Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; methodology, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; software, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; validation, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; formal analysis, S.F.-C. and N.C.-Z.; investigation, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; resources, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; data curation, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; writing—original draft preparation, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; writing—review and editing, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; visualization, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; supervision, S.F.-C.; project administration, R.L.-C., E.R.-A., A.C.-C., S.F.-C., N.C.-Z., D.P.-M., F.S.-S., and S.N.-N.; funding acquisition, S.F.-C., D.P.-M., and S.N.-N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Flowchart diagram.
Figure 1.
Flowchart diagram.
Figure 2.
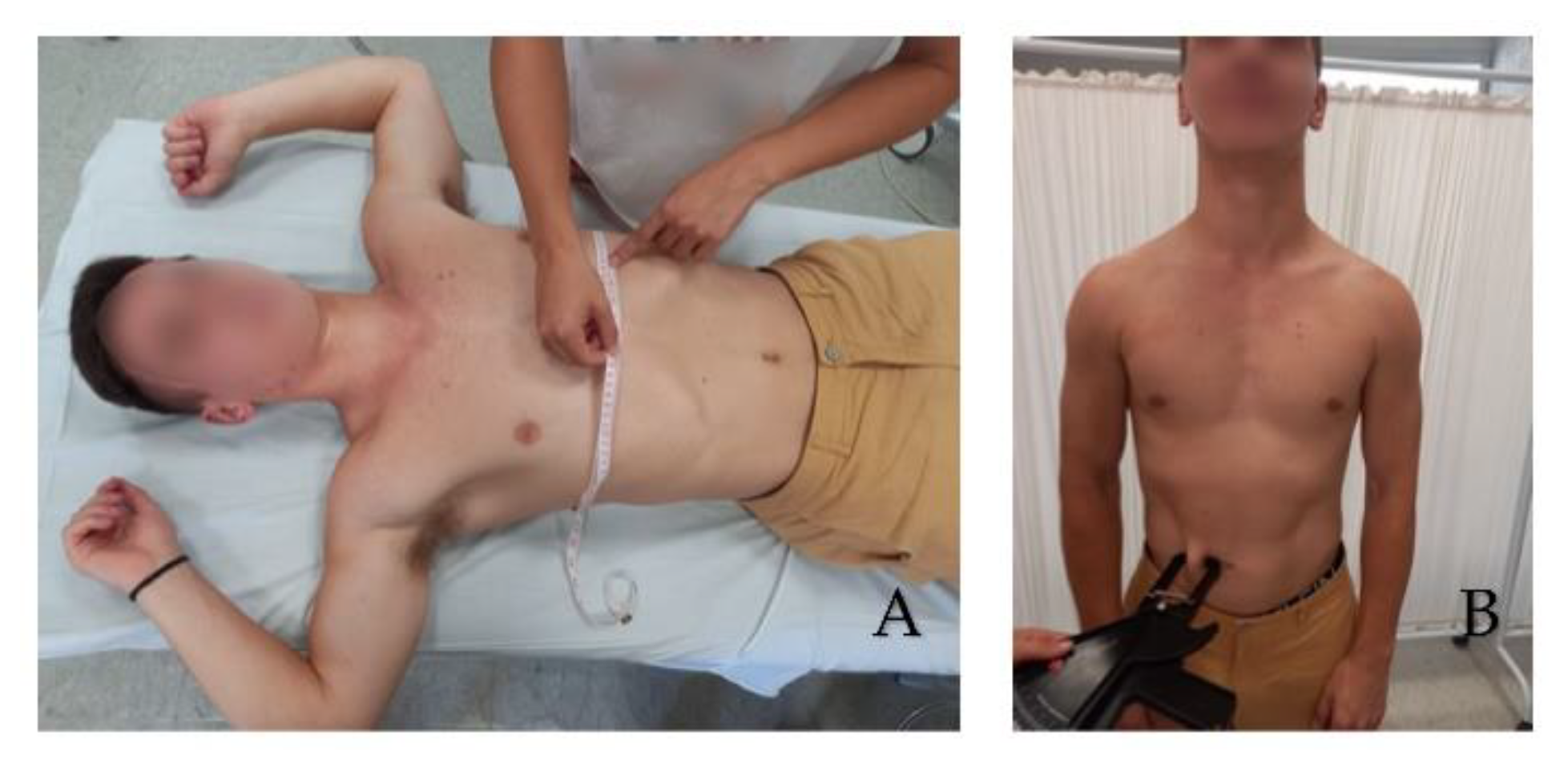
Thorax Circumference in maximum inspiration at the level of the xiphoid process (A). Abdominal skinfold test (B).
