Feasibility of Muscle Endurance Testing in Critically Ill Trauma Patients: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ultrasound
2.3. Muscle Strength
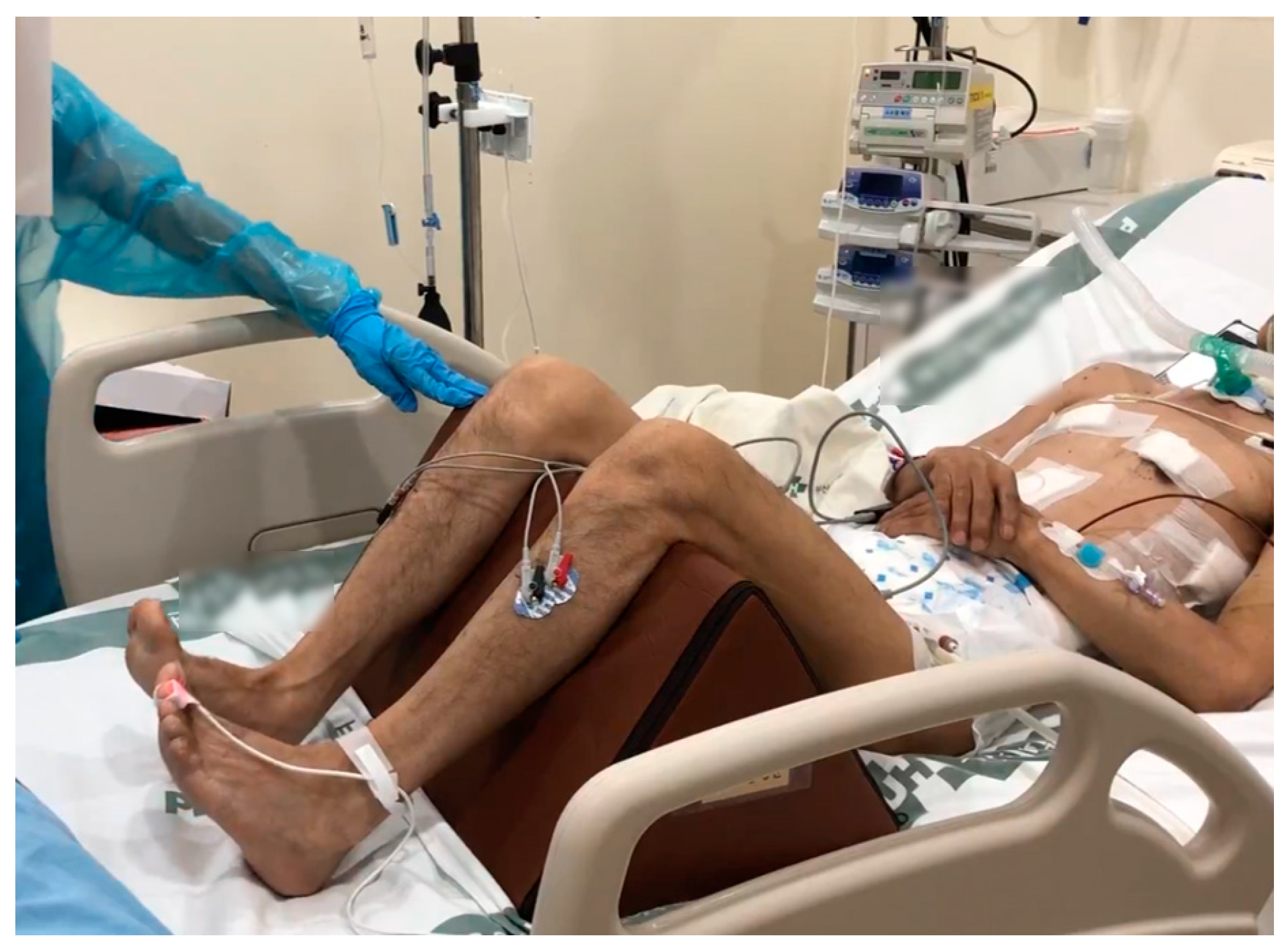
2.4. Modified FI2 Endurance Testing
2.5. Surface EMG
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Jonghe, B.; Sharshar, T.; Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Authier, F.-J.; Durand-Zaleski, I.; Boussarsar, M.; Cerf, C.; Renaud, E.; Mesrati, F.; Carlet, J. Paresis acquired in the intensive care unit: A prospective multicenter study. JAMA 2002, 288, 2859–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieske, L.; Dettling-Ihnenfeldt, D.S.; Verhamme, C.; Nollet, F.; Ivo, N.; Schultz, M.J.; Horn, J.; van der Schaaf, M.; Wieske, L.; Dettling-Ihnenfeldt, D. Impact of ICU-acquired weakness on post-ICU physical functioning. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, G.; Van den Berghe, G. Clinical review: Intensive care unit acquired weakness. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, D.R.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Pagkatipunan, R.; Mears, A.; De Lorenzo, R.; Tiniakou, E.; Albayda, J.; Paik, J.J.; Lloyd, T.E.; Christopher-STINE, L. Muscle endurance deficits in myositis patients despite normal manual muscle testing scores. Muscle Nerve 2019, 59, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, S.J.; Anstey, M.; Blobner, M.; Edrich, T.; Grabitz, S.D.; Gradwohl-Matis, I.; Heim, M.; Houle, T.; Kurth, T.; Latronico, N. Early, goal-directed mobilisation in the surgical intensive care unit: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallbridge, P.; Parry, S.M.; Das, S.; Law, C.; Hammerschlag, G.; Irving, L.; Hew, M.; Steinfort, D. Parasternal intercostal muscle ultrasound in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease correlates with spirometric severity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanpee, G.; Hermans, G.; Segers, J.; Gosselink, R. Assessment of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients: A systematic review. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexanderson, H.; Broman, L.; TollbÄck, A.; Josefson, A.; Lundberg, I.E.; StenstrÖm, C.H. Functional index-2: Validity and reliability of a disease-specific measure of impairment in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Care Res. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2006, 55, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermens, H.J.; Freriks, B.; Merletti, R.; Stegeman, D.; Blok, J.; Rau, G.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Hägg, G. European recommendations for surface electromyography. Roessingh Res. Dev. 1999, 8, 13–54. [Google Scholar]
