | 0.472 ** | 0.305 ** | |
| DextQ-24 | Buttoning | Eating | Drinking | Brushing Teeth | Shaving/ Making Up | Combing | Dialing a Phone Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADLQ (IADL’s) | ||||||||
| Using telephone | 0.376 ** | 0.180 * | 0.423 ** | 0.257 ** | 0.109 | 0.301 ** | 0.468 ** | |
| Public transportation | 0.045 | 0.037 | 0.021 | 0.130 | 0.055 | 0.088 | 0.059 | |
| Mobility in neighborhood | 0.443 ** | 0.290 ** | 0.394 ** | 0.225 * | 0.312 ** | 0.341 ** | 0.408 ** | |
| Handling cash | 0.422 ** | 0.342 ** | 0.467 ** | 0.304 ** | 0.259 ** | 0.508 ** | 0.363 ** | |
| Taking pills | 0.285 ** | 0.152 | 0.217 * | 0.237 ** | 0.144 | 0.171 | 0.279 ** | |
| Housekeeping | 0.151 | 0.179 | 0.196 | 0.092 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.057 | |
| Meal preparation | 0.358 ** | 0.420 ** | 0.282 * | 0.027 | 0.093 | 0.145 | 0.361 ** | |
| Food shopping | 0.1224 | 0.372 * | 0.258 * | 0.201 | 0.211 | 0.278 * | 0.163 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Herrera-Baeza, P.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.P.; Fernández-Gómez, G.; Bustamante-Palomo, N.; Serrada-Tejeda, S.; Obeso-Benítez, P.; Morales-Cabezas, M.; Martínez-Piédrola, R.M.; Pérez-de-Heredia-Torres, M. The Impact of Social Distancing Due to COVID-19 on Activities of Daily Living in Parkinson’s Disease. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121688
Sánchez-Herrera-Baeza P, Rodríguez-Pérez MP, Fernández-Gómez G, Bustamante-Palomo N, Serrada-Tejeda S, Obeso-Benítez P, Morales-Cabezas M, Martínez-Piédrola RM, Pérez-de-Heredia-Torres M. The Impact of Social Distancing Due to COVID-19 on Activities of Daily Living in Parkinson’s Disease. Healthcare. 2023; 11(12):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121688
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Herrera-Baeza, Patricia, M.ª Pilar Rodríguez-Pérez, Gemma Fernández-Gómez, Nerea Bustamante-Palomo, Sergio Serrada-Tejeda, Paula Obeso-Benítez, Matilde Morales-Cabezas, Rosa M. Martínez-Piédrola, and Marta Pérez-de-Heredia-Torres. 2023. "The Impact of Social Distancing Due to COVID-19 on Activities of Daily Living in Parkinson’s Disease" Healthcare 11, no. 12: 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121688
APA StyleSánchez-Herrera-Baeza, P., Rodríguez-Pérez, M. P., Fernández-Gómez, G., Bustamante-Palomo, N., Serrada-Tejeda, S., Obeso-Benítez, P., Morales-Cabezas, M., Martínez-Piédrola, R. M., & Pérez-de-Heredia-Torres, M. (2023). The Impact of Social Distancing Due to COVID-19 on Activities of Daily Living in Parkinson’s Disease. Healthcare, 11(12), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121688