Figure 2.
Thorax Circumference in maximum inspiration at the level of the xiphoid process (A). Abdominal skinfold test (B).
Figure 3.
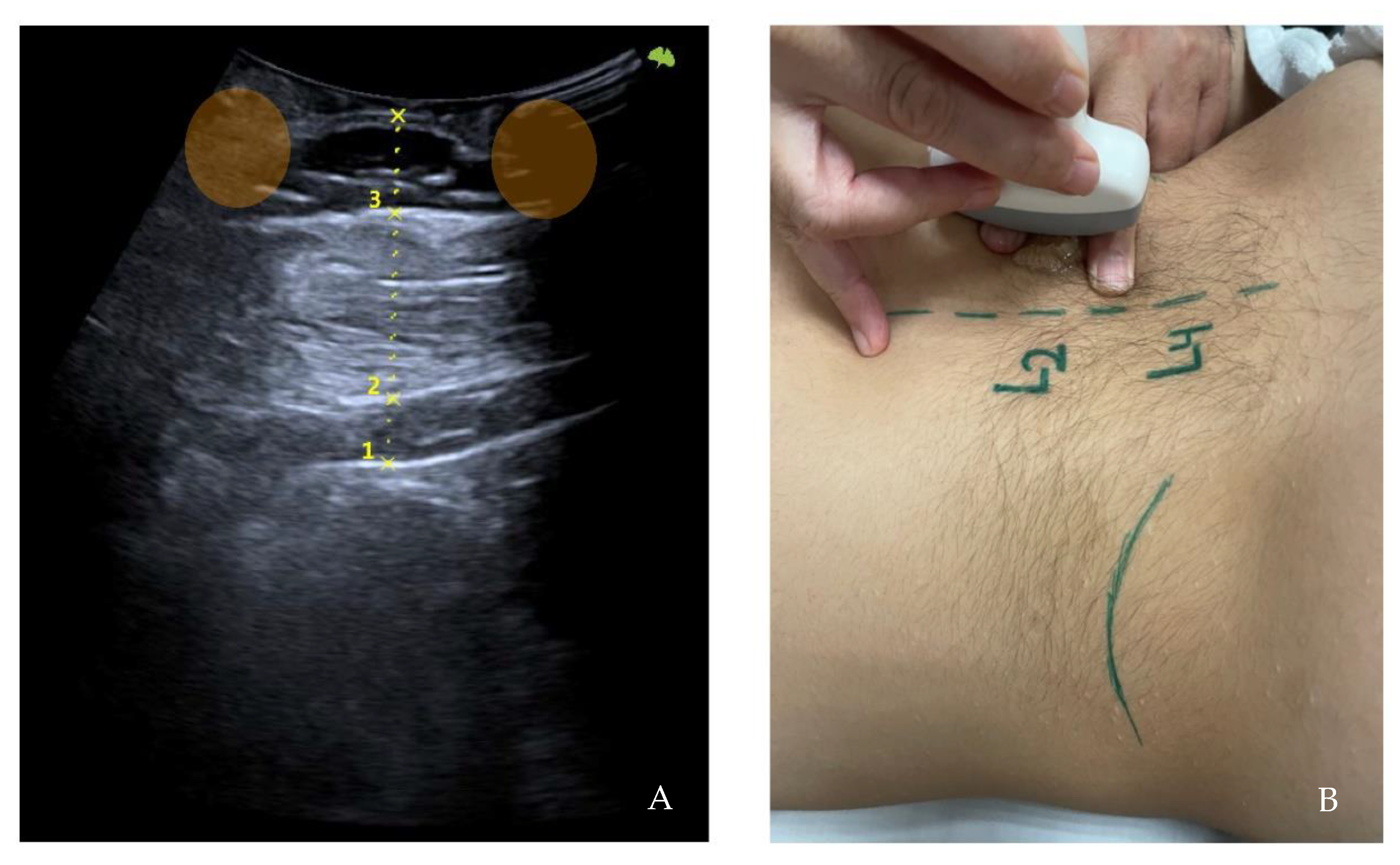
Ultrasonography image. Short-axis measurements in L2 level, left side at rest. Skin-kidney (1), skin-iliocostalis lumborum bottom edge (2), and skin-iliocostalis lumborum top edge (3).