- Schefold, J.C.; Wollersheim, T.; Grunow, J.J.; Luedi, M.M.; Z’Graggen, W.J.; Weber-Carstens, S. Muscular weakness and muscle wasting in the critically ill. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serres, I.; Gautier, V.; Varray, A.; Prefaut, C. Impaired skeletal muscle endurance related to physical inactivity and altered lung function in COPD patients. Chest 1998, 113, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Socorro, C.R.; Saavedra, P.; López-Fernández, J.C.; Ruiz-Santana, S. Assessment of muscle wasting in long-stay ICU patients using a new ultrasound protocol. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrush, A.; Rozek, M.; Dekerlegand, J.L. The clinical utility of the functional status score for the intensive care unit (FSS-ICU) at a long-term acute care hospital: A prospective cohort study. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Kouzaki, M.; Ogawa, M.; Akima, H.; Moritani, T. Relationships between muscle strength and multi-channel surface EMG parameters in eighty-eight elderly. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2018, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latronico, N.; Bolton, C.F. Critical illness polyneuropathy and myopathy: A major cause of muscle weakness and paralysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, W.; Kollmar, R.; Schwab, S. Critical illness polyneuropathy and myopathy in the intensive care unit. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, A.; Ney, J.; Gellhorn, A.; Hough, C.L. Quantitative neuromuscular ultrasound in intensive care unit–acquired weakness: A systematic review. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, M.S.; Kwayisi, G.; Griffin, L.P.; Sarwal, A.; Walker, F.O.; Harris, J.M.; Berry, M.J.; Chahal, P.S.; Morris, P.E. Quantitative neuromuscular ultrasound in the intensive care unit. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

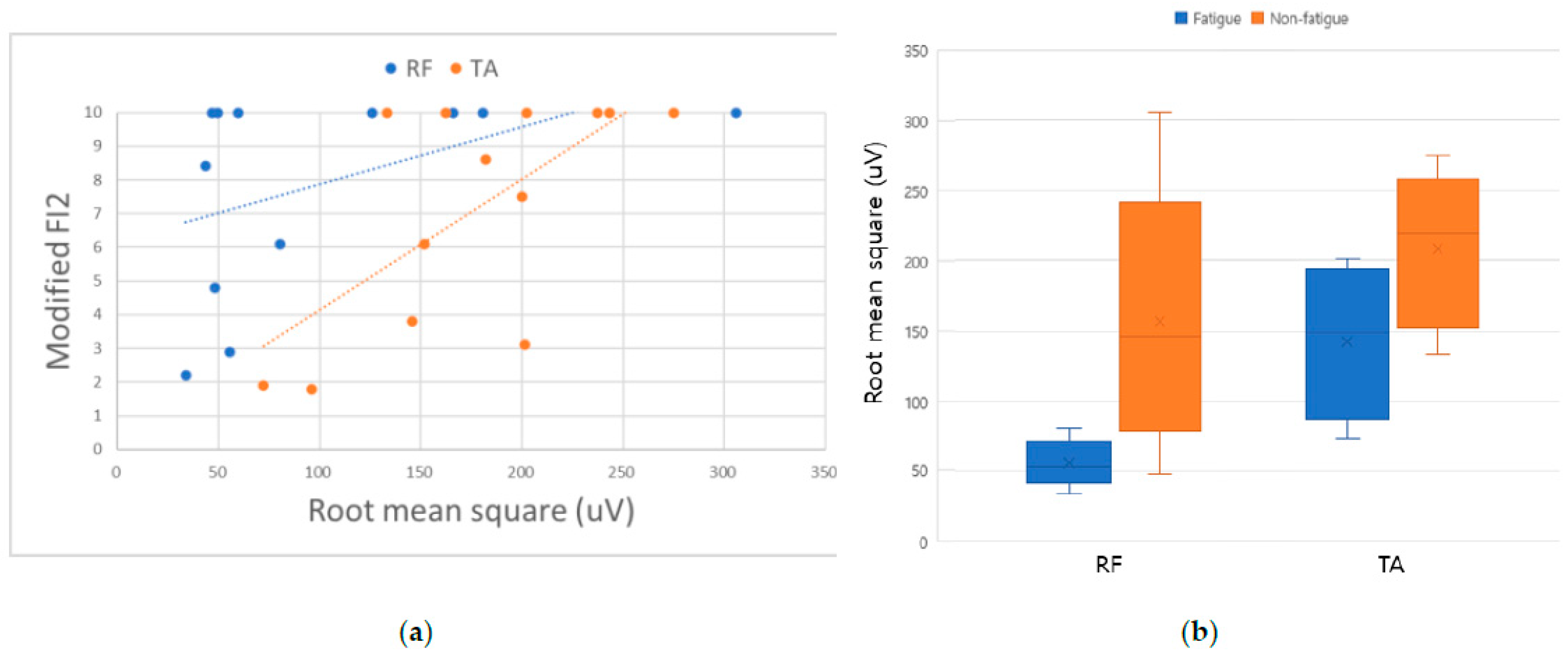
| Fatigue Patients (n = 8) | Non-Fatigue Patients (n = 6) | p–Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified FI2 Score (0–10) | RF | 6.3 ± 3.2 | 10.0 | 0.048 |