Figure 3.
Ultrasonography image. Short-axis measurements in L2 level, left side at rest. Skin-kidney (1), skin-iliocostalis lumborum bottom edge (2), and skin-iliocostalis lumborum top edge (3).
Figure 4.
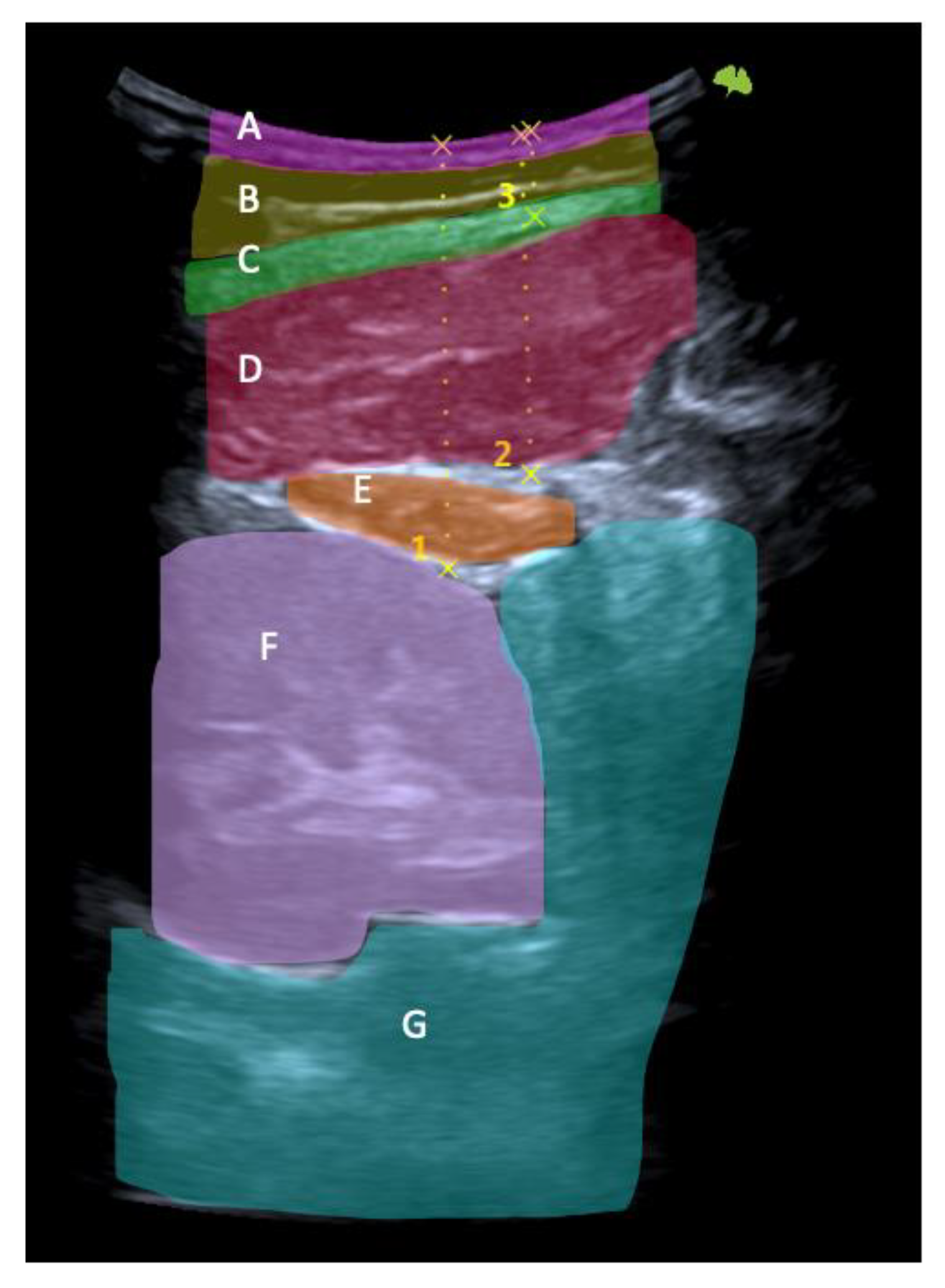
Ultrasonography image. Short-axis view: skin (A), fat (B), thoracolumbar fascia (C), iliocostalis muscle (D), quadratus lumborum muscle (E), kidney (F), and peritoneum (G). Skin-kidney (1), skin-iliocostalis lumborum bottom edge (2), and skin-iliocostalis lumborum top edge (3).
Figure 4.
Ultrasonography image. Short-axis view: skin (A), fat (B), thoracolumbar fascia (C), iliocostalis muscle (D), quadratus lumborum muscle (E), kidney (F), and peritoneum (G). Skin-kidney (1), skin-iliocostalis lumborum bottom edge (2), and skin-iliocostalis lumborum top edge (3).
Figure 5.
Ultrasonography image. Long-axis measurements in L2 level, left side at rest. Skin-kidney (1), skin-iliocostalis lumborum bottom edge (2), and skin-iliocostalis lumborum top edge (3) with the finger’s acoustic shadow painted (orange) (A). Moment of the sampling technique (B).
Figure 5.
Ultrasonography image. Long-axis measurements in L2 level, left side at rest. Skin-kidney (1), skin-iliocostalis lumborum bottom edge (2), and skin-iliocostalis lumborum top edge (3) with the finger’s acoustic shadow painted (orange) (A). Moment of the sampling technique (B).