| TA | 4.7 ± 2.7 | 0.001 | ||
| Age, in years | 54.9 ± 17.2 | 50.5 ± 8.4 | 0.755 | |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 5 (62.5) | 6 (100) | 0.282 | |
| Admission diagnosis, n (%) | 1.000 | |||
| Chest trauma | 3 (37.5) | 1 (16.7) | ||
| Abdominal blunt trauma | 1 (12.5) | 3 (50.0) | ||
| Both (chest and abdomen) | 4 (50.0) | 2 (33.3) | ||
| Severity of trauma (ISS) | 22.5 ± 7.6 | 19.0 ± 5.9 | 0.491 | |
| ICU Stay (d) | 16.8 ± 19.0 | 24.7 ± 23.0 | 0.755 | |
| Mechanical ventilation (d) | 12.0 ± 18.0 | 18.3 ± 16.7 | 0.573 | |
| MRC-SS (0–60) | 52.3 ± 9.0 | 55.0 ± 3.6 | 0.755 | |
| Grip strength (kg, dominant hand) | 21.5 ± 12.2 | 27.2 ± 8.9 | 0.240 | |
| Fatigue Patients (n = 8) | Non-Fatigue Patients (n = 6) | p–Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface EMG | RF MVC (uV) | 55.0 ± 14.8 | 154.9 ± 88.0 | 0.020 * |
| RF %MVC (%) | 42.7 ± 21.5 | 47.0 ± 12.0 | 0.755 | |
| RF MDF (Hz) | 66.3 ± 7.8 | 67.8 ± 9.5 | 1.000 | |
| RF FI (%) | 3.9 ± 3.8 | 4.6 ± 6.8 | 0.639 | |
| TA MVC (uV) | 144.0 ± 49.2 | 208.8 ± 53.5 | 0.043 * | |
| TA %MVC (%) | 42.9 ± 22.9 | 42.5 ± 14.4 | 1.000 | |
| TA MDF (Hz) | 82.0 ± 8.1 | 81.2 ± 5.9 | 0.589 | |
| TA FI (%) | 9.3 ± 7.3 | 5.4 ± 6.2 | 0.445 | |
| Ultrasound | RF 2nd Echogenicity | 67.7 ± 12.5 | 59.8 ± 15.2 | 0.662 |
| RF Echogenicity Δ | 4.97 ± 10.0 | 1.8 ± 15.9 | 0.755 | |
| TA 2nd Echogenicity | 71.0 ± 15.1 | 61.4 ± 10.0 | 0.228 | |
| TA Echogenicity Δ | 7.2 ± 10.1 | −1.4 ± 7.3 | 0.081 | |
| Borg CR10 (0–10) | 3.5 ± 2.1 | 2.0 ± 2.1 | 0.228 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.H.; Shin, H.J.; Shin, M.-J.; Jang, M.H. Feasibility of Muscle Endurance Testing in Critically Ill Trauma Patients: A Pilot Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010053
Kim SH, Shin HJ, Shin M-J, Jang MH. Feasibility of Muscle Endurance Testing in Critically Ill Trauma Patients: A Pilot Study. Healthcare. 2023; 11(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sun Hyun, Ho Jeong Shin, Myung-Jun Shin, and Myung Hun Jang. 2023. "Feasibility of Muscle Endurance Testing in Critically Ill Trauma Patients: A Pilot Study" Healthcare 11, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010053
APA StyleKim, S. H., Shin, H. J., Shin, M.-J., & Jang, M. H. (2023). Feasibility of Muscle Endurance Testing in Critically Ill Trauma Patients: A Pilot Study. Healthcare, 11(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010053