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic characteristics of the participants.
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic characteristics of the participants.
| N | | 68 |
|---|
| Gender n, (%) | Men | 31 (45.6) |
| Woman | 37 (54.4) |
| Age | 28.26 ± 11.03 |
| Dominance, n (%) | Right | 61 (89.7) |
| Left | 7 (10.3) |
| Weight (kg) | 67.60 ± 13.38 |
| Height (cm) | 169.57 ± 9.84 |
| Body mass index | 23.33 ± 3.05 |
| Neutral axillary circumference | 93.91 ± 10.04 |
| Neutral xiphoid circumference | 83.99 ± 9.85 |
| Neutral abdominal circumference | 81.63 ± 10.57 |
| Inspiration axillary circumference | 96.22 ± 10.30 |
| Expiration axillary circumference | 93.41 ± 10.15 |
| Inspiration xiphoid circumference | 86.75 ± 9.69 |
| Expiration xiphoid circumference | 83.01 ± 10.20 |
| Inspiration abdominal circumference | 81.54 ± 10.55 |
| Expiration abdominal circumference | 81.24 ± 10.57 |
| Chest-triceps skinfold thickness | 13.47 ± 7.39 |
| Abdomen-iliac crest skinfold thickness | 14.66 ± 9.35 |
| Thigh skinfold thickness | 24.40 ± 11.32 |
| Fat percentage | 18.41 ± 7.57 |
Table 2.
Intra-observer reliability.
Table 2.
Intra-observer reliability.
| | ICC (IC95%) | ap Valor | ICC Categorical | SEM (IC95%) |
|---|
| L2 right without compression: skin-kidney | 0.92 (0.792, 0.977) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.206 (0.114, 0.298) |
| L2 right with compression: skin-kidney. | 0.96 (0.889, 0.989) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.161 (0.101, 0.221) |
| L4 right without compression: skin-peritoneum. | 0.951 (0.869, 0.986) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.202 (0.127, 0.277) |
| L4 right with compression: skin-peritoneum. | 0.962 (0.895, 0.99) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.177 (0.125, 0.229) |
| L2 left without compression: skin-kidney. | 0.952 (0.864, 0.987) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.144 (0.086, 0.202) |
| L2 left with compression: skin-kidney. | 0.948 (0.86, 0.986) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.129 (0.089, 0.17) |
| L4 left without compression: skin-peritoneum | 0.947 (0.858, 0.985) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.201 (0.124, 0.278) |
| L4 left with compression: skin-peritoneum. | 0.979 (0.94, 0.994) | <0.001 | Excellent | 0.139 (0.092, 0.187) |
Table 3.
Reliability with compression vs. without compression.
Table 3.
Reliability with compression vs. without compression.
| | ICC (IC95%) | ap Valor | ICC Categories | SEM (IC95%) |
|---|
| L2 right: skin-kidney without vs. with compression. | 0.402 (−0.057, 0.82) | 0.13 | Poor | 0.284 (0.081, 0.488) |
| L4 right: skin-peritoneum without vs. with compression | 0.75 (0.083, 0.938) | 0.015 | Moderate | 0.36 (0.111, 0.608) |
| L2 left: skin-kidney without vs. with compression | 0.696 (0.054, 0.92) | 0.017 | Moderate | 0.29 (0.132, 0.448) |
| L4 left: skin-peritoneum without vs. with compression | 0.902 (0.244, 0.98) | 0.008 | Excellent | 0.202 (0.066, 0.337) |
Table 4.
Smoothed model of L4 without compression.
Table 4.
Smoothed model of L4 without compression.
| | EDF | dfref | F | ap Valor |
|---|
| Body mass index | 1.419 | 2 | 2.147 | 0.048 |
| Neutral axillary circumference | 0.839 | 3 | 1.225 | 0.033 |
| Neutral abdominal circumference | 1.975 | 3 | 8.726 | <0.001 |
| Chest-triceps skinfold thickness | 1.458 | 3 | 2.412 | 0.012 |
| Abdomen-iliac crest skinfold thickness | 1.000 | 3 | 4.957 | <0.001 |
Table 5.
Smoothed model of L4 with compression.
Table 5.
Smoothed model of L4 with compression.
| | EDF | dfref | F | ap Valor |
|---|
| Body mass index | 1.907 | 3 | 2.873 | 0.009 |
| Neutral abdominal circumference | 1.997 | 3 | 10.260 | <0.001 |
| Chest-triceps skinfold thickness | 0.892 | 3 | 2.684 | 0.003 |
| Abdomen-iliac crest skinfold thickness | 0.963 | 3 | 4.604 | <0.001 |
Table 6.
Parametric model of L2 without compression.
Table 6.
Parametric model of L2 without compression.
| | Coefficient | Standard Error | t | ap Valor |
|---|
| (Intercept) | 16.019 | 0.408 | 39.227 | <0.001 |
| Gender (female) | 4.387 | 0.695 | 6.310 | <0.001 |
Table 7.
Smoothed model with the dependent variable L2 with compression.
Table 7.
Smoothed model with the dependent variable L2 with compression.
| | EDF | dfref | F | ap Value |
|---|
| Neutral axillary circumference | 0.863 | 3 | 1.596 | 0.017 |
| Neutral abdominal circumference | 1.962 | 3 | 10.198 | <0.001 |
| Chest-triceps skinfold thickness | 0.874 | 3 | 2.073 | 0.009 |
| Abdomen-iliac crest skinfold thickness | 1.000 | 3 | 4.677 | <0.001 |